#Apollo Applications Program
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Portraits of all three Skylab Astronaut crews.
source
#Skylab II#Skylab 2#SL-2#SLM-1#Skylab III#Skylab 3#SL-3#SLM-2#Skylab IV#Skylab 4#SL-4#SLM-3#NASA#Apollo Program#Apollo Applications Program#Skylab Orbital Workshop#Skylab OWS#Skylab#Skylab I#Skylab 1#SL-1#undated#1970s#my post
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Martin Titan III-L
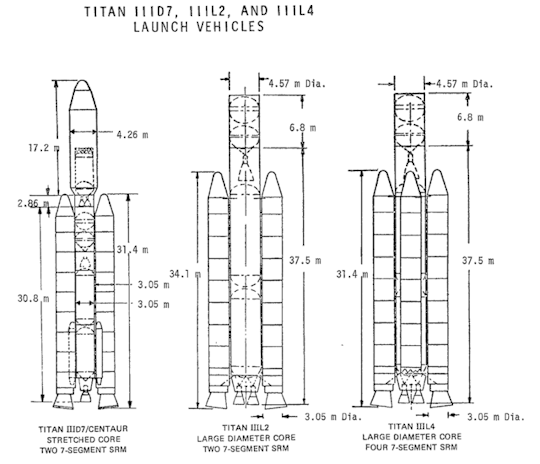
"The Titan III-L series was a Martin Marietta concept (late 1960’s into early 1970’s) for a heavy lift derivative of the Titan IIIC launch vehicle. The core would be increased in diameter from 10 feet to 15, and the number of liquid propellant rocket engines increased from two to four. Additionally, the vehicle could be given two, four or six solid rocket motors (Titan III-L2, Titan III-L4, Titan III-L6). The Titan III-L6 concept was considered as a first stage booster for the Space Shuttle.

