#2020 US Census
Note
Re: lying on the census about sensitive info. I worked as a census man on the street in 2020, and people definitely do lie, but we also tell them that they don’t have to fill in anything that they’re uncomfortable sharing. The only quasi mandatory data is if the home or dwelling is occupied, because the census official is allowed to ascertain that without asking the residents directly. They aren’t required to tell us anything if they don’t want to.
Thank you for the information.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
1990 Top 10 US Cities
See also: 1990 United States Census § City rankings
The 1990 Census was the Twenty-first, and the first census in which all ten of the largest cities have populations of over one million. A different ranking is evident when considering U.S. metro area populations which count both city and suburban populations.

The total population of these 10 cities was 31,312,875.
#silly wiki goof for dc population#top 10 us cities of dc have about 10.000.000 more of the population than the top ten of real life#also in real life the first census for all ten to be over 1-mil was the most recent 2020#fun differences#nik reads dc
1 note
·
View note
Text
‘Street Race' question could enhance federal data on Latino racial experiences, UCLA report suggests
0 notes
Note
Can you please, pretty-please do a "3 linguistics papers to read" about neopronouns? I'd love to get some academic perspectives on them! :)
Ooh, yes, I can do this!
Three papers to read about neopronouns
The first one I'm linking is by Em Miltersen from 2016, which I am highlighting because the data comes specifically from tumblr!
Miltersen, E. H. (2016). Nounself pronouns: 3rd person personal pronouns as identity expression. Journal of Language Works-Sprogvidenskabeligt Studentertidsskrift, 1(1), 37-62. Open access to the paper here
Next, a very short paper by Rose et al., 2023, which is just looking at whether people even find neopronouns acceptable / grammatical:
Rose, E., Winig, M., Nash, J., Roepke, K., & Conrod, K. (2023). Variation in acceptability of neologistic English pronouns. Proceedings of the Linguistic Society of America, 8(1), 5526-5526. Open access paper is here
And then finally, I'd recommend this super cool paper by Laura Hekanaho, 2022, looking at the metalinguistic commentary and ways people talk about neopronouns - overlaps a bit with Rose et al.'s paper, but goes into much greater depth:
Hekanaho, L. (2022). A thematic analysis of attitudes towards English nonbinary pronouns. Journal of language and sexuality, 11(2), 190-216. Author's copy of the paper here
One thing about neopronouns is that there's comparatively little linguistics research published about them, and what does exist is very focused on English. Part of this is because the ways neopronouns are cropping up in English speech communities (especially online) are different than in other language communities, and the other part of the reason is that they're just super rare -- best estimates of how many people use neopronouns are very very low (the US Trans Census and the Gender Census report numbers <10%, and that's out of only trans people), and their appearance in every day language appears to be very rare.
What this means (frustratingly! and I hope this is changing!) is that at best neopronouns are mentioned in footnotes of linguistics articles and books about other stuff. There's also Dennis Baron's 2020 book, What's Your Pronoun, which is a really thorough documentation of historical attempts to coin gender-neutral pronouns in English... but Baron kind of comes to the conclusion that singular 'they' has 'won' the competition, and that none of the neopronouns he tracks have become mainstream.
Anyways, my personal opinion as a linguist is that I get frustrated with linguists who dismiss neopronouns because they're rare. Just because something's rare doesn't mean it's not a part of the language, and therefore a real part of the phenomenon we've decided to study! Devil's hole pupfish of english, tbh.
(Previous "3 papers to read" post was "3 papers to read about singular 'they'." If you like these posts, you can request a topic in linguistics and I'll do my best to recommend 3 open-access published papers to read!)
369 notes
·
View notes
Text
For all the concern in recent years that U.S. democracy is on the brink, in danger or under threat, a report out Tuesday offers a glimmer of good news for American voters worried that casting a ballot will be difficult in 2024.
Put simply, the new data shows that voting in America has gotten easier over the past two decades. More voters have the ability to cast a ballot before Election Day, with the majority of U.S. states now offering some form of early in-person voting and mail voting to all voters.
"Although we often talk in a partisan context about voter fraud and voter suppression and whether voters have access to the ballot, the reality is, over the past 25 years, we've greatly increased the convenience of voting for almost all Americans," said David Becker, the founder and executive director of the Center for Election Innovation & Research (CEIR), which authored the new report...
The data shows that, despite real efforts by some Republican-led legislatures to restrict access at the margins, the trend in the U.S. since 2000 has been toward making it easier to vote: Nearly 97% of voting-age American citizens now live in states that offer the option to vote before Election Day.
"The lies about early voting, the lies about voting machines and efforts in some state legislatures to roll back some of the election integrity and convenience measures that have evolved over the last several decades, those efforts almost all failed," Becker said. "In almost every single state, voters can choose to vote when they want to."
Forty-six states and Washington, D.C., offer some form of early in-person voting, the report tallied, and 37 of those jurisdictions also offer mail voting to all voters without requiring an excuse...
In 2000
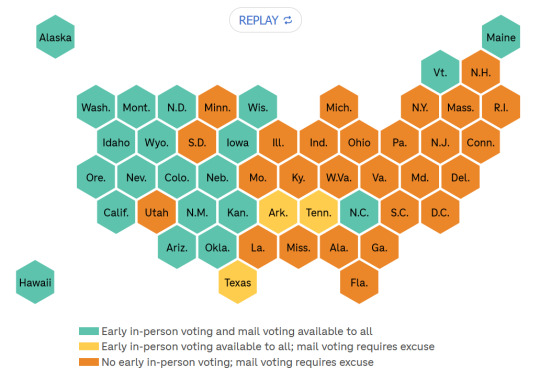
In 2024
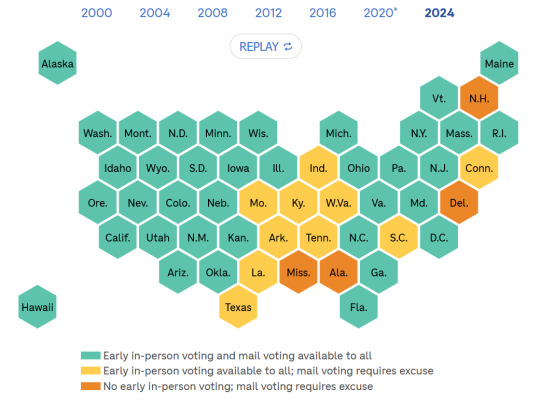
Infographic via NPR. If you go to the article, you can watch an animation of this map that shows voting availability in every election since 2000.
There are some political trends that show up in the data. Of the 14 states that don't offer mail voting to all voters, for instance, 12 have Republican-led legislatures.
-via NPR, March 19, 2024. Article continues below.
But maybe the more striking trends are geographic. Every single state in the western U.S. has offered some form of early and mail voting to all voters since 2004, according to the data. And those states span the political spectrum, from conservative Idaho to liberal California.
"It's really hard to talk about partisanship around this issue because historically there just hasn't been much," Mann said. "We've seen voting by mail and early in-person voting supported by Republican legislatures, Democratic legislatures, Republican governors, Democratic governors. We see voters in both parties use both methods." ...
In 2020, New York, Connecticut and Massachusetts all made changes to make voting more easily accessible, which have since partially or fully become permanent. Delaware is currently embroiled in a legal fight over whether it can implement early and mail voting changes this election cycle as well.
The South, with its history of slavery and Jim Crow laws, has long lagged behind when it comes to voting access. The CEIR data shows that, although some states have slowly started expanding options for voters, generally it is still the most difficult region for voters to cast a ballot.
As options nationwide have become more widely available, voters have also responded by taking advantage.
In the 2000 election, 86% of voters voted at a polling place on Election Day, according to U.S. Census Bureau data.
In 2020, during the pandemic, that number dropped to less than 31% of voters. It went back up in 2022, to roughly half of the electorate, but was still in line with the two-decade trend toward more ballots being cast early.
...in reality, Becker says, more voting options actually make elections more secure and less susceptible to malicious activity or even human error.
"If there were a problem, if there were a cyber event, if there were a malfunction, if there were bad weather, if there were traffic, if there were was a power outage, you could think of all kinds of circumstances. ... The more you spread voting out over a series of days and over multiple modes, the less likely it's going to impact voters," he said...
-via NPR, March 19, 2024
#united states#voting#voting matters#early voting#mail in ballots#voting access#american politics#us elections#election 2024#us politics#democrats#republicans#election day#election news#good news#hope
475 notes
·
View notes
Note
What might decolonization in the US after a successful socialist revolution look like? Would there be one big government still? A sort of union of socialist republics? Something else entirely? Honestly I don't know how to ask.
Post-revolutionary decolonization (and realistically, the only kind of meaningful decolonization that is ever happening) in the US is a complicated matter given the relative success of the USAmerican genocidal project. The native population is 1.1% of the total population as of the 2020 census, this means that unlike in other, incomplete, settler projects such as the Sahrawi Republic or Palestine, it isn't feasible to restore the relation of the native population to the totality of the country. Regardless of population proportions though, the main focus of socialist decolonization is the struggle against any conflict between nationalities by removing the economic basis of that antagonism, which would then allow to also begin to remove the cultural elements that reinforced that dynamic of oppression. The focus is not to create more landlords but native, it's to remove the structure around private property in general, and make sure every worker, native or otherwise, receives as is needed. Taking into account the already relative dispossession of native people even before a pre-revolution context, there will have to be a great effort to bring the conditions of native people at the same level of non-native people.
Regarding the form of the new state, this will evidently depend on the form of the US state as the revolution happens. In other countries this would not be such a pressing question, but given the role and strength of the USAmerican bourgeoisie, it's not hard to believe that for any revolution to take place, the US state would need to be considerably weakened. Keeping this in mind, the strategy followed by all hitherto socialist revolutions is to not further fragment the new state. Given the complexity of navigating the construction of the first elements of a socialist economy, with the simultaneous effort needed for security, it would be both counterproductive and hypocritical to explicitly seek the independence of a portion of the population, as a part of the political program, it would be taking two steps forward and one step back. The communist revolution is national in form, because it happens within the structure of the capitalist state, but it is also international in content, because it explicitly repudiates the division of the proletariat along national lines.
We must understand that nationality, as much as it is relevant today and as much as it influences the course of history, is a byproduct of the development of capitalism, and that since it arose from the infrastructure to justify and protect it, it will also have to seize to exist and be replaced with proletarian internationalism for the duration of the transition to socialism-communism. Keeping this in mind, it would be hypocritical and regressive to, after taking control of the state and beginning the transition away from capitalism, to then turn around and divide the working class of the new country into even more national categories than they already are divided into.
The early USSR is a good comparison because of the sheer quantity of national diversity contained within the bounds of the corpse of the Tsarist Empire. The policy of the bolsheviks was neither of Russian supremacy or of immediate splintering into hundreds of nation states. Even during the very complicated and desperate context of the civil war, Finland was allowed its independence without much fuss from the CC, even if they were immediately incorporated into the German sphere via Von Mannerheim. When the 1936 constitution was being discussed, it was Stalin himself who went against the wishes of many bolsheviks to prevent the republics from gaining independence if they wished. No republics requested this however, because the oppressive mechanisms of capitalism and feudalism that had kept them under the Tsar's thumb for centuries had been replaced with an economic system that assured the equal development of all peoples within the USSR. The USSR itself was also not absolutely centralist, and the many constituent republics had varying degrees of autonomy, reflecting in some aspects the structure of democratic centralism.
I don't think the answer is to replicate the USSR, of course. The context and general state of things are very different, but there are lessons to be learnt from this successful, albeit flawed, tackling of the national question. Again though, we can't really speculate on the way that the US will look right before a revolution, and consequently the structures and problems a revolutionary government will have to start from.
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
To continue the theme of "wtaf is up with that sanctuary that feeds bears Twizzlers and camels Mountain Dew", here's another recent social media post I find rather concerning. Who the heck is giving cheetah - vulnerable animals with a very small population - to a sanctuary that is rabidly, openly anti-zoo and anti-conservation breeding?

