#And that's always good at least lol
Text









Leo learns something about himself 🏳️⚧️
Based roughly on this old post.
Bonus:

[Leo is taking the fact that he was born biologically female simultaneously very well and also not so well but overall he’s mostly coping with the fact that it was Draxum that just essentially gave him the turtle equivalent of ‘The Talk’.]
#rottmnt#rise of the teenage mutant ninja turtles#rottmnt leo#rise leo#trans leonardo#trans leo#rottmnt headcanons#turtle art tag#rise draxum#happy pride everyone~#if you’re wondering why there’s no backgrounds that’s because my files got messed up so just blankness in the bg sorry#but yeah!#this is forever and always my fav headcanon for Leo it makes too much sense to me#I wanted to make sure I got it done in time for pride haha#I don’t know if it’s obvious by the end but Draxum ran off because he was for once doing something nice for Leo#that being leading him somewhere else not in front of everyone so Leo can process the fact that he was born female in peace haha#(but he also just - wanted to avoid the ensuing awkward Talk as long as he could lol)#“how would Leo NOT know’’ he had an inkling but never thought much of it because he’s a teenage turtle mutant with no access to healthcare#also yeah that’s splinter’s hand at the end there I just KNOW he’d want those pics#also also - Leo here can technically be trans or even intersex in some way too#both is good#making this made me remember why I never do color#at least for comics#it just takes sooo long#but it was fun and worth it for my fave hc#this is like the first time I’ve drawn Draxum and man he’s kinda hard to draw#also their sizes are just 1 2 and 3 because Draxum had a simple system in place for sizing his subjects#(aka I was too lazy to think of anything else to put there)#also dunno if anyone noticed but look at Raph’s paper and look at his baby’s self’s photo
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
friend wanted to see my tumblr, and when i told him i can’t show it to him bc it’s basically my personal diary he went “oh so I can’t see it but a bunch of strangers on tumblr can??” he literally does not get me. no one will get me like the people in my phone get me
#It’s just so different#even though it’s public it still feels secret and safe. i feel comfy sharing a lot more on here than I do in my actual day to day life lol#in my head I’m also just speaking to myself 90% of the time which helps#if a friend off tumblr saw my thoughts I’d feel so weird ab it#esp bc they might get the vagueposting about certain situations and tell mutual friends#no thank u. this is for me. I’m not about to start censoring my thoughts bc someone I know knows my tumblr#u guys literally saw me have LIVE BREAKDOWNS#meanwhile I’ll have the worst fucking day in history and tell no one about it. I’m already cripplingly private but way more so in real life#this is basically a low stress journaling outlet for me. it’s so important for me to maintain the separation#like this is actually my diary & has been so handy for letting out emotions / articulating thoughts / staying on track !!#& I’ve met so many kind people on here who actually get me. which is so hard to find irl bc I’m surrounded by pre-med gunners/overachievers#who are by standard not very good w emotion & can be competitive/judgmental. or at least it’s hard for me to be vulnerable in front of them#and I’m part of that crowd so I reserve my emotions only to a handful of very close friends#it’s nice to hop on here and express negative emotions!! or positive emotions!! just whatever I want and it’s low stress and people get me#I don’t have to worry about judgment or competitiveness etc etc#like everyone on here is so kind & nice & understanding. & just a breath of fresh air from the types I run w. it’s just nice to have this#so idk that’s why I think I’ll always be strict about keeping the worlds separate. it just works#p
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
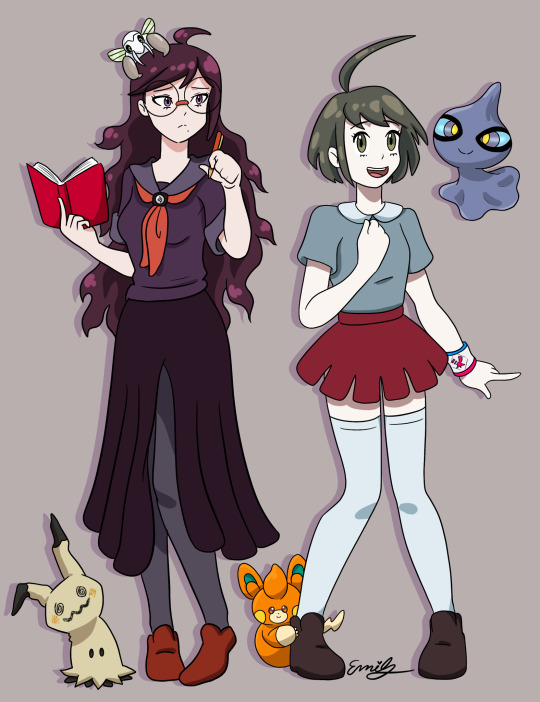