The Titan III-L2 had enough lift capacity to launch an Apollo-derived capsule and service module, providing an alternative to the Saturn IB for space station logistics and crew transfer."
source
#Titan III-L#Titan III#Rocket#NASA#Apollo Program#Apollo Applications Program#1970s#concept art#my post
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHY DIGITIZE CULTURAL HERITAGE, AND FOR WHOM?
Many museums around the world make high-quality 3D scans of important artwork and ancient artifacts in their collections. Several forward-thinking organizations freely share their 3D scans, allowing the public to view, copy, adapt, and experiment with the underlying works in ways that have never before been possible.
Anyone in the world with an internet connection can view, interact with, and download the British Museum’s 3D scan of the Rosetta Stone, for example. The public can freely access hundreds of scans of classical sculpture from the National Gallery of Denmark, and visitors to the Smithsonian’s website can view, navigate, and freely download thousands of high-quality scans of artifacts ranging from dinosaur fossils to the Apollo 11 space capsule.
With access to digitizations like these, artists can rework and incorporate our common cultural heritage into new works, such as films, video games, virtual reality, clothing, architecture, sculpture, and more. Researchers and educators can use 3D scans to further our understanding of the arts, and the art-loving public can use them to appreciate, study, and even replicate beloved works in new ways that are not possible within the confines of a museum or with the original works. [...]
Unfortunately, some ostensibly public-spirited organizations do keep their 3D scans hidden. I’ve been trying to help them see the light. Beginning in 2017 I spent three years using German freedom of information law to successfully pressure the Egyptian Museum of Berlin to release its 3D scan of its most prized possession and national treasure, the 3,000 year-old Bust of Nefertiti. Since then I’ve turned my attention to the digital treasures being hoarded by taxpayer funded institutions in France.
The Louvre, for example, will not allow the public to access its ultra-high quality 3D scan of Winged Victory, the Nike of Samothrace, despite its aggressive public and corporate fundraising campaign to digitize the iconic Greek sculpture. Nor its scan of Venus de Milo.
The French Ministry of Culture’s Réunion des musées nationaux (RMN) receives tens of millions of dollars anually in public subsidies to provide services to French national museums. [...] RMN advertises its scans’ availability to the public, which makes for great PR, but its ads are false. In fact, RMN has a strict look-but-don’t-touch policy for its 3D scans and absolutely refuses to allow the public to access them directly. My own investigation has revealed that, in private, RMN admits it won’t release its scans because it wants to protect its gift shops’ sales revenue from competition from the public making their own replicas. For practical applications and creative potential, and direct value to the public, it is as though these scans simply do not exist.
And then there is the Rodin Museum. Founded in 1917 shortly after the death of famed sculptor Auguste Rodin, le musée Rodin is a state-run administrative agency and an arm of the Ministry of Culture. It has a legally mandated mission to preserve, study, enhance and disseminate Rodin’s works, all of which have been in the public domain since their copyrights expired decades ago. Even though musée Rodin never passes up an opportunity to remind the public that it is France’s sole “self-funded” national museum, it sought and obtained direct public funding from the Ministry of Culture’s national digitization program, and in 2010 as part of its public service mission began 3D scanning its collection with the stated purpose of publishing the results.
Fourteen years later, musée Rodin’s scans have not been shared with the public. [keep reading]
- Cosmo Venman
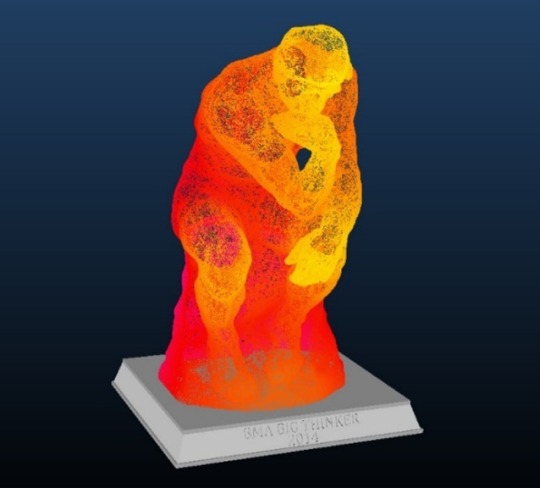
The Baltimore Museum of Art’s unpublished 3D scan of The Thinker.
15 notes
·
View notes
Note
Wait. Math logic is second year of college? Wait. Wait. Wait. I’m actually dumbfounded. Ridiculed. Gobsmacked.
Long story short, in my quaint little southern town the schools had this “intense, mathematically focused” summer program going on with the colleges nearby. 30 students would be chosen from all the middle schools (there were 5 or 6 so 5 or 6 kids were chosen from every middle school) based on resumes and essays on why they should be chosen. They had us compete for it. And me, being thrust into a classroom of about four others at the time routinely every week as a gifted child holding promise, was basically told “You are expected to sign up for this.” So I did. And I got a spot. So summer rolls around, and this thing is for like four years, alright? Four summers. Each summer is different. But that first summer for first years, you guessed it, included math logic. I was in 6th grade at the time. Learning math logic. They didn’t even introduce it as a lesson. In the middle of summer they gave us a test, and we had tests basically every other day to record our progress, but the second half of this particular test had graphs of carrots and p’s and q’s and squiggly lines. After, our professor went “Haha, you weren’t expecting that, were you?” NO. No, sir, I wasn’t. Then I checked the packet they handed us at the beginning of the summer, and there it was: Year 1. Logic and its Applications to Mathematics. Oh, goody. (Conveniently right before Introduction to Engineering.) Then for the rest of my high school years I never saw it come up in its full form. It was maybe teased once or twice. If that isn’t enough to figure out what the rest of the three summers was like, good. (Year 2 was Physics-based. Year 3 computer science and computer engineering based. Year 4 was straight up a well-oiled machine of the 9 nine rings of hell. Fun. Somehow.)
I love casually nerd Apollo, anyway. Makes me feel it all wasn’t for nothing when I nonchalantly bring something up in conversation and see them remember before my eyes that I was a child genius of some sort. <3
(For reference, this is referring to this post lmao)
I'm starting to think my school was either behind on math education or everyone else is put ahead lmao
NERD APOLLOOOOOOO
#the oracle speaks#asked and answered#anonymous#the trials of apollo#trials of apollo#pjo apollo#toa apollo
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
SwRI is sending its first instrument to the lunar surface to survey the Moon’s interior
LMS instrument aboard the Blue Ghost Lander heading to Mare Crisium in early 2025
Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Southwest Research Institute developed the Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) to characterize the structure and composition of the Moon’s mantle by measuring electric and magnetic fields. The LMS instrument — manifested on the Blue Ghost lunar lander developed by Firefly Aerospace and targeted to launch on January 15, 2025 — will be the first SwRI instrument to touch the lunar surface. “For more than 50 years, scientists have used magnetotellurics on Earth for a wide variety of purposes, including to find oil, water, geothermal and mineral resources as well as to understand geologic processes such as the growth of continents,” said SwRI’s Dr. Robert Grimm, principal investigator of LMS. “The LMS instrument will be the first extraterrestrial application of magnetotellurics. NASA’s Artemis program is developing a series of increasingly complex missions to ultimately build a sustained human presence at the Moon for decades to come. To support these goals, LMS is part of a 14-day lunar lander mission to help understand the Moon’s subsurface in a previously unexplored location. Mare Crisium is an ancient, 350-mile-diameter impact basin that subsequently filled with lava, creating a dark spot visible to the naked eye on the Moon. Early astronomers who dubbed dark spots on the moon “maria,” Latin for seas, mistook them for actual seas. Mare Crisium stands apart from the large, connected areas of dark lava to the west where most of the Apollo missions landed. These vast, linked lava plains are now thought to be compositionally and structurally anomalous with respect to the rest of the Moon. From this separate vantage point, LMS may provide the first geophysical measurements representative of most of the Moon. Magnetotellurics uses natural variations in surface electric and magnetic fields to calculate how easily electricity flows in subsurface materials, which can reveal their composition and structure. LMS will allow scientists to probe the interior of the Moon to depths up to 700 miles or two-thirds of the lunar radius. The measurements will shed light on the material differentiation and thermal history of our Moon, a cornerstone to understanding the evolution of solid worlds. The LMS instrument ejects cables with electrodes at 90-degree angles to each other and distances up to 60 feet. The instrument measures voltages across opposite pairs of electrodes, much like the probes of a conventional voltmeter. The magnetometer is deployed via an extendable mast to reduce interference from the lander. The method reveals a vertical profile of the electrical conductivity, providing insight into the temperature and composition of the penetrated materials in the lunar interior. “The five individual subsystems of LMS, together with connecting cables, weigh about 14 pounds and consume about 11 watts of power,” Grimm said. “While stowed, each electrode is surrounded by a ‘yarn ball’ of cable, so the assembly is roughly spherical and the size of a softball.” The LMS payload was funded for delivery to the lunar surface through NASA’s CLPS initiative. SwRI designed the instrument, built the electronics box and leads the science investigation. Goddard Space Flight Center provided the LMS magnetometer to measure the magnetic fields, and Heliospace Corp. provided the magnetometer mast and four electrodes used to measure the electrical fields. Under the CLPS model, NASA is investing in commercial delivery services to the Moon to enable industry growth and support long-term lunar exploration. As a primary customer for CLPS deliveries, NASA aims to be one of many customers on future flights. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development of seven of the 10 CLPS payloads carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
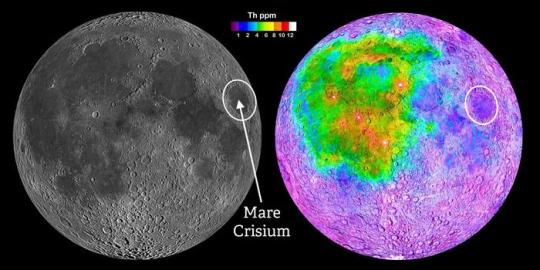
TOP IMAGE: From within the Mare Crisium impact basin, the SwRI-led Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) may provide the first geophysical measurements representative of the bulk of the Moon. Most of the Apollo missions landed in the region of linked maria to the west (left image), whose crust was later shown to be compositionally distinct (right image) as exemplified by the concentration of the element thorium. Mare Crisium provides a smooth landing site on the near side of the Moon outside of this anomalous region. Credit NASA
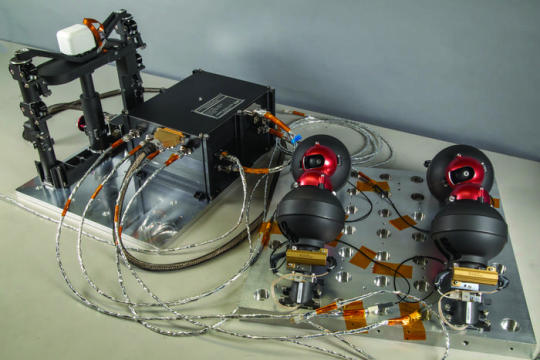
LOWER IMAGE: LMSwRI led the development of the LMS instrument for the Mare Crisium lander mission, which includes (from left) a magnetometer, a central electronics box and four spring-launched electrodes. Credit Southwest Research Institute
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just ordered this after having added it to wish list last year. Insomnia, pain, it was the perfect time to order a book with money I really needed to save for the upcoming heating bill. ;D But, hey, book was about 20% off, got free shipping, and there was a seven dollar gift card balance I didn't know I had that amazon applied to it. I'm going to call it a wise order. ;D

