#7th century china
Text

~ Armored Guardian (Tomb Figure).
Place of origin: China
Date: A.D. 675–725
Medium: Buff earthenware with polychromy and gilding.
#history#museum#archeology#archaeology#asian art#china#chinese#armored guardian#tomb figure#7th century#8th century#a.d. 675#a.d. 775
383 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The empire of Wu Zetian of the Tang dynasty, 7th century.
by LegendesCarto
53 notes
·
View notes
Photo
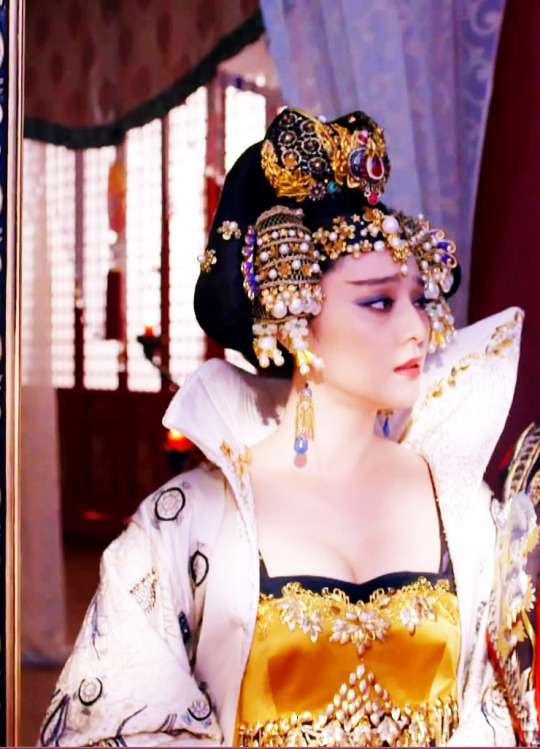

Fan Bingbing as Wu Zetian in The Empress of China (TV Series, 2014-2015).
89 notes
·
View notes
Text
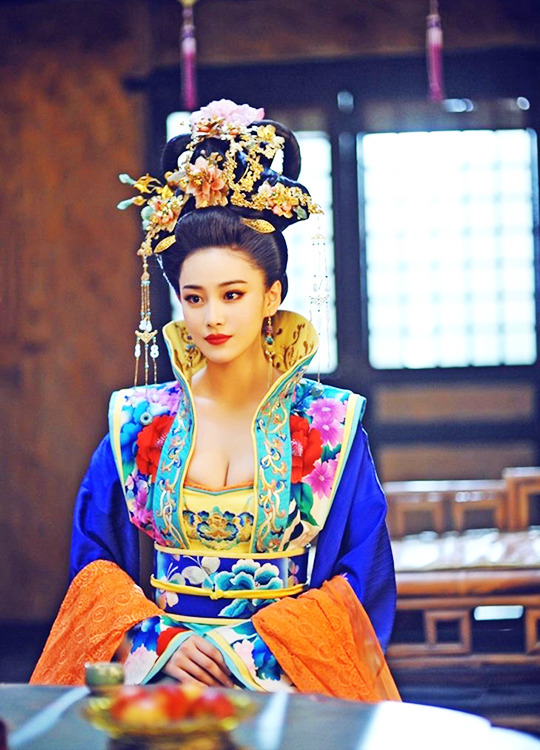

Viann Zhang in The Empress of China
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
When late-fifteenth-century European musicians came up with the idea of taking a bow of stretched hair to their vilhuelas and lutes, producing viola da gambas and viols, they set in train a series of innovations that would ultimately generate one of the most important instruments of subsequent centuries: the violin. But the idea was not a new one.
Bowed instruments had been around for centuries in other continents, notably Asia. In China, there is written evidence of the xiqin – a couple of lengths of cord, animal gut or taut silk attached to a wooden stick and stretched across a resonating box – dating from the Tang dynasty (618–907). More elaborate versions featured a spike on the bottom to root it to the ground and a carved horse’s head on the top, the latter being a popular detail, not surprisingly, for horse-riding players from the nomadic communities of Central Asia. Early forms of the xiqin could be bowed with a strip of bamboo but horsehair had become the preferred material by the Song dynasty (960–1279).
The Arabic rebab or rabab, which, like the al’Ud, came to Europe via Muslim Spain during what is known as the Islamic Golden Age – the Abbasid era of 750–1258 – shares so many characteristics with the xiqin that it is tempting to conclude that its basic design was brought from the East by traders, but the reverse hypothesis has also been advanced.
The contemporaneous Byzantine Empire, which fell in 1453, had its own stringed archetype, the lyra, which initially had two strings, a pear-shaped wooden body with holes in it, for resonance, and adjustable pegs to grip and tune the strings – not unlike those on later violins and guitars.
A Persian scholar of the early tenth century, Ibn Khurradadhbih, reported the lyra to be in widespread use throughout the empire, along with organs and bagpipes. A detailed picture of one, from around the eleventh century, survives on a casket in the Palazzo del Podesta in Florence, and the remains of two early-twelfth-century Byzantine lyras have been dug up in the Russian city of Novgorod.
#europe#15th century#musical instruments#tang dynasty#china#central asia#asia#song dynasty#abbasid era#byzantine empire#russia#7th century#8th century#9th century#10th century#11th century#12th century#13th century#book : story of music
0 notes
Text
it just now occurred to me that for most of history, combs would've had to be made out of wood or bone until the advent of plastic
#thats until 1907 dude thats wild#and youve seen all the crazy rococo up dos#how do they keep it from breaking or the teeth immediately snapping???#glass combs maybe????#but like when was glass even invented????#or maybe porcelain i guess? because tang dynasty china was making that in like the 7th or 8th century#but then what about people who never had that kind of trade or diffusion to get porcelain is it just wood and bone then????
