#DevOps automation frameworks
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
DevOps Platforms And Software Development

28 Best DevOps Platforms And Tools: The ULTIMATE Guide
These best DevOps platforms and software can be a game-changer for businesses aiming to streamline their software deployment and development processes. The right platform or tool automates tasks and boosts collaboration between the operations and development teams. This, in turn, leads to quicker deployment of high-quality software that meets user expectations. Selecting from the Best DevOps Platforms and Software requires understanding your team's specific needs and how each tool can address them effectively. Tech Ahead provides cutting-edge DevOps platforms and software development solutions to streamline and enhance the software delivery lifecycle.
Understanding DevOps Platforms and Software
'DevOps' amalgamates two pivotal roles in software development: Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops). It's a methodology that encourages collaboration between these traditionally separate teams to streamline the entire software development lifecycle. Focusing on DevOps platforms and tools, they are integrated systems designed to support this collaborative approach by automating many routine tasks involved in developing applications from design through deployment stages.
Purpose of DevOps Tools
A range of specialized DevOps tools have been developed for different aspects of DevOps practices. Some handle code creation, while others manage testing or deployment processes. These popular DevOps automation tools enable faster releases with fewer errors due to their automation capabilities at various stages. Besides accelerating release cycles, these open-source DevOps tools also promote better communication among operations teams, thus fostering a culture where continuous improvement becomes part of everyday work habits within agile software development environments.
Monitoring and Error Reporting Platforms: The Backbone of App Performance
The effectiveness of a web app or mobile application is essential for its success. Monitoring and error reporting platforms are the backbones for maintaining this performance, offering tools that track application behavior, detect anomalies, and diagnose issues in real time.
Let's dive into these top 28 Best DevOps Platforms and Tools:
Raygun: Comprehensive Error Tracking
Nagios: Pioneer in IT Infrastructure Monitoring
Firebase Crashlytics: Specialized Mobile App Support
Opsgenie by Atlassian
Puppet Enterprise: The Model-Driven Approach
Cooking up Configurations with Progress Chef
An Open Source Solution: Ansible
SysAid: An All-Rounder In Configuration Management
Jenkins: A Versatile Open-Source Tool
Bamboo: Seamless Release Management
Amazon ECS: Containerized Deployments Simplified
Octopus Deploy: Advanced Deployment Functionalities
CircleCI: Speedy Builds And Tests
Docker: A Popular DevOps Tool
Redhat Openshift: Enterprise-Grade Solution
Kubernetes: The Container Orchestration King
LXC/LXD: Linux-Based Virtualization
Git: A Leading SCM Tool
Mercurial: User-friendly SCM
Apache (SVN) Subversion
SonarQube
Jira
Gradle
Atlassian Open DevOps
Azure DevOps Services
AWS (Amazon Web Services) DevOps
Terraform: An Open-Source Tool for Infrastructure Management
Google Cloud Build: Streamlining Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment
TechAhead: Pioneering Global Excellence In The Field Of Development Work With Best-in-class Software
An industry leader in this domain - TechAhead has earned global recognition for their expertise in developing high-performing digital products using these best-in-class DevOps Platforms and software. They understand the importance of selecting appropriate DevOps automation tools tailored to client requirements, ensuring efficient workflow throughout the entire software development lifecycle. Their commitment to quality deliverables sets them apart, making them a one-stop solution provider for all application and software development automation needs.
Navigating numerous options might seem daunting, but it becomes easier to pick suitable ones once you identify what your team requires. No two projects are alike, so finding the right fit for your needs is essential. And if you ever find yourself needing expert guidance, remember companies like TechAhead are always ready to help.
The DevOps landscape is vast and diverse, with many platforms and software tools available to facilitate the development, deployment, monitoring, and maintenance of web apps and mobile applications. These popular DevOps tools are essential in streamlining operations teams' workflows while fostering collaboration among DevOps teams.
Conclusion
Exploring the world of DevOps platforms and software can feel like navigating a labyrinth. But, with this comprehensive guide, you've been armed with knowledge about top tools in various categories - from monitoring to DevOps configuration management tools, CI/CD deployment, and containerization. We've dived into source code management and build tools while shedding light on cloud-based solutions. We even touched upon security essentials for your applications.
The key takeaway? No single answer fits all when it comes to the best DevOps tools. It all concerns what works best with your team's needs and workflow. Understanding these Best DevOps Platforms and Software is part of the journey towards efficient software development. The real magic happens when you leverage them effectively. Contact TechAhead today for all your DevOps development, web, and mobile app development!
#https://www.techaheadcorp.com/blog/best-devops-platforms-software/#DevOps tools#DevOps practices#DevOps solutions#DevOps automation frameworks#DevOps software stack#DevOps security tools#Best DevOps Platforms and software#DevOps Platforms and Software#DevOps Platforms and Software Development#DevOps Platforms#DevOps Platforms Tools#TechAhead Corp#TechAheadCorp#techaheadcorp.com
0 notes
Text
Java is an established programming language and an ecosystem that has dominated the software business for many years. According to TIOBE index rankings, Java was the #1 popular programming language in 2020 and the fourth best currently for bespoke software development.
The key factor for its intensive popularity is its security, which is why it is extensively used in a broad range of disciplines such as Big data processing, AI application development, Android app development, Core Java software development, and many more. It provides a large set of tools and libraries, as well as cross-platform interoperability, allowing customers to build applications of their choice.
#java development#future of java#java trends#java developer for hire#Java programming language for cloud-native development#Java frameworks for microservices architecture#Java ecosystem tools for DevOps automation#Java web development trends in 2023#Agile Java development with DevOps best practices#software development company
0 notes
Text
Automation Testing Insights: Transforming Testing
The global automation testing market size is expected to reach USD 92.45 billion by 2030. Prominent technological advancement in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is propelling the demand for the market. Mobile application usage is growing across various end-user industries, and smartphone penetration is rising, opening an attractive potential for market expansion. Furthermore, there is a rising demand for automation testing as web-based applications have developed significantly and new software technologies have emerged. The market is growing rapidly due to the increasing usage of ML and AI for advanced analytics and continuous testing across DevOps and DevSecOps areas.
Automation Testing Market Report Highlights
The services segment dominated the market and accounted for over 56% of the global revenue owing to rapid advancements in implementation services, which make it easier to include automation into a functioning infrastructure for software testing
With the aid of this service, automation is integrated into an existing software automation testing setup
The large enterprises segment held the largest revenue share in 2022 as it helps improve efficiency, reduce manual effort, increase test coverage, and ensure the quality of software applications
The BFSI segment is estimated to have significant growth over the forecast period; adopting digitalization in the BFSI sector creates a significant demand for application software automation testing
Gain deeper insights on the market and receive your free copy with TOC now @: Automation Testing Market Report
The emerging use of RPA to automate time-consuming, error-prone manual processes are just a few instances of the usage of AI & ML in automation testing. Moreover, a bot uses the page’s numerous links and web forms to systematically explore through an online application when web crawling or spidering. This is a new use for AI and ML in automation testing. This approach is typically used for indexing online browsing. It may be improved further to perform reverse engineering on an application being tested and automatically find Test Cases. Emerging automation testing tools are significantly fueling market growth.
For instance, Testcraft, a codeless Selenium test automation platform for regression and continuous testing, as well as monitoring of web applications, is gaining traction among users. Their revolutionary AI tech removes maintenance time and cost, as it certainly affects changes in the app. Similarly, Applitools Eyes, Testim, and Test.ai are more automation testing tools propelling the market growth. Furthermore, mergers and acquisitions by other key players are propelling market growth. For instance, in 2022, to improve the user experience on 5G smartphones, Key sight introduced AI-driven and automated testing. Automation and AI enable mobile service providers and app developers to more swiftly evaluate how smartphone users engage with native apps in the real world.
#Automation Testing#Quality Assurance#Software Testing#Test Automation#Continuous Testing#Test Automation Framework#DevOps Testing#Selenium#Test Automation Tools#Performance Testing#Regression Testing#Agile Testing#UIAutomation#Test Scripting#Test Automation Engineer#Codeless Automation#Automation Strategy#CI/CDTesting#Test Automation Best Practices
0 notes
Text
DevOps as Service
1. PILOT FRAMEWORK CREATION
We leverage and integrate your existing tools with our robust ecosystem of open source and licensed software.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Python Will Thrive: Future Trends and Applications
Python has already made a significant impact in the tech world, and its trajectory for the future is even more promising. From its simplicity and versatility to its widespread use in cutting-edge technologies, Python is expected to continue thriving in the coming years. Considering the kind support of Python Course in Chennai Whatever your level of experience or reason for switching from another programming language, learning Python gets much more fun.