Nuclear Rockets: To the Moon and Mars Paperback – April 16, 2023 by Manfred "Dutch" von Ehrenfried (Author) 4.0 out of 5 stars (2) See all formats and editions So why is NASA refocusing its efforts on Nuclear Thermal Propulsion now, when chemical propulsion is so well established for human spaceflight? The reason is that future proposed flights are getting much longer and studies have shown that long-duration, weightless spaceflight has a lot of deleterious effects on the human body. When considering a flight to Mars takes a minimum of 2-3 years roundtrip, anything we can do to shorten the total mission time is highly desirable; if not mandatory. The longer the mission, the more exposure to galactic cosmic radiation, solar particles and coronal mass ejections, medical problems, and potential emergencies. A first-generation nuclear cryogenic propulsion system could propel human explorers to Mars more efficiently than conventional spacecraft, reducing the crews' exposure to harmful space radiation and other effects of long-term space missions. It could also transport heavy cargo and science payloads. A nuclear rocket engine uses a nuclear reactor to heat hydrogen to very high temperatures, which expands through a nozzle to generate thrust. Nuclear rocket engines generate higher thrust and are more than twice as efficient as conventional chemical rocket engines; just what’s needed for the crew to better survive the long-duration missions to Mars. In 1959, NASA replaced the Air Force in the development of the nuclear rocket and the mission changed from a nuclear missile to a nuclear rocket for long-duration space flight. Working with the DOE National Laboratories they worked on various research projects for 17 years including the Rover, NERVA, Kiwi, Pewee, and Phoebus rockets. In the late 1960s, the rising cost of the Vietnam War put increased pressure on budgets. It was determined that the Apollo program did not need nuclear rockets. Over the years, Congress support for the nuclear thermal propulsion projects including the Saturn upper stage, lunar and Mars missions, and the "Grand Tour" of the Solar System waned; nuclear rocket efforts were canceled in 1973. Now, there is renewed interest in picking up from those early efforts to produce nuclear rockets using state-of-the-art technology for deep space missions. NASA, DOD, and DARPA have teamed up to let contracts to many aerospace companies in order to define the best designs for nuclear thermal propulsion and nuclear fission power for surface energy applications. This book covers the past and present efforts that will lead to supporting near future cis-lunar and Mars missions. " Publisher : Independently published (April 16, 2023) Language : English Paperback : 270 pages ISBN-13 : 979-8377421252 Item Weight : 1.22 pounds Dimensions : 6.69 x 0.64 x 9.61 inches
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
i always see your apollo posting and i was just reminded by my dad today when black history month came up that one of my great aunts was one of the seamstresses that made the spacesuits for the apollo missions which is super cool and you’re like the only person i know who would find that interesting lol
she was a seamstress and made girdles and bras at playtex and was hired by ILC because her skills were applicable!
Oh wow that is awesome!!! Seamstresses have been such a critical part of the space program since its inception for things like parachutes and spacesuits because they require a level of precision sewing that only seamstresses were able to achieve. The thing with a spacesuit is that it is basically a self-contained little spaceship, with its own life support system and everything, so you have to be able to bind it in such a way that it maintains air pressure inside while still allowing for maneuverability for the astronaut. Without seamstresses like your great aunt, we wouldn't have been able to put people on the moon!
Post-Apollo, some of those seamstresses went on to work on the Shuttle in a couple different ways. There's the Shuttle pressure suits for launch and reentry, the Shuttle spacewalk suits (known as EMUs), and the Shuttle itself! A number of areas on the space shuttle orbiters had as part of their heat shield system these thermal blankets. On the exterior, they looked a little like quilts, and part of that is because they hired quilters to do precision sewing.
Theres still a lot of sewing that goes into modern space suits, too. The David Clark Company in Worcester MA, whose relationship with NASA goes back to the Gemini program, is currently making the launch and reentry pressure suits for the Artemis program based around their work on the Shuttle suits. And for moonwalking, Axiom Space is working with fashion company Prada to design the suits for future moon missions. The Prada partnership really hearkens back to those Apollo-era partnerships to me I really enjoy that.
You are correct in your assumption that I find that interesting lmao but yeah no that is literally so cool. And whether or not other people find it interesting, it's still a remarkable thing that your great aunt did, and many of the astronauts made a point of acknowledging the hardworking people on Earth who created the technology that allowed us to bring humanity to the moon.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