1 note
·
View note
Text


Ceramic figurine of a Bactrian camel, China, 7th-8th century AD
from The Yale University Art Gallery
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fireworks in the UK
Though fireworks were invented in China and were first used around 7th century, in the United Kingdom, they were first fired in the 13th century but was first documented in 1486 during the marriage of Henry VII and Elizabeth of York whose parents were Elizabeth of Woodville and Edward IV. Her brothers were the murdered young princes in the Tower. But one monarch was so fascinated with them that it gained so much popularity she even created a post only for firing the fireworks and managing the display events as the Fire Master of England and it is none other than Queen Elizabeth I.
And during the Victorian era, fireworks display was a common sight to celebrate events like the Guy Fawkes Night in November and the famous New Year’s Eve celebrations at the Thames. ( x, x )
And I am pretty sure everyone of us has witnessed fireworks once (or often) in our lives. Experiencing it in person is truly a magical feeling. It feels like it is coming at you closer and closer. A beautiful optical illusion.
No wonder Ciel’s reaction is very understandable and Lawrence’s emotions were all over the place.
Commending CloverWorks for spending a part of their budget to make the fireworks display so realistic.
#kuroshitsuji#black butler#ciel phantomhive#sebastian michaelis#yana toboso#cloverworks#lawrence bluewer#episode 8#public school arc#maaya sakamoto#junya enoki
329 notes
·
View notes
Text
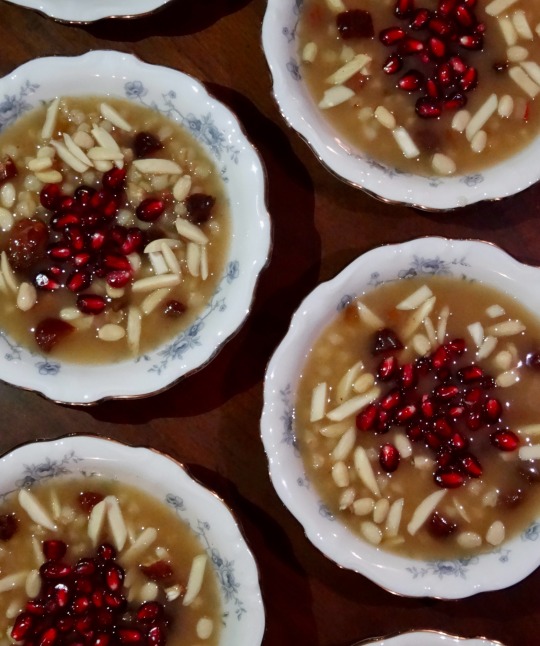
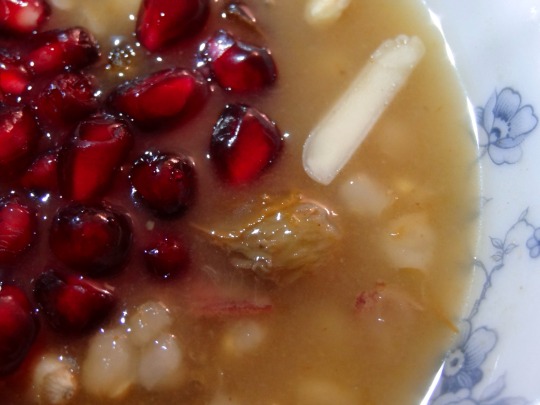


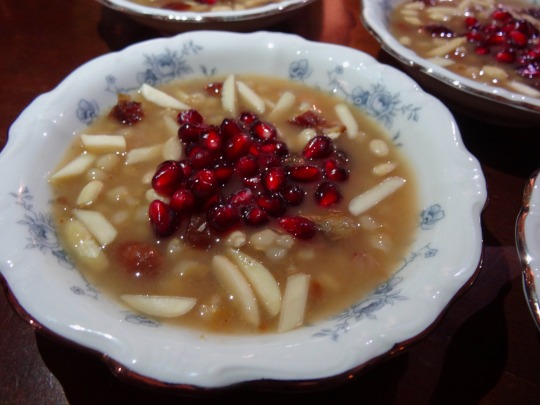
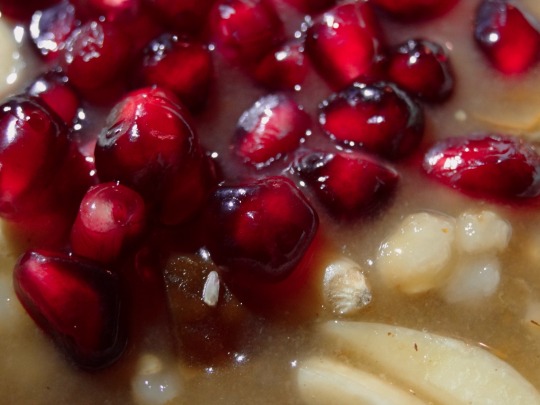
[ID: First image shows four small porcelain bowls of a pudding topped with slivered almonds and pomegranates seeds, seen from above. Second image is an extreme close-up showing the blue floral pattern on the china, slivered almonds, golden raisins, and pomegranate seeds on top of part of the pudding. End ID]
անուշապուր / Anush apur (Armenian wheat dessert)
Anush apur is a sweet boiled wheat pudding, enriched with nuts and dried fruits, that is eaten by Armenians to celebrate special occasions. One legend associates the dish with Noah's Ark: standing on Mt. Ararat (Արարատ լեռը) and seeing the rainbow of God's covenant with humanity, Noah wished to celebrate, and called for a stew to be prepared; because the Ark's stores were diminishing, the stew had to be made with small amounts of many different ingredients.
The consumption of boiled grains is of ancient origin throughout the Levant and elsewhere in West Asia, and so variations of this dish are widespread. The Armenian term is from "անուշ" ("anush") "sweet" + "ապուր" ("apur") "soup," but closely related dishes (or, arguably, versions of the same dish) have many different, overlapping names.