The reason this stands out to me so much is that there just like... are not cheetah in sanctuaries in the US. Most cheetah in the US are part of a breeding program, either AZA's SSP or ZAA's AMP - it's not common to find them in even unaccredited zoos, much less newly moved to sanctuaries. Of the 400-some cheetah I found doing the big cat census in 2020, there were less than 10 in facilities that branded themselves as sanctuaries. So where did these cats come from?
What's more, okay, there's no trace of these ladies on social media before now. The Wild Animal Sanctuary is normally very open about their acquisitions, and no facility they've gotten animals from since their last USDA inspection has had cheetah. I haven't heard about any imported cheetah recently either, which is another thing you can check for this facility, because the majority of their rescues are imported from all over the world.
There's another weird thing about this post, too. Look at the language. It's all very "here's a cheetah! they're very happy outdoors in their nice habitat." And if you're not facility with this institution and their messaging, you might not catch why that's odd. This facility emphasizes, in every post they can, that their animals are rescued from horrible no-good very-bad abusive situations. Normally they name and shame if they can, or talk about how they came from the cub petting industry or private exploitation or such. There's none of that in this post, and it stands out because of it - especially because it's the first time these very rare, very charismatic big cats are being shared with their audience.
So where the heck did these cats come from?
Whelp.
Turns out the answer is AZA-accredited zoos. And whew, man, does that raise some questions.
Luckily these girls have some pretty distinctive names, so I was able to find them in the international and regional cheetah studbooks pretty easily. For both cats, the most recent listing in the studbooks was at AZA-accredited zoos in Texas: in 2020 Dahlila was living at Caldwell Zoo, and in 2022 Jaina was at Fossil Rim Wildlife Center.
Now, we don't know for sure that Caldwell and Fossil Rim are the facilities that chose to dump their cheetah in a sanctuary. There's some important context to know about exotic animal ownership and how animals leave AZA SSPs. General practice is that large charismatic mammals aren't bought and sold at AZA zoos, especially SSP animals, so animals sent out to other facilities for breeding or exhibition are moved around on loan. Sometimes their ownership changes with the transfer, but not always - it really depends on the species and how much control each facility wants to have over their animals. On top of that, the ownership of offspring sometimes alternates by litter or individual between the institutions that own the parents. When they're part of a cooperative breeding program none of that matters very much because all the animals are managed as a single population and moved as required for breeding and to fill empty display spaces. Where it's relevant is when an animal is removed from the SSP population - at that point it's totally up to the facility that owns it to choose where they live, as long as they send them somewhere AZA agrees is providing a reasonable standard of care. (This will be important in a little bit.)
So what we can tell from this situation is that Jaina and Dahlila were, for some reason, probably excessioned from the SSP in the last couple years. And whichever AZA facilities owned them decided to send them to The Wild Animal Sanctuary instead of finding a display-only placement at a zoo or safari park or similar facility.
Since I started writing this post, TWAS confirmed the origin of these girls in a Facebook comment.
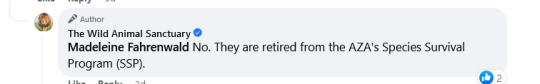
I have real concerns about what appears to be an emerging trend of exotic animal exhibition facilities using sanctuaries as a "dumping ground" for their elderly or extra animals, in order to prioritize space for breeding or more desirable animals. I can't prove it yet, but there's been just enough weird transfers to have caught my attention. (In some cases, there's a good reason - sometimes all the habitats designed for the physical needs of elderly animals of a certain species already are full, and it's better for them to go somewhere they can exist more easily rather than trying to retrofit their current habitat - but it isn't every case). And here's the thing: many sanctuaries, like TWAS, message about how they have to exist to take all the discards from the zoo industry. In recent years that hasn't really been accurate, and historically, it did happen but not as commonly as it's portrayed. So... if that's true... and it's a bad thing... why are sanctuaries encouraging it by taking the animals zoos are transferring out to free up space? You'd think they'd want to say "find space in your own institutions and only call us if there's a crisis." (Money. The answer is money. Every new intake is used for marketing and drives additional donations.) Heck, why are zoos playing into that narrative, when they're frequently rebutting attacks claiming they discard the animals that aren't useful or aesthetic anymore?
All of this actually makes a lot of sense given how short on space all the AZA SSP programs are. Both in general, and for big cats, there are not enough spaces across accredited zoos to hold all the animals needed for sustainable populations. (This is why AZA just recently re-imagined their SSP programs, which is a whole other complicated mess that I am working on a writeup about). Recent political shifts within AZA corporate leadership have also discouraged collaborations between AZA-accredited zoos and non-AZA facilities, so while 20 years ago it would have been fine to move extraneous / non-breeding cats to smaller unaccredited facilities for display, that's less of an option. Which leaves sanctuaries as kind of the only politically appropriate option. This would also explain why the text of the post is so weird: there's probably a contract in place to prevent using their images to bash zoos.
The problem with sanctuaries as a solution for housing extra animals is, well, the quality of care they provide. If you haven't seen me say it before: sanctuaries are as varied in their expertise and function as zoos. In the case of The Wild Animal Sanctuary (and their other facilities, like the Refuge these cheetah are at) everything I have learned about them indicates that their animal care is highly questionable. Which is a problem, because - as mentioned earlier - AZA-accredited facilities are required to follow a responsible population management policy, which means ensuring that animals they send outside of AZA go somewhere that gives them high-quality care.

TWAS is an organization that prefers to feed big cats at multiple facilities frozen meat puree "frisbees" by chucking them over the fence. They don't have any way to separate co-housed cats to prevent conflict during feeding or resource guarding, because they don't build their enclosures with any sort of shift or lock-out areas. It's also unclear how they remove food waste without a way to shift animals out to go find it. (For bears they drive in on a truck into the habitat and then go on foot to clean, but I don't know if that's done with the big cats once they’ve been released from quarantine pens.


(These are my photos of food in carnivore habitats at TWAS this summer. Given the pest accumulation on the meat frisbee and the fact that I visited early in the day, it seems probable it was at least a day old.)
This is an organization that is ethically against training their animals for any reason: it's literally written into their statement of purpose as a “true sanctuary.” It's also described below, in a recent book published about the facility.


That policy means these cheetahs will not have a recall behavior, will not be trained for medical examinations or as a way to lower stress for procedures, and will not get the mental enrichment and interaction they're used to from regular training sessions. According to the book, medications are delivered on a long spoon / tongs tucked inside the cat equivalent of a pill pocket. (Which anyone with a pet cat knows falls apart as a plan if they're sick enough to not feel hungry).
I'm pretty sure there's no heated shelter for the large carnivores or bears at TWAS. The main shelter for animals at the Sanctuary is single-entrance concrete culverts buried underground far enough they're supposed to maintain a constant temperature all winter.

Sounds nice in theory, but with no second exit animals can get trapped down there, and there's no way to monitor them when they're inside. I don't know what type of shelter the Refuge provides, but it probably isn't much different. Even the quarantine spaces - smaller outdoor kennel-type pens with three exposed mesh panel walls - have no heat, and just an above-ground culvert block for them to curl up in. While cheetah are surprisingly adaptable to cold weather, winters in Colorado can be very harsh for prolonged periods of time.
As far as I know, most of the animals at facilities TWAS runs don't get regularly changed, novel enrichment. I've certainly never seen much in the habitats other than climbing structures when I've visited their main facility over the years, and most of their messaging around “toys” is semi-permanent furniture like giant telephone wire spools or a suspension bridge for climbing. I think some of the bears get balls? The messaging from TWAS is that their animal care is better because it's close to a natural life in the wild. Animals can be animals! When returned to their wild roots, animals shouldn't need anything from humans and are happier that way, etc.
When animals come to the Sanctuary (or the partner facility, the Refuge) they're literally chucked into a big fenced-off piece of land and left out there to "be cats" without human interaction except for feeding time and observations. Which is the polar opposite of what these cheetah are used to! AZA cheetahs, even those that aren't program animals, are intensely managed. They're used to regular human contact, frequent training, and constant enrichment. So what's "normal" for a wild cat is a far cry from what these cheetah girls have always known. That's not better - that's a loss of quality of life.
I don't understand how moving animals to places like TWAS is in line with AZA's Responsible Collection Management policy. I don't understand how AZA facilities think the type of husbandry the facility describes providing is acceptable. If another zoo utilized half the same care practices, they'd be drawn and quartered by their industry peers as well as by the public - and rightfully so. I don't understand why anyone wants to send animals there, based even just on what's easily observable. I don't have more information or really a conclusion, just that’s what's observable from an external vantage point is upsetting as heck and I worry for those cheetah girls.
#big cats#cheetahs#animal welfare#sanctuary politics#zoo industry politics#animal care#AZA#long post#this originally said cheetah are highly endangered which was a fact checking error#updated it to reflect that#bug tw
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
FOTV'S PLOT MAKES NO SENSE
So since this is going to have MASSIVE spoilers for the new show, I'll put most of it behind a readmore.
But, TL/DR: Destroying Shady Sands would not bring down the NCR, because they have at least seven other major cities that could and would take over!
So, lets start with a map:
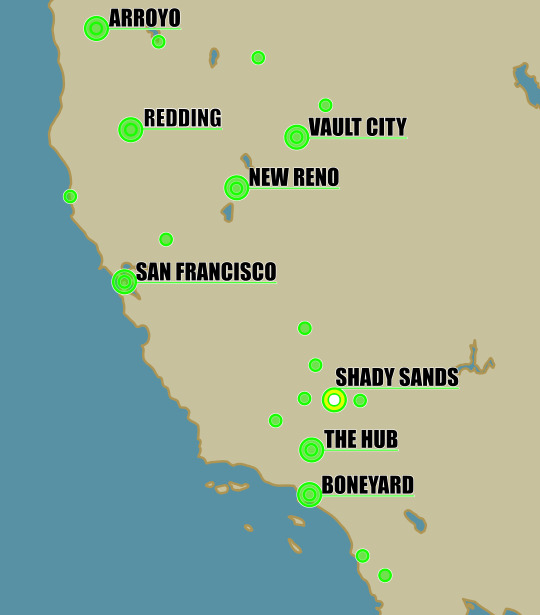
This is map (made by me) very roughly represents the NCR as it exist circa 2277. All major settlements are labelled, but do note that there are dozens of minor settlements scattered around the whole of California, and into Oregon, Nevada, and Mexico.
Nuking Shady Sands, even if you used the largest nuclear bomb ever made, (The Tsar bomb: coming in at 100 megatons, it is the upper limit of practicality for a bomb, because any larger and the explosion would've vented into the upper atmosphere and reduced the bomb's effect), it would still only destroy Shady Sands. Maybe vaults 13 and 15, the closest settlements to it (given their nature as vaults, however, I think they'd survive).
Notice all the other settlements? WHERE DID THEY GO, TODD?
Now, exploding Shady Sands would still be really fucking bad for the republic, but I think it would be fully survivable. We don't have hard numbers for the population of the NCR, but in New Vegas it is explicitly in the hundreds of thousands, (and rising). So we can substitute the demographics of, say, Alaska (710,000 people). The largest city in Alaska, Anchorage, has ~290,000 people living in it, as of the 2020 census. That's a large chunk of the state's population, but its not even half.
I think Shady Sands would probably be a lot smaller than the Hub or Boneyard (not to mention San Francisco, Vault City, or New Reno) because it started out as a small farming village when the others were already major settlements. So, at most, nuking Shady Sands would only disrupt the NCR, not kill it. Even if the NCR broke up in the aftermath, Lucy's vault should still be smack in the middle of the Boneyard, probably one of California's largest settlements.
But! That's not all! Not only does this show contradict established canon at every turn, it doesn't even do it well, because there is an argument to be made that a few well placed nukes could bring down the NCR!
And its already part of the damn game:

This handsome, gravelly-voiced genius already mathed out how to, as he calls it, "cut the bear's throat": bomb the NCR's trade routes to the outside world, and watch them wither away on their own. His plan is a thousand times more interesting, and more feasible, than how the show brought down the NCR (blowing up one (1) city and acting like that would destroy an entire nation).