The interior of the rocket is instantly disconcerting. The entire thing is turned sideways. You can see several rows of seats extending downwards. The backs of the seats are against a wall, which houses a hefty-looking DOOR. There are rungs built into the wall that would allow you to climb down safely. Above you is an array of CRT MONITORS covering most of the wall.
Look around>
The lights are warm and dim, something much more comforting than the concerning red that bathes most of the Apollo facilities. The interior is made of glossy, smooth plastic and even has carpeted floors. You're surprised by the level of comfort it prioritizes. There also appears to be a communications TERMINAL next to the ladder.
Go to door>
You climb down the ladder and walk on the "wall", then lean down and examine the door. It has a large WHEEL on it.
Turn wheel>
You crank the wheel and pull. The door swings open. Looks like it was designed to keep the air inside in case of a breach. That's a smart safety feature. You look down at the room below. It's all empty racks and shelves, abandoned straps and hooks, and slots on the floor. It looks like it was designed to keep luggage and supplies secure. You close the door behind you and turn the handle back. There doesn't seem like any reason to keep it open.
Look at monitors>
You climb back up and look at the monitors. You recall that you never saw any windows on the rocket when you looked at it from the outside. Maybe the monitors are what let you see the outside?
Look at terminal>
The only familiar thing on the terminal is the INSTANT MESSENGER. There's also a program called STARTUP. You could probably use Heresy's advice now.
Talk to Heresy>
[HERESY is ONLINE]
Luna1: Hi Heresy.
Heresy: I see you made it to the rocket.
Luna1: Yeah, I did.
Luna1: But I don't know how to launch it.
Luna1: There's no obvious launch button.
Heresy: Those rockets were surprisingly autonomous and automated.
Heresy: They used a computer to run it.
Heresy: I should be able to help you launch.
Luna1: This seems kinda dangerous…
Heresy: You'll be ok, Sofia.
Heresy: Nothing can happen to you.
Heresy: I promise.
Luna1: Ok….
Luna1: So what do I do?
Heresy: Make sure the doors are closed and buckle yourself in.
Heresy: The terminal should have a few options for starting up the monitors and putting it in launch mode.
Heresy: Once you set those things up I can start it from my side.
You minimize the messenger. It sounds like Heresy was talking about the STARTUP program.
Use startup>
You double-click the application and it opens. The screen lights up with a flashy UI which features a short list of BUTTONS. They read monitors, safety check, and launch mode.
Use buttons>
You click every button in turn. The monitors start to whine and turn on soon after, displaying a clear view of the sky from the rocket's position on the launchpad. The cameras must be on the nose of the ship. When you click the safety check, a diagnostic program starts running and a loading bar appears. You barely even see it before it disappears, though. Seems like it's perfectly functional despite everything. Finally, you click launch mode. The program changes to a message.
"PLEASE TAKE YOUR SEAT AND BUCKLE UP FOR YOUR SAFETY. CLOSE MAIN HATCH BEFORE LAUNCH."
Ah, right, the HATCH. It would be a bad idea to leave it open during launch.
Close hatch>
You swing the hatch shut and turn the wheel on your side. Everything should be set up now. You need to let Heresy know.
Talk to Heresy>
Luna1: I think everything is set up now.
Heresy: Good.
Heresy: I saw that you set it to launch mode.
Luna1: Yeah.
Luna1: So I guess this is it then?
Heresy: Yeah. Buckle yourself in and I'll trigger the launch remotely.
Heresy: The course is already projected.
Something is bothering you. You pause a bit before sending your next message.
Luna1: Do I really have to go?
Heresy: What do you mean?
Luna1: I'm not sure if I'm ready to leave yet.
Luna1: I'm going to miss everyone a lot.
Heresy: You don't have to leave right now.
Heresy: You can stay as long as you like.
Heresy: But the thing is, your fate was already decided.
Heresy: At some point you'll decide to come anyway.
You think about her words for a while.
Luna1: How do you know?
Heresy: Because God told me, Sofia.
Heresy: I reached out to Luna for a reason.
Heresy: And I knew when you found me that you were who I was sent to find.
Heresy: We're both part of something bigger than us.
Heresy: That's why I need you.
You leave her waiting for a while again, trying to sort out your own conflicting emotions. But eventually you decide.
Luna1: Ok, I'm going to buckle up now.
You get into the seat nearest to the terminal and strap yourself in. The chair has excessive padding and buckles, and the headrest feels like more than just comfort. You look up at the grid of monitors. Something new has started to form on them. There's an overlap charting out the course to Earth from Luna. And then a countdown. As the countdown the rocket starts to rumble, more and more, and you can see the camera views start to show smoke drifting up. As soon as it begins the camera view cuts out, showing only the grid and leaving you in the dark to wait in anticipation. And then, liftoff.
You're pressed back into the seat as the rocket launches. Everything it shaking violently. You can faintly hear ripping and tearing metal and the booms of scattered vehicles and equipment flying from the thrust of the launch. The entire facility is probably demolished. But you can't afford to focus on that now. More and more pressure is piled onto you, and then you black out.
…
….
…..
You wake up suddenly, gasping desperately for air and trembling. You look around. Things are floating in the cabin. The cameras are back on, and you can see Earth in view, surrounded by the inky void and twinkling stars. As you slowly approach the planet, you notice what looks like a dense glittering silver ring around it. You're left to this view for quite a while. A timer in the corner of the grid says it'll be a number of hours before you make it. Eventually, you pass out.
…
….
…..
You awake at the jolt of the rocket. You're right inside the dense ring now. Now that you're closer, you can see what it's made of; metal scraps and debris. The rocket rumbles and shakes again. You must be bumping into the space debris. How many satellites and facilities were launched into orbit to create a ring this dense? You wonder for a moment, and the rocket shakes again. The lights flicker this time. You're getting nervous. Suddenly, you feel the thrusters again, and the pressure builds. It looks like you're coming in for an entry. The rocket slowly descends into the atmosphere, and as flames appear to build against the nose of the rocket the cameras cut out again. The ship rumbles and shakes more and more, and the pressure against you builds. A warning message appears and the lights flash red.
"WARNING: CRASH LANDING"
You close your eyes and feel the impact of the rocket slamming into the ground.
And then nothing.
NEXT
PREVIOUS
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Are there any scholarship opportunities at Zarmed University?
For many international students, especially those from India, affordability plays a significant role in choosing a medical school abroad. Zarmed University, a private institution with campuses in Bukhara and Samarkand, understands this and has developed a multi-tiered system of scholarships, grants, and financial assistance geared toward deserving and needy students. Here’s a comprehensive overview.

