#cloud solution architecture
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Going Over the Cloud: An Investigation into the Architecture of Cloud Solutions

Because the cloud offers unprecedented levels of size, flexibility, and accessibility, it has fundamentally altered the way we approach technology in the present digital era. As more and more businesses shift their infrastructure to the cloud, it is imperative that they understand the architecture of cloud solutions. Join me as we examine the core concepts, industry best practices, and transformative impacts on modern enterprises.
The Basics of Cloud Solution Architecture A well-designed architecture that balances dependability, performance, and cost-effectiveness is the foundation of any successful cloud deployment. Cloud solutions' architecture is made up of many different components, including networking, computing, storage, security, and scalability. By creating solutions that are tailored to the requirements of each workload, organizations can optimize return on investment and fully utilize the cloud.
Flexibility and Resilience in Design The flexibility of cloud computing to grow resources on-demand to meet varying workloads and guarantee flawless performance is one of its distinguishing characteristics. Cloud solution architecture create resilient systems that can endure failures and sustain uptime by utilizing fault-tolerant design principles, load balancing, and auto-scaling. Workloads can be distributed over several availability zones and regions to help enterprises increase fault tolerance and lessen the effect of outages.
Protection of Data in the Cloud and Security by Design
As data thefts become more common, security becomes a top priority in cloud solution architecture. Architects include identity management, access controls, encryption, and monitoring into their designs using a multi-layered security strategy. By adhering to industry standards and best practices, such as the shared responsibility model and compliance frameworks, organizations may safeguard confidential information and guarantee regulatory compliance in the cloud.
Using Professional Services to Increase Productivity Cloud service providers offer a variety of managed services that streamline operations and reduce the stress of maintaining infrastructure. These services allow firms to focus on innovation instead of infrastructure maintenance. They include server less computing, machine learning, databases, and analytics. With cloud-native applications, architects may reduce costs, increase time-to-market, and optimize performance by selecting the right mix of managed services.
Cost control and ongoing optimization Cost optimization is essential since inefficient resource use can quickly drive up costs. Architects monitor resource utilization, analyze cost trends, and identify opportunities for optimization with the aid of tools and techniques. Businesses can cut waste and maximize their cloud computing expenses by using spot instances, reserved instances, and cost allocation tags.
Acknowledging Automation and DevOps Important elements of cloud solution design include automation and DevOps concepts, which enable companies to develop software more rapidly, reliably, and efficiently. Architects create pipelines for continuous integration, delivery, and deployment, which expedites the software development process and allows for rapid iterations. By provisioning and managing infrastructure programmatically with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Configuration Management systems, teams may minimize human labor and guarantee consistency across environments.
Multiple-cloud and hybrid strategies In an increasingly interconnected world, many firms employ hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to leverage the benefits of many cloud providers in addition to on-premises infrastructure. Cloud solution architects have to design systems that seamlessly integrate several environments while ensuring interoperability, data consistency, and regulatory compliance. By implementing hybrid connection options like VPNs, Direct Connect, or Express Route, organizations may develop hybrid cloud deployments that include the best aspects of both public and on-premises data centers. Analytics and Data Management Modern organizations depend on data because it fosters innovation and informed decision-making. Thanks to the advanced data management and analytics solutions developed by cloud solution architects, organizations can effortlessly gather, store, process, and analyze large volumes of data. By leveraging cloud-native data services like data warehouses, data lakes, and real-time analytics platforms, organizations may gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries and extract valuable insights. Architects implement data governance frameworks and privacy-enhancing technologies to ensure adherence to data protection rules and safeguard sensitive information.
Computing Without a Server Server less computing, a significant shift in cloud architecture, frees organizations to focus on creating applications rather than maintaining infrastructure or managing servers. Cloud solution architects develop server less programs using event-driven architectures and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions. By abstracting away the underlying infrastructure, server less architectures offer unparalleled scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility, empowering companies to innovate swiftly and change course without incurring additional costs.
Conclusion As we come to the close of our investigation into cloud solution architecture, it is evident that the cloud is more than just a platform for technology; it is a force for innovation and transformation. By embracing the ideas of scalability, resilience, and security, and efficiency, organizations can take advantage of new opportunities, drive business expansion, and preserve their competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving digital market. Thus, to ensure success, remember to leverage cloud solution architecture when developing a new cloud-native application or initiating a cloud migration.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Maximizing the Potential of ChatGPT: Unveiling Unique Strategies for Cloud Solution Architects
The role of Cloud Solution Architects is ever-evolving, demanding adaptability to the latest tools and technologies. Amid this landscape, ChatGPT emerges as a game-changer, offering AI-powered capabilities that can significantly enhance the architect’s effectiveness. This article delves deep into the lesser-known secrets of using ChatGPT, revealing how Cloud Solution Architects can leverage its…