In fact, if they really wanted to get rid of the NCR, they could've easily just made that ending to Lonesome Road canon. But, lets face it, this show cannot be bothered to even look at the games for inspiration.
I like almost nothing I see coming out of the show. Its a thin veneer of fallout painted onto a story that bulldozes the very series it claims to be part of. The zombification of ghouls, the centering of the Brotherhood, the badly written raiders playground of a wasteland: its all of Bethesda's worst writing choices, just transmitted to a new medium.
I hate it here.
#fallout show spoilers#fallout meta#fallout amazon prime#fallout new vegas#If you liked the show I don't hate you. I just wish they hadn't made the show overwrite west coast canon for Todd's petty vendetta#The show pisses on half the entries in the series because Todd can't stand people liking them more than his loot'n'shoot slop.#I don't even like the NCR. They're an imperialist capitalist hellhole. But they deserved a better story than this bullshit#Honestly if they had just placed the show in like. Montana. it would've been fine. They didn't have to break the setting for it#Anyway if you love the show and haven't played the games: please play fallout New Vegas. Its a good game.#If you come at me with 'you just hate fallout 4' I actually really liked 4! I think about it a lot! Its what got me into this fandom!
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
Know Your Neopronouns
If you look around online, you can find lists of neopronouns. (Neopronouns are words that get can be used instead of 'he' or 'she' when refering to someone.) Most show just the first 2 terms (‘Ey/Em,’ or ‘Ze/Zim’). Few provide any info about how to pronounce them. And even less provide examples of how messy real usage is. This guide is an attempt to show how real people are using neopronouns. It’s based off the data of the 2020-2023 (Nonbinary) Gender Censuses.
-
English Pronoun Sets include:
Subject (the person acting) – ie. They
Object (the person the action is happening to) – ie. Them
Dependent Possessive (ownership, thing owned is named) - ie. Their
Independent Possessive (ownership, thing owned is not named) – ie. Theirs
Reflexive (action affecting the person who is acting) – ie. Themself
In a sentence:
They walked in and told me their name was Chris. I said hi, and showed them the name tags. They found theirs and put it on themself.
-
Neopronouns come in 3 flavours:
The first type is based off the most common English personal pronouns:
‘They/Them/Their/Theirs/Themself (or Themselves)’
‘He/Him/His/His/Himself’
‘She/Her/Her/Hers/Herself’
This type of neopronoun usually mimics the ending sounds of one or more of the common pronoun sets. For example, ‘Ze/Zem’ pronouns are based on ‘he’ and ‘them.’
The second type includes pronouns not usually used as personal pronouns (like indefinite ('One'), neuter ('It'), or definite (‘that’)). It also includes neopronouns derived from them ('Thon').
The third type is based on various nouns not usually considered related to gender at all ('Star' or 'Pup'). These are called ‘nounself pronouns.’
-
I’ve listed both the common pronouns, as well as the most used neopronouns. For each entry, I include a variety of forms and spellings. I do my best to provide pronunciation. (I have not heard all of them pronounced, and what little I was able to find online might not match what real people are saying.) And I mention if they mimic feminine or masculine pronouns, singular they, indefinite pronouns, nouns, etc.
List of the 25 Most Common Pronouns Used By Nonbinary People in 2023 (According to the Gender Census):
They
He
She
It
Xe
Fae
Hir
Ey
E
Ae
Ve
Ze
Star
Hy
Thon
Void
Ne
Kit, Cat
Pup
Vae, Vey
Xey
Mew, Meow
Bun
One
Moon, Lun
Other pronouns with more than 30 users in the census (not included as separate entries)
That, Thing (that/that/thats/thats/thatself, thing/thing/things/things/thingself, that thing/that thing/that thing’s/that thing’s/that thing – 56 people)
Vamp (vamp/vamp/vamps/vamps/vampself – 54 people)
Sun, Sol (sun/sun/suns/suns/sunself, sol/sol/sols/sols/solself – 51 people)
Dey, Dae (dey/dem/deir/deirs/demself, dae/daem/daer/daers/daemself – 46 people)
Zey (zey/zem/zeir/zeirs/zemself – 46 people)
Per (per/per//per/pers/perself – 18 people)
Rot (rot/rot/rots/rots/rotself – 37 people)
Sie/Sier (sie/sier/sier/siers/sierself - 36 people)
Nya/Nyan (nya/nya/nyas/nyas/nyaself, nya/nyan/nyans/nyas/nyanself – 36 people)
Bug (bug/bug/bugs/bugs/bugself – 35 people)
Ix, X (ix/ix/ixs/ixs/ixself, x/x/xs/xs/xself – 34 people)
Ce (ce/cer/cer/cers/cerself – 33 people)
1. Singular They (They/Them)
Most common nonbinary pronoun set, this was used by 30,188 people in the 2023 Gender Census.
Usual Set:
They / Them / Their / Theirs / Themself (30,107 people)
Pronunciation: ðeɪ / ðɛm / ðeɪɹ / ðeɪɹz / ðɛmsɛlf (dhay / dhem / dhayr / dhayrz / dhemself)
Nonstandard Sets:
They / Them / Their / Theirs / Themselves (67 people)
Pronunciation: ðeɪ / ðɛm / ðeɪɹ / ðeɪɹz / ðɛmsɛlvz (dhay / dhem / dhayr / dhayrz / dhemselvz)
Plural they.
They / Them / Their / Theirs / Theirself (3 people)
Pronunciation: ðeɪ / ðɛm / ðeɪɹ / ðeɪɹz / ðɛɹsɛlf (dhay / dhem / dhayr / dhayrz / dherself)
Nonstandard They
Using them when talking:
They walked in and told me their name was Chris. I said hi, and showed them the name tags. They found theirs and put it on themself.
Nonstandard sets:
They walked in and told me their name was Chris. I said hi, and showed them the name tags. They found theirs and put it on themselves.
They walked in and told me their name was Chris. I said hi, and showed them the name tags. They found theirs and put it on theirself.
-
2. Masculine Pronouns (He/Him)
Second most common nonbinary pronoun set, this was used by 17,182 people in the 2023 Gender Census.
Usual Set:
He / Him / His / His / Himself
Pronunciation: hiː / hɪm / hɪz / hɪz / hɪmsɛlf (hee / him /hiz / hiz / himself)
Nonstandard Sets:
He / Him / His / His / Hisself
Pronunciation: hiː / hɪm / hɪz / hɪz / hɪsɛlf (hee / him /hiz / hiz / hiself)
Using them when talking:
He walked in and told me his name was Chris. I said hi, and showed him the name tags. He found his and put it on himself.
Nonstandard set would end with: He found his and put it on hisself.
-
3. Feminine Pronouns (She/Her)
Third most common nonbinary pronoun set, this was used by 13,220 people in the 2023 Gender Census.
Usual Set:
She / Her / Her / Hers / Herself
Pronunciation: ʃiː / hɚ / hɚ / hɚz / hɚsɛlf (shee / her /her / herz / herself)
Using them when talking:
She walked in and told me her name was Chris. I said hi, and showed her the name tags. She found hers and put it on herself.
-
4. Neuter Pronouns (It/It)
4th most common set of pronouns (up from 5th last year), and probably the most controversal. Seen as dehumanizing by many people, and as validating by others. (7,859 people)
Usual Set:
It / It /Its / Its / Itself
Pronunciation: ɪt / ɪt / ɪts / ɪts / ɪtsɛlf (it / it / its / its / itself)
Using them when talking:
It walked in and told me its name was Chris. I said hi, and showed it the name tags. It found its and put it on itself.
-
5. Xe/Xem Pronouns
5th most common set of nonbinary pronouns, and the most popular neopronoun set. (4,649 people)
Usual Set:
Xe / Xem / Xyr / Xyrs / Xymself (4,504 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɛm / zɚ / zɚz / zɛmsɛlf (zee / zem / zer / zerz / zemself)
Based on: Singular They, with Feminine subject and possessive pronouns
Nonstandard Sets:
Xe / Xir / Xir / Xirs / Xirself (74 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɚ / zɚ / zɚz / zɚsɛlf (zee / zer / zer / zerz / zerself)
Based on: Feminine
Xe / Xim / Xis / Xis / Ximself (27 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɪm / zɪz / zɪz / zɪmsɛlf (zee / zim / ziz / ziz / zimself)
Based on: Masculine
Xe / Xem / Xir / Xirs / Xirself (23 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɛm / zɚ / zɚz / zɚsɛlf (zee / zem / zer / zerz / zerself)
Based on: Nonstandard They, with Feminine possessive pronouns
Spelling:
Subject - Xe (4604), Xie (18), Xi (10), Xy (9), Xhe (7)
Object - Xem (4508), Xim (38), Xym (10), Xiem (3) | Xir (38), Xer (24), Xyr (18), Xher (3)
Dep. Possessive - Xyr (4472), Xir (62), Xer (43), Xeir (23), Xier (5) | Xis (32)
Ind. Possessive - Xyrs (4469), Xirs (54), Xir's (4), Xers (42), Xeirs (22), Xiers (5), Xhers (3) | Xis (25) | Xir (7), Xyr (3)
Reflexive - Xemself (4495), Ximself (31), Xymself (9) | Xirself (42), Xerself (28), Xyrself (22), Xeirself (7)
Using them when talking:
Xe walked in and told me xyr name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xem the name tags. Xe found xyrs and put it on xymself.
Nonstandard sets:
Xe walked in and told me xir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xir the name tags. Xe found xirs and put it on xirself.
Xe walked in and told me xis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xim the name tags. Xe found xis and put it on ximself.
Xe walked in and told me xir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xem the name tags. Xe found xirs and put it on xirself.
-
6. Faerself Pronouns (Fae/Faer)
6th most common set of pronouns, and the 2nd most popular neopronoun set. (2,662 people)
Usual Set:
Fae / Faer / Faer / Faers / Faeself (2,623)
Pronunciation: feɪ / feɪɹ / feɪɹ / feɪɹz / feɪsɛlf (fay / fayr / fayr / fayrz / fayself)
Based on: the noun Fae/Fairy, with Feminine object and possessive pronouns
Nonstandard Sets:
Fey / Fem / Feir / Feirs / Femself (10 people)
Pronunciation: feɪ / fɛm / feɪɹ / feɪɹz / fɛmsɛlf (fay / fem / fayr / fayrz / femself)
Based on: Singular They
Fey / Fem / Feir / Feirs / Feirself (9 people)
Pronunciation: feɪ / fɛm / feɪɹ / feɪɹz / feɪɹsɛlf (fay / fem / fayr / fayrz / fayrself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Fey / Feyr / Feyr / Feyrs / Feyrself (6 people)
Pronunciation: feɪ / feɪɹ / feɪɹ / feɪɹz / feɪɹsɛlf (fay / fayr / fayr / fayrz / fayrself)
Based on: Feminine
Spelling:
Subject - Fae (2638), Fey (18)
Object -Faer (2625), Feyr (3) | Fem (14), Faem (7)
Dep. Possessive - Faer (2637), Feir (11), Feyr (7)
Ind. Possessive - Faers (2636), Feirs (11), Feyrs (6)| Faes (3)
Reflexive - Faeself (2625) | Faerself (7), Feirself (5), Feyrself (5) | Femself (7), Faemself (4)
Using them when talking:
Fae walked in and told me faer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed faer the name tags. Fae found faers and put it on faeself.
Nonstandard sets:
Fey walked in and told me feir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed fem the name tags. Fey found feirs and put it on femself.
Fey walked in and told me feir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed fem the name tags. Fey found feirs and put it on feirself.
Fey walked in and told me feyr name was Chris. I said hi, and showed feyr the name tags. Fey found feyrs and put it on feyrself.
-
7. Hir Pronouns (Ze or Sie/Hir)
The set associated with older users. Shi/Hir is also associated with the furry fandom and intersex people (who may consider it a completely different set. Research suggests there might have been drama in the 90s.) (2,190 people)
Usual Set:
Ze / Hir / Hir / Hirs / Hirself (2,148 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / hiːɹ / hiːɹ / hiːɹz / hiːɹsɛlf (zee / heer / heer / heerz / heerself)
Based on: Feminine, with a long ‘ee’ for all forms.