In Arabic, an enriched wheat pudding may be known as "سْنَينِيّة" ("snaynīyya"), presumably from "سِنّ" "sinn" "tooth" and related to the tradition of serving it on the occasion of an infant's teething; "قَمْح مَسْلُوق" ("qamḥ masluq"), "boiled wheat"; or "سَلِيقَة" ("salīqa") or "سَلِيقَة القَمْح" ("salīqa al-qamḥ"), "stew" or "wheat stew," from "سَلَقَ" "salaqa" "to boil." Though these dishes are often related to celebrations and happy occasions, in some places they retain an ancient association with death and funerary rites: qamh masluq is often served at funerals in the Christian town of بَيْت جَالَا ("bayt jālā," Beit Jala, near Bethlehem).
A Lebanese iteration, often made with milk rather than water, is known as "قَمْحِيَّة" ("qamḥīyya," from "qamḥ" "wheat" + "ـِيَّة" "iyya," noun suffix).
A similar dish is known as "بُرْبَارَة" ("burbāra") by Palestinian and Jordanian Christians when eaten to celebrate the feast of Saint Barbara, which falls on the 4th of December (compare Greek "βαρβάρα" "varvára"). It may be garnished with sugar-coated chickpeas and small, brightly colored fennel candies in addition to the expected dried fruits and nuts.
In Turkish it is "aşure," from the Arabic "عَاشُوْرَاء" ("'āshūrā"), itself from "عَاشِر" ("'āshir") "tenth"—because it is often served on the tenth day of the month of ٱلْمُحَرَّم ("muḥarram"), to commemorate Gabriel's teaching Adam and Eve how to farm wheat; Noah's disembarkment from the Ark; Moses' parting of the Red Sea; and the killing of the prophet الْحُسَيْن بْنِ عَلِي (Husayn ibn 'Ali), all of which took place on this day in the Islamic calendar. Here it also includes various types of beans and chickpeas. There is also "diş buğdayı," "tooth wheat" (compare "snayniyya").
These dishes, as well as slight variations in add-ins, have varying consistencies. At one extreme, koliva (Greek: "κόλλυβα"; Serbian: "Кољиво"; Bulgarian: "Кутя"; Romanian: "colivă"; Georgian: "კოლიო") is made from wheat that has been boiled and then strained to remove the boiling water; at the other, Armenian anush apur is usually made thin, and cools to a jelly-like consistency.
Anush apur is eaten to celebrate occasions including New Year's Eve, Easter, and Christmas. In Palestine, Christmas is celebrated by members of the Armenian Apostolic church from the evening of December 24th to the day of December 25th by the old Julian calendar (January 6th–7th, according to the new Gregorian calendar); Armenian Catholics celebrate on December 24th and 25th by the Gregorian calendar. Families will make large batches of anush apur and exchange bowls with their neighbors and friends.
The history of Armenians in Palestine is deeply interwoven with the history of Palestinian Christianity. Armenian Christian pilgrimages to holy sites in Palestine date back to the 4th century A.D., and permanent Armenian monastic communities have existed in Jerusalem since the 6th century. This enduring presence, bolstered by subsequent waves of immigration which have increased and changed the character of the Armenian population in Palestine in the intervening centuries, has produced a rich history of mutual influence between Armenian and Palestinian food cultures.
In the centuries following the establishment of the monasteries, communities of Armenian laypeople arose and grew, centered around Jerusalem's Վանք Հայոց Սրբոց Յակոբեանց ("vank hayots surbots yakobeants"; Monastery of St. James) (Arabic: دَيْر مَار يَعْقُوب "dayr mār ya'qūb"). Some of these laypeople were descended from the earlier pilgrims. By the end of the 11th century, what is now called the Armenian Quarter—an area covering about a sixth of the Old City of Jerusalem, to the southwest—had largely attained its present boundaries.
Throughout the 16th and 17th centuries, the Patriarchate in Jerusalem came to have direct administrative authority over Armenian Christians across Palestine, Lebanon, Egypt, and Cyprus, and was an important figure in Christian leadership and management of holy sites in Jerusalem (alongside the Greek Orthodox and Roman Catholic churches). By the middle of the 19th century, a small population of Armenian Catholics had joined the larger Armenian Apostolic community as permanent residents in Jerusalem, living throughout the Muslim Quarter (but mostly in a concentrated enclave in the southwest); in the beginning of the 20th century, there were between 2,000 and 3,000 Armenians of both churches in Palestine, a plurality of whom (1,200) lived in Jerusalem.
The Turkish genocide of Armenians beginning in 1915 caused significant increases in the populations of Armenian enclaves in Palestine. The Armenian population in Jerusalem grew from 1,500 to 5,000 between the years of 1918 and 1922; over the next 3 years, the total number of Armenians in Palestine (according to Patriarchate data) would grow to 15,000. More than 800 children were taken into Armenian orphanages in Jerusalem; students from the destroyed Չարխափան Սուրբ Աստվածածին վանք (Charkhapan Surb Astvatsatsin Monastery) and theological seminary in Armash, Armenia were brought to the Jerusalem Seminary. The population of Armenian Catholics in the Muslim Quarter also increased during the first half of the 20th century as immigrants from Cilicia and elsewhere arrived.
The immediate importance of feeding and housing the refugees despite a new lack of donations from Armenian pilgrims, who had stopped coming during WW1—as well as the fact that the established Armenian-Palestinians were now outnumbered by recent immigrants who largely did not share their reformist views—disrupted efforts on the part of lay communities and some priests to give Armenian laypeople a say in church governance.
The British Mandate, under which Britain assumed political and military control of Palestine from 1923–1948, would further decrease the Armenian lay community's voice in Jerusalem (removing, for example, their say in elections of new church Patriarchs). The British knew that the indigenous population would be easier to control if they were politically and socially divided into their separate religious groups and subjected to the authority of their various religious hierarchies, rather than having direct political representation in government; they also took advantage of the fact that the ecclesiastical orders of several Palestinian Christian sects (including the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem) comprised people from outside of Palestine, who identified with religious hierarchy and the British authorities more than they identified with the Palestinian lay communities.
