#Building Codes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hey, I'll fucking take it. Cheers to avoiding rampant public safety disasters and strobing-induced seizures!
--
"A brightly flashing “X” sign has been removed from the San Francisco headquarters of the company formerly known as Twitter just days after it was installed.
The San Francisco Department of Building Inspection said Monday it received 24 complaints about the unpermitted structure over the weekend. Complaints included concerns about its structural safety and illumination."
-via AP, July 31, 2023
#twitter#twitter drama#elon twitter#twitter rebrand#social media#elon musk#elongated muskrat#epilepsy#photosensitivity#seizures#public safety#building codes#united states#san francisco#good news
874 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cornelia Oberlanders's "Stramp", stairs with a ramp incorporated for those with accessibility needs.
#stairs#staircase#Cornelia Oberlanders#stramp#canadian#architecture#architect design#wheelchair#wheelchair accessible#accessibility#vancouver#building codes#university#urbanism#landscape#ramp stairs#crazy stairs
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can’t wait for the Trump administration to get rid of building and fire codes and workplace safety requirements on the grounds that they are overly burdensome and government overreach government. Imagine how much money they could save if they didn’t have to buy so many fire extinguishers!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Urgent Action - Comment by 6/15/25
Want accessibility in federally funded buildings to continue? Please check this out and comment on the proposed regulation changes. https://www.respectability.org/act/accessible-buildings-doe/
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is currently working to quietly rollback two regulations that help implement Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act: 10 CFR 1040.73 and 10 CFR 1040.72(c) & (d). These regulations guarantee individuals with disabilities the right to access buildings constructed or modified with federal funding, as well as require existing facilities to have a plan to remove access barriers over time.
If this change is implemented, builders would no longer be required to meet established accessibility standards, such as providing elevators, ramps, accessible bathrooms, as well as the placement of accessories, such as changing tables, grab bars, towel dispensers, etc.
These changes would represent a significant setback for disability rights and could undermine years of progress toward ensuring access for all.
#disability#disabled#accessibility#building codes#regulations#roll back#public comment#action needed
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
About Here (Uytae Lee) looks at why the double-staircase building code limits apartments to one-bedroom or studios, meaning family-sized multi-room apartments can’t be built.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Decoding Density
#video#urban planning#apartments#building codes#north america#Canada#united states#Europe#Seattle#architecture#Youtube
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Modular vs. Manufactured Homes: Making the Right Choice

Choosing a new home can feel overwhelming. Many terms cause real confusion. People often mix up modular vs manufactured homes. I certainly did at first. It seems like "mobile home" is used for everything. However, significant differences exist. These impact your finances and daily life. Both are factory-built. Both generally cost less than traditional houses. Yet, their similarities largely end there.
Built Differently: Key Distinctions
Let's dive into what sets them apart. Imagine building a house. Manufactured homes follow a different path. They are entirely built in a factory. They sit on a permanent steel frame with wheels. This allows for quick setup once delivered. These homes adhere to federal HUD building codes. HUD inspectors check them at the factory. These codes ensure basic safety. Think of vinyl siding and lighter materials. This construction method is efficient. A double-wide can be produced in about a week.
Modular homes are quite different. They are built in sections, or "modules," in a factory. These sections are transported on flatbed trucks. A crane then lifts each piece onto your land. They are assembled on a permanent foundation. Critically, modular homes must meet all local building codes. This includes the International Residential Code (IRC). So, a modular home in a snowy area is as strong as any site-built house. They use materials identical to traditional construction. Often, they feature sturdy 2x6 exterior walls. This differs from the 2x4 construction seen in manufactured homes. Once finished, they often look just like regular houses.
The Financial Impact: Value and Loans
And then there is the investment. This is a significant consideration. Manufactured homes generally lose value. They depreciate, just like automobiles. They lose roughly 3-5% in value per year. Modular homes appreciate. They appreciate just like sticks and bricks. They gain roughly 1-4% in value per year. In ten years, this could flip your equity by 30-80%. That is a tremendous financial effect.
Financing also varies greatly. Manufactured homes often have higher interest rates. Their loan terms are shorter. For example, a chattel loan might be 8-9% over 15-20 years. Modular homes qualify for conventional mortgages. These are similar to site-built homes. Interest rates are lower, around 6-7% over 30 years. This difference truly adds up. A $150,000 loan could mean $60,000 more in interest for a manufactured home.