Tokomaru Pokémon au! Komaru has an affinity for ghost Pokémon lol hence her Shuppet, and giving her a Pawmi was mostly just based on vibes. Similarly giving Toko a Mimikyu just seemed right, and then her Nincada is because of her pet stink bug in canon. Toko can’t actually use the mega stone that’s on her tie, it’s only Syo’s (I’m thinking mega mawile 👀) and then I gave Komaru a Dynamax band bc I think she should get to use giant kaiju Pokémon, as a treat. I haven’t given too much thought to how the udg plot would fit in the Pokémon universe, but I do think the Warriors of Hope would each have one of the Unova genies instead of their giant robots (Monaca gets something bigger)
#might draw the woh too#because it’s always fun to draw in the Pokémon art style#good practice at least lol#udg Pokémon au#Pokémon#komaru naegi#toko fukawa#tokomaru#pawmi#shuppet#mimikyu#nincada#pokémon au#danganronpa udg#udg#dr udg
212 notes
·
View notes
Text







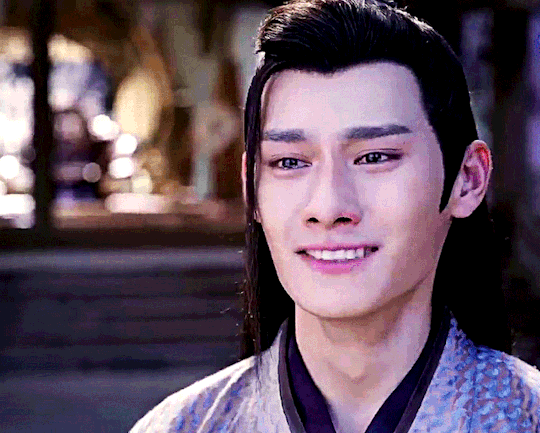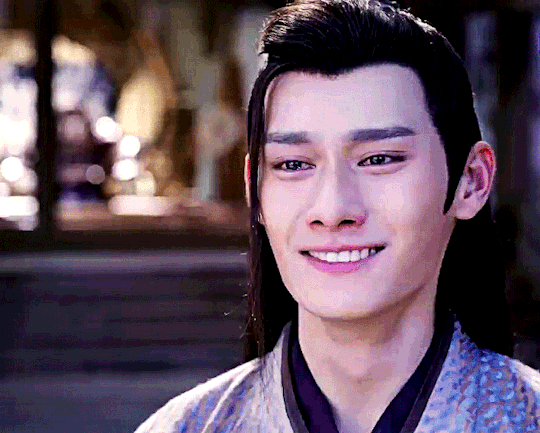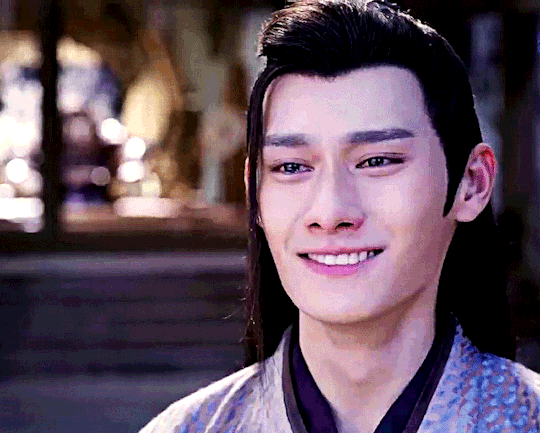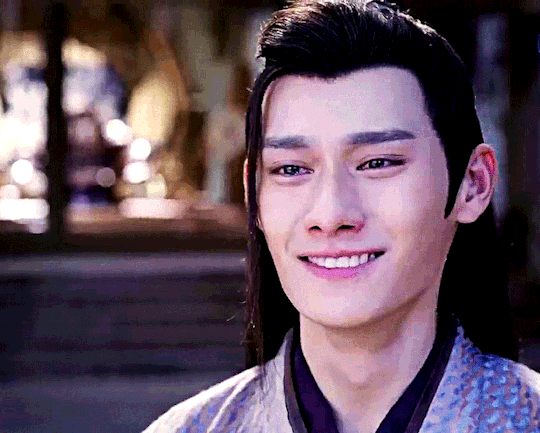
The Untamed - Episode 19
Throughout the night, he [Jiang Cheng] had somehow managed to sleep a couple of times. The first reason was that, having been too tired from crying himself weak, he couldn't help from passing out. The second reason was that he still had the hope that this might be a nightmare. He couldn't wait to wake up after some rest and open his eyes to find himself lying inside of his room back in Lotus Pier. His father would be wiping his sword in the main hall. His mother would be angry again and complaining, scolding Wei Wuxian who winked in a funny way. His sister would be in the kitchen, thinking as hard as she could about what to make today. His shidi would be refusing to do their morning lessons properly and jumping around.
The Grandmaster of Demonic Cultivation, Chapter 59, Poisons- Part Four
#This crappy gifset is born to show that the 'look how different cql!jc is from mean novel!jc' advertisement is exaggerated lol#look there! jc always yearns for his family! Like. While cql!jc dreams of his family in a 'better light'#Novel!jc dreams of his real crappy family lol. which is understandable when you think that#Novel!jc is a bit sadder lmao. he probably got hugged 5 times by his father while cql!jc at least seven times#The fact is that novel!jc doesn't have a lot of scenes in particular in the present but he is mentioned a lot in an unflattering way#because novel!wwx has jc brainrot#but he's bitter and resentful so his thoughts are quite mean lol#I've read so many 'I don't want to read the novel because I fear I won't like jc'#My point is that approaching the novel you shouldn't worry about jc lol#jiang cheng#*mgifs#Uh. Tbc. Both dreams are set after lotus pier's fall#Also. Another thing to understand novel!jc is to remember that he grows up with novel!wwx who doesn't like when people - in particular men-#cry in front of him#This is not to say there aren't differences obv. But tbh the propaganda is exaggerated#Anyway. In every canon jc is not having a good day
390 notes
·
View notes
Text
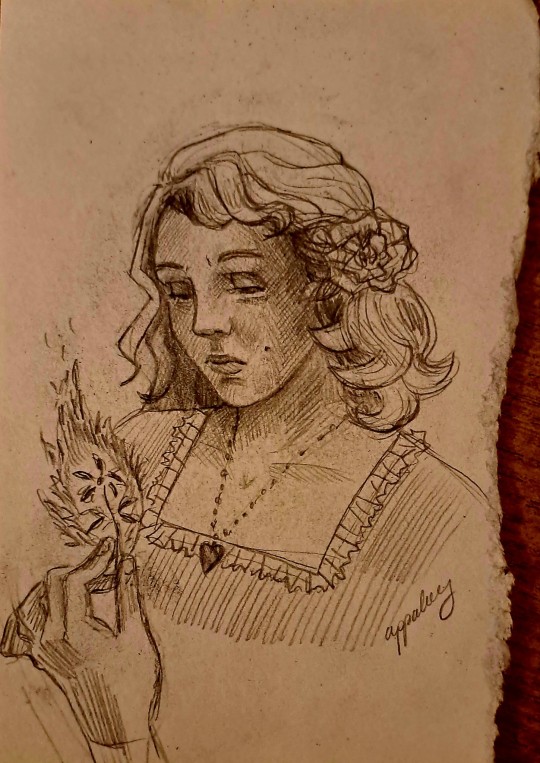
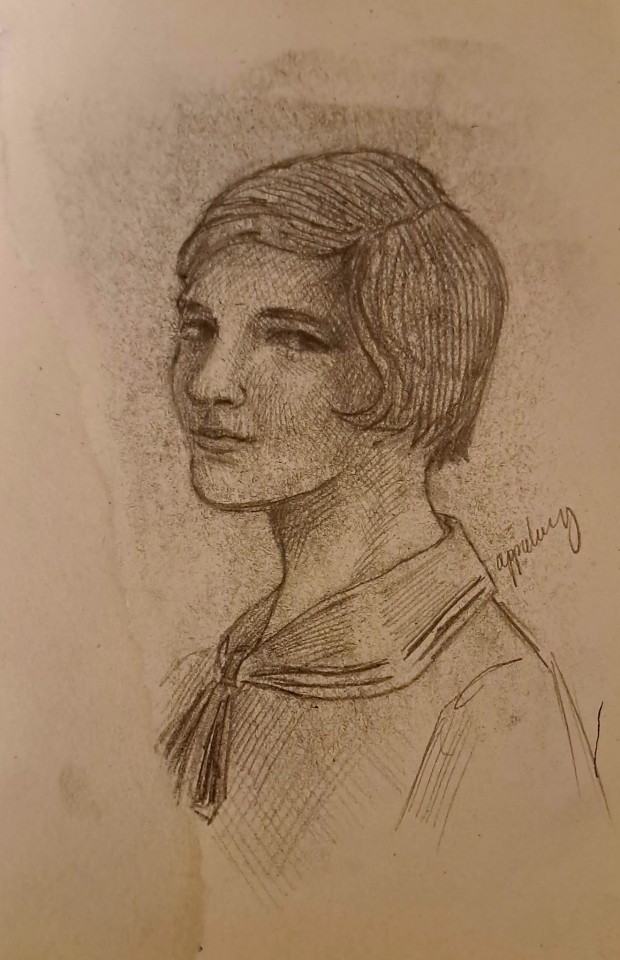


🔥🔥💪💪
#hii guys lol 🤓#sorry for the cringe filter#i always fail to be neat sorry for drawing on literal scraps of paper at least it fits the vibe lool but#idk not fully happy with these but whateev#bronwyn started out good but along the way i lost my vision i think 😔#and emma tbh i wanted her to be more 40s especially her hairstyle but also whatev#these look like two different ppl drew them bc thats just my range and it was planned 💯 dont worry guys#will try to do them justice next time 🥺#mphfpc#my art#emma bloom#bronwyn bruntley#nooo i signed them with my main blog name lmaooo#bro is anyone secretly working on some book accurate mphfpc tv series? i would watch that shit fr let me know
80 notes
·
View notes
Text