1. University-Based Grants & Discounts
Zarmed University offers direct financial aid on tuition to eligible students:
Up to 5 million UZS (~USD 450) in tuition fee discounts for students with excellent academic achievements or special needs .
For broader programs, they provide discount tiers of 25%, 50%, 75%, and even 100% tuition coverage, subject to competition and quotas .
The Samarkand campus also offers 100 scholarships of up to 10 million UZS (~USD 900), and 200 smaller grants of up to 5 million UZS (~USD 450) .
These university-specific scholarships recognize merit and socio-economic background, giving students substantial financial relief.
2. Government-Funded Scholarships
Uzbekistan, aiming to bolster its global student base, provides several national scholarships:
Presidential Scholarships: Awarded to top-performing foreign students, these cover tuition, accommodation, and a monthly stipend.
State Scholarships: Administered by the Ministry of Education, they often cover tuition and, occasionally, living expenses; open to international undergraduates .
While these are open to students across Uzbekistan, applicants to Zarmed can compete alongside entrants to other universities.
3. International & Exchange Program Funding
Zarmed University’s growing international profile comes with compelling multinational partnerships and learning opportunities:
2+2, 3+1, and 1+3 collaborative models with institutions in the USA, South Korea, Turkey, and beyond.
Semester/year-long exchange programs often come with partial scholarships or subsidy packages through partner institutions in the U.S., Russia, Turkey, etc. .
Since Apollo MedSkills (India) has partnered with Zarmed, Indian faculty exchange and potential scholarships—especially for healthcare education—are expanding .
These global tie-ups not only offer enriched academic exposure but also financial aid during abroad stints.
4. Student Council & Merit Awards
Active contributors to university life are duly supported:
Members of the Student Council may be awarded special scholarships as recognition for leadership, event organization, or community service .
Beyond formal grants, merit-based performance stipends and recognition are occasionally given to high-achievers and student organizers.
These awards highlight the university’s efforts to foster leadership and involvement.
5. Eligibility Criteria
Scholarships at Zarmed University are awarded based on:
Academic excellence (high school grades, entrance exam marks, performance during studies).
Financial need (socio-economic documentation).
Extracurricular and leadership involvement (especially for student council awards).
Interview or entrance test results, especially for programs awarding up to 100% tuition waiver.
It’s important to apply early (admissions open June–September) with a full documentation set—transcripts, exam scores, recommendation letters, and socio-economic credentials.
6. How to Apply
Step 1: Submit admission application with academic documents.
Step 2: Express interest in financial aid, grants, or scholarships.
Step 3: Sit for campus interviews or tests if applicable (especially for medicine).
Step 4: Await offers—scholarship amounts are generally communicated with admission letters.
Step 5: Accept offers and complete enrollment by the deadline (around September) .
7. Tips for Indian Students
Document your academic achievements thoroughly; NEET scores, high GPA, Olympiad medals, etc., help in securing merit-based aid.
Detail your financial background—low-income documents may qualify you for socio-economic discounts.
Engage in early: applying early gives access to limited slots and the best aid available.
Look beyond tuition: state and presidential scholarships provide room and living stipends—confirm with the international office.
8. Final Thoughts
MBBS at Zarmed University offers significant scholarship options for international students, especially those studying medicine:
Institutional scholarships up to 100% tuition
Generous fixed grants for academic merit or financial need
Government-funded scholarships covering full study and living costs
International program funding via global collaborations
Student leadership awards for campus engagement
Through a combination of internal support, government funding, and global tie-ups, Zarmed ensures that capable students are not held back by finances.
In summary, Indian applicants with strong academic backgrounds, leadership experience, or economic needs stand a strong chance of securing substantial scholarships at Zarmed University—often covering up to full tuition, and sometimes more. Interested applicants should begin preparations early and maintain comprehensive documentation to maximize their chances.
0 notes
Text
Apollo TV: A Modern Alternative to Traditional Television
Apollo TV is an IPTV-based streaming service that provides access to live television channels, movies, series, and sports content. It offers a digital solution for users seeking more apollo tv control, flexibility, and variety in their viewing experience without being tied to traditional cable or satellite TV. Known for its wide content selection and user-focused features, Apollo TV has become a favored option for those looking to cut the cord and move toward online entertainment.
What Is Apollo TV?
Apollo TV is a subscription-based service that delivers television programming over the internet. Unlike conventional broadcasting methods, IPTV services like Apollo TV use high-speed connections to stream content directly to compatible devices. This allows users to watch live channels, stream movies on demand, and access international content from the comfort of their home or on the go.
The service is built around convenience and content variety. It is designed for users who want the freedom to choose what they watch and when they watch it, without the limitations of preset TV schedules.
Content and Categories
Apollo TV offers an extensive library of content across multiple genres and languages. Some of the most common categories include:
Live TV channels from the United States, United Kingdom, Canada, and other international markets
Sports networks covering both local and global events
News channels offering 24/7 coverage
Entertainment channels for series, reality shows, and talk shows
A large collection of movies, ranging from classics to the latest releases
Dedicated sections for kids’ programming, documentaries, and lifestyle content
This wide variety ensures that users of all ages and preferences can find something that suits their interests.
Features and Functionality
Apollo TV includes a number of features aimed at improving the viewing experience:
High-definition and 4K video support for superior image quality
An electronic program guide (EPG) to help users see what’s currently airing and what’s coming up next
On-demand playback for movies and series
Multi-device support for users who want to watch on more than one screen
Easy navigation with categorized menus, search functionality, and favorites lists
Compatibility with IPTV apps such as IPTV Smarters and TiviMate for broader access
The service also incorporates buffering protection and stability enhancements to reduce interruptions during streaming.
Device Compatibility
One of the strengths of Apollo TV is its ability to work across a range of devices. This includes:
Android smartphones and tablets
Android TV and smart TVs
Amazon Fire TV devices
Computers using Android emulators
iOS devices through third-party IPTV players
Streaming boxes and sticks
The ability to use the service on multiple platforms makes it easy for users to enjoy their favorite content at home or while traveling.
Subscription and Access
To use Apollo TV, users must purchase a subscription. Plans are typically offered in monthly, quarterly, and annual formats, with discounts available for longer commitments. Some packages support multiple devices, which is ideal for families or shared households.
Upon subscribing, users receive login credentials that include a username, password, and server URL. These credentials are used to access the service through the Apollo TV App or other compatible IPTV applications.
Why Choose Apollo TV?
Apollo TV stands out for its content diversity, user-friendly setup, and high-quality streaming performance. It appeals to viewers who are tired of expensive cable bills and limited programming choices. With flexible subscription options and reliable streaming, Apollo TV is positioned as a valuable choice for modern digital entertainment.
Final Thoughts
Apollo TV represents a shift in how people access and enjoy television content. By offering a broad selection of channels, on-demand media, and premium features in one platform, it delivers an efficient and customizable viewing experience. Whether you’re a sports fan, a movie lover, or just someone looking for an affordable way to stream TV, Apollo TV provides a convenient solution tailored to today’s digital lifestyle.
0 notes
Text
Major Changes to SBI Credit Card Rewards (Effective April 2025)
If you’re an SBI Credit Card holder, there’s some important news that could impact how you earn and redeem your reward points. Starting April 2025, SBI Card has announced major changes to its rewards program across various popular cards. Whether you use your SBI Credit Card for online shopping, flight bookings, or day-to-day expenses, it’s crucial to understand how these changes might affect your benefits.
In this article, we’ll break down the revised reward structure, discontinued benefits, and what it means for both new and existing SBI credit card users. If you're considering getting an Instant SBI Credit Card, this guide will help you make an informed decision.
Why the Changes?
The credit card landscape is constantly evolving. With rising operational costs, regulatory changes, and increased customer acquisition, SBI Card has reviewed its reward offerings to remain sustainable and competitive. However, these changes come at a cost for some loyal customers, especially those who heavily relied on SBI cards for travel and online purchases.

SimplyCLICK SBI Card – Reduced Reward Points
The SimplyCLICK SBI Card, known for its accelerated rewards on online platforms, is seeing significant modifications. Until now, users earned 10X reward points on partner platforms such as Swiggy, Myntra, Cleartrip, and others.
Effective April 2025, reward points on Swiggy have been reduced to 5X. However, you can still earn 10X on:
Apollo 24/7
BookMyShow
Cleartrip
Dominos
Myntra
Netmeds
Yatra
This means food delivery lovers will see a dip in point accumulation, while travel and fashion enthusiasts can continue to enjoy existing rewards.
Air India SBI Platinum and Signature – Major Reductions
If you hold an Air India SBI Platinum or Signature Credit Card, the reward downgrade might come as a disappointment. Previously, users earned:
15 reward points per ₹100 spent on Air India (Platinum Card)
30 reward points per ₹100 spent on Air India (Signature Card)
From April 2025, these rates are slashed to just:
5 points per ₹100 for Platinum
10 points per ₹100 for Signature
The reduction significantly impacts frequent flyers who used these cards to accumulate Air India miles. It’s advisable to reconsider your travel card if you relied on SBI for mileage benefits.
Club Vistara SBI Cards – Discontinuation of Milestones
For Club Vistara SBI Credit Card holders, another significant update is the removal of milestone benefits. Earlier, customers enjoyed complimentary Vistara flight tickets on achieving annual spends. However, SBI Card has now discontinued the milestone ticket vouchers and some renewal benefits.
While the annual fee waiver based on spending continues, the loss of ticket rewards reduces the overall value of the card for frequent Vistara travelers.
Insurance Benefits Discontinued
Another key change is the removal of complimentary air accident insurance. Previously, many premium SBI Credit Cards came with a ₹50 lakh air accident cover. As of July 26, 2025, this benefit will be completely discontinued.
This may be particularly relevant for customers who opted for SBI cards due to bundled insurance features. If travel protection is a priority, consider looking into third-party coverage or alternative premium cards.
Impact on Instant SBI Credit Card Applicants
The Instant SBI Credit Card option, available through online application or via YONO SBI, has gained popularity due to its quick approval process and virtual card availability within minutes. However, new applicants should carefully evaluate the revised benefits.
If you're planning to apply for an Instant SBI Credit Card primarily for rewards and travel perks, these recent changes might influence your decision. For example:
Instant approvals still offer convenience.
But the value you derive from rewards has decreased on key categories like flights and food delivery.
Be sure to check the updated terms and conditions before proceeding.
Should You Switch or Stay?
For existing SBI Credit Card users, these changes may feel like a downgrade. However, whether you should continue using your card depends on your individual spending habits.
Stick with SBI Credit Card if:
You shop regularly on Myntra, Apollo, Yatra, etc.
You value seamless integration with SBI banking services.
You prefer instant approvals and a large merchant acceptance network.
Consider switching if:
You primarily used the card for Air India or Vistara travel rewards.
You relied on air insurance coverage as a benefit.
You expect high reward returns on food delivery and offline shopping.
Final Thoughts
The major changes to SBI Credit Card rewards effective April 2025 reflect a broader shift in how credit card issuers are restructuring loyalty programs. While some reductions in benefits may seem drastic, SBI still offers reliable services, strong brand trust, and quick approval processes through Instant SBI Credit Card options.
Before applying or renewing, make sure to compare benefits, analyze your spending behavior, and choose a card that aligns with your financial goals.
Stay informed, spend wisely, and keep maximizing your credit card benefits—because every point still counts!
0 notes
Text
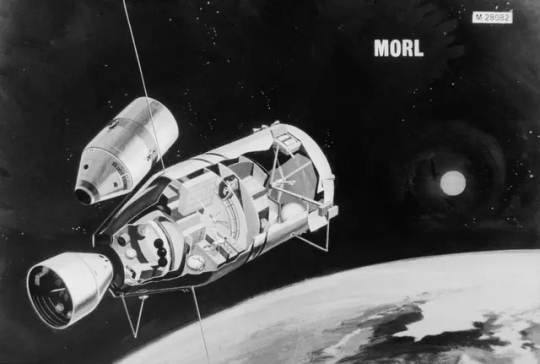
Cancelled Missions/Station: Manned Orbital Research Laboratory (MORL)