Other Important Considerations
Insurance Costs: Manufactured homes often cost 15-20% more to insure. They also have more coverage limitations. Modular home insurance costs are comparable to traditional homes.
Energy Efficiency: Modular homes can have 20-40% lower energy bills. This is due to better insulation.
Legal Status: Manufactured homes are often personal property. Modular homes are always real estate. This affects taxes and resale.
Design Flexibility: Manufactured homes offer some variety. However, structural changes are not possible after construction. Modular homes provide much more design freedom. Custom floor plans are available. Multi-story designs are common. You can choose nearly any exterior finish. This flexibility is a key advantage.
Knowing these differences is important. It enables you to make an educated choice for your home ownership experience.
Ready to fund your next home? Sky-Root specializes in helping homeowners navigate these important housing decisions with confidence. Our team guides you through every step of the process, from initial planning to move-in day, ensuring you make informed choices that align with your vision and budget. Schedule a consultation with our housing experts.
#Modular Homes#Manufactured Homes#Home Buying#Real Estate#Housing#Home Ownership#Building Codes#HUD#Home Loans#Property Value#Pre-fabricated Homes#Housing Comparison
0 notes
Text
Spending the evening in any building in the US
#America#housing#housing codes#up to code#black mold#mold#black mold welcome#wood sticks#basically#plywood#america has a problem#healthcare#american healthcare#health#chronic illness#mold toxicity#mold illness#crawl space#basement#Midwest#flooding#school#school buildings#building codes#us architecture#USA#the united states of america#the USA#careless#government
0 notes
Text
The Legal Risks of Converting Single-Family Homes Into Multifamily Units

Key TakeawaysConverting single-family homes into multifamily units involves navigating complex legal challenges such as zoning battles, board approvals, and obtaining costly permits.There are additional requirements to address, including fire safety retrofits, insurance increases, stricter building codes, and heightened landlord liability with each new tenant.Failing to adhere to zoning laws or building codes can result in fines, delays, or even litigation, making it crucial for investors to be meticulous in their planning. Navigating the Legal Maze of Property ConversionWhen you convert a single-family home into multifamily units, you’re stepping straight into legal quicksand—think zoning battles, board approvals, and costly permits. You’ll need to steer through fire safety retrofits, insurance hikes, stricter building codes, and face increased landlord liability with every new tenant.If you miss a zoning detail or violate building codes, expect fines, delays, or litigation.Wondering how savvy investors sidestep legal landmines and still profit? You’re about to find out.Zoning Laws and Approval RoadblocksEven if you spot a single-family home with multifamily potential, zoning laws often stand between ambition and opportunity. You’ll quickly realize that zoning classifications—the rules dictating single-family versus multifamily use—vary dramatically, city by city.Before moving forward, you must apply for zoning variances and secure permission from local boards, typically through public Board of Adjustment hearings. Neighborhood opposition can derail your plans, as neighbors frequently voice concerns about increased density or character changes. Understanding long-term success in real estate often means anticipating these types of community objections and preparing solutions in advance.Sometimes, jurisdictions offer zoning exceptions, but these rarely come without lengthy debates and strict scrutiny. Realistically, expect requirements for community impact assessments, limitations on the number of units, and infrastructure reviews. Properties must also meet specific safety and building code requirements, such as having separate exits and adequate fire protection for each new unit.Will your idea withstand these legal tests? Knowing the common roadblocks and local sentiment helps you prepare and strategize effectively.Building Code Compliance and Permit ChallengesOnce you’ve cleared the zoning gauntlet, you’ll find the regulatory game is far from over. Building code compliance and permit challenges can make or break your conversion. You must adhere to structural requirements under the International Building Code, ensuring your property can handle added weight and stress.Fire safety compliance is essential—multifamily units require upgrades like fire-rated doors and modern alarms, meeting the International Fire Code’s strict guidelines. Ensuring you work with qualified inspectors is crucial to accurately identify all necessary upgrades and prevent missed violations. Don’t underestimate the complexity of obtaining permits—each system, from electrical to mechanical, demands its paperwork and inspections.Retrofitting older homes often reveals unexpected cost hurdles.Inspectors may interpret codes differently, causing frustrating project delays.Failing to meet requirements can lead to hefty fines, future liability, or even ordered removal.Staying proactive and informed is your best defense. In many jurisdictions, facility-specific designations such as halfway houses or residential care homes have distinct requirements under land use regulations, meaning conversions may trigger additional standards or approvals.Nonconforming Use ComplicationsIf you’re eyeing a single-family home in a neighborhood that’s shifted its zoning rules over the years, you’re stepping into the complicated arena of nonconforming use. You’ll find that nonconforming homes—grandfathered under old zoning—face tough hurdles when converting to multifamily units. Municipalities