Nonstandard Sets:
Shi / Hir / Hir / Hirs / Hirself (34 people)
Pronunciation: ʃaɪ / hiːɹ / hiːɹ / hiːɹz / hiːɹsɛlf (shy / heer / heer / heerz / heerself)
Based on: Feminine, with the same long ‘ee.’
Spelling:
Subject - Ze (2107), Sie (30), Zie (6), Se (3) | Shi (26), Shy (6)
Object - Hir (2177), Hyr (9)
Dep. Possessive - Hir (2174), Hyr (8) | Hirs (5)
Ind. Possessive - Hirs (2177), Hyrs (7)
Reflexive - Hirself (2173), Hyrself (7) | Hemself (3)
Using them when talking:
Ze walked in and told me hir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed hir the name tags. Ze found hirs and put it on hirself.
Nonstandard set:
Shi walked in and told me hir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed hir the name tags. Shi found hirs and put it on hirself.
-
8. Elverson Pronouns (Ey/Em)
Very similar to Spivak pronouns (next), these ones have the subject pronoun (‘ey’) based on ‘they,’ rather than ‘he’ or ‘she.’ (2,056 people)
Usual Set:
Ey / Em / Eir / Eirs / Emself (2,037 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / ɛm / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / ɛmsɛlf (ay / em / ayr / ayrz / emself)
Based on: Singular They
Nonstandard sets:
Ey / Em / Eir / Eirs / Eirself (10 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / ɛm / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / eɪɹsɛlf (ay / em / ayr / ayrz / ayrself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Spelling:
Subject - Ey (2051), Ei (3)
Object - Em (2048)
Dep. Possessive - Eir (2049)
Ind. Possessive - Eirs (2049)
Reflexive - Emself (2037), Eimself (3) | Eirself (11)
Using them when talking:
Ey walked in and told me eir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed em the name tags. Ey found eirs and put it on emself.
Nonstandard set would end with: Ey found eirs and put it on eirself.
-
9. Spivak Pronouns (E/Em)
The set most often named in articles explaining neopronouns. (1,624 people)
Usual Set:
E / Em / Eir / Eirs / Emself (1,575 people)
Pronunciation: iː / ɛm / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / ɛmsɛlf (ee / em / ayr / ayrz / emself)
Based on: Singular They, with Feminine/Masculine subject pronoun.
Nonstandard sets:
E / Em / Es / Es / Emself (13 people)
Pronunciation: iː / ɛm / iːz / iːz / ɛmsɛlf (ee / em / eez / eez / emself)
Based on: Masculine
Spelling:
Subject - E (1604), 'E (3) | En (7) | Em (8)
Object - Em (1600), Im (6) | E (5) |En (4)
Dep. Possessive - Eir (1577), Er (5) | Es (14), Is (5) | Ems (6) | Ens (4)
Ind. Possessive - Eirs (1576), Ers (5) | Es (10), Is (5), 'Is (3) | Ems (9) | Ens (3)
Reflexive - Emself (1593), Imself (4) | Eself (4) | Enself (4)
Using them when talking:
E walked in and told me eir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed em the name tags. E found eirs and put it on emself.
Nonstandard set:
E walked in and told me es name was Chris. I said hi, and showed em the name tags. E found es and put it on emself.
-
10. Lindsay Pronouns (Ae/Aer) (344 people)
Very similar to Spivak and Elverson pronouns. Created for a scifi alien race in 1920.
Usual Set:
Ae / Aer / Aer / Aers / Aerself (236 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / eɪɹ / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / eɪɹsɛlf (ay / ayr / ayr / ayrz / ayrself)
Based on: Feminine, with vowels similar to Singular They.
Nonstandard sets:
Ae / Aem / Aer / Aers / Aemself (22 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / ɛm / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / ɛmsɛlf (ay / em / ayr / ayrz / emself)
Based on: Singular They
Ae / Aer / Aers / Aers / Aerself (20 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / eɪɹz / eɪɹsɛlf (ay / ayr / ayrz / ayrz / ayrself)
Based on: Feminine, with possessives based on nouns.
Ae / Aem / Aer / Aers / Aerself (19 people)
Pronunciation: eɪ / ɛm / eɪɹ / eɪɹz / eɪɹsɛlf (ay / em / ayr / ayrz / ayrself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Spelling:
Subject - Ae (328), Æ (4), Ay (4) | Aer (3)
Object - Aer (268) | Aem (44) | Ae (13)
Dep. Possessive - Aer (285), Ær (3), Aeir (5), Ayr (4) | Aers (24) | Aes (8)
Ind. Possessive - Aers (296), Aer's (4), Ærs (3), Aeirs (5), Ayrs (4) | Aer (6) | Aes (12)
Reflexive - Aerself (280), Ærself (3), Aeirself (3) | Aemself (25) | Aeself (14)
Using them when talking:
Ae walked in and told me aer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed aer the name tags. Ae found aers and put it on aerself.
Nonstandard sets:
Ae walked in and told me aer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed aem the name tags. Ae found aers and put it on aemself.
Ae walked in and told me aers name was Chris. I said hi, and showed aer the name tags. Ae found aers and put it on aerself.
Ae walked in and told me aer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed aem the name tags. Ae found aers and put it on aerself.
-
11. Ve/Ver Pronouns
These seem to be the neopronouns to play around with! Many of the sets here alternate masculine and feminine forms, sometimes in unpredictable ways. (304 people)
Usual Set:
Ve / Ver / Ver / Vers / Verself (70 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɚ / vɚ / vɚz / vɚsɛlf (vee / ver / ver / verz / verself)
Based on: Feminine
Nonstandard Sets:
Ve / Ver / Vis / Vis / Verself (42 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɚ / vɪz / vɪz / vɚsɛlf (vee / ver / viz / viz / verself)
Based on: Masculine and Feminine
Ve / Vem / Ver / Vers / Vemself (32 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɛm / vɚ / vɚz / vɛmsɛlf (vee / vem / ver / verz / vemself)
Based on: Singular They
Ve / Vim / Vis / Vis / Vimself (30 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɪm / vɪz / vɪz / vɪmsɛlf (vee / vim / viz / viz / vimself)
Based on: Masculine
Ve / Vem / Vir / Virs / Virself (29 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɛm / viːɹ / viːɹz / vɚsɛlf (vee / vem / veer / veerz / verself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Ve / Ver / Vis / Vers / Verself (22 people)
Pronunciation: viː / vɚ / vɪz / vɚz / vɚsɛlf (vee / ver / viz / verz / verself)
Based on: Feminine, with one Masculine possessive
Spelling:
Subject - Ve (230), Vi (59), Vy (4)
Object - Ver (90), Vir (57), Zher (6) | Vim (59), Vem (56), Vym (5) | Ven (8) | Vis (4)
Dep. Possessive - Vir (73), Ver (56), Veir (18), Vyr (10), Vier (4) | Vis (107) | Virs (4), Vers (3) | Vens (3)
Ind. Possessive - Virs (83), Vers (67), Veirs (18), Vyrs (9), Vaers (3) | Vis (92) | Vens (3)
Reflexive - Verself (100), Virself (75), Vyrself (5), Verrself (4) | Vimself (48), Vemself (33) | Viself (4), Veself (4) | Venself (6)
Using them when talking:
Ve walked in and told me ver name was Chris. I said hi, and showed ver the name tags. Ve found vers and put it on verself.
Nonstandard sets:
Ve walked in and told me vis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed ver the name tags. Ve found vis and put it on verself.
Ve walked in and told me ver name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vem the name tags. Ve found vers and put it on vemself.
Ve walked in and told me vis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vim the name tags. Ve found vis and put it on vimself.
Ve walked in and told me vir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vem the name tags. Ve found virs and put it on virself.
Ve walked in and told me vis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed ver the name tags. Ve found vers and put it on vimself.
-
12. Ze Pronouns
Pronounced almost identically to Xe pronouns, but derives from Ze/Hir pronouns (286 people)
Usual Set:
Ze / Zir / Zir / Zirs / Zirself (140 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / ziːɹ / ziːɹ / ziːɹz / ziːɹsɛlf (zee / zeer / zeer / zeerz / zeerself)
Based on: Ze/Hir, which is based on Feminine, with a long ‘ee’ for all forms.
Nonstandard Sets:
Ze / Zem / Zir / Zirs / Zemself (76 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɛm / ziːɹ / ziːɹz / zɛmsɛlf (zee / zem / zeer / zeerz / zemself)
Based on: Singular They
Ze / Zem / Zir / Zirs / Zirself (26 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɛm / ziːɹ / ziːɹz / ziːɹsɛlf (zee / zem / zeer / zeerz / zeerself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Ze / Zim / Zis / Zis / Zimself (76 people)
Pronunciation: ziː / zɪm / zɪz / zɪz / zɪmsɛlf (zee / zim / ziz / ziz / zimself)
Based on: Masculine
Spelling:
Subject - Ze (237), Zie (27), Zhe (17), Zi (3)
Object - Zir (126), Zer (8), Zher (6) | Zem (83), Zim (31), Zhim (7)
Dep. Possessive - Zir (181), Zer (31), Zeir (20), Zyr (12), Zher (10), Zhir (3) | Zis (10) | Zirs (5)
Ind. Possessive - Zirs (178), Zers (31), Zeirs (22), Zyrs (12), Zhers (10), Zhirs (3) | Zis (8) | Zir (3)
Reflexive - Zirself (149), Zerself (14), Zherself (6), Zyrself (4), Zeirself (3) | Zemself (78), Zimself (25), Zymself (4), Zhimself (7) | Zeself (4)
Using them when talking:
Ze walked in and told me zir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed zir the name tags. Ze found zirs and put it on zirself.
Nonstandard sets:
Ze walked in and told me zir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed zem the name tags. Ze found zirs and put it on zemself.
Ze walked in and told me zir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed zem the name tags. Ze found zirs and put it on zirself.
Ze walked in and told me zis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed zim the name tags. Ze found zis and put it on zimself.
-
13. Star Pronouns
The most popular nounself pronouns (13th overall)! (157 people)
Usual Set:
Star / Star / Stars / Stars / Starself (133 people)
Pronunciation: stɑɹ / stɑɹ / stɑɹz / stɑɹz / stɑɹsɛlf (star / star / starz / starz / starself)
Based on: Nouns
Nonstandard Sets:
Usual Set: Star / Star / Star / Stars / Starself (9 people)
Pronunciation: stɑɹ / stɑɹ / stɑɹ / stɑɹz / stɑɹsɛlf (star / star / star / starz / starself)
Based on: Nouns, with possessives influenced by Feminine/Singular They
Spelling:
Subject - Star (150) | Sta (3)
Object - Star (144) | Stars (4)
Dep. Possessive - Stars (119), Star's (16) | Star (12)
Ind. Possessive - Stars (130), Star's (19)
Reflexive - Starself (150)
Using them when talking:
Star walked in and told me stars name was Chris. I said hi, and showed star the name tags. Star found stars and put it on starself.
Nonstandard sets:
Star walked in and told me star name was Chris. I said hi, and showed star the name tags. Star found stars and put it on starself.
-
14. Hy/Hym Pronouns
Pronounced identically to masculine pronouns. (130 people)
Usual Set:
Hy / Hym / Hys / Hys / Hymself (103 people)
Pronunciation: hiː / hɪm / hɪz / hɪz / hɪmsɛlf (hee / him /hiz / hiz / himself)
Based on: Masculine
Nonstandard Set:
Hey / Hem / Heir / Heirs / Hemself (9 people)
Pronunciation: heɪ / hɛm / heɪɹ / heɪɹz / heɪɹsɛlf (hay / hem /hayr / hayrz / hemself)
Based on: Singular They
Spelling:
Subject - Hy (97), He (10), Hie (5) | Hey (10)
Object - Hym (65), Hymn (44), Hem (15)
Dep. Possessive - Hys (97) | Heir (11), Hyr (3) | Hymns (4)
Ind. Possessive - Hys (97) | Heirs (1) | Hymns (5)
Reflexive - Hymself (58), Hymnself (46), Hemself (12)
Using them when talking:
Hy walked in and told me hys name was Chris. I said hi, and showed hym the name tags. Hy found hys and put it on hymself.