This was a study initiated in 1962 for space stations designs using the Gemini Spacecraft and later on the Apollo CSM. Boeing and Douglas received Phase I contracts in June 1964.


MORL/S-IVB Concept
"A 5 metric ton 'dry' space station, launched by Saturn IB, with Gemini or Apollo being used for crew rotation. The 6.5 meter diameter and 12.6 meter long station included a docking adapter, hangar section, airlock, and a dual-place centrifuge. Douglas was selected by NASA LaRC for further Phase 2 and 3 studies in 1963 to 1966. Although MORL was NASA's 'baseline station' during this period, it was dropped by the late 1960's in preference to the more capable station that would become Skylab.



Different docking concepts studied.
The Manned Orbital Research Laboratory was the brainchild of Carl M Houson and Allen C. Gilbert, two engineers at Douglas. In 1963 they proposed a Mini Space Station using existing hardware, to be launched by 1965. A Titan II or Atlas would be launched with a payload of control system, docking adapter and hangar module. The visiting crew would use the payload to transform the empty fuel tank of the last stage of the rocket into pressurized habitat (a so-called 'wet' space station). Provisions were available for 4 astronauts for a 100 day stay. Crew members would arrive two at a time aboard Gemini spacecraft. Equipment included a two-place centrifuge for the astronauts to readapt to gravity before their return to earth.

An early MORL concert. Artwork by Gordon Phillips.


In June 1964 Boeing and Douglas received Phase I contracts for further refinement of MORL station designs. The recommended concept was now for a 13.5 metric ton 'dry' space station, launched by Saturn IB, with Gemini or Apollo being used for crew rotation. The 6.5 meter diameter and 12.6 meter long station included a docking adapter, Hangar section, airlock, and a dual-place centrifuge.

"Medium-sized orbiting lab is this Manned Orbital Research Laboratory (MORL) developed for NASA's Langley Lab by Douglas Missiles & Spacecraft Division. The lab which weighs about 35,000 pounds, could maintain 3 to 6 men in orbit for a year.
Orbiting Stations: Stopovers to Space Travel by Irwin Stambler, G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1965."
Douglas was selected by NASA LaRC for further Phase 2 and 3 studies in 1963 to 1966. The major system elements of the baseline that emerged included:
A 660-cm-diameter laboratory launched by the Saturn IB into a 370-km orbit inclined at 28.72 degrees to the equator
A Saturn IB launched Apollo logistics vehicle, consisting of a modified Apollo command module, a service pack for rendezvous and re-entry propulsion, and a multi-mission module for cargo, experiments, laboratory facility modification, or a spacecraft excursion propulsion system.
Supporting ground systems.
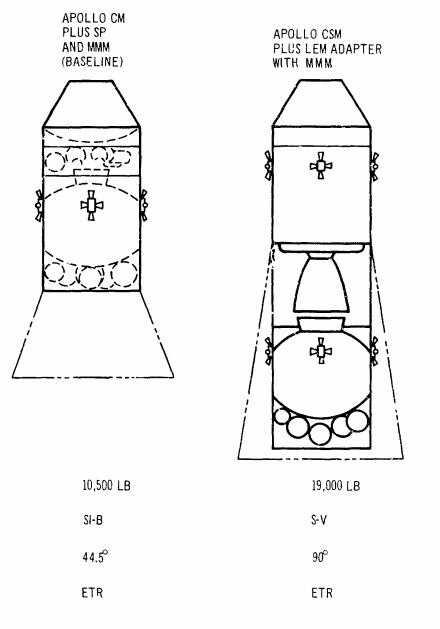

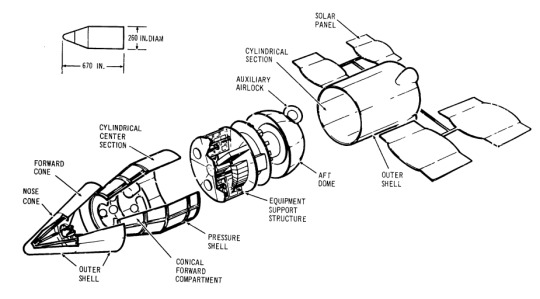
MORL Phase IIb examined the utilization of the MORL for space research in the 1970s. Subcontractors included:
Eclipse-Pioneer Division of Bendix, stabilization and control
Federal Systems Division of IBM, communications, data management, and ground support systems
Hamilton Standard Division of the United Aircraft Corporation, environmental control/life support
Stanford Research Institute, priority analysis of space- related objectives
Bissett-Berman, oceanography
Marine Advisors, oceanography
Aero Services, cartography and photogrammetry
Marquardt, orientation propulsion
TRW, main engine propulsion.
The original MORL program envisioned one or two Saturn IB and three Titan II launches. Crew would be 6 to 9 Astronauts. After each Gemini docked to the MORL at the nose of the adapter, the crew would shut down the Gemini systems, put the spacecraft into hibernation, and transfer by EVA to the MORL airlock. The Gemini would then be moved by a small manipulator to side of the station to clear docking adapter for arrival of the next crew."