View On WordPress
#AI-powered Solutions#Architecture Design#ChatGPT#cloud computing#Cloud Cost Management#Cloud Solution Architecture#Code Automation#cost optimization#Dynamic Documentation#Innovative Strategies#Real-time Troubleshooting#Simulation
1 note
·
View note
Text
Jade Tower by Tiger at Majan Dubai
Jade Tower by Tiger Properties, a new residential development in Dubai, offers 707 units between studios and apartments. your luxury choice from a variety of spaces and layouts, featuring a serene view of lush green landscapes.
Delve into a lavish lifestyle in Dubai by Tiger Group at Jade Tower at Majan Dubai, offering studios and apartments with affordable prices starting at 533,000 AED and providing many options in unit sizes, starting from 340 square feet to 1020 square feet and above.
The payment plan at Jade Tower is the top feature, as there are two options to choose from, even 80\20 or 70\30. The installment plan extends over 2 years. Lastly, the handover will be in Q1 2027.

#real estate#architecture#dubai#business#clouds#interiors#decor#city#home#kitchen#ACLA24#ACLA24Leaders#youtube#youtube video#climate leaders#climate solutions#climate action#climate and environment#climate#climate change#climate and health#climate blog#climate justice#climate news#weather and climate#environmental news#environment#environmental awareness#environment and health#environmental
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Integration Solutions with Cloud-Based Architectural Design
W3 Partnership, founded in 2007, provides solutions and services that help organizations make sense of their digital applications and services through integrated platforms and patterns. SMEs in their respective fields, our in-house integration consultants are specialists in IBM and MuleSoft products, and our cloud consultants and developers are experts in AWS and Azure. We design, develop, manage, and monitor such platforms.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Solution Architecture
Job title: Cloud Solution Architecture Company: Microsoft Job description: your skills in technical leadership, cloud computing, software development, problem solving and systems architecture…, architecture, and/or consulting OR Master’s Degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, Engineering, Business… Expected salary: $83400 per year Location: USA Job date: Thu, 24 Apr 2025 03:47:24…
0 notes
Text
Data Unbound: Embracing NoSQL & NewSQL for the Real-Time Era.
Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo. skm.stayingalive.in Explore how NoSQL and NewSQL databases revolutionize data management by handling unstructured data, supporting distributed architectures, and enabling real-time analytics. In today’s digital-first landscape, businesses and institutions are under mounting pressure to process massive volumes of data with greater speed,…
#ACID compliance#CIO decision-making#cloud data platforms#cloud-native data systems#column-family databases#data strategy#data-driven applications#database modernization#digital transformation#distributed database architecture#document stores#enterprise database platforms#graph databases#horizontal scaling#hybrid data stack#in-memory processing#IT modernization#key-value databases#News#NewSQL databases#next-gen data architecture#NoSQL databases#performance-driven applications#real-time data analytics#real-time data infrastructure#Sanjay Kumar Mohindroo#scalable database solutions#scalable systems for growth#schema-less databases#Tech Leadership
0 notes
Text
How to Build an Effective Cloud Organization
#ai#azure#Cloud#Cloud Architecture#Cloud Operating Model#cloud-computing#Enterprise Architecture#IT Strategy#Michael Griffin#Solution Architecure#technology
0 notes
Text
Serverless Vs. Microservices: Which Architecture is Best for Your Business?

