#C++ Boolean DataType
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
C++ Boolean DataType in Hindi | What is Boolean Data Type in C++ | C++ Tutorials
In C++, the bool data type is used to store Boolean values, which can be either true or false. This data type is commonly used in conditional statements and loops to represent binary states (true/false, yes/no, 1/0). For more details, Kindly check my website URL. https://www.removeload.com/cpp-boolean
0 notes
Text
C++ Datatypes
Here are the seven basic C++ data types:
Boolean
Character
Integer
Floating point
Double floating point
Valueless
Wide character
Many of these basic data types can be modified. If you want to dive further into the topic, go through the below link.

0 notes
Photo

Datatypes in python :: 1. Numeric datatypes:: Integer( for real numbers) Complex( for inputting the complex numbers) Float( for decimal numbers) 2. Dictionary:: dictionary is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. In Python dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and they have keys and values Eg:: thisdict = { "brand": "Ford", "model": "Mustang", "year": 1964 } print(thisdict) 3. Boolean:: In programming you often need to know if an expression is True or False. You can evaluate any expression in Python, and get one of two answers, True or False. When you compare two values, the expression is evaluated and Python returns the Boolean answer 4. Set:: set is an unordered collection of items. Every set element is unique (no duplicates) and must be immutable (cannot be changed). However, a set itself is mutable. We can add or remove items from it. Sets can also be used to perform mathematical set operations like union, intersection, symmetric difference, etc. 5. Strings:: String literals in python are surrounded by either single quotation marks, or double quotation marks. Enjoy the post ? Drop a like and comment If you like the content Do Like comment share save 🤍 💬 📲 📁 _____________________LIKE___ ------------------COMMENT----- ------------SHARE--------- ______SAVE ____________________________ For more updates Follow us Facebook :: https://m.facebook.com/Coding_basics-109490784148247/?ref=bookmarks Instagram :: https://www.instagram.com/coding_basics/ YouTube :: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLx9JC9ithJllNRyIBuUGnurkvLZ2MHCgs ______________________________________________ ************************************************** #programming #code #c #c++ #java #javaprogramming #c_basics #python #pythonprogramming #coding #program #progress #coding_with_chakri #c_programming_language #c++_programming_language #java_programming_language #input #output #input_statements #input #LEARN_APPLY_GROW #learn #apply #grow #basics #basictraining #codingbootcamp #suray #chakri #local #global ______________________________________________ *************************************************** https://www.instagram.com/p/CDJN7OwH5Du/?igshid=xhpxjrmyccen
#programming#code#c#java#javaprogramming#c_basics#python#pythonprogramming#coding#program#progress#coding_with_chakri#c_programming_language#java_programming_language#input#output#input_statements#learn_apply_grow#learn#apply#grow#basics#basictraining#codingbootcamp#suray#chakri#local#global
1 note
·
View note
Text
Data types in Python: Numeric Data Type
Python is a clear and powerful object-oriented programming language, comparable to Perl, Ruby, Scheme, or Java. In my last blog we have discussed the key features of python. Now we are going to dive into the programming concepts of python. In this blog we will discuss about data types used in the python
Data Types
Data types are the classification or categorization of data items. It represents the kind of value a particular variable can hold and tells what operations can be performed on that particular data.
Since everything is an object in Python programming, data types are actually classes and variables are instance (object) of these classes. The type of a variable in the python is decided by the type of value assigned to that variable.
Example:
# type() function is used to identify the datatype of variable or object.
>>> x = 10
>>> type(x)
<class 'int'>
>>> x = 10.0
>>> type(x)
<class 'float'>
>>> x = 5+8j
>>> type(x)
<class 'complex'>
>>> x = 'Mukesh'
>>> type(x)
<class 'str'>
>>> x = ['Mukesh','Kumar']
>>> type(x)
<class 'list'>
>>> x = ('Mukesh', 'Kumar')
>>> type(x)
<class 'tuple'>
>>> x = {'fname':'Mukesh', 'lname':'Kumar'}
>>> type(x)
<class 'dict'>
>>>
Built-in data type of python are as follows:
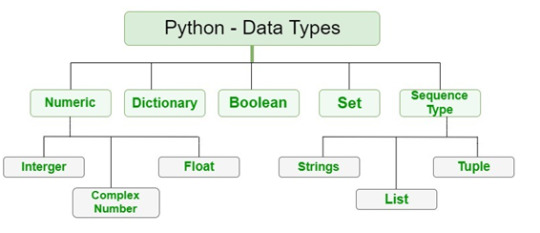

Let us discuss about Numeric Data type
Numbers
The Python interpreter acts as a simple calculator, You can write an expression and interpreter will display the value. Expression syntax is straight forward: the operators +, -, * and / work just like in most other languages (for example, Pascal or C); parentheses (()) can be used for grouping.
Examples
>>> 7 + 3
10
>>> 70 - 5*6
40
>>> (70 - 5*6) / 4
10.0
>>> 9 / 5 # division always returns a floating point number
1.8
There are three distinct numeric types: integers, floating point numbers, and complex numbers. In addition, Booleans are a subtype of integers.
Integers
This value is represented by ‘int’ class. It contains positive or negative whole numbers (without fraction or decimal). In Python there is no limit to how long an integer value can be.
Float
This value is represented by ‘float’ class. It is a real number with floating point representation and specified by a decimal point.
Complex Numbers
Complex number is represented by ‘complex’ class. It is specified as (real part) + (imaginary part)j. For example – 5+8j
Basic Operations on Numeric Type
The integer numbers (e.g. 2, 4, 20) have type ‘int’, the ones with a fractional part (e.g. 5.0, 1.6) have type ‘float’.
Division (/) always returns a float. To do floor division and get an integer result (discarding any fractional result) you can use the // operator; to calculate the remainder you can use %:
Examples
>>> 7+3 # addition operator
10
>>> 7-3 #minus operator
4
>>> 7*3 #multiplication operator
21
>>> 17 / 3 # classic division returns a float
5.666666666666667
>>>
>>> 17 // 3 # floor division discards the fractional part
5
>>> 17 % 3 # the % operator returns the remainder of the division
2
>>> 5 * 3 + 2 # result * divisor + remainder
17
With Python, it is possible to use the ** operator to calculate powers
>>> 5 ** 2 # 5 squared
25
>>> 2 ** 7 # 2 to the power of 7
128
The equal sign (=) is used to assign a value to a variable. Afterwards, no result is displayed before the next interactive prompt:
>>> width = 20
>>> height = 5 * 9
>>> width * height
900
If a variable is not “defined” (assigned a value), trying to use it will give you an error:
>>> n # try to access an undefined variable
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'n' is not defined
There is full support for floating point; operators with mixed type operands convert the integer operand to floating point:
>>> 4 * 3.75 - 1
14.0
In interactive mode, the last printed expression is assigned to the variable _. This means that when you are using Python as a desk calculator, it is somewhat easier to continue calculations, for example:
>>> tax = 12.5 / 100
>>> price = 100.50
>>> price * tax
12.5625
>>> price + _
113.0625
>>> round(_, 2)
113.06
This variable should be treated as read-only by the user. Don’t explicitly assign a value to it — you would create an independent local variable with the same name masking the built-in variable with its magic behavior.
All numeric types (except complex) support the following operations:
Operation
Result
Full documentation
x + y
sum of x and y
x – y
difference of x and y
x * y
product of x and y
x / y
quotient of x and y
x // y
floored quotient of x and y
x % y
remainder of x / y
-x
x negated
+x
x unchanged
abs(x)
absolute value or magnitude of x
abs()
int(x)
x converted to integer
int()
float(x)
x converted to floating point
float()
complex(re, im)
a complex number with real part ‘re’, imaginary part ‘im’. im defaults to zero.
complex()
c.conjugate()
conjugate of the complex number c
divmod(x, y)
the pair (x // y, x % y)
divmod()
pow(x, y)
x to the power y
pow()
x ** y
x to the power y

1 note
·
View note
Text
Detail DataTypes In Golang you should know 2019
New Post has been published on https://is.gd/3yYUgT
Detail DataTypes In Golang you should know 2019

In Detail DataTypes in Golang By Sagar Jaybhay
Part 1 – https://sagarjaybhay.net/google-go-tutorial-by-sagar-jaybhay-blog-1/
Part 2- https://sagarjaybhay.net/packages-and-golang-command-part-2/
The data types specify the data which is valid Go Variable. In Go programming language data types divided into 4 different categories.
Basic Data Type: basic data types are categorized into 3 different types
Numbers
Booleans
String
Number DataType in Go Language
DATA TYPE DESCRIPTION int8 8-bit signed integer int16 16-bit signed integer int32 32-bit signed integer int64 64-bit signed integer uint8 8-bit unsigned integer uint16 16-bit unsigned integer uint32 32-bit unsigned integer uint64 64-bit unsigned integer int Both in and uint contain the same size, either 32 or 64 bit. uint Both in and uint contain the same size, either 32 or 64 bit. rune It is a synonym of int32 and also represent Unicode code points. byte It is a synonym of int8. uintptr It is an unsigned integer type. Its width is not defined, but it can hold all the bits of a pointer value.
Floating Point Number
This is used to store numbers with a decimal component. Go language has 2 types of floating-point which are float32 and float64.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push();
The default values of floating point s float64. What is means? When you initialize variable with without specifying type then the variable is referred to as float64.
var a=3214.567
Operations on Numeric Types
Go provides several operators for performing operations on numeric types.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push();
Arithmetic Operators: +, -, *, /, %
Comparison Operators: ==, !=, <, >, <=, >=
Bitwise Operators: &, |, ^, <<, >>
Increment and Decrement Operators: ++, —
Assignment Operators: +=, -=, *=, /=, %=, <<=, >>=, &=, |=, ^=
Booleans in Golang
Go language provides bool data type which stores a Boolean value and it has only 2 different values true and false.
Operations on Boolean data types
&& (logical and)
|| (logical or)
! (negation)
Complex numbers
The complex numbers are one of the basic data types. It also has 2 different sizes complex64 and complex128
Complex64- has real and imaginary part of float32
Complex128: has a real and imaginary part of float64
var v= 4+7i;
If you want to create a complex number then go language has a built-in complex function for creating a complex number.
var a = 10.11 var b = 22.33 // var c = a + bi won't work. Create a complex number like this - var c = complex(a, b)
both real and imaginary parts of complex numbers must be the same floating-point type.
But if you try to create a complex number with different real and imaginary part types then it will throw an error.
Operations on complex numbers: it is addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Strings datatype in golang
It is a sequence of bytes. We can declare a string with double-quotes. If string enclosed in double-quotes then they can have escape character like \n, \t. this escaped character replaced with newline and tab space.
If you enclosed string with backtick then this string treated as a raw string.

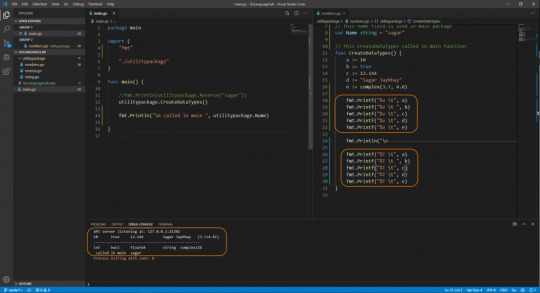
Datatypes in golang
Number.go file
package utilitypackage import ( "fmt" "reflect" ) var Name string = "sagar" func CreateDataTypes() a := 10 b := true c := 12.144 d := "Sagar Jaybhay" e := complex(3.7, 4.8) fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(b), b) fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(a), a) fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(c), c) fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(d), d) fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(e), e)
Main.go file
package main import ( "fmt" "./utilitypackage" ) func main() //fmt.Println(utilitypackage.Reverse("sagar")) utilitypackage.CreateDataTypes() fmt.Println(utilitypackage.Name)
Point to remember whenever you want to access something outside of file your First letter of variable or function should be capital.
Formating the value:
The package fmt implements formatted I/ O.
Refer link https://golang.org/pkg/fmt/
For example:
%v the value in a default format when printing structs, the plus flag (%+v) adds field names %#v a Go-syntax representation of the value %T a Go-syntax representation of the type of value %% a literal percent sign; consumes no value
Boolean
%t the word true or false
Integer
%b base 2 %c the character represented by the corresponding Unicode code point %d base 10 %o base 8 %O base 8 with 0o prefix %q a single-quoted character literal safely escaped with Go syntax. %x base 16, with lower-case letters for a-f %X base 16, with upper-case letters for A-F %U Unicode format: U+1234; same as "U+%04X"
Floating-point and complex constituents:
%b decimal less scientific notation with exponent a power of two, in the manner of strconv.FormatFloat with the 'b' format, e.g. -123456p-78 %e scientific notation, e.g. -1.234456e+78 %E scientific notation, e.g. -1.234456E+78 %f decimal point but no exponent, e.g. 123.456 %F synonym for %f %g %e for large exponents, %f otherwise. The precision is discussed below. %G %E for large exponents, %F otherwise %x hexadecimal notation (with decimal power of two exponent), e.g. -0x1.23abcp+20 %X upper-case hexadecimal notation, e.g. -0X1.23ABCP+20
String and slice of bytes (treated equivalently with these verbs):
%s the uninterpreted bytes of the string or slice %q a double-quoted string safely escaped with Go syntax %x base 16, lower-case, two characters per byte %X base 16, upper-case, two characters per byte
Slice
%p address of 0th element in base 16 notation, with leading 0x
Pointer
%p base 16 notation, with leading 0x The %b, %d, %o, %x and %X verbs also work with pointers, formatting the value exactly as if it were an integer.
The default format for %v is:
bool: %t int, int8 etc.: %d uint, uint8 etc.: %d, %#x if printed with %#v float32, complex64, etc: %g string: %s chan: %p pointer: %p
For compound objects, the elements are printed using these rules, recursively, laid out like this:
struct: field0 field1 ... array, slice: [elem0 elem1 ...] maps: map[key1:value1 key2:value2 ...] pointer to above: &, &[], &map[]
Formating in golang
Number.go file
package utilitypackage import ( "fmt" ) // this name field is used in the main package var Name string = "sagar" // This CreateDataTypes called in main function func CreateDataTypes() a := 10 b := true c := 12.144 d := "Sagar Jaybhay" e := complex(3.7, 4.8) fmt.Printf("%v \t", a) fmt.Printf("%v \t ", b) fmt.Printf("%v \t", c) fmt.Printf("%v \t", d) fmt.Printf("%v \t", e) fmt.Println("\n-------------------------------------------------") fmt.Printf("%T \t", a) fmt.Printf("%T \t ", b) fmt.Printf("%T \t", c) fmt.Printf("%T \t", d) fmt.Printf("%T \t", e)
Main.go file
package main import ( "fmt" "./utilitypackage" ) func main() //fmt.Println(utilitypackage.Reverse("sagar")) utilitypackage.CreateDataTypes() fmt.Println("\n called in main ", utilitypackage.Name)
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push();
0 notes
Text
400+ TOP C#.NET Interview Questions and Answers
C#.NET Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is C#? C# is an object oriented, type safe and managed language that is compiled by .Net framework to generate Microsoft Intermediate Language. 2. What are the types of comment in C# with examples? Single line Eg: //This is a Single line comment ii. Multiple line (/* */) Eg: /*This is a multiple line comment We are in line 2 Last line of comment*/ iii. XML Comments (///). Eg: /// summary; /// Set error message for multilingual language. /// summary 3. What's The Difference Between The System.array.copyto() And System.array.clone()? The first one performs a deep copy of the array, the second one is shallow. 4. How Can You Sort The Elements Of The Array In Descending Order? By calling Sort() and then Reverse() methods. 5. What's The .net Datatype That Allows The Retrieval Of Data By A Unique Key? HashTable. 6. What's Class Sortedlist Underneath? A sorted HashTable. 7. Will Finally Block Get Executed If The Exception Had Not Occurred? Yes. 8. What's The C# Equivalent Of C++ Catch (....), Which Was A Catch-all Statement For Any Possible Exception? A catch block that catches the exception of type System.Exception. You can also omit the parameter data type in this case and just write catch {}. 9. Can Multiple Catch Blocks Be Executed? No, once the proper catch code fires off, the control is transferred to the finally block (if there are any), and then whatever follows the finally block. 10. Why Is It A Bad Idea To Throw Your Own Exceptions? Well, if at that point you know that an error has occurred, then why not write the proper code to handle that error instead of passing a new Exception object to the catch block? Throwing your own exceptions signifies some design flaws in the project.