"Docking was to have 3 ports, all Nose Dock config, with spacecraft modifications totaling +405 lbs over the baseline Gemini spacecraft (structure beef-up, dock provisions, added retro-rockets, batteries, a data link for rendezvous, temp. control equip. for long-term, unoccupied Gemini storage on-orbit and removal of R&D instruments)."
"Later concepts including docking a Saturn-IB launched space telescope to MORL. At 4 meter diameter and 15 meter long, this would be the same size as the later Hubble Space Telescope. The crew would have to make EVA's to recover the film from the camera.
In 1965 Robert Sohn, head of the Technical Requirements Staff, TRW Space Technology Laboratories, proposed a detailed plan for early manned flight to Mars using MORL. The enlarged MORL-derived mission module would house six to eight men and be hurled on a Mars flyby by a single Saturn MLV-V-1 launch. MORL-derived Mars mission modules cropped up in other Douglas Mars studies until superseded by the 10-m diameter Planetary Mission Module in 1969.

MORL/Space Telescope
Why was MORL never launched ?
NASA had a need for a Space Station and MORL was little, easy and cheap. But NASA had more ambitious plans, embodied in the Apollo Applications Orbital Workshop (later called Skylab)."
-information from astronautix.com: link
source, source, source
NARA: 6375661, S66-17592
Posted on Flickr by Numbers Station: link
#Manned Orbital Research Laboratory#MORL#Space Station#Gemini#Gemini Program#Project Gemini#Apollo CSM Block II#Apollo Program#Saturn IB#Saturn I#S-IV#S-IVB#Apollo Applications Program#Cancelled#Study#1962#June#1965#my post
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
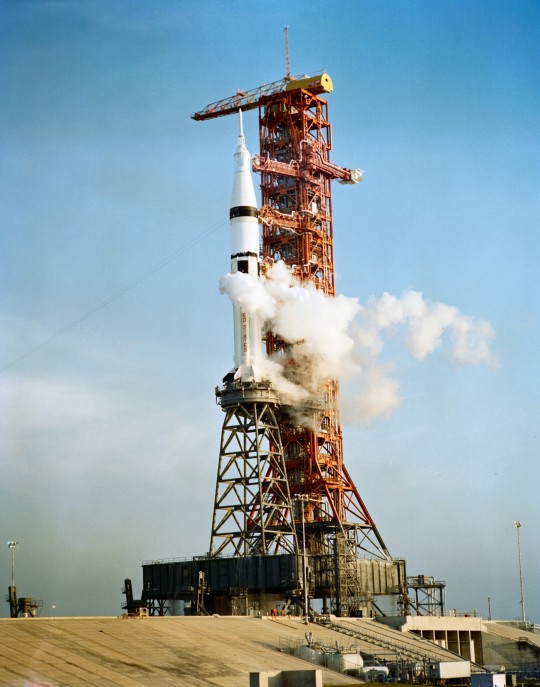

"A ground-level view of Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, showing the Skylab 3/Saturn IB (CSM-117/SA-207) space vehicle during prelaunch preparations. The launch vehicle is venting liquid oxygen during pre-final countdown cryogenic loading."
Date: July 20, 1973
NASA ID: S73-31697
#Skylab III#Skylab 3#SL-3#SLM-2#CSM-117#SA-207#Saturn IB#Rocket#NASA#Apollo Program#Apollo Applications Program#LC-39B#Kennedy Space Center#Florida#July#1973#my post
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Analytics Certification Course in Mysore | Chanakya Digital Academy

Description This Data Analytics Certification Course transforms you into a well-rounded data analytics professional. The course syllabus is designed to meet the latest and trending industry requirements, ensuring relevance and applicability. This program is created and developed by industry experts with years of experience in data analytics. Trainers will guide you with practical exercises and real-world examples to boost your confidence in the data analytics profession. The data analytics course offered by Chanakya Digital Academy in Mysore is handled by experienced trainers certified in industry-leading tools and technologies. The program aims to enable trainees to master concepts, from basic to advanced levels, through hands-on practical knowledge.
Contact Details No.904, First Floor, New Kantharaj Urs Rd, near Apollo Hospital, Kuvempu Nagara, Mysuru, Karnataka 570023
www.chanakayadigitalacademy.com [email protected] +91 95388 58589
0 notes
Text
Radiology Courses in Thrissur: Complete Guide