#dbtag#silly hours#god#I feel like that's a really clear and consistent thing throughout the entirety of the manga but OTL leave it to Toei!!!!#lays on the floor I wish people were less afraid of letting “good guys” be flawed and selfish and reckless without having to like.#idk vilify them?#like Goku does and always has had a ton of negative qualities about him but what keeps him a protag and what keeps those negatives charming#is that 1) he never promises to be anything Else. If you're upset by his behavior that's a you problem Goku's just doing Goku#He's only upset when Other People get hurt because 2) almost none of those negative qualities contain any malice whatsoever#even as a kid when he was 'i killed that guy' it was like 'i solved a problem why are you mad (gen)' not 'good fucking riddance lol'#and he kept that as an adult too even when he learned more about compassion he's still 'well if you're not gonna stop i have to kill you'#it's never 'fuck off and die' it's always 'listen buddy either you knock it off or i knock you out there is no option c '#and god i love that Goku. I spent so long thinking I hated Goku growing up but I only hated Toei's Goku. Toriyama's Goku is GREAT.#like look if an antagonist is just a hero with the wrong perspective a hero is just a villain with the right one#and the fact that Goku has all of the qualities of a villain with none of the malice or intention makes him SO POWERFUL as a character#Goku doesn't like bystanders getting hurt. That doesn't make him less chaotic and self-centered and simplistic in his worldview.#A hero sacrifices his loved ones to save the world -- a villain sacrifices the world to save his loved ones --#Goku sacrifices himself because you cannot kill him in any way that matters#idskahds anyway here's another essay in the tags for your wednesday evening scroll#the justification the interviewer gave was that the anime was for kids but my beef with that is that Hero Tropes strip chaotic characters#of their emotions. Goku's conflicts are emotional. Goku's power is emotional. Goku's childlikeness keep him authentically emotional.#MORE kids -- ESPECIALLY little boys -- deserve a male protagonist who leans into his emotions to persevere and win.#Super deciding his “angelic state” would kill him makes me want to tear my hair out lmao Goku's EMOTIONS are too strong to hold it.#you could've just asked toriyama about it why'd you decide on the most basic high-stakes shorthand possible OTL#aNYWAY#media analysis#in the tags at least lol
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

box me up until i spill | bkg x reader blurb
“what are you doing?” bakugou mumbles
“nothing, will you just go back to sleep?” you don’t look at him when you speak, but instead you focus all of your attention onto your current task
“well i can’t when you’re just making random metal clashing noises next to me, just get back onto the bed and leave it for later when we wake up again, it’s not that fucking urgent”
you take a deep breath, but with the way you roughly slam the spoons into the box that houses the forks, it sends a grimace onto his face. in turn, he rolls over from facing you and now the wall
“if you did this when i asked you to yesterday maybe i wouldn’t have to do it right now but you didn’t, so just wait two more god damn minutes and then you can sleep again okay?”
he sighs, and for a moment you think that he’ll keep his mouth shut and keep quiet for once, suddenly the utensils you’re organising feel cold and biting against your skin, they feel like they’re drooping and melting into putty right in between your grasp, and you can’t catch it
“can you just give it a rest?” he goes from facing the wall to sitting up, the curtains flutter slightly in the wind and it tussles his hair in a way that makes you want to cry
“no i can’t fucking do that! i’ve laid out my life right in front of you and i’ve given you myself yet it’s still not enough! you’re a hero who doesn’t get to sleep at night fine i get it! but i’m not any less important so don’t you ever go around and speak to me like that ever again! you promised me all those eight years ago in that basketball court the day we graduated, and you remember what i said yeah? if you did i’d fucking leave!”