C#.NET Interview Questions 11. What's A Delegate? A delegate object encapsulates a reference to a method. In C++ they were referred to as function pointers. 12. What's A Multicast Delegate? It’s a delegate that points to and eventually fires off several methods. 13. How's The Dll Hell Problem Solved In .net? Assembly versioning allows the application to specify not only the library it needs to run (which was available under Win32), but also the version of the assembly. 14. What Are The Ways To Deploy An Assembly? An MSI installer, a CAB archive, and XCOPY command. 15. What's A Satellite Assembly? When you write a multilingual or multi-cultural application in .NET, and want to distribute the core application separately from the localized modules, the localized assemblies that modify the core application are called satellite assemblies. 16. What Namespaces Are Necessary To Create A Localized Application? System.Globalization, System.Resources. 17. What's The Difference Between // Comments, /* */ Comments And /// Comments? Single-line, multi-line and XML documentation comments. 18. How Do You Generate Documentation From The C# File Commented Properly With A Command-line Compiler? Compile it with a /doc switch. 19. What's The Difference Between And Xml Documentation Tag? Single line code example and multiple-line code example. 20. Is Xml Case-sensitive? Yes, so and are different elements. 21. What Debugging Tools Come With The .net Sdk? CorDBG – command-line debugger, and DbgCLR – graphic debugger. Visual Studio .NET uses the DbgCLR. To use CorDbg, you must compile the original C# file using the /debug switch. 22. What Does The This Window Show In The Debugger? It points to the object that’s pointed to by this reference. Object’s instance data is shown. 23. What Does Assert() Do? In debug compilation, assert takes in a Boolean condition as a parameter, and shows the error dialog if the condition is false. The program proceeds without any interruption if the condition is true. 24. What's The Difference Between The Debug Class And Trace Class? Documentation Looks The Same. Use Debug class for debug builds, use Trace class for both debug and release builds. 25. Why Are There Five Tracing Levels In System.diagnostics.traceswitcher? The tracing dumps can be quite verbose and for some applications that are constantly running you run the risk of overloading the machine and the hard drive there. Five levels range from None to Verbose, allowing to fine-tune the tracing activities. 26. Where Is The Output Of Textwritertracelistener Redirected? To the Console or a text file depending on the parameter passed to the constructor. 27. How Do You Debug An Asp.net Web Application? Attach the aspnet_wp.exe process to the DbgClr debugger. 28. What Are Three Test Cases You Should Go Through In Unit Testing? Positive test cases (correct data, correct output), negative test cases (broken or missing data, proper handling), exception test cases (exceptions are thrown and caught properly). 29. Can You Change The Value Of A Variable While Debugging A C# Application? Yes, if you are debugging via Visual Studio.NET, just go to Immediate window. 30. Explain The Three Services Model (three-tier Application). Presentation (UI), business (logic and underlying code) and data (from storage or other sources). 31. What Are Advantages And Disadvantages Of Microsoft-provided Data Provider Classes In Ado.net? SQLServer.NET data provider is high-speed and robust, but requires SQL Server license purchased from Microsoft. OLE-DB.NET is universal for accessing other sources, like Oracle, DB2, Microsoft Access and Informix, but it’s a .NET layer on top of OLE layer, so not the fastest thing in the world. ODBC.NET is a deprecated layer provided for backward compatibility to ODBC engines. 32. What's The Role Of The Datareader Class In Ado.net Connections? It returns a read-only dataset from the data source when the command is executed. 33. What Is The Wildcard Character In Sql? Let's Say You Want To Query Database With Like For All Employees Whose Name Starts With La. The wildcard character is %, the proper query with LIKE would involve ‘La%’. 34. Explain Acid Rule Of Thumb For Transactions. Transaction must be Atomic (it is one unit of work and does not dependent on previous and following transactions), Consistent (data is either committed or roll back, no “in-between” case where something has been updated and something hasn’t), Isolated (no transaction sees the intermediate results of the current transaction), Durable (the values persist if the data had been committed even if the system crashes right after). 35. What Connections Does Microsoft Sql Server Support? Windows Authentication (via Active Directory) and SQL Server authentication (via Microsoft SQL Server user name and passwords). 36. Which One Is Trusted And Which One Is Untrusted? Windows Authentication is trusted because the username and password are checked with the Active Directory, the SQL Server authentication is untrusted, since SQL Server is the only verifier participating in the transaction. 37. Why Would You Use Untrusted Verificaion? Web Services might use it, as well as non-Windows applications. 38. What Does The Parameter Initial Catalog Define Inside Connection String? The database name to connect to. 39. What's The Data Provider Name To Connect To Access Database? Microsoft.Access. 40. What Does Dispose Method Do With The Connection Object? Deletes it from the memory. 41. What Is A Pre-requisite For Connection Pooling? Multiple processes must agree that they will share the same connection, where every parameter is the same, including the security settings. 42. What Is C#? C# is a programming language designed by Microsoft. It is loosely based on C/C++, and bears a striking similarity to Java. Microsoft describe C# as follows: "C# is a simple, modern, object oriented, and type-safe programming language derived from C and C++. C# (pronounced 'C sharp') is firmly planted in the C and C++ family tree of languages, and will immediately be familiar to C and C++ programmers. C# aims to combine the high productivity of Visual Basic and the raw power of C++." 43. How Do I Develop C# Apps? The (free) .NET SDK contains the C# command-line compiler (csc.exe). Visual Studio has fully integrated support for C# development. On Linux you can use Mono. 44. Does C# Replace C++? There are three options open to the Windows developer from a C++ background: Stick with standard C++. Don't use .NET at all. Use C++ with .NET. Microsoft supply a .NET C++ compiler that produces IL rather than machine code. However to make full use of the .NET environment (e.g. garbage collection), a set of extensions are required to standard C++. In .NET 1.x this extended language is called Managed Extensions for C++. In .NET 2.0 ME C++ has been completely redesigned under the stewardship of Stan Lippman, and renamed C++/CLI. Forget C++ and use C#. Each of these options has merits, depending on the developer and the application. For my own part, I intend to use C# where possible, falling back to C++ only where necessary. ME C++ (soon to be C++/CLI) is very useful for interop between new .NET code and old C++ code - simply write a managed wrapper class using ME C++, then use the managed class from C#. From experience, this works well. 45. Does C# Have Its Own Class Library? Not exactly. The .NET Framework has a comprehensive class library, which C# can make use of. C# does not have its own class library. 46. What Standard Types Does C# Use? C# supports a very similar range of basic types to C++, including int, long, float, double, char, string, arrays, structs and classes. However, don't assume too much. The names may be familiar, but many of the details are different. For example, a long is 64 bits in C#, whereas in C++ the size of a long depends on the platform (typically 32 bits on a 32-bit platform, 64 bits on a 64-bit platform). Also classes and structs are almost the same in C++ - this is not true for C#. Finally, chars and strings in .NET are 16-bit (Unicode/UTF-16), not 8-bit like C++. 47. Is It True That All C# Types Derive From A Common Base Class? Yes and no. All types can be treated as if they derive from object (System.Object), but in order to treat an instance of a value type (e.g. int, float) as object-derived, the instance must be converted to a reference type using a process called 'boxing'. In theory a developer can forget about this and let the run-time worry about when the conversion is necessary, but in reality this implicit conversion can have side-effects that may trip up the unwary. 48. What Are The Fundamental Differences Between Value Types And Reference Types? C# divides types into two categories - value types and reference types. Most of the intrinsic types (e.g. int, char) are value types. Structs are also value types. Reference types include classes, arrays and strings. The basic idea is straightforward - an instance of a value type represents the actual data, whereas an instance of a reference type represents a pointer or reference to the data. The most confusing aspect of this for C++ developers is that C# has predetermined which types are represented as values, and which are represented as references. A C++ developer expects to take responsibility for this decision. For example, in C++ we can do this: int x1 = 3; // x1 is a value on the stack int *x2 = new int(3) // x2 is a pointer to a value on the heap but in C# there is no control: int x1 = 3; // x1 is a value on the stack int x2 = new int(); x2 = 3; // x2 is also a value on the stack! 49. Okay, So An Int Is A Value Type, And A Class Is A Reference Type. How Can Int Be Derived From Object? It isn't, really. When an int is being used as an int, it is a value. However, when it is being used as an object, it is a reference to an integer value (on the managed heap). In other words, when you treat an int as an object, the runtime automatically converts the int value to an object reference. This process is called boxing. The conversion involves copying the int to the heap, and creating an object instance which refers to it. Unboxing is the reverse process - the object is converted back to a value. int x = 3; // new int value 3 on the stack object objx = x; // new int on heap, set to value 3 - still have x=3 on stack int y = (int)objx; // new value 3 on stack, still got x=3 on stack and objx=3 on heap 50. Are C# References The Same As C++ References? Not quite. The basic idea is the same, but one significant difference is that C# references can be null . So you cannot rely on a C# reference pointing to a valid object. In that respect a C# reference is more like a C++ pointer than a C++ reference. If you try to use a null reference, a NullReferenceException is thrown. For example, look at the following method: void displayStringLength( string s ) { Console.WriteLine( "String is length {0}", s.Length ); } The problem with this method is that it will throw a NullReferenceException if called like this: string s = null; displayStringLength( s ); Of course for some situations you may deem a NullReferenceException to be a perfectly acceptable outcome, but in this case it might be better to re-write the method like this: void displayStringLength( string s ) { if( s == null ) Console.WriteLine( "String is null" ); else Console.WriteLine( "String is length {0}", s.Length ); } 51. Structs Are Largely Redundant In C++. Why Does C# Have Them? In C++, a struct and a class are pretty much the same thing. The only difference is the default visibility level (public for structs, private for classes). However, in C# structs and classes are very different. In C#, structs are value types (instances stored directly on the stack, or inline within heap-based objects), whereas classes are reference types (instances stored on the heap, accessed indirectly via a reference). Also structs cannot inherit from structs or classes, though they can implement interfaces. Structs cannot have destructors. A C# struct is much more like a C struct than a C++ struct. 52. Does C# Support Multiple Inheritance (mi)? No, though it does support implementation of multiple interfaces on a single class or struct. 53. Is A C# Interface The Same As A C++ Abstract Class? No, not quite. An abstract class in C++ cannot be instantiated, but it can (and often does) contain implementation code and/or data members. A C# interface cannot contain any implementation code or data members - it is simply a group of method names & signatures. A C# interface is more like a COM interface than a C++ abstract class. 54. Are C# Constructors The Same As C++ Constructors? Very similar, but there are some significant differences. First, C# supports constructor chaining. This means one constructor can call another: class Person { public Person( string name, int age ) { ... } public Person( string name ) : this( name, 0 ) {} public Person() : this( "", 0 ) {} } Another difference is that virtual method calls within a constructor are routed to the most derived implementation - see Can I Call a virtual method from a constructor. Error handling is also somewhat different. If an exception occurs during construction of a C# object, the destuctor (finalizer) will still be called. This is unlike C++ where the destructor is not called if construction is not completed. (Thanks to Jon Jagger for pointing this out.) Finally, C# has static constructors. The static constructor for a class runs before the first instance of the class is created. Also note that (like C++) some C# developers prefer the factory method pattern over constructors. See Brad Wilson's article. 55. Are C# Destructors The Same As C++ Destructors? No. They look the same but they are very different. The C# destructor syntax (with the familiar ~ character) is just syntactic sugar for an override of the System.Object Finalize method. This Finalize method is called by the garbage collector when it determines that an object is no longer referenced, before it frees the memory associated with the object. So far this sounds like a C++ destructor. The difference is that the garbage collector makes no guarantees about when this procedure happens. Indeed, the algorithm employed by the CLR garbage collector means that it may be a long time after the application has finished with the object. This lack of certainty is often termed 'non-deterministic finalization', and it means that C# destructors are not suitable for releasing scarce resources such as database connections, file handles etc. To achieve deterministic destruction, a class must offer a method to be used for the purpose. The standard approach is for the class to implement the IDisposable interface. The user of the object must call the Dispose() method when it has finished with the object. C# offers the 'using' construct to make this easier. 56. If C# Destructors Are So Different To C++ Destructors, Why Did Ms Use The Same Syntax? Presumably they wanted C++ programmers to feel at home. I think they made a mistake. 57. Are All Methods Virtual In C#? No. Like C++, methods are non-virtual by default, but can be marked as virtual. 58. How Do I Declare A Pure Virtual Function In C#? Use the abstract modifier on the method. The class must also be marked as abstract (naturally). Note that abstract methods cannot have an implementation (unlike pure virtual C++ methods). 59. Can I Call A Virtual Method From A Constructor/destructor? Yes, but it's generally not a good idea. The mechanics of object construction in .NET are quite different from C++, and this affects virtual method calls in constructors. C++ constructs objects from base to derived, so when the base constructor is executing the object is effectively a base object, and virtual method calls are routed to the base class implementation. By contrast, in .NET the derived constructor is executed first, which means the object is always a derived object and virtual method calls are always routed to the derived implementation. (Note that the C# compiler inserts a call to the base class constructor at the start of the derived constructor, thus preserving standard OO semantics by creating the illusion that the base constructor is executed first.) The same issue arises when calling virtual methods from C# destructors. A virtual method call in a base destructor will be routed to the derived implementation. 60. Should I Make My Destructor Virtual? A C# destructor is really just an override of the System.Object Finalize method, and so is virtual by definition. 61. Can I Use Exceptions In C#? Yes, in fact exceptions are the recommended error-handling mechanism in C# (and in .NET in general). Most of the .NET framework classes use exceptions to signal errors. 62. What Types Of Object Can I Throw As Exceptions? Only instances of the System.Exception classes, or classes derived from System.Exception. This is in sharp contrast with C++ where instances of almost any type can be thrown. 63. Can I Define My Own Exceptions? Yes, just derive your exception class from System.Exception. 64. Does The System.exception Class Have Any Cool Features? Yes - the feature which stands out is the StackTrace property. This provides a call stack which records where the exception was thrown from. For example, the following code: using System; class CApp { public static void Main() { try { f(); } catch( Exception e ) { Console.WriteLine( "System.Exception stack trace = \n{0}", e.StackTrace ); } } static void f() { throw new Exception( "f went pear-shaped" ); } } produces this output: System.Exception stack trace = at CApp.f() at CApp.Main() Note, however, that this stack trace was produced from a debug build. A release build may optimise away some of the method calls which could mean that the call stack isn't quite what you expect. 65. When Should I Throw An Exception? This is the subject of some debate, and is partly a matter of taste. However, it is accepted by many that exceptions should be thrown only when an 'unexpected' error occurs. How do you decide if an error is expected or unexpected? This is a judgement call, but a straightforward example of an expected error is failing to read from a file because the seek pointer is at the end of the file, whereas an example of an unexpected error is failing to allocate memory from the heap. 66. Does C# Have A 'throws' Clause? No, unlike Java, C# does not require (or even allow) the developer to specify the exceptions that a method can throw. 67. How Can I Check The Type Of An Object At Runtime? You can use the is keyword. For example: using System; class CApp { public static void Main() { string s = "fred"; long i = 10; Console.WriteLine( "{0} is {1}an integer", s, (IsInteger(s) ? "" : "not ") ); Console.WriteLine( "{0} is {1}an integer", i, (IsInteger(i) ? "" : "not ") ); } static bool IsInteger( object obj ) { if( obj is int || obj is long ) return true; else return false; } } produces the output: fred is not an integer 10 is an integer 68. Can I Get The Name Of A Type At Runtime? Yes, use the GetType method of the object class (which all types inherit from). For example: using System; class CTest { class CApp { public static void Main() { long i = 10; CTest ctest = new CTest(); DisplayTypeInfo( ctest ); DisplayTypeInfo( i ); } static void DisplayTypeInfo( object obj ) { Console.WriteLine( "Type name = {0}, full type name = {1}", obj.GetType(), obj.GetType().FullName ); } } } produces the following output: Type name = CTest, full type name = CTest Type name = Int64, full type name = System.Int64 69. How Do I Do A Case-insensitive String Comparison? Use the String.Compare function. Its third parameter is a boolean which specifies whether case should be ignored or not. "fred" == "Fred" // false System.String.Compare( "fred", "Fred", true ) // true 70. Does C# Support A Variable Number Of Arguments? Yes, using the params keyword. The arguments are specified as a list of arguments of a specific type, e.g. int. For ultimate flexibility, the type can be object. The standard example of a method which uses this approach is System.Console.WriteLine(). 71. How Can I Process Command-line Arguments? Like this: using System; class CApp { public static void Main( string args ) { Console.WriteLine( "You passed the following arguments:" ); foreach( string arg in args ) Console.WriteLine( arg ); } } 72. Does C# Do Array Bounds Checking? Yes. An IndexOutOfRange exception is used to signal an error. 73. How Can I Make Sure My C# Classes Will Interoperate With Other .net Languages? Make sure your C# code conforms to the Common Language Subset (CLS). To help with this, add the global attribute to your C# source files. The compiler will emit an error if you use a C# feature which is not CLS-compliant. 74. How Do I Use The 'using' Keyword With Multiple Objects? You can nest using statements, like this: using( obj1 ) { using( obj2 ) { ... } } However consider using this more aesthetically pleasing (but functionally identical) formatting: using( obj1 ) using( obj2 ) { ... } 75. What Is The Difference Between == And Object.equals? For value types, == and Equals() usually compare two objects by value. For example: int x = 10; int y = 10; Console.WriteLine( x == y ); Console.WriteLine( x.Equals(y) ); will display: True True However things are more complex for reference types. Generally speaking, for reference types == is expected to perform an identity comparison, i.e. it will only return true if both references point to the same object. By contrast, Equals() is expected to perform a value comparison, i.e. it will return true if the references point to objects that are equivalent. For example: StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder("fred"); StringBuilder s2 = new StringBuilder("fred"); Console.WriteLine( s1 == s2 ); Console.WriteLine( s1.Equals(s2) ); will display: False True s1 and s2 are different objects (hence == returns false), but they are equivalent (hence Equals() returns true). Unfortunately there are exceptions to these rules. The implementation of Equals() in System.Object (the one you'll inherit by default if you write a class) compares identity, i.e. it's the same as operator==. So Equals() only tests for equivalence if the class author overrides the method (and implements it correctly). Another exception is the string class - its operator== compares value rather than identity. Bottom line: If you want to perform an identity comparison use the ReferenceEquals() method. If you want to perform a value comparison, use Equals() but be aware that it will only work if the type has overridden the default implementation. Avoid operator== with reference types (except perhaps strings), as it's simply too ambiguous. 76. How Do I Enforce Const Correctness In C#? You can't - at least not in the same way you do in C++. C# (actually, the CLI) has no real concept of const correctness, For example, there's no way to specify that a method should not modify an argument passed in to it. And there's no way to specify that a method does not modify the object on which it is acting. To get a feel for the angst this causes among some C++ programmers, read the feedback on this post from Raymond Chen. There are of course ways of addressing this issue. For example, see Brad Abram's post (and associated feedback) for some ideas on adding optional read-only behaviour to collection classes. 77. What Are The New Features In C# 2.0? Support for all of the new framework features such as generics, anonymous methods, partial classes, iterators and static classes. Delegate inference is a new feature of the C# compiler which makes delegate usage a little simpler. It allows you to write this: Thread t = new Thread(ThreadFunc); instead of this: Thread t = new Thread( new ThreadStart(ThreadFunc) ); Another minor but welcome addition is the explicit global namespace, which fixes a hole in namespace usage in C# 1.x. You can prefix a type name with global:: to indicate that the type belongs to the global namespace, thus avoiding problems where the compiler infers the namespace and gets it wrong. Finally C# 2.0 includes some syntactic sugar for the new System.Nullable type. You can use T? as a synonym for System.Nullable, where T is a value type. As suggested by the name, this allows values of the type to be 'null', or 'undefined'. 78. Are C# Generics The Same As C++ Templates? No, not really. There are some similarities, but there are also fundamental differences. 79. What Is An Interface In C#? An Interface in C# is created using the interface keyword. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface IBankCustomer { void DepositMoney(); void WithdrawMoney(); } public class Demo : IBankCustomer { public void DepositMoney() { Console.WriteLine("Deposit Money"); } public void WithdrawMoney() { Console.WriteLine("Withdraw Money"); } public static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); DemoObject.DepositMoney(); DemoObject.WithdrawMoney(); } } } In our example we created IBankCustomer interface. The interface declares 2 methods. 