What is Radiology?
Radiology is a medical field that uses imaging techniques like X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds to diagnose and treat diseases. Think of it as the eyes of modern medicine—without radiology, it’s like flying a plane blindfolded.
Why Choose Radiology as a Career?
Are you fascinated by technology and want to contribute to patient care without going under the scalpel? Radiology could be your calling. It’s a perfect blend of innovation, diagnostics, and healthcare service.
Scope of Radiology in India
With the growth of hospitals and diagnostic centers, radiology has become a booming field in India. Whether it's government hospitals or private chains like Apollo or Aster, skilled radiologists are always in demand.
Overview of Radiology Courses
Types of Radiology Courses Available
Certificate Courses
These are short-term programs (3–6 months) ideal for quick specialization, such as X-ray or CT scan technician.
Diploma Courses
Usually 1–2 years long, they cover fundamental aspects of imaging and diagnostics. Popular among students after 10+2.
Undergraduate Courses
Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) in Radiology or Medical Imaging Technology spans 3 years and is more comprehensive.
Postgraduate Courses
For those with a medical degree, postgraduate diplomas (DMRD) or MD in Radiodiagnosis are advanced options.
Eligibility Criteria
Certificate/Diploma: 10+2 with Science stream.
B.Sc.: 10+2 with PCB/M subjects.
PG: MBBS degree with NEET-PG qualification.
Top Institutes Offering Radiology Courses in Thrissur
Government Medical College, Thrissur
One of Kerala’s top government colleges, known for its strong faculty and hospital-based training.
Jubilee Mission Medical College and Research Institute
Offers diploma and PG-level courses in radiology with cutting-edge imaging facilities.
Amala Institute of Medical Sciences
A well-established name offering comprehensive B.Sc. and MD programs in Radiodiagnosis.
Elite Mission Hospital & Institute
Popular for short-term technician courses and hands-on training.
Course Details
Duration and Structure
Courses vary from 3 months (certificate) to 3 years (UG) to 2–3 years (PG). Expect both theoretical and clinical modules.
Course Syllabus Highlights
Includes anatomy, imaging techniques, radiation physics, pathology, and advanced diagnostics.
Hands-On Training and Internships
Institutes in Thrissur emphasize internships at their affiliated hospitals, giving students real-time patient exposure.
Admission Process
How to Apply?
Applications are either online via the institute’s website or offline through direct visits.
Entrance Exams (if any)
For PG: NEET-PG is mandatory.
For UG/Diploma: Some institutes conduct their own aptitude tests.
Admission Tips for Students
Prepare a strong statement of purpose (SOP), highlight science scores, and gather recommendation letters if needed.
Fees and Financial Aid
Fee Structure
Certificate: ₹20,000–₹50,000
Diploma: ₹50,000–₹1.5 Lakh
B.Sc.: ₹1–3 Lakhs total
MD: ₹6–10 Lakhs (Private), subsidized in Govt. colleges
Scholarships and Financial Assistance Options
Many institutes offer merit-based scholarships. SC/ST students can avail government-sponsored grants.
Career Opportunities After Radiology Courses
Job Roles and Responsibilities
Radiologist
Radiology Technician
MRI/CT Scan Technologist
Ultrasound Specialist
Employment Areas
Hospitals, diagnostic centers, private clinics, research institutions, and mobile imaging services.
Expected Salary Range
Freshers can earn ₹2–4 LPA. Experienced radiologists earn ₹10–30 LPA, especially in urban areas.
Advantages of Studying in Thrissur
Thrissur’s Growing Healthcare Infrastructure
Home to multi-specialty hospitals and diagnostic labs, it's a regional medical hub.
Affordable Living and Education
Cost of living is moderate compared to metros, yet the quality of education is top-tier.
Cultural and Student-Friendly Environment
With festivals, heritage, and friendly locals, Thrissur offers a balanced lifestyle for students.
Online vs Offline Radiology Courses
Pros and Cons of Online Courses
Online courses offer flexibility but lack hands-on training, which is vital in radiology.
Why Offline Courses Are Still Relevant
Nothing beats real-life exposure to medical equipment and patient interaction, making offline courses preferable.
Skills Required for a Successful Career in Radiology
Technical Skills
Imaging software proficiency
Understanding of human anatomy
Equipment handling
Soft Skills
Attention to detail
Communication with patients and doctors
Ethical decision-making
Challenges in the Field of Radiology
Ethical and Legal Issues
Handling sensitive patient data and reporting errors can have serious consequences.
Workload and Stress Management
Long hours and critical decision-making can lead to burnout if not managed well.
Future Trends in Radiology
Use of AI and Machine Learning
AI is revolutionizing diagnosis speed and accuracy—radiologists must adapt or get left behind.
Remote Radiology and Telemedicine
Rural areas now get expert diagnostics remotely thanks to tele-radiology.
Testimonials from Past Students in Thrissur
Real-Life Experiences
“I joined Amala for B.Sc. in Radiology and got placed in a leading hospital before graduation!” — Arjun M.
Student Success Stories
“A certificate from Elite Mission helped me switch careers and land a job in just six months.” — Priya R.
Expert Tips for Aspiring Radiologists
How to Stay Updated
Follow journals, attend seminars, and take refresher courses.
Building a Strong Professional Network
Join professional associations and LinkedIn groups to connect with industry experts.
Conclusion
Radiology is more than just reading X-rays—it's about being at the forefront of medical science. Thrissur, with its blend of modern education and cultural richness, offers a stellar launchpad for aspiring radiology professionals. Whether you're looking for a short-term course or a full-fledged degree, you'll find something that suits your goals in this vibrant city.
FAQs
Q1. What is the best radiology course after 12th in Thrissur? A B.Sc. in Radiology or a Diploma in Radiological Techniques are great choices after 12th.
Q2. Are radiology courses in Thrissur affordable? Yes, especially compared to metro cities. Fees range from ₹20,000 to ₹3 Lakhs depending on the course level.
Q3. Do I need NEET for radiology courses? Only for postgraduate courses like MD in Radiodiagnosis. UG and diploma programs generally don’t require NEET.
Q4. Can I study radiology online? Some theory-based certificate courses are available online, but practical training is best done offline.
Q5. What is the salary of a radiologist in India? Starting salary ranges between ₹2–4 LPA and can go up to ₹30 LPA with experience and specialization.
0 notes
Text


Geologists discover hidden magmatism on the moon
Lunar igneous activities including intrusive and extrusive magmatism, and their products contain significant information about the lunar interior and its thermal state. Their distribution is asymmetrical on the nearside and farside, reflecting the global lunar dichotomy. In addition to previously returned lunar samples all from nearside (Apollo, Luna, and Chang’e-5), samples from the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin on the farside have long been thought to hold the key to rebalancing the asymmetrical understandings of the Moon and disclosing the lunar dichotomy conundrum.
Earlier this year, the Chang’e-6 mission of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, successfully launched on May 3, landed on the lunar surface on June 2, and returned to the Earth on June 25 carrying a total of 1935.3g of lunar soils. It is the world’s first lunar farside sample-return mission, which landed in the south of the Apollo basin within the SPA basin on the farside. These precious samples would open a window to solve the long-standing question of lunar dichotomy, even reshape human’s knowledge of our closest neighbour. However, compared with the well-known mare volcanism surrounding the Chang’e-6 landing site, the intrusive magmatic activities have a much more obscure presence and origin, impeding future sample analyses when they are available for application.
In a recent research paper published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Dr Yuqi QIAN, Professor Joseph MICHALSKI and Professor Guochun ZHAO from the Department of Earth Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) and their domestic and international collaborators have comprehensively studied the intrusive magmatism of the Chang’e-6 landing site and its surroundings based on remote sensing data. The study revealed their extensive distributions and obscure nature with significant implications for the petrogenesis of lunar plutonic rocks and the Chang’e-6 mission, which will facilitate scientists’ further study of lunar farside.
Key Findings The study has found that intrusive magmatism is widespread in the SPA basin. They occur in various forms including sills beneath floor-modified craters, linear and ring dikes shown by gravity data, and Mg-suite intrusions with characteristic spectral absorptions. These observations agree with the intermediate-thick crust of SPA where intrusion is favored. Landing in the SPA basin, Chang’e-6 likely collected plutonic rocks, excavated and transported by adjacent impact craters to the sampling site, that could be examined by the ongoing sample studies. They have discovered two heavily degraded floor-fractured craters (see Apollo X and Apollo Q craters in Figure 1), inspiring to identify more similar features on the Moon. All indicate that intrusive magmatism is abundant in the Chang’e-6 sampling region.
This study has traced potential plutonic materials in the Chang’e-6 samples and found that Mg-suite materials highly likely exist, primarily from the western peak ring of the Apollo basin delivered by Chaffee S crater. These Mg-rich materials contain crucial information on the origin of mysterious KREEP-poor Mg-suite rocks. Samples from both the intrusive and extrusive magmatism from the never sampled farside, especially the mysterious Mg-suite, will shed further light on solving the lunar dichotomy conundrum and a series of fundamental scientific questions relating to secondary crust building and early evolution of the Moon.
TOP IMAGE: Chang’e-6 landing site locates to the southern Apollo basin in the northeast of the South Pole-Aitken basin, lunar farside. Credit Y. Qian
LOWER IMAGE: Intrusive magmatism is extensive across the South Pole-Aitken basin, whose products highly likely collected by the Chang’e-6 mission. Credit Y. Qian
5 notes
·
View notes