One of the core challenges in computer science is problem decomposition, breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts. This is key for addressing each part independently; programming is about mastering complexity through effective organization. In development, architects and developers work to structure these complexities to build robust business functionalities. Strong architecture lays the groundwork for effectively handling these complexities.
Software architecture defines boundaries that separate components. These boundaries prevent elements on one side from depending on or interacting with those on the other.
Every decision architecture is a balance between trade-offs to manage complexity. Effective architecture depends on making these trade-offs wisely. It is more vital to understand why we choose a solution than to know how to implement it. Choosing a solution thoughtfully helps manage complexity by structuring the software, defining component interactions, and establishing clear separations.
A well-designed architecture uses best practices, design patterns, and structured layers, making complex systems more manageable and maintainable. Conversely, poor architecture increases complexity, complicating the process of maintenance, understanding, and scaling.
This blog delves into two widely used architectures: serverless and microservices. Both approaches aim to balance these complexities with scalable, modular solutions.
Key Takeaways:
Effective software architecture helps manage complexity by breaking down applications into smaller, manageable components. Both serverless and microservices architectures support this approach with unique benefits.
Serverless architecture allows developers to focus on coding without managing infrastructure. It automatically scales with demand and follows a pay-as-you-go model, making it cost-effective for applications with fluctuating usage.
Microservices architecture divides applications into autonomous services. Each service can scale independently, offering flexibility and resilience for complex applications.
Choosing between serverless and microservices depends on business needs. Serverless offers simplicity and low cost for dynamic workloads, whereas microservices provide control and scalability for large, interdependent applications.
What is Serverless?

Serverless computing, also known as serverless architecture, allows developers to deploy applications without managing infrastructure. In a serverless setup, cloud providers oversee routine tasks, such as operating system installations, security patches, and performance monitoring, ensuring a secure and optimized environment.
Contrary to its name, serverless doesn’t mean the absence of servers. Instead, it shifts server management from developers to the cloud service provider, allowing developers to focus on code and business requirements. This approach offers a pay-as-you-go model where billing aligns with actual code execution time, ensuring cost efficiency and reducing idle resource expenses.
Serverless application development also supports rapid scaling. Resources automatically adjust based on real-time demand, maintaining performance without manual intervention. Serverless, alongside Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS), is a powerful solution for modern cloud computing applications.
You would love to read more about Infrastructure-as-Code in DevOps.
How Does Serverless Work?

Serverless architecture is an innovative model where companies leverage third-party resources to host application functions efficiently. This setup divides application logic into small, manageable units called functions, with each designed for a specific task and executed over a short duration. Functions activate repeatedly in response to predefined triggers, allowing for a high degree of responsiveness.
Key stages in serverless architecture creation include:
Functions: Developers design code for specific tasks within the app. Functions focus on single, straightforward operations, ensuring efficiency and minimal resource use.
Events: Events trigger each function. When specific conditions are met—like receiving an HTTP request—the event activates the function, seamlessly initiating the next task.
Triggers: Triggers act as signals that prompt a function to execute. They occur when a user interacts, such as pressing a button or tapping a screen point.
Execution: The function then initiates, running only as long as needed to complete the task. This short-duration execution saves resources and minimizes overhead.
Output: Users receive the function’s output in real-time, typically on the client side. This design creates a responsive user experience.
For effective serverless applications, developers need to carefully segment functions and designate triggers. Functions can operate simultaneously, responding to distinct interactions without slowing down performance. Defining relationships among functions is essential to maintain harmony and responsiveness across interactions.
Advantages of Using Serverless Architecture