all the work you’ve been doing the past ten minutes is rinsed down the drain, useless and helpless to end, the flailing of your arms has caused the box that stored all the metal utensils to fall onto the floor. chopsticks, spoons, forks and knives poke at the hardwood floor and at the edges of furniture, it doesn’t chip the wall, it chips your heart instead.
you’re tired, and even when you’re not dressed for the outside, in mere pyjama pants and a random shirt that you go to sleep in, you walk towards the door and leave the mess behind you

#saw a yter talk about writing good dialogues and i wanted to try#since i’ve always been the worst at writing ppl talk LOL#his name is localscriptman fyi#tried my best to follow his advice#snuck in some information in the least robotic way i can#how long they’ve been tgt n to use the tasks the characters r doing to reflect their inner thoughts#also sorry for the absolute behemoth of punctuation usage in this thing it was way too haphazardly put tgt lol#sy.katsuki#bakugou x reader#bakugou headcanons#mha bakugou#bakugou x you#bnha bakugo katsuki#katsuki bakugo x reader#bakugou katsuki#bnha bakugou#bakugo katsuki#bakugo x reader#katsuki bakugo#bakugo katuski#katsuki bakugou#katsuki bakugo mha#katsuki x reader#katsuki#katsuki x y/n#katsuki x you#bakugou drabble#bakugou x y/n#bakugou katuski x reader
115 notes
·
View notes
Text


Trixie & Katya behind the scenes
#the two of them driving around town and working on furniture#wish the show was just about that lol#anyways at least they looked good together as always#katya#katya zamo#katya zamolodchikova#trixie mattel#trixie and katya
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
Every single member of the Hamato family is equipped with the cantrip Vicious Mockery and 80% of its use is friendly fire.
#rottmnt#rise of the teenage mutant ninja turtles#rottmnt headcanons#is it a headcanon if it’s true#2% of the non-friendly fire time it’s used on villains#3% on randos#and the last 15% is exclusively for Warren Stone#for the 80% friendly fire a good 50% is directly to Leo#25% Donnie#3% Raph and Splinter#2% everyone else#Leo: *breathes*#Literally Everyone: You gotta be humbled#Leo’s wisdom stat being shocking high is what saves him from insta death on the regular#meanwhile Warren Stone exists in the Hamatos’ lives exclusively to be mocked and you know what#he’s the villain who’s treated most like family ❤️#by virtue of being mocked just like them lol#even a regular chill day isn’t enough to save the fam’s hit points#they’re always missing at least some from vicious mockery alone#rip Leo at least a quarter of his hit points are gone daily 😔
816 notes
·
View notes
Text
thinking about the (probably) unintentional symbolism of the master sword's state often reflecting link's in the botw trilogy, swords being frequently described as an extension of yourself in popular media, the master sword as an extension of link and link an extension of it. he really is a living weapon if you think about it too hard
#botw#the legend of zelda#breath of the wild#i think about this WAY too much for my own good#botw link always wins the link most dehumanized by the narrative award#the 2d links dont have a lot of character yeah but at least they werent treated like a tool#ww/oot/tp/ss obviously toy with this idea and go 'hey this is actually kind of bad?' but botw is like 'lol'#'we're going to briefly criticize our own metanarrative and then actively say that the people suffering from it were actually in the wrong'#i say this as someone is has been obsessed with botw for the past...shit. like since it came out#my hyperfixation just causes me to criticize the media i like more because i literally eat it#and yet: we stay silly
156 notes
·
View notes
Photo
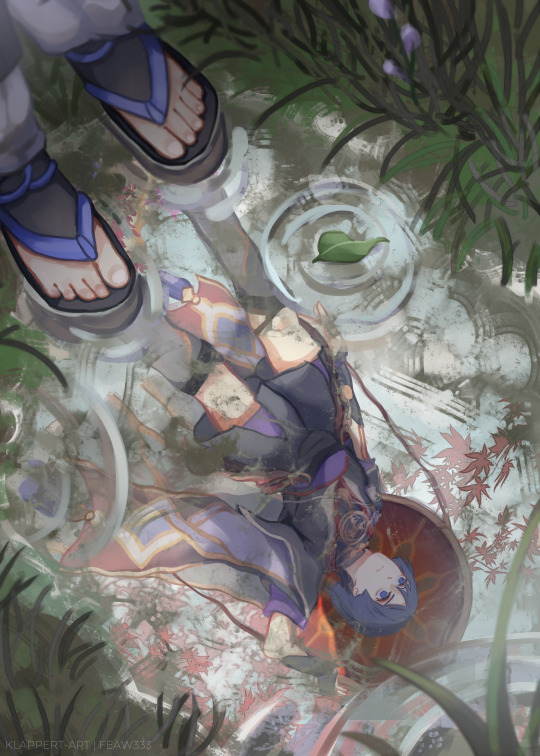

Fabricated past
#scaramouche#genshin impact#wanderer#原神#artists on tumblr#my man my dude my bro i never imagined i'd draw scara LOLL#actually.. brutally honest.. personality wise he's one of my least fav HAHA#but the quest was good and yknow what it means??#my hand aching to draw something#i also pulled him.. so I can throw him off from any cliff XD#jokes aside this was hard to draw like 50x harder#oh also i always willing to collect anemo. dude was fun for explore#*explorATION!! lol
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

island posing again 🏝️
#sorry for huge cori at least there is only one#bc i couldnt do another pose i liked lol#oc: corisande ymir#ffxiv#gpose#one thing about me is i am always on the island in my mind. this is not a good thing for me or them <3#despite the pictures.#they looked cute tho
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

#something he keeps saying lately#also idk how to word this but my stuff almost never looks good when i flip the canvas but aiming for symmetrical too Stiff#i hope my stuff is at least a Good wonky and not a ''dude this looks so bad you just cant tell yet'' wonky...#i want it to look like i made it bad on purpose not like its bad because im just unskilled....#but it definitely is not ever on purpose or in an informed; breaking the rules ive learned way lol.#<- speaking generally here bc as of rn i dont think this doodle Sucks its just lopsided i think...thats what the canvas flip says at least#i always say this but i wish i cld switch between my perception of my stuff and someone else's perception#i hate feeling so in the dark about my own stuff. i wont even be able to tell if this sucks bad until anywhere from one day to 5 years#from now. ykwim.#a doodley#ok gn ^_^
153 notes
·
View notes
Text

cut my face up
#ocs#original characters#oc tag#blood#gore#monster#<- ? viewer is technically at least lol. so implied more like#crows art#quill tag#viewer tag#WOW I ACTUALLY FINISHED THIS ONE#this ones been sitting in the files for a good few months now woof#BUT I AM. VERY HAPPY WITH THE OUTCOME#blood practice pays off yall it rlly does. fuck yes fuck yes#ask to tag#uhhh idk what else to tag x-P#i hope the. colors look okay on mobile. they always look different on my laptop grrrr#EDIT: OKAY LAST EDIT TO THIS UGH. quality is slightly better now