1. void DepositMoney(); 2. void WithdrawMoney(); Notice that method declarations does not have access modifiers like public, private, etc. By default all interface members are public. It is a compile time error to use access modifiers on interface member declarations. Also notice that the interface methods have only declarations and not implementation. It is a compile time error to provide implementation for any interface member. In our example as the Demo class is inherited from the IBankCustomer interface, the Demo class has to provide the implementation for both the methods (WithdrawMoney() and DepositMoney()) that is inherited from the interface. If the class fails to provide implementation for any of the inherited interface member, a compile time error will be generated. Interfaces can consist of methods, properties, events, indexers, or any combination of those four member types. When a class or a struct inherits an interface, the class or struct must provide implementation for all of the members declared in the interface. The interface itself provides no functionality that a class or struct can inherit in the way that base class functionality can be inherited. However, if a base class implements an interface, the derived class inherits that implementation. 80. Can An Interface Contain Fields? No, an Interface cannot contain fields. 81. What Is The Difference Between Class Inheritance And Interface Inheritance? Classes and structs can inherit from interfaces just like how classes can inherit a base class or struct. However there are 2 differences. 1. A class or a struct can inherit from more than one interface at the same time where as A class or a struct cannot inherit from more than one class at the same time. An example depicting the same is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } interface Interface2 { void Interface2Method(); } class BaseClass1 { public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } class BaseClass2 { public void BaseClass2Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass2 Method"); } } //Error : A class cannot inherit from more than one class at the same time //class DerivedClass : BaseClass1, BaseClass2 //{ //} //A class can inherit from more than one interface at the same time public class Demo : Interface1, Interface2 { public void Interface1Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface1 Method"); } public void Interface2Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface2 Method"); } public static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); DemoObject.Interface1Method(); DemoObject.Interface2Method(); } } } 2. When a class or struct inherits an interface, it inherits only the method names and signatures, because the interface itself contains no implementations. 82. Can An Interface Inherit From Another Interface? Yes, an interface can inherit from another interface. It is possible for a class to inherit an interface multiple times, through base classes or interfaces it inherits. In this case, the class can only implement the interface one time, if it is declared as part of the new class. If the inherited interface is not declared as part of the new class, its implementation is provided by the base class that declared it. It is possible for a base class to implement interface members using virtual members; in that case, the class inheriting the interface can change the interface behavior by overriding the virtual members. 83. Can You Create An Instance Of An Interface? No, you cannot create an instance of an interface. 84. If A Class Inherits An Interface, What Are The 2 Options Available For That Class? Option 1: Provide Implementation for all the members inheirted from the interface. namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } class BaseClass1 : Interface1 { public void Interface1Method() { Console.WriteLine("Interface1 Method"); } public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } } Option 2: If the class does not wish to provide Implementation for all the members inheirted from the interface, then the class has to be marked as abstract. namespace Interfaces { interface Interface1 { void Interface1Method(); } abstract class BaseClass1 : Interface1 { abstract public void Interface1Method(); public void BaseClass1Method() { Console.WriteLine("BaseClass1 Method"); } } } 85. A Class Inherits From 2 Interfaces And Both The Interfaces Have The Same Method Name As Shown Below. How Should The Class Implement The Drive Method For Both Car And Bus Interface? namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } interface Bus { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car,Bus { //How to implement the Drive() Method inherited from Bus and Car } } To implement the Drive() method use the fully qualified name as shown in the example below. To call the respective interface drive method type cast the demo object to the respective interface and then call the drive method. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } interface Bus { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car,Bus { void Car.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Car"); } void Bus.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Bus"); } static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); ((Car)DemoObject).Drive(); ((Bus)DemoObject).Drive(); } } } 86. What Do You Mean By "explicitly Implemeting An Interface". Give An Example? If a class is implementing the inherited interface member by prefixing the name of the interface, then the class is "Explicitly Implemeting an Interface member". The disadvantage of Explicitly Implemeting an Interface member is that, the class object has to be type casted to the interface type to invoke the interface member. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Interfaces { interface Car { void Drive(); } class Demo : Car { // Explicit implementation of an interface member void Car.Drive() { Console.WriteLine("Drive Car"); } static void Main() { Demo DemoObject = new Demo(); //DemoObject.Drive(); // Error: Cannot call explicitly implemented interface method // using the class object. // Type cast the demo object to interface type Car ((Car)DemoObject).Drive(); } } } 87. What Is A Partial Class. Give An Example? A partial class is a class whose definition is present in 2 or more files. Each source file contains a section of the class, and all parts are combined when the application is compiled. To split a class definition, use the partial keyword as shown in the example below. Student class is split into 2 parts. The first part defines the study() method and the second part defines the Play() method. When we compile this program both the parts will be combined and compiled. Note that both the parts uses partial keyword and public access modifier. using System; namespace PartialClass { public partial class Student { public void Study() { Console.WriteLine("I am studying"); } } public partial class Student { public void Play() { Console.WriteLine("I am Playing"); } } public class Demo { public static void Main() { Student StudentObject = new Student(); StudentObject.Study(); StudentObject.Play(); } }} It is very important to keep the following points in mind when creating partial classes. All the parts must use the partial keyword. All the parts must be available at compile time to form the final class. All the parts must have the same access modifiers - public, private, protected etc. Any class members declared in a partial definition are available to all the other parts. The final class is the combination of all the parts at compile time. 88. What Are The Advantages Of Using Partial Classes? When working on large projects, spreading a class over separate files enables multiple programmers to work on it at the same time. When working with automatically generated source, code can be added to the class without having to recreate the source file. Visual Studio uses this approach when it creates Windows Forms, Web service wrapper code, and so on. You can create code that uses these classes without having to modify the file created by Visual Studio. 89. Is It Possible To Create Partial Structs, Interfaces And Methods? Yes, it is possible to create partial structs, interfaces and methods. We can create partial structs, interfaces and methods the same way as we create partial classes. 90. Will The Following Code Compile? using System; namespace PartialClass { public partial class Student { public void Study() { Console.WriteLine("I am studying"); } } public abstract partial class Student { public void Play() { Console.WriteLine("I am Playing"); } } public class Demo { public static void Main() { Student StudentObject = new Student(); } }} No, a compile time error will be generated stating "Cannot create an instance of the abstract class or interface "PartialClass.Student". This is because, if any part is declared abstract, then the whole class becomes abstract. Similarly if any part is declared sealed, then the whole class becomes sealed and if any part declares a base class, then the whole class inherits that base class. 91. Can You Create Partial Delegates And Enumerations? No, you cannot create partial delegates and enumerations. 92. Can Different Parts Of A Partial Class Inherit From Different Interfaces? Yes, different parts of a partial class can inherit from different interfaces. 93. Can You Specify Nested Classes As Partial Classes? Yes, nested classes can be specified as partial classes even if the containing class is not partial. An example is shown below. class ContainerClass { public partial class Nested { void Test1() { } } public partial class Nested { void Test2() { } } } 94. How Do You Create Partial Methods? To create a partial method we create the declaration of the method in one part of the partial class and implementation in the other part of the partial class. The implementation is optional. If the implementation is not provided, then the method and all the calls to the method are removed at compile time. Therefore, any code in the partial class can freely use a partial method, even if the implementation is not supplied. No compile-time or run-time errors will result if the method is called but not implemented. In summary a partial method declaration consists of two parts. The definition, and the implementation. These may be in separate parts of a partial class, or in the same part. If there is no implementation declaration, then the compiler optimizes away both the defining declaration and all calls to the method. The following are the points to keep in mind when creating partial methods. Partial method declarations must begin partial keyword. The return type of a partial method must be void. Partial methods can have ref but not out parameters. Partial methods are implicitly private, and therefore they cannot be virtual. Partial methods cannot be extern, because the presence of the body determines whether they are defining or implementing. 95. What Is The Use Of Partial Methods? Partial methods can be used to customize generated code. They allow for a method name and signature to be reserved, so that generated code can call the method but the developer can decide whether to implement the method. Much like partial classes, partial methods enable code created by a code generator and code created by a human developer to work together without run-time costs. 96. What Is A Nested Type. Give An Example? A type(class or a struct) defined inside another class or struct is called a nested type. An example is shown below. InnerClass is inside ContainerClass, Hence InnerClass is called as nested class. using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { class InnerClass { public string str = "A string variable in nested class"; } public static void Main() { InnerClass nestedClassObj = new InnerClass(); Console.WriteLine(nestedClassObj.str); } } } 97. Can The Nested Class Access, The Containing Class. Give An Example? Yes, the nested class, or inner class can access the containing or outer class as shown in the example below. Nested types can access private and protected members of the containing type, including any inherited private or protected members. using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { string OuterClassVariable = "I am an outer class variable"; public class InnerClass { ContainerClass ContainerClassObject = new ContainerClass(); string InnerClassVariable = "I am an Inner class variable"; public InnerClass() { Console.WriteLine(ContainerClassObject.OuterClassVariable); Console.WriteLine(this.InnerClassVariable); } } } class Demo { public static void Main() { ContainerClass.InnerClass nestedClassObj = new ContainerClass.InnerClass(); } } } 98. What Is The Ouput Of The Following Program? using System; namespace Nested { class ContainerClass { public ContainerClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a container class"); } public class InnerClass : ContainerClass { public InnerClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am an inner class"); } } } class DemoClass : ContainerClass.InnerClass { public DemoClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Demo class"); } public static void Main() { DemoClass DC = new DemoClass(); } } } Output: I am a container class I am an inner class I am a Demo class The above program has used the concepts of inheritance and nested classes. The ContainerClass is at the top in the inheritance chain. The nested InnerClass derives from outer ContainerClass. Finally the DemoClass derives from nested InnerClass. As all the 3 classes are related by inheritance we have the above output. 99. What Is A Destructor? A Destructor has the same name as the class with a tilde character and is used to destroy an instance of a class. 100. Can A Class Have More Than 1 Destructor? No, a class can have only 1 destructor. 101. Can Structs In C# Have Destructors? No, structs can have constructors but not destructors, only classes can have destructors. 102. Can You Pass Parameters To Destructors? No, you cannot pass parameters to destructors. Hence, you cannot overload destructors. 103. Can You Explicitly Call A Destructor? No, you cannot explicitly call a destructor. Destructors are invoked automatically by the garbage collector. 104. Why Is It Not A Good Idea To Use Empty Destructors? When a class contains a destructor, an entry is created in the Finalize queue. When the destructor is called, the garbage collector is invoked to process the queue. If the destructor is empty, this just causes a needless loss of performance. 105. Is It Possible To Force Garbage Collector To Run? Yes, it possible to force garbage collector to run by calling the Collect() method, but this is not considered a good practice because this might create a performance over head. Usually the programmer has no control over when the garbage collector runs. The garbage collector checks for objects that are no longer being used by the application. If it considers an object eligible for destruction, it calls the destructor(if there is one) and reclaims the memory used to store the object. 106. Usually In .net, The Clr Takes Care Of Memory Management. Is There Any Need For A Programmer To Explicitly Release Memory And Resources? If Yes, Why And How? If the application is using expensive external resource, it is recommend to explicitly release the resource before the garbage collector runs and frees the object. We can do this by implementing the Dispose method from the IDisposable interface that performs the necessary cleanup for the object. This can considerably improve the performance of the application. 107. When Do We Generally Use Destructors To Release Resources? If the application uses unmanaged resources such as windows, files, and network connections, we use destructors to release resources. 108. What Is A Constructor In C#? Constructor is a class method that is executed when an object of a class is created. Constructor has the same name as the class, and usually used to initialize the data members of the new object. 109. In C#, What Will Happen If You Do Not Explicitly Provide A Constructor For A Class? If you do not provide a constructor explicitly for your class, C# will create one by default that instantiates the object and sets all the member variables to their default values. 110. Structs Are Not Reference Types. Can Structs Have Constructors? Yes, even though Structs are not reference types, structs can have constructors. 111. We Cannot Create Instances Of Static Classes. Can We Have Constructors For Static Classes? Yes, static classes can also have constructors. 112. Can You Prevent A Class From Being Instantiated? Yes, a class can be prevented from being instantiated by using a private constructor as shown in the example below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class Program { public static void Main() { //Error cannot create instance of a class with private constructor SampleClass SC = new SampleClass(); } } class SampleClass { double PI = 3.141; private SampleClass() { } } } 113. Can A Class Or A Struct Have Multiple Constructors? Yes, a class or a struct can have multiple constructors. Constructors in csharp can be overloaded. 114. Can A Child Class Call The Constructor Of A Base Class? Yes, a child class can call the constructor of a base class by using the base keyword as shown in the example below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class BaseClass { public BaseClass(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str); } } class ChildClass : BaseClass { public ChildClass(string str): base(str) { } public static void Main() { ChildClass CC = new ChildClass("Calling base class constructor from child class"); } } } 115. If A Child Class Instance Is Created, Which Class Constructor Is Called First - Base Class Or Child Class? When an instance of a child class is created, the base class constructor is called before the child class constructor. An example is shown below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class BaseClass { public BaseClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class constructor"); } } class ChildClass : BaseClass { public ChildClass() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class constructor"); } public static void Main() { ChildClass CC = new ChildClass(); } } } 116. Can A Class Have Static Constructor? Yes, a class can have static constructor. Static constructors are called automatically, immediately before any static fields are accessed, and are generally used to initialize static class members. It is called automatically before the first instance is created or any static members are referenced. Static constructors are called before instance constructors. An example is shown below. using System; namespace TestConsole { class Program { static int I; static Program() { I = 100; Console.WriteLine("Static Constructor called"); } public Program() { Console.WriteLine("Instance Constructor called"); } public static void Main() { Program P = new Program(); } } } 117. Can You Mark Static Constructor With Access Modifiers? No, we cannot use access modifiers on static constructor. 118. Can You Have Parameters For Static Constructors? No, static constructors cannot have parameters. 119. What Happens If A Static Constructor Throws An Exception? If a static constructor throws an exception, the runtime will not invoke it a second time, and the type will remain uninitialized for the lifetime of the application domain in which your program is running. 120. Give 2 Scenarios Where Static Constructors Can Be Used? 1. A typical use of static constructors is when the class is using a log file and the constructor is used to write entries to this file. 2. Static constructors are also useful when creating wrapper classes for unmanaged code, when the constructor can call the LoadLibrary method. 121. Does C# Provide Copy Constructor? No, C# does not provide copy constructor. 122. Is The Following Code Legal? using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { } public void Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; } public int Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; } } } No, The above code does not compile. You cannot overload a method based on the return type. To overload a method in C# either the number or type of parameters should be different. In general the return type of a method is not part of the signature of the method for the purposes of method overloading. However, it is part of the signature of the method when determining the compatibility between a delegate and the method that it points to. 123. What Is The Difference Between Method Parameters And Method Arguments. Give An Example? In the example below FirstNumber and SecondNumber are method parameters where as FN and LN are method arguments. The method definition specifies the names and types of any parameters that are required. When calling code calls the method, it provides concrete values called arguments for each parameter. The arguments must be compatible with the parameter type but the argument name (if any) used in the calling code does not have to be the same as the parameter named defined in the method. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int FN = 10; int SN = 20; //FN and LN are method arguments int Total = Sum(FN, SN); Console.WriteLine(Total); } //FirstNumber and SecondNumber are method parameters public static int Sum(int FirstNumber, int SecondNumber) { int Result = FirstNumber + SecondNumber; return Result; } } } 124. Explain The Difference Between Passing Parameters By Value And Passing Parameters By Reference With An Example? We can pass parameters to a method by value or by reference. By default all value types are passed by value where as all reference types are passed by reference. By default, when a value type is passed to a method, a copy is passed instead of the object itself. Therefore, changes to the argument have no effect on the original copy in the calling method.An example is shown below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int I = 10; int K = Function(I); Console.WriteLine("I = " + I); Console.WriteLine("K = " + K); } public static int Function(int Number) { int ChangedValue = Number + 1; return ChangedValue; } } } By default, reference types are passed by reference. When an object of a reference type is passed to a method, the reference points to the original object, not a copy of the object. Changes made through this reference will therefore be reflected in the calling method. Reference types are created by using the class keyword as shown in the example below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { ReferenceTypeExample Object = new ReferenceTypeExample(); Object.Number = 20; Console.WriteLine("Original Object Value = " + Object.Number); Function(Object); Console.WriteLine("Object Value after passed to the method= " + Object.Number); } public static void Function(ReferenceTypeExample ReferenceTypeObject) { ReferenceTypeObject.Number = ReferenceTypeObject.Number + 5; } } class ReferenceTypeExample { public int Number; } } 125. Can You Pass Value Types By Reference To A Method? Yes, we can pass value types by by reference to a method. An example is shown below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { int I = 10; Console.WriteLine("Value of I before passing to the method = " + I); Function(ref I); Console.WriteLine("Value of I after passing to the method by reference= " + I); } public static void Function(ref int Number) { Number = Number + 5; } } } 126. If A Method's Return Type Is Void, Can You Use A Return Keyword In The Method? Yes, Even though a method's return type is void, you can use the return keyword to stop the execution of the method as shown in the example below. using System; namespace Demo { class Program { public static void Main() { SayHi(); } public static void SayHi() { Console.WriteLine("Hi"); return; Console.WriteLine("This statement will never be executed"); } } } 127. What Are Properties In C#. Explain With An Example? Properties in C# are class members that provide a flexible mechanism to read, write, or compute the values of private fields. Properties can be used as if they are public data members, but they are actually special methods called accessors. This enables data to be accessed easily and still helps promote the safety and flexibility of methods. In the example below _firstName and _lastName are private string variables which are accessible only inside the Customer class. _firstName and _lastName are exposed using FirstName and LastName public properties respectively. The get property accessor is used to return the property value, and a set accessor is used to assign a new value. These accessors can have different access levels. The value keyword is used to define the value being assigned by the set accessor. The FullName property computes the full name of the customer. Full Name property is readonly, because it has only the get accessor. Properties that do not implement a set accessor are read only. The code block for the get accessor is executed when the property is read and the code block for the set accessor is executed when the property is assigned a new value. using System; class Customer { // Private fileds not accessible outside the class. private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; private string _coutry = string.Empty; // public FirstName property exposes _firstName variable public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } // public LastName property exposes _lastName variable public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName property is readonly and computes customer full name. public string FullName { get { return _lastName + ", " + _firstName; } } //Country Property is Write Only public string Country { set { _coutry = value; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer CustomerObject = new Customer(); //This line will call the set accessor of FirstName Property CustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; //This line will call the set accessor of LastName Property CustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; //This line will call the get accessor of FullName Property Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + CustomerObject.FullName); } } 128. Explain The 3 Types Of Properties In C# With An Example? Read Only Properties: Properties without a set accessor are considered read-only. In the above example FullName is read only property. Write Only Properties: Properties without a get accessor are considered write-only. In the above example Country is write only property. Read Write Properties: Properties with both a get and set accessor are considered read-write properties. In the above example FirstName and LastName are read write properties. 