British policy, as well as alienating Armenians from politics affecting their communities, isolated them from Arab Palestinians. Though the previously extant Armenian community (called "քաղաքացի" "kaghakatsi," "city-dwellers") were thoroughly integrated with the Arab Palestinians in the 1920s, speaking Arabic and Arabic-accented Armenian and eating Palestinian foods, the newer arrivals (called "زُوَّار" / "զուվվար" "zuwwar," "visitors") were unfamiliar with Palestinian cuisine and customs, and spoke only Armenian and/or Turkish. Thus British policies, which differentiated people based on status as "Arab" (Muslim and Christian) versus "Jewish," left new Armenian immigrants, who did not identify as Arab, disconnected from the issues that concerned most Palestinians. They were predominantly interested in preserving Armenian culture, and more concerned with the politics of the Armenian diaspora than with local ones.
Despite these challenges, the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem came to be a vital center of religious and secular culture for the Armenian diaspora during the British Mandate years. In 1929, Patriarch Yeghishe Turian reëstablished the Սուրբ Յակոբեանց Տպարան ("surbots yakobeants taparan"; St. James printing house); the Patriarchate housed important archives relating to the history of the Armenian people; pilgrimages of Armenians from Syria, Lebanon, and Egypt increased and the economy improved, attracting Armenian immigrants in higher numbers; Armenians held secular roles in governance, policing, and business, and founded social, religious, and educational organizations and institutions; Armenians in the Old and New Cities of Jerusalem were able to send financial aid to Armenian victims of a 1933 earthquake in Beirut, and to Armenians expelled in 1939 when Turkey annexed Alexandretta.
The situation would decline rapidly after the 1947 UN partition resolution gave Zionists tacit permission to expel Palestinians from broad swathes of Palestine. Jerusalem, intended by the plan to be a "corpus separatum" under international administration, was in fact subjected to a months-long war that ended with its being divided into western (Israeli) and eastern (Palestinian) sections. The Armenian population of Palestine began to decline; already, 1947 saw 1,500 Armenians resettled in Soviet Armenia. The Armenian populations in Yafa and Haifa would fall yet more significantly.
Still, the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem maintained its role as the center of Armenian life in Palestine; the compound provided food and shelter to thousands of Armenians during the Battle for Jerusalem and the Nakba (which began in 1948). Some Armenians formed a militia to defend the Armenian Quarter against Haganah shelling during the battle.
In the following years, historical British contributions to the shoring up of insular power in the Patriarchate would cause new problems. The Armenian secular community, no longer empowered to oversee the internal workings of the Patriarchate, could do nothing to prevent embezzling, corruption, and even the sale of church-owned land and buildings to settlers.
In 1967, Israeli military forces annexed East Jerusalem, causing another, albeit smaller, surge in Armenian emigration from the city. Daphne Tsimhoni estimates based on various censuses that the Armenian population of Jerusalem, which had reached 5,000-7,000 at its peak in 1945–6, had fallen back to 1,200 by 1978.
Today, as in the 20th century, Armenians in Jerusalem (who made up nearly 90% of the Armenian population of Palestine as of 1972) are known for the insularity of their community, and for their skill at various crafts. Armenian food culture has been kept alive and well-defined by successive waves of immigrants. As of 2017, the Armenian Patriarchate supplied about 120 people a day with Armenian dishes, including Ղափամա / غاباما "ghapama" (pumpkin stuffed with rice and dried fruits), թոփիկ / توبيك "topig" (chickpea-and-potato dough stuffed with an onion, nut, fruit, and herb filling, often eaten during Lent), and Իչ / ايتش "eetch" (bulgur salad with tomatoes and herbs).
Restaurants lining the streets of the Armenian and Christian quarters serve a mixture of Armenian and Palestinian food. Լահմաջո "lahmadjoun" (meat-topped flatbread), and հարիսա / هريس "harisa" (stew with wheat and lamb) are served alongside ֆալաֆել / فلافل ("falafel") and մուսախան / مسخن ("musakhkhan"). One such restaurant, Taboon Wine Bar, was the site of a settler attack on Armenian diners in January 2023.
Up until 2023, despite fluctuations in population, the Armenian community in Jerusalem had been relatively stable when compared to other Armenian communities and to other quarters of the Old City; the Armenian Quarter had not been subjected to the development projects to which other quarters had been subjected. However, a deal which the Armenian Patriarchate had secretly and unilaterally made with Israel real estate developer Danny Rotham in 2021 to lease land and buildings (including family homes) in the Quarter led Jordan and Palestine to suspend their recognition of the Patriarch in May of 2023.
On 26th October, the Patriarchate announced that it was cancelling the leasing deal. Later the same day, Israeli bulldozers tore up pavement and part of a wall in حديقة البقر ("ḥadīqa al-baqar"; Cows' Garden; Armenian: "Կովերի այգու"), the planned site of a new luxury hotel. On 5th November, Rothman and other representatives of Xana Gardens arrived with 15 settlers—some of them with guns and attack dogs—and told local Armenians to leave. About 200 Armenian Palestinians arrived and forced the settlers to stand down.
On 12th and 13th November, the developer again arrived with bulldozers and attempted to continue demolition. In response, Armenian Palestinians have executed constant sit-ins, faced off against bulldozers, and set up barricades to prevent further destruction. The Israeli occupation police backed settlers on another incursion on 15th November, ordering Armenian residents to vacate the land and arresting three.
On December 28th, a group of Armenian bishops, priests, deacons, and seminary students (including Bishop Koryoun Baghdasaryan, the director of the Patriarchate's real estate department) were attacked by a group of more than 30 people armed with sticks and tear gas. The Patriarchate attributed this attack to Israeli real estate interests trying to intimidate the Patriarchate into abandoning their attempt to reverse the lease through the court system. Meanwhile, anti-Armenian hate crimes (including spitting on priests) had noticeably increased for the year of 2023.
These events in Palestine come immediately after the ethnic cleansing of Լեռնային Ղարաբաղ ("Lernayin Gharabagh"; Nagorno-Karabakh); Israel supplied exploding drones, long-range missiles, and rocket launchers to help Azerbaijan force nearly 120,000 Armenians out of the historically Armenian territory in September of 2023 (Azerbaijan receives about 70% of its weapons from Israel, and supplies about 40% of Israel's oil).
