#Boolean search string generator
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
because you mentioned research, do you have any advice or methods of doing efficient research? I enjoy research too but it always takes me such a long time to filter out the information I actually need that I often lose my momentum ;__;
I'm not sure if I'm the best resource for this; I'm so dogged that once I start, it's hard for me to stop. The more tangled or difficult a research question, the more engaging I find it. In addition to loving cats, part of why I have cats is because they are very routine-oriented, and they'll pull me out of my hyperfocus for meals and sleep if I become too caught in what I'm researching; otherwise I don't notice I'm hungry or exhausted. It's not uncommon for me to focus so intensely that I'll look up and suddenly realize I've been researching something for 8+ hours.
But, in general, while it depends on what you're researching, I recommend having an expansive toolkit of resources. Google is fine, but it's only one index of many. I also use other databases and indexes like JSTOR, ResearchGate, SSRN, and Google Scholar (which is helpful for navigating Proquest, too, since Proquest's search function is incompetent). I also use DuckDuckGo, which is infinitely better for privacy than Google and which doesn't filter your searches or tailor them based on your location and search history, so you receive more robust results and significantly fewer ads (this has a tradeoff, which is that sometimes the searches are less precise).
Sometimes, I use Perplexity, but I do not recommend using Perplexity unless you are willing to thoroughly review the sources linked in its results because, like any generative AI tool, it relies on statistical probability to synthesize a representation of the information. In other words, it's not a tool for precision, and you should never rely on generated summaries, but it can help pluck and isolate resources that search indexes aren't dredging for you.
I also rely on print resources, and I enjoy collecting physical books. For books, I use Amazon to search for titles, but also Bookshop.org, e-Bay, Thriftbooks, AbeBooks, Common Crow Books, Paperback Swap, Biblio, and university presses (my favorite being the University of Hawaii Press, especially its On Sale page, and the Harvard East Asian Monographs series from Harvard University Press). This is how I both find titles that may seem interesting (by searching keywords and seeing what comes up) and also how I shop around for affordable and used versions of the books I would like to purchase. (If you don't want to buy books, local and online libraries and the Internet Archive are great resources.)
Most relevantly, and I assume most people might already know this, but I can't emphasize its importance enough: use Boolean logic. If you are not using operators and modifiers in your search strings, you are going to have immense difficulty filtering any relevant information from indexes.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Boolean Search in Recruitment?
As recruiters and hiring managers, we know that the process of sourcing and identifying the right candidate can be time-consuming and challenging. With an ever-increasing number of applicants, it can be overwhelming to sift through hundreds or thousands of resumes and online profiles to find the best fit for your organization. That’s where Boolean search comes in – a powerful tool that can help you search for candidates with greater efficiency and precision.
What is Boolean Search?
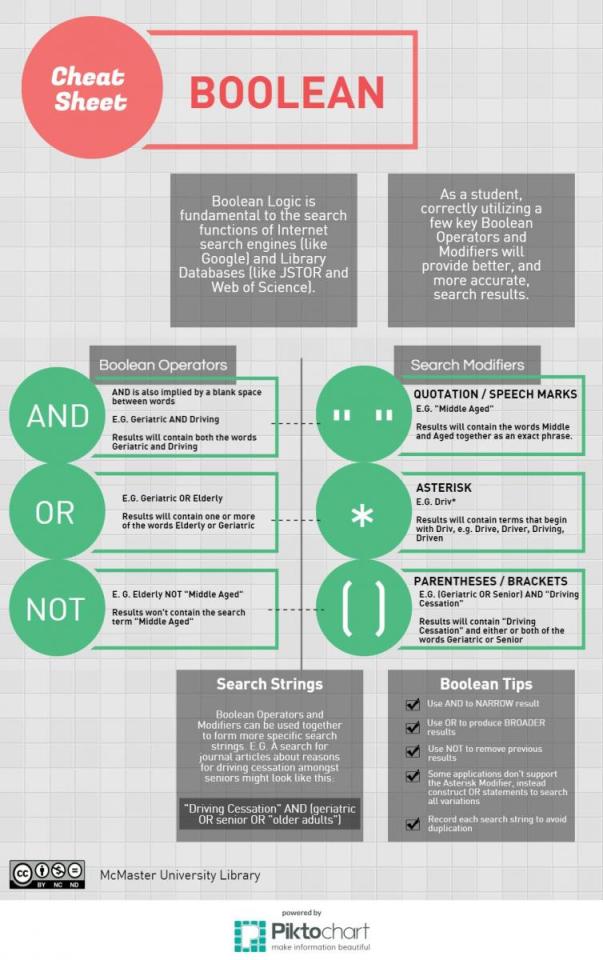
Boolean search is a technique used to narrow down and refine search results by using specific keywords and phrases. It is named after the mathematician George Boole, who developed the concept of Boolean algebra in the mid-19th century. The boolean search involves using logical operators such as “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT” to create complex search strings that return more relevant results.
With respect to recruitment, it means using a specific set of search techniques to find the right candidates for a particular job. Boolean search allows recruiters to search for candidates based on specific criteria. It uses the operators AND, OR, and NOT to combine search terms, and produce more targeted results and relevant candidates.
How does Boolean Search work in Recruitment?
In recruitment, Boolean search is commonly used to identify candidates with specific skills or experience. Let’s say you’re looking for a marketing manager with experience in both digital marketing and branding. You can use Boolean search in your ATS to find candidates who meet these criteria. You would enter the search terms “marketing manager” AND “digital marketing” AND “branding” into the search bar. The AND operator ensures that all three search terms are present in the results, narrowing down the pool of potential candidates.
If the recruiter finds that they’re getting too many irrelevant results, they can use the NOT operator to exclude certain terms. For example, they might add NOT “social media” to the search query to exclude candidates who specialize in social media marketing.
On the other hand, if the recruiter wants to broaden their search, they can use the OR operator to include multiple variations of a term. For instance, they might enter “marketing manager” AND (“digital marketing” OR “online marketing”) to include candidates who may have experience in different types of digital marketing.
By using Boolean search in recruitment, you can save time and effort by quickly identifying qualified candidates based on specific criteria, leading to more successful hiring outcomes.
Tips for using Boolean Search in Recruitment
Be specific
Use specific keywords and phrases that accurately describe the qualifications and experience you are looking for in a candidate. Avoid using generic terms that could return irrelevant results.
Instead of searching for “marketing jobs,” use specific keywords like “digital marketing specialist” or “content marketing manager.” This will help to narrow down the search results and provide more relevant candidates.
Experiment with different search strings
Try different combinations of keywords and Boolean operators to see which ones return the best results. Be flexible and willing to adjust your search parameters as needed.
Try different combinations of keywords and Boolean operators to see which ones return the best results. For example, you could use “developer” AND (“Java” OR “Python”) to find candidates with experience in either Java or Python programming languages.
Use quotation marks
Enclose phrases in quotation marks to search for an exact match. This will ensure that the search results only include the exact phrase you’re looking for.
For instance, if you are looking for candidates with experience in “customer relationship management,” using quotation marks will ensure that the search results only include that exact phrase.
Utilize advanced search features
Many online job boards and resume databases have advanced search features that allow you to filter search results by criteria such as location, education, and years of experience. Take advantage of these features to narrow down your search even further.
#BooleanRecruitment#RecruitmentTech#SearchStrategies#RecruitmentTools#TalentAcquisition#RecruitmentTips#HRTech#SearchSkills#RecruitingTools
0 notes
Note
Hi! Research librarian here! All good thoughts, but some more specific advice because I love teaching people about this stuff!
So first, Google Scholar is still an adequate resource if you don’t have access to other databases or are just trying to get a feel for what is out there. Where you go next is going to depend on the kind of library you have access to. If you have access to a public library only, take what I say next and apply it to google scholar or open source databases like the aforementioned JSTOR and other open source journals. However, if you have access to a college or university library, your day is made because they were made for questions like yours.
So, go to your library’s website and poke around to find out if they have a list of databases and the links to them. They should. While you’re there, see if your library has any libguides or research guides on indigenous studies. These will more than likely have a list of databases your library subscribes to and links to them. Not to dox myself, but this is the one for my library. The links won’t work for you but the journals listed can be found elsewhere (remember, InterLibrary Loan is a thing for ANY library, and includes articles. If you find an article looks interesting in a journal you don’t have paid access to, submit a request through YOUR library, public or research, and they will source the article from an institution that has it and send it to you, usually digitally if you ask).
Right, so you’ve picked your databases, but how are you going to search? Well, databases, even including google scholar, do not do great with just a long phrase or full question. You want to create a Boolean search string. For your specific question, it might look something like the below:
Diplomatic relationships OR diplomacy OR tribal relationships AND North American AND indigenous tribes OR indigenous people AND pre-colonial
The Ands and Ors are important here. They are telling your search engine that you want any of the OR search terms, but only in conjunction with all the AND search terms. You can even eliminate some things by including a AND NOT or NOT term, which in your case might be something like “NOT modern era, NOT colonial era” or some such. However the search string above is specific enough that you should get some good results in the right databases.
Every database search is set up differently, but most of them have an advanced option which is designed to give you a Boolean search with the Boolean terms built in usually in a little drop box. But if you type the whole string out in the general search box that often works as well because almost all databases are set up to recognize Boolean searches. This is even true of google, but I beg you not to search google because general google (as opposed to google scholar) has become hot garbage. Try Duck Duck Go, it’s my new preferred search engine, protects your privacy and gives better results. But you will get the best results in a database.
I will say, do NOT reach out to indigenous tribes Willy nilly. They generally don’t like that. However, there are many indigenous scholars and librarians around who would be happy to help you with your research. The tribal government itself is probably going to ignore you, but specific scholars and librarians will be there for you. Look up tribal colleges associated with the tribes you’re most interested in and try their librarians. They are often Native American themselves, and are deeply embedded with the tribe.
Finally, do a search for whatever university has the largest indigenous studies program in the states. It’s not my field so I don’t have any directions there, but it’s probably out west somewhere if I had to guess. Even prestigious schools or private institutions will have librarians. If they have a large indigenous studies program, they will have a librarian assigned to them who will be more than happy to help with your research as that is the main point of their job. And they will not care whether you’re associated with their institution or not, we help people from outside the institution all the time. You will want to tell them though because that will affect the advice they give you and specific links they can provide you with.
Anyway, hope you see this anon and good luck! Your topic sounds fascinating!
hi! i have a question about trying to find specific books. i know what i'm looking for, but when i try and search online every website just takes keywords and ignores what i actually wrote. i can't go to my library at the moment (health issues), so i was wondering if you had any advice on trying to find books about specific subjects online? the subject i'm looking for is diplomatic relationships between indigenous tribes in north america/the usa, pre-colonialism. sorry if this is the wrong place to ask this!
You might be able to get in contact with your library virtually and see if they can help you out, they might have a live chat you can access on their website, or if not they ought to have an email address (Though you might have to wait to talk to them until later this week since they might be closed for New Year's.). Even if you're not able to go in person, they might be able to point you in the right direction for digital resources.
With the usual caveat that I'm not at all an expert in this kind of stuff, to the best of my knowledge maybe checking a digital library like JSTOR or looking into more specific journals might be helpful if you haven't tried that yet.
Otherwise, maybe some of the fancy things you can do with search engines might be useful. I'm vaguley aware that Google is swiftly becoming....not very good, I'm not sure if the same can be said for Google Scholar or not, though it does have an advanced search option in the sidebar that could help with your keywords. I personally use DuckDuckGo for most of my daily needs, here's their article on their advanced search syntax in case that's at all useful.
Finally, I'd suggest seeing if you can get in contact with any representatives of the indigenous tribes you're researching. I am absolutely not able to give any authoritative advice on this range of topics, but I'm at least somewhat aware that the scholarship about indigenous people can be rife with all sorts of colonialist bullshit if you're not getting it from a good source. If its feasible for your project, I think it'd be worthwhile if you're able to defer to their scholarship and sources they recommend. If getting in direct contact is beyond the scope or timeframe of your project, at the very least you should be extremely mindful of the sources you do end up using.
As usual I'm positive someone out there better information than me so I welcome any replies or reblogs you guys have to share. Best of luck for your search ^^
242 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boolean search string generator

The sheer amount of information makes it hard to locate qualified candidates among the trillions or quadrillions of online profiles, communities and social networks. The Internet is the noisy and extremely complex. It is an effective way of sourcing and searching for very specific skills, traits and qualifications of candidates you want to find on the Internet. Boolean allows you to combine words and phrases using the words AND, OR, NOT (known as Boolean operators) to limit, broaden, or define your search. You’re all set! Now, use this utility with any number of rows in your list of items to create a Boolean expression made for you automagically.One of the most effective ways to source for talent online is using what is called Boolean search. This leaves you with the strong you want to paste into a search form: 'Orange' OR 'Apple' OR 'Banana' OR 'Grapefruit' This string looks for a specific string right before the end of the line (represented by $) OR '' RegEx is sort of like Black Magic, so you will probably need to use a helper site like Rubular. Our second formula, REGEXREPLACE, removes the last “OR ”” from the string. And there is one problem here: that we need to remove the trailing “OR ”” that resulted from the expression. Now that we have our formula, it creates the string: 'Orange' OR 'Apple' OR 'Banana' OR 'Grapefruit' OR ''įrom the rows of Orange, Apple, Banana, Grapefruit above. COUNTBLANK returns the number of blank rows in a range, so that our calculation of rows minus the number of blank rows leaves us with the number of rows containing values (4) or the total number of rows including the header (5).ROWS counts the number of rows in a range – the standard number in a Google Spreadsheet is 1000 – and returns an integer to feed back to the expression inside of TEXT.This results in a range from A2:A5 to feed back to JOIN TEXT converts a complex expression into a value – in this case a calculation of the number of rows in the column of this spreadsheet minus the number of blank rows in the column of this spreadsheet – so that INDIRECT will take result of this expression and substitute “5”, the last row above that has a value.INDIRECT tells the spreadsheet to wait until the range expression in the formula from A2 to the last unblank value in column A is completed and we know the number of the last row to select.JOIN combines an expression of values into a string connecting each item with the string ‘ OR ‘.There are five functions in this expression: The first one joins a range of values into a concatenated string (turns list of Orange and Apple into ‘Orange’ OR ‘Apple’ OR ”): This spreadsheet has two formulas that do the work for you. Whether you’d like to create a list of criteria to find your next job, search Twitter more effectively, or simply create a customized search for Google, this expression builder can help. Let’s take a look.Īs an example, I created a utility spreadsheet that takes a range of values, counts those values, and outputs a result string that delivers a boolean expression to paste into your favorite advanced search page. Never fear: Google Sheets to the rescue! This is a perfect example of a task for a Lazy Programmer™ to solve, as it’s much easier to have a spreadsheet count values and rearrange text for you than it is for you to do the work by hand. Yet when someone gives you a list of 10, 20, 50, or 100 items the idea of making a delimited list of “Item1” OR “Item2” OR “Item3” is more difficult than you’d like to be. When you need to filter your results, a powerful method is to make a list of companies, individuals, skills – whatever you are using to get more precise answers – and create a Boolean expression to get a better initial set of results from a search engine. You know Boolean expressions as “This OR That” – an inclusive search that increases results – or “This AND That” – an exclusive search that limits results. There’s usually an advanced search form of some sort that allows you to enter a boolean expression.

0 notes
Text
Social Talent Tutorial - Free Boolean tool
Social Talent Tutorial – Free Boolean tool
Hello all,lets go through the most google searched free Boolean search generator i.e Social Talent or called as Source Hub
Social talent is a free boolean search generator with inbuilt synonym algorithm in it.
Weblink : https://source.socialtalent.co/
This is an absolutely free tool to generate search string and to have in-depth sourcing and user friendly.
How to create account in Social Talent…
View On WordPress
#Boolean generator#boolean search#boolean tool#free boolean generator#free search tool#free string generator#recruiter#recruitment#socialtalent#usirecruit
1 note
·
View note
Text
High Secret LinkedIn Tool To Get High-Quality Clients

LinkedIn has a lot of growth hacking methods one can use to get the most this popular social media platform for professionals. The one that we are going to discuss in this article is the most mystical of the growth hacking methods available and is mostly underrated in contrast to the result it generates. Several international marketing agencies and their business development professionals use this technique daily.