Let's explore why Python will remain at the forefront of software development and what trends and applications will contribute to its ongoing dominance.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Python is already the go-to language for AI and machine learning, and its role in these fields is set to expand further. With powerful libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn, Python simplifies the development of machine learning models and artificial intelligence applications. As more industries integrate AI for automation, personalization, and predictive analytics, Python will remain a core language for developing intelligent systems.
2. Data Science and Big Data
Data science is one of the most significant areas where Python has excelled. Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib make data manipulation and visualization simple and efficient. As companies and organizations continue to generate and analyze vast amounts of data, Python’s ability to process, clean, and visualize big data will only become more critical. Additionally, Python’s compatibility with big data platforms like Hadoop and Apache Spark ensures that it will remain a major player in data-driven decision-making.
3. Web Development
Python’s role in web development is growing thanks to frameworks like Django and Flask, which provide robust, scalable, and secure solutions for building web applications. With the increasing demand for interactive websites and APIs, Python is well-positioned to continue serving as a top language for backend development. Its integration with cloud computing platforms will also fuel its growth in building modern web applications that scale efficiently.
4. Automation and Scripting
Automation is another area where Python excels. Developers use Python to automate tasks ranging from system administration to testing and deployment. With the rise of DevOps practices and the growing demand for workflow automation, Python’s role in streamlining repetitive processes will continue to grow. Businesses across industries will rely on Python to boost productivity, reduce errors, and optimize performance. With the aid of Best Online Training & Placement Programs, which offer comprehensive training and job placement support to anyone looking to develop their talents, it’s easier to learn this tool and advance your career.

5. Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking
With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses worldwide. Python is widely used for penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and threat detection due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Libraries like Scapy and PyCrypto make Python an excellent choice for ethical hacking and security professionals. As the need for robust cybersecurity measures increases, Python’s role in safeguarding digital assets will continue to thrive.
6. Internet of Things (IoT)
Python’s compatibility with microcontrollers and embedded systems makes it a strong contender in the growing field of IoT. Frameworks like MicroPython and CircuitPython enable developers to build IoT applications efficiently, whether for home automation, smart cities, or industrial systems. As the number of connected devices continues to rise, Python will remain a dominant language for creating scalable and reliable IoT solutions.
7. Cloud Computing and Serverless Architectures
The rise of cloud computing and serverless architectures has created new opportunities for Python. Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure all support Python, allowing developers to build scalable and cost-efficient applications. With its flexibility and integration capabilities, Python is perfectly suited for developing cloud-based applications, serverless functions, and microservices.
8. Gaming and Virtual Reality
Python has long been used in game development, with libraries such as Pygame offering simple tools to create 2D games. However, as gaming and virtual reality (VR) technologies evolve, Python’s role in developing immersive experiences will grow. The language’s ease of use and integration with game engines will make it a popular choice for building gaming platforms, VR applications, and simulations.
9. Expanding Job Market
As Python’s applications continue to grow, so does the demand for Python developers. From startups to tech giants like Google, Facebook, and Amazon, companies across industries are seeking professionals who are proficient in Python. The increasing adoption of Python in various fields, including data science, AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, ensures a thriving job market for Python developers in the future.
10. Constant Evolution and Community Support
Python’s open-source nature means that it’s constantly evolving with new libraries, frameworks, and features. Its vibrant community of developers contributes to its growth and ensures that Python stays relevant to emerging trends and technologies. Whether it’s a new tool for AI or a breakthrough in web development, Python’s community is always working to improve the language and make it more efficient for developers.
Conclusion
Python’s future is bright, with its presence continuing to grow in AI, data science, automation, web development, and beyond. As industries become increasingly data-driven, automated, and connected, Python’s simplicity, versatility, and strong community support make it an ideal choice for developers. Whether you are a beginner looking to start your coding journey or a seasoned professional exploring new career opportunities, learning Python offers long-term benefits in a rapidly evolving tech landscape.
#python course#python training#python#technology#tech#python programming#python online training#python online course#python online classes#python certification
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Python Powers Scalable and Cost-Effective Cloud Solutions