Support Palestinian resistance by donating to Palestine Action’s bail fund; buying an e-sim for distribution in Gaza; or donating to help a family leave Gaza.
Ingredients
180g (1 cup) pearled wheat (قمح مقشور / խոշոր ձաւար), soaked overnight
3 cups water
180-360g (a scant cup - 1 3/4 cup) sugar, or to taste
Honey or agave nectar (optional)
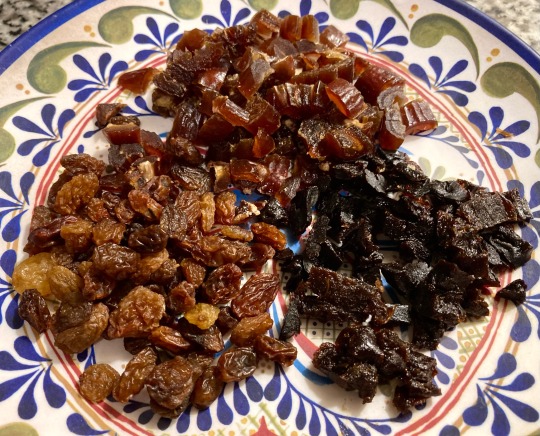
1 cup total diced dried apricots, prunes, golden raisins, dried figs
1 cup total chopped walnuts, almonds, pistachios
1 tsp rosewater (optional)
Ceylon cinnamon (դարչին) or cassia cinnamon (կասիա)
Aniseed (անիսոն) (optional)
Large pinch of salt
Pomegranate seeds, to top (optional)
A Palestinian version of this dish may add pine nuts and ground fennel.
Pearled wheat is whole wheat berry that has gone through a "pearling" process to remove the bran. It can be found sold as "pearled wheat" or "haleem wheat" in a halal grocery store, or a store specializing in South Asian produce.
Amounts of sugar called for in Armenian recipes range from none (honey is stirred into the dish after cooking) to twice the amount of wheat by weight. If you want to add less sugar than is called for here, cook down to a thicker consistency than called for (as the sugar will not be able to thicken the pudding as much).

Instructions
1. Submerge wheat in water and scrub between your hands to clean and remove excess starch. Drain and cover by a couple inches with hot water. Cover and leave overnight.
2. Drain wheat and add to a large pot. Add water to cover and simmer for about 30 minutes until softened, stirring and adding more hot water as necessary.
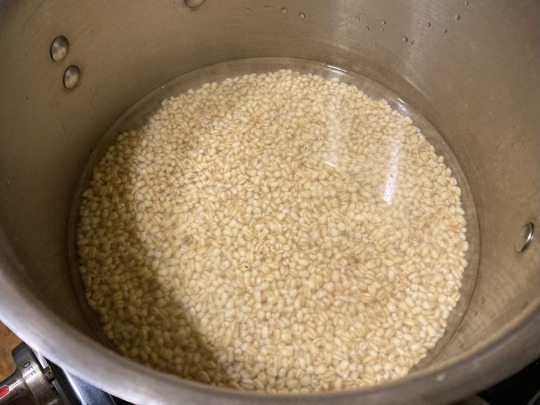

Wheat before cooking
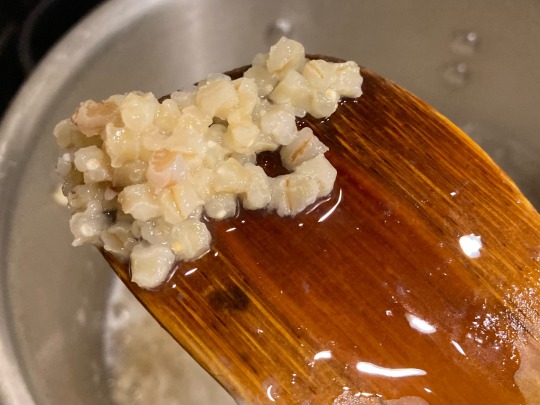

Wheat after cooking
3. Add dried fruit, sugar, salt, and spices and simmer for another 30 minutes, stirring occasionally, until wheat is very tender. Add water as necessary; the pudding should be relatively thin, but still able to coat the back of a spoon.
4. Remove from heat and stir in rosewater and honey. Ladle pudding into individual serving bowls and let cool in the refrigerator. Serve cold decorated with nuts and pomegranate seeds.


#the last link is a different / new fundraiser#Armenian#Palestinian#fusion#wheat berries#pearled wheats#pomegranate#prunes#dried apricot#dates#long post /
372 notes
·
View notes
Text
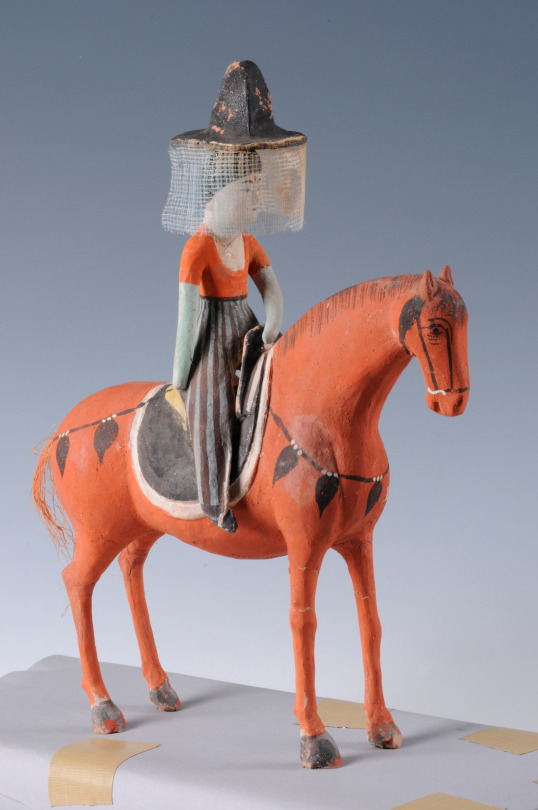

Painted clay figure of an equestrienne, ca. 7th-9th century AD
Excavated from Tomb No. 187, Astana (Turfan), Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China
Xinjiang Museum
506 notes
·
View notes
Note
sorry if it's a dumb question but i've wondered about the nations' skills or what suits their personalities, and who do u think would win in a swordfight between yao and kiku? japan does have such a kenjutsu culture but what about china, since china has a very old history too?