It’s called the LinkedIn Boolean Operator Search Technique. Like I mentioned earlier, this is an underrated tool, and doesn't have in-depth blogs or videos discussing this method.
So, when I found that so many professionals are using this method, I decided to test the results generated by this method. Only after trying this method several times with success, I have decided to write this article and share it with you. You can also benefit from this tool and implement this method in your own business growth and create profitable inquiries. So let us see how this tool can be used to its maximum potential with an example to make things clearer for you to implement. Let’s hunt some live potential clients using this methodology.
Search Strings or Search Phrases
So, let’s go to our LinkedIn home page and we will start using this rarest of the growth hacks. Before we start, we need to have the list of search strings or phrases or keywords, business professionals use, to help us quickly apply the method. Let us have something like the below search phrases relevant to your niche that you are operating. I am using search phrase relevant to my niche such as:
require Facebook advertiser require FB advertiser require Facebook ads, expert require FB ads, expert require a freelance content writer need content writers hiring freelance writers hiring freelance web designers
These phrases are the ones that business owners and decision-makers use in their posts. these are the keywords agencies use in their job posts or project requirement posts before they hire an agency or before they hire a freelancer. So, first of all, you need to clearly understand the customer’s psychology and user search psychology before we can begin implementing the LinkedIn Boolean Operator Search Technique (LBOST).
The Double Quotes Operator
So, on the LinkedIn home page, you have the search bar. all I have to do is copy one of the search strings that we have listed and paste it into the search bar. The moment I paste the string I will be using the operator called the “doubled quote operator. in this way there are many operators that we can use in LBOST a few examples would be:
“NOR” operator
“NOT” operators
“OR” operator
So, if use the double quote operator in my LinkedIn search bar.
Using the Search String with Double Quotes Operator
Let's say we decide to search for “require freelance content writer” then LinkedIn will search for me the exact keyword phrases in its posts database and pull only those posts that match your search query. To make sure that you are getting the latest posts. You can use this for multiple services where you know that hiring is possible and change the string accordingly.
You need to understand that LinkedIn is such a platform where serious professionals are connected and are highly active, recruiters are highly active, hiring managers and sales managers are highly active and require services genuinely. And, that can only mean one thing. Get more clients!
That is your chances of securing a lead are far more successful than any other social media platform on this earth. It is common knowledge that you can get highly professional people on LinkedIn and hence these decision-makers use LinkedIn to their advantage. This is also the reason why you can secure elite clients from all over the world.
Getting The Results
The moment I get the results the next thing that I do is click on Posts and date posted and check for the relevance and click on All Filters and select Past 24 hours or Past week, select Top Match to get the best results. Click on show results.

You will find that not many comments are there for these posts. This means you can be the one who can be the first to comment and secure a meeting with these clients. Had this post been on Facebook and Google you would have got hundreds of comments.
Just imagine the competition between hundreds of applications would be a next to impossible feat both for you and a hiring nightmare for the client. So, all that you need to do is send a message to the person, start connecting with him, share your portfolio, share your offer and seal the deal.
Check out for such posts where people have not yet engaged and be the first one to engage with your potential clients. Who knows you might end up getting most of the offers?
So, as I mentioned earlier create your industry-related search strings and use the double quote operator for your search. Figure out the perfect client hiring post that matches your skill set. Engage with the client with an inspirational message, send your portfolio, and check if the position is still open. Go on a call, share your offer and crack the deal. It's as simple as that.
Have The Right Mindset
So, people this method that we discussed today in this article is an outreach method. You need to have the business and sales acumen to crack the deals with your clients. If you are a freelancer and want to scale your business, or you are an unstable freelancer and want to stabilize your career as a freelancer.
You need to understand that a business functions on a few fundamental criteria like marketing, sales, operations, customer satisfaction, and most importantly, an entrepreneurial mindset.
As mentioned in the title LinkedIn can be used to get high-quality clients, their queries, and requirements. All you need is to figure out the client's psyche and create search strings that they are most likely to use to get the best results.
Hey! I hope you liked this article and will use the above method in your client searching endeavors. Do let me know your experiences in the comments section. If you want to read such quality articles, follow me on LinkedIn. I am super active there, churning out rare nuggets like this, that can help you grow your business.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I will do b2b lead generation, web research and data entry
If you are looking for a virtual assistant to generate email list using LinkedIn sales navigator, web research or data entry I am the right person for you.
Gig Link: https://www.fiverr.com/share/B85Vlz
The resources I use frequently:
Services: LinkedIn sales navigator, Uplead, Crunchbase, XING, Google search engine.
Reason: To source and sort out targeted leads.
Services: Snovio, Nymeria, Contactout, Kendo, Clearbit, Rocketreach, Findorg and some other unique techniques.
Reason: To find email addresses.
Services: Emaillistverify, Mailtester.
Reason: Verify collected email addresses validity.
Areas where I am strong best:
B2B lead generation to find email addresses(personal/business).
LinkedIn research and management.
Web research.
Boolean Search String.
Database cleaning.
Email Marketing.
CRM Entry.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Font-Like SVG Icon System for Vue
Managing a custom collection of icons in a Vue app can be challenging at times. An icon font is easy to use, but for customization, you have to rely on third-party font generators, and merge conflicts can be painful to resolve since fonts are binary files.
Using SVG files instead can eliminate those pain points, but how can we ensure they’re just as easy to use while also making it easy to add or remove icons?
Here is what my ideal icon system looks like:
To add icons, you just drop them into a designated icons folder. If you no longer need an icon, you simply delete it.
To use the rocket.svg icon in a template, the syntax is as simple as <svg-icon icon="rocket" />.
The icons can be scaled and colored using the CSS font-size and color properties (just like an icon font).
If multiple instances of the same icon appear on the page, the SVG code is not duplicated each time.
No webpack config editing is required.
This is what we will build by writing two small, single-file components. There are a few specific requirements for this implementation, though I’m sure many of you wizards out there could rework this system for other frameworks and build tools:
webpack: If you used the Vue CLI to scaffold your app, then you’re already using webpack.
svg-inline-loader: This allows us to load all of our SVG code and clean up portions we do not want. Go ahead and run npm install svg-inline-loader --save-dev from the terminal to get started.
The SVG sprite component
To meet our requirement of not repeating SVG code for each instance of an icon on the page, we need to build an SVG “sprite.” If you haven’t heard of an SVG sprite before, think of it as a hidden SVG that houses other SVGs. Anywhere we need to display an icon, we can copy it out of the sprite by referencing the id of the icon inside a <use> tag like this:
<svg><use xlink:href="#rocket" /></svg>
That little bit of code is essentially how our <SvgIcon> component will work, but let’s go ahead create the <SvgSprite> component first. Here is the entire SvgSprite.vue file; some of it may seem daunting at first, but I will break it all down.
<!-- SvgSprite.vue --> <template> <svg width="0" height="0" style="display: none;" v-html="$options.svgSprite" /> </template> <script> const svgContext = require.context( '!svg-inline-loader?' + 'removeTags=true' + // remove title tags, etc. '&removeSVGTagAttrs=true' + // enable removing attributes '&removingTagAttrs=fill' + // remove fill attributes '!@/assets/icons', // search this directory true, // search subdirectories /\w+\.svg$/i // only include SVG files ) const symbols = svgContext.keys().map(path => { // get SVG file content const content = svgContext(path) // extract icon id from filename const id = path.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1') // replace svg tags with symbol tags and id attribute return content.replace('<svg', `<symbol id="${id}"`).replace('svg>', 'symbol>') }) export default { name: 'SvgSprite', svgSprite: symbols.join('\n'), // concatenate all symbols into $options.svgSprite } </script>
In the template, our lone <svg> element has its content bound to $options.svgSprite. In case you’re unfamiliar with $options it contains properties that are directly attached to our Vue component. We could have attached svgSprite to our component’s data, but we don’t really need Vue to set up reactivity for this since our SVG loader is only going to run when our app builds.
In our script, we use require.context to retrieve all of our SVG files and clean them up while we’re at it. We invoke svg-inline-loader and pass it several parameters using syntax that is very similar to query string parameters. I’ve broken these up into multiple lines to make them easier to understand.
const svgContext = require.context( '!svg-inline-loader?' + 'removeTags=true' + // remove title tags, etc. '&removeSVGTagAttrs=true' + // enable removing attributes '&removingTagAttrs=fill' + // remove fill attributes '!@/assets/icons', // search this directory true, // search subdirectories /\w+\.svg$/i // only include SVG files )
What we’re basically doing here is cleaning up the SVG files that live in a specific directory (/assets/icons) so that they’re in good shape to use anywhere we need them.
The removeTags parameter strips out tags that we do not need for our icons, such as title and style. We especially want to remove title tags since those can cause unwanted tooltips. If you would like to preserve any hard-coded styling in your icons, then add removingTags=title as an additional parameter so that only title tags are removed.
We also tell our loader to remove fill attributes, so that we can set our own fill colors with CSS later. It’s possible you will want to retain your fill colors. If that’s the case, then simply remove the removeSVGTagAttrs and removingTagAttrs parameters.
The last loader parameter is the path to our SVG icon folder. We then provide require.context with two more parameters so that it searches subdirectories and only loads SVG files.
In order to nest all of our SVG elements inside our SVG sprite, we have to convert them from <svg> elements into SVG <symbol> elements. This is as simple as changing the tag and giving each one a unique id, which we extract from the filename.
const symbols = svgContext.keys().map(path => { // extract icon id from filename const id = path.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1') // get SVG file content const content = svgContext(path) // replace svg tags with symbol tags and id attribute return content.replace('<svg', `<symbol id="${id}"`).replace('svg>', 'symbol>') })
What do we do with this <SvgSprite> component? We place it on our page before any icons that depend on it. I recommend adding it to the top of the App.vue file.
<!-- App.vue --> <template> <div id="app"> <svg-sprite /> <!-- ... -->
The icon component
Now let’s build the SvgIcon.vue component.
<!-- SvgIcon.vue --> <template> <svg class="icon" :class="{ 'icon-spin': spin }"> <use :xlink:href="`#${icon}`" /> </svg> </template> <script> export default { name: 'SvgIcon', props: { icon: { type: String, required: true, }, spin: { type: Boolean, default: false, }, }, } </script> <style> svg.icon { fill: currentColor; height: 1em; margin-bottom: 0.125em; vertical-align: middle; width: 1em; } svg.icon-spin { animation: icon-spin 2s infinite linear; } @keyframes icon-spin { from { transform: rotate(0deg); } to { transform: rotate(359deg); } } </style>
This component is much simpler. As previously mentioned, we leverage the <use> tag to reference an id inside our sprite. That id comes from our component’s icon prop.
I’ve added a spin prop in there that toggles an .icon-spin class as an optional bit of animation, should we ever need. This could, for example, be useful for a loading spinner icon.
<svg-icon v-if="isLoading" icon="spinner" spin />
Depending on your needs, you may want to add additional props, such as rotate or flip. You could simply add the classes directly to the component without using props if you’d like.
Most of our component’s content is CSS. Other than the spinning animation, most of this is used to make our SVG icon act more like an icon font¹. To align the icons to the text baseline, I’ve found that applying vertical-align: middle, along with a bottom margin of 0.125em, works for most cases. We also set the fill attribute value to currentColor, which allows us to color the icon just like text.
<p style="font-size: 2em; color: red;"> <svg-icon icon="exclamation-circle" /><!-- This icon will be 2em and red. --> Error! </p>
That’s it! If you want to use the icon component anywhere in your app without having to import it into every component that needs it, be sure to register the component in your main.js file:
// main.js import Vue from 'vue' import SvgIcon from '@/components/SvgIcon.vue' Vue.component('svg-icon', SvgIcon) // ...
Final thoughts
Here are a few ideas for improvements, which I intentionally left out to keep this solution approachable:
Scale icons that have non-square dimensions to maintain their proportions
Inject the SVG sprite into the page without needing an additional component.
Make it work with vite, which is a new, fast (and webpack-free) build tool from Vue creator Evan You.
Leverage the Vue 3 Composition API.
If you want to quickly take these components for a spin, I’ve created a demo app based on the default vue-cli template. I hope this helps you develop an implementation that fits your app’s needs!
¹ If you’re wondering why we’re using SVG when we want it to behave like an icon font, then check out the classic post that pits the two against one another.
The post A Font-Like SVG Icon System for Vue appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
A Font-Like SVG Icon System for Vue published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
XML, JSON and AJAX

What is XML?
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that is widely used for data storage and transport between systems. It provides a standardized format for representing data in an easy-to-read and understand hierarchical structure. XML documents are made up of elements, which are the language's basic building blocks, and attributes, which provide additional information about those elements. The versatility of XML is one of its primary advantages. It has a wide range of applications, including web services, database management, and document publishing. XML is also extensible, which means it can be tailored and expanded to meet the specific requirements of a given application or system.
One disadvantage of XML is that it can be verbose and complex, making it more difficult to read and write than other data formats. Furthermore, XML is frequently chastised for being slower and more resource-intensive than other data formats such as JSON.
Overall, XML is still widely used in many applications and systems, but it is frequently combined with other technologies, such as JSON and AJAX, to provide a more flexible and efficient data exchange solution.

What is JSON?
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data interchange format that is simple to read and write for humans while also being simple for machines to parse and generate. As an alternative to XML, it is a text-based format used to transmit data between a server and a web application. JSON is based on a subset of JavaScript, but it can be used with any programming language.
JSON is a simple, flexible, and user-friendly data representation and exchange format. It is commonly used to send and receive data between the client and server in web applications and RESTful APIs. JSON supports a wide range of data types such as strings, numbers, booleans, null, objects, and arrays and is simple to parse and generate in most programming languages.
Because of its simplicity and ease of use, JSON has grown in popularity as an alternative to XML. It is a small and efficient format that works well in web applications and APIs. JSON is also human-readable and simple to edit, making it an excellent choice for configuration files and other settings data.