safeguard neighborhood character with strict zoning enforcement, and historical preservation concerns often clash with your development plans. Ensuring compliance prevents legal issues in subdivision projects, so overlooking current zoning or permit requirements could jeopardize your entire investment. Neighbor complaints due to aesthetic conflicts and density worries frequently lead to legal disputes or even court battles. In addition, investing in proper surface preparation can help boost curb appeal and strengthen your case for community acceptance or future resale value.Here’s a breakdown to clarify these risks:ChallengeKey Risk or BarrierZoning NonconformanceLegal disputes, finesHistorical PreservationRestrictions, delaysAesthetic ConflictsNeighbor oppositionRegulatory BarriersFuture development restrictionsCommunity ResistanceLoss of neighborhood characterIncreased Landlord Liability and Tenant RisksZoning hurdles are just the start—once you’ve steered through nonconforming use, you’re faced with a different set of legal hazards as a landlord. Converting a single-family home into multifamily units triggers new layers of responsibility, particularly relating to tenant rights and safety standards. Legal precedents in the real estate field have shown that ignoring these responsibilities increases your exposure to fraud allegations and other serious liabilities.You’re now on the hook for stricter code compliance and must verify tenants’ living spaces remain safe and habitable at every stage.You’re required to maintain rigorous safety standards and respond to tenant repair requests promptly.Tenants gain eviction protections and limits on rent increases, which you must guide carefully to avoid legal trouble. Maintenance costs are usually lower for single-family homes compared to multi-family properties, so after conversion, you should account for higher ongoing expenses and plan for more frequent repairs and inspections.Disclosures, notices, and participation in public hearings become mandatory parts of the conversion process.Failing to comply can expose you to fines, lawsuits, and damaged tenant relationships.Financial and Insurance ConsequencesEvery conversion from a single-family home to multifamily living reshapes your financial terrain, often in ways investors don’t expect until the bills come due. Are you ready for higher upfront costs, larger mortgage payments, and insurance premiums that climb with each added unit? Strategic financial planning becomes critical—not just to manage cash flow but also to anticipate ongoing expenses that come with zoning, regulatory compliance, and multi-unit maintenance. Local zoning regulations can restrict or prohibit multifamily conversions, and failing to comply can result in costly legal challenges or mandated removal of additional units. Considering the need for comprehensive agreements between partners can also help prevent misunderstandings about shared financial responsibilities in these projects. Take a closer look at some financial and insurance impacts:Cost FactorMultifamily ImpactUpfront Renovationmarkedly higherMortgage PaymentsLarger and harder to financeInsurance PremiumsIncreased liability & risk coverageTax/Accounting ComplexityMore sophisticated requirementsWithout diligent planning, the dream of high rental yields risks being overwhelmed by unanticipated financial pressures and rising premiums.AssessmentConverting a single-family home into a multifamily unit can feel like navigating a river with shifting currents.You need the right map, or you might run aground.Zoning, building codes, and liability are all lurking below the surface.So, have you charted every legal eddy?With some foresight and legal know-how, you'll steer clear of disaster and reach profitable shores.Don't just drift—take control of your investment with diligence, strategy, and expert advice.Are you ready to transform risk into reward?The current is yours to command.Take the next step today and consult with a legal expert to ensure a smooth journey.
0 notes
Text
Colorado Senate Bill 2: Regional Building Codes for Factory-Built Structures
0 notes
Text
Tips for Installing Budget Cable Railing with Muzata
If you're considering installing a budget cable railing system, Muzata is an excellent brand to explore. With their innovative designs and high-quality materials, you can achieve a stylish look without breaking the bank.