i have thought about this before, actually 🤔 when thinking about pre-modern sino-japanese power dynamics between yao and kiku. personally, i say it actually depends on which point in history. this is my headcanon:
before the kamakura period/shogunate (which overlaps with the sengoku/feudal era of japan) tbh I'd say yao wins. one reason is well, the symbolic power balance between china and japan. the first time china and japan properly met face-to-face in conflict was in the 7th century CE, during the baekje-tang war at the battle of baekgang in korea. long story short: it was a power struggle between korean kingdoms, and the korean kingdom of baekje (yong-soo's brother) was allied to japan, so japan came to help them. their enemy was the other korean kingdom of silla (aka: yong-soo long before he becomes south korea), who...was allied to china. despite being outnumbered 3 to 1, china pretty much crushed japan in that battle. then, kiku is very much an inexperienced upstart challenging the regional hegemon who has far far more notches on his sword. getting wrecked like that by yao is imo, quite a formative experience for kiku (to put it mildly).
but as the centuries go by, yeah no, kiku is the swordsman alright. because of samurai culture, and its elevation to power during the muromachi and edo period. further, there's of course the imjin war, where the samurai lord toyotomi hideyoshi invaded korea with the goal of overthrowing ming china too. even during the successive edo period/tokugawa shogunate, where japan was unified, far more peaceful under isolationism and many samurai became more like bureaucrats, i think kiku continued practising kenjutsu or at least in the form of kendo—swordsmanship and his swords became very much an extension of his personality and identity by then, as well as a way he'd blow off steam even during peacetime. his katana and wakizashi would always be properly maintained and you'd see him carefully oiling it with the mix of mineral and clove oil to prevent rusting, even during the most chill years of edo japan. they'd be nicely displayed like this somewhere in his quarters.

this is compared to how, for all that pre-modern china was an empire and all empires need military violence to expand themselves, warriors as a class in chinese culture never quite ascended to the same type of political prestige as the samurai. it was a very different cultural/political context. it's like, you can't underestimate yao still, as an experienced old empire (tm), but by the 1400s/ming dynasty, i think he might've shifted more to being that kind of general presiding over maps in his military tent, and directing strategy, compared to the younger warlord he was in his earlier years, who was down in the dirt all the time fighting in every single skirmish. so, while yao can and will get his hands dirty if need be with a blade, i think kiku edges him out by then in sheer focus, skill and devotion re: kenjutsu becoming a pretty core aspect of his personality/experiences. to me, it’s also an “old and experienced soldier surpassed by his younger, hungry protégé” dynamic too.
65 notes
·
View notes
Photo
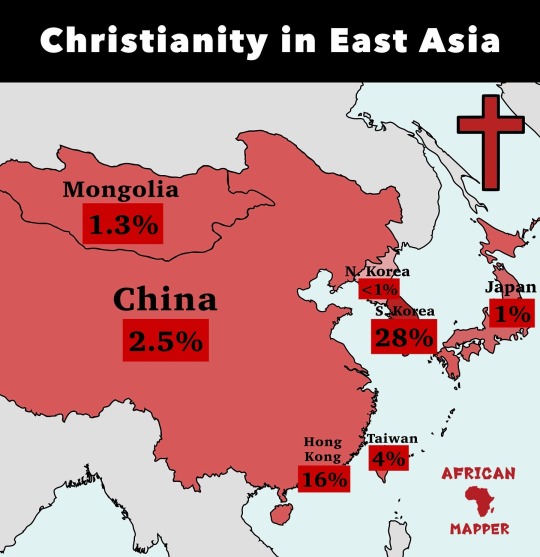
Christianity in East Asia
Christianity may have existed earlier in China, but the first documented introduction was during the Tang dynasty (618–907) A Christian mission under the leadership of the priest Alopen was known to have arrived in 635, where he and his followers received an Imperial Edict allowing for the establishment of a church. In China, the religion was known as the Luminous Religion of the Romans. Mongols had been proselytized by Nestorian Christians since about the 7th century, and several Mongol tribes, such as the Kerait, Naimans, Merkit, and to a large extent the Kara Khitan (who practiced it side by side with Buddhism), were also Christian.
by african.mapper
144 notes
·
View notes
Text


Shirdal 'Lion-Eagle'
Talon Abraxas
Ancient origins of the griffin
A legendary creature with the body, tail, and back legs of a lion, the head and wings of an eagle, and, sometimes, an eagle's talons as its front feet first appears in ancient Iranian and Egyptian art dating back to before 3000 BCE. In Egypt, a griffin-like animal can be seen on a cosmetic palette from Hierakonpolis, known as the "Two Dog Palette", dated to 3300–3100 BCE. The divine storm-bird, Anzu, half man and half bird, associated with the chief sky god Enlil was revered by the ancient Sumerians and Akkadians. The Lamassu, a similar hybrid deity depicted with the body of a bull or lion, eagle's wings, and a human head, was a common guardian figure in Assyrian palaces.
In Iranian mythology, the griffin is called Shirdal, which means "Lion-Eagle." Shirdals appeared on cylinder seals from Susa as early as 3000 BCE. Shirdals also are common motifs in the art of Luristan, the North and North West region of Iran in the Iron Age, and Achaemenid art. The 15th century BCE frescoes in the Throne Room of the Bronze Age Palace of Knossos are among the earliest depictions of the mythical creatures in ancient Greek art. In Central Asia, the griffin image was later included in Scythian "animal style" artifacts of the 6th–4th centuries BCE.