129. What Are The Advantages Of Properties In C#? Properties can validate data before allowing a change. Properties can transparently expose data on a class where that data is actually retrieved from some other source such as a database. Properties can take an action when data is changed, such as raising an event or changing the value of other fields. 130. What Is A Static Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with a static keyword is considered as static property. This makes the property available to callers at any time, even if no instance of the class exists. In the example below PI is a static property. using System; class Circle { private static double _pi = 3.14; public static double PI { get { return _pi; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); } } 131. What Is A Virtual Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with virtual keyword is considered virtual property. Virtual properties enable derived classes to override the property behavior by using the override keyword. In the example below FullName is virtual property in the Customer class. BankCustomer class inherits from Customer class and overrides the FullName virtual property. In the output you can see the over riden implementation. A property overriding a virtual property can also be sealed, specifying that for derived classes it is no longer virtual. using System; class Customer { private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName is virtual public virtual string FullName { get { return _lastName + ", " + _firstName; } } } class BankCustomer : Customer { // Overiding the FullName virtual property derived from customer class public override string FullName { get { return "Mr. " + FirstName + " " + LastName; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { BankCustomer BankCustomerObject = new BankCustomer(); BankCustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; BankCustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + BankCustomerObject.FullName); } } 132. What Is An Abstract Property. Give An Example? A property that is marked with abstract keyword is considered abstract property. An abstract property should not have any implementation in the class. The derived classes must write their own implementation. In the example below FullName property is abstract in the Customer class. BankCustomer class overrides the inherited abstract FullName property with its own implementation. using System; abstract class Customer { private string _firstName = string.Empty; private string _lastName = string.Empty; public string FirstName { get { return _firstName; } set { _firstName = value; } } public string LastName { get { return _lastName; } set { _lastName = value; } } // FullName is abstract public abstract string FullName { get; } } class BankCustomer : Customer { // Overiding the FullName abstract property derived from customer class public override string FullName { get { return "Mr. " + FirstName + " " + LastName; } } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { BankCustomer BankCustomerObject = new BankCustomer(); BankCustomerObject.FirstName = "David"; BankCustomerObject.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine("Customer Full Name is : " + BankCustomerObject.FullName); } } 133. Can You Use Virtual, Override Or Abstract Keywords On An Accessor Of A Static Property? No, it is a compile time error to use a virtual, abstract or override keywords on an accessor of a static property. 134. What Are Constants In C#? Constants in C# are immutable values which are known at compile time and do not change for the life of the program. Constants are declared using the const keyword. Constants must be initialized as they are declared. You cannot assign a value to a constant after it isdeclared. An example is shown below. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; public Circle() { //Error : You can only assign a value to a constant field at the time of declaration //PI = 3.15; } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); } } 135. Can You Declare A Class Or A Struct As Constant? No, User-defined types including classes, structs, and arrays, cannot be const. Only the C# built-in types excluding System.Object may be declared as const. Use the readonly modifier to create a class, struct, or array that is initialized one time at runtime (for example in a constructor) and thereafter cannot be changed. 136. Does C# Support Const Methods, Properties, Or Events? No, C# does not support const methods, properties, or events. 137. Can You Change The Value Of A Constant Filed After Its Declaration? No, you cannot change the value of a constant filed after its declaration. In the example below, the constant field PI is always 3.14, and it cannot be changed even by the class itself. In fact, when the compiler encounters a constant identifier in C# source code (for example, PI), it substitutes the literal value directly into the intermediate language (IL) code that it produces. Because there is no variable address associated with a constant at run time, const fields cannot be passed by reference. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; } 138. How Do You Access A Constant Field Declared In A Class? Constants are accessed as if they were static fields because the value of the constant is the same for all instances of the type. You do not use the static keyword to declare them. Expressions that are not in the class that defines the constant must use the class name, a period, and the name of the constant to access the constant. In the example below constant field PI can be accessed in the Main method using the class name and not the instance of the class. Trying to access a constant field using a class instance will generate a compile time error. using System; class Circle { public const double PI = 3.14; } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Circle.PI); Circle C = new Circle(); // Error : PI cannot be accessed using an instance // Console.WriteLine(C.PI); } } 139. What Are The 2 Broad Classifications Of Fields In C#? Instance fields Static fields 140. What Are Instance Fields In C#? Instance fields are specific to an instance of a type. If you have a class T, with an instance field F, you can create two objects of type T, and modify the value of F in each object without affecting the value in the other object. 141. What Is A Static Field? A static field belongs to the class itself, and is shared among all instances of that class. Changes made from instance A will be visible immediately to instances B and C if they access the field. 142. Can You Declare A Field Readonly? Yes, a field can be declared readonly. A read-only field can only be assigned a value during initialization or in a constructor. An example is shown below. using System; class Area { public readonly double PI = 3.14; } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Area A = new Area(); Console.WriteLine(A.PI); } } 143. What Is Wrong With The Sample Program Below? using System; class Area { public const double PI = 3.14; static Area() { Area.PI = 3.15; } } class MainClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(Area.PI); } } You cannot assign a value to the constant PI field. 144. What Is The Difference Between A Constant And A Static Readonly Field? A static readonly field is very similar to a constant, except that the C# compiler does not have access to the value of a static read-only field at compile time, only at run time. 145. What Are Access Modifiers In C#? In C# there are 5 different types of Access Modifiers. 1. Public The public type or member can be accessed by any other code in the same assembly or another assembly that references it. 2. Private The type or member can only be accessed by code in the same class or struct. 3. Protected The type or member can only be accessed by code in the same class or struct, or in a derived class. 4. Internal The type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, but not from another assembly. 5. Protected Internal The type or member can be accessed by any code in the same assembly, or by any derived class in another assembly. 146. What Are Access Modifiers Used For? Access Modifiers are used to control the accessibilty of types and members with in the types. 147. Can You Use All Access Modifiers For All Types? No, Not all access modifiers can be used by all types or members in all contexts, and in some cases the accessibility of a type member is constrained by the accessibility of its containing type. 148. Can Derived Classes Have Greater Accessibility Than Their Base Types? No, Derived classes cannot have greater accessibility than their base types. For example the following code is illegal. using System; internal class InternalBaseClass { public void Print() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Base Class Method"); } } public class PublicDerivedClass : InternalBaseClass { public static void Main() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Public Derived Class Method"); } } When you compile the above code an error will be generated stating "Inconsistent accessibility: base class InternalBaseClass is less accessible than class PublicDerivedClass".To make this simple, you cannot have a public class B that derives from an internal class A. If this were allowed, it would have the effect of making A public, because all protected or internal members of A are accessible from the derived class. 149. Can You Declare Struct Members As Protected? No, struct members cannot be declared protected. This is because structs do not support inheritance. 150. Can The Accessibility Of A Type Member Be Greater Than The Accessibility Of Its Containing Type? No, the accessibility of a type member can never be greater than the accessibility of its containing type. For example, a public method declared in an internal class has only internal accessibility. 151. Can Destructors Have Access Modifiers? No, destructors cannot have access modifiers. 152. What Does Protected Internal Access Modifier Mean? The protected internal access means protected OR internal, not protected AND internal. In simple terms, a protected internal member is accessible from any class in the same assembly, including derived classes. To limit accessibility to only derived classes in the same assembly, declare the class itself internal, and declare its members as protected. 153. What Is The Default Access Modifier For A Class,struct And An Interface Declared Directly With A Namespace? internal. 154. Can You Specify An Access Modifier For An Enumeration? Enumeration members are always public, and no access modifiers can be specified. 155. What Are The 3 Types Of Comments In C#? 1. Single Line Comments. You define single line comments with // as shown below. //This is an example for single line comment 2. Multi line comments. You define multi line comments with /* */ as shown below. /*This is an example for Multi Line comments*/ 3. XML Comments. You define XML comments with /// as shown below. ///This is an example for defining XML comments. 156. Is C# A Strongly-typed Language? Yes. 157. What Are The 2 Broad Classifications Of Data Types Available In C#? Built in data types. User defined data types. 158. Give Some Examples For Built In Datatypes In C#? int float bool 159. How Do You Create User Defined Data Types In C#? You use the struct, class, interface, and enum constructs to create your own custom types. The .NET Framework class library itself is a collection of custom types provided by Microsoft that you can use in your own applications. 160. What Are The 2 Types Of Data Types Available In C#? Value Types Reference Types 161. If You Define A User Defined Data Type By Using The Struct Keyword, Is It A Value Type Or Reference Type? Value Type. 162. If You Define A User Defined Data Type By Using The Class Keyword, Is It A Value Type Or Reference Type? Reference type 163. Are Value Types Sealed? Yes, Value types are sealed. 164. What Is The Base Class From Which All Value Types Are Derived? System.ValueType. 165. Give Examples For Value Types? Enum Struct 166. Give Examples For Reference Types? Class Delegate Array Interface. 167. What Are The Differences Between Value Types And Reference Types? Value types are stored on the stack where as reference types are stored on the managed heap. Value type variables directly contain their values where as reference variables holds only a reference to the location of the object that is created on the managed heap. There is no heap allocation or garbage collection overhead for value-type variables. As reference types are stored on the managed heap, they have the over head of object allocation and garbage collection. Value Types cannot inherit from another class or struct. Value types can only inherit from interfaces. Reference types can inherit from another class or interface. 168. What Do You Mean By Casting A Data Type? Converting a variable of one data type to another data type is called casting. This is also called as data type conversion. 169. What Are The 2 Kinds Of Data Type Conversions In C#? Implicit conversions: No special syntax is required because the conversion is type safe and no data will be lost. Examples include conversions from smaller to larger integral types, and conversions from derived classes to base classes. Explicit conversions: Explicit conversions require a cast operator. The source and destination variables are compatible, but there is a risk of data loss because the type of the destination variable is a smaller size than (or is a base class of) the source variable. 170. What Is The Difference Between An Implicit Conversion And An Explicit Conversion? Explicit conversions require a cast operator where as an implicit converstion is done automatically. Explicit conversion can lead to data loss where as with implicit conversions there is no data loss. 171. What Type Of Data Type Conversion Happens When The Compiler Encounters The Following Code? ChildClass CC = new ChildClass(); ParentClass PC = new ParentClass(); Implicit Conversion. For reference types, an implicit conversion always exists from a class to any one of its direct or indirect base classes or interfaces. No special syntax is necessary because a derived class always contains all the members of a base class. 172. If You Want To Convert A Base Type To A Derived Type, What Type Of Conversion Do You Use? Explicit conversion as shown below. //Create a new derived type. Car C1 = new Car(); // Implicit conversion to base type is safe. Vehicle V = C1; // Explicit conversion is required to cast back to derived type. The code below will compile but throw an exception at run time if the right-side object is not a Car object. Car C2 = (Car) V; 173. What Operators Can Be Used To Cast From One Reference Type To Another Without The Risk Of Throwing An Exception? The is and as operators can be used to cast from one reference type to another without the risk of throwing an exception. 174. If Casting Fails What Type Of Exception Is Thrown? InvalidCastException. 175. What Is Boxing And Unboxing? Boxing - Converting a value type to reference type is called boxing. An example is shown below. int i = 101; object obj = (object)i; // Boxing Unboxing - Converting a reference type to a value typpe is called unboxing. An example is shown below. obj = 101; i = (int)obj; // Unboxing 176. Is Boxing An Implicit Conversion? Yes, boxing happens implicitly. 177. Is Unboxing An Implicit Conversion? No, unboxing is an explicit conversion. 178. What Happens During The Process Of Boxing? Boxing is used to store value types in the garbage-collected heap. Boxing is an implicit conversion of a value type to the type object or to any interface type implemented by this value type. Boxing a value type allocates an object instance on the heap and copies the value into the new object. Due to this boxing and unboxing can have performance impact. 179. What Is An Array? An array is a data structure that contains several variables of the same type. 180. What Are The 3 Different Types Of Arrays? Single-Dimensional Multidimensional Jagged 181. What Is Jagged Array? A jagged array is an array of arrays. 182. Are Arrays Value Types Or Reference Types? Arrays are reference types. 183. What Is The Base Class For Array Types? System.Array. 184. Can You Use Foreach Iteration On Arrays In C#? Yes,Since array type implements IEnumerable, you can use foreach iteration on all arrays in C#. 185. What Is The Difference Between String Keyword And System.string Class? string keyword is an alias for Syste.String class. Therefore, System.String and string keyword are the same, and you can use whichever naming convention you prefer. The String class provides many methods for safely creating, manipulating, and comparing strings. 186. Are String Objects Mutable Or Immutable? String objects are immutable. 187. What Do You Mean By String Objects Are Immutable? String objects are immutable means, they cannot be changed after they have been created. All of the String methods and C# operators that appear to modify a string actually return the results in a new string object. In the following example, when the contents of s1 and s2 are concatenated to form a single string, the two original strings are unmodified. The += operator creates a new string that contains the combined contents. That new object is assigned to the variable s1, and the original object that was assigned to s1 is released for garbage collection because no other variable holds a reference to it. string s1 = "First String "; string s2 = "Second String"; // Concatenate s1 and s2. This actually creates a new // string object and stores it in s1, releasing the // reference to the original object. s1 += s2; System.Console.WriteLine(s1); // Output: First String Second String. 188. What Will Be The Output Of The Following Code? string str1 = "Hello "; string str2 = s1; str1 = str1 + "C#"; System.Console.WriteLine(s2); The output of the above code is "Hello" and not "Hello C#". This is bcos, if you create a reference to a string, and then "modify" the original string, the reference will continue to point to the original object instead of the new object that was created when the string was modified. 189. What Is A Verbatim String Literal And Why Do We Use It? The "@" symbol is the verbatim string literal. Use verbatim strings for convenience and better readability when the string text contains backslash characters, for example in file paths. Because verbatim strings preserve new line characters as part of the string text, they can be used to initialize multiline strings. Use double quotation marks to embed a quotation mark inside a verbatim string. The following example shows some common uses for verbatim strings: string ImagePath = @"C:\Images\Buttons\SaveButton.jpg"; //Output: C:\Images\Buttons\SaveButton.jpg string MultiLineText = @"This is multiline Text written to be in three lines."; /* Output: This is multiline Text written to be in three lines. */ string DoubleQuotesString = @"My Name is ""Vankat."""; //Output: My Name is "Vankat." 190. Will The Following Code Compile And Run? string str = null; Console.WriteLine(str.Length); The above code will compile, but at runtime System.NullReferenceException will be thrown 191. How Do You Create Empty Strings In C#? Using string.empty as shown in the example below. string EmptyString = string.empty; 192. What Is The Difference Between System.text.stringbuilder And System.string? Objects of type StringBuilder are mutable where as objects of type System.String are immutable. As StringBuilder objects are mutable, they offer better performance than string objects of type System.String StringBuilder class is present in System.Text namespace where String class is present in System namespace. 193. How Do You Determine Whether A String Represents A Numeric Value? To determine whether a String represents a numeric value use TryParse method as shown in the example below. If the string contains nonnumeric characters or the numeric value is too large or too small for the particular type you have specified, TryParse returns false and sets the out parameter to zero. Otherwise, it returns true and sets the out parameter to the numeric value of the string. string str = "One"; int i = 0; if(int.TryParse(str,out i)) { Console.WriteLine("Yes string contains Integer and it is " + i); } else { Console.WriteLine("string does not contain Integer"); } 194. What Is The Difference Between Int.parse And Int.tryparse Methods? Parse method throws an exception if the string you are trying to parse is not a valid number where as TryParse returns false and does not throw an exception if parsing fails. Hence TryParse is more efficient than Parse. 195. Why Should You Override The Tostring() Method? All types in .Net inherit from system.object directly or indirectly. Because of this inheritance, every type in .Net inherit the ToString() method from System.Object class. Consider the example below. using System; public class MainClass { public static void Main() { int Number = 10; Console.WriteLine(Number.ToString()); } } In the above example Number.ToString() method will correctly give the string representaion of int 10, when you call the ToString() method. If you have a Customer class as shown in the below example and when you call the ToString() method the output doesnot make any sense. Hence you have to override the ToString() method, that is inherited from the System.Object class. using System; public class Customer { public string FirstName; public string LastName; } public class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer C = new Customer(); C.FirstName = "David"; C.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine(C.ToString()); } } The code sample below shows how to override the ToString() method in a class, that would give the output you want. using System; public class Customer { public string FirstName; public string LastName; public override string ToString() { return LastName + ", " + FirstName; } } public class MainClass { public static void Main() { Customer C = new Customer(); C.FirstName = "David"; C.LastName = "Boon"; Console.WriteLine(C.ToString()); } } Conclusion : If you have a class or a struct, make sure you override the inherited ToString() method. 196. Explain Polymorphism In C# With A Simple Example? Polymorphism allows you to invoke derived class methods through a base class reference during run-time. An example is shown below. using System; public class DrawingObject { public virtual void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a drawing object."); } } public class Triangle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Triangle."); } } public class Circle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Circle."); } } public class Rectangle : DrawingObject { public override void Draw() { Console.WriteLine("I am a Rectangle."); } } public class DrawDemo { public static void Main() { DrawingObject DrawObj = new DrawingObject; DrawObj = new Triangle(); DrawObj = new Circle(); DrawObj = new Rectangle(); DrawObj = new DrawingObject(); foreach (DrawingObject drawObj in DrawObj) { drawObj.Draw(); } } } 197. When Can A Derived Class Override A Base Class Member? A derived class can override a base class member only if the base class member is declared as virtual or abstract. 198. What Is The Difference Between A Virtual Method And An Abstract Method? A virtual method must have a body where as an abstract method should not have a body. 199. Can Fields Inside A Class Be Virtual? No, Fields inside a class cannot be virtua. Only methods, properties, events and indexers can be virtual. 