Explore the role of Python in developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. This guide covers Python's advantages in cloud computing, addresses potential challenges, and highlights real-world applications, providing insights into leveraging Python for efficient cloud development.
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly leveraging cloud computing to enhance scalability, optimize costs, and drive innovation. Among the myriad of programming languages available, Python has emerged as a preferred choice for developing robust cloud solutions. Its simplicity, versatility, and extensive library support make it an ideal candidate for cloud-based applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into how Python empowers scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions, explore its advantages, address potential challenges, and highlight real-world applications.
Why Python is the Preferred Choice for Cloud Computing?
Python's popularity in cloud computing is driven by several factors, making it the preferred language for developing and managing cloud solutions. Here are some key reasons why Python stands out:
Simplicity and Readability: Python's clean and straightforward syntax allows developers to write and maintain code efficiently, reducing development time and costs.
Extensive Library Support: Python offers a rich set of libraries and frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI for building cloud applications.
Seamless Integration with Cloud Services: Python is well-supported across major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Automation and DevOps Friendly: Python supports infrastructure automation with tools like Ansible, Terraform, and Boto3.
Strong Community and Enterprise Adoption: Python has a massive global community that continuously improves and innovates cloud-related solutions.
How Python Enables Scalable Cloud Solutions?
Scalability is a critical factor in cloud computing, and Python provides multiple ways to achieve it:
1. Automation of Cloud Infrastructure
Python's compatibility with cloud service provider SDKs, such as AWS Boto3, Azure SDK for Python, and Google Cloud Client Library, enables developers to automate the provisioning and management of cloud resources efficiently.
2. Containerization and Orchestration
Python integrates seamlessly with Docker and Kubernetes, enabling businesses to deploy scalable containerized applications efficiently.
3. Cloud-Native Development
Frameworks like Flask, Django, and FastAPI support microservices architecture, allowing businesses to develop lightweight, scalable cloud applications.
4. Serverless Computing
Python's support for serverless platforms, including AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, allows developers to build applications that automatically scale in response to demand, optimizing resource utilization and cost.
5. AI and Big Data Scalability
Python’s dominance in AI and data science makes it an ideal choice for cloud-based AI/ML services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI, and Azure Machine Learning.
Looking for expert Python developers to build scalable cloud solutions? Hire Python Developers now!
Advantages of Using Python for Cloud Computing
Cost Efficiency: Python’s compatibility with serverless computing and auto-scaling strategies minimizes cloud costs.
Faster Development: Python’s simplicity accelerates cloud application development, reducing time-to-market.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python runs seamlessly across different cloud platforms.
Security and Reliability: Python-based security tools help in encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring.
Strong Community Support: Python developers worldwide contribute to continuous improvements, making it future-proof.
Challenges and Considerations
While Python offers many benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
Performance Limitations: Python is an interpreted language, which may not be as fast as compiled languages like Java or C++.
Memory Consumption: Python applications might require optimization to handle large-scale cloud workloads efficiently.
Learning Curve for Beginners: Though Python is simple, mastering cloud-specific frameworks requires time and expertise.
Python Libraries and Tools for Cloud Computing
Python’s ecosystem includes powerful libraries and tools tailored for cloud computing, such as:
Boto3: AWS SDK for Python, used for cloud automation.
Google Cloud Client Library: Helps interact with Google Cloud services.
Azure SDK for Python: Enables seamless integration with Microsoft Azure.
Apache Libcloud: Provides a unified interface for multiple cloud providers.
PyCaret: Simplifies machine learning deployment in cloud environments.
Real-World Applications of Python in Cloud Computing
1. Netflix - Scalable Streaming with Python
Netflix extensively uses Python for automation, data analysis, and managing cloud infrastructure, enabling seamless content delivery to millions of users.
2. Spotify - Cloud-Based Music Streaming
Spotify leverages Python for big data processing, recommendation algorithms, and cloud automation, ensuring high availability and scalability.
3. Reddit - Handling Massive Traffic
Reddit uses Python and AWS cloud solutions to manage heavy traffic while optimizing server costs efficiently.
Future of Python in Cloud Computing
The future of Python in cloud computing looks promising with emerging trends such as:
AI-Driven Cloud Automation: Python-powered AI and machine learning will drive intelligent cloud automation.
Edge Computing: Python will play a crucial role in processing data at the edge for IoT and real-time applications.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Python’s flexibility will enable seamless integration across multiple cloud platforms.
Increased Adoption of Serverless Computing: More enterprises will adopt Python for cost-effective serverless applications.
Conclusion
Python's simplicity, versatility, and robust ecosystem make it a powerful tool for developing scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. By leveraging Python's capabilities, businesses can enhance their cloud applications' performance, flexibility, and efficiency.
Ready to harness the power of Python for your cloud solutions? Explore our Python Development Services to discover how we can assist you in building scalable and efficient cloud applications.
FAQs
1. Why is Python used in cloud computing?
Python is widely used in cloud computing due to its simplicity, extensive libraries, and seamless integration with cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
2. Is Python good for serverless computing?
Yes! Python works efficiently in serverless environments like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions, making it an ideal choice for cost-effective, auto-scaling applications.
3. Which companies use Python for cloud solutions?
Major companies like Netflix, Spotify, Dropbox, and Reddit use Python for cloud automation, AI, and scalable infrastructure management.
4. How does Python help with cloud security?
Python offers robust security libraries like PyCryptodome and OpenSSL, enabling encryption, authentication, and cloud monitoring for secure cloud applications.
5. Can Python handle big data in the cloud?
Yes! Python supports big data processing with tools like Apache Spark, Pandas, and NumPy, making it suitable for data-driven cloud applications.
#Python development company#Python in Cloud Computing#Hire Python Developers#Python for Multi-Cloud Environments
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Automated Testing vs. Manual Testing: Which One is Right for Your Project?

Achieving high-quality, reliable software stands as a fundamental requirement in software development. Successful testing functions as an essential tool to discover faults and build performance capabilities that create better user experience outcomes. Two main testing methods dominate the field: automated testing and manual testing. The process of quality software assurance uses different testing approaches that demonstrate their own advantages as well as weaknesses according to specific project requirements and scenarios. We will explore the specifics to determine which testing process works best for your system development efforts.
1. What Is Manual Testing?

Manual testing involves a human tester manually executing test cases without using automation tools. Key Characteristics:
The methodology focuses its efforts on user interface together with usability and experience testing.
Human-centered applications where selection requires discretion include ad hoc testing and enumerative testing as well as examinations that need human evaluation.
Human performers are required during this approach; thus, it demands substantial time.
2. What Is Automated Testing?