Nonstandard sets:
Hey walked in and told me heir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed hem the name tags. Hey found heirs and put it on hemself.
-
15. Thon Pronouns
One of the oldest neopronouns, dating to 1858. A contraction of 'that one'. Linguists and social reformers LOVED these pronouns, actual users are much rarer. (122 people)
Usual Set:
Thon / Thon / Thons / Thons / Thonself (104 people)
Pronunciation: ðʌn / ðʌn / ðʌnz / ðʌnz / ðʌnsɛlf (dhuhn / dhuhn / dhuhnz / dhuhnz / dhuhnself – ‘the’ + n)
Based on: One (Indefinite Pronoun), which works identically to nouns
Nonstandard Set:
Thon / Thon / Thon / Thons / Thonself (6 people)
Pronunciation: ðʌn / ðʌn / ðʌn / ðʌnz / ðʌnsɛlf (dhuhn / dhuhn / dhuhn / dhuhnz / dhuhnself)
Based on: One, with possessives influenced by Feminine/Singular They
Spelling:
Subject - Thon (119)
Object - Thon (114) | Thons (5)
Dep. Possessive - Thons (104), Thon's (5) | Thon (7)
Ind. Possessive - Thons (101), Thon's (12) | Thon (4)
Reflexive - Thonself (119)
Using them when talking:
Thon walked in and told me thons name was Chris. I said hi, and showed thon the name tags. Thon found thons and put it on thonself.
Nonstandard sets:
Thon walked in and told me thon name was Chris. I said hi, and showed thon the name tags. Thon found thons and put it on thonself.
-
16. Void Pronouns
The 2nd most popular nounself pronouns (16th overall) (117 people)
Usual Set:
Void / Void / Voids / Voids / Voidself (72 people)
Pronunciation: voɪd / voɪd / voɪdz / voɪdz / voɪdsɛlf (voyd / voyd / voydz / voydz / voydself)
Based on: Nouns (Void)
Nonstandard Sets:
Voi / Void / Voids / Voids / Voidself (69 people)
Pronunciation: voɪ / voɪd / voɪdz / voɪdz / voɪdsɛlf (voy / voyd / voydz / voydz / voydself)
Based on: Nouns (Void), with subject form shortened to better match established pronouns
Voi / Void / Void / Voids / Voidself (10 people)
Pronunciation: voɪ / voɪd / voɪd / voɪdz / voɪdsɛlf (voy / voyd / voyd / voydz / voydself)
Based on: Nouns (Void), with subject form shortened, and possessives influenced by Feminine/Singular They
Spelling:
Subject - Voi (108), Vo (3) | Void (80) | Vi (3)
Object - Void (180) | Voi (9)
Dep. Possessive - Voids (134), Void's (14) | Void (18) | Vois (14) | Voi (4)
Ind. Possessive - Voids (153), Void's (19) | Vois (12)
Reflexive - Voidself (181) | Voiself (9)
Using them when talking:
Void walked in and told me voids name was Chris. I said hi, and showed void the name tags. Void found voids and put it on voidself.
Nonstandard sets:
Voi walked in and told me voids name was Chris. I said hi, and showed void the name tags. Voi found voids and put it on voidself.
Voi walked in and told me void name was Chris. I said hi, and showed void the name tags. Voi found voids and put it on voidself.
-
17. Ne/Nem Pronouns
(114 people)
Usual Set:
Ne / Nem / Nir / Nirs / Nemself (61 people)
Pronunciation: niː / nɛm / nɚ / nɚz / nɛmsɛlf (nee / nem / ner / nerz / nemself)
Based on: Singular They, with Feminine subject and possessive pronouns
Nonstandard Sets:
Ne / Nim / Nis / Nis / Nimself (19 people)
Pronunciation: niː / nɪm / nɪz / nɪz / nɪmsɛlf (nee / nim / niz / niz / nimself)
Based on: Masculine
Ne / Nem / Nir / Nirs / Nirself (8 people)
Pronunciation: niː / nɛm / nɚ / nɚz / nɚsɛlf (nee / nem / ner / nerz / nerself)
Based on: Nonstandard They, with Feminine subject and possessive pronouns
Ne / Nem / Nems / Nems / Nemself (7 people)
Pronunciation: niː / nɛm / nɛmz / nɛmz / nɛmsɛlf (nee / nem / nemz / nemz / nemself)
Based on: Nouns
Spelling:
Subject - Ne (98), Nie (4), Ni (3)
Object - Nem (65), Nym (25), Nim (16)
Dep. Possessive - Nir (48), Neir (11), Nyr (10), Ner (7) | Nis (13), Nys (6) | Nems (3), Nims (3)
Ind. Possessive - Nirs (45), Neirs (11), Nyrs (9), Ners (5) | Nis (15), Nys (5) | Nems (5), Nims (4)
Reflexive - Nemself (68), Nymself (22), Nimself (15) | Nirself (5), Neirself (3), Nyrself (3)
Using them when talking:
Ne walked in and told me nir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed nem the name tags. Ne found nirs and put it on nemself.
Nonstandard sets:
Ne walked in and told me nis name was Chris. I said hi, and showed nim the name tags. Ne found nis and put it on nimself.
Ne walked in and told me nir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed nem the name tags. Ne found nirs and put it on nirself.
Ne walked in and told me nems name was Chris. I said hi, and showed nem the name tags. Ne found nems and put it on nemself.
-
18. Kit, Cat Pronouns
The first of the animal based pronouns! People using animal based pronouns frequently alternate between multiple sets - based off animals (kit, bug), their sounds (meow, caw), and their body parts (paw). (103 people)
Usual Set:
Kit / Kit / Kits / Kits / Kitself (60 people)
Pronunciation: kɪt / kɪt / kɪts / kɪts / kɪtsɛlf (kit / kit / kits / kits / kitself)
Based on: Nouns (Kit/Kitty)
Nonstandard Sets:
Cat / Cat / Cats / Cats / Catself (23 people)
Pronunciation: kat / kat / kats / kats / katsɛlf (kat / kat / kats / kats / katself)
Based on: Nouns (Cat)
Spelling:
Subject - Kit (69) | Kitty (6) | Cat (23)
Object - Kit (64) | Kits (3) | Kitty (8) | Cat (23)
Dep. Possessive - Kits (65), Kit's (3) | Kittys (4), Kitty's (3) | Cats (18), Cat's (4)
Ind. Possessive - Kits (62), Kit's (4) | Kitty's (4) | Kittens (3) | Cats (17), Cat's (6)
Reflexive - Kitself (67) | Kittyself (4) | Kittenself (4) | Catself (23)
Using them when talking:
Kit walked in and told me kits name was Chris. I said hi, and showed kit the name tags. Kit found kits and put it on kitself.
Nonstandard sets:
Cat walked in and told me cats name was Chris. I said hi, and showed cat the name tags. Cat found cats and put it on catself.
-
19. Pup Pronouns
(102 people)
Usual Set: Pup / Pup / Pups / Pups / Pupself (75 people)
Pronunciation: pʌp / pʌp / pʌps / pʌps / pʌpsɛlf (puhp / puhp / puhps / puhps / puhpself)
Based on: Nouns (Pup/Puppy)
Spelling:
Subject - Pup (85) | Dog (6), The Dog (5) | Mutt (4)
Object - Pup (75) | Pups (6)| Dog (5), The Dog (4) | Mutt (4)
Dep. Possessive - Pups (69), Pup's (12) | Dogs (3), The Dog's (4) | Mutts (4)
Ind. Possessive - Pups (69), Pup's (13) | Dogs (5), The Dog's (4) | Mutts (4)
Reflexive - Pupself (82) | Dogself (6) | Itself (4) | Muttself (4)
Using them when talking:
Pup walked in and told me pups name was Chris. I said hi, and showed pup the name tags. Pup found pups and put it on pupself.
-
20. Vae Pronouns
Ve pronouns have endless variations! These ones use a subject form based on They, rather than He/She, and seem to be influenced by Ae and Fae pronouns. (91 people)
Usual Set:
Vae / Vaem / Vaer / Vaers / Vaemself (42 people)
Pronunciation: veɪ / vɛm / veɪɹ / veɪɹz / veɪmsɛlf (vay / vem / vayr / vayrz / vemself)
Based on: Singular They
Nonstandard Sets:
Vae / Vaer / Vaer / Vaers / Vaerself (27 people)
Pronunciation: veɪ / veɪɹ / veɪɹ / veɪɹz / veɪɹsɛlf (vay / vayr / vayr / vayrz / vayrself)
Based on: Feminine
Vae / Vaem / Vaer / Vaers / Vaerself (11 people)
Pronunciation: veɪ / vɛm / veɪɹ / veɪɹz / veɪɹsɛlf (vay / vem / vayr / vayrz / vayrself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Spelling:
Subject - Vae (63), Vey (24)
Object - Vem (26), Vaem (22) | Vaer (28) | Vae (3)
Dep. Possessive - Vaer (59), Veir (14), Ver (4)
Ind. Possessive - Vaers (58), Veirs (14), Vers (5)
Reflexive – Vaerself (37), Veirself (4) | Vymself (20), Vaemself (16) | Vaeself (4)
Using them when talking:
Vae walked in and told me vaer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vaem the name tags. Vae found vaers and put it on vaemself.
Nonstandard sets:
Vae walked in and told me vaer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vaer the name tags. Vae found vaers and put it on vaerself.
Vae walked in and told me vaer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed vaem the name tags. Vae found vaers and put it on vaerself.
-
21. Xey Pronouns
Xe pronouns also have a version based on They in the subject form. (91 people)
Usual Set:
Xey / Xem / Xeir / Xeirs / Xemself (37 people)
Pronunciation: zeɪ / zɛm / zeɪɹ / zeɪɹz / zeɪmsɛlf (zay / zem / zayr / zayrz / zemself)
Based on: Singular They
Nonstandard Sets:
Xey / Xem / Xeir / Xeirs / Xeirself (37 people)
Pronunciation: zeɪ / zɛm / zeɪɹ / zeɪɹz / zeɪɹsɛlf (zay / zem / zayr / zayrz / zayrself)
Based on: Nonstandard They
Xae / Xaem / Xaer / Xaers / Xaerself (11 people)
Pronunciation: zeɪ / zeɪɹ / zeɪɹ / zeɪɹz / zeɪɹsɛlf (zay / zayr / zayr / zayrz / zayrself)
Based on: Feminine
Spelling:
Subject - Xey (71), Xae (10)
Object - Xem (70), Xaem (4) | Xaer (4)
Dep. Possessive - Xeir (49), Xyr (12), Xaer (8), Xer (7), Xeyr (3)
Ind. Possessive - Xeirs (46), Xyrs (12), Xaers (7), Xers (7), Xeyrs (3)
Reflexive - Xemself (61), Xaemself (3) | Xeirself (5), Xaerself (4)
Using them when talking:
Xey walked in and told me xeir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xem the name tags. Xey found xeirs and put it on xemself.
Nonstandard sets:
Xey walked in and told me xeir name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xem the name tags. Xey found xeirs and put it on xeirself.
Xae walked in and told me xaer name was Chris. I said hi, and showed xaer the name tags. Xae found xaers and put it on xaerself.