Serverless architecture divides applications into two core segments. A cloud provider fully manages the backend, freeing developers from handling infrastructure and hardware integrations. The second part, Function as a Service (FaaS), comprises user-facing, event-triggered functions. This structure empowers developers to streamline creation and boost performance.
Here are the key advantages of serverless:
Easy Deployment
In traditional setups, developers must configure and manage servers, databases, and middleware. Serverless eliminates this overhead, letting developers concentrate on creating the application’s core logic. Cloud vendors automate infrastructure deployment, reducing the time from code development to production. This rapid deployment can be a competitive edge, particularly for startups or companies working on tight schedules.
Cost Efficiency
Serverless architecture operates on a usage-based billing model, meaning companies pay only for the compute resources their functions consume. This benefits businesses with fluctuating demands, freeing them from fixed infrastructure costs. Additionally, the vendor handles routine maintenance, security updates, and scaling infrastructure, sparing organizations from hiring specialized staff or investing in physical servers and hardware. This can lead to substantial cost savings and financial flexibility.
On-Demand Scalability
The serverless architecture supports seamless scaling in response to varying demand levels. When more users access the application or perform resource-intensive operations, serverless platforms automatically allocate additional resources to handle the workload. This elasticity ensures the application runs smoothly, even during traffic spikes, while scaling back during low demand to minimize costs. For instance, an e-commerce app could accommodate holiday season surges without any manual intervention from the development team.
Enhanced Flexibility and Agility
Developers can easily add or update individual functions without impacting other components, enabling faster iteration cycles. This modular approach also allows teams to build, test, and deploy new features independently, enhancing productivity. Serverless platforms often offer pre-built templates and integrations with code repositories, which helps streamline for custom app development company. Existing code can be reused efficiently across multiple applications, minimizing repetitive work.
Reduced Latency Through Proximity
Global cloud vendors have distributed data centers worldwide, which minimizes latency for users. When a user triggers a function, the platform selects the nearest available server to process the request. This leads to faster response times, as data doesn’t have to travel long distances. Such latency reduction can be crucial for applications that rely on real-time interactions, like online gaming or live streaming services.
Access to advanced Infrastructure Without Large Capital Investment
Adopting serverless architecture enables organizations to leverage the robust infrastructure of leading technology companies without hefty upfront investments. Building similar server resources in-house could be prohibitively expensive, especially for smaller firms. With serverless, companies gain access to high-performance computing, storage, and networking solutions backed by enterprise-grade security and scalability, typically reserved for large corporations.
What are Microservices?
Microservices, or microservices architecture, is a cloud-centric approach that structures applications as a suite of loosely coupled, independent modules. Each microservice operates autonomously, processing its own technology stack, database, and management system. This separation allows for easy scaling and management of individual parts without impacting the entire system.
Communication among microservices typically occurs through REST APIs, event streaming, or massage brokers, ensuring efficient data flow across the applications. This modular setup enables organizations to categorize microservices by business functions, such as order processing or search functions, each confined within a “bounded context” to prevent interference across services.
Microservices thrive alongside cloud infrastructure, as both enable rapid development and scalability. With cloud adoption on the rise, investments in microservices are forecast to surpass $6 billion within four years.
From a business perspective, microservices offer distinct advantages:
Seamless updates: Teams can update specific services without affecting the overall application, reducing risk and downtime.
Flexible technology choices: Microservices enable diverse technology stacks and languages, allowing teams to select the best tools per component.
Independent scalability: Each service scales independently based on demand, ensuring optimal resource usage and performance across the application.
How Do Microservices Architecture Works?

Microservices architecture operates by dividing applications into independent, self-sufficient components, each designed to handle a specific function.
Here’s a deeper look at the process:
Core Concept of Microservices
In microservices, each service functions as an autonomous unit that fulfills a designated role within the application. These components run independently and remain isolated from each other, ensuring resilience and modularity. This architecture enables services to operate without interference, even if other components experience issues.
Containerized Execution
Typically, microservices are deployed within containers, like those created using Docker. Containers are packaged environments containing all necessary code, libraries, and dependencies required by each microservice. This ensures consistency in various environments, simplifying scaling and maintenance. Docker is widely adopted for containerized microservices due to its flexibility and ease of use, allowing teams to create efficient, portable applications.
Stages of Microservices Development

Decomposition: In this initial phase, the application’s core functionalities are dissected into smaller, manageable services. Each microservice addresses a specific function, which can range from processing payments to handling user authentication. This decentralized model allows teams to tackle each function individually, fostering a clear division of labor and better resource allocation.
Design: Once each microservice’s purpose is defined, the relationships and dependencies among them are mapped. This step involves creating a hierarchy, indicating which services rely on others to function optimally. Effective design minimizes potential bottlenecks by establishing clear communication protocols and dependencies between services.
Development: When the architecture is established, development teams (usually small units of 2-5 developers) begin building each service. By working in smaller teams focused on a single service, development cycles are faster and more efficient. Each team can implement specific technologies, frameworks, or programming languages best suited for their assigned service.
Deployment: Deployment options for microservices are versatile. Services can be deployed in isolated containers, virtual machines (VMs), or even as functions in a serverless environment, depending on the application’s infrastructure needs. Deploying containers provides scalability and flexibility, as each service can be updated or scaled independently without disrupting other components.
Advantages of Microservices Architecture