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
it makes me so happy to see more people are starting to write multi chap / series fics on here again
#don’t get me wrong i love one shots and drabbles too#but my heart will always belong to loonnnggg slowburn stories like if i find a good 100k word fic on ao3 i'm sold lol#and i feel like for a while there these kinds of fics were really starting to die out :(#and ik it’s probably bc they don’t do as well on tumblr unfortunately#but i'm excited to see people are picking them back up !!! i hope this trend continues !!#also if you are writing one you enjoy pls pls don’t get discouraged ! :( and send them my way!!! at least one person on here will enjoy the#(me)
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
In lieu of @motions1ckn3ss ‘s absolutely WONDERFUL essay about ellwood’s relationship with poetry, I’ve been inspired to post my history essay that analyzes the way WWI is shown in In Memoriam! (Strap in this will be long lol)
Nothing Is Worth This: How In Memoriam Portrays WWI
Alice Winn’s debut novel In Memoriam is a hidden gem amongst the growing popularity of historical fiction. Published in 2023, the novel follows the lives of English schoolboys Henry Gaunt and Sidney Ellwood. As the First World War breaks out in 1914, they face two battles; the Western Front and their growing feelings for each other. Together they watch as friends die around them, and as the war changes their lives forever.
The novel explores tumultuous conditions soldiers faced in the trenches, such as mud, poor rations, and gas attacks. Classism, social dynamics during WWI, attitudes towards homosexuality, and trauma are also touched on.
When one thinks of trenches, the first image that comes to mind is likely muddy, rat-infested mazes that snake around a war-torn No Man’s Land. Winn perfectly portrays the horrors of trench warfare throughout the novel, one notable interaction is from a letter Gaunt sends to Ellwood when he reaches the front:
“I throw myself to the ground, and the mud is foul. It’s not like mud, Elly, it’s cursed. It’s– Like everything else, I can’t explain” (Winn, 35).
There is no greater example of the terror of mud in the Western Front than the fields of Passchendaele. In August of 1917, Belgium saw unprecedented amounts of rain which led to treacherous conditions. Bombardier JW Palmer, 26 Brigade Royal Field Artillery, writes in his account:
“It was mud, mud, everywhere: mud in the trenches, mud in front of the trenches, mud behind the trenches. Every shell hole was a sea of filthy oozing mud. I suppose there is a limit to everything but the mud of Passchendaele – to see men keep on sinking into the slime, dying in the slime – I think it absolutely finished me off” (Battersby).
One of the most dreaded side effects of mud was trench foot, an infection that ravaged soldiers. It is caused by prolonged exposure in cold, damp and unsanitary conditions. Symptoms include swelling, numbness, blotchy skin, and if it develops enough, blisters and dying skin tissue (CDC).
When not on the battlefield, men were treated to daily food rations. Rations in the trenches consisted of corned beef, bread, plum and apple jam, tea, whiskey and rum. Water was often disinfected with chlorine and had a chemical aftertaste. The novel discusses food supply on both the British and German sides, and even touches on food shortages throughout the rest of Europe. A scene where Ellwood and Gaunt’s sister, Maud, eat at a cafe details the pitiable amount of butter on their scones. At the front, flies and rats infested everything, eating the men’s rations and spreading disease. British infantryman Victor Silvester wrote in his diary:
“That night I had been asleep in a dugout [for] about three hours when I woke up feeling something biting my hip. I put my hand down and my fingers closed on a big rat. It had nibbled through my haversack, my tunic and pleated kilt to get at my flesh. With a cry of horror I threw it from me.” (Hamilton, 18).
A few passages in the novel are dedicated to the conditions of the food. Often it is writtens in a way that a reader may interpret as gallows humour.
“The flies plagued them, feasting on the dead and then coming to sit amicably on the men’s rations. They got stuck in the jam, which was always plum and apple […] As to apples, the sour, fly-covered substance that they ate with bread at five each evening had as little relation to them as the ‘meat cutlets’ had to meat” (Winn, 91).
“‘D’you want a cup of tea?’
‘Will it taste of disinfectant?’
‘’Fraid so.’
‘Well, better have it all the same’” (Winn, 95).
It is often described that soldiers had two emotions at the front: boredom and terror. One of the harbingers of terror included poison gas. First used at the Second Battle of Ypres on 22 April 1915, the Allies were devastated by the chlorine gas that was unleashed in unprecedented quantities by the Germans.
The British then managed to use gas at the Battle of Loos, prompting both sides to develop protections against gas attacks. These defences started out as cotton pads covering their mouths, soaked in chemicals–or in desperate situations, urine–and goggles to protect their eyes. Throughout the war the makeshift masks developed into more sophisticated gas masks.
The brutality of poison gas in warfare was so acute that it was outlawed by the Geneva Protocol in 1925. Just ten years after its initial use. Renowned poet Wilfred Owen captures the trauma of gas in his famous poem Dulce Et Decorum Est.
“Gas! GAS! Quick, boys!—An ecstasy of fumbling/Fitting the clumsy helmets just in time,/But someone still was yelling out and stumbling/And flound’ring like a man in fire or lime.—/Dim through the misty panes and thick green light,/As under a green sea, I saw him drowning” (Owen, 9-14).
A similarly moving passage is found within the novel, when Gaunt is faced with Algerian soldiers fleeing from gas at Ypres.
“More Algerians came flooding by. Some were only choking, but others were coughing up scrambled bits of lung, their lungs were melting inside them and drowning them” (Winn, 75).