-
22. Mew Pronouns
These pronouns often alternate with Kit/Cat pronouns, or other cat sounds like Nyan or Purr (89 people)
Usual Set:
Mew / Mew / Mews / Mews / Mewself (48 people)
Pronunciation: mjuː / mjuː / mjuːz / mjuːz / mjusɛlf (myoo / myoo / myooz / myooz / myooself)
Based on: Nouns (Mew)
Nonstandard Sets:
Meow / Meow / Meows / Meows / Meowself (27 people)
Pronunciation: mjaʊ or mi‧aʊ / mjaʊ / mjaʊz / mjaʊz / mjaʊsɛlf (myow / myow / myowz / myowz / myowself)
Based on: Nouns (Meow)
Spelling:
Subject - Mew (53) | Meow (29) | Mrr (3)
Object - Mew (49) | Meow (29) | Mrrp (4)
Dep. Possessive - Mews (47) | Meows (25), Meow's (4) | Mrrps (3)
Ind. Possessive - Mews (45) | Meows (27), Meow's (4) | Mrrps (3)
Reflexive - Mewself (50) | Meowself (31) | Mrrpself (3)
Using them when talking:
Mew walked in and told me mews name was Chris. I said hi, and showed mew the name tags. Mew found mews and put it on mewself.
Nonstandard sets:
Meow walked in and told me meows name was Chris. I said hi, and showed meow the name tags. Meow found meows and put it on meowself.
-
23. Bun Pronouns
(71 people)
Usual Set:
Bun / Bun / Buns / Buns / Bunself (60 people)
Pronunciation: bʌn / bʌn / bʌnz / bʌnz / bʌnsɛlf (buhn / buhn / buhnz / buhnz / buhnself)
Based on: Nouns (Bunny)
Spelling:
Subject - Bun (69)
Object - Bun (69)
Dep. Possessive - Buns (59), Bun's (10)
Ind. Possessive - Buns (55), Bun's (10)
Reflexive - Bunself (68)
Using them when talking:
Bun walked in and told me buns name was Chris. I said hi, and showed bun the name tags. Bun found buns and put it on bunself.
-
24. Indefinite Pronouns (One)
The 'formal' option - this is what grammarians used to suggest (64 people)
Usual Set:
One / One / One's / One's / Oneself (51 people)
Pronunciation: wʌn / wʌn / wʌnz / wʌnz / wʌnsɛlf (wuhn / wuhn / wuhnz / wuhnz / wuhnself)
Based on: Indefinite Pronoun
Spelling:
Subject - One (53), That One (7), This One (4)
Object - One (50), That One (8), This One (3)
Dep. Possessive - One's (30), Ones (23), That One's (6), This One's (3)
Ind. Possessive - One's (31), Ones (22), That One's (6)
Reflexive - Oneself (53), That One's Self (4)
Using them when talking:
One walked in and told me one's name was Chris. I said hi, and showed one the name tags. One found one's and put it on oneself.
-
25. Moon/Lun Pronouns
(57 people)
Usual Set:
Moon / Moon / Moons / Moons / Moonself (32 people)
Pronunciation: muːn / muːn / muːnz / muːnz / muːnsɛlf (moon / moon / moonz / moonz / moonself)
Based on: Nouns (Moon)
Nonstandard sets:
Lun / Lun / Luns / Luns / Lunself (9 people)
Pronunciation: luːn / luːn / luːnz / luːnz / luːnsɛlf (loon / loon / loonz / loonz / loonself)
Based on: Nouns (Lunar)
Spelling:
Subject - Moon (33) | Lun (9) | Lu (8)
Object - Moon (33) | Lun (10) | Luna (6) | Lunar (3)
Dep. Possessive - Moons (26), Moon's (8) | Luns (12)
Ind. Possessive - Moons (26), Moon's (7) | Luns (12)
Reflexive - Moonself (34) | Lunself (12) | Lunaself (4)
Using them when talking:
Moon walked in and told me moons name was Chris. I said hi, and showed moon the name tags. Moon found moons and put it on moonself.
Nonstandard sets:
Lun walked in and told me luns name was Chris. I said hi, and showed lun the name tags. Lun found luns and put it on lunself.
-
A note on defining sets:
Deciding what to consider a variant, and what to consider a different set altogether, wasn't easy.
Elverson and Spivak pronouns are mostly separated because of their history, and how (relatively) well known they are. I then tried to stay consistent, and separated things like 'ze' and 'zey' sets.
Animal and sound based nounself pronouns are grouped based on how difficult it was to separate them. A relatively high percentage of people wrote 'kit' and 'cat' forms into the same entry. Less people grouped 'mew' and 'nya' forms. And, while 'mew' and 'nya' forms were FREQUENTLY grouped with 'kit' and 'cat' forms, I kept them separate for my own sanity.
I am also VERY glad that 'sie/sier' pronouns didn't make the top 25. 'Sie', 'se', 'sea', 'ce', and 'ke' are probably unsortable without talking to their users individually. (There's at least three pronunciations in there - 'zee', see' and 'kee'!) But I love the 4 people using 'sir' as a pronoun. That amuses me!
266 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2020 US Census Largest Detailed White Ethnicities Per County
232 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! A while ago I saw one of your tiktoks about how northern democrats typically view people from Appalachia, and it really made me re-examine some biases I had and I deeply appreciated that. I'm from New Hampshire, and basically this primary season we were completely ignored by democratic candidates because of some issues with the DNC and our primary being labeled "unsanctioned". It was weird to not feel supported or valued by my party for the first time ever, (especially when NH tends to get a lot of attention) and it reminded me of your tiktok and how you mentioned that republicans tend to reach out to people in the south while democrats tend to ignore them as a lost cause. Because I saw that happening here with an insanly disproportionate republican presence in my state leading to the primaries. I know the comparisons aren't equal, but it helped drive home the message for me and gave me just a taste of what you explained so clearly in your tiktok. I understand if you choose not to post this, but I really wanted to thank you for opening my eyes and helping me face some biases I didn't know I had.
hello and thank you (for re-examining your biases and for writing me this message). i'm gonna use this as a chance to restate some of the things i mentioned in the video you're talking about.
i'd like to start this by saying i know appalachia and the south aren't perfect. there's racism and homophobia and bigotry. being someone who is marginalized or minoritized in appalachia/the south isn't always easy. but appalachia/the south doesn't have the monopoly on bigotry. america is rife with it. it's something marginalized folks all over the country have to face. and when northern dems act like racism and homophobia and bigotry are things that don't occur in their state simply because it's a blue state, they're doing an incredible disservice to the marginalized people that live in their communities who are facing the results of bigotry.
the folks living in appalachia/the south are heavily stereotyped as nothing more than ignorant backwood cousin fucking hillbillies, and while there are people that live here that fit that bill, appalachia/the south is not a monolith.
appalachia is region that spans from mississippi all the way to new york. the south (depending on who you ask) consists of 17 different states. and here's a little fun fact about the south for ya: according to the 2020 census, out of the 41.6 million black people that live in america, 38.9% of them live in the south.
so when that entire region is written off, forgotten about, and treated as a lost cause it's not the bigots that are being left behind; it's the marginalized people that live here that are being written off. the very same folks democrats and liberals love claiming they care about are the ones being left behind.
one of the reasons republicans have such a strong hold on appalachia/the south is because they put in the work to earn the trust of the voter. work that democrats just don't do. so of course republicans are gonna get the vote, they earned it.
other reasons for the stronghold existing (that people never wanna talk about for some reason) are: gerrymandering, voter suppression, lack of state funding that leads to lack of education, general lack of education, high poverty rates, lack of internet access. i could go on and on.
there are so many marginalized people that live in this region that are working themselves to the bone and trying their damndest to make appalachia/the south a better place for EVERYONE to live and when high falutin yankees act like every single person that lives here is the racist uncle you have to ignore at christmas, they are discrediting the work being done to try and change the region for the better.
allow me to say this again: when appalachia/the south is written off as nothing more than a home to bigots, it's not the bigots being written off, it's the people affected by bigotry.
there are people fighting to make these areas better. we are trying. so please, please stop writing us off.
we are not a lost cause.
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
While the Cass Review has been presented by the U.K. media, politicians and some prominent doctors as a triumph of objective inquiry, its most controversial recommendations are based on prejudice rather than evidence. Instead of helping young people, the review has caused enormous harm to children and their families, to democratic discourse and to wider principles of scientific endeavour. There is an urgent need to critically examine the actual context and findings of the report.
Since its 2020 inception, the Cass Review’s anti-trans credentials have been clear. It explicitly excluded trans people from key roles in research, analysis and oversight of the project, while sidelining most practitioners with experience in trans health care. The project centered and sympathized with anti-trans voices, including professionals who deny the very existence of trans children. Former U.K. minister for women and equalities Kemi Badenoch, who has a history of hostility toward trans people even though her role was to promote equality within the government, boasted that the Cass Review was only possible because of her active involvement.
The methodology underpinning the Cass Review has been extensively criticized by medical experts and academics from a range of disciplines. Criticism has focused especially on the effect of bias on the Cass approach, double standards in the interpretation of data, substandard scientific rigor, methodological flaws and a failure to properly substantiate claims. For example, although the existing literature reports a wide range of important benefits of social transition and no credible evidence of harm, the Cass Review cautions against it. The review also dismisses substantial documented benefits of adolescent medical transition as underevidenced while highlighting risks based on evidence of significantly worse quality. A warning about impaired brain maturation, for instance, cites a single, very short speculative paper that in turn rests on one experimental study with female mice. Meanwhile extensive qualitative data and clinical consensus are almost entirely ignored. These issues help explain why the Cass recommendations differ from previous academic reviews and expert guidance from major medical organisations such as the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) and the American Academy of Pediatrics.
WPATH’s experts themselves highlight the Cass report’s “selective and inconsistent use of evidence,” with recommendations that “often do not follow from the data presented in the systematic reviews.” Leading specialists in transgender medical care from the U.S. and Australia emphasize that “the Review obscures key findings, misrepresents its own data, and is rife with misapplications of the scientific method.” For instance, the Cass report warns that an “exponential change in referrals” to England’s child and adolescent gender clinic during the 2010s is “very much faster than would be expected.” But this increase has not been exponential, and the maximum 5,000 referrals it notes in 2021 represents a very small proportion of the 44,000 trans adolescents in the U.K. estimated from 2021 census data.
7 August 2024
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Taiwanese?
As part of my return to posting on this blog, I want to start posting a bit more about Taiwanese! It's not really a language I've seen discussed much on langblr blogs, so I'm going to start with some basics.
Where is Taiwanese spoken?
Unsurprisingly, Taiwan! It's most commonly spoken in the central and southern parts of Taiwan, and less commonly spoken in the northern and eastern parts, but you can hear it spoken pretty much anywhere.
What else is Taiwanese called?
台語 tâi-gí and 台灣話 tâi-uân-uē "Taiwanese" are the most common names colloquially. Officially, (台灣)閩南語 (tâi-uân) bân-lâm-gí "Taiwanese Southern Min" is used as the name of the language. You'll also occasionally see terms like 福建 hok-kiàn or 福佬 hô-ló used. I've given the transcriptions of these terms in Taiwanese, but the same terms are used with their Mandarin pronunciations in Mandarin.
Where does Taiwanese come from?
Taiwanese is a member of the Southern Min branch of the Sinitic language family. During the late Ming and Qing dynasties, Han settlers came over from the Fujian province of China, especially the Zhangzhou and Quanzhou areas, and brought their own languages with them. For a while, there was conflict between Zhangzhou and Quanzhou speakers, but eventually the two varieties coalesced into one language, with dialectal differences causing some dialects to be closer to one or the other. This means that Taiwanese is mutually intelligible with Xiamen/Amoy and Zhangzhou Southern Min, and related to other varieties of Southern Min, also called Hokkien, spoken in China and Southeast Asia. Taiwanese also has loanwords from Japanese due to the island's having undergone 50 years of Japanese colonization, and younger people's Taiwanese has also been influenced by Mandarin.
Is Taiwanese a language or a dialect?