Microservices architecture addresses the limitations of monolithic systems, offering flexibility and enabling feature enhancements individually. This architecture is inherently scalable and allows streamlined management.
Here are the primary advantages:
Component-Based Structure
Microservices break applications into independent, smaller services. Each component is isolated, enabling developers to modify or update specific services without impacting the whole system. Components can be developed, tested, and deployed separately, enhancing control over each service.
Decentralized Data Management
Each microservice operates with its database, ensuring security and flexibility. If one service faces a vulnerability, the issue is contained, safeguarding other data within the system. Teams can apply tailored security measures to specific services, prioritizing high-security needs for critical data-handling components.
Risk Mitigation
Microservices limit risk by allowing services to substitute for failed components. If one service fails, the architecture allows redistributing functions to other operational services, ensuring continued performance. Unlike monolithic systems, where a single failure can disrupt the entire application, microservices maintain stability and reduce downtime.
Scalability
Microservices excel in scalability, making them an ideal choice for growing applications. Companies like Netflix adopted microservices to restructure their platform, leveraging Node.js for backend operations, ultimately saving billions through increased efficiency and modular scalability. Each service can scale independently, allowing applications to handle fluctuating demand without overhauling the entire system.
Compatibility with Agile and DevOps
Microservices align with Agile methodology and DevOps methodologies, empowering small teams to manage entire tasks, including individual services. This compatibility facilitates rapid development cycles, continuous integration, and efficient team collaboration, enhancing adaptability and productivity.
Difference Between Serverless and Microservices Architecture

Microservices and serverless architectures, while both aimed at enhancing modularity and scalability, differ fundamentally. Here’s a side-by-side comparison to clarify how each framework operates and the advantages it brings.
Granularity
Microservices divide large applications into smaller, standalone services, each responsible for a specific business function. These services can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Ensuring precise control over specific functionalities.
Serverless operates at a granularity, breaking down applications into functions. Each function performs a single, focused task and triggers based on specific events. This approach takes modularity further, enabling.
Scalability
Serverless automatically scales functions according to the demand, activating additional resources only as needed. Cloud providers handle all infrastructure management, letting developers focus on code rather than configuration.
Microservices allow each service to be scaled independently, but scaling may require manual configuration or automated systems. This independence provides flexibility but often involves greater setup and monitoring efforts.
Development and Deployment
Serverless enables streamlined development and deployment, simplifying operational complexities. Cloud providers abstract infrastructure management, supporting faster continuous integration and delivery cycles. Functions can be deployed individually, promoting rapid iteration and agile development.
Microservices development involves containers, such as Docker, to package services. This approach demands coordination for inter-service communication, fault tolerance, and data consistency. While it provides independence, it also introduces operational overhead and requires comprehensive DevOps management.
Runtime
Serverless functions run in a stateless environment. Each function executes, completes, and loses its state immediately afterward, making it ideal for tasks that don’t need persistent data storage.
Microservices are deployed to virtual machines (VMs) or containers, allowing them to retain state over time. This persistence suits applications that require continuous data storage and retrieval across sessions.
Cost
Serverless follows a pay-per-use model, where costs align directly with the volume of events processed. This flexibility lowers overall expenses, especially for applications with fluctuating or low-frequency usage.
Microservices require dedicated infrastructure, resulting in fixed costs for resources even when not actively processing requests. This model may be less cost-effective for applications with inconsistent traffic but can be advantageous for high-demand services.
Infrastructure Management
In serverless, cloud consulting manages all infrastructure. Full-stack developers don’t handle provisioning, maintenance, or scaling, allowing them to focus solely on coding and deployment.
Microservices require developers to oversee the entire tech stack, including infrastructure, deployment, and networking. This approach provides control but demands expertise in DevOps practices like CI/CD and infrastructure management.
Conclusion
Deciding between serverless and microservice architecture depends on the unique requirements of your business. Serverless provides a streamlined, cost-effective solution for dynamic, event-driven tasks, allowing developers to focus solely on code.
Microservices, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility and control, making them suitable for complex applications that need independent scalability and resilience. Both architectures have their advantages, and understanding their differences helps in making an informed decision that aligns with your scalability, cost, and operational goals.
Ready to optimize your software architecture? Reach out to us to discuss which solution fits best for your business needs.
Source URL: https://www.techaheadcorp.com/blog/serverless-vs-microservices-architecture/
0 notes
Text
Why Cloud Technology is Essential for Scalable Mobile Apps