Gaunt continues to reflect on the effect colonialism has on war and the useless attempts to try and make war ‘civilised’ by using laws such as the Hague Convention, which are so easily ignored.
“We swarmed through Africa and America because we were better than they, of course we were, we were making war humane, and now it has broken down and they are dragged into hell with us. We have doomed the world with our advancements, with our democracy that is so much better than whatever they thought of, with our technology that will so improve their lives, and now Algerian men must choke to death on their own melted insides in wet Belgian trenches” (Winn, 75).
Empires such as Britain invaded countless countries, stealing their resources and enslaving people. They exploited those countries so they had to rely on their economy, and used it to justify their ownership. All because they believed that they were more civilised than everyone else; despite the ungodly circumstances modern warfare put soldiers in.
Winn captures the grime, fear and misery that comes with living in the trenches. From vivid descriptions of shellfire and gas, to the bland and occasionally humorous details regarding a soldier’s diet. Undoubtedly, one can imagine themselves slogging through the muddied land of war-torn Belgium with each turn of a page.
Moreover, one theme that is prevalently explored throughout the novel is classism and how it affects soldiers during the war. Gaunt and Ellwood come from privileged backgrounds, going to a public school called Preshute and immediately receiving their commission when they enlisted. When writing to Gaunt, Ellwood discussed how he was even able to choose his own regiment.
“When we next meet I shall be a second lieutenant in the Royal Kennet Fusiliers, Third Battalion. I’m glad I was able to pick my regiment! (It’s all about who you know)” (Winn, 80).
Having connections with the higher class means receiving certain privileges that others don’t have access to. Officers frequented the same upper class social circles, due to there being so few prestigious universities in England. Favours for friends or family members was extremely common and gave commissioned officers opportunities that weren’t available to the working class.
By contrast, they meet a fellow junior officer Lieutenant David Hayes, who did not come from a rich background. Throughout the book his uniform is described as poorly fitting, due to his inability to afford a proper tailor. Hayes quickly becomes friends with Gaunt but is wary of Ellwood, the stark contrast between their socioeconomic positions leading to a strained relationship.
“‘I say, is it really true he was a factory worker before all this?’
‘He’s awfully sharp, isn’t he?’
‘Do you think he’d take offence if I recommended him a new tailor?’
‘Yes,’ said Ellwood, flatly” (Winn, 269).
“‘Said it’s a stone ginger.’
‘...Translate,” Gaunt said to Hayes, as they climbed into the train carriage. Hayes understood Cockney and trench slang far better than the public school officers did” (Winn, 120).
“I’ve been made captain. Seems a well-tailored uniform and the right accent make me a better candidate than Hayes, despite his years of experience” (Winn, 77).
Additionally, Gaunt writes in a letter that one of their schoolmates would hypothetically refer to Hayes as a “temporary gentleman.” This phrase was used throughout WWI and continued into the interwar period and WWII. The phrase refers to non-commissioned officers who gained a temporary commission for the duration of the war, especially if they came from outside the upper class.
“He’s what someone like Burgoyne would call a ‘temporary gentleman’ (disgusting term), that is to say, he was a factory worker in Lewisham before he joined the War” (Winn, 40).
Gaunt continues further, noting that lower-class officers related more to the men, and were more effective on the battlefield. While both Gaunt and Ellwood know that Hayes is a more than capable officer, Hayes recognizes that due to his class, it is unlikely he will ever be promoted to captain.
Life in the trenches caused a mixing of race, class, religions, etc. Before the war, commissioned officers were upperclassmen who were educated in public schools and universities, sometimes coming from previous military backgrounds. The ideal “officer material” of the time was more akin to the “perfect gentleman” than a skilled soldier. When the war started, junior officers had an extremely high mortality rate. Officer training schools could not keep up with the demand, so soldiers and NCOs were promoted and received commissions (Root, 3-4).
English poet Robert Graves wrote about his wartime experiences in his autobiography Goodbye To All That. He details that certain social manners and behaviours among officers were more relaxed than in civilian life. Graves was also an instructor at an Officer Cadet Battalion in 1916, in order to train new officers. All recruits were treated and trained equally, and though he disparages that many men lacked the proper manners; he understands that this new way of training was considerably more effective (Root, 5).
“Their greater efficiency in action amply compensated for their deficiency in
manners” (Root, 5).
Another famous war poet from the time, Siegfried Sassoon, had a similar view. However, he held greater scorn for the lower class officers. In May of 1916 he wrote in his diary:
“Of all the officers having dinner, I saw no face with any touch of distinction in it. They were either utterly commonplace or self-satisfied, or else tired-looking, feeble, goggle-eyed, or otherwise deficient. Why does one see so few proper-looking officers?” (Root, 6).
But he also found that some commissioned officers had acute character flaws. Such as an interaction he had with an officer who was constantly drunk and “quite irresponsible and not trustworthy.” Thus, we can see how life on the frontline can blur the lines between classes. Men judged each other on their personal merit rather than their alma mater.
With much more relaxed ideas of social responsibility being so prevalent amongst soldiers, it allowed for more men to engage in relationships that were heavily frowned upon at the time.
In Memoriam is a love story first. Gaunt and Ellwood spend a large amount of the novel pining for one another, understanding the great amount of risk that comes with pursuing such a relationship. Ellwood is more outwards with his homosexuality, he is revered throughout the school and is able to get away with more risky behaviours. This is opposed to Gaunt who keeps any sort of interaction of that nature a secret. The politics of homosexuality in public schools at the time are explored in the novel and are indeed quite interesting, but it differs from attitudes in the trenches.
During the early 1900s, homosexuality was at the forefront of moral panic. Public trials from previous years such as that of Oscar Wilde and the Eulenburg Affair brought a topic that was usually brushed aside into the spotlight. Homosexuality was punished with jail time and years of hard labour under the Gross Indecency Law. Alongside that was social discrimination and the loss of reputation amongst family and loved ones.
In the late 1800s, Germany had a large scandal known as the Eulenburg Affair. Members of Kaiser Wilhelm II’s cabinet were outed for being gay, resulting in several trials and court-martials. As a result of this public scandal, the British found homosexual acts to be ‘unpatriotic’ and associated with German sympathies (McGhee).