200. Give An Example To Show For Hiding Base Class Methods? Use the new keyword to hide a base class method in the derived class as shown in the example below. using System; public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class method."); } } public class DerivedClass : BaseClass { public new void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class method."); } public static void Main() { DerivedClass DC = new DerivedClass(); DC.Method(); } } 201. Can You Access A Hidden Base Class Method In The Derived Class? Yes, Hidden base class methods can be accessed from the derived class by casting the instance of the derived class to an instance of the base class as shown in the example below. using System; public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a base class method."); } } public class DerivedClass : BaseClass { public new void Method() { Console.WriteLine("I am a child class method."); } public static void Main() { DerivedClass DC = new DerivedClass(); ((BaseClass)DC).Method(); } } 202. What Is An Abstract Class? An abstract class is an incomplete class and must be implemented in a derived class. 203. Can You Create An Instance Of An Abstract Class? No, abstract classes are incomplete and you cannot create an instance of an abstract class. 204. What Is A Sealed Class? A sealed class is a class that cannot be inherited from. This means, If you have a class called Customer that is marked as sealed. No other class can inherit from Customer class. For example, the below code generates a compile time error "MainClass cannot derive from sealed type Customer. using System; public sealed class Customer { } public class MainClass : Customer { public static void Main() { } } 205. What Are Abstract Methods? Abstract methods are methods that only the declaration of the method and no implementation. 206. How Can You Force Derived Classes To Provide New Method Implementations For Virtual Methods? Abstract classes can be used to force derived classes to provide new method implementations for virtual methods. An example is shown below. public class BaseClass { public virtual void Method() { // Original Implementation. } } public abstract class AbstractClass : BaseClass { public abstract override void Method(); } public class NonAbstractChildClass : AbstractClass { public override void Method() { // New implementation. } } When an abstract class inherits a virtual method from a base class, the abstract class can override the virtual method with an abstract method. If a virtual method is declared abstract, it is still virtual to any class inheriting from the abstract class. A class inheriting an abstract method cannot access the original implementation of the method. In the above example, Method() on class NonAbstractChildClass cannot call Method() on class BaseClass. In this way, an abstract class can force derived classes to provide new method implementations for virtual methods. 207. Can A Sealed Class Be Used As A Base Class? No, sealed class cannot be used as a base class. A compile time error will be generated. 208. What Are The 4 Pillars Of Any Object Oriented Programming Language? 1. Abstraction 2. Inheritance 3. Encapsulation 4. Polymorphism 209. Do Structs Support Inheritance? No, structs do not support inheritance, but they can implement interfaces. 210. What Is The Main Advantage Of Using Inheritance? Code reuse. 211. Does C# Support Multiple Class Inheritance? No, C# supports single class inheritance only. However classes can implement multiple interfaces at the same time. 212. Can A Struct Have A Default Constructor (a Constructor Without Parameters) Or A Destructor In C#? No. 213. Can You Instantiate A Struct Without Using A New Operator In C#? Yes, you can instantiate a struct without using a new operator. 214. Can A Struct Inherit From Another Struct Or Class In C#? No, a struct cannot inherit from another struct or class, and it cannot be the base of a class. 215. Can A Struct Inherit From An Interface In C#? Yes. 216. Are Structs Value Types Or Reference Types? Structs are value types. 217. What Is The Base Type From Which All Structs Inherit Directly? All structs inherit directly from System.ValueType, which inherits from System.Object. 218. What Do You Mean By Saying A "class Is A Reference Type"? A class is a reference type means when an object of the class is created, the variable to which the object is assigned holds only a reference to that memory. When the object reference is assigned to a new variable, the new variable refers to the original object. Changes made through one variable are reflected in the other variable because they both refer to the same data. 219. What Do You Mean By Saying A "struct Is A Value Type"? A struct is a value type mean when a struct is created, the variable to which the struct is assigned holds the struct's actual data. When the struct is assigned to a new variable, it is copied. The new variable and the original variable therefore contain two separate copies of the same data. Changes made to one copy do not affect the other copy. 220. When Do You Generally Use A Class Over A Struct? A class is used to model more complex behavior, or data that is intended to be modified after a class object is created. A struct is best suited for small data structures that contain primarily data that is not intended to be modified after the struct is created. 221. List The 5 Different Access Modifiers In C#? 1. public 2. protected 3. internal 4. protected internal 5. private 222. If You Donot Specify An Access Modifier For A Method, What Is The Default Access Modifier? private. 223. Classes And Structs Support Inheritance. Is This Statement True Or False? False, Only classes support inheritance. structs donot support inheritance. 224. If A Class Derives From Another Class, Will The Derived Class Automatically Contain All The Public, Protected, And Internal Members Of The Base Class? Yes, the derived class will automatically contain all the public, protected, and internal members of the base class except its constructors and destructors. 225. Can You Create An Instance For An Abstract Class? No, you cannot create an instance for an abstract class. 226. How Do You Prevent A Class From Being Inherited By Another Class? Use the sealed keyword to prevent a class from being inherited by another class. 227. Classes And Structs Can Be Declared As Static, Is This Statement True Or False? False, only classes can be declared as static and not structs. 228. Can You Create An Instance Of A Static Class? No, you cannot create an instance of a static class. 229. Can A Static Class Contain Non Static Members? No, a static class can contain only static members. 230. Does C# Support Multiple-inheritance? No, but you can implement more than one interfaces. 231. Who Is A Protected Class-level Variable Available To? It is available to any sub-class (a class inheriting this class). 232. Are Private Class-level Variables Inherited? Yes, but they are not accessible. Although they are not visible or accessible via the class interface, they are inherited. 233. Describe The Accessibility Modifier "protected Internal". It is available to classes that are within the same assembly and derived from the specified base class. 234. What's The Top .net Class That Everything Is Derived From? System.Object. 235. What Does The Term Immutable Mean? The data value may not be changed. Note: The variable value may be changed, but the original immutable data value was discarded and a new data value was created in memory. 236. What's The Difference Between System.string And System.text.stringbuilder Classes? System.String is immutable. System.StringBuilder was designed with the purpose of having a mutable string where a variety of operations can be performed. 237. What's The .net Collection Class That Allows An Element To Be Accessed Using A Unique Key? HashTable, Dictionary, NameValueCollection. 238. What Class Is Underneath The Sortedlist Class? A sorted HashTable. 239. Will The Finally Block Get Executed If An Exception Has Not Occurred? Yes. Finally block always get executed. 240. What's The C# Syntax To Catch Any Possible Exception? A catch block that catches the exception of type System.Exception. You can also omit the parameter data type in this case and just write catch {}. 241. Can Multiple Catch Blocks Be Executed For A Single Try Statement? No. Once the proper catch block processed, control is transferred to the finally block (if there are any). 242. Explain The Three Services Model Commonly Know As A Three-tier Application. Presentation (UI), Business (logic and underlying code) and Data (from storage or other sources). 243. If A.equals(b) Is True Then A.gethashcode & B.gethashcode Must Always Return Same Hash Code. The answer is False because it is given that A.equals(B) returns true i.e. objects are equal and now its hash Code is asked which is always independent of the fact that whether objects are equal or not. So, Get HashCode for both of the objects returns different value. 244. What Is The Syntax To Inherit From A Class In C#? Place a colon and then the name of the base class. Example: class MyNewClass : MyBaseClass. 245. Can You Prevent Your Class From Being Inherited By Another Class? Yes. The keyword “sealed” will prevent the class from being inherited. 246. Can You Allow A Class To Be Inherited, But Prevent The Method From Being Over-ridden? Yes. Just leave the class public and make the method sealed. 247. What's An Abstract Class? A class that cannot be instantiated. An abstract class is a class that must be inherited and have the methods overridden. An abstract class is essentially a blueprint for a class without any implementation. 248. When Do You Absolutely Have To Declare A Class As Abstract? 1. When the class itself is inherited from an abstract class, but not all base abstract methods have been overridden. 2. When at least one of the methods in the class is abstract. 249. What Is An Interface Class? Interfaces, like classes, define a set of properties, methods, and events. But unlike classes, interfaces do not provide implementation. They are implemented by classes, and defined as separate entities from classes. 250. Why Can't You Specify The Accessibility Modifier For Methods Inside The Interface? They all must be public, and are therefore public by default. 251. Can You Inherit Multiple Interfaces? Yes. .NET does support multiple interfaces. 252. What Happens If You Inherit Multiple Interfaces And They Have Conflicting Method Names? It’s up to you to implement the method inside your own class, so implementation is left entirely up to you. This might cause a problem on a higher-level scale if similarly named methods from different interfaces expect different data, but as far as compiler cares you’re okay. To Do: Investigate. 253. What's The Difference Between An Interface And Abstract Class? In an interface class, all methods are abstract - there is no implementation. In an abstract class some methods can be concrete. In an interface class, no accessibility modifiers are allowed. An abstract class may have accessibility modifiers. 254. What Is The Difference Between A Struct And A Class? Structs are value-type variables and are thus saved on the stack, additional overhead but faster retrieval. Another difference is that structs cannot inherit. 255. What's The Implicit Name Of The Parameter That Gets Passed Into The Set Method/property Of A Class? Value. The data type of the value parameter is defined by whatever data type the property is declared as. 256. What Does The Keyword "virtual" Declare For A Method Or Property? The method or property can be overridden. 257. How Is Method Overriding Different From Method Overloading? When overriding a method, you change the behavior of the method for the derived class. Overloading a method simply involves having another method with the same name within the class. 258. Can You Declare An Override Method To Be Static If The Original Method Is Not Static? No. The signature of the virtual method must remain the same. (Note: Only the keyword virtual is changed to keyword override) 259. What Are The Different Ways A Method Can Be Overloaded? Different parameter data types, different number of parameters, different order of parameters. 260. If A Base Class Has A Number Of Overloaded Constructors, And An Inheriting Class Has A Number Of Overloaded Constructors; Can You Enforce A Call From An Inherited Constructor To A Specific Base Constructor? Yes, just place a colon, and then keyword base (parameter list to invoke the appropriate constructor) in the overloaded constructor definition inside the inherited class. 261. What Does Assert() Method Do? In debug compilation, assert takes in a Boolean condition as a parameter, and shows the error dialog if the condition is false. The program proceeds without any interruption if the condition is true. 262. What's The Difference Between The Debug Class And Trace Class? Documentation looks the same. Use Debug class for debug builds, use Trace class for both debug and release builds. 263. What Is The Role Of The Datareader Class In Ado.net Connections? It returns a read-only, forward-only rowset from the data source. A DataReader provides fast access when a forward-only sequential read is needed. 264. What Is The Wildcard Character In Sql? Let’s say you want to query database with LIKE for all employees whose name starts with La. The wildcard character is %, the proper query with LIKE would involve ‘La%’. 265. Between Windows Authentication And Sql Server Authentication, Which One Is Trusted And Which One Is Untrusted? Windows Authentication is trusted because the username and password are checked with the Active Directory, the SQL Server authentication is untrusted, since SQL Server is the only verifier participating in the transaction. 266. What Does The Dispose Method Do With The Connection Object? Dispose places the connection backing the managed pool. So that other objects/class can use the connection for further use. 267. How Is The Dll Hell Problem Solved In .net? Assembly versioning allows the application to specify not only the library it needs to run (which was available under Win32), but also the version of the assembly. 268. What Is A Satellite Assembly? When you write a multilingual or multi-cultural application in .NET, and want to distribute the core application separately from the localized modules, the localized assemblies that modify the core application are called satellite assemblies. 269. What Is The Smallest Unit Of Execution In .net? an Assembly. 270. When Should You Call The Garbage Collector In .net? As a good rule, you should not call the garbage collector. However, you could call the garbage collector when you are done using a large object (or set of objects) to force the garbage collector to dispose of those very large objects from memory. However, this is usually not a good practice. 271. How Do You Convert A Value-type To A Reference-type? Use Boxing. 272. What Happens In Memory When You Box And Unbox A Value-type? Boxing converts a value-type to a reference-type, thus storing the object on the heap. Unboxing converts a reference-type to a value-type, thus storing the value on the stack. 273. What's C# ? C# (pronounced C-sharp) is a new object oriented language from Microsoft and is derived from C and C++. It also borrows a lot of concepts from Java too including garbage collection. 274. Is It Possible To Inline Assembly Or Il In C# Code? No. 275. Is It Possible To Have Different Access Modifiers On The Get/set Methods Of A Property? No. The access modifier on a property applies to both its get and set accessors. What you need to do if you want them to be different is make the property read-only (by only providing a get accessor) and create a private/internal set method that is separate from the property. 276. Is It Possible To Have A Static Indexer In C#? Allowed In C#. No. Static indexers are not 277. If I Return Out Of A Try/finally In C#, Does The Code In The Finally-clause Run? Yes. The code in the finally always runs. If you return out of the try block, or even if you do a goto out of the try, the finally block always runs: using System; class main { public static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine(\"In Try block\"); return; } finally { Console.WriteLine(\"In Finally block\"); } } } Both In Try block and In Finally block will be displayed. Whether the return is in the try block or after the try-finally block, performance is not affected either way. The compiler treats it as if the return were outside the try block anyway. If it’s a return without an expression (as it is above), the IL emitted is identical whether the return is inside or outside of the try. If the return has an expression, there’s an extra store/load of the value of the expression (since it has to be computed within the try block). 278. I Was Trying To Use An Out Int Parameter In One Of My Functions. How Should I Declare The Variable That I Am Passing To It? You should declare the variable as an int, but when you pass it in you must specify it as ‘out’, like the following: int i; foo(out i); where foo is declared as follows: foo(out int o) { } 279. How Does One Compare Strings In C#? In the past, you had to call .ToString() on the strings when using the == or != operators to compare the strings’ values. That will still work, but the C# compiler now automatically compares the values instead of the references when the == or != operators are used on string types. If you actually do want to compare references, it can be done as follows: if ((object) str1 == (object) str2) { } Here’s an example showing how string compares work: using System; public class StringTest { public static void Main(string args) { Object nullObj = null; Object realObj = new StringTest(); int i = 10; Console.WriteLine(\"Null Object is \n\" + \"Real Object is \n\" + \"i is \n\"); // Show string equality operators string str1 = \"foo\"; string str2 = \"bar\"; string str3 = \"bar\"; Console.WriteLine(\"{0} == {1} ? {2}\", str1, str2, str1 == str2 ); Console.WriteLine(\"{0} == {1} ? {2}\", str2, str3, str2 == str3 ); } } Output: Null Object is Real Object is i is foo == bar ? False bar == bar ? True 280. How Do You Specify A Custom Attribute For The Entire Assembly (rather Than For A Class)? Global attributes must appear after any top-level using clauses and before the first type or namespace declarations. An example of this is as follows: using System; class X {} Note that in an IDE-created project, by convention, these attributes are placed in AssemblyInfo.cs. 281. How Do You Mark A Method Obsolete? public int Foo() {...} or public int Foo() {...} Note: The O in Obsolete is always capitalized. 282. How Do You Implement Thread Synchronization (object.wait, Notify,and Criticalsection) In C#? You want the lock statement, which is the same as Monitor Enter/Exit: lock(obj) { // code } translates to try { CriticalSection.Enter(obj); // code } finally { CriticalSection.Exit(obj); } 283. How Do You Directly Call A Native Function Exported From A Dll? Here’s a quick example of the DllImport attribute in action: using System.Runtime.InteropServices; class C { public static extern int MessageBoxA(int h, string m, string c, int type); public static int Main() { return MessageBoxA(0, \"Hello World!\", \"Caption\", 0); } } This example shows the minimum requirements for declaring a C# method that is implemented in a native DLL. The method C.MessageBoxA() is declared with the static and external modifiers, and has the DllImport attribute, which tells the compiler that the implementation comes from the user32.dll, using the default name of Message BoxA. For more information, look at the Platform Invoke tutorial in the documentation. 284. How Do I Simulate Optional Parameters To Com Calls? You must use the Missing class and pass Missing.Value (in System.Reflection) for any values that have optional parameters. 285. What Do You Know About .net Assemblies? Assemblies are the smallest units of versioning and deployment in the .NET application. Assemblies are also the building blocks for programs such as Web services, Windows services, serviced components, and .NET remoting applications. 286. What's The Difference Between Private And Shared Assembly? Private assembly is used inside an application only and does not have to be identified by a strong name. Shared assembly can be used by multiple applications and has to have a strong name. 287. What's A Strong Name? A strong name includes the name of the assembly, version number, culture identity, and a public key token. 288. How Can You Tell The Application To Look For Assemblies At The Locations Other Than Its Own Install? Use the directive in the XML .config file for a given application. should do the trick. Or you can add additional search paths in the Properties box of the deployed application. 289. How Can You Debug Failed Assembly Binds? Use the Assembly Binding Log Viewer (fuslogvw.exe) to find out the paths searched. 290. Where Are Shared Assemblies Stored? Global assembly cache. 291. How Can You Create A Strong Name For A .net Assembly? With the help of Strong Name tool (sn.exe). 292. Where's Global Assembly Cache Located On The System? Usually C:\winnt\assembly or C:\windows\assembly. 293. Can You Have Two Files With The Same File Name In Gac? Yes, remember that GAC is a very special folder, and while normally you would not be able to place two files with the same name into a Windows folder, GAC differentiates by version number as well, so it’s possible for MyApp.dll and MyApp.dll to co-exist in GAC if the first one is version 1.0.0.0 and the second one is 1.1.0.0. 294. So Let's Say I Have An Application That Uses Myapp.dll Assembly, Version 1.0.0.0. There Is A Security Bug In That Assembly, And I Publish The Patch, Issuing It Under Name Myapp.dll 1.1.0.0. How Do I Tell The Client Applications That Are Already Installed To Start Using This New Myapp.dll? Use publisher policy. To configure a publisher policy, use the publisher policy configuration file, which uses a format similar app .config file. But unlike the app .config file, a publisher policy file needs to be compiled into an assembly and placed in the GAC. 295. What Is Delay Signing? Delay signing allows you to place a shared assembly in the GAC by signing the assembly with just the public key. This allows the assembly to be signed with the private key at a later stage, when the development process is complete and the component or assembly is ready to be deployed. This process enables developers to work with shared assemblies as if they were strongly named, and it secures the private key of the signature from being accessed at different stages of development. 296. Is There An Equivalent Of Exit() For Quitting A C# .net Application? Yes, you can use System.Environment.Exit(int exitCode) to exit the application or Application.Exit() if it's a Windows Forms app. 297. Can You Prevent Your Class From Being Inherited And Becoming A Base Class For Some Other Classes? Yes, that is what keyword sealed in the class definition is for. The developer trying to derive from your class will get a message: cannot inherit from Sealed class WhateverBaseClassName. It is the same concept as final class in Java. 298. If A Base Class Has A Bunch Of Overloaded Constructors, And An Inherited Class Has Another Bunch Of Overloaded Constructors, Can You Enforce A Call From An Inherited Constructor To An Arbitrary Base Constructor? Yes, just place a colon, and then keyword base (parameter list to invoke the appropriate constructor) in the overloaded constructor definition inside the inherited class. 299. I Was Trying To Use An "out Int" Parameter In One Of My Functions. How Should I Declare The Variable That I Am Passing To It? You should declare the variable as an int, but when you pass it in you must specify it as 'out', like the following: int i; foo(out i); where foo is declared as follows: foo(out int o) { } 300. How Do I Make A Dll In C#? You need to use the /target:library compiler option. 301. What Is The C# Equivalent Of C++ Catch (....), Which Was A Catch-all Statement For Any Possible Exception? Does C# Support Try-catch-finally Blocks? Yes. Try-catch-finally blocks are supported by the C# compiler. Here's an example of a try-catch-finally block: using System; public class TryTest { static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine("In Try block"); throw new ArgumentException(); } catch(ArgumentException n1) { Console.WriteLine("Catch Block"); } finally { Console.WriteLine("Finally Block"); } } } Output: In Try Block Catch Block Finally Block If I return out of a try/finally in C#, does the code in the finally-clause run? Yes. The code in the finally always runs. If you return out of the try block, or even if you do a "goto" out of the try, the finally block always runs, as shown in the following example: using System; class main { public static void Main() { try { Console.WriteLine("In Try block"); return; } finally { Console.WriteLine("In Finally block"); } } } Both "In Try block" and "In Finally block" will be displayed. Whether the return is in the try block or after the try-finally block, performance is not affected either way. The compiler treats it as if the return were outside the try block anyway. If it's a return without an expression (as it is above), the IL emitted is identical whether the return is inside or outside of the try. If the return has an expression, there's an extra store/load of the value of the expression (since it has to be computed within the try block). 