In his Histories, Herodotus relates travelers' reports of a land in the northeast where griffins guard gold and where the North Wind issues from a mountain cave. Scholars have speculated that this location may be referring to the Dzungarian Gate, a mountain pass between China and Central Asia. Some modern scholars including Adrienne Mayor have theorized that the legend of the griffin was derived from numerous fossilized remains of Protoceratops found in conjunction with gold mining in the mountains of Scythia, present day eastern Kazakhstan. Recent linguistic and archaeological studies confirm that Greek and Roman trade with Saka-Scythian nomads flourished in that region from the 7th century BCE, when the semi-legendary Greek poet Aristeas wrote of his travels in the far north, to about 300 CE when Aelian reported details about the griffin - exactly the period during which griffins were most prominently featured in Greco-Roman art and literature. Mayor argues that over-repeated retelling and drawing or recopying its bony neck frill (which is rather fragile and may have been frequently broken or entirely weathered away) may have been thought to be large mammal-type external ears, and its beak treated as evidence of a part-bird nature that lead to bird-type wings being added. Others argue fragments of the neck frill may have been mistook for remnants of wings.
Lucius Flavius Philostratus (170 – 247/250 CE), a Greek sophist who lived during the reign of the Roman emperor Philip the Arab, in his "Life of Apollonius of Tyana" also writes about griffins that quarried gold because of the strength of their beak. He describes them as having the strength to overcome lions, elephants, and even dragons, although he notes they had no great power of flying long distances because their wings were not attached the same way as birds. He also described their feet webbed with red membranes. Philostratus says the creatures were found in India and venerated there as sacred to the sun. He observed that griffins were often drawn by Indian artists as yoked four abreast to represent the sun.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
#HumpDay anyone? 😉


Pair of Southern Yellow Cattle (Zebu)
China (probably Shaanxi province), Tang dynasty (618-907), late 7th century
earthenware w/ traces of pigment
Baltimore Museum of Art
“Southern Yellow cattle, a Chinese breed depicted here, were primarily used as draught animals to pull farm implements and carts, including those that transported coffins and other furnishings to tombs. Usually yellow or brown in color, the breed is distinguished by a prominent hump and long dewlap, the fold of loose skin hanging from an animal's throat.”
#Zebu#cattle#domesticated animals#livestock#Chinese art#East Asian art#Asian art#ancient art#Tang Dynasty#ceramics#pair#Baltimore Museum of Art#HumpDay#museum visit#animals in art
354 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think it'd be fun to sort of liveblog looking for countries that haven't abused/exiled Jews
I haven't found a list. So I'm making one.
Let's start with China. China has Jewish communities, and maybe not enough of them to become a target! The perfect amount?
Wow, Jews have lived in China since the 7th century CE. I've heard of the Kaifeng Jews!
Oh, this is ominous: "In the first half of the 20th century, thousands of Jewish refugees escaping from pogroms in the Russian Empire arrived in China. By the time of the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, only a few Jews were known to have maintained the practice of their religion and culture."
Wow, fun fact:
According to an oral tradition dictated by Xu Xin, Director of the Centre for Judaic Studies at Nanjing University, in his book Legends of the Chinese Jews of Kaifeng, the Kaifeng Jews called Judaism Yīcìlèyè jiào (一賜樂業教), lit. the religion of Israel. Yīcìlèyè is a transliteration and partial translation of "Israel".
Surprising and cool:
Famous Venetian traveler Marco Polo, who visited China, then under the Yuan dynasty, in the late 13th century, described the prominence of Jewish traders in Beijing.
Neither surprising nor cool:
Genghis Khan called both Jews and Muslims Huihui when he forbade Jews and Muslims from practicing kosher and halal preparation of their food, calling both of them "slaves" and forcing them to eat Mongol food, and banned them from practicing circumcision.
In the late 1800s a lot of Jews emigrated from India and Iraq to China; they "took a considerable part in developing trade in China, and several served on the municipal councils."
In the early 1900s, 20,000 Jewish refugees from Russian pogroms emigrated to Harbin, in northeast China and "and played a key role in the shaping of local politics, economy and international trade."
Surprisingly:
Dr. Sun Yat-sen, founder of the Republic of China, admired the Jewish people and Zionism, and he also saw parallels between the persecution of Jews and the domination of China by the Western powers. He stated, "Though their country was destroyed, the Jewish nation has existed to this day ... [Zionism] is one of the greatest movements of the present time. All lovers of democracy cannot help but support wholeheartedly and welcome with enthusiasm the movement to restore your wonderful and historic nation, which has contributed so much to the civilization of the world and which rightfully deserve [sic] an honorable place in the family of nations."
Wow. It really doesn't go into any more detail about the SMALL gap between "40,000 Jews moved to China from 1845-1945," and "most of these Jews emigrated to Israel or the West... by the time of the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, only a few Jews were known to have maintained the practice of their religion and culture."
That's four years.
Let's look at other sources.
At first, life in Shanghai was peaceful for its newest residents. The Jewish refugees were welcomed by Shanghai residents and they created a strong community with schools and a vibrant social scene. Some refugees began working as dentists and doctors, while others set up shops, cafes and clubs in the neighbourhood.
What the refugees couldn't foresee was they would travel across the globe only to fall into the clutches of the Nazis' most powerful ally. In 1941, Japan seized Shanghai. Acting under instruction from the Nazis, Japanese troops rounded up all of the city's Jews and confined them in Tilanqiao. Shanghai's Jewish ghetto had been born....
According to [historian Dvir] Bar-Gal, even prior to the Japanese invasion, many Jewish refugees in Tilanqiao lived in poverty compared to their comfortable lifestyles back in Europe. Conditions worsened greatly after Japanese soldiers gathered Jews from across Shanghai and forced them to all live within the borders of this newly formed ghetto. Jews were banned from leaving the area, even for work, unless they received permission from Japanese officers, which rarely happened.
Disease and malnutrition plagued the many heinously overcrowded group homes. "It went from a poor neighbourhood to an extremely poor neighbourhood," Bar-Gal said. "Many people had no jobs and lived in communal housing with many other beds and common bathrooms and kitchens. They had zero privacy and almost no food."