Software performing automated testing executes test cases through workflows and helpers. Key Characteristics:
Efficient for repetitive and regression testing.
Users must spend money on tools along with developing custom scripts for testing.
Reduces human error.
3. Advantages of Manual Testing

Human Intuition: Software testing professionals can detect kernels through their human cognitive ability that automated tools cannot match. The observation and evaluation of visual elements runs more efficiently through human operatives instead of advanced tools.
Flexibility: This method suits exploratory testing specifically because there are no pre-determined scripts available.
Low Initial Investment: Running this approach does not need tool purchases or applications to develop automation frameworks.
Adaptable for UI/UX Testing: Running this approach does not need tool purchases or applications to develop automation frameworks.
4. Advantages of Automated Testing

Speed: Executes repetitive tests much faster than humans.
Scalability: The system proves most effective for extensive projects that need constant system updates.
Accuracy: When performing recurring actions, automated systems minimize the chances of human mistakes.
Cost-Efficient in the Long Run: Once established and implemented, the system demands costly investments but ensures continuous development expenses decrease over time.
Better for CI/CD Pipelines: Such testing technology connects various development pipelines that support agile and DevOps methodologies.
5. Disadvantages of Manual Testing

Time-Consuming: The manual performance of repeated tests leads to delayed completion of projects.
Error-Prone: Large applications contain tiny bugs that human testers commonly fail to detect.
Not Ideal for Scalability: The process of increasing manual testing needs additional testers to avoid cost escalations.
6. Disadvantages of Automated Testing

Initial Costs: Organizations must provide high financial resources to procure testing tools together with developing programming constructs.
Limited to Pre-Defined Scenarios: These testing approaches work poorly for handling exploratory or ad hoc testing.
Requires Maintenance: Test scripts need frequent updates when application changes occur.
Not Suitable for UI/UX Testing: Struggles with subjective user experience evaluations.
7. When to Use Manual Testing

Small Projects: The testing method proves beneficial at a low cost for small applications and provides quick assessments.
Exploratory Testing: Testing this approach benefits projects whose scripts have not been defined yet or need evaluation for newly added features.
Visual and Usability Testing: Performing assessments on interface components together with design features.
8. When to Use Automated Testing

Large Projects: Handles scalability for projects with frequent updates.
Regression Testing: Program testing becomes more efficient through automation since automated assessments perform multiple tests following each update process.
Performance Testing: The system performs efficient capabilities to conduct load testing and stress testing.
Continuous Development Environments: Agile progression and DevOps implementations need automation as a core requirement.
READ MORE- https://www.precisio.tech/automated-testing-vs-manual-testing-which-one-is-right-for-your-project/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 10 In- Demand Tech Jobs in 2025

Technology is growing faster than ever, and so is the need for skilled professionals in the field. From artificial intelligence to cloud computing, businesses are looking for experts who can keep up with the latest advancements. These tech jobs not only pay well but also offer great career growth and exciting challenges.
In this blog, we’ll look at the top 10 tech jobs that are in high demand today. Whether you’re starting your career or thinking of learning new skills, these jobs can help you plan a bright future in the tech world.
1. AI and Machine Learning Specialists
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are changing the game by helping machines learn and improve on their own without needing step-by-step instructions. They’re being used in many areas, like chatbots, spotting fraud, and predicting trends.
Key Skills: Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, data analysis, deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP).
Industries Hiring: Healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing.
Career Tip: Keep up with AI and machine learning by working on projects and getting an AI certification. Joining AI hackathons helps you learn and meet others in the field.
2. Data Scientists
Data scientists work with large sets of data to find patterns, trends, and useful insights that help businesses make smart decisions. They play a key role in everything from personalized marketing to predicting health outcomes.
Key Skills: Data visualization, statistical analysis, R, Python, SQL, and data mining.
Industries Hiring: E-commerce, telecommunications, and pharmaceuticals.
Career Tip: Work with real-world data and build a strong portfolio to showcase your skills. Earning certifications in data science tools can help you stand out.
3. Cloud Computing Engineers: These professionals create and manage cloud systems that allow businesses to store data and run apps without needing physical servers, making operations more efficient.
Key Skills: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), DevOps, and containerization (Docker, Kubernetes).
Industries Hiring: IT services, startups, and enterprises undergoing digital transformation.
Career Tip: Get certified in cloud platforms like AWS (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect).
4. Cybersecurity Experts
Cybersecurity professionals protect companies from data breaches, malware, and other online threats. As remote work grows, keeping digital information safe is more crucial than ever.
Key Skills: Ethical hacking, penetration testing, risk management, and cybersecurity tools.
Industries Hiring: Banking, IT, and government agencies.
Career Tip: Stay updated on new cybersecurity threats and trends. Certifications like CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker) or CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) can help you advance in your career.
5. Full-Stack Developers
Full-stack developers are skilled programmers who can work on both the front-end (what users see) and the back-end (server and database) of web applications.
Key Skills: JavaScript, React, Node.js, HTML/CSS, and APIs.
Industries Hiring: Tech startups, e-commerce, and digital media.
Career Tip: Create a strong GitHub profile with projects that highlight your full-stack skills. Learn popular frameworks like React Native to expand into mobile app development.
6. DevOps Engineers
DevOps engineers help make software faster and more reliable by connecting development and operations teams. They streamline the process for quicker deployments.
Key Skills: CI/CD pipelines, automation tools, scripting, and system administration.
Industries Hiring: SaaS companies, cloud service providers, and enterprise IT.
Career Tip: Earn key tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Kubernetes, and develop scripting skills in languages like Bash or Python. Earning a DevOps certification is a plus and can enhance your expertise in the field.
7. Blockchain Developers
They build secure, transparent, and unchangeable systems. Blockchain is not just for cryptocurrencies; it’s also used in tracking supply chains, managing healthcare records, and even in voting systems.
Key Skills: Solidity, Ethereum, smart contracts, cryptography, and DApp development.
Industries Hiring: Fintech, logistics, and healthcare.
Career Tip: Create and share your own blockchain projects to show your skills. Joining blockchain communities can help you learn more and connect with others in the field.
8. Robotics Engineers
Robotics engineers design, build, and program robots to do tasks faster or safer than humans. Their work is especially important in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
Key Skills: Programming (C++, Python), robotics process automation (RPA), and mechanical engineering.
Industries Hiring: Automotive, healthcare, and logistics.
Career Tip: Stay updated on new trends like self-driving cars and AI in robotics.
9. Internet of Things (IoT) Specialists
IoT specialists work on systems that connect devices to the internet, allowing them to communicate and be controlled easily. This is crucial for creating smart cities, homes, and industries.
Key Skills: Embedded systems, wireless communication protocols, data analytics, and IoT platforms.
Industries Hiring: Consumer electronics, automotive, and smart city projects.
Career Tip: Create IoT prototypes and learn to use platforms like AWS IoT or Microsoft Azure IoT. Stay updated on 5G technology and edge computing trends.
10. Product Managers
Product managers oversee the development of products, from idea to launch, making sure they are both technically possible and meet market demands. They connect technical teams with business stakeholders.
Key Skills: Agile methodologies, market research, UX design, and project management.
Industries Hiring: Software development, e-commerce, and SaaS companies.
Career Tip: Work on improving your communication and leadership skills. Getting certifications like PMP (Project Management Professional) or CSPO (Certified Scrum Product Owner) can help you advance.
Importance of Upskilling in the Tech Industry
Stay Up-to-Date: Technology changes fast, and learning new skills helps you keep up with the latest trends and tools.
Grow in Your Career: By learning new skills, you open doors to better job opportunities and promotions.
Earn a Higher Salary: The more skills you have, the more valuable you are to employers, which can lead to higher-paying jobs.
Feel More Confident: Learning new things makes you feel more prepared and ready to take on tougher tasks.
Adapt to Changes: Technology keeps evolving, and upskilling helps you stay flexible and ready for any new changes in the industry.
Top Companies Hiring for These Roles
Global Tech Giants: Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and IBM.
Startups: Fintech, health tech, and AI-based startups are often at the forefront of innovation.
Consulting Firms: Companies like Accenture, Deloitte, and PwC increasingly seek tech talent.
In conclusion, the tech world is constantly changing, and staying updated is key to having a successful career. In 2025, jobs in fields like AI, cybersecurity, data science, and software development will be in high demand. By learning the right skills and keeping up with new trends, you can prepare yourself for these exciting roles. Whether you're just starting or looking to improve your skills, the tech industry offers many opportunities for growth and success.
#Top 10 Tech Jobs in 2025#In- Demand Tech Jobs#High paying Tech Jobs#artificial intelligence#datascience#cybersecurity
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Full Stack Testing vs. Full Stack Development: What’s the Difference?