Though some people will refer to Taiwanese as a dialect, it's generally an argument based in a denigration of the language and not really defensible on linguistic or social grounds. I've come to believe that the distinction between language and dialect is mostly social, with some influence from factors such as mutual intelligibility. Taiwanese is treated as a language by the Taiwanese government and taught as a language in public schools. Taiwanese is also not mutually intelligible with Mandarin or other languages outside of the Southern Min family. Some people point to the mutual intelligibility of Chinese characters as evidence that all Sinitic languages are in fact dialects, but even that doesn't hold-- Taiwanese is frequently written in romanization, and even when it isn't, there are plenty of sentences that would be pretty much unintelligible to a Mandarin speaker. For example, the Mandarin sentences 那個女人很美 ("that woman is beautiful") could theoretically be read aloud with Taiwanese pronunciation, but the more natural way to translate and write that sentence is 彼个查某真媠, which is very hard to parse in Mandarin.
How many people speak Taiwanese?
This is a shockingly hard question to answer! Taiwanese is often considered endangered, though it is in a much more stable position than languages such as Hakka and Taiwanese indigenous languages. One common estimate is that 70% of people in Taiwan speak Taiwanese. The 2020 census listed Taiwanese as the primary language of 32% Taiwan's population and the secondary language of 54% of Taiwan's population. This would add up to over 80%, which may seem high, but many people are partial or non-fluent speakers of Taiwanese.
What are the dialects of Taiwanese?
The prestige dialect of Taiwanese is the variety spoken in Kaohsiung and Tainan, which has a mixture of Zhangzhou and Quanzhou features. The Taiwanese spoken in coastal Taiwan, Penghu and Taipei tends to have more Quanzhou features, while the Taiwanese spoken in inland central Taiwan and Yilan tends to have more Zhangzhou features. However, Taiwanese dialectology is complicated, and some people have argued for other forms of classification. The Southern and Taipei dialects are going to be most relevant and salient to most learners.
Why should I learn Taiwanese?
Taiwanese is definitely worth learning if you're planning to spend a significant amount of time in Taiwan, especially central/southern or rural Taiwan. In my experience, I almost never needed Taiwanese to get around in Taiwan, but studying even just a little helped me form relationships with the people around me. Taiwanese has impacted the way that people in Taiwan speak Mandarin, and is commonly seen in culture and politics. Taiwanese-language culture includes traditional art forms like 布袋戲 pòo-tē-hì puppet theater or 歌仔戲 kua-á-hì opera, and modern music, literature and entertainment.
What resources are available for learning Taiwanese?
At some point, I'll make a full post about resources for Taiwanese. But for now, I'll mention that Bite-Size Taiwanese makes some easily accessible resources. There are textbooks out there in both English and Mandarin, as well as books in/about Taiwanese that can be purchased from books.com.tw and shipped internationally. Most language learning apps don't have Taiwanese, but glossika does. Unfortunately, most of these materials assume some knowledge of (but not necessarily total fluency in) Mandarin. There are also podcasts, youtube videos, music, tv/movies, literature, and more materials made for native speakers of Taiwanese that can serve as learning materials.
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where It’s Most Dangerous to Be Black in America
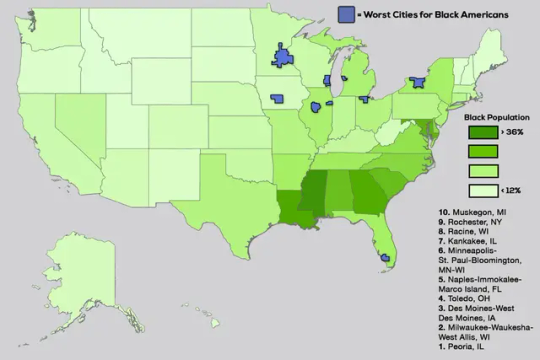
Black Americans made up 13.6% of the US population in 2022 and 54.1% of the victims of murder and non-negligent manslaughter, aka homicide. That works out, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, to a homicide rate of 29.8 per 100,000 Black Americans and four per 100,000 of everybody else.(1)

A homicide rate of four per 100,000 is still quite high by wealthy-nation standards. The most up-to-date statistics available from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development show a homicide of rate one per 100,000 in Canada as of 2019, 0.8 in Australia (2021), 0.4 in France (2017) and Germany (2020), 0.3 in the UK (2020) and 0.2 in Japan (2020).
But 29.8 per 100,000 is appalling, similar to or higher than the homicide rates of notoriously dangerous Brazil, Colombia and Mexico. It also represents a sharp increase from the early and mid-2010s, when the Black homicide rate in the US hit new (post-1968) lows and so did the gap between it and the rate for everybody else. When the homicide rate goes up, Black Americans suffer disproportionately. When it falls, as it did last year and appears to be doing again this year, it is mostly Black lives that are saved.
As hinted in the chart, racial definitions have changed a bit lately; the US Census Bureau and other government statistics agencies have become more open to classifying Americans as multiracial. The statistics cited in the first paragraph of this column are for those counted as Black or African American only. An additional 1.4% of the US population was Black and one or more other race in 2022, according to the Census Bureau, but the CDC Wonder (for “Wide-ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research”) databases from which most of the statistics in this column are drawn don’t provide population estimates or calculate mortality rates for this group. My estimate is that its homicide rate in 2022 was about six per 100,000.
A more detailed breakdown by race, ethnicity and gender reveals that Asian Americans had by far the lowest homicide rate in 2022, 1.6, which didn’t rise during the pandemic, that Hispanic Americans had similar homicide rates to the nation as a whole and that men were more than four times likelier than women to die by homicide in 2022. The biggest standout remained the homicide rate for Black Americans.

Black people are also more likely to be victims of other violent crime, although the differential is smaller than with homicides. In the 2021 National Crime Victimization Survey from the Bureau of Justice Statistics (the 2022 edition will be out soon), the rate of violent crime victimization was 18.5 per 1,000 Black Americans, 16.1 for Whites, 15.9 for Hispanics and 9.9 for Asians, Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders. Understandably, Black Americans are more concerned about crime than others, with 81% telling Pew Research Center pollsters before the 2022 midterm elections that violent crime was a “very important” issue, compared with 65% of Hispanics and 56% of Whites.
These disparities mainly involve communities caught in cycles of violence, not external predators. Of the killers of Black Americans in 2020 whose race was known, 89.4% were Black, according to the FBI. That doesn’t make those deaths any less of a tragedy or public health emergency. Homicide is seventh on the CDC’s list of the 15 leading causes of death among Black Americans, while for other Americans it’s nowhere near the top 15. For Black men ages 15 to 39, the highest-risk group, it’s usually No. 1, although in 2022 the rise in accidental drug overdoses appears to have pushed accidents just past it. For other young men, it’s a distant third behind accidents and suicides.
To be clear, I do not have a solution for this awful problem, or even much of an explanation. But the CDC statistics make clear that sky-high Black homicide rates are not inevitable. They were much lower just a few years ago, for one thing, and they’re far lower in some parts of the US than in others. Here are the overall 2022 homicide rates for the country’s 30 most populous metropolitan areas.
Metropolitan areas are agglomerations of counties by which economic and demographic data are frequently reported, but seldom crime statistics because the patchwork of different law enforcement agencies in each metro area makes it so hard. Even the CDC, which gets its mortality data from state health departments, doesn’t make it easy, which is why I stopped at 30 metro areas.(2)
Sorting the data this way does obscure one key fact about homicide rates: They tend to be much higher in the main city of a metro area than in the surrounding suburbs.
But looking at homicides by metro area allows for more informative comparisons across regions than city crime statistics do, given that cities vary in how much territory they cover and how well they reflect an area’s demographic makeup. Because the CDC suppresses mortality data for privacy reasons whenever there are fewer than 10 deaths to report, large metro areas are good vehicles for looking at racial disparities. Here are the 30 largest metro areas, ranked by the gap between the homicide rates for Black residents and for everybody else.
The biggest gap by far is in metropolitan St. Louis, which also has the highest overall homicide rate. The smallest gaps are in metropolitan San Diego, New York and Boston, which have the lowest homicide rates. Homicide rates are higher for everybody in metro St. Louis than in metro New York, but for Black residents they’re six times higher while for everyone else they’re just less than twice as high.
There do seem to be some regional patterns to this mayhem. The metro areas with the biggest racial gaps are (with the glaring exception of Portland, Oregon) mostly in the Rust Belt, those with the smallest are mostly (with the glaring exceptions of Boston and New York) in the Sun Belt. Look at a map of Black homicide rates by state, and the highest are clustered along the Mississippi River and its major tributaries. Southern states outside of that zone and Western states occupy roughly the same middle ground, while the Northeast and a few middle-of-the-country states with small Black populations are the safest for their Black inhabitants.(3)
Metropolitan areas in the Rust Belt and parts of the South stand out for the isolation of their Black residents, according to a 2021 study of Census data from Brown University’s Diversity and Disparities Project, with the average Black person living in a neighborhood that is 60% or more Black in the Detroit; Jackson, Mississippi; Memphis; Chicago; Cleveland and Milwaukee metro areas in 2020 (in metro St. Louis the percentage was 57.6%). Then again, metro New York and Boston score near the top on another of the project’s measures of residential segregation, which tracks the percentage of a minority group’s members who live in neighborhoods where they are over-concentrated compared with White residents, so segregation clearly doesn’t explain everything.
Looking at changes over time in homicide rates may explain more. Here’s the long view for Black residents of the three biggest metro areas. Again, racial definitions have changed recently. This time I’ve used the new, narrower definition of Black or African American for 2018 onward, and given estimates in a footnote of how much it biases the rates upward compared with the old definition.
All three metro areas had very high Black homicide rates in the 1970s and 1980s, and all three experienced big declines in the 1990s and 2000s. But metro Chicago’s stayed relatively high in the early 2010s then began a rebound in mid-decade that as of 2021 had brought the homicide rate for its Black residents to a record high, even factoring in the boost to the rate from the definitional change.
What happened in Chicago? One answer may lie in the growing body of research documenting what some have called the “Ferguson effect,” in which incidents of police violence that go viral and beget widespread protests are followed by local increases in violent crime, most likely because police pull back on enforcement. Ferguson is the St. Louis suburb where a 2014 killing by police that local prosecutors and the US Justice Department later deemed to have been in self-defense led to widespread protests that were followed by big increases in St. Louis-area homicide rates. Baltimore had a similar viral death in police custody and homicide-rate increase in 2015. In Chicago, it was the October 2014 shooting death of a teenager, and more specifically the release a year later of a video that contradicted police accounts of the incident, leading eventually to the conviction of a police officer for second-degree murder.

It’s not that police killings themselves are a leading cause of death among Black Americans. The Mapping Police Violence database lists 285 killings of Black victims by police in 2022, and the CDC reports 209 Black victims of “legal intervention,” compared with 13,435 Black homicide victims. And while Black Americans are killed by police at a higher rate relative to population than White Americans, this disparity — 2.9 to 1 since 2013, according to Mapping Police Violence — is much less than the 7.5-to-1 ratio for homicides overall in 2022. It’s the loss of trust between law enforcement agencies and the communities they serve that seems to be disproportionately deadly for Black residents of those communities.
The May 2020 murder of George Floyd by a Minneapolis police officer was the most viral such incident yet, leading to protests nationwide and even abroad, as well as an abortive local attempt to disband and replace the police department. The Minneapolis area subsequently experienced large increases in homicides and especially homicides of Black residents. But nine other large metro areas experienced even bigger increases in the Black homicide rate from 2019 to 2022.
A lot of other things happened between 2019 and 2022 besides the Floyd protests, of course, and I certainly wouldn’t ascribe all or most of the pandemic homicide-rate increase to the Ferguson effect. It is interesting, though, that the St. Louis area experienced one of the smallest percentage increases in the Black homicide rate during this period, and it decreased in metro Baltimore.
Also interesting is that the metro areas experiencing the biggest percentage increases in Black residents’ homicide rates were all in the West (if your definition of West is expansive enough to include San Antonio). If this were confined to affluent areas such as Portland, Seattle, San Diego and San Francisco, I could probably spin a plausible-sounding story about it being linked to especially stringent pandemic policies and high work-from-home rates, but that doesn’t fit Phoenix, San Antonio or Las Vegas, so I think I should just admit that I’m stumped.