Yet, while six million Jews were murdered during the Holocaust, and up to 14 million Chinese soldiers and civilians were killed during their nation's war with Japan from 1937 to 1945, the majority of Shanghai's Jewish refugees survived. This remarkable feat was described by Holocaust historian David Kranzler as the "Miracle of Shanghai", and according to Bar-Gal, they survived because Jews weren't a primary target of the Japanese forces.
In 1945, when World War Two ended with the defeat of Japan and Nazi Germany, Japanese troops retreated and most of Shanghai's Jews quickly left, relocating to places like the US, Australia and Canada. But had Shanghai not taken these refugees in, many of these more-than-20,000 Jews may have never survived the Nazi death squads....
The first structure I came across was the imposing old Tilanqiao Prison. During World War Two, the Japanese incarcerated dozens of Jewish refugees and Chinese dissidents behind its thick stone walls. The brutality of the Japanese gave the Jews and the Chinese a common enemy and a shared experience. This connection remains strong, according to Tian.
That still leaves at least another 20,000, though? (I would say almost 20,000, but for the ones who already lived in China.)
Hmm. Here's a paper that says Jews "not only took part in the revolution but had also helped igniting it and then stayed on or joined later. While dealing with this puzzle in my paper, I’ll try to offer a typology of Jewish activists and revolutionaries in China, to explain their motives (by choice or not), and to evaluate their contributions in perspective. It appears that their Jewish identity did not play a direct role in their revolutionary activism, but it did play an indirect role. Included in this study are Grigorii Gershuni, Grigorii Voitinski, Boris Shumiatsky, Michail Borodin, Adolf Joffe, Pavel Mif, David Crook, Sidney Rittenberg, Israel Epstein, Sidney Shapiro, Solomon Adler, Sam Ginsbourg, Michael Shapiro, and more. Their main value to the revolution was mainly writing, translation, communication and publication. Although they were all deeply committed to the Chinese Communist revolution, some of them were jailed – for years – and occasionally more than once. Nonetheless, they continued to believe in, and even to justify, the Chinese Communist Party."
Wait, waaaaait. I was about to try to find the full paper (titled "Combining contradictions: Jewish contributions to the Chinese revolution"), but I ran across this first:
A century ago, the Communist International and the then-Russian Communist Party dispatched several agents to help foment revolution in China, including Russians like Grigori Voitinsky and Vladimir Neiman-Nikolsky and the Dutch Communist Henk Sneevliet. In addition to their shared commitment to Communism, all three were of Jewish heritage.
O rly??
They came with SKILLS!
On the evening of July 30, less than a month after the founding of the Communist Party of China (CPC), members of the CPC’s First National Congress met for a vote on a new party program. Suddenly, an unfamiliar middle-aged man barged into the meeting hall. “Sorry, I’m in the wrong place,” the man declared before hurrying off.
Sneevliet, well-versed in the techniques used by the police around the world to crack down on revolutionary activities, suggested that the meeting be adjourned and urged members to leave. By the time police arrived 10 minutes later, the building was already cleared out.
If you think that's impressive, try this!
Richard Frey... was an Austrian Jew who fled to Shanghai in the late 1930s. He worked for a hospital in the city until 1941, when he moved to a Communist military base in North China to teach medicine. In 1944, Frey was transferred to the central Communist base in Yan’an in China’s northwest Shaanxi province, where he soon succeeded in producing a crude but much-needed form of penicillin.
He just. Made up his own penicillin for them.
What the entire fuck.
HERE we go!
International Journal of China Studies, December 2020. "Combining Contradictions: Jewish Contributions to the Chinese Revolution," by Yitzhak Shichor, University of Haifa and Hebrew University of Jerusalem.

Fun Fact:
Jewish Lithuanian activist Grigory Gershuni emigrated from Russia to China by hiding in a barrel of sauerkraut.
Yeah okay, I think China's number one on the list of Hey, Some Countries Didn't Try That!
Next time: Japan? Or Brazil? Hmmmm.
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
This gets long, feel free to ignore I don’t want to bother you.
I really like your fic of Macaque being afraid of snakes, after I read that it got me thinking about an old head cannon I had; I really like your work and writing so I wanted to see what you think.
I think it would be really funny if macaque was afraid of the doctor.
JTTW (to my not expert understanding) took place in 7th century China, so macaque must have died in that time, macaque is then revived into modern times.
Seeing as macaque missed a lot of human history due to the fact he was dead, it would not be unreasonable to think that he has a general misunderstanding of how the modern day works.
What if macaque was still working under the assumption that doctors and healers and hospitals were still operating the same way they did way back when.
Basically I really just think it would be funny for macaque to get ill and insist on dealing with it himself like he always has, only for MK and the others to get worried and insist on taking him to a hospital.
Macaque starts acting weird about the subject, bla bla bal shenanigans happen MK and the rest put 2 and 2 together and realise macaque is scared of the doctor and drag him there against his will, only for him to realise just how much has changed since he last bothered to check.
Wether or not macaque would still have a small fear if the doctor after finding out about vaccines and medicine side effects is up to interpretation.
(This entire head cannon can about from that one scene in season 4 when MK and macaque are looking for wukong in the memory scroll and we see that macaque is tucked away taking care of himself, instead of seeking the others out)
ME AND @skellebonez WERE TALKING ABOUT THIS THE OTHER DAY, KINDA
we were talking about Wukong and Macaque being scared of needles, specifically. someone asks them when they last got a tetanus shot and Wukong goes "what's a vaccine?" (cause he thinks if he plays innocent they'll drop it), and Macaque is already halfway out the window-
once they finally convince Wukong to yknow, get some shots to prevent diseases (he probably has to suffer through like, the chikenpox before he's convinced), they discover that needles shatter upon impact with his skin
so of course this basically makes Wukong incapable of being vaccinated against illnesses. which of course means everyone around him should be vaccinated for his safety. which means Macaque gets forcibly dragged to the doctor-
it takes like. everyone to keep him in there long enough to get him vaccinated. don't worry though everyone acknowledges that this is distressing for him and he does get comforted afterwards.
19 notes
·
View notes