In today’s fast-evolving tech world, buzzwords like Full Stack Development and Full Stack Testing have gained immense popularity. Both roles are vital in the software lifecycle, but they serve very different purposes. Whether you’re a beginner exploring your career options or a professional looking to expand your skills, understanding the differences between Full Stack Testing and Full Stack Development is crucial. Let’s dive into what makes these two roles unique!
What Is Full Stack Development?
Full Stack Development refers to the ability to build an entire software application – from the user interface to the backend logic – using a wide range of tools and technologies. A Full Stack Developer is proficient in both front-end (user-facing) and back-end (server-side) development.
Key Responsibilities of a Full Stack Developer:
Front-End Development: Building the user interface using tools like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, or Angular.
Back-End Development: Creating server-side logic using languages like Node.js, Python, Java, or PHP.
Database Management: Handling databases such as MySQL, MongoDB, or PostgreSQL.
API Integration: Connecting applications through RESTful or GraphQL APIs.
Version Control: Using tools like Git for collaborative development.
Skills Required for Full Stack Development:
Proficiency in programming languages (JavaScript, Python, Java, etc.)
Knowledge of web frameworks (React, Django, etc.)
Experience with databases and cloud platforms
Understanding of DevOps tools
In short, a Full Stack Developer handles everything from designing the UI to writing server-side code, ensuring the software runs smoothly.
What Is Full Stack Testing?
Full Stack Testing is all about ensuring quality at every stage of the software development lifecycle. A Full Stack Tester is responsible for testing applications across multiple layers – from front-end UI testing to back-end database validation – ensuring a seamless user experience. They blend manual and automation testing skills to detect issues early and prevent software failures.
Key Responsibilities of a Full Stack Tester:
UI Testing: Ensuring the application looks and behaves correctly on the front end.
API Testing: Validating data flow and communication between services.
Database Testing: Verifying data integrity and backend operations.
Performance Testing: Ensuring the application performs well under load using tools like JMeter.
Automation Testing: Automating repetitive tests with tools like Selenium or Cypress.
Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities to prevent cyber-attacks.
Skills Required for Full Stack Testing:
Knowledge of testing tools like Selenium, Postman, JMeter, or TOSCA
Proficiency in both manual and automation testing
Understanding of test frameworks like TestNG or Cucumber
Familiarity with Agile and DevOps practices
Basic knowledge of programming for writing test scripts
A Full Stack Tester plays a critical role in identifying bugs early in the development process and ensuring the software functions flawlessly.
Which Career Path Should You Choose?
The choice between Full Stack Development and Full Stack Testing depends on your interests and strengths:
Choose Full Stack Development if you love coding, creating interfaces, and building software solutions from scratch. This role is ideal for those who enjoy developing creative products and working with both front-end and back-end technologies.
Choose Full Stack Testing if you have a keen eye for detail and enjoy problem-solving by finding bugs and ensuring software quality. If you love automation, performance testing, and working with multiple testing tools, Full Stack Testing is the right path.
Why Both Roles Are Essential :
Both Full Stack Developers and Full Stack Testers are integral to software development. While developers focus on creating functional features, testers ensure that everything runs smoothly and meets user expectations. In an Agile or DevOps environment, these roles often overlap, with testers and developers working closely to deliver high-quality software in shorter cycles.
Final Thoughts :
Whether you opt for Full Stack Testing or Full Stack Development, both fields offer exciting opportunities with tremendous growth potential. With software becoming increasingly complex, the demand for skilled developers and testers is higher than ever.
At TestoMeter Pvt. Ltd., we provide comprehensive training in both Full Stack Development and Full Stack Testing to help you build a future-proof career. Whether you want to build software or ensure its quality, we’ve got the perfect course for you.
Ready to take the next step? Explore our Full Stack courses today and start your journey toward a successful IT career!
This blog not only provides a crisp comparison but also encourages potential students to explore both career paths with TestoMeter.
For more Details :
Interested in kick-starting your Software Developer/Software Tester career? Contact us today or Visit our website for course details, success stories, and more!
🌐visit - https://www.testometer.co.in/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Python: Features and Where It's Used
Python is a versatile programming language that has gained significant popularity in recent times. It's known for its ease of use, readability, and adaptability, making it an excellent choice for both newcomers and experienced programmers. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of what Python is and explore its various applications.
What is Python?
Python is an interpreted programming language that is high-level and serves multiple purposes. Created by Guido van Rossum and released in 1991, Python is designed to prioritize code readability and simplicity, with a clean and minimalistic syntax. It places emphasis on using proper indentation and whitespace, making it more convenient for programmers to write and comprehend code.
Key Traits of Python :
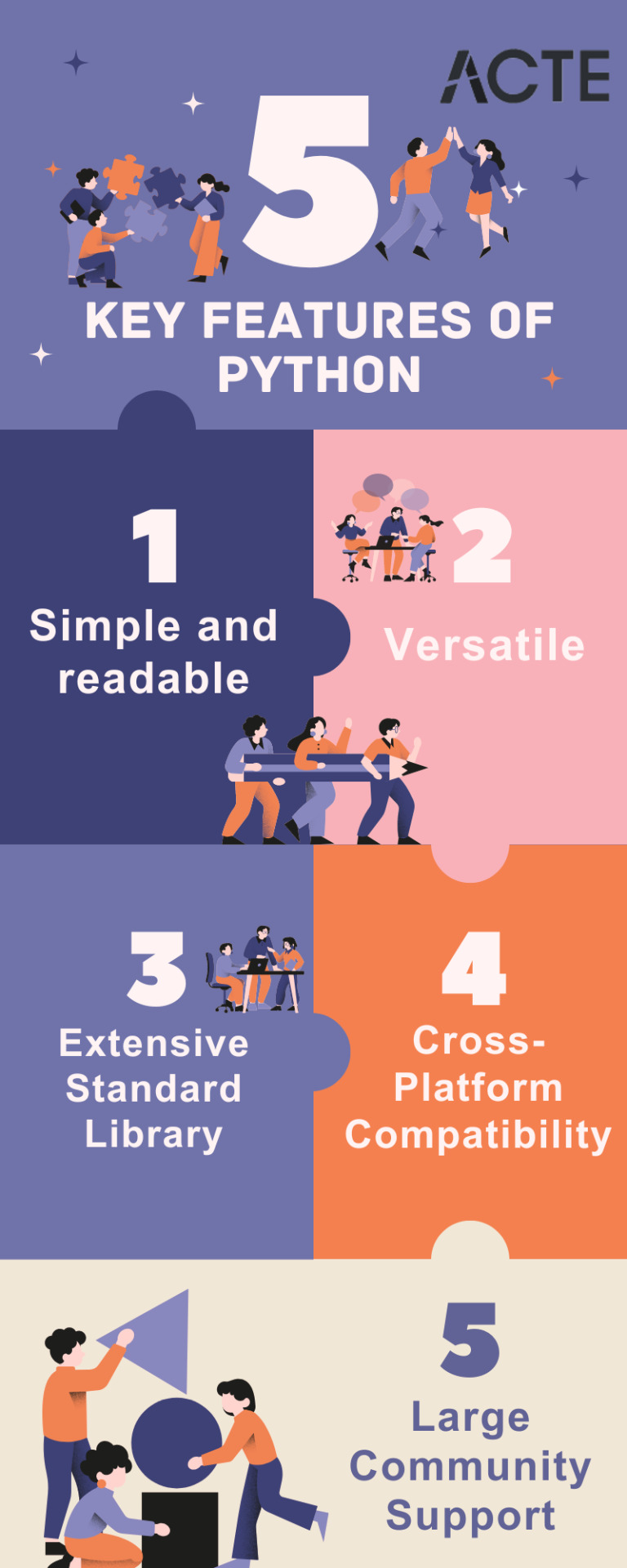
Simplicity and Readability: Python code is structured in a way that's easy to read and understand. This reduces the time and effort required for both creating and maintaining software.
Python code example: print("Hello, World!")
Versatility: Python is applicable across various domains, from web development and scientific computing to data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more.
Python code example: import numpy as np
Extensive Standard Library: Python offers an extensive collection of pre-built libraries and modules. These resources provide developers with ready-made tools and functions to tackle complex tasks efficiently.
Python code example: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Compatibility Across Platforms: Python is available on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This allows programmers to create and run code seamlessly across different platforms.
Strong Community Support: Python boasts an active community of developers who contribute to its growth and provide support through online forums, documentation, and open-source contributions. This community support makes Python an excellent choice for developers seeking assistance or collaboration.
Where is Python Utilized?