The standout in a bad way has been the Portland area, which had some of the longest-running and most contentious protests over policing, along with many other sources of dysfunction. The area’s homicide rate for Black residents has more than tripled since 2019 and is now second highest among the 30 biggest metro areas after St. Louis. Again, I don’t have any real solutions to offer here, but whatever the Portland area has been doing since 2019 isn’t working.
(1) The CDC data for 2022 are provisional, with a few revisions still being made in the causes assigned to deaths (was it a homicide or an accident, for example), but I’ve been watching for weeks now, and the changes have been minimal. The CDC is still using 2021 population numbers to calculate 2022 mortality rates, and when it updates those, the homicide rates will change again, but again only slightly. The metropolitan-area numbers also don’t reflect a recent update by the White House Office of Management and Budget to its list of metro areas and the counties that belong to them, which when incorporated will bring yet more small mortality-rate changes. To get these statistics from the CDC mortality databases, I clicked on “Injury Intent and Mechanism” and then on “Homicide”; in some past columns I instead chose “ICD-10 Codes” and then “Assault,” which delivered slightly different numbers.
(2) It’s easy to download mortality statistics by metro area for the years 1999 to 2016, but the databases covering earlier and later years do not offer this option, and one instead has to select all the counties in a metro area to get area-wide statistics, which takes a while.
(3) The map covers the years 2018-2022 to maximize the number of states for which CDC Wonder will cough up data, although as you can see it wouldn’t divulge any numbers for Idaho, Maine, Vermont and Wyoming (meaning there were fewer than 10 homicides of Black residents in each state over that period) and given the small numbers involved, I wouldn’t put a whole lot of stock in the rates for the Dakotas, Hawaii, Maine and Montana.
(https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2023/09/14/where-it-s-most-dangerous-to-be-black-in-america/cdea7922-52f0-11ee-accf-88c266213aac_story.html)
139 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's crazy that there are only 7,500 jews in New Zealand per the 2018 census.
According to 2020 statistics, there are only 7,499 other jews in my country
There are roughly 5.3 million people in New Zealand.
0.14% of the population of my country is Jewish.
There are so few of us, yet I still face antisemitism in real life. I still get targeted.
From data recorded from January 2022 to April 2023, hate crimes reported against jews were the second most amount of hate crimes against a religious group.
There are 0.4 hate crimes per jew in New Zealand reported.
Whilst jews are the second most religious group affected by hate crimes, we experience the most reported hate crimes per person as there are less jews.
And that's only reported hate crimes! If we only knew how many crimes were not reported, that statistics would be worse
And people say antisemitism isn't a problem
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
DREAMBLR CENSUS 2023
Hi, hello and welcome everyone to the 2023 Dreamblr census results!
Let me start by thanking all of you for taking part - I love looking at statistics like that and making this has been a real joy. I hope at least some of you will find the results interesting as well <3
So, first things first - some numbers. 353 people have taken part in the census. There are over 350 people that say ‘yes I am a part of Dreamblr’. That’s amazing! I am so happy to see this community thrive :D
Now let’s get to the questions.
What continent are you from?
One of the more straightforward questions on this census.
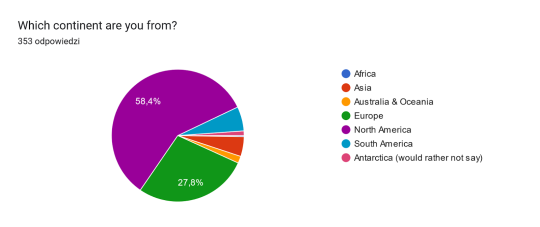
The results are not surprising in the slightest - over 85% of the people that have taken the survey are from North America or Europe. 5.9% come from South America, 4.8% from Asia, 1.7% from Australia and Oceania. 4 people decided not to answer and thus became citizens of Antarctica and one person comes from Africa.
What country are you from (optional)?
Before we get to the statistics, it’s important to mention a couple of things. First of all - this question was optional. The survey site let you pass without putting anything in and the question itself had the word ‘optional’ in it. Despite that 2 of the 4 people that chose Antarctica also wrote in the countries they lived in. All in all 270 out of the 353 people decided to answer this question.
Second of all.
Americans.
For the love of everything holy.
Please. PLEASE. Decide on one way to call your country.
As I was using google forms, the survey was sensitive to lower- and upper-case letters, which meant that in the end there were 25 versions of the your country’s name, including (but not limited) to: America, Murica (including ‘eagle noise’ once), the U.S, The U.S., u.s, U.S.A., U.S.A, United States, united states, United States of America, United states of america, US, Us, us, USA, USA! and u s of a.
Special shoutout to the person who just wrote in ‘Arizona’ as well.
In the end the top 10 (eh kind of) most popular countries on the survey were……
Drumroll please!!
USA - 133
Canada - 26
Germany - 17
Poland & UK - 8
Brazil - 7
England - 6
Russia - 5
Chile, France, Sweden and the Netherlands - each with 4
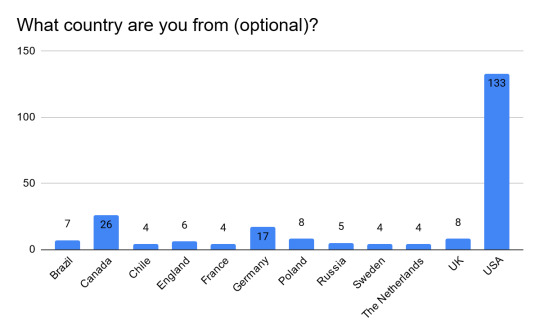
As you can see, I have decided to treat ‘England’ and ‘UK’ as two different answers, since that’s how the survey responders decided to specify their countries.
What age are you?
Another straightforward question. Over 70% of us are between 18 and 25 years old. 13 are 31-45 years old and 8 people decided not to specify their age. 1 person has declared to be over 45 years old. You can see all the answers on this awesome pie chart as well!

I think it’s pretty cool how while a lot of us are young adults or even still teenagers, there are also older fandom enjoyers among us :D I hope you are all enjoying your time!!
When did you join the fandom?
First of the more fandom-specific questions. And probably the first question, where the answers genuinely surprised me!

A lot of us are OGs! Either having joined in 2019 or early/late 2020! Those people remember it all - the beginning of Dream SMP, the first vlog, Antfrost’s coming out and even the beginning of manhunts in some cases!
Out of the rest, early 2021 was another popular entry point to the fandom. Which shouldn’t surprise anyone either - it was still during the pandemic, probably the peak of Dream’s (and Dream Team’s/Dream SMP’s popularity).
9 people did not remember when they joined the fandom.
Similarly, 9 people are newbies! They’ve joined us in late 2022, while 23 joined in early 2022.
No one has joined in 2023 yet. (or haven’t seen the census. also possible.)
Who is your main?
This is a question that I could have made better in hindsight. I think a better answer than ‘I can’t decide’ would be ‘I like them all equally’, since I was assuming that all participants of the census did like the Dream Team members either way. It’s not a big mistake, just a small note I wanted to add.
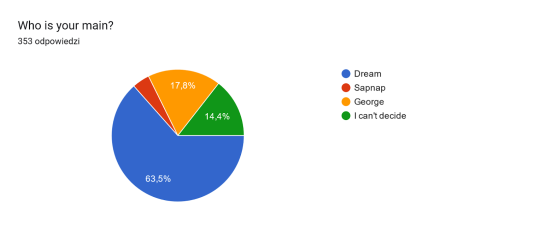
To most likely no one’s surprise - the most popular person among Dreamblr’s population is Dream (224), followed by George (63) and Sapnap (15). 51 participants couldn’t decide on one of them.
Who do you watch besides the DTeam the most (out of other mcyts)? Please list 3 people max.
This question caused more problems than I'd imagined. Guys. I was asking about other MCYT (aka Minecraft Youtubers and Streamers) besides the DTeam. That means that I had to unfortunately eliminate some answers, the most popular out of which was Hasan, who I don’t think has ever played Minecraft before.
To answer some of you, who had some doubts about who counts as a MCYT….
Yes, Wilbur Soot does count.
Yes, Charlie Slimecicle also counts.
Yes, Hermits also count.
I am also counting Ludwig, since he did make Minecraft content.
PeteZahHutt also counts.
Corpse Husband counts as well, since he is technically a DSMP member.
RTGame counts as well - again, Minecraft content on his channel.
Again - Hasan does not count.
So now, without further ado… The top 10 most popular answers!
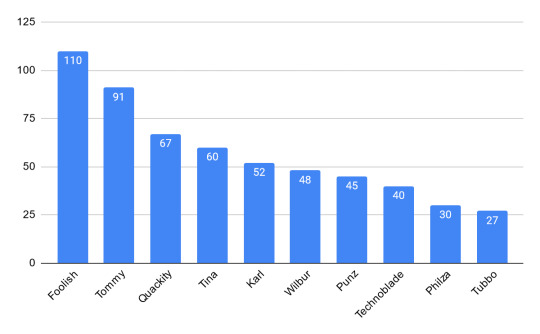
I have also not counted answers that went over 3 people (as in, I have only counted the first 3 names).
If any of you were wondering - 8 people really wish Hasan did play Minecraft.
Which Dream content is the best content?
Another easy question with an easy answer, where most people either prefer Dream’s Youtube content or just love it all.
Quick shout out to the two people who love Dream’s music the most and two who prefer other content than specified in the survey.
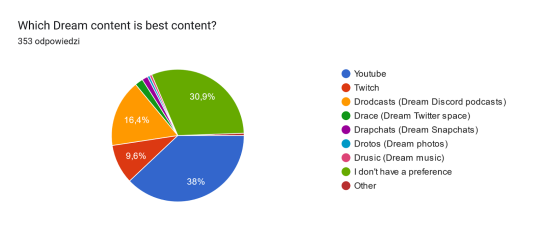
What got you into the fandom?
The toughest question to count. I did not expect so many different answers, so in the end I’ve decided to sort all the answers into a few categories (and I am sorry about that I know it’s not the best way to go about it, but here you guys can see all the answers to the question in an google spreadsheet if you want to).
dnf (answers included: ao3, heatwaves, dnf compilations on youtube or tiktok…)
manhunts (answers included: youtube recommendation of manhunts, binge watching manhunts…)
art (answers included: sad-ist animations, art in general, cosplays…)
lore (answers included: Dream SMP, lore vods…)
Other MCYT creators (answers included: SMP live, wilbur soot’s videos…)
Friend/family member recommendation
Among us streams
Twitter (answers included: seeing drama, twitter trending page…)
Other Dream Team content (answers included: other Dteam videos, tiktoks by them…)
Fandom (answers included: a tumblr mutual started posting about them, tiktok compilations, youtube compilations…)
Hot (answers included: found George/Sapnap hot)
I don’t remember
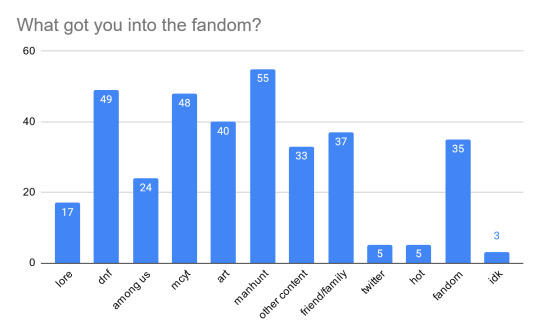
And finally. The last question of the census. The one we all have been wondering about.
Have you been here since before the face reveal?
As it turns out…
Only 2 people joined us since the face reveal!
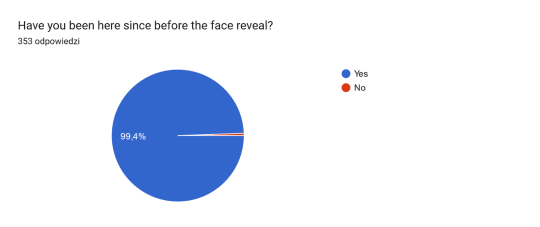
The rest of us has known about this community and about Dream earlier and was waiting the day of the face reveal impatiently.
And that’s it! Thank you once again for taking part, hopefully my rambling won’t make this post too boring to read!
Have a great day/night! <3
289 notes
·
View notes