Within the British army, punishments for homosexuality included court martialing, loss of rank, and imprisonment. “Cashiering” was a humiliation ritual that was performed when an officer was dismissed for scandalous misconduct. It involved ripping off insignias, badges and other symbols in front of other officers (Bronskill). This concern is portrayed in the novel by characters such as John Maitland, who warns Gaunt about his letters between Ellwood, and Hayes who warns Ellwood about his behaviour with a lower ranking soldier.
“‘Shut up. I’m not reporting you. I’m trying to help. Can’t you see that if you let Sidney write this sort of letter, you’ll get him imprisoned?’” (Winn, 66).
“‘Do you know what would happen if someone caught you and him? They’d say he assaulted you. That it was all his fault. He’d be court-martialed and shot so fast for daring to besmirch his precious public school captain—’ Ellwood stared at Hayes. It hadn’t occurred to him, any of it” (Winn, 192-3).
Despite all of this, the trenches fostered a culture of male affection that was able to be masked within the realm of hyper-masculinity and the guise of being bonded by war. Figures such as Robert Graves, Siegfried Sassoon (who were the inspirations for Gaunt and Ellwood), E.M. Forster, Ethel Mary Smyth and Wilfred Owen all served in WWI and are widely understood to be a part of the LGBTQ+ community. Attitudes towards homosexuality on the front varied. In rare cases some men were able to come out to their comrades, being met with acceptance. But generally it was frowned upon.
The very foundation of an effective army is camaraderie, and when men are facing constant traumas together a kind of brotherhood is formed. These homosocial behaviours allowed for more physically affectionate relationships. Even heterosexual men found these special friendships to be a relief from the stresses of war.
“Thomas Kühne has argued, men celebrated the “softer” side of comradeship, including bonds of love and friendship that sustained them in the other-worldly environment of the trenches” (Crouthamel).
Within these bonds, homosexual men were able to find an avenue for building lasting romantic and sexual relationships with other men under the guise of it being platonic. The novel delves into these kinds of relationships in passages such as a scene in the officer’s train carriage. We see it again in a discussion between Gaunt and Ellwood about using a sexual relationship to distract them from the war.
“Ellwood’s head drooped onto Gaunt’s shoulder. Gaunt stiffened, but when he looked around the carriage, he saw that the other officers were all in physical contact with one another. Huxton had his feet in Hayes’ lap. Hayes rested his head against the arm of an officer from C Company. Men sprawled all over each other. In the hyper-masculine atmosphere of war, they were not overly concerned with manliness” (Winn, 120).
“‘Did it help you forget about the War?’ pressed Ellwood. Gaunt nodded once, jerkily.
‘Well, then.’
‘And after the War? asked Gaunt.
‘It’ll be as if it never happened. I promise.’
‘You promise, do you?’
‘Yes. It doesn’t mean anything, Henry. Only that we want to forget things, once in a while” (Winn, 108).
Letters were another way for men to bond with one another, though it was a hazardous form of communication. Officers would read through letters and censor them before they were sent. If any illegal actions were mentioned the sender or recipient was at risk of being reported. Wilfred Owen’s letter to his cousin in 1918 reflects this anxiety:
“There are two French girls in my billet…Naturally I talk to them a good deal; so much so that the jealousy of other officers resulted in a Subalterns' Court Martial being held on me! The dramatic irony was too killing, considering certain other things, not possible to tell in a letter” (The Week).
A particularly striking scene in In Memoriam touches on this topic.
“He lifted the cover and looked at the first sheet of paper, instantly recognizing Gaunt’s neat blue handwriting: My dearest, darling Sidney,” (Winn, 189).
After the war, Germany had a spark in their gay rights movement. Many men felt that they had fought the war for nothing, with gay men knowing that they fought for a country that did not allow them rights as citizens (Marhoefer). Men used their military service as a reason to be accepted into society, showing it as proof of their patriotism and dedication to their country.
Magnus Hirschfeld opened his Institut für Sexualwissenschaft (Institute for Sexual Science), which pushed for the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals and was one of the pioneers of gender-affirming surgery. The Scientific Humanitarian Committee was one of the leading gay rights groups in the world during that time. This progress continued throughout the interwar period, with Weimar Germany becoming a hotspot for LGBTQ+ individuals. Berlin’s nightlife thrived with gay clubs before the Nazi party rose to power.
Near the end of the novel, Gaunt’s sister Maud explains how she is moving to Berlin to study at the Scientific Humanitarian Committee and encourages Gaunt and Ellwood to visit. She even mentions Paragraph 175, which was a law criminalising homosexuality in Germany. Paragraph 175 wouldn’t be abolished until 1994.
“The Weimar Republic is more open to progress than the governments of Englnd and France. I know you miss Europe. I hope you miss me. I cannot say whether Paragraph 175 will be revoked this year, or this decade, but I can tell you that there is a world for you and Sidney here. There has never been a movement like this before” (Winn, 371).
As previously mentioned, men used close intimate connections to deal with the trauma of war, but the rest of the world was less kind to those relationships. Similarly, those struggling with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder also faced social ridicule. PTSD, formerly known by many names such as shellshock, war neurosis and combat fatigue, was seen as a new phenomenon amongst men returning from war. Despite this view, soldiers from across history had suffered from the psychological effects of warfare. About 80 000 British soldiers suffered from shellshock after the First World War. There is a wide variety of symptoms but prominent ones include tremors, nightmares, insomnia, anxiety, flashbacks, amnesia and paralysis (Jewell). The effects of trauma are heavily explored in the novel, with Gaunt suffering from vivid nightmares and insomnia and Ellwood undergoing a complete change in personality after the war.
“Gaunt never seemed to sleep. Sometimes Ellwood would return to the dugout to find him lying on his wire bench, candlelight glinting in his bloodshot eyes” (Winn, 93).
“Ellwood did not say anything. He could not explain why that drop of blood on his mother’s finger had so appalled him, when he had seen West’s brain pulse with his last heartbeats and felt nothing except dispassionate curiosity” (Winn, 181).