Here are some helpful tips for installing your Muzata cable railing:
Measure Carefully: Before purchasing your materials, take measurements of your railing area. This will ensure you buy the right amount of cable and fittings.
Choose the Right Materials: Muzata offers a variety of cable railing kits, so select the one that best fits your style and needs. Stainless steel cables are durable and provide a sleek appearance.
Follow the Instructions: Muzata provides clear installation instructions. Be sure to follow them step-by-step to ensure a successful installation.
Use the Right Tools: Having the right tools on hand can make the installation process smoother. Common tools you might need include a drill, level, and cable cutters.
Check Local Building Codes: Before you start, check your local building codes to ensure your installation meets safety standards.
Take Your Time: Rushing through the installation can lead to mistakes. Take your time to ensure everything is installed correctly for a safe and attractive result.
With these tips, you'll be well on your way to installing a beautiful and functional cable railing system with Muzata. Enjoy your new space!
0 notes
Text
I have a question for any prospective City planning students or anyone with a passing interest in it:
What are the worst design decisions you could have when planning a city from the ground up? the antithesis of human-friendly architecture?
I'm talking borderline code violation stuff. Cruel and unusual punishment type shit.
I ask because I have this idea for a noir story that takes place in the worst city in the world. I have an Idea about what that place looks like, but I don't know any design elements for urban environments that are objectively incorrect that would be incorporated into the city.
I would greatly appreciate any response!
#urban planning#infrastructure#bad design#noir#pulp magazine#pulp art#comic art#sin city#city planners on tumblr#Any other noir recommends along the lines of Sin City?#architecture#buildings#building codes
0 notes
Text
Building Codes and Regulations: Guide for Safe and Compliant Construction

Building codes and regulations are an essential aspect of construction that ensure the safety, functionality, and sustainability of structures. Whether you're developing a residential home, commercial building, or industrial facility, compliance with these codes is not only mandatory but crucial for the long-term integrity of the project.
This blog post provides an overview of building codes and regulations, highlighting their importance, the key areas they cover, and how to navigate the compliance process.
What Are Building Codes and Regulations?

Building codes are a set of standards that govern the design, construction, alteration, and maintenance of buildings. They are designed to ensure structures are safe, accessible, and durable, addressing various aspects such as fire safety, structural integrity, electrical systems, plumbing, and energy efficiency.
Building regulations are legal requirements enforced by local or national authorities to ensure compliance with these codes. They may vary by region, but the goal is to protect the health, safety, and welfare of the public.
Why Are Building Codes Important?
Building codes serve several crucial purposes:
Safety: The primary goal of building codes is to ensure that buildings are safe for occupants. They set standards for structural strength, fire prevention, emergency exits, and other safety measures that reduce the risk of accidents, injuries, or fatalities.
Health: Codes regulate ventilation, lighting, plumbing, and heating to create healthy living and working environments. Proper air circulation, clean water supply, and sanitary facilities all contribute to the health and well-being of occupants.
Energy Efficiency: Modern building codes often include provisions for energy-efficient design, reducing the environmental impact of buildings. This can lead to significant savings on energy bills and contribute to sustainability efforts.
Accessibility: Building codes ensure that structures are accessible to people with disabilities. This includes standards for ramps, elevators, wide doorways, and accessible restrooms, promoting inclusivity.
Key Areas Covered by Building Codes
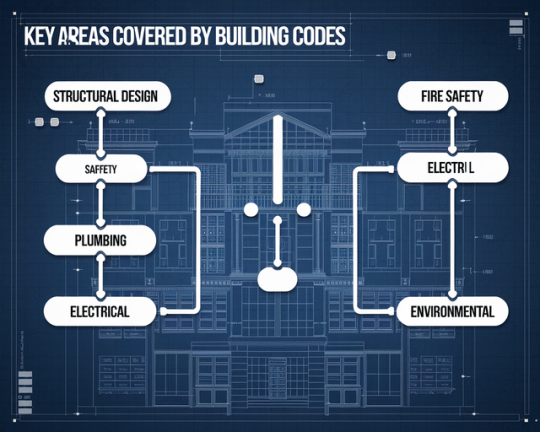
Building codes cover a wide range of areas to ensure that all aspects of construction meet safety and functional standards.