Due to its versatility, Python is utilized in various domains and industries. Some key areas where Python is widely applied include:
Web Development: Python is highly suitable for web development tasks. It offers powerful frameworks like Django and Flask, simplifying the process of building robust web applications. The simplicity and readability of Python code enable developers to create clean and maintainable web applications efficiently.
Data Science and Machine Learning: Python has become the go-to language for data scientists and machine learning practitioners. Its extensive libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and SciPy, along with specialized libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch, facilitate a seamless workflow for data analysis, modeling, and implementing machine learning algorithms.
Scientific Computing: Python is extensively used in scientific computing and research due to its rich scientific libraries and tools. Libraries like SciPy, Matplotlib, and NumPy enable efficient handling of scientific data, visualization, and numerical computations, making Python indispensable for scientists and researchers.
Automation and Scripting: Python's simplicity and versatility make it a preferred language for automating repetitive tasks and writing scripts. Its comprehensive standard library empowers developers to automate various processes within the operating system, network operations, and file manipulation, making it popular among system administrators and DevOps professionals.
Game Development: Python's ease of use and availability of libraries like Pygame make it an excellent choice for game development. Developers can create interactive and engaging games efficiently, and the language's simplicity allows for quick prototyping and development cycles.
Internet of Things (IoT): Python's lightweight nature and compatibility with microcontrollers make it suitable for developing applications for the Internet of Things. Libraries like Circuit Python enable developers to work with sensors, create interactive hardware projects, and connect devices to the internet.
Python's versatility and simplicity have made it one of the most widely used programming languages across diverse domains. Its clean syntax, extensive libraries, and cross-platform compatibility make it a powerful tool for developers. Whether for web development, data science, automation, or game development, Python proves to be an excellent choice for programmers seeking efficiency and user-friendliness. If you're considering learning a programming language or expanding your skills, Python is undoubtedly worth exploring.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Software Development: Unveiling the Transformative Impact of DevOps as a Service
In the dynamic realm of software development, the adoption of DevOps as a service (DaaS) has emerged as a revolutionary force, reshaping the fundamental dynamics of how organizations conceive, construct, and manage their software ecosystems. This transformative approach brings a host of advantages, fundamentally altering the collaborative, innovative, and delivery landscape. Here are seven pivotal benefits encapsulating the essence of embracing DevOps as a service:

1. Swift Time-to-Market Acceleration: DevOps as a service functions as a catalyst, propelling the software development lifecycle into unprecedented speeds. Streamlined and automated processes facilitate quicker and more frequent releases, granting organizations a competitive edge by swiftly introducing new features and updates to the market.
2. Reinforced Collaboration Framework: At its core, DevOps champions a culture of collaboration, and DevOps as a service takes this ethos to new heights by dismantling traditional silos between development and operations teams. The heightened communication and cooperation create an integrated and efficient workflow, fostering shared responsibility across the software delivery spectrum.
3. Elevated Software Quality and Reliability: Automation, a cornerstone of DevOps as a service, especially in testing and deployment, ensures uniform and dependable software releases. This automated precision results in superior code quality, diminished errors, and an overall elevation in the reliability of software systems.
4. Strategic Cost-Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks, DevOps as a service strategically optimizes resource usage, leading to tangible and substantial cost savings. The reduction in manual efforts, coupled with astute infrastructure management, translates into financial advantages for organizations keen on maximizing efficiency.
5. Unparalleled Scalability and Flexibility: A defining feature of DevOps as a service is its innate scalability, allowing organizations to seamlessly adjust resources based on demand fluctuations. This unparalleled flexibility ensures optimal performance without incurring unnecessary infrastructure costs, making it an ideal fit for businesses navigating varying workloads.

6. Streamlined Deployment Efficiency: Automation within the deployment pipeline is a hallmark of DevOps as a service. By eradicating manual interventions, this approach reduces deployment errors and minimizes downtime, creating a more efficient, reliable, and streamlined deployment process.
7. Empowered Focus on Innovation: Liberated from routine tasks through automation, teams can now channel their efforts into innovation. DevOps as a service empowers organizations to invest time and resources in developing new features, refining user experiences, and positioning themselves as pioneers in a competitive market.
In conclusion, the incorporation of DevOps as a service heralds a revolutionary shift in the conventional approach to software development. It transcends traditional boundaries, fostering collaboration, innovation, and efficiency. As organizations navigate the intricate digital landscape, DevOps as a service emerges as a transformative force, offering a strategic advantage for those poised not only to adapt to technological advancements but to lead the charge in delivering impactful, high-quality software solutions.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a world where security is paramount, Java looks to be an unrivaled platform getting better with every new update. It is a premier programming language and an extraordinary ecosystem with the ability to deal with security concerns more effectively, thanks to its important tools and libraries.
Another aspect of Java’s unrivaled success is its “Write Once, Run Anywhere” principle. It doesn’t require recompilation when developing Java applications, which makes it the best choice for cross-platform software development.
Java is highly chosen for a wide range of projects, including AI/ML application development, Android app development, Bespoke Java software development, bespoke Blockchain development, and many more.
#java development#future of Java#java trends#java developer for hire#Java programming language for cloud-native development#Java frameworks for microservices architecture#Java ecosystem tools for DevOps automation#Java web development trends in 2023#Agile Java development with DevOps best practices#Java Development Unleashed#software development#angular development
0 notes
Text
Leading the Way in IT- ChatGPT's Transformative Impact
In the dynamic world of Information Technology, a transformative force is reshaping the field: ChatGPT. This advanced AI, built on the sophisticated GPT-3.5 framework, is not just a revolutionary tool but a catalyst for unprecedented innovation, efficiency, and enhanced human-AI collaboration.

The ChatGPT Edge With its deep understanding of context, nuanced responses, and adaptive learning, ChatGPT stands as a groundbreaking advancement in natural language processing. It's a boon for IT professionals, enabling them to tackle complex problems, improve team communication, and offer solutions tailored to the unique challenges of the IT realm. Revolutionizing DevOps Communication ChatGPT marks a significant leap in DevOps, facilitating smoother communication and collaboration. It excels in interpreting natural language, allowing real-time issue resolution, task automation, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. DevOps teams can leverage ChatGPT for enhanced decision-making and adaptability in the ever-changing landscape of software development. Enhancing Product Development Cycles In product development, ChatGPT's contribution is invaluable. It streamlines the lifecycle by grasping complex requirements and generating structured specifications. Teams can use ChatGPT to refine ideas rapidly, leading to more effective development processes and innovative solutions that align with user expectations. Advancing Mobile and Web Application Development For web and mobile app developers, ChatGPT accelerates the coding process. Its ability to understand context and generate code quickens development cycles. Integrating ChatGPT into workflows helps tackle coding challenges, troubleshoot, and enhance code quality, resulting in a more agile and responsive development process. The Future of IT with ChatGPT Looking ahead, ChatGPT's role in IT is poised to expand significantly. This fusion of conversational AI and technical acumen will revolutionize collaboration and innovation across DevOps, product development, and app development. ChatGPT is set to be a key driver in creating an adaptable, efficient, and collaborative IT ecosystem.
ChatGPT is guiding the IT industry towards an era where efficiency and collaboration take center stage. As organizations adopt this transformative technology, the sectors of DevOps, product development, and app development are on the cusp of a major evolution. Embrace ChatGPT as it leads the charge in IT innovation, where efficiency meets creativity in the digital world.
#devops#product engineering#information technology#software development#product development#upperthrusttechnologies#chatgpt#ai tools#ai technology#openai
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Going Over the Cloud: An Investigation into the Architecture of Cloud Solutions