Charles Myers, one of the first to write about shellshock, theorised that exposure to explosive blasts caused a form of brain trauma that aligned with the symptoms. After various tests, his ideas were disproven. As PTSD became less linked with physical injury, it became closer associated with cowardice (McDonald et al.).
At the time, a large ideal men strived for, especially amongst the upper class, was fulfilling the idea of bravery. The widows of men who were executed for cowardice often weren’t financially compensated. The ideal soldier at the time was one who would fight ‘for King and Country’ and a large amount of shame was put on those who, quite naturally, fled during the line of fire.
Cowardice is shown on multiple occasions in the novel. One officer by the name of Carrington suffers from severe PTSD, being shown screaming in the faces of other soldiers and having bouts of paralysis. He’s ashamed of his unwanted behaviour and confesses to Ellwood through tears about his cowardice.
“Ellwood threatened to shoot him if he didn’t get up. Carringon tried and collapsed again. Ellwood trained his pistol at his head.
‘You’d better do it.’ said Carrington. ‘I’m a dreadful coward. I know I am.’
[...]
‘There’s nothing wrong with his legs, he just wants to go home!’
‘I do,’ said Carrington, miserably. ‘I do want to go home. I know that’s shameful.’
[...]
Carrington was taken away, whispering ‘I’m a dreadful coward!’ in between spasms” (Winn, 187).
“Don’t know if you heard that Lantham was shot by firing squad. Anyone could see he had neurasthenia; it’s a scandal, but he didn’t go over the top on July 1st, so General Haig signed off” (Winn, 323).
Due to misconceptions at the time, doctors tried many different ineffective and harmful treatments for shellshock. One famous treatment is electroshock therapy. Electroshock therapy was used for a variety of mental disorders throughout the 20th century. Painful electric shocks were administered to the head and neck, in hopes of treating symptoms. These treatments were undergone without any anaesthetic, and often it did not relieve all of the symptoms (McDonald et al.).
Today we have electroconvulsive therapy, which uses controlled shocks on certain parts of the brain to induce seizures in order to treat mental illnesses such as severe depression and bipolar disorder (Psychiatry.org). These treatments are done under anaesthetic and in controlled environments, with studies proving it to be effective.
More often than not, soldiers would self-medicate their symptoms, leading to alcoholism and substance abuse. Alcohol was already offered to soldiers, and drugs such as morphine and cocaine were used during treatments or to boost morale and performance (Kamieński).
“‘Bring out the whiskey,’ said Gaunt, as he did at every meal. Daniels twisted his hands.
‘There’s only one more bottle, sir.’
‘What’s happened to them all? Have you been at them?’
‘No, sir! There were seven, and six have been drunk, sir.’
‘By whom?’ demanded Gaunt.
‘Well, sir, there was the one you had on our first day, and two the day Lieutenant Ellwood arrived—’
‘All right, all right, no need to enumerate them like crimes. Fetch the last one, and we’ll have rum tomorrow.’
‘Yes, sir.’ Daniels hurried away” (Winn, 93-94).
Luckily, not all treatments were dangerous or ineffective. An army physician by the name of Arthur Hurst developed talking therapies after the war. His treatments included using films and simulations to reconstruct soldier’s experiences in order to talk them through the traumatic memories. His treatments boasted vastly higher success rates and his focus on treating cognitive and behavioural symptoms was the blueprint for modern PTSD therapy (Butterworth).
In the modern day, there are many effective treatments for PTSD and trauma, but there is still an underlying stigma that prevents people from seeking out proper care for their mental health.
Although In Memoriam is a fictional retelling of real historical events, there is no doubt that Winn put extensive amounts of research into her novel. Her vivid writing style captures the inhumanity of the First World War and its effects on the psyche of characters and the greater world around them. The novel shows us the love between friends, comrades, family and lovers while tackling topics such as classism, trauma, and LGBTQ+ rights through the lense of our schoolboy protagonists; giving us a glimpse into history while telling a compelling story of love, death, and heartbreak.
Works Cited
“An army marches on its stomach.” National Army Museum.
Battersby, Eileen. “Passchendaele: A killing field of mud – The Irish Times.” The Irish Times.
Bronskill, Jim. “WWI: Study details punishment for soldiers' sexuality.” CTV News.
Butterworth, Benjamin Russell. “What World War I taught us about PTSD.” The Conversation.
McGhee, Beth. “Homosexuality in the First World War - WW1 East Sussex.” East Sussex WW1.
Crouthamel, Jason. “Sexuality, Sexual Relations, Homosexuality | International Encyclopedia of the First World War (WW1).” International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
Dwyer, Kassandre. “Trench Warfare in World War I: Rot, Rats, Ruin.” The Collector.
Freedman, Russell. The War To End All Wars: World War I. Clarion Books, 2010.
Hamilton, John. Trench Fighting Of World War I. ABDO & Daughters, 2004.
Kamieński, Łukasz. “Drugs | International Encyclopedia of the First World War (WW1).” International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
Marhoefer, Laurie. “How WWI Sparked the Gay Rights Movement.” Smithsonian Magazine.
McDonald, MaryCatherine, et al. “From shell-shock to PTSD, a century of invisible war trauma.” The Conversation.
Owen, Wilfred, et al. “Dulce et Decorum Est by Wilfred Owen.” Poetry Foundation.
“Psychiatry.org - What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)?” American Psychiatric Association.
Root, Laura. “Temporary Gentlemen” on the Western Front: Class Consciousness and the British Army Officer, 1914-1918.” UNF Digital Commons.
“Second Battle of Ypres 22 April – 25 May 1915.” Imperial War Museums.
“The secret history of the gay soldiers who served in the First World War.” The Week.
“Trench Foot or Immersion Foot|Natural Disasters and Severe Weather.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Washington, Nicole. “Shell Shock and PTSD: Connections, Symptoms, Support, More.” Healthline.
Winn, Alice. In Memoriam: A Novel. Alfred A. Knopf, 2023.
#this is my magnum opus I think#I’ve always dreamed about infodumping about IM as an assignment and here I am lol#I had a blast writing this it was great and it let me annotate the book lol#anyways yeah I hope it was good!!!!!!#I like it at least lol#in memoriam alice winn#in memoriam#alice winn#gauntwood#henry gaunt#sidney ellwood
44 notes
·
View notes