Here are some of the key areas:
Structural Integrity: This section covers the strength and stability of the building. It includes requirements for the foundation, load-bearing walls, floors, and roofs to ensure the building can withstand external forces such as wind, earthquakes, and snow loads.
Fire Safety: Fire safety regulations are critical for protecting both property and human life. This includes the installation of fire alarms, smoke detectors, fire exits, sprinkler systems, and the use of fire-resistant materials.
Electrical Systems: Building codes outline the safe installation of electrical wiring, outlets, lighting, and appliances to prevent electrical fires and accidents. It also includes guidelines for grounding, circuit protection, and load management.
Plumbing Systems: Plumbing codes regulate the installation of water supply lines, drainage systems, and sanitation facilities. They ensure clean drinking water, proper waste disposal, and the prevention of leaks or contamination.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): Codes in this area ensure that heating and cooling systems are installed safely and efficiently, promoting a comfortable indoor environment and energy savings.
Energy Efficiency: Energy codes dictate the use of energy-efficient materials and systems. This may include insulation requirements, window glazing standards, and the use of energy-saving appliances and lighting.
Accessibility Standards: These regulations ensure that buildings are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities. This includes accessible entrances, restrooms, elevators, and signage.
Navigating Building Code Compliance
Building code compliance is a vital step in any construction project. Here’s how to ensure your project meets all necessary standards:
1. Research Local Building Codes
Building codes can vary widely depending on the location of your project. Always check with local or regional authorities to obtain the most up-to-date regulations. In many countries, codes are standardized at the national level, but local amendments may apply.
2. Work with Qualified Professionals
Architects, engineers, and contractors should be well-versed in building codes and regulations. Hiring professionals who are knowledgeable about the specific codes in your area can save time and prevent costly mistakes during construction.
3. Obtain Necessary Permits
Before starting construction, you’ll need to obtain the necessary building permits from your local authority. The permitting process typically involves submitting detailed plans and specifications, which are reviewed to ensure they comply with all relevant codes.
4. Schedule Inspections
Throughout the construction process, inspectors will visit the site to ensure that the work complies with the approved plans and codes. Inspections typically cover critical phases such as foundation work, framing, electrical systems, and final completion. Failing an inspection may delay the project, so it’s crucial to adhere to codes from the outset.
5. Stay Updated on Code Changes
Building codes are regularly updated to incorporate new safety standards, technological advancements, and environmental considerations. Staying informed about these changes ensures that your projects remain compliant over time.
Consequences of Non-Compliance

Failing to comply with building codes can lead to a range of negative consequences:
Fines and Legal Penalties: Non-compliance may result in significant fines or legal action by authorities.
Project Delays: If an inspection uncovers code violations, construction may be halted until corrections are made, leading to costly delays.
Unsafe Buildings: Ignoring building codes can compromise the safety and integrity of the structure, putting occupants at risk of accidents, fires, or even structural collapse.
Decreased Property Value: Buildings that do not meet code standards may have lower market value or be more difficult to sell, as buyers will likely be concerned about safety and potential legal issues.
The Future of Building Codes
Building codes are continuously evolving to meet modern challenges, including climate change, technological advances, and growing urban populations. Future trends in building regulations may include:
Stricter Energy Efficiency Standards: With increasing focus on sustainability, building codes are expected to place greater emphasis on renewable energy sources, smart building systems, and net-zero energy designs.
Resilience to Natural Disasters: As climate change increases the frequency of extreme weather events, codes will likely require buildings to be more resilient to hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and earthquakes.
Technological Integration: As smart buildings and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies become more common, building codes will adapt to include standards for the integration of these advanced systems.
Conclusion
Building codes and regulations are a critical part of the construction process, ensuring that structures are safe, sustainable, and accessible. By understanding the purpose of building codes, the key areas they cover, and the steps to achieve compliance, you can ensure that your project is built to the highest standards. Failing to adhere to these regulations can have serious consequences, so it's essential to work with professionals and stay informed about the latest updates.
0 notes
Text
Regulations are written in blood.
1 note
·
View note