What is AJAX?
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) is a web development technique used to create fast and dynamic web pages. It allows a web page's content to be updated without having to reload the entire page. AJAX creates asynchronous web applications by combining technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and XML/JSON.
AJAX allows a web application to request data from a server and receive a response without reloading the entire page. This improves the responsiveness and speed of web applications, resulting in a better user experience. AJAX requests can be initiated by either the user or the web application.
AJAX sends requests to the server and receives responses using the XMLHttpRequest object. The response can be in a variety of formats, including XML, JSON, or plain text. After receiving the response, the web application can use JavaScript to dynamically update the page content.
AJAX can be used to implement auto-complete search fields, real-time chat applications, and infinite scrolling pages, among other things.
0 notes
Text
Boolean search generator

BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR HOW TO
BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR ANDROID
BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR SOFTWARE
For example, account* will provide you with results both for accounting and accountant. You could use an asterisk (*) to get more results for the term you’re looking for. If you only look for ‘Web developer’ you’ll probably miss a lot of good profiles that use a different title, like ‘Software developer’ or ‘Web programmer.’ You could combine AND and OR commands to search multiple terms.
BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR SOFTWARE
Let’s say you want to hire a Software developer. When searching, you need to think from your ideal candidate’s point of view. LinkedIn is useful to search for all kinds of professionals, but for more targeted searches you should crawl niche websites instead. The key here is to look in the right place. You can search through a specific site for candidates with your desired skill set or any additional details that are a top priority for you. ‘site:’Ī site: search is also known as an x-ray search. Here’s a short guide to help you with common searches. Crafting effective commands can be a little tricky, at first, if you’re not familiar with Boolean logic. Using Google Boolean search strings for recruiters will improve your search results and eventually get you closer to your potential candidates. Search for an exact phrase (Consider keywords in quotation marks as a whole word) Group multiple search strings and set priorities *Google doesn’t recognize the operator NOT, so use the minus symbol, instead. Results include either keyword or all of themĮxcludes a keyword from your search (When using the minus symbol don’t leave a space before the unwanted term) Results include all keywords linked with AND Start sourcing Boolean search operators list Boolean operator You’re always top of mind, whether they’re actively looking or not. Workable helps you build and promote your brand where your next candidates are.
BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR HOW TO
Related: How to source passive candidates You should type “customer service” to get more relevant results when sourcing passive candidates. For example, leaving a blank space between ‘customer’ and ‘service’ will provide pages that contain both of the words ‘customer’ and ‘service,’ but not necessarily together. If you want Google to consider the phrase you’re searching for as a complete phrase, you should put it in quotation marks. (A OR B) AND C | (A∪B) ∩ C Quotation marks “ “ But, in a ‘designer OR (developer AND Java)’ search, Java knowledge is important only for the developers you’re looking for – not the designers. For example, ‘(developer OR designer) AND Java’ indicates that Java knowledge is a must-have both for developers and designers. This will come in handy, as most candidate searches are complex and combine different keywords. You can use brackets to group multiple search strings and set your priorities. ‘NOT recruiter’ or ‘-recruiter.’) A NOT B | A – B Brackets () Instead of NOT, you could also use the minus symbol followed by your unwanted term without leaving a space (e.g. The NOT operator excludes unwanted terms from your Google sourcing search. OR is particularly useful for synonyms, like ‘bank OR finance OR financial.’ A OR B | A ∪ B NOT People might use different words to say the same thing. The OR operator, on the other hand, allows us to expand our Boolean search results. This will produce results that include both keywords.
BOOLEAN SEARCH GENERATOR ANDROID
For example, a Boolean search string for recruiting Android developers should include ‘developer AND android’. When you want to include two (or more) criteria in your search, the operator AND narrows down your search. Here are the basic operators for Boolean search strings for recruiters: AND The definition of Boolean search is that it’s a type of search that allows users to combine keywords with operators such as AND, NOT and OR to produce more relevant results. How recruiters can use boolean commandsīased on George Boole’s mathematical theory in which all variables are either ‘true’ or ‘false’, Boolean search on Google is one of the best sourcing tools for recruiters.

0 notes
Text
Rational license key server 8.1.6 download

#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD HOW TO#
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 10#
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD SOFTWARE#
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD LICENSE#
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 8#
KV store is enabled by default on Splunk Enterprise 6.2+.Īpps that use the KV store typically have nf defined in $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps//default. Look for error messages in splunkd.log and on the console that executes splunk start. If you enable FIPS but do not provide the required settings ( caCertFile, sslKeysPath, and sslKeysPassword), KV store does not run. If Splunk FIPS is not enabled, those settings will be ignored. To use FIPS with KV store, see the "KV store configuration" section in. For information about other ports that Splunk Enterprise uses, see " System requirements and other deployment considerations for search head clusters" in the Distributed Search Manual.įor information about other configurations that you can change in KV store, see the "KV store configuration" section in. You can change the port number in nf's stanza. See the Splunk Enterprise system requirements. KV store is also not available on universal forwarders. It is not available on 32-bit Splunk Enterprise builds. KV store is available and supported on all Splunk Enterprise 64-bit builds. The KV store keeps the reads local, however. In a search head cluster, if any node receives a write, the KV store delegates the write to the KV store captain. The KV store files reside on search heads. Accelerations store a small portion of the collection's data set in an easy-to-traverse form. Accelerations improve search performance by making searches that contain accelerated fields return faster._user is a reserved field that contains the user ID for each record.If you don't explicitly specify the _key value, the app auto-generates one. _key is a reserved field that contains the unique ID for each record.Although it is not required, you can enforce data types (number, boolean, time, and string) for field values. Fields contain the values of your data as a JSON file. Fields correspond to key names, similar to the columns in a database table.Records contain each entry of your data, similar to a row in a database table.Collections exist within the context of a given app. Collections are the containers for your data, similar to a database table.The KV store stores your data as key-value pairs in collections. Storing checkpoint data for modular inputs.įor information on using the KV store, see app key value store documentation for Splunk app developers.Caching results from search queries by Splunk or an external data store.Managing a UI session by storing the user or application state as the user interacts with the app.Keeping a list of environment assets provided by users.Tracking workflow in an incident-review system that moves an issue from one user to another.Here are some ways that Splunk apps might use the KV Store: In old versions of Office (Office 2000 and below), the 'Product Key' value is not available.The app key value store (or KV store) provides a way to save and retrieve data within your Splunk apps, thereby letting you manage and maintain the state of the application.NET is written in the Registry as Office XP product. From unknown reason, the product key of Visual Stuido.This problem is mostly reported with Dell computers. If you bought your computer with installed operating system, you may find the Windows product key appeared in ProduKey utility is different from the product key on your Windows CD.
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD LICENSE#
For some types of license keys under Windows, the product key is not stored in the Registry, and thus 'Product key was not found' message will be displayed.
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD HOW TO#
How to Report Malware or False Positives to Multiple Antivirus Vendors.
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD SOFTWARE#
If your Antivirus software shows a false alert, you can use the following article that explains how to send a report about a false positive issue to your Antivirus company:.
Click here to read more about false alerts in Antivirus programs
When running produkey.exe, Some Antivirus programs displays an alert and/or block you from running it.
This option also works on a remote machine, as long as you have permission to access WMI on the remote machine.
If you turn on this option, ProduKey will extract the last 5 characters of the product key from SoftwareLicensingProduct class, using WMI.
Added new option: Extract Partial Key With WMI.
Updated to work properly in high DPI mode.
Some of the Adobe and Autodesk products.
Microsoft Office 2000 (Only ProductID is displayed).
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 10#
Microsoft Windows 10 (Doesn't work with all types of licenses).
#RATIONAL LICENSE KEY SERVER 8.1.6 DOWNLOAD WINDOWS 8#
Microsoft Windows 8 (Doesn't work with Microsoft Volume Licensing).
Microsoft Windows 7 (Doesn't work with Microsoft Volume Licensing).
This utility can be useful if you lost the product key of your Windows/Office, and you want to reinstall it on your computer. You can view this information for your current running operating system, or for another operating system/computer - by using command-line options.