302. Is There Regular Expression (regex) Support Available To C# Developers? Yes. The .NET class libraries provide support for regular expressions. Look at the documentation for the System. Text.Regular Expressions namespace. 303. Is There A Way To Force Garbage Collection? Yes. Set all references to null and then call System.GC.Collect(). If you need to have some objects destructed, and System.GC.Collect() doesn't seem to be doing it for you, you can force finalizers to be run by setting all the references to the object to null and then calling System.GC.RunFinalizers(). 304. Does C# Support Properties Of Array Types? Yes. Here's a simple example: using System; class Class1 { private string MyField; public string MyProperty { get { return MyField; } set { MyField = value; } } } class MainClass { public static int Main(string args) { Class1 c = new Class1(); string arr = new string {"apple", "banana"}; c.MyProperty = arr; Console.WriteLine(c.MyProperty); // "apple" return 0; } } 305. How Is Method Overriding Different From Overloading? When overriding, you change the method behavior for a derived class. Overloading simply involves having a method with the same name within the class. 306. When Do You Absolutely Have To Declare A Class As Abstract (as Opposed To Free-willed Educated Choice Or Decision Based On Uml Diagram)? When at least one of the methods in the class is abstract. When the class itself is inherited from an abstract class, but not all base abstract methods have been over-ridden. 307. Why Would You Use Untrusted Verification? Web Services might use it, as well as non-Windows applications. 308. What Is The Implicit Name Of The Parameter That Gets Passed Into The Class Set Method? Value, and its datatype depends on whatever variable we are changing. 309. How Do I Register My Code For Use By Classic Com Clients? Use the regasm.exe utility to generate a type library (if needed) and the necessary entries in the Windows Registry to make a class available to classic COM clients. Once a class is registered in the Windows Registry with regasm.exe, a COM client can use the class as though it were a COM class. 310. How Do I Do Implement A Trace And Assert? Use a conditional attribute on the method, as shown below: class Debug { public void Trace(string s) { Console.WriteLine(s); } } class MyClass { public static void Main() { Debug.Trace("hello"); } } In this example, the call to Debug.Trace() is made only if the preprocessor symbol TRACE is defined at the call site. You can define preprocessor symbols on the command line by using the /D switch. The restriction on conditional methods is that they must have void return type. 311. How Do I Create A Multi Language, Multi File Assembly? Unfortunately, this is currently not supported in the IDE. To do this from the command line, you must compile your projects into netmodules (/target:module on the C# compiler), and then use the command line tool al.exe (alink) to link these netmodules together. 312. C# Provides A Default Constructor For Me. I Write A Constructor That Takes A String As A Parameter, But Want To Keep The No Parameter One. How Many Constructors Should I Write? Two. Once you write at least one constructor, C# cancels the freebie constructor, and now you have to write one yourself, even if there is no implementation in. 313. What Is The Equivalent To Regsvr32 And Regsvr32 /u A File In .net Development? Try using RegAsm.exe. The general syntax would be: RegAsm. A good description of RegAsm and its associated switches is located in the .NET SDK docs. Just search on "Assembly Registration Tool".Explain ACID rule of thumb for transactions. Transaction must be Atomic (it is one unit of work and does not dependent on previous and following transactions), Consistent (data is either committed or roll back, no in-between case where something has been updated and something hasnot), Isolated (no transaction sees the intermediate results of the current transaction), Durable (the values persist if the data had been committed even if the system crashes right after). 314. How Do I Create A Multilanguage, Single-file Assembly? This is currently not supported by Visual Studio .NET. 315. Why Cannot You Specify The Accessibility Modifier For Methods Inside The Interface? They all must be public. Therefore, to prevent you from getting the false impression that you have any freedom of choice, you are not allowed to specify any accessibility, it is public by default. 316. Is It Possible To Restrict The Scope Of A Field/method Of A Class To The Classes In The Same Namespace? There is no way to restrict to a namespace. Namespaces are never units of protection. But if you're using assemblies, you can use the 'internal' access modifier to restrict access to only within the assembly. 317. Why Do I Get A Syntax Error When Trying To Declare A Variable Called Checked? The word checked is a keyword in C#. 318. What Is The Syntax For Calling An Overloaded Constructor Within A Constructor (this() And Constructorname() Does Not Compile)? The syntax for calling another constructor is as follows: class B { B(int i) { } } class C : B { C() : base(5) // call base constructor B(5) { } C(int i) : this() // call C() { } public static void Main() {} } 319. Why Do I Get A "cs5001: Does Not Have An Entry Point Defined" Error When Compiling? The most common problem is that you used a lowercase 'm' when defining the Main method. The correct way to implement the entry point is as follows: class test { static void Main(string args) {} } 320. What Does The Keyword Virtual Mean In The Method Definition? The method can be over-ridden. 321. What Optimizations Does The C# Compiler Perform When You Use The /optimize+ Compiler Option? The following is a response from a developer on the C# compiler team: We get rid of unused locals (i.e., locals that are never read, even if assigned). We get rid of unreachable code. We get rid of try-catch w/ an empty try. We get rid of try-finally w/ an empty try (convert to normal code...). We get rid of try-finally w/ an empty finally (convert to normal code...). We optimize branches over branches: gotoif A, lab1 goto lab2: lab1: turns into: gotoif !A, lab2 lab1: We optimize branches to ret, branches to next instruction, and branches to branches. 322. How Can I Create A Process That Is Running A Supplied Native Executable (e.g., Cmd.exe)? The following code should run the executable and wait for it to exit before continuing: using System; using System.Diagnostics; public class ProcessTest { public static void Main(string args) { Process p = Process.Start(args); p.WaitForExit(); Console.WriteLine(args + " exited."); } } Remember to add a reference to System.Diagnostics.dll when you compile. 323. What Is The Difference Between The System.array.copyto() And System.array.clone()? The first one performs a deep copy of the array, the second one is shallow. 324. How Do I Declare Inout Arguments In C#? The equivalent of inout in C# is ref. , as shown in the following example: public void MyMethod (ref String str1, out String str2) { ... } When calling the method, it would be called like this: String s1; String s2; s1 = "Hello"; MyMethod(ref s1, out s2); Console.WriteLine(s1); Console.WriteLine(s2); Notice that you need to specify ref when declaring the function and calling it. 325. Is There A Way Of Specifying Which Block Or Loop To Break Out Of When Working With Nested Loops? The easiest way is to use goto: using System; class BreakExample { public static void Main(String args) { for(int i=0; i Read the full article
0 notes
Text
class 10 computer string chapter explanation: Java
Introduction to Java String Handling
String is probably the most commonly used class in java library. String class is encapsulated under java.lang package. In java, every string that you create is actually an object of type String. One important thing to notice about string object is that string objects are immutable that means once a string object is created it cannot be altered. In Java, java.lang.String class is implementes using Serializable, Comparable and CharSequence interface.
In Java, CharSequence Interface is used for representing a sequence of characters. CharSequence interface is implemented by String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes. This three classes can be used for creating strings in java.
What is an Immutable object?
An object whose state cannot be changed after it is created is known as an Immutable object. String, Integer, Byte, Short, Float, Double and all other wrapper classes objects are immutable.
Creating an Immutable class
public final class MyString
{
final String str;
MyString(String s)
{
this.str = s;
}
public String get()
{
return str;
}
}
In this example MyString is an immutable class. MyString's state cannot be changed once it is created. Creating a String object
String can be created in number of ways, here are a few ways of creating string object.
1) Using a String literal
String literal is a simple string enclosed in double quotes " ". A string literal is treated as a String object.
String str1 = "Hello";
2) Using another String object
String str2 = new String(str1);
3) Using new Keyword
String str3 = new String("Java");
4) Using + operator (Concatenation)
String str4 = str1 + str2;
or,
String str5 = "hello"+"Java";
Each time you create a String literal, the JVM checks the string pool first. If the string literal already exists in the pool, a reference to the pool instance is returned. If string does not exist in the pool, a new string object is created, and is placed in the pool. String objects are stored in a special memory area known as string constant pool inside the heap memory.
Concatenating String
There are 2 methods to concatenate two or more string.
1. Using concat() method
2. Using + operator
1) Using concat() method
string s = "Hello";
string str = "Java";
string str2 = s.concat(str);
String str1 = "Hello".concat("Java"); //works with string literals too.
2) Using + operator
string str = "Rahul";
string str1 = "Dravid";
string str2 = str + str1;
string st = "Rahul"+"Dravid";
String Comparison
String comparison can be done in 3 ways.
1. Using equals() method
2. Using == operator
3. By CompareTo() method
Using equals() method
equals() method compares two strings for equality. Its general syntax is,
boolean equals (Object str)
It compares the content of the strings. It will return true if string matches, else returns false.
String s = "Hell";
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = "Hello";
s1.equals(s2); //true
s.equals(s1) ; //false
Using == operator
== operator compares two object references to check whether they refer to same instance. This also, will return true on successful match.
String s1 = "Java";
String s2 = "Java";
String s3 = new string ("Java");
test(s1 == s2) //true
test(s1 == s3) //false
By compareTo() method
compareTo() method compares values and returns an int which tells if the string compared is less than, equal to or greater than the other string. It compares the String based on natural ordering i.e alphabetically. Its general syntax is,
int compareTo(String str)
String s1 = "Abhi";
String s2 = "Viraaj";
String s3 = "Abhi";
s1.compareTo(S2); //return -1 because s1 < s2
s1.compareTo(S3); //return 0 because s1 == s3
s2.compareTo(s1); //return 1 because s2 > s1
Java String class functions
The methods specified below are some of the most commonly used methods of the String class in Java. We will learn about each method with help of small code examples for better understanding.
charAt() method
charAt() function returns the character located at the specified index.
String str = "studytonight";
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
Output: u
NOTE: Index of a String starts from 0, hence str.charAt(2) means third character of the String str. equalsIgnoreCase() method
equalsIgnoreCase() determines the equality of two Strings, ignoring thier case (upper or lower case doesn't matters with this fuction ).
String str = "java";
System.out.println(str.equalsIgnoreCase("JAVA"));
Output: true
indexOf() method
indexOf() function returns the index of first occurrence of a substring or a character. indexOf() method has four forms:
· int indexOf(String str): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring.
· int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character, starting the search at the specified index.
· int indexOf(int ch): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character.
· int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring, starting at the specified index.
Example:
public class StudyTonight {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="StudyTonight";
System.out.println(str.indexOf('u')); //3rd form
System.out.println(str.indexOf('t', 3)); //2nd form
String subString="Ton";
System.out.println(str.indexOf(subString)); //1st form
System.out.println(str.indexOf(subString,7)); //4th form
}
}
Java String class functions
The methods specified below are some of the most commonly used methods of the String class in Java. We will learn about each method with help of small code examples for better understanding.
charAt() method
charAt() function returns the character located at the specified index.
String str = "studytonight";
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
Output: u
equalsIgnoreCase() method
equalsIgnoreCase() determines the equality of two Strings, ignoring thier case (upper or lower case doesn't matters with this fuction ).
String str = "java";
System.out.println(str.equalsIgnoreCase("JAVA"));
Output: true
indexOf() method
indexOf() function returns the index of first occurrence of a substring or a character. indexOf() method has four forms:
int indexOf(String str): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring.
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character, starting the search at the specified index.
int indexOf(int ch): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified character.
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): It returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the specified substring, starting at the specified index.
Example:
public class StudyTonight {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="StudyTonight";
System.out.println(str.indexOf('u')); //3rd form
System.out.println(str.indexOf('t', 3)); //2nd form
String subString="Ton";
System.out.println(str.indexOf(subString)); //1st form
System.out.println(str.indexOf(subString,7)); //4th form
}
}
length() method
length() function returns the number of characters in a String.
String str = "Count me";
System.out.println(str.length());
8
replace() method
replace() method replaces occurances of character with a specified new character.
String str = "Change me";
System.out.println(str.replace('m','M'));
Output: Change Me
substring() method
substring() method returns a part of the string. substring() method has two forms,
public String substring(int begin);
public String substring(int begin, int end);
/*
character of begin index is inclusive and character of end index is exclusive.
*/
The first argument represents the starting point of the subtring. If the substring() method is called with only one argument, the subtring returned, will contain characters from specified starting point to the end of original string.But, if the call to substring() method has two arguments, the second argument specify the end point of substring.
String str = "0123456789";
System.out.println(str.substring(4));
456789
System.out.println(str.substring(4,7));
Output:456
toLowerCase() method
toLowerCase() method returns string with all uppercase characters converted to lowercase.
String str = "ABCDEF";
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());
Output:abcdef
toUpperCase() method
This method returns string with all lowercase character changed to uppercase.
String str = "abcdef";
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
Output:ABCDEF
trim() method
This method returns a string from which any leading and trailing whitespaces has been removed.
String str = " hello ";
System.out.println(str.trim());
Output:hello
NOTE: If the whitespaces are between the string, for example: String s1 = "study tonight"; then System.out.println(s1.trim()); will output "study tonight".
trim() method removes only the leading and trailing whitespaces.
Extra note:
format() Method
format() is a string method. It is used to the format of the given string.
Following are the format specifier and their datatype:
Format Specifier Datatype
%a
floating point
%b
Any type
%c
character
%d
integer
%e
floating point
%f
floating point
%g
floating point
%h
any type
%n
none
%o
integer
%s
any type
%t
Date/Time
%x
integer
public class FormatDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String a1 = String.format("%d", 125);
String a2 = String.format("%s", "studytonight");
String a3 = String.format("%f", 125.00);
String a4 = String.format("%x", 125);
String a5 = String.format("%c", 'a');
System.out.println("Integer Value: "+a1);
System.out.println("String Value: "+a2);
System.out.println("Float Value: "+a3);
System.out.println("Hexadecimal Value: "+a4);
System.out.println("Char Value: "+a5); }}
";msoū��g�
0 notes
Text
Oracle 12c new features?
Oracle database 12c (c for cloud) a multi tenant database management system introduce so many important new capability in so many areas – database consolidation, query optimization, performance tuning, high availability, partitioning, backup and recovery .Pluggable Databases:In Oracle 12c, in a pluggable database environment, we can create a single database container, and plug multiple databases into this container. All these databases then share the exact same oracle server/background processes and memory, unlike the previous versions where each database has its own background processes and shared memory. This helps in database consolidation and reduces the overhead of managing multiple desperate databases.Consolidation is an important business strategy to reduce the cost of infrastructure and operational expense. In many production database servers, a big portion of CPU cycles go unused. By consolidating many databases into fewer database servers, both the hardware and operational staff can be more effectively utilized.Oracle's new pluggable database feature reduces the risk of consolidation because the DBA can easily plug or unplug an existing database to or from a container database. There is no need to change any code in the application.It is also easy to unplug a database and convert the pluggable database to a traditional database if required. In addition, you can back up and recover pluggable databases independently of the container database; you can also perform a point-in-time recovery of a pluggable database. Further, Resource Manager can be used to control resources consumed by a pluggable database.Optimizer features:Oracle 12c introduces a few useful SQL Optimizer features, and most of these are automatically enabled.It is not uncommon for Optimizer to choose an inefficient execution plan due to incorrect cardinality estimates, invalid statistics, or even stale statistics. This can have dire results. A SQL statement estimated to run for a few seconds might take hours to execute if the chosen execution plan is not optimal.SQL:Identity columns which are auto incremented at the time of insertionSQL> create table emp (emp_id number generated as identity, emp_name varchar);SQL> create table emp (emp_id number generated as identity (start with 1 increment by 1 cache 20 noorder), emp_name varchar;Increased size limit for VARCHAR2, NVARCHAR2, and RAW datatypes to 32K (from 4K).Default on Null (A default value is inserted into the null column).Session private statistics for GTTs (Table and index statistics are held private for each session)UNDO for temporary tables can now managed in TEMP, rather than regular UNDO tablespace.For global temporary tables will not generate UNDO. Reduces contents of regular UNDO allowing better flashback operation.In oracle 12c we are able to make column invisibleSQL> create table ss (column-name column-type invisible); SQL> alter table ss1 modify column-name invisible; SQL> alter table ss1 modify column-name visible;In oracle 12c, No need to shutdown the database for changing Archive log mode.Datapump now allow tuning off redo for the import (only) operation.Now can create duplicate indexes using the same column, in the same order, as an existing index.The truncate command is enhanced with a CASCADE option which allows child record.Oracle 12c allows using DDL inside the SQL statements (PL/SQL inside SQL). Moving and Renaming datafile is now ONLINE, no needs to put datafile in offline.PL/SQL:A role can now be granted to a code unit (PL/SQL Unit Security). Thus one can determine at a very fine grain, which can access a specific unit of code.We can declare PL/SQL functions in the WITH Clause of a select statement.Map Reduce can be run from PL/SQL directly in the database.We can use Booleans values in dynamic PL/SQL. Still no Booleans as database types.ASM:Introduction of Flex ASM, with this feature, database instances uses remote ASM instances. In normal conditions in a node if ASM fails the entire node will be useless, where in 12c the ability to get the extent map from remote ASM instance makes the node useful.Introduction of Flex Cluster, with light weight cluster stack, leaf node and traditional stack hub node (application layer is the typical example of leaf nodes) where they don't require any network heartbeat.Oracle ASM disk scrubbing (Checks for logical data corruptions and repair them automatically.)RMAN:Accidental Drop table, Truncate Table, Wrong scripts human error recovery.RMAN TABLE Point-In-Time Recovery (combination of Data Pump and RMAN, auxiliary instance required).Recover or copy files from Standby databases.Restore & Recover individual tables from RMAN backup.Incremental recovery more faster, many of the tasks removed. You can automate the use of incremental backup to bring the standby db in sync.Import from older export files possibilities.Partitioning:Partitioning enhancements, Multiples partition operations in a single DDL.Online move of a partition (without DBMS_REDEFINTIION).Interval-Ref Partitions - we can create a ref partition (to relate several tables with the same partitions) as a sub-partition to the interval type.Cascade for TRUNCATE and EXCHANGE partition.Asynchronous Global Index maintenance for DROP and TRUNCATE. Command returns instantly, but index cleanup happens later.Patching:Centralized patching - We can test patches on database copies, rolling patches out centrally once testing is complete.Compression: Automated compression with heat map. Optimization can be run on live databases with no disruption. Data optimization will monitor the data usage and with policy archive old data and hot data will be compressed for faster access. Inactive data can be more aggressively compressed or archived, greatly reducing storage costs.Data Guard:1. Oracle Database 12c introduces a new redo transportation method (Fast Sync redo transport) which omits the acknowledgement to primary of the transaction on the standby.2. Creating a new type of redo destination (“Far Sync Standby” composed only of the standby control files), the standby redo logs and some disk space for archive logs which shall be sent to the Standby database. Failover & Switchover operations are totally transparent as the "Far Sync Standby" cannot be used as the target.3. Data Guard Broker commands have been extended. The "validate database" command to checks whether the database is ready for role transition or not.4. Dataguard Broker now supports cascaded standby.5. Global Temporary Tables can now be used on an Active Guard standby database.New Views/Packages in Oracle 12c Releasedba_pdbs, v$pdbs, cdb_data_files, dbms_pdb, dbms_qopatchUsing DBUA to upgrade the existing database is the simple and quickest method.For step by step details follow the below link: Upgrade Oracle Database 11g to 12c
0 notes
Text
HTDP Ch 1 test
Chapter 1. Arithmetic:
1. What characterizes atomic data? Name two types.
2. How would you write 5 * 3 + 12 * 7 in order to accurately evaluate it in DrRacket?
1.1
3. Name 3 operations that can be done on numbers
1.2: The Arithmetic of Strings
4. Why do most programming languages abstract from machine code?
5. write a function that concatenates two strings to produce the phrase “swag is for men”
1.3: Mixing it Up
6. take the string “123456″. What is the string length according to DrRacket’s built in function?
7. take the string “abcdef”. Write an expression using string-ith to produce the letter “d” from this string. bonus: what datatype is produced from this process?
8. evaluate the following expression: You may use a calculator for multiplication, addition, subtraction, etc, but you must evaluate the logic yourself. (string-ith (number->string (* (string-length “012345″) 135) ) 1)
9. consider the string “hello world”. a. Does (substring “hello world” 5) include (string-ith “hello world” 5)? b. Does (substring “hello world” 2 4) include (string-ith “hello world” 4)? b-2. Does it include (string-ith “hello world” 2)? c. What is the value of (string-length (substring “hello world” 2 4))? d. If string-ith 5 of a string is the last character, what is string-length of that string?
10. Which of the following are numbers? 42 “42″ (string->number “forty two”) (number->string 42)
1.4 Arithmetic of Images
11. Write a function that prints a snowman in a scene. Ensure that it includes a single variable that can be used to adjust the snowman’s size without affecting its proportions.
12. What are 3 functions that take an image as input?
1.5 The Arithmetic of Booleans
13. What values are valid for a boolean?
14. resolve the following expressions a. (or #true #false) b. (and #false #true) c. (not #false) d. (and (not #false) #true) e. (or (and #false (not #true)) #false)
1.6 Mixing it Up with Booleans
15. Evaluate the following statement: (if (= (string-length “537″) 3) “wow!” “oh no!”)
16. Write an expression that compares two integers and returns the larger of the two.
1.7 Predicates: Know thy Data
17. Write an expression that checks if its input is a number, and adds 5 to it if it is, or returns the same input if it isn’t.
Other
18. Write an expression using a conditional statement that tells you if its input is a string, a number, an image, or a boolean.
0 notes
Text
What are Variables in Programming?
Check this out https://bizanosa.com/fc/what-are-variables/
What are Variables in Programming?
What are Variables in programming ?
A variable is a reference to some information. This could be information you may need to use later on in your program .
For instance, assume you want to store two values 1001 and 12020 in your program so that later on you may use these values. The way that you will achieve this is by using variables.
The steps involved in storing and later using these values include:
Create the variables with appropriate identifiers (names).
Store your values of 1001 and 12020 in those two variables you’ve created . This is called assigning a value to a variable.
Retrieve and use the stored values from the variables.
Note that with variables you can change the values they store. For instance if you no longer need 1001 and 12020, you will just assign new values to your stored variable names.
Unlike constants in most programming languages, variables are changeable values.
A variable must have an identifier. Some programming languages are statically typed while others are dynamically typed. This is in reference to the data type the programming language can hold and execute in the variable once it is declared.
Statically typed
In strict programming languages such as C++ and Java, you must declare your variables before you can use them.In these programming languages once you declare a variable you cannot change the data type it can hold. For instance once you declare a variable as an integer, it can not be used to hold a string or a character because an integer is a number value. This is called static typing . These are statically typed programming languages.
Examples of statically typed programming languages: Java, C, C++, Haskell, Scala, Kotlin , COBOL,Ada, Rust, Pascal, C# etc .
Dynamically Typed programming languages
In dynamic typing , data types of your variables can be changed at run time. If you declare a variable as a number. Later on you could store a different data type in that variable and your program would still execute without any run time errors.
Certain programs such as Javascript, allows you to use a variable even before it has been declared. However in ecmascript 2015, there are limitations to this depending on the keyword definitions you use for defining your variables,
Examples of dynamically typed programming languages: Ruby, Javascript, Python, PHP, Clojure, erlang ,Lisp, Perl etc .
Examples of Variable declarations
Variable declaration in C
The following are some of the Variable data types in C . You need to use the correct one to declare your variable .For example if you want to store absolute negative or positive digits with no decimals you may use int .
Type Description char Typically a single octet(one byte). int Integer value float A single-precision floating point value. double A double-precision floating point value. void Represents the absence of type.
How to declare variables in C – The syntax
data-type variable-identifier;
eg :
int tax;
If you want to declare a list of variables :
data-type variable-identifier0,variable-identifier1,variable-identifier2;
float price, profit,cost;
Initializing a variable in C :
Initializing a variable means , giving it an initial value when it is declared.
int tax = 16;
float price=199.99, profit= 57.2, cost;
Variable declaration in C++
Here is the complete list of fundamental types in C++:
Group Type names* Notes on size / precision Character types char Exactly one byte in size. At least 8 bits. char16_t Not smaller than char. At least 16 bits. char32_t Not smaller than char16_t. At least 32 bits. wchar_t Can represent the largest supported character set. Integer types (signed) signed char Same size as char. At least 8 bits. signed short int Not smaller than char. At least 16 bits. signed int Not smaller than short. At least 16 bits. signed long int Not smaller than int. At least 32 bits. signed long long int Not smaller than long. At least 64 bits. Integer types (unsigned) unsigned char (same size as their signed counterparts) unsigned short int unsigned int unsigned long int unsigned long long int Floating-point types float double Precision not less than float long double Precision not less than double Boolean type bool Void type void no storage Null pointer decltype(nullptr)
Source : http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/variables/
How to declare variables in C++ – The syntax
C++ is a direct child of the C programming language. This means that variable declaration in C++ is just like it is in C.
data-type variable-identifier;
eg :
int tax;
If you want to declare a list of variables :
data-type variable-identifier0,variable-identifier1,variable-identifier2;
float price, profit,cost;
Initializing a variable in C :
Initializing a variable means , giving it an initial value when it is declared.
int tax = 16;
float price=199.99, profit= 57.2, cost;
Example code in CPP:
CPP code to calculate Gross profit per unit
// operating with variables #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () // declaring variables: float cost, sellingPrice, profit; // process and initialization: cost = 55.50; sellingPrice = 119.99; profit = sellingPrice - cost ; // print out the result: cout << "The profit is : " << profit; // end program: return 0;
To run the above code, copy it and paste it here : http://cpp.sh
Read More about CPP variables .
Variable declaration in C#
Things to note : – variables can be declared with or without modifiers. A modifier defines the scope of a variable, i.e. is it a public variable or a private variable. You will use these access modifiers to secure your variables appropriately. – Variables defined without a modifier are only available within the methods in which they are defined. (Instance variables)
How to declare variables in C# – The syntax
Variable with a modifier
modifier dataType variableIdentifier;
example:
/*...public variable declaration...*/ private float cost, sellingPrice; /*...private variable declaration...*/ public float profit;
Assign initial value to variable
modifier dataType variableIdentifier = value;
Example:
/*...public variable declaration...*/ private float cost = 99.99, sellingPrice = 199.90;
Variable without a modifier
type variableName = value; // Usable and accessible within a method / object .
Example :
int age = 5;
Read more about types and variables .
Variable declaration in java
The following are acceptable and valid Java variables declaration
int x, y, z; // Declares three integers int x = 10, y = 10; // Example of variable initialization in Java byte B = 22; // initializes a byte type variable B. double pi = 3.14159; // declares and assigns a value of PI. char c = 'c'; // the char variable a is initialized with value 'c'
Variable declaration in Python
The following is valid code with variables in python
sales = 235 # An integer assignment sellingPrice = 99.90 # A floating point variable product = "Microphone" # A string variable assignment revenue = sellingPrice * sales # calculates revenue from the given variables # The Output via print print sales # outputs 235 print revenue # prints total revenue print product # Outputs Microphone
You can run the above code in ideone
Variable declaration in Javascript
Watch this video on YouTube
Variable declaration in PHP
Points to note about PHP variables
Variables are denoted with a leading dollar sign ($) e.g. $profit, $loss , $sellingPrice.
The variable value is its most recent assigned value.
Variables are assigned with the = operator, i.e. $profit = 20; .
Variables can be declared before assignment or not.
Variables in PHP are dynamic. refer up there for dynamically typed programming languages.
The following code is taken from the php manual here . It shows a sample of variable code in PHP
<?php class foo var $bar = 'I am bar.'; var $arr = array('I am A.', 'I am B.', 'I am C.'); var $r = 'I am r.'; $foo = new foo(); $bar = 'bar'; $baz = array('foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'quux'); echo $foo->$bar . "\n"; echo $foo->$baz[1] . "\n"; $start = 'b'; $end = 'ar'; echo $foo->$start . $end . "\n"; $arr = 'arr'; echo $foo->$arr[1] . "\n"; ?>
To learn more about Programming, click the button below.
Join the FULL Intro to Programming Here >>
0 notes
Text
ASP.NET Test Questions
1) What is the name of the Page object’s property that determines if a Web page is being requested without data being submitted to server? a. IsCallback b. IsReusable c. IsValid d. IsPostBack Answer Explanation ANSWER: IsPostBack 2) ______________ is the DataType return in IsPostback property. a. bit b. boolean c. int d. object e. string Answer Explanation ANSWER: boolean 3) When does Garbage…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
DataTypes and Scope In JavaScript
New Post has been published on https://is.gd/o5hIW7
DataTypes and Scope In JavaScript

DataTypes and Scope In JavaScript By Sagar Jaybhay
JavaScript is the most popular language In the world and it runs on the most popular environment means web(browser); By using JavaScript you can create complete web and desktop application.
DataTypes in Javascript:
In JavaScript, there are 3 types of primitive data-types.
Number
String
Boolean
Number: in this, you can assign values like 10,10.2 means even if you assign a floating-point number to a variable it is treated like a number data-types.
String: in this, you can assign a single character or multiple characters it is treated as string datatype.
Boolean: You can assign true and false value in this.
Undefined: in this, you declared a variable but you don’t assign the value to it is undefined.
Null: if a variable can not contain value other than null it is null.
Datatypes in JavaScript can be defined at run-time.
Suppose I declared a variable
Var x=10;
And after that, I assign string value like this x=”sagar” so at run-time if you use like below you will know the data types are changed.
var x=10; console.log(typeof(x));//number x="sagar"; console.log(typeof(x)); //string
Points to remember:
Datatypes are not strongly typed like java, c# language.
Whatever value you assigned of right-hand side the left-hand side variable becomes of that data-type.
Scope In JavaScript:
In JavaScript, we have only two scopes Private and Global. In strongly typed language we have a different type of scopes like public, private, protected,internal like that but in JavaScript we have only 2 scopes Private and Global.
var x=10; // global scope console.log(x); //output-10 function PrintX() var x=12; //private scope console.log(x); //output-12 PrintX();
Global Scope In JavaScript
In this above example, you can see x variable which declared outside the function Printx is treated as a global variable. And this global variable access throughout the page or that respective javascript file.
Private: In this, the variable which is declared inside the function is treated as a private variable and it is not accessed outside that function see below example
function PrintX() var x=12; //private scope console.log(x); //output-12 console.log(x); PrintX();
In this example, if run this code it throws an error.
ReferenceError: x is not defined
which is a reference error.
To decide the scope of variable in JavaScript, it uses lexical scope approach. So what is meaning lexical approach it says that depending on the position of a word the meaning of word change. In JavaScript depending on the position left or right the scope will change means whether it is inside the function or outside of a function.
Auto global variable or scope:
In JavaScript when you didn’t declare the variable and assign value to that variable it will become a global variable.
function display() x = 10; console.log(x); //output-10 display(); console.log(x);////output-10
Use Strict:
But to avoid this functionality you can use “use strict”. So what is the use of use strict is that you can’t use a variable before declaration means by using this “use strict” we can raise an error if we use a variable before declaration.
"use strict" function display() x = 10; console.log(x); //output-10 display(); console.log(x);////output-10
the out of this code is as below which throws an error.
index.htm:13 Uncaught ReferenceError: x is not defined at display (index.htm:13) at index.htm:17
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Ruby on Rails Interview Questions and Answers
Ruby on Rails Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Ruby on Rails? Ruby: It is an object oriented programming language inspired by PERL and PYTHON. Rails: It is a framework used for building web application 2. What is class libraries in Ruby? Class libraries in Ruby consist of a variety of domains, such as data types, thread programming, various domains, etc. 3. What is the naming convention in Rails? Variables: For declaring Variables, all letters are lowercase, and words are separated by underscores Class and Module: Modules and Classes uses MixedCase and have no underscore; each word starts with a uppercase letter Database Table: The database table name should have lowercase letters and underscore between words, and all table names should be in the plural form for example invoice_items Model: It is represented by unbroken MixedCase and always have singular with the table name Controller: Controller class names are represented in plural form, such that OrdersController would be the controller for the order table. 4. What is “Yield” in Ruby on Rails? A Ruby method that receives a code block invokes it by calling it with the “Yield”. 5. What is ORM (Object-Relationship-Model) in Rails? ORM or Object Relationship Model in Rails indicate that your classes are mapped to the table in the database, and objects are directly mapped to the rows in the table. 6. What the difference is between false and nil in Ruby? In Ruby False indicates a Boolean datatype, while Nil is not a data type, it have an object_id 4. 7. What are the positive aspects of Rails? Rails provides many features like Meta-programming: Rails uses code generation but for heavy lifting it relies on meta-programming. Ruby is considered as one of the best language for Meta-programming. Active Record: It saves object to the database through Active Record Framework. The Rails version of Active Record identifies the column in a schema and automatically binds them to your domain objects using metaprogramming Scaffolding: Rails have an ability to create scaffolding or temporary code automatically Convention over configuration: Unlike other development framework, Rails does not require much configuration, if you follow the naming convention carefully Three environments: Rails comes with three default environment testing, development, and production. Built-in-testing: It supports code called harness and fixtures that make test cases to write and execute. 8. What is the role of sub-directory app/controllers and app/helpers? App/controllers: A web request from the user is handled by the Controller. The controller sub-directory is where Rails looks to find controller classes App/helpers: The helper’s sub-directory holds any helper classes used to assist the view, model and controller classes. 9. What is the difference between String and Symbol? They both act in the same way only they differ in their behaviors which are opposite to each other. The difference lies in the object_id, memory and process tune when they are used together. Symbol belongs to the category of immutable objects whereas Strings are considered as mutable objects. 10. How Symbol is different from variables? Symbol is different from variables in following aspects It is more like a string than variable In Ruby string is mutable but a Symbol is immutable Only one copy of the symbol requires to be created Symbols are often used as the corresponding to enums in Ruby

Ruby on Rails Interview Questions 11. What is Rails Active Record in Ruby on Rails? Rails active record is the Object/Relational Mapping (ORM) layer supplied with Rails. It follows the standard ORM model as Table map to classes Rows map to objects Columns map to object attributes 12. How Rails implements Ajax? Ajax powered web page retrieves the web page from the server which is new or changed unlike other web-page where you have to refresh the page to get the latest information. Rails triggers an Ajax Operation in following ways Some trigger fires: The trigger could be a user clicking on a link or button, the users inducing changes to the data in the field or on a form Web client calls the server: A Java-script method, XMLHttpRequest, sends data linked with the trigger to an action handler on the server. The data might be the ID of a checkbox, the whole form or the text in the entry field Server does process: The server side action handler does something with the data and retrieves an HTML fragment to the web client Client receives the response: The client side JavaScript, which Rails generates automatically, receives the HTML fragment and uses it to update a particular part of the current 13. How you can create a controller for subject? To create a controller for subject you can use the following command C:\ruby\library> ruby script/generate controller subject 14. What is Rails Migration? Rails Migration enables Ruby to make changes to the database schema, making it possible to use a version control system to leave things synchronized with the actual code. 15. List out what can Rails Migration do? Rails Migration can do following things Create table Drop table Rename table Add column Rename column Change column Remove column and so on 16. What is the command to create a migration? To create migration command includes C:\ruby\application>ruby script/generate migration table_name 17. When self.up and self.down method is used? When migrating to a new version, self.up method is used while self.down method is used to roll back my changes if needed. 18. What is the role of Rails Controller? The Rails controller is the logical center of the application. It faciliates the interaction between the users, views, and the model. It also performs other activities like It is capable of routing external requests to internal actions. It handles URL extremely well It regulates helper modules, which extend the capabilities of the view templates without bulking of their code It regulates sessions; that gives users the impression of an ongoing interaction with our applications 19. What is the difference between Active support’s “HashWithIndifferent” and Ruby’s “Hash” ? The Hash class in Ruby’s core library returns value by using a standard “= =” comparison on the keys. It means that the value stored for a symbol key cannot be retrieved using the equivalent string. While the HashWithIndifferentAccess treats Symbol keys and String keys as equivalent. 20. What is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and how Rails is protected against it? CSRF is a form of attack where hacker submits a page request on your behalf to a different website, causing damage or revealing your sensitive data. To protect from CSRF attacks, you have to add “protect_from_forgery” to your ApplicationController. This will cause Rails to require a CSRF token to process the request. CSRF token is given as a hidden field in every form created using Rails form builders. 21. What is Mixin in Rails? Mixin in Ruby offers an alternative to multiple inheritances, using mixin modules can be imported inside other class. 22. How you define Instance Variable, Global Variable and Class Variable in Ruby? Ruby Instance variable begins with — @ Ruby Class variables begin with — @@ Ruby Global variables begin with — $ 23. How you can run Rails application without creating databases? You can execute your application by uncommenting the line in environment.rb path=> rootpath conf/environment.rb config.frameworks = 24. What is the difference between the Observers and Callbacks in Ruby on Rails? Rails Observers: Observers is same as Callback, but it is used when method is not directly associated to object lifecycle. Also, the observer lives longer, and it can be detached or attached at any time. For example, displaying values from a model in the UI and updating model from user input. Rails Callback: Callbacks are methods, which can be called at certain moments of an object’s life cycle for example it can be called when an object is validated, created, updated, deleted, A call back is short lived. For example, running a thread and giving a call-back that is called when thread terminates 25. What is rake in Rails? Rake is a Ruby Make; it is a Ruby utility that substitutes the Unix utility ‘make’, and uses a ‘Rakefile’ and ‘.rake files’ to build up a list of tasks. In Rails, Rake is used for normal administration tasks like migrating the database through scripts, loading a schema into the database, etc. 26. How you can list all routes for an application? To list out all routes for an application you can write rake routes in the terminal. 27. What is sweeper in Rails? Sweepers are responsible for expiring or terminating caches when model object changes. 28. Mention the log that has to be seen to report errors in Ruby Rails? Rails will report errors from Apache in the log/Apache.log and errors from the Ruby code in log/development.log. 29. What is the difference between Dynamic and Static Scaffolding? Dynamic Scaffolding Static Scaffolding It automatically creates the entire content and user interface at runtime It enables to generation of new, delete, edit methods for the use in application It does not need a database to be synchronized It requires manual entry in the command to create the data with their fields It does not require any such generation to take place It requires the database to be migrated 30. What is the function of garbage collection in Ruby on Rails? The functions of garbage collection in Ruby on Rails includes It enables the removal of the pointer values which is left behind when the execution of the program ends It frees the programmer from tracking the object that is being created dynamically on runtime It gives the advantage of removing the inaccessible objects from the memory, and allows other processes to use the memory 31. What is the difference between redirect and render in Ruby on Rails? Redirect is a method that is used to issue the error message in case the page is not issued or found to the browser. It tells browser to process and issue a new request. Render is a method used to make the content. Render only works when the controller is being set up properly with the variables that require to be rendered. 32. What is the purpose of RJs in Rails? RJs is a template that produces JavaScript which is run in an eval block by the browser in response to an AJAX request. It is sometimes used to define the JavaScript, Prototype and helpers provided by Rails. 33. What is Polymorphic Association in Ruby on Rails? Polymorphic Association allows an ActiveRecord object to be connected with Multiple ActiveRecord objects. A perfect example of Polymorphic Association is a social site where users can comment on anywhere whether it is a videos, photos, link, status updates etc. It would be not feasible if you have to create an individual comment like photos_comments, videos_comment and so on. 34. What are the limits of Ruby on Rails? Ruby on Rails has been designed for creating a CRUD web application using MVC. This might make Rails not useful for other programmers. Some of the features that Rails does not support include Foreign key in databases Linking to multiple data-base at once Soap web services Connection to multiple data-base servers at once 35. What is the difference between calling super() and super call? super(): A call to super() invokes the parent method without any arguments, as presumably expected. As always, being explicit in your code is a good thing. super call: A call to super invokes the parent method with the same arguments that were passed to the child method. An error will therefore occur if the arguments passed to the child method don’t match what the parent is expecting. 36. What about Dig, Float and Max? Float class is used whenever the function changes constantly. Dig is used whenever you want to represent a float in decimal digits. Max is used whenever there is a huge need of Float. 37. How can we define Ruby regular expressions? Ruby regular expression is a special sequence of characters that helps you match or find other strings. A regular expression literal is a pattern between arbitrary delimiters or slashes followed by %r. 38. What is the defined operator? Define operator states whether a passed expression is defined or not. If the expression is defined, it returns the description string and if it is not defined it returns a null value. 39. List out the few features of Ruby? Free format – You can start writing from program from any line and column Case sensitive – The uppercase and lowercase letters are distinct Comments – Anything followed by an unquoted #, to the end of the line on which it appears, is ignored by the interpreter Statement delimiters- Multiple statements on one line must be separated by semicolons, but they are not required at the end of a line. 40. Mention the types of variables available in Ruby Class? Types of variables available in Ruby Class are, Local Variables Global Variables Class Variables Instance Variables 41. How can you declare a block in Ruby? In Ruby, the code in the block is always enclosed within braces ({}). You can invoke a block by using “yield statement”. 42. What is the difference between put and putc statement? Unlike the puts statement, which outputs the entire string onto the screen. The Putc statement can be used to output one character at a time. 43. What is a class library in Ruby? Ruby class libraries consist of a variety of domains, such as thread programming, data types, various domains, etc. These classes give flexible capabilities at a high level of abstraction, giving you the ability to create powerful Ruby scripts useful in a variety of problem domains. The following domains which have relevant class libraries are, GUI programming Network programming CGI Programming Text processing 44. In Ruby, it explains about the defined operator? The defined operator tells whether a passed expression is defined or not. If the expression is not defined, it gives null, and if the expression is defined it returns the description string. 45. What is the difference in scope for these two variables: @@name and @name? The difference in scope for these two variables is that: @@name is a class variable @name is an instance variable 46. What is the syntax for Ruby collect Iterator? The syntax for Ruby collect Iterator collection = collection.collect. 47. In Ruby code, often it is observed that coder uses a short hand form of using an expression like array.map(&:method_name) instead of array.map { |element| element.method_name }. How this trick actually works? When a parameter is passed with “&” in front of it. Ruby will call to_proc on it in an attempt to make it usable as a block. So, symbol to_Proc will invoke the method of the corresponding name on whatever is passed to it. Thus helping our shorthand trick to work. 48. What is Interpolation in Ruby? Ruby Interpolation is the process of inserting a string into a literal. By placing a Hash (#) within {} open and close brackets, one can interpolate a string into the literal. 49. What is the Notation used for denoting class variables in Ruby? In Ruby, A constant should begin with an uppercase letter, and it should not be defined inside a method A local must begin with the _ underscore sign or a lowercase letter A global variable should begin with the $ sign. An uninitialized global has the value of “nil” and it should raise a warning. It can be referred anywhere in the program. A class variable should begin with double @@ and have to be first initialized before being used in a method definition 50. What is the difference between Procs and Blocks? The difference between Procs and Blocks, Block is just the part of the syntax of a method while proc has the characteristics of a block Procs are objects, blocks are not At most one block can appear in an argument list Only block is not able to be stored into a variable while Proc can 51. What is the difference between a single quote and double quote? A single-quoted strings don’t process ASCII escape codes, and they don’t do string interpolation. 52. What is the difference between a gem and a plugin in Ruby? Gem: A gem is a just ruby code. It is installed on a machine, and it’s available for all ruby applications running on that machine. Plugin: Plugin is also ruby code, but it is installed in the application folder and only available for that specific application. 53. What is the difference extend and include? The “include” makes the module’s methods available to the instance of a class, while “extend” makes these methods available to the class itself. 54. Why Ruby on Rails? There are lot of advantages of using ruby on rails: 1. DRY Principal 2. Convention over Configuration 3. Gems and Plugins 4. Scaffolding 5. Pure OOP Concept 6. Rest Support 7. Rack support 8. Action Mailer 9. Rpc support 10. Rexml Support 11. etc.. 55. What is the Difference between Symbol and String? Symbol are same like string but both behaviors is different based on object_id, memory and process time (cpu time) Strings are mutable , Symbols are immutable. Mutable objects can be changed after assignment while immutable objects can only be overwritten. For example p "string object jak".object_id #=> 22956070 p "string object jak".object_id #=> 22956030 p "string object jak".object_id #=> 22956090 p :symbol_object_jak.object_id #=> 247378 p :symbol_object_jak.object_id #=> 247378 p :symbol_object_jak.object_id #=> 247378 p " string object jak ".to_sym.object_id #=> 247518 p " string object jak ".to_sym.object_id #=> 247518 p " string object jak ".to_sym.object_id #=> 247518 p :symbol_object_jak.to_s.object_id #=> 22704460 p :symbol_object_jak.to_s.object_id #=> 22687010 p :symbol_object_jak.to_s.object_id #=> 21141310 And also it will differ by process time For example: Testing two symbol values for equality (or non-equality) is faster than testing two string values for equality, Note : Each unique string value has an associated symbol 56. What things we can define in the model? There are lot of things you can define in models few are: 1. Validations (like validates_presence_of, numeracility_of, format_of etc.) 2. Relationships(like has_one, has_many, HABTM etc.) 3. Callbacks(like before_save, after_save, before_create etc.) 4. Suppose you installed a plugin say validation_group, So you can also define validation_group settings in your model 5. ROR Queries in Sql 6. Active record Associations Relationship 57. What do you mean by the term Rail Migration? It is basically an approach with the help of which the users can make the changes to the already existing database Schema in Ruby and can implement a version control system. The main aim is to synchronize the objects to get the quality outcomes. 58. What exactly do you know about the Rail Observers? It is very much similar to that of Callback. They can be deployed directly in case the methods are not integrated with the lifecycle of the object. It is possible for the users to attach the observer to any file and perform the reverse action by the user. 59. Name the two types of Scaffolding in the Ruby? These are Static and Dynamic Scaffolding 60. Explain some of the looping structures available in Ruby? For loop, While loop, Until Loop. Be able to explain situations in which you would use one over another. Ruby on Rails Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
C# DataTypes
Data Types in a programming language describes that what type of data a variable can hold . CSharp is a strongly typed language, therefore every variable and object must have a declared type. The CSharp type system contains three Type categories. They areValue Types , Reference Types and Pointer Types . In CSharp it is possible to convert a value of one type into a value of another type . The operation of Converting a Value Type to a Reference Type is called Boxing and the reverse operation is called unboxing .
When we declare a variable, we have to tell the compiler about what type of the data the variable can hold or which data type the variable belongs to.
Syntax : DataType VariableName DataType : The type of data that the variable can hold VariableName : the variable we declare for hold the values.
Example:
int count; int : is the data type count : is the variable name
The above example shows , declare a variable 'count' for holding an integer values.
The following are the commonly using datatypes in C# .
bool
The bool keyword is an alias of System.Boolean. It is used to declare variables to store the Boolean values, true and false. In C# , there is no conversion between the bool type and other types.
C# Runtime type : System.Boolean CSharp declaration : bool flag; CSharp Initialization : flag = true; CSharp default initialization value : false
int
int variables are stored signed 32 bit integer values in the range of -2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647
C# Runtime type : System.Int32 CSharp declaration : int count; CSharp Initialization : count = 100; CSharp default initialization value : 0
decimal
The decimal keyword denotes a 128-bit data type.The approximate range and precision for the decimal type are -1.0 X 10-28 to 7.9 X 1028
C# Runtime type : System.Decimal CSharp declaration : decimal val; CSharp Initialization : val = 0.12; CSharp default initialization value : 0.0M
string
The string type represents a string of Unicode characters. string variables are stored any number of alphabetic,
numerical, and special characters .
C# Runtime type : System.String CSharp declaration : string str; CSharp Initialization : str = "csharp string";
0 notes
Text
C++ STL Multimap Container – std::multimap
In this tutorial you will learn about stl multimap i.e., std::multimap and all functions applicable on it with some example code.
In previous articles we already learned about std::map container. It is an associative container which give priority to key values. But problem with map is it won’t allow duplicate values. But multimap allows duplicate values. Here in multimap both key and value pair becomes unique. And we already know that one of the great property of map and multimap is always elements automatically inserted into sorted order on fly. Keys can’t be modified once inserted. Only possible way is we have to delete and update with a new value.
Implementation of multimaps follows a binary search tree type of implementation.
C++ STL Multimap Container – std::multimap
To work with multimap we need to include map header file.
#include <map>
Iterators that can be applicable on multimap:
begin(): returns iterator to the beginning.
end(): returns iterator to the end of the map.
rbegin(): returns reverse iterator to reverse beginning.
rend(): returns reverse iterator to reverse end.
cbegin(): Returns constant iterator to the beginning.
cend(): Returns constant iterator to the end.
Declaring a multimap:
multimap < datatype, datatype > multiMapName;
This is for key and value pair.
Now see some basic operations on multimap:
Insert operation: Insert operations effects size of multimap.
multiMapName.insert (pair (datatype, datatype ) ( keyt, value ))
Another type of insertion is, we can directly assign one multimap elements to other multimap elements directly by giving range using iterators.
multimap <datatype, datatype> newMmap (oldMmap.begin(), oldMmap.end())
size(): This will return the number of key value pairs in the multimap.
max_size(): This will return the what is the maximum capacity of the multimap
clear(): This will truncate all elements from multimap
empty(): This is a Boolean operation. Returns true if multimap is empty. Returns false if multimap is not empty.
Example program to explain all above functions is:
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <iterator> using namespace std; int main() { multimap <int, int> mmp; // declaring an empty multimap multimap <int, int> :: iterator it; // inserting elements for (int i=1; i<=5; i++ ) { mmp.insert (pair <int, int> (i, 10*i)); } // printing elements in multimap cout << "Elements in multimap (key and value) pair wise" << endl; for (it = mmp.begin(); it != mmp.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; // assigning all elements of multimap1 to multimap2 multimap <int, int> mmp2(mmp.begin(),mmp.end()); //printing elements of multimap2 cout << "Elements in multimap2 (key and value) pair wise" << endl; for (it = mmp2.begin(); it != mmp2.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; cout << "Size of the multimap is " ; cout << mmp.size() << endl; cout << endl << "Maximum size of the multimap is " ; cout << mmp.max_size() << endl; cout << endl << "Applying clear operation on multimap2..." <<endl; mmp2.clear(); cout << endl << "Checking wheter multimap2 is empty or not using empty() operation" << endl; if (mmp2.empty()) { cout << "Multimap2 is empty " << endl; } else { cout << "Multimap2 is not empty " << endl; } return 0; }
Output
Elements in multimap (key and value) pair wise 1 10 2 20 3 30 4 40 5 50
Elements in multimap2 (key and value) pair wise 1 10 2 20 3 30 4 40 5 50
Size of the multimap is 5
Maximum size of the multimap is 461168601842738790
Applying clear operation on multimap2…
Checking wheter multimap2 is empty or not using empty() operation Multimap2 is empty
Some other operations are:
find(key): This will find all elements with specified key value.
erase(key): This will delete the value with specified key value.
swap(): This operations swaps all key value pairs of multimap1 to multimap2 and same way multimap2 to multimap1.
upper_bound(): This will return the iterator to upper bound.
lower_bound(): This will return the iterator to lower bound.
Example program to show above operations:
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <iterator> using namespace std; int main() { multimap <int, int> mmp; multimap <int, int> mmp2; multimap <int, int> :: iterator it; multimap <int, int> :: iterator it1; multimap <int, int> :: iterator it2; for (int i=1; i<=5; i++ ) { mmp.insert (pair <int, int> (i, 10*i)); } for (int i=1; i<=5; i++ ) { mmp2.insert (pair <int, int> (i*3, i*i*i)); } cout << "Elements in multimap1 before swapping are" << endl; for (it = mmp.begin(); it != mmp.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; cout << "Elements in multimap2 before swapping are" << endl; for (it = mmp2.begin(); it != mmp2.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; cout << "Performing swapping operation......" << endl; mmp.swap(mmp2); cout << "Elements in multimap1 after swapping are" << endl; for (it = mmp.begin(); it != mmp.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; cout << "Elements in multimap2 after swapping are" << endl; for (it = mmp2.begin(); it != mmp2.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << endl; it= mmp.begin(); mmp.erase (it); // erasing first element of the mmp cout << "After erasing first element in multimap1" << endl; for (it = mmp.begin(); it != mmp.end(); it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } cout << "\nUsing lower bound and upper bound for printing" << endl; it1= mmp2.lower_bound(2); it2= mmp2.upper_bound(4); for (it = it1; it != it2; it++ ) { cout << it->first << '\t' << it->second << endl; } return 0; }
Output
Elements in multimap1 before swapping are 1 10 2 20 3 30 4 40 5 50
Elements in multimap2 before swapping are 3 1 6 8 9 27 12 64 15 125
Performing swapping operation…… Elements in multimap1 after swapping are 3 1 6 8 9 27 12 64 15 125
Elements in multimap2 after swapping are 1 10 2 20 3 30 4 40 5 50
After erasing first element in multimap1 6 8 9 27 12 64 15 125
Using lower bound and upper bound for printing 2 20 3 30 4 40
Comment below if you have any queries related to above stl multimap or std::multimap tutorial.
The post C++ STL Multimap Container – std::multimap appeared first on The Crazy Programmer.
0 notes
Text
Java Data type and Identifier
In this tutorial we are going to see about Data types and Identifiers in Java. Java language has a rich implementation of data types. Data types specify size and the type of values that can be stored in an identifier. Java data types are classified into two categories :
Primitive Data type
Non-Primitive Data type
The Primitive Types
Java defines eight primitive types of data: byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, and boolean. The primitive types are also commonly referred to as simple types. These can be put in four groups:
Integers : This group includes byte, short, int, and long, which are for whole-valued signed numbers.
Floating-point numbers : This group includes float and double, which represent numbers with fractional precision.
Characters : This group includes char, which represents symbols in a character set, like letters and numbers.
Boolean : This group includes boolean, which is a special type for representing true/false values.
We will see the each types in details with example program in upcoming chapters.
Integers
Java defines four integer types: byte, short, int, and long. All of these are signed, positive and negative values. Java does not support unsigned, positive-only integers. Many other computer languages support both signed and unsigned integers. However, Java’s designers felt that unsigned integers were unnecessary.
byte : It is 1 byte(8-bits) integer data type. Value range from -128 to 127. Default value zero. example: byte b=10;
short : It is 2 bytes(16-bits) integer data type. Value range from -32768 to 32767. Default value zero. example: short s=11;
int : It is 4 bytes(32-bits) integer data type. Value range from -2147483648 to 2147483647. Default value zero. example: int i=10;
long : It is 8 bytes(64-bits) integer data type. Value range from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Default value zero. example: long l=100012;
Floating-Point Types
Floating-point numbers, also known as real numbers, are used when evaluating expressions that require fractional precision. For example, calculations such as square root, or transcendental
such as sine and cosine, result in a value whose precision requires a floating-point type.
float : It is 4 bytes(32-bits) float data type. Default value 0.0f. example: float ff=10.3f;
double : It is 8 bytes(64-bits) float data type. Default value 0.0d. example: double db=11.123;
Characters
In Java, the data type used to store characters is char. However, C/C++ programmers beware: char in Java is not the same as char in C or C++. In C/C++, char is 8 bits wide.
char : It is 2 bytes(16-bits) unsigned unicode character. Range 0 to 65,535. example: char c='a';
Booleans
Java has a primitive type, called boolean, for logical values. It can have only one of two possible values, true or false. This is the type returned by all relational operators, as in the case of a < b. boolean is also the type required by the conditional expressions that govern the control statements such as if and for.
Example: boolean b=true;
Non-Primitive(Reference) Data type
Reference variables are created using defined constructors of the classes. They are used to access objects. These variables are declared to be of a specific type that cannot be changed. For example, Employee, Student, etc.
Class objects and various type of array variables come under reference datatype.
Default value of any reference variable is null.
A reference variable can be used to refer any object of the declared type or any compatible type.
Example: Employee employee= new Employee("Arun");
String :
String is a special data type in Java. We will see more about String in upcoming chapter.
Identifiers in Java
All Java components require names. Name used for classes, methods, interfaces and variables are called Identifier. Identifier must follow some rules. Here are the rules:
All identifiers must start with either a letter( a to z or A to Z ) or currency character($) or an underscore.
After the first character, an identifier can have any combination of characters.
A Java keyword cannot be used as an identifier.
Identifiers in Java are case sensitive, foo and Foo are two different identifiers.
Read more about Java Best practices in Naming Conventions here.
from Java Tutorials Corner http://ift.tt/2fJAdKD via IFTTT
0 notes