1. Introduction
As mobile applications continue to evolve and grow in popularity, ensuring their scalability becomes more critical than ever. The capacity to handle increasing loads and provide a seamless user experience is no longer just a technical challenge; it’s a business imperative. Cloud technology has emerged as a key solution to these challenges, offering the flexibility and resources necessary for scalable mobile app development. In this article, we’ll explore why cloud technology is essential for scalable mobile app development, with a focus on custom mobile app development in Saudi Arabia.
2. Understanding Cloud Technology
Cloud technology involves utilizing remote servers accessed online to store, manage, and process data, instead of depending on local servers or personal devices. It has revolutionized the way mobile applications are developed, offering a range of services that cater to the needs of developers and businesses alike.
2.1 Types of Cloud Services
Three primary cloud service models exist:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Offers virtual computing resources delivered over the internet. Developers can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks, allowing them to scale resources up or down as needed.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications, easing the scaling process without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications online on a subscription model. Users can access these applications via the web without managing the infrastructure or platform.
2.2 Benefits of Cloud Technology
Cloud technology offers numerous benefits that make it indispensable for modern mobile app development:
Scalability: Cloud services can quickly scale to accommodate increasing traffic or data loads, ensuring that apps remain responsive and efficient.
Flexibility: Developers can deploy and manage apps across multiple regions and platforms, providing users with consistent experiences regardless of location.
Cost-Efficiency: With pay-as-you-go pricing models, businesses can optimize costs by paying only for the resources they use, avoiding the need for significant upfront investments.
3. Importance of Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a mobile app to handle a growing number of users and transactions without compromising performance. In markets like Saudi Arabia, where mobile app usage is on the rise, scalability is crucial for maintaining user satisfaction and ensuring long-term success.
3.1 Challenges in Traditional Scaling
Traditional scaling methods, such as adding more physical servers or upgrading existing hardware, can be both expensive and time-consuming. They also often fail to provide the flexibility needed to adapt to sudden changes in demand, leading to performance issues and potential downtime.
4. Cloud Technology for Mobile App Scalability
Cloud technology addresses the limitations of traditional scaling by offering advanced tools and services that make it easier to scale mobile apps efficiently.
4.1 Elasticity and Auto-Scaling
Elasticity is a key feature of cloud computing, allowing resources to be automatically scaled up or down based on current demand. Auto-scaling ensures that mobile apps can handle traffic spikes without compromising performance, providing a seamless user experience.
4.2 Load Balancing and Traffic Management
Cloud-based load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This not only improves app performance but also enhances its reliability and availability.
4.3 Data Management and Storage
Cloud services offer scalable data storage solutions that can accommodate vast amounts of data generated by mobile apps. These solutions are designed to be both secure and accessible, ensuring that app data is managed efficiently.
5. Custom Mobile App Development in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is experiencing rapid growth in mobile app usage, driven by a tech-savvy population and a strong economy. Custom mobile app development is essential for businesses looking to meet the specific needs of Saudi users and gain a competitive edge in the market.
5.1 Market Trends and Demands
The Saudi Arabian market is characterized by a high demand for innovative, user-friendly apps that cater to both consumers and businesses. As the government pushes for digital transformation under its Vision 2030 initiative, the demand for custom mobile apps is expected to increase significantly.
5.2 Considerations for Local Developers
Developers targeting the Saudi market must consider local preferences, cultural nuances, and regulatory requirements. Additionally, they must ensure that their apps are scalable to handle the growing number of users in the region.
6. Case Studies and Success Stories
To understand the impact of cloud technology on scalable mobile app development, we can look at successful case studies from around the world and within Saudi Arabia.
6.1 Global Case Study
An example of a global mobile app that successfully leveraged cloud technology for scalability is Netflix. By utilizing cloud