0 notes
Text
[PHP]
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; About php.ini ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; PHP's initialization file, generally called php.ini, is responsible for ; configuring many of the aspects of PHP's behavior.
; PHP attempts to find and load this configuration from a number of locations. ; The following is a summary of its search order: ; 1. SAPI module specific location. ; 2. The PHPRC environment variable. (As of PHP 5.2.0) ; 3. A number of predefined registry keys on Windows (As of PHP 5.2.0) ; 4. Current working directory (except CLI) ; 5. The web server's directory (for SAPI modules), or directory of PHP ; (otherwise in Windows) ; 6. The directory from the --with-config-file-path compile time option, or the ; Windows directory (usually C:\windows) ; See the PHP docs for more specific information. ; http://php.net/configuration.file
; The syntax of the file is extremely simple. Whitespace and lines ; beginning with a semicolon are silently ignored (as you probably guessed). ; Section headers (e.g. [Foo]) are also silently ignored, even though ; they might mean something in the future.
; Directives following the section heading [PATH=/www/mysite] only ; apply to PHP files in the /www/mysite directory. Directives ; following the section heading [HOST=www.example.com] only apply to ; PHP files served from www.example.com. Directives set in these ; special sections cannot be overridden by user-defined INI files or ; at runtime. Currently, [PATH=] and [HOST=] sections only work under ; CGI/FastCGI. ; http://php.net/ini.sections
; Directives are specified using the following syntax: ; directive = value ; Directive names are *case sensitive* - foo=bar is different from FOO=bar. ; Directives are variables used to configure PHP or PHP extensions. ; There is no name validation. If PHP can't find an expected ; directive because it is not set or is mistyped, a default value will be used.
; The value can be a string, a number, a PHP constant (e.g. E_ALL or M_PI), one ; of the INI constants (On, Off, True, False, Yes, No and None) or an expression ; (e.g. E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE), a quoted string ("bar"), or a reference to a ; previously set variable or directive (e.g. ${foo})
; Expressions in the INI file are limited to bitwise operators and parentheses: ; | bitwise OR ; ^ bitwise XOR ; & bitwise AND ; ~ bitwise NOT ; ! boolean NOT
; Boolean flags can be turned on using the values 1, On, True or Yes. ; They can be turned off using the values 0, Off, False or No.
; An empty string can be denoted by simply not writing anything after the equal ; sign, or by using the None keyword:
; foo = ; sets foo to an empty string ; foo = None ; sets foo to an empty string ; foo = "None" ; sets foo to the string 'None'
; If you use constants in your value, and these constants belong to a ; dynamically loaded extension (either a PHP extension or a Zend extension), ; you may only use these constants *after* the line that loads the extension.
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; About this file ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; PHP comes packaged with two INI files. One that is recommended to be used ; in production environments and one that is recommended to be used in ; development environments.
; php.ini-production contains settings which hold security, performance and ; best practices at its core. But please be aware, these settings may break ; compatibility with older or less security conscience applications. We ; recommending using the production ini in production and testing environments.
; php.ini-development is very similar to its production variant, except it is ; much more verbose when it comes to errors. We recommend using the ; development version only in development environments, as errors shown to ; application users can inadvertently leak otherwise secure information.
; This is the php.ini-development INI file.
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Quick Reference ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; The following are all the settings which are different in either the production ; or development versions of the INIs with respect to PHP's default behavior. ; Please see the actual settings later in the document for more details as to why ; we recommend these changes in PHP's behavior.
; display_errors ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off
; display_startup_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off
; error_reporting ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED ; Development Value: E_ALL ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; log_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On
; max_input_time ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited) ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds)
; output_buffering ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: 4096 ; Production Value: 4096
; register_argc_argv ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off
; request_order ; Default Value: None ; Development Value: "GP" ; Production Value: "GP"
; session.gc_divisor ; Default Value: 100 ; Development Value: 1000 ; Production Value: 1000
; session.sid_bits_per_character ; Default Value: 4 ; Development Value: 5 ; Production Value: 5
; short_open_tag ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off
; variables_order ; Default Value: "EGPCS" ; Development Value: "GPCS" ; Production Value: "GPCS"
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; php.ini Options ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Name for user-defined php.ini (.htaccess) files. Default is ".user.ini" ;user_ini.filename = ".user.ini"
; To disable this feature set this option to an empty value ;user_ini.filename =
; TTL for user-defined php.ini files (time-to-live) in seconds. Default is 300 seconds (5 minutes) ;user_ini.cache_ttl = 300
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Language Options ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Enable the PHP scripting language engine under Apache. ; http://php.net/engine engine=On
; This directive determines whether or not PHP will recognize code between ; <? and ?> tags as PHP source which should be processed as such. It is ; generally recommended that <?php and ?> should be used and that this feature ; should be disabled, as enabling it may result in issues when generating XML ; documents, however this remains supported for backward compatibility reasons. ; Note that this directive does not control the <?= shorthand tag, which can be ; used regardless of this directive. ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/short-open-tag short_open_tag=Off
; The number of significant digits displayed in floating point numbers. ; http://php.net/precision precision=14
; Output buffering is a mechanism for controlling how much output data ; (excluding headers and cookies) PHP should keep internally before pushing that ; data to the client. If your application's output exceeds this setting, PHP ; will send that data in chunks of roughly the size you specify. ; Turning on this setting and managing its maximum buffer size can yield some ; interesting side-effects depending on your application and web server. ; You may be able to send headers and cookies after you've already sent output ; through print or echo. You also may see performance benefits if your server is ; emitting less packets due to buffered output versus PHP streaming the output ; as it gets it. On production servers, 4096 bytes is a good setting for performance ; reasons. ; Note: Output buffering can also be controlled via Output Buffering Control ; functions. ; Possible Values: ; On = Enabled and buffer is unlimited. (Use with caution) ; Off = Disabled ; Integer = Enables the buffer and sets its maximum size in bytes. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: 4096 ; Production Value: 4096 ; http://php.net/output-buffering output_buffering=4096
; You can redirect all of the output of your scripts to a function. For ; example, if you set output_handler to "mb_output_handler", character ; encoding will be transparently converted to the specified encoding. ; Setting any output handler automatically turns on output buffering. ; Note: People who wrote portable scripts should not depend on this ini ; directive. Instead, explicitly set the output handler using ob_start(). ; Using this ini directive may cause problems unless you know what script ; is doing. ; Note: You cannot use both "mb_output_handler" with "ob_iconv_handler" ; and you cannot use both "ob_gzhandler" and "zlib.output_compression". ; Note: output_handler must be empty if this is set 'On' !!!! ; Instead you must use zlib.output_handler. ; http://php.net/output-handler ;output_handler =
; URL rewriter function rewrites URL on the fly by using ; output buffer. You can set target tags by this configuration. ; "form" tag is special tag. It will add hidden input tag to pass values. ; Refer to session.trans_sid_tags for usage. ; Default Value: "form=" ; Development Value: "form=" ; Production Value: "form=" ;url_rewriter.tags
; URL rewriter will not rewrite absolute URL nor form by default. To enable ; absolute URL rewrite, allowed hosts must be defined at RUNTIME. ; Refer to session.trans_sid_hosts for more details. ; Default Value: "" ; Development Value: "" ; Production Value: "" ;url_rewriter.hosts
; Transparent output compression using the zlib library ; Valid values for this option are 'off', 'on', or a specific buffer size ; to be used for compression (default is 4KB) ; Note: Resulting chunk size may vary due to nature of compression. PHP ; outputs chunks that are few hundreds bytes each as a result of ; compression. If you prefer a larger chunk size for better ; performance, enable output_buffering in addition. ; Note: You need to use zlib.output_handler instead of the standard ; output_handler, or otherwise the output will be corrupted. ; http://php.net/zlib.output-compression zlib.output_compression=Off
; http://php.net/zlib.output-compression-level ;zlib.output_compression_level = -1
; You cannot specify additional output handlers if zlib.output_compression ; is activated here. This setting does the same as output_handler but in ; a different order. ; http://php.net/zlib.output-handler ;zlib.output_handler =
; Implicit flush tells PHP to tell the output layer to flush itself ; automatically after every output block. This is equivalent to calling the ; PHP function flush() after each and every call to print() or echo() and each ; and every HTML block. Turning this option on has serious performance ; implications and is generally recommended for debugging purposes only. ; http://php.net/implicit-flush ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI implicit_flush=Off
; The unserialize callback function will be called (with the undefined class' ; name as parameter), if the unserializer finds an undefined class ; which should be instantiated. A warning appears if the specified function is ; not defined, or if the function doesn't include/implement the missing class. ; So only set this entry, if you really want to implement such a ; callback-function. unserialize_callback_func=
; The unserialize_max_depth specifies the default depth limit for unserialized ; structures. Setting the depth limit too high may result in stack overflows ; during unserialization. The unserialize_max_depth ini setting can be ; overridden by the max_depth option on individual unserialize() calls. ; A value of 0 disables the depth limit. ;unserialize_max_depth = 4096
; When floats & doubles are serialized, store serialize_precision significant ; digits after the floating point. The default value ensures that when floats ; are decoded with unserialize, the data will remain the same. ; The value is also used for json_encode when encoding double values. ; If -1 is used, then dtoa mode 0 is used which automatically select the best ; precision. serialize_precision=-1
; open_basedir, if set, limits all file operations to the defined directory ; and below. This directive makes most sense if used in a per-directory ; or per-virtualhost web server configuration file. ; Note: disables the realpath cache ; http://php.net/open-basedir ;open_basedir =
; This directive allows you to disable certain functions. ; It receives a comma-delimited list of function names. ; http://php.net/disable-functions disable_functions=
; This directive allows you to disable certain classes. ; It receives a comma-delimited list of class names. ; http://php.net/disable-classes disable_classes=
; Colors for Syntax Highlighting mode. Anything that's acceptable in ; <span style="color: ???????"> would work. ; http://php.net/syntax-highlighting ;highlight.string = #DD0000 ;highlight.comment = #FF9900 ;highlight.keyword = #007700 ;highlight.default = #0000BB ;highlight.html = #000000
; If enabled, the request will be allowed to complete even if the user aborts ; the request. Consider enabling it if executing long requests, which may end up ; being interrupted by the user or a browser timing out. PHP's default behavior ; is to disable this feature. ; http://php.net/ignore-user-abort ;ignore_user_abort = On
; Determines the size of the realpath cache to be used by PHP. This value should ; be increased on systems where PHP opens many files to reflect the quantity of ; the file operations performed. ; Note: if open_basedir is set, the cache is disabled ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-size ;realpath_cache_size = 4096k
; Duration of time, in seconds for which to cache realpath information for a given ; file or directory. For systems with rarely changing files, consider increasing this ; value. ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-ttl ;realpath_cache_ttl = 120
; Enables or disables the circular reference collector. ; http://php.net/zend.enable-gc zend.enable_gc=On
; If enabled, scripts may be written in encodings that are incompatible with ; the scanner. CP936, Big5, CP949 and Shift_JIS are the examples of such ; encodings. To use this feature, mbstring extension must be enabled. ; Default: Off ;zend.multibyte = Off
; Allows to set the default encoding for the scripts. This value will be used ; unless "declare(encoding=...)" directive appears at the top of the script. ; Only affects if zend.multibyte is set. ; Default: "" ;zend.script_encoding =
; Allows to include or exclude arguments from stack traces generated for exceptions. ; In production, it is recommended to turn this setting on to prohibit the output ; of sensitive information in stack traces ; Default: Off zend.exception_ignore_args=Off
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Miscellaneous ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Decides whether PHP may expose the fact that it is installed on the server ; (e.g. by adding its signature to the Web server header). It is no security ; threat in any way, but it makes it possible to determine whether you use PHP ; on your server or not. ; http://php.net/expose-php expose_php=On
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Resource Limits ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Maximum execution time of each script, in seconds ; http://php.net/max-execution-time ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to 0 for the CLI SAPI max_execution_time=120
; Maximum amount of time each script may spend parsing request data. It's a good ; idea to limit this time on productions servers in order to eliminate unexpectedly ; long running scripts. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to -1 for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited) ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; http://php.net/max-input-time max_input_time=60
; Maximum input variable nesting level ; http://php.net/max-input-nesting-level ;max_input_nesting_level = 64
; How many GET/POST/COOKIE input variables may be accepted ;max_input_vars = 1000
; Maximum amount of memory a script may consume ; http://php.net/memory-limit memory_limit=512M
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Error handling and logging ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; This directive informs PHP of which errors, warnings and notices you would like ; it to take action for. The recommended way of setting values for this ; directive is through the use of the error level constants and bitwise ; operators. The error level constants are below here for convenience as well as ; some common settings and their meanings. ; By default, PHP is set to take action on all errors, notices and warnings EXCEPT ; those related to E_NOTICE and E_STRICT, which together cover best practices and ; recommended coding standards in PHP. For performance reasons, this is the ; recommend error reporting setting. Your production server shouldn't be wasting ; resources complaining about best practices and coding standards. That's what ; development servers and development settings are for. ; Note: The php.ini-development file has this setting as E_ALL. This ; means it pretty much reports everything which is exactly what you want during ; development and early testing. ; ; Error Level Constants: ; E_ALL - All errors and warnings (includes E_STRICT as of PHP 5.4.0) ; E_ERROR - fatal run-time errors ; E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR - almost fatal run-time errors ; E_WARNING - run-time warnings (non-fatal errors) ; E_PARSE - compile-time parse errors ; E_NOTICE - run-time notices (these are warnings which often result ; from a bug in your code, but it's possible that it was ; intentional (e.g., using an uninitialized variable and ; relying on the fact it is automatically initialized to an ; empty string) ; E_STRICT - run-time notices, enable to have PHP suggest changes ; to your code which will ensure the best interoperability ; and forward compatibility of your code ; E_CORE_ERROR - fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup ; E_CORE_WARNING - warnings (non-fatal errors) that occur during PHP's ; initial startup ; E_COMPILE_ERROR - fatal compile-time errors ; E_COMPILE_WARNING - compile-time warnings (non-fatal errors) ; E_USER_ERROR - user-generated error message ; E_USER_WARNING - user-generated warning message ; E_USER_NOTICE - user-generated notice message ; E_DEPRECATED - warn about code that will not work in future versions ; of PHP ; E_USER_DEPRECATED - user-generated deprecation warnings ; ; Common Values: ; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.) ; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors) ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED ; Development Value: E_ALL ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT ; http://php.net/error-reporting error_reporting=E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
; This directive controls whether or not and where PHP will output errors, ; notices and warnings too. Error output is very useful during development, but ; it could be very dangerous in production environments. Depending on the code ; which is triggering the error, sensitive information could potentially leak ; out of your application such as database usernames and passwords or worse. ; For production environments, we recommend logging errors rather than ; sending them to STDOUT. ; Possible Values: ; Off = Do not display any errors ; stderr = Display errors to STDERR (affects only CGI/CLI binaries!) ; On or stdout = Display errors to STDOUT ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/display-errors display_errors=On
; The display of errors which occur during PHP's startup sequence are handled ; separately from display_errors. PHP's default behavior is to suppress those ; errors from clients. Turning the display of startup errors on can be useful in ; debugging configuration problems. We strongly recommend you ; set this to 'off' for production servers. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/display-startup-errors display_startup_errors=On
; Besides displaying errors, PHP can also log errors to locations such as a ; server-specific log, STDERR, or a location specified by the error_log ; directive found below. While errors should not be displayed on productions ; servers they should still be monitored and logging is a great way to do that. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/log-errors log_errors=On
; Set maximum length of log_errors. In error_log information about the source is ; added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply any maximum length at all. ; http://php.net/log-errors-max-len log_errors_max_len=1024
; Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in same file on same ; line unless ignore_repeated_source is set true. ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-errors ignore_repeated_errors=Off
; Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting ; is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or ; source lines. ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-source ignore_repeated_source=Off
; If this parameter is set to Off, then memory leaks will not be shown (on ; stdout or in the log). This is only effective in a debug compile, and if ; error reporting includes E_WARNING in the allowed list ; http://php.net/report-memleaks report_memleaks=On
; This setting is on by default. ;report_zend_debug = 0
; Store the last error/warning message in $php_errormsg (boolean). Setting this value ; to On can assist in debugging and is appropriate for development servers. It should ; however be disabled on production servers. ; This directive is DEPRECATED. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/track-errors ;track_errors = Off
; Turn off normal error reporting and emit XML-RPC error XML ; http://php.net/xmlrpc-errors xmlrpc_errors = 0
; An XML-RPC faultCode xmlrpc_error_number = 0
; When PHP displays or logs an error, it has the capability of formatting the ; error message as HTML for easier reading. This directive controls whether ; the error message is formatted as HTML or not. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI ; http://php.net/html-errors ;html_errors = On
; If html_errors is set to On *and* docref_root is not empty, then PHP ; produces clickable error messages that direct to a page describing the error ; or function causing the error in detail. ; You can download a copy of the PHP manual from http://php.net/docs ; and change docref_root to the base URL of your local copy including the ; leading '/'. You must also specify the file extension being used including ; the dot. PHP's default behavior is to leave these settings empty, in which ; case no links to documentation are generated. ; Note: Never use this feature for production boxes. ; http://php.net/docref-root ; Examples ;docref_root = "/phpmanual/"
; http://php.net/docref-ext ;docref_ext = .html
; String to output before an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave ; this setting blank. ; http://php.net/error-prepend-string ; Example: ;error_prepend_string = "<span style='color: #ff0000'>"
; String to output after an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave ; this setting blank. ; http://php.net/error-append-string ; Example: ;error_append_string = "</span>"
; Log errors to specified file. PHP's default behavior is to leave this value ; empty. ; http://php.net/error-log ; Example: ;error_log = php_errors.log ; Log errors to syslog (Event Log on Windows). ;error_log = syslog
; The syslog ident is a string which is prepended to every message logged ; to syslog. Only used when error_log is set to syslog. ;syslog.ident = php
; The syslog facility is used to specify what type of program is logging ; the message. Only used when error_log is set to syslog. ;syslog.facility = user
; Set this to disable filtering control characters (the default). ; Some loggers only accept NVT-ASCII, others accept anything that's not ; control characters. If your logger accepts everything, then no filtering ; is needed at all. ; Allowed values are: ; ascii (all printable ASCII characters and NL) ; no-ctrl (all characters except control characters) ; all (all characters) ; raw (like "all", but messages are not split at newlines) ; http://php.net/syslog.filter ;syslog.filter = ascii
;windows.show_crt_warning ; Default value: 0 ; Development value: 0 ; Production value: 0
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Data Handling ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; The separator used in PHP generated URLs to separate arguments. ; PHP's default setting is "&". ; http://php.net/arg-separator.output ; Example: ;arg_separator.output = "&"
; List of separator(s) used by PHP to parse input URLs into variables. ; PHP's default setting is "&". ; NOTE: Every character in this directive is considered as separator! ; http://php.net/arg-separator.input ; Example: ;arg_separator.input = ";&"
; This directive determines which super global arrays are registered when PHP ; starts up. G,P,C,E & S are abbreviations for the following respective super ; globals: GET, POST, COOKIE, ENV and SERVER. There is a performance penalty ; paid for the registration of these arrays and because ENV is not as commonly ; used as the others, ENV is not recommended on productions servers. You ; can still get access to the environment variables through getenv() should you ; need to. ; Default Value: "EGPCS" ; Development Value: "GPCS" ; Production Value: "GPCS"; ; http://php.net/variables-order variables_order="GPCS"
; This directive determines which super global data (G,P & C) should be ; registered into the super global array REQUEST. If so, it also determines ; the order in which that data is registered. The values for this directive ; are specified in the same manner as the variables_order directive, ; EXCEPT one. Leaving this value empty will cause PHP to use the value set ; in the variables_order directive. It does not mean it will leave the super ; globals array REQUEST empty. ; Default Value: None ; Development Value: "GP" ; Production Value: "GP" ; http://php.net/request-order request_order="GP"
; This directive determines whether PHP registers $argv & $argc each time it ; runs. $argv contains an array of all the arguments passed to PHP when a script ; is invoked. $argc contains an integer representing the number of arguments ; that were passed when the script was invoked. These arrays are extremely ; useful when running scripts from the command line. When this directive is ; enabled, registering these variables consumes CPU cycles and memory each time ; a script is executed. For performance reasons, this feature should be disabled ; on production servers. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/register-argc-argv register_argc_argv=Off
; When enabled, the ENV, REQUEST and SERVER variables are created when they're ; first used (Just In Time) instead of when the script starts. If these ; variables are not used within a script, having this directive on will result ; in a performance gain. The PHP directive register_argc_argv must be disabled ; for this directive to have any effect. ; http://php.net/auto-globals-jit auto_globals_jit=On
; Whether PHP will read the POST data. ; This option is enabled by default. ; Most likely, you won't want to disable this option globally. It causes $_POST ; and $_FILES to always be empty; the only way you will be able to read the ; POST data will be through the php://input stream wrapper. This can be useful ; to proxy requests or to process the POST data in a memory efficient fashion. ; http://php.net/enable-post-data-reading ;enable_post_data_reading = Off
; Maximum size of POST data that PHP will accept. ; Its value may be 0 to disable the limit. It is ignored if POST data reading ; is disabled through enable_post_data_reading. ; http://php.net/post-max-size post_max_size=40M
; Automatically add files before PHP document. ; http://php.net/auto-prepend-file auto_prepend_file=
; Automatically add files after PHP document. ; http://php.net/auto-append-file auto_append_file=
; By default, PHP will output a media type using the Content-Type header. To ; disable this, simply set it to be empty. ; ; PHP's built-in default media type is set to text/html. ; http://php.net/default-mimetype default_mimetype="text/html"
; PHP's default character set is set to UTF-8. ; http://php.net/default-charset default_charset="UTF-8"
; PHP internal character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; http://php.net/internal-encoding ;internal_encoding =
; PHP input character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; http://php.net/input-encoding ;input_encoding =
; PHP output character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; See also output_buffer. ; http://php.net/output-encoding ;output_encoding =
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Paths and Directories ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; UNIX: "/path1:/path2" include_path=C:\xampp\php\PEAR ; ; Windows: "\path1;\path2" ;include_path = ".;c:\php\includes" ; ; PHP's default setting for include_path is ".;/path/to/php/pear" ; http://php.net/include-path
; The root of the PHP pages, used only if nonempty. ; if PHP was not compiled with FORCE_REDIRECT, you SHOULD set doc_root ; if you are running php as a CGI under any web server (other than IIS) ; see documentation for security issues. The alternate is to use the ; cgi.force_redirect configuration below ; http://php.net/doc-root doc_root=
; The directory under which PHP opens the script using /~username used only ; if nonempty. ; http://php.net/user-dir user_dir=
; Directory in which the loadable extensions (modules) reside. ; http://php.net/extension-dir ;extension_dir = "./" ; On windows: extension_dir="C:\xampp\php\ext"
; Directory where the temporary files should be placed. ; Defaults to the system default (see sys_get_temp_dir) ;sys_temp_dir = "/tmp"
; Whether or not to enable the dl() function. The dl() function does NOT work ; properly in multithreaded servers, such as IIS or Zeus, and is automatically ; disabled on them. ; http://php.net/enable-dl enable_dl=Off
; cgi.force_redirect is necessary to provide security running PHP as a CGI under ; most web servers. Left undefined, PHP turns this on by default. You can ; turn it off here AT YOUR OWN RISK ; **You CAN safely turn this off for IIS, in fact, you MUST.** ; http://php.net/cgi.force-redirect ;cgi.force_redirect = 1
; if cgi.nph is enabled it will force cgi to always sent Status: 200 with ; every request. PHP's default behavior is to disable this feature. ;cgi.nph = 1
; if cgi.force_redirect is turned on, and you are not running under Apache or Netscape ; (iPlanet) web servers, you MAY need to set an environment variable name that PHP ; will look for to know it is OK to continue execution. Setting this variable MAY ; cause security issues, KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING FIRST. ; http://php.net/cgi.redirect-status-env ;cgi.redirect_status_env =
; cgi.fix_pathinfo provides *real* PATH_INFO/PATH_TRANSLATED support for CGI. PHP's ; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok ; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting ; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting ; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts ; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED. ; http://php.net/cgi.fix-pathinfo ;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1
; if cgi.discard_path is enabled, the PHP CGI binary can safely be placed outside ; of the web tree and people will not be able to circumvent .htaccess security. ;cgi.discard_path=1
; FastCGI under IIS supports the ability to impersonate ; security tokens of the calling client. This allows IIS to define the ; security context that the request runs under. mod_fastcgi under Apache ; does not currently support this feature (03/17/2002) ; Set to 1 if running under IIS. Default is zero. ; http://php.net/fastcgi.impersonate ;fastcgi.impersonate = 1
; Disable logging through FastCGI connection. PHP's default behavior is to enable ; this feature. ;fastcgi.logging = 0
; cgi.rfc2616_headers configuration option tells PHP what type of headers to ; use when sending HTTP response code. If set to 0, PHP sends Status: header that ; is supported by Apache. When this option is set to 1, PHP will send ; RFC2616 compliant header. ; Default is zero. ; http://php.net/cgi.rfc2616-headers ;cgi.rfc2616_headers = 0
; cgi.check_shebang_line controls whether CGI PHP checks for line starting with #! ; (shebang) at the top of the running script. This line might be needed if the ; script support running both as stand-alone script and via PHP CGI<. PHP in CGI ; mode skips this line and ignores its content if this directive is turned on. ; http://php.net/cgi.check-shebang-line ;cgi.check_shebang_line=1
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; File Uploads ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Whether to allow HTTP file uploads. ; http://php.net/file-uploads file_uploads=On
; Temporary directory for HTTP uploaded files (will use system default if not ; specified). ; http://php.net/upload-tmp-dir upload_tmp_dir="C:\xampp\tmp"
; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files. ; http://php.net/upload-max-filesize upload_max_filesize=40M
; Maximum number of files that can be uploaded via a single request max_file_uploads=20
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Fopen wrappers ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Whether to allow the treatment of URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files. ; http://php.net/allow-url-fopen allow_url_fopen=On
; Whether to allow include/require to open URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files. ; http://php.net/allow-url-include allow_url_include=Off
; Define the anonymous ftp password (your email address). PHP's default setting ; for this is empty. ; http://php.net/from ;from="[email protected]"
; Define the User-Agent string. PHP's default setting for this is empty. ; http://php.net/user-agent ;user_agent="PHP"
; Default timeout for socket based streams (seconds) ; http://php.net/default-socket-timeout default_socket_timeout=60
; If your scripts have to deal with files from Macintosh systems, ; or you are running on a Mac and need to deal with files from ; unix or win32 systems, setting this flag will cause PHP to ; automatically detect the EOL character in those files so that ; fgets() and file() will work regardless of the source of the file. ; http://php.net/auto-detect-line-endings ;auto_detect_line_endings = Off
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Dynamic Extensions ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; If you wish to have an extension loaded automatically, use the following ; syntax: ; ; extension=modulename ; ; For example: ; ; extension=mysqli ; ; When the extension library to load is not located in the default extension ; directory, You may specify an absolute path to the library file: ; ; extension=/path/to/extension/mysqli.so ; ; Note : The syntax used in previous PHP versions ('extension=<ext>.so' and ; 'extension='php_<ext>.dll') is supported for legacy reasons and may be ; deprecated in a future PHP major version. So, when it is possible, please ; move to the new ('extension=<ext>) syntax. ; ; Notes for Windows environments : ; ; - Many DLL files are located in the extensions/ (PHP 4) or ext/ (PHP 5+) ; extension folders as well as the separate PECL DLL download (PHP 5+). ; Be sure to appropriately set the extension_dir directive. ; extension=bz2 extension=curl ;extension=ffi ;extension=ftp extension=fileinfo extension=gd2 extension=gettext ;extension=gmp extension=intl ;extension=imap ;extension=ldap extension=mbstring extension=exif ; Must be after mbstring as it depends on it extension=mysqli ;extension=oci8_12c ; Use with Oracle Database 12c Instant Client ;extension=odbc ;extension=openssl ;extension=pdo_firebird extension=pdo_mysql ;extension=pdo_oci ;extension=pdo_odbc ;extension=pdo_pgsql extension=pdo_sqlite ;extension=pgsql ;extension=shmop
; The MIBS data available in the PHP distribution must be installed. ; See http://www.php.net/manual/en/snmp.installation.php ;extension=snmp
extension=soap ;extension=sockets ;extension=sodium ;extension=sqlite3 ;extension=tidy extension=xmlrpc ;extension=xsl
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Module Settings ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; asp_tags=Off display_startup_errors=On track_errors=Off y2k_compliance=On allow_call_time_pass_reference=Off safe_mode=Off safe_mode_gid=Off safe_mode_allowed_env_vars=PHP_ safe_mode_protected_env_vars=LD_LIBRARY_PATH error_log="C:\xampp\php\logs\php_error_log" register_globals=Off register_long_arrays=Off magic_quotes_gpc=Off magic_quotes_runtime=Off magic_quotes_sybase=Off extension=php_openssl.dll extension=php_ftp.dll
[CLI Server] ; Whether the CLI web server uses ANSI color coding in its terminal output. cli_server.color=On
[Date] ; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions ; http://php.net/date.timezone ;date.timezone =
; http://php.net/date.default-latitude ;date.default_latitude = 31.7667
; http://php.net/date.default-longitude ;date.default_longitude = 35.2333
; http://php.net/date.sunrise-zenith ;date.sunrise_zenith = 90.583333
; http://php.net/date.sunset-zenith ;date.sunset_zenith = 90.583333
[filter] ; http://php.net/filter.default ;filter.default = unsafe_raw
; http://php.net/filter.default-flags ;filter.default_flags =
[iconv] ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or iconv.input_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < input_encoding < iconv.input_encoding ;iconv.input_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding ;iconv.internal_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or iconv.output_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < iconv.output_encoding ; To use an output encoding conversion, iconv's output handler must be set ; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed. ;iconv.output_encoding =
[imap] ; rsh/ssh logins are disabled by default. Use this INI entry if you want to ; enable them. Note that the IMAP library does not filter mailbox names before ; passing them to rsh/ssh command, thus passing untrusted data to this function ; with rsh/ssh enabled is insecure. ;imap.enable_insecure_rsh=0
[intl] ;intl.default_locale = ; This directive allows you to produce PHP errors when some error ; happens within intl functions. The value is the level of the error produced. ; Default is 0, which does not produce any errors. ;intl.error_level = E_WARNING ;intl.use_exceptions = 0
[sqlite3] ; Directory pointing to SQLite3 extensions ; http://php.net/sqlite3.extension-dir ;sqlite3.extension_dir =
; SQLite defensive mode flag (only available from SQLite 3.26+) ; When the defensive flag is enabled, language features that allow ordinary ; SQL to deliberately corrupt the database file are disabled. This forbids ; writing directly to the schema, shadow tables (eg. FTS data tables), or ; the sqlite_dbpage virtual table. ; https://www.sqlite.org/c3ref/c_dbconfig_defensive.html ; (for older SQLite versions, this flag has no use) ;sqlite3.defensive = 1
[Pcre] ; PCRE library backtracking limit. ; http://php.net/pcre.backtrack-limit ;pcre.backtrack_limit=100000
; PCRE library recursion limit. ; Please note that if you set this value to a high number you may consume all ; the available process stack and eventually crash PHP (due to reaching the ; stack size limit imposed by the Operating System). ; http://php.net/pcre.recursion-limit ;pcre.recursion_limit=100000
; Enables or disables JIT compilation of patterns. This requires the PCRE ; library to be compiled with JIT support. ;pcre.jit=1
[Pdo] pdo_mysql.default_socket="MySQL" ; Whether to pool ODBC connections. Can be one of "strict", "relaxed" or "off" ; http://php.net/pdo-odbc.connection-pooling ;pdo_odbc.connection_pooling=strict
;pdo_odbc.db2_instance_name
[Pdo_mysql] ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in ; MySQL defaults. pdo_mysql.default_socket=
[Phar] ; http://php.net/phar.readonly ;phar.readonly = On
; http://php.net/phar.require-hash ;phar.require_hash = On
;phar.cache_list =
[mail function] ; For Win32 only. ; http://php.net/smtp SMTP=localhost ; http://php.net/smtp-port smtp_port=25
; For Win32 only. ; http://php.net/sendmail-from ;sendmail_from = [email protected]
; For Unix only. You may supply arguments as well (default: "sendmail -t -i"). ; http://php.net/sendmail-path ;sendmail_path =
; Force the addition of the specified parameters to be passed as extra parameters ; to the sendmail binary. These parameters will always replace the value of ; the 5th parameter to mail(). ;mail.force_extra_parameters =
; Add X-PHP-Originating-Script: that will include uid of the script followed by the filename mail.add_x_header=Off
; The path to a log file that will log all mail() calls. Log entries include ; the full path of the script, line number, To address and headers. ;mail.log = ; Log mail to syslog (Event Log on Windows). ;mail.log = syslog
[ODBC] ; http://php.net/odbc.default-db ;odbc.default_db = Not yet implemented
; http://php.net/odbc.default-user ;odbc.default_user = Not yet implemented
; http://php.net/odbc.default-pw ;odbc.default_pw = Not yet implemented
; Controls the ODBC cursor model. ; Default: SQL_CURSOR_STATIC (default). ;odbc.default_cursortype
; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/odbc.allow-persistent odbc.allow_persistent=On
; Check that a connection is still valid before reuse. ; http://php.net/odbc.check-persistent odbc.check_persistent=On
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/odbc.max-persistent odbc.max_persistent=-1
; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/odbc.max-links odbc.max_links=-1
; Handling of LONG fields. Returns number of bytes to variables. 0 means ; passthru. ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultlrl odbc.defaultlrl=4096
; Handling of binary data. 0 means passthru, 1 return as is, 2 convert to char. ; See the documentation on odbc_binmode and odbc_longreadlen for an explanation ; of odbc.defaultlrl and odbc.defaultbinmode ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultbinmode odbc.defaultbinmode=1
[MySQLi]
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-persistent mysqli.max_persistent=-1
; Allow accessing, from PHP's perspective, local files with LOAD DATA statements ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow_local_infile ;mysqli.allow_local_infile = On
; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow-persistent mysqli.allow_persistent=On
; Maximum number of links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-links mysqli.max_links=-1
; Default port number for mysqli_connect(). If unset, mysqli_connect() will use ; the $MYSQL_TCP_PORT or the mysql-tcp entry in /etc/services or the ; compile-time value defined MYSQL_PORT (in that order). Win32 will only look ; at MYSQL_PORT. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-port mysqli.default_port=3306
; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in ; MySQL defaults. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-socket mysqli.default_socket=
; Default host for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-host mysqli.default_host=
; Default user for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-user mysqli.default_user=
; Default password for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; Note that this is generally a *bad* idea to store passwords in this file. ; *Any* user with PHP access can run 'echo get_cfg_var("mysqli.default_pw") ; and reveal this password! And of course, any users with read access to this ; file will be able to reveal the password as well. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-pw mysqli.default_pw=
; Allow or prevent reconnect mysqli.reconnect=Off
[mysqlnd] ; Enable / Disable collection of general statistics by mysqlnd which can be ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations. mysqlnd.collect_statistics=On
; Enable / Disable collection of memory usage statistics by mysqlnd which can be ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations. mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics=On
; Records communication from all extensions using mysqlnd to the specified log ; file. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.debug ;mysqlnd.debug =
; Defines which queries will be logged. ;mysqlnd.log_mask = 0
; Default size of the mysqlnd memory pool, which is used by result sets. ;mysqlnd.mempool_default_size = 16000
; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used when sending commands to MySQL in bytes. ;mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size = 2048
; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used for reading data sent by the server in ; bytes. ;mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size = 32768
; Timeout for network requests in seconds. ;mysqlnd.net_read_timeout = 31536000
; SHA-256 Authentication Plugin related. File with the MySQL server public RSA ; key. ;mysqlnd.sha256_server_public_key =
[OCI8]
; Connection: Enables privileged connections using external ; credentials (OCI_SYSOPER, OCI_SYSDBA) ; http://php.net/oci8.privileged-connect ;oci8.privileged_connect = Off
; Connection: The maximum number of persistent OCI8 connections per ; process. Using -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/oci8.max-persistent ;oci8.max_persistent = -1
; Connection: The maximum number of seconds a process is allowed to ; maintain an idle persistent connection. Using -1 means idle ; persistent connections will be maintained forever. ; http://php.net/oci8.persistent-timeout ;oci8.persistent_timeout = -1
; Connection: The number of seconds that must pass before issuing a ; ping during oci_pconnect() to check the connection validity. When ; set to 0, each oci_pconnect() will cause a ping. Using -1 disables ; pings completely. ; http://php.net/oci8.ping-interval ;oci8.ping_interval = 60
; Connection: Set this to a user chosen connection class to be used ; for all pooled server requests with Oracle 11g Database Resident ; Connection Pooling (DRCP). To use DRCP, this value should be set to ; the same string for all web servers running the same application, ; the database pool must be configured, and the connection string must ; specify to use a pooled server. ;oci8.connection_class =
; High Availability: Using On lets PHP receive Fast Application ; Notification (FAN) events generated when a database node fails. The ; database must also be configured to post FAN events. ;oci8.events = Off
; Tuning: This option enables statement caching, and specifies how ; many statements to cache. Using 0 disables statement caching. ; http://php.net/oci8.statement-cache-size ;oci8.statement_cache_size = 20
; Tuning: Enables statement prefetching and sets the default number of ; rows that will be fetched automatically after statement execution. ; http://php.net/oci8.default-prefetch ;oci8.default_prefetch = 100
; Compatibility. Using On means oci_close() will not close ; oci_connect() and oci_new_connect() connections. ; http://php.net/oci8.old-oci-close-semantics ;oci8.old_oci_close_semantics = Off
[PostgreSQL] ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/pgsql.allow-persistent pgsql.allow_persistent=On
; Detect broken persistent links always with pg_pconnect(). ; Auto reset feature requires a little overheads. ; http://php.net/pgsql.auto-reset-persistent pgsql.auto_reset_persistent=Off
; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-persistent pgsql.max_persistent=-1
; Maximum number of links (persistent+non persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-links pgsql.max_links=-1
; Ignore PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not. ; Notice message logging require a little overheads. ; http://php.net/pgsql.ignore-notice pgsql.ignore_notice=0
; Log PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not. ; Unless pgsql.ignore_notice=0, module cannot log notice message. ; http://php.net/pgsql.log-notice pgsql.log_notice=0
[bcmath] ; Number of decimal digits for all bcmath functions. ; http://php.net/bcmath.scale bcmath.scale=0
[browscap] ; http://php.net/browscap browscap="C:\xampp\php\extras\browscap.ini"
[Session] ; Handler used to store/retrieve data. ; http://php.net/session.save-handler session.save_handler=files
; Argument passed to save_handler. In the case of files, this is the path ; where data files are stored. Note: Windows users have to change this ; variable in order to use PHP's session functions. ; ; The path can be defined as: ; ; session.save_path = "N;/path" ; ; where N is an integer. Instead of storing all the session files in ; /path, what this will do is use subdirectories N-levels deep, and ; store the session data in those directories. This is useful if ; your OS has problems with many files in one directory, and is ; a more efficient layout for servers that handle many sessions. ; ; NOTE 1: PHP will not create this directory structure automatically. ; You can use the script in the ext/session dir for that purpose. ; NOTE 2: See the section on garbage collection below if you choose to ; use subdirectories for session storage ; ; The file storage module creates files using mode 600 by default. ; You can change that by using ; ; session.save_path = "N;MODE;/path" ; ; where MODE is the octal representation of the mode. Note that this ; does not overwrite the process's umask. ; http://php.net/session.save-path session.save_path="C:\xampp\tmp"
; Whether to use strict session mode. ; Strict session mode does not accept an uninitialized session ID, and ; regenerates the session ID if the browser sends an uninitialized session ID. ; Strict mode protects applications from session fixation via a session adoption ; vulnerability. It is disabled by default for maximum compatibility, but ; enabling it is encouraged. ; https://wiki.php.net/rfc/strict_sessions session.use_strict_mode=0
; Whether to use cookies. ; http://php.net/session.use-cookies session.use_cookies=1
; http://php.net/session.cookie-secure ;session.cookie_secure =
; This option forces PHP to fetch and use a cookie for storing and maintaining ; the session id. We encourage this operation as it's very helpful in combating ; session hijacking when not specifying and managing your own session id. It is ; not the be-all and end-all of session hijacking defense, but it's a good start. ; http://php.net/session.use-only-cookies session.use_only_cookies=1
; Name of the session (used as cookie name). ; http://php.net/session.name session.name=PHPSESSID
; Initialize session on request startup. ; http://php.net/session.auto-start session.auto_start=0
; Lifetime in seconds of cookie or, if 0, until browser is restarted. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-lifetime session.cookie_lifetime=0
; The path for which the cookie is valid. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-path session.cookie_path=/
; The domain for which the cookie is valid. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-domain session.cookie_domain=
; Whether or not to add the httpOnly flag to the cookie, which makes it ; inaccessible to browser scripting languages such as JavaScript. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-httponly session.cookie_httponly=
; Add SameSite attribute to cookie to help mitigate Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF) ; Current valid values are "Strict", "Lax" or "None". When using "None", ; make sure to include the quotes, as `none` is interpreted like `false` in ini files. ; https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-west-first-party-cookies-07 session.cookie_samesite=
; Handler used to serialize data. php is the standard serializer of PHP. ; http://php.net/session.serialize-handler session.serialize_handler=php
; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every ; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using gc_probability/gc_divisor, ; e.g. 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process starts on each request. ; Default Value: 1 ; Development Value: 1 ; Production Value: 1 ; http://php.net/session.gc-probability session.gc_probability=1
; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every ; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using gc_probability/gc_divisor, ; e.g. 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process starts on each request. ; For high volume production servers, using a value of 1000 is a more efficient approach. ; Default Value: 100 ; Development Value: 1000 ; Production Value: 1000 ; http://php.net/session.gc-divisor session.gc_divisor=1000
; After this number of seconds, stored data will be seen as 'garbage' and ; cleaned up by the garbage collection process. ; http://php.net/session.gc-maxlifetime session.gc_maxlifetime=1440
; NOTE: If you are using the subdirectory option for storing session files ; (see session.save_path above), then garbage collection does *not* ; happen automatically. You will need to do your own garbage ; collection through a shell script, cron entry, or some other method. ; For example, the following script is the equivalent of setting ; session.gc_maxlifetime to 1440 (1440 seconds = 24 minutes): ; find /path/to/sessions -cmin +24 -type f | xargs rm
; Check HTTP Referer to invalidate externally stored URLs containing ids. ; HTTP_REFERER has to contain this substring for the session to be ; considered as valid. ; http://php.net/session.referer-check session.referer_check=
; Set to {nocache,private,public,} to determine HTTP caching aspects ; or leave this empty to avoid sending anti-caching headers. ; http://php.net/session.cache-limiter session.cache_limiter=nocache
; Document expires after n minutes. ; http://php.net/session.cache-expire session.cache_expire=180
; trans sid support is disabled by default. ; Use of trans sid may risk your users' security. ; Use this option with caution. ; - User may send URL contains active session ID ; to other person via. email/irc/etc. ; - URL that contains active session ID may be stored ; in publicly accessible computer. ; - User may access your site with the same session ID ; always using URL stored in browser's history or bookmarks. ; http://php.net/session.use-trans-sid session.use_trans_sid=0
; Set session ID character length. This value could be between 22 to 256. ; Shorter length than default is supported only for compatibility reason. ; Users should use 32 or more chars. ; http://php.net/session.sid-length ; Default Value: 32 ; Development Value: 26 ; Production Value: 26 session.sid_length=26
; The URL rewriter will look for URLs in a defined set of HTML tags. ; <form> is special; if you include them here, the rewriter will ; add a hidden <input> field with the info which is otherwise appended ; to URLs. <form> tag's action attribute URL will not be modified ; unless it is specified. ; Note that all valid entries require a "=", even if no value follows. ; Default Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=" ; Development Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=" ; Production Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=" ; http://php.net/url-rewriter.tags session.trans_sid_tags="a=href,area=href,frame=src,form="
; URL rewriter does not rewrite absolute URLs by default. ; To enable rewrites for absolute paths, target hosts must be specified ; at RUNTIME. i.e. use ini_set() ; <form> tags is special. PHP will check action attribute's URL regardless ; of session.trans_sid_tags setting. ; If no host is defined, HTTP_HOST will be used for allowed host. ; Example value: php.net,www.php.net,wiki.php.net ; Use "," for multiple hosts. No spaces are allowed. ; Default Value: "" ; Development Value: "" ; Production Value: "" ;session.trans_sid_hosts=""
; Define how many bits are stored in each character when converting ; the binary hash data to something readable. ; Possible values: ; 4 (4 bits: 0-9, a-f) ; 5 (5 bits: 0-9, a-v) ; 6 (6 bits: 0-9, a-z, A-Z, "-", ",") ; Default Value: 4 ; Development Value: 5 ; Production Value: 5 ; http://php.net/session.hash-bits-per-character session.sid_bits_per_character=5
; Enable upload progress tracking in $_SESSION ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.enabled ;session.upload_progress.enabled = On
; Cleanup the progress information as soon as all POST data has been read ; (i.e. upload completed). ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.cleanup ;session.upload_progress.cleanup = On
; A prefix used for the upload progress key in $_SESSION ; Default Value: "upload_progress_" ; Development Value: "upload_progress_" ; Production Value: "upload_progress_" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.prefix ;session.upload_progress.prefix = "upload_progress_"
; The index name (concatenated with the prefix) in $_SESSION ; containing the upload progress information ; Default Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; Development Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; Production Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.name ;session.upload_progress.name = "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS"
; How frequently the upload progress should be updated. ; Given either in percentages (per-file), or in bytes ; Default Value: "1%" ; Development Value: "1%" ; Production Value: "1%" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.freq ;session.upload_progress.freq = "1%"
; The minimum delay between updates, in seconds ; Default Value: 1 ; Development Value: 1 ; Production Value: 1 ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.min-freq ;session.upload_progress.min_freq = "1"
; Only write session data when session data is changed. Enabled by default. ; http://php.net/session.lazy-write ;session.lazy_write = On
[Assertion] ; Switch whether to compile assertions at all (to have no overhead at run-time) ; -1: Do not compile at all ; 0: Jump over assertion at run-time ; 1: Execute assertions ; Changing from or to a negative value is only possible in php.ini! (For turning assertions on and off at run-time, see assert.active, when zend.assertions = 1) ; Default Value: 1 ; Development Value: 1 ; Production Value: -1 ; http://php.net/zend.assertions zend.assertions=1
; Assert(expr); active by default. ; http://php.net/assert.active ;assert.active = On
; Throw an AssertionError on failed assertions ; http://php.net/assert.exception ;assert.exception = On
; Issue a PHP warning for each failed assertion. (Overridden by assert.exception if active) ; http://php.net/assert.warning ;assert.warning = On
; Don't bail out by default. ; http://php.net/assert.bail ;assert.bail = Off
; User-function to be called if an assertion fails. ; http://php.net/assert.callback ;assert.callback = 0
; Eval the expression with current error_reporting(). Set to true if you want ; error_reporting(0) around the eval(). ; http://php.net/assert.quiet-eval ;assert.quiet_eval = 0
[COM] ; path to a file containing GUIDs, IIDs or filenames of files with TypeLibs ; http://php.net/com.typelib-file ;com.typelib_file =
; allow Distributed-COM calls ; http://php.net/com.allow-dcom ;com.allow_dcom = true
; autoregister constants of a component's typlib on com_load() ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-typelib ;com.autoregister_typelib = true
; register constants casesensitive ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-casesensitive ;com.autoregister_casesensitive = false
; show warnings on duplicate constant registrations ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-verbose ;com.autoregister_verbose = true
; The default character set code-page to use when passing strings to and from COM objects. ; Default: system ANSI code page ;com.code_page=
[mbstring] ; language for internal character representation. ; This affects mb_send_mail() and mbstring.detect_order. ; http://php.net/mbstring.language ;mbstring.language = Japanese
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead. ; internal/script encoding. ; Some encoding cannot work as internal encoding. (e.g. SJIS, BIG5, ISO-2022-*) ; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding ;mbstring.internal_encoding =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead. ; http input encoding. ; mbstring.encoding_translation = On is needed to use this setting. ; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or mbstring.input is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < input_encoding < mbstring.http_input ; http://php.net/mbstring.http-input ;mbstring.http_input =
; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead. ; http output encoding. ; mb_output_handler must be registered as output buffer to function. ; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or mbstring.http_output is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < mbstring.http_output ; To use an output encoding conversion, mbstring's output handler must be set ; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed. ; http://php.net/mbstring.http-output ;mbstring.http_output =
; enable automatic encoding translation according to ; mbstring.internal_encoding setting. Input chars are ; converted to internal encoding by setting this to On. ; Note: Do _not_ use automatic encoding translation for ; portable libs/applications. ; http://php.net/mbstring.encoding-translation ;mbstring.encoding_translation = Off
; automatic encoding detection order. ; "auto" detect order is changed according to mbstring.language ; http://php.net/mbstring.detect-order ;mbstring.detect_order = auto
; substitute_character used when character cannot be converted ; one from another ; http://php.net/mbstring.substitute-character ;mbstring.substitute_character = none
; overload(replace) single byte functions by mbstring functions. ; mail(), ereg(), etc are overloaded by mb_send_mail(), mb_ereg(), ; etc. Possible values are 0,1,2,4 or combination of them. ; For example, 7 for overload everything. ; 0: No overload ; 1: Overload mail() function ; 2: Overload str*() functions ; 4: Overload ereg*() functions ; http://php.net/mbstring.func-overload ;mbstring.func_overload = 0
; enable strict encoding detection. ; Default: Off ;mbstring.strict_detection = On
; This directive specifies the regex pattern of content types for which mb_output_handler() ; is activated. ; Default: mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype=^(text/|application/xhtml\+xml) ;mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype=
; This directive specifies maximum stack depth for mbstring regular expressions. It is similar ; to the pcre.recursion_limit for PCRE. ; Default: 100000 ;mbstring.regex_stack_limit=100000
; This directive specifies maximum retry count for mbstring regular expressions. It is similar ; to the pcre.backtrack_limit for PCRE. ; Default: 1000000 ;mbstring.regex_retry_limit=1000000
[gd] ; Tell the jpeg decode to ignore warnings and try to create ; a gd image. The warning will then be displayed as notices ; disabled by default ; http://php.net/gd.jpeg-ignore-warning ;gd.jpeg_ignore_warning = 1
[exif] ; Exif UNICODE user comments are handled as UCS-2BE/UCS-2LE and JIS as JIS. ; With mbstring support this will automatically be converted into the encoding ; given by corresponding encode setting. When empty mbstring.internal_encoding ; is used. For the decode settings you can distinguish between motorola and ; intel byte order. A decode setting cannot be empty. ; http://php.net/exif.encode-unicode ;exif.encode_unicode = ISO-8859-15
; http://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-motorola ;exif.decode_unicode_motorola = UCS-2BE
; http://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-intel ;exif.decode_unicode_intel = UCS-2LE
; http://php.net/exif.encode-jis ;exif.encode_jis =
; http://php.net/exif.decode-jis-motorola ;exif.decode_jis_motorola = JIS
; http://php.net/exif.decode-jis-intel ;exif.decode_jis_intel = JIS
[Tidy] ; The path to a default tidy configuration file to use when using tidy ; http://php.net/tidy.default-config ;tidy.default_config = /usr/local/lib/php/default.tcfg
; Should tidy clean and repair output automatically? ; WARNING: Do not use this option if you are generating non-html content ; such as dynamic images ; http://php.net/tidy.clean-output tidy.clean_output=Off
[soap] ; Enables or disables WSDL caching feature. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-enabled soap.wsdl_cache_enabled=1
; Sets the directory name where SOAP extension will put cache files. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-dir soap.wsdl_cache_dir="/tmp"
; (time to live) Sets the number of second while cached file will be used ; instead of original one. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-ttl soap.wsdl_cache_ttl=86400
; Sets the size of the cache limit. (Max. number of WSDL files to cache) soap.wsdl_cache_limit=5
[sysvshm] ; A default size of the shared memory segment ;sysvshm.init_mem = 10000
[ldap] ; Sets the maximum number of open links or -1 for unlimited. ldap.max_links=-1
[dba] ;dba.default_handler=
[opcache] ; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled opcache.enable=1
; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled for the CLI version of PHP opcache.enable_cli=0
; The OPcache shared memory storage size. opcache.memory_consumption=128
; The amount of memory for interned strings in Mbytes. opcache.interned_strings_buffer=8
; The maximum number of keys (scripts) in the OPcache hash table. ; Only numbers between 200 and 1000000 are allowed. opcache.max_accelerated_files=10000
; The maximum percentage of "wasted" memory until a restart is scheduled. opcache.max_wasted_percentage=5
; When this directive is enabled, the OPcache appends the current working ; directory to the script key, thus eliminating possible collisions between ; files with the same name (basename). Disabling the directive improves ; performance, but may break existing applications. opcache.use_cwd=1
; When disabled, you must reset the OPcache manually or restart the ; webserver for changes to the filesystem to take effect. opcache.validate_timestamps=1
; How often (in seconds) to check file timestamps for changes to the shared ; memory storage allocation. ("1" means validate once per second, but only ; once per request. "0" means always validate) opcache.revalidate_freq=60
; Enables or disables file search in include_path optimization opcache.revalidate_path=0
; If disabled, all PHPDoc comments are dropped from the code to reduce the ; size of the optimized code. opcache.save_comments=1
; Allow file existence override (file_exists, etc.) performance feature. opcache.enable_file_override=0
; A bitmask, where each bit enables or disables the appropriate OPcache ; passes opcache.optimization_level=0x7FFFBFFF
opcache.dups_fix=0
; The location of the OPcache blacklist file (wildcards allowed). ; Each OPcache blacklist file is a text file that holds the names of files ; that should not be accelerated. The file format is to add each filename ; to a new line. The filename may be a full path or just a file prefix ; (i.e., /var/www/x blacklists all the files and directories in /var/www ; that start with 'x'). Line starting with a ; are ignored (comments). opcache.blacklist_filename=
; Allows exclusion of large files from being cached. By default all files ; are cached. opcache.max_file_size=0
; Check the cache checksum each N requests. ; The default value of "0" means that the checks are disabled. opcache.consistency_checks=0
; How long to wait (in seconds) for a scheduled restart to begin if the cache ; is not being accessed. opcache.force_restart_timeout=180
; OPcache error_log file name. Empty string assumes "stderr". opcache.error_log=
; All OPcache errors go to the Web server log. ; By default, only fatal errors (level 0) or errors (level 1) are logged. ; You can also enable warnings (level 2), info messages (level 3) or ; debug messages (level 4). opcache.log_verbosity_level=1
; Preferred Shared Memory back-end. Leave empty and let the system decide. opcache.preferred_memory_model=
; Protect the shared memory from unexpected writing during script execution. ; Useful for internal debugging only. opcache.protect_memory=0
; Allows calling OPcache API functions only from PHP scripts which path is ; started from specified string. The default "" means no restriction opcache.restrict_api=
; Mapping base of shared memory segments (for Windows only). All the PHP ; processes have to map shared memory into the same address space. This ; directive allows to manually fix the "Unable to reattach to base address" ; errors. opcache.mmap_base=
; Facilitates multiple OPcache instances per user (for Windows only). All PHP ; processes with the same cache ID and user share an OPcache instance. opcache.cache_id=
; Enables and sets the second level cache directory. ; It should improve performance when SHM memory is full, at server restart or ; SHM reset. The default "" disables file based caching. opcache.file_cache=
; Enables or disables opcode caching in shared memory. opcache.file_cache_only=0
; Enables or disables checksum validation when script loaded from file cache. opcache.file_cache_consistency_checks=1
; Implies opcache.file_cache_only=1 for a certain process that failed to ; reattach to the shared memory (for Windows only). Explicitly enabled file ; cache is required. opcache.file_cache_fallback=1
; Enables or disables copying of PHP code (text segment) into HUGE PAGES. ; This should improve performance, but requires appropriate OS configuration. opcache.huge_code_pages=0
; Validate cached file permissions. opcache.validate_permission=0
; Prevent name collisions in chroot'ed environment. opcache.validate_root=0
; If specified, it produces opcode dumps for debugging different stages of ; optimizations. opcache.opt_debug_level=0
; Specifies a PHP script that is going to be compiled and executed at server ; start-up. ; http://php.net/opcache.preload opcache.preload=
; Preloading code as root is not allowed for security reasons. This directive ; facilitates to let the preloading to be run as another user. ; http://php.net/opcache.preload_user opcache.preload_user=
; Prevents caching files that are less than this number of seconds old. It ; protects from caching of incompletely updated files. In case all file updates ; on your site are atomic, you may increase performance by setting it to "0". opcache.file_update_protection=2
; Absolute path used to store shared lockfiles (for *nix only). opcache.lockfile_path=/tmp
[curl] ; A default value for the CURLOPT_CAINFO option. This is required to be an ; absolute path. curl.cainfo="C:\xampp\apache\bin\curl-ca-bundle.crt"
[openssl] ; The location of a Certificate Authority (CA) file on the local filesystem ; to use when verifying the identity of SSL/TLS peers. Most users should ; not specify a value for this directive as PHP will attempt to use the ; OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified, this value may still ; be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "cafile" SSL stream context ; option. openssl.cafile="C:\xampp\apache\bin\curl-ca-bundle.crt"
; If openssl.cafile is not specified or if the CA file is not found, the ; directory pointed to by openssl.capath is searched for a suitable ; certificate. This value must be a correctly hashed certificate directory. ; Most users should not specify a value for this directive as PHP will ; attempt to use the OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified, ; this value may still be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "capath" ; SSL stream context option. ;openssl.capath=
[ffi] ; FFI API restriction. Possible values: ; "preload" - enabled in CLI scripts and preloaded files (default) ; "false" - always disabled ; "true" - always enabled ;ffi.enable=preload
; List of headers files to preload, wildcard patterns allowed. ;ffi.preload= [Syslog] define_syslog_variables=Off [Session] define_syslog_variables=Off [Date] date.timezone=Europe/Berlin [MySQL] mysql.allow_local_infile=On mysql.allow_persistent=On mysql.cache_size=2000 mysql.max_persistent=-1 mysql.max_link=-1 mysql.default_port=3306 mysql.default_socket="MySQL" mysql.connect_timeout=3 mysql.trace_mode=Off [Sybase-CT] sybct.allow_persistent=On sybct.max_persistent=-1 sybct.max_links=-1 sybct.min_server_severity=10 sybct.min_client_severity=10 [MSSQL] mssql.allow_persistent=On mssql.max_persistent=-1 mssql.max_links=-1 mssql.min_error_severity=10 mssql.min_message_severity=10 mssql.compatability_mode=Off mssql.secure_connection=Off
0 notes
Text
Data Quality Operations
Identification Analysis
To take advantage of the value of your data, you need to know the types of data that you have. Identification Analysis helps you understand your data by naming the type of the content in each variable. Identifying your data enables data profiling, data preparation, data cleansing, and data analysis.
Identification Analysis generates text classifications; it does not determine the database data type of your data, such as CHAR, BOOLEAN, or INTEGER. Instead, Identification Analysis reads text values and determines the semantic type of those values.
The output of Identification Analysis is a named classification that is known as an identity. The following example shows how identities are derived from text values:
Gender Analysis
When your data represents individual persons, you can analyze that data to determine the gender of each person. Gender data can be useful in subsequent statistical analysis, particularly in the domains of medical reporting and product marketing.
The input for Gender Analysis is a text string, and the output is gender code, as shown in the following example:
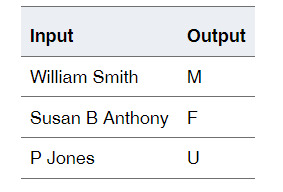
Parsing Parsing breaks a text string into a set of constituent sub-strings. The sub-strings represent a set of semantically atomic portions of the original string. In other words, each of the outputs has meaning in its own right.
For example, consider the sub-strings that can make up a person’s name. Most names contain a given name and a family name. A given name and a family name both have meaning of their own. You can use a Parsing operation to generate separate instances of the given name and family name:
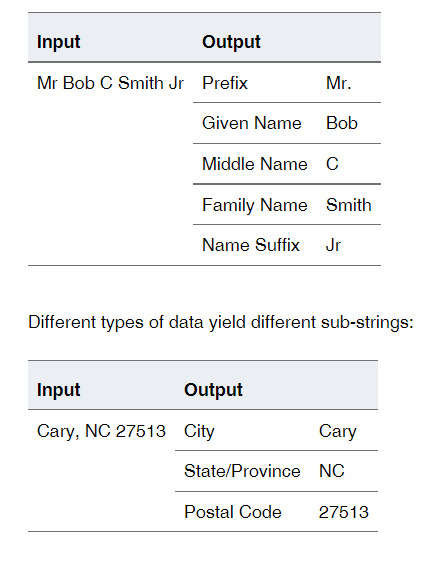
Extraction Sometimes, even in relational data, you can have text strings with little or no structure. It might not always be possible to parse such strings into constituent components. Instead, you might want to simply scan the string and extract a few meaningful attributes. An example of such an Extraction operation is as follows:
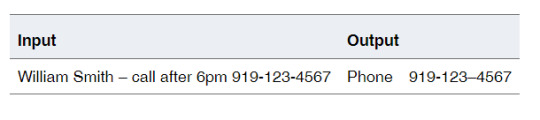
Standardization Standardization transforms text strings by rendering them in a preferred format. A Standardization operation can rearrange words, change individual words or symbols, and apply casing rules.
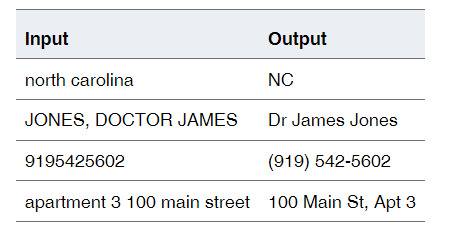
Matching
Matching operations provide a way to apply fuzzy matching logic in various data cleansing and data integration operations. You can use fuzzy matching logic to find and remove duplicate records, implement fuzzy searches, perform fuzzy joins, and more.
Matching operations are based on the generation of text strings called matchcodes. A matchcode is a fuzzy representation of an input text string. If two or more text strings yield the same matchcode, then those strings match. For example, the following records constitute a match:

You perform fuzzy matching operations by generating matchcodes for your data and then sorting and comparing the matchcodes, or using them as criteria for joins or other data integration operations.
Reference:
https://documentation.sas.com/doc/en/dqcdc/3.5/dqgs/p04xj2uanyz22wn1mnyv7if0924n.htm
0 notes
Text
A lot of functions for .NET5
We have just released a lot of functions for .NET5 in a NuGet package that you can download for free. We collected in this package functions for everyday work to help you with claim, strings, enums, date and time, expressions…
ClaimExtensions Methods
Name Description


GetClaim Gets a claim from a list of claims


GetClaimValue Gets the value of the requested claim if it exists


HasRole Determines whether the specified role name has role.


HasRoles Determines whether the specified role name has roles.


UpdateClaim Updates a claim with a new value
Crypto
Name Description


BytesToHex Byteses to hexadecimal.


Decrypt Decrypts the specified data.


Encrypt Encrypts the specified data.


HexToBytes Hexadecimals to bytes.


RandomString Randoms the string (lowercase string)
DateExtensions Methods
Name Description


AscensionDay Calculate Ascencion day


AshWednesday Calculate Ash Wednesday


ChristmasDay Get the first day of christmas


DateDiff Dates the difference.


EasterSunday Calculate Easter Sunday day


FirstSundayOfAdvent Calculate the first Sunday of Advent


GetRandomDateTime Generate random DateTime between range


GoodFriday Calculate Good Friday


PalmSunday Calculate Palm Sunday


WhitSunday Calculate Whit Sunday
EnumerableExtensions Methods
Name Description


PickRandom<T>(IEnumerable<T>) Return a random item for an IEnumerable T


PickRandom<T>(IEnumerable<T>, Int32) Return a random item for an IEnumerable T


Shuffle<T>) Return source ordered by a new Guid
EnumExtension Methods
Name Description


GetLocalizedDescription Gets localized description


GetDescription<T> Gets the description.


ToEnum<T>(String) Extension method to return an enum value of type T for the given string.


ToEnum<T>(Int32) Extension method to return an enum value of type T for the given int.
ExpressionExtensions Methods
Name Description


And<T> Combines the first predicate with the second using the logical "and".


BuildPredicate<T> Builds the predicate.


Not<T> Negates the predicate.


Or<T> Combines the first predicate with the second using the logical "or".


Replace Replaces the specified search ex.
JsonSerializationExtension Methods
Name Description


ReadFromJsonFile<T> Reads an object instance from an Json file. Object type must have a parameterless constructor.


WriteToJsonFile<T> Writes the given object instance to a Json file. Object type must have a parameterless constructor.Only Public properties and variables will be written to the file. These can be any type though, even other classes.If there are public properties/variables that you do not want written to the file, decorate them with the [JsonIgnore] attribute.
ListExtensions Methods
Name Description


TrimSpace Remove spece for each element of a list of string
StringExtensions Methods
Name Description


CheckIPValid Checks the ip valid.


ExtractDomainNameFromURL Extract a domain name from a full URL


GetLast Gets the last.


IPToNumber Gets a number from a IPv4


IsDate Determines whether the specified date is date.


IsNumeric Is the numeric.


PadNumber Pads the number.


RandomString Returns a random string with random alphanumeric characters


RemoveSpecialCharacter Replace special character with another string


ReplaceSpace Replace spaces with another string


ReplaceSpecialCharacters Replace non-ASCII characters with their ASCII value


Right Return the last n characters from a string


StripHTML Remove all HTML tags from a string


SubstringBetween Takes a substring between two anchor strings (or the end of the string if that anchor is null)


TruncateString(String, Int32) Truncate a string after maxLength characters.


TruncateString(String, Int32, Boolean) Truncate a string after maxLength characters.
The post A lot of functions for .NET5 appeared first on PureSourceCode.
from WordPress https://www.puresourcecode.com/dotnet/net-core/a-lot-of-functions-for-net5/
0 notes
Text
Iris publishers-Online Journal of Complementary & Alternative Medicine (OJCAM)
Visualizing Traditional Chinese Medicine and Information Representation and Retrieval: Opportunities and Challenges in a New Era of Big Data
Authored by David C Mainenti*
Abstract
Computer-based medical diagnostic systems have seen tremendous growth since the 1950s, particularly with the arrival of personal computers, the Internet, portable devices, and big data analytical environments. Such technologies utilize the fundamental principles of information representation and retrieval (IRR) to solve complex questions pertaining to health and disease. However, since inception, such systems have virtually ignored traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) techniques, oftentimes due to their lack of success in randomized controlled trials. To this day, little is known about how TCM works scientifically and, yet, it remains an essential part of the world’s healthcare system, particularly in several Asian countries. As disease remains widespread across society, the diagnostic and treatment methods of TCM should be compared alongside Western medical models, in light of modern IRR techniques, to determine if a new, futuristic form of translational medicine can be developed that improves medical outcomes and reduces health care costs worldwide. This study analyzes all published research in SCOPUS relating to TCM and IRR for the period 1985-2020 and employs bibliometric techniques, multiple correspondence analysis, and data visualizations to investigate author productivity, collaborations, and research trends. Opportunities and challenges were discovered that will help identify future directions within the field as we enter a new era of data-intensive scientific discovery in medicine.
Keywords:Bibliometrics; Computer-based medical diagnostic systems; Data visualization; Herbal pharmaceutical technology; Multiple correspondence analysis; Traditional Chinese medicine; Information retrieval
Abbreviations:IRR: Information Representation and Retrieval; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; IoT: Internet of Things; AI: Artificial Intelligence; ISO: International Organization for Standardization
The Ecological Model
Since its creation thousands of years ago [1], scholars of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) have provided a wide variety of resources for biomedical and health science, comprised of published literature, medicinal materials, herbs, diagnostic matrices, clinical records, medical formularies, and the like. In many ways, the founders of TCM were true pioneers of information science – they identified problems affecting society in their day and consciously searched available data at the time, represented mainly by classical medical literature passed down from the sages of antiquity in chant and song prior to the development of the written record, in addition to plants and other natural substances garnered from the environment [2]. These early medical leaders proceeded to organize and index such information into influential works (e.g., primitive expert knowledge systems) to prevent the spread of epidemic disease so that all those who followed would have retrieval access to a robust decisioning mechanism designed to solve a host of medical issues [3]. These ancient systems, based primarily on natural patterns of disharmony, herbal medical information representation, and treatment models, resemble mathematical thinking based on the presence or absence of human biological information [4] and utilize a binary system of numbers and probabilities that closely identifies with the concept of bits and bytes that form the working principle found in our current computing environment [5].
With the advent of big data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, and society’s continued pursuit of optimal health and well-being, the idea of developing computer-aided medical decision-making using artificial intelligence (AI) models to simulate the deductive procedure of disease diagnosis is soon to become a common reality that laid roots down over forty years ago [6]. In the future, Samsung [7] predicts sensors embedded all around us monitoring our health in a continuous manner, linked to one giant AI network, picking up signs of illness, automatically nudging users to make healthier choices, acting as a virtual doctor, directing future medical research but also potentially ranking us and shifting health and life insurance premiums to a pay-as-you-live model. Through the use of information representation and retrieval (IRR) technology, medical data gathered from a multitude of sources can now be gleaned and aggregated with appropriate criteria for use in complex TCM algorithms that bridge gaps currently existing in Western diagnostic practices by imitating classical deductive and reasoning procedures for solving medical problems and recommending treatment protocols [8]. Unfortunately, the complexity of medical knowledge creates a number of IRR difficulties [9] including, but not limited to standardized data formats; formulated inputs; and good feature representation with efficient key factors of the target problem. This is further complicated [10] by the fact that there remains, to this day, no single system able to accurately read the many medical manuscripts written in numerous dialects and stored at different locations all over the world, a literary necessity to ground TCM theory with modern science, due to the historical nature of the medicine. In particular, due to thousands of years of medical development and evolution, regional cultural differences and language variations exist which, while providing a richness and diversity to the TCM terminology system, creates standardization problems with the modernization of this classical medical modality, especially when compared to Western medical systems [11], which also experience similar vocabulary issues. On top of this, the use of natural herbal medicinal and other applications such as acupuncture are widely viewed as experimental by the Western scientific community, due, in part, to the individualistic nature in which such modalities are prescribed to human beings. Moving forward, a shift in research ideology will be required, gravitating away from controlled clinical trials to big data based, informationrich experiments with IRR at its core and mobile technologies as a means to collect large volumes of TCM data in a quantitative manner. To identify research opportunities and challenges that may exist in the design and implementation of a TCM-based diagnostic and medical recommendation system, the purpose of this work is to perform a bibliometric analysis with data visualizations related to IRR and TCM, particularly through author, paper, and co-word analysis, so as to better understand the conceptual structure of the field.
Materials and Methods
Scopus® (http://www.scopus.com), considered by some to be the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature, including scientific journals, books and conference proceedings, was initially searched on October 9, 2019 and again on November 16, 2019 for all citations with the Boolean string [(“Chinese medicine”) AND (“information retrieval”) OR (“information representation”)] located in the article title, abstract, or keywords. The results of the search revealed 192 documents for the period 1985-2020; a BibTeX export file was saved and read into R, a free software environment for statistical computing and graphics (http://www.r-project.org), using bibliometrix [12], a tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. The function *readFiles* was initially used to create a single large character vector; this object was then converted into a data frame using the function *convert2df*, with cases corresponding to manuscripts and variables to field tags in the original export file, comprising all bibliographic attributes of each document based on Clarivate Analytics WoS Field Tag codified industry standards [13]. During data cleansing, four entries were removed from the data frame due to a lack of author and other document information: three represented conference proceeding introductions and a fourth represented an introductory chapter on semantic grid applications for traditional Chinese medicine.
Results and Discussion
Descriptive analysis
To begin, a descriptive analysis was performed on the bibliographic data frame using the function *biblioAnalysis*; a display of the main results are included in Table 1. A total of 188 documents from 105 sources and 899 author appearances were noted, including a collaboration index of 2.49. Figure 1 illustrates/+*-*/-*//-+ `` of publications per year for the collection period 1985-2020; one large spike occurs in 2006 (28 citations) which continues into 2008, followed by a dip and then another, slower increase cumulating in 2017. This trend mirrors publications on IRR in general, which also peaks in 2006, according to Scopus, representing the maturation of computer browsing and the initial transition to mobile smart devices.
Table 2 contains the top 10 most cited papers in the collection, with Kanehisa M, et al. [14] having been cited over 1,500 times for their work in Japan on computerizing disease information using pathway maps, all Japanese drugs (including every TCM herbal formula), and gene/molecule lists. The second most-cited paper, Tang JL, et al. [15], represents one of the oldest papers in the current collection and is a summary of issues relating to randomized controlled trials in TCM, specifically: lack of blinding; low sample sizes; using another, unproven TCM treatment as the control; not long-term in nature; incompleteness; lack of quantitative data; missing intention to treat; lack of data on baseline characteristics or side effects; short reporting; and presence of publication bias. The third most-cited paper [16], was published in an American Heart Association journal and concludes, in similar fashion, the insufficiency of TCM evidence in using herbal medicinal for stroke patients, due to bias from poor methodology, even though the agents used appeared to be potentially beneficial and nontoxic in nature. The fourth document with the most citations [17] discusses newly published guidelines and technical notes by the European Union, in collaboration with Chinese scientists, to encourage good practice in the collection, assessment, and publication of TCM literature. The fifth most-cited document [18] reviews advances in automated tongue diagnosis, a key requirement for the accurate gathering of quantitative data, while the sixth most-cited document [19] discusses the development of ontology for TCM IRR. Fang YC, et al. [20] and Qiao X, et al. [21] both discuss the creation of TCM databaes, while Wojcikowski K, et al. [22] again point to difficultie with randomized controlled trials in TCM, particularly relating to the use of herbal medicinals in the treatment of kidney disorders. The tenth most-cited document [23] concludes that text mining of TCM literature and clinical data carries with it the potential to clarify misunderstandings, but clear operational definitions are first required.
Table 3 lists total citations by country, along with average article citations; Japan leads this metric due to the Kanehisa M, et al. [24] document noted above, with China positioned strongly behind with 865 total citations. As expected, over 50% of the top 10 countries are located in Asia; the United States remains far behind in this research area with only 10 total citations related to one published article. Table 4 illustrates the top author countries in the collection, with China strongly in the lead with 109 articles (a frequency of 0.76224) – additionally, 89% of these articles (97) are considered single country publications. Given the nature of this data, TCM and IRR research in the East has been mainly conducted as single country publications (China, Hong Kong, Korea, and Japan) while Australia, Canada, and Germany research has been more multicountry in nature.
Table 5 lists the top 10 most productive authors in the collection, based on both number of published articles (full counting) and number of published articles fractionalized (which assigns coauthored publications a fraction of one to each of the co-authors); studies have illustrated that, oftentimes, fractional counting offers a more useful perspective than full counting, especially as a means to avoid misunderstanding or misinterpretation [25]. Fractionalized counting does not affect the most productive author (Zhang Y) but does shift the order of the others slightly and results in the appearance of one new author (Xiong X) in the top 10.
Figure 2 applies the *authorProdOverTime* function on the collection to calculate and visualize the production of these top 10 authors over time, in terms of number of publications and total citations per year, for the period 1985-2020. This illustration clearly depicts the top producing author (Zhang Y) as covering both a wide period (2005-2019) along with more recent proliferation, oftentimes as a co-author, as noted by the number of articles fractionalized (2.09). Other authors with more recent production include Yu T (8 overall publications), Li J and Wang Y (6 overall publications each), and Liu L (5 overall publications).
Table 6 contains the top 10 most frequent journals, based on number of published articles in the collection – led by the Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation with 25 articles and followed by Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine with 11 publications. However, it is important to also look at this data from the perspective of number of documents published annually; this information for each of the top five sources is visualized in Fig. 3 using the function *sourceGrowth*, which illustrates that the Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation was only in existence from 2002-2006. Since then, four newer journals have increased their publication rate, particularly Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, which is second in number of articles but clearly the leading publication in this field, particularly as the journal currently holds an h-index of 72 and sits as the sixth ranked journal in complementary and alternative medicine [26].
Table 4: Top 10 corresponding author’s countries.
Table 5: Top 10 Most productive authors.
Table 6: Top 10 Most frequent journals.
Table 7: Top 10 Most frequent keywords.
Table 8: Historiograph legend.
Table 7 contains the top 10 most frequent keywords using two keyword variations: authors’ keywords, as specifically selected by each author, and keywords-plus, which are those keywords extracted from the publication by Scopus’ database algorithms. The results vary, with keywords-plus identifying many more in common across the collection – for example, information retrieval was only selected by seven authors as a keyword but appears 173 times as a keywords-plus. Overall, while keywords-plus is as effective as authors’ keywords in terms of bibliometric analysis investigating the knowledge structure of a particular field, it is often less comprehensive in representing an article’s specific content [27]. However, within this collection, the use of keywords-plus may lead to a greater understanding than simply using those keywords identified by the authors, due to the increased volume and commonality of terms; this is particularly evident in Figure 4a and Figure 4b, which clearly illustrate greater and more prolific growth of keyword-plus over time, as compared to authors’ keywords.
Network visualizations
To summarize the activity of top authors, journals and keywords presented below, Figure 5 employs the *threeFieldsPlot* function to generate a Sankey diagram that visualizes multiple attributes at the same time; top authors on the left, top author keywords in the center, and major cited references on the right. The width of the bands is linearly proportional to frequency, and the size of the boxes correspond to overall production.
Figure 6 visualizes scientific collaboration networks in and across countries using the *biblioNetwork* function to develop each matrix and the *networkPlot* function to illustrate it. A sphere layout is used with the size of the sphere correlating to overall production, lines density relating to collaboration strength, and color relating to the nature of the collaboration. As expected, the majority of research is clustered in and around China, particularly with Western countries, while six additional countries are illustrated as working independently (Taiwan, Brazil, Japan, Spain, Hungary, and Korea). The main collaboration networks, however faint, are represented by Germany-United Kingdom-China, USACanada- China, and Singapore-China, based on the density of the lines.
Figure 7 depicts a word co-occurrence network that maps and clusters terms extracted from author abstracts. The *termExtraction* function was first used with word stemming to gather this information from the textual abstract field of each manuscript. In this visualization, TCM stands alone at the bottom left in its relation to the larger clusters of information science (red), herbology (green), and biomedicine (blue). Similarly, Figure 8 illustrates author keyword co-occurrences, which follows a similar pattern as to the extracted words from the author abstracts but, due to each individual author’s knowledge of the work during the keyword selection process, this visualization displays in a more orderly fashion, showing a logical progression from TCM, through a main section of information retrieval, to herbology, and ultimately across to Western biomedicine.
Visualizing influential papers
In each and every scientific field, a number of publications play influential roles in its evolution; these articles and their impacts can be accelerating factors in research development [28]. It is therefore important to identify and visualize the most influential articles on TCM and IRR published between 1985 and 2020, in order to better understand the nature and chronology of the field through its key authors, papers, and subjects. Using the *histNetwork* function, we created a historical citation network from the collection, using a minimum number of one global citation for the documents included in the analysis (see Table 8 for legend). We then employed the *histPlot* function to plot the historical co-citation network in the style of Garfield [29], using both local and total citation distributions; nodes displayed in Fig. 9 identify the thirty two specific articles identified in the collection and sort the main bibliography in ascending order by year. Each circle represents a paper, and arrows, pointing from one node to the next (usually to an older paper), indicates the citation relationship between these key works.
In the historiograph for TCM and IRR, the paper by Tang JL, et al. [30] serves as the first work noted and surveyed the efficacy of randomized controlled trials in TCM literature; this spurned a line of research (highlighted in blue) extending to Flower A, et al. [31] who advocated for the Delphi method, Sampson M, et al. [32] who searched for additional databases to identify more successful controlled trials, and Jiang M, et al. [33] who evaluated evidencebased literature for TCM diagnosis and knowledge discovery.
The second and most dominant area of research in Figure 9 (highlighted in red) focuses on TCM information databases and begins with Chang IM [34] who investigated anti-aging and healthpromoting elements derived from traditional herbal remedies found in the Traditional Oriental Medicine Database, leading to future research by Boehm K, et al. [35], who provided an overview of 45 published database resources for complementary and alternative medicine. Bensoussan A, et al. [36] established research goals for the search and retrieval of scientific evidence regarding the toxicity of Chinese herbal medicine, which contributed to Wang JF, et al. [37] and the construction of a TCM information database. Qiao X, et al. [38] created a structured database of components extracted from TCM herbs, while Zhou X, et al. [39] wrote an influential paper (5 local citations) that used ontology to construct a unified TCM language system for information retrieval and integration. This led to Zhou X, et al. [40], which investigated research issues regarding TCM text mining, You M, et al. [41], who developed an intelligent system for customized clinical TCM case management and analysis, Wan H, et al. [42], who constructed a heterogeneous factor graph model for extracting relations from TCM literature, and Yu T, et al. [43], who utilized semantic web technologies to build cross-cultural communication between TCM and Western medicine.
A third, smaller research group in Fig. 9 (highlighted in green) begins with Ka WF [56], who introduced journals and other TCM research materials available online and May BH, et al. [57], who searched English and Chinese databases to review the effectiveness and safety of Chinese herbal medicines for use in the treatment of cognitive and memory impairment. These two works led to additional research by May BH, et al. [58], comparing and evaluating published TCM collections for research and drug discovery searches, and May BH, et al. [59], who searched a database of over 1,000 classical and pre-modern TCM texts for the treatment of memory impairment. A fourth research group was also mapped on the historiograph (highlighted in purple) relating to difficulties in drawing clinical conclusions in the treatment of specific Western medicine disorders with TCM: Xiong X [60] reviewed an article on randomized controlled trials for the treatment of cardiovascular disease with TCM, while Xiong X, et al. [61] researched the clinical effects of a TCM herbal decoction in the treatment of hypertension. A fifth and final research group (highlighted in yellow), albeit small, begins late and relates to the standardization of TCM: Liu YQ, et al. [62] focused on standards and proposals established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which Yoon SH, et al. [63] built from this to investigate the pros and cons of proposing standard terminology for acupotomy, a treatment modality which involves the use of both an acupuncture needle and a surgical scalpel. These five pathways of research in TCM and IRR help illustrate both the research difficulties in the field as well as opportunities in the treatment of specific diseases and the construction of modern databases and ontologies for the future use of this medical modality.
Visualizing the conceptual structure of the field
Multiple correspondence analysis is an exploratory multivariate technique that allows for the graphical and numerical analysis of the patters in relationships of categorical dependent variables, such as keywords [64]. We used the *conceptualStructure* function to draw a conceptual map of the field using keywords-plus with a maximum of five clusters and no stemming. Results are interpreted based on the relative position of the points and their distribution across the dimensions; as words are more similar in distribution, the closer they are represented in Figure 10. According to Cuccurullo C, et al. [65], map data can be translated as follows: point size is proportional to the keyword’s absolute contribution; proximity between keywords corresponds to shared substance, or lack thereof; and the dimensions of the map reflect characteristic poles of topical orientation within TCM and IRR, with the middle of the map representing the average position of all the articles and thus the center of the research field.
Cluster one (highlighted in red) resides in the top right quadrant and contains keywords from articles that relate to the use of TCM herbs and natural substances as viable treatment options for both acute and chronic diseases. Cluster two (highlighted in blue) is the largest, residing in the middle and bottom center of the map; it contains keywords from articles that relate to the design of databases and retrieval systems for scientific TCM medical literature (including Zhou X, et al. [66]). The third cluster (highlighted in green), resides center left and contains keywords from articles specific to TCM diagnosis, ontology, and data mining. Cluster four (highlighted in purple) resides in the lower right quadrant and contains keywords from articles relating to the success, or lack thereof, of evidence-based research and TCM, particularly as it pertains to clinical trials. Cluster five (highlighted in orange) resides in the top left-center quadrant and contains keywords from articles relating to the representation of TCM information in IRR systems.
From this conceptual structure analysis, one can see that the first dimension of published research extends horizontally from theoretical on the left to experimental on the right. The second dimension, extending vertically, defines published works and their keywords over a spectrum ranging from technical on the top to clinical on the bottom. There are clear research gaps in the upper and lower left quadrants, indicating that more scientific research is required to ground both clinical and technical IRR work in TCM theory – an area we know is sorely lacking at the time, due to the fact that TCM is an individualized medicine, treating each patient according to their specific pattern of disharmony, gleaned from information gathered mainly, at this point, through quantitativelybased examinations performed by human beings. As a result, a great portion of research exists on the right side of the map that is considered, according to Western biomedicine, to be experimental in nature – namely Chinese herbal pharmaceutical medicine, its integration with biomedicine, and the lack of success to date with measuring TCM treatment outcomes and drug efficacy in controlled trials. This map, therefore, charts the course for where future research should be headed as it relates to TCM and IRR – to employ new research paradigms and instruments, namely big data analytics and IoT technologies, to merge Eastern and Western medicine together, in a translational way, so as to better understand the nature of disease progression and its effects on the body.
Conclusion
It may be time for the broad discipline of information studies to come out of its proverbial shell; in the future of both Samsung [67] and Sinclair DA, et al. [68], as our lives become monitored, accentuated and refined as a means to achieve a new state of existence, behind and underneath it all will be a vast, universallyencompassing network of medical IRR systems. Such structures have already begun to take shape in other areas of existence: industry is refining algorithms that learn our preferences, activities, motives, and bioactivities; cars have begun to program themselves to reach destinations; drivers are learning where passengers are headed, before they actually meet them; and music is constantly indexed and streamed around the world across language and culture. These systems all require underlying IRR architecture so that the consumer, the device, the network, and the provider can communicate digitally, behind the scenes, in a grand dance of capitalistic-driven mobile technology. However, by applying these conceptual structures to problems like ancient TCM practitioners faced but with new goals of health and well-being over profit and market share, one could only image if, in the future, through a combination of TCM and IRR, we might be able to one day think out at least half of our medical problems. Such a vision is worth pursuing, particularly in times where many diseases, especially chronic ones like obesity and mental illness, appear to be on the upswing. Further TCM research is therefore warranted, particularly with respect to IRR as it relates to grounding modern research, both clinical and technical, with classical theory. In the style of Jim Gray’s vision of scientific discovery, driven by the collection, analysis, and comprehension of digital data by an ever-increasing interdisciplinary community of both professional and citizen-like scientists alike [69], perhaps the future of TCM lies in a big data design and deployment methodology with a new medical IRR at its core that is translational in nature, reducing health care costs and improving medical outcomes worldwide.
To read more about this article: https://irispublishers.com/ojcam/fulltext/visualizing-traditional-chinese-medicine-and-information-representation.ID.000631.php
Indexing List of Iris Publishers: https://medium.com/@irispublishers/what-is-the-indexing-list-of-iris-publishers-4ace353e4eee
Iris publishers google scholar citations:
https://scholar.google.co.in/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=irispublishers&btnG=
0 notes