Because the cloud offers unprecedented levels of size, flexibility, and accessibility, it has fundamentally altered the way we approach technology in the present digital era. As more and more businesses shift their infrastructure to the cloud, it is imperative that they understand the architecture of cloud solutions. Join me as we examine the core concepts, industry best practices, and transformative impacts on modern enterprises.
The Basics of Cloud Solution Architecture A well-designed architecture that balances dependability, performance, and cost-effectiveness is the foundation of any successful cloud deployment. Cloud solutions' architecture is made up of many different components, including networking, computing, storage, security, and scalability. By creating solutions that are tailored to the requirements of each workload, organizations can optimize return on investment and fully utilize the cloud.
Flexibility and Resilience in Design The flexibility of cloud computing to grow resources on-demand to meet varying workloads and guarantee flawless performance is one of its distinguishing characteristics. Cloud solution architecture create resilient systems that can endure failures and sustain uptime by utilizing fault-tolerant design principles, load balancing, and auto-scaling. Workloads can be distributed over several availability zones and regions to help enterprises increase fault tolerance and lessen the effect of outages.
Protection of Data in the Cloud and Security by Design
As data thefts become more common, security becomes a top priority in cloud solution architecture. Architects include identity management, access controls, encryption, and monitoring into their designs using a multi-layered security strategy. By adhering to industry standards and best practices, such as the shared responsibility model and compliance frameworks, organizations may safeguard confidential information and guarantee regulatory compliance in the cloud.
Using Professional Services to Increase Productivity Cloud service providers offer a variety of managed services that streamline operations and reduce the stress of maintaining infrastructure. These services allow firms to focus on innovation instead of infrastructure maintenance. They include server less computing, machine learning, databases, and analytics. With cloud-native applications, architects may reduce costs, increase time-to-market, and optimize performance by selecting the right mix of managed services.
Cost control and ongoing optimization Cost optimization is essential since inefficient resource use can quickly drive up costs. Architects monitor resource utilization, analyze cost trends, and identify opportunities for optimization with the aid of tools and techniques. Businesses can cut waste and maximize their cloud computing expenses by using spot instances, reserved instances, and cost allocation tags.
Acknowledging Automation and DevOps Important elements of cloud solution design include automation and DevOps concepts, which enable companies to develop software more rapidly, reliably, and efficiently. Architects create pipelines for continuous integration, delivery, and deployment, which expedites the software development process and allows for rapid iterations. By provisioning and managing infrastructure programmatically with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Configuration Management systems, teams may minimize human labor and guarantee consistency across environments.
Multiple-cloud and hybrid strategies In an increasingly interconnected world, many firms employ hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to leverage the benefits of many cloud providers in addition to on-premises infrastructure. Cloud solution architects have to design systems that seamlessly integrate several environments while ensuring interoperability, data consistency, and regulatory compliance. By implementing hybrid connection options like VPNs, Direct Connect, or Express Route, organizations may develop hybrid cloud deployments that include the best aspects of both public and on-premises data centers. Analytics and Data Management Modern organizations depend on data because it fosters innovation and informed decision-making. Thanks to the advanced data management and analytics solutions developed by cloud solution architects, organizations can effortlessly gather, store, process, and analyze large volumes of data. By leveraging cloud-native data services like data warehouses, data lakes, and real-time analytics platforms, organizations may gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries and extract valuable insights. Architects implement data governance frameworks and privacy-enhancing technologies to ensure adherence to data protection rules and safeguard sensitive information.
Computing Without a Server Server less computing, a significant shift in cloud architecture, frees organizations to focus on creating applications rather than maintaining infrastructure or managing servers. Cloud solution architects develop server less programs using event-driven architectures and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions. By abstracting away the underlying infrastructure, server less architectures offer unparalleled scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility, empowering companies to innovate swiftly and change course without incurring additional costs.
Conclusion As we come to the close of our investigation into cloud solution architecture, it is evident that the cloud is more than just a platform for technology; it is a force for innovation and transformation. By embracing the ideas of scalability, resilience, and security, and efficiency, organizations can take advantage of new opportunities, drive business expansion, and preserve their competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving digital market. Thus, to ensure success, remember to leverage cloud solution architecture when developing a new cloud-native application or initiating a cloud migration.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Explore Career Opportunities: The Importance of Selenium WebDriver Training"
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software testing, proficiency in Selenium WebDriver has become a key differentiator for professionals. Whether you're already in the field or aspiring to enter it, investing time in Selenium WebDriver training can significantly boost your career prospects. Embracing Selenium's capabilities becomes even more accessible and impactful with Selenium Training in Hyderabad. This training equips individuals with the skills and knowledge to harness the full potential of Selenium, enabling them to proficiently navigate web automation challenges and contribute effectively to their respective fields. Let's delve into the reasons why acquiring skills in Selenium WebDriver is essential for a successful career in software testing.

1. Industry Relevance:
Selenium WebDriver is not just another tool; it's an industry-standard for automating web applications. Its widespread adoption across various sectors makes it a must-have skill for professionals in the field of software testing and quality assurance. Knowing Selenium WebDriver is a clear indicator of industry relevance.
2. Career Opportunities:
The demand for professionals with Selenium skills is on the rise. Many organizations specifically seek candidates well-versed in Selenium when hiring for testing roles. Whether you're aiming for a test automation engineer position or a quality assurance role, Selenium proficiency enhances your employability.
3. Efficient Testing Practices:
One of the primary benefits of Selenium WebDriver is its ability to automate repetitive testing tasks. This not only accelerates the testing process but also ensures more reliable results. Automated testing with Selenium can significantly reduce the time and effort required for regression testing, enabling faster and more efficient releases.
4. Cross-Browser Testing:
Web applications need to provide a consistent user experience across various browsers. Selenium WebDriver supports cross-browser testing, allowing you to test your applications on different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and more. This capability is crucial for identifying and addressing compatibility issues.
5. Integration with Other Tools:
Selenium WebDriver seamlessly integrates with other tools and frameworks, such as TestNG and JUnit. This integration enhances the overall test automation capabilities, making it easier to manage and report test results. A well-integrated testing environment is a valuable asset for any QA professional. To unlock the full potential of Selenium and master the art of web automation, consider enrolling in the Top Selenium Training Institute.
6. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
In the era of DevOps, where continuous integration and continuous deployment are standard practices, Selenium WebDriver plays a pivotal role. Automated testing is a critical component of CI/CD pipelines, ensuring that new code changes don't introduce regressions. Knowledge of Selenium is, therefore, advantageous in a DevOps environment.

7. Cost-Efficiency:
Automated testing with Selenium proves to be cost-efficient, particularly for large and complex applications. While setting up automated scripts requires an initial investment of time and resources, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced manual testing efforts and faster release cycles outweigh the initial costs.
8. Skill Diversification:
Adding Selenium WebDriver to your skill set goes beyond just mastering a tool; it's about diversifying your expertise. For professionals in software development or quality assurance, knowing Selenium showcases your commitment to staying abreast of industry-relevant tools and technologies.
In conclusion, Selenium WebDriver training is not just about learning a tool; it's about unlocking a world of career opportunities. As the demand for skilled software testing professionals continues to grow, those with Selenium proficiency will find themselves well-positioned for success. Whether you're aiming to advance in your current role or explore new career horizons, investing in Selenium WebDriver training is a strategic move that can propel your career to new heights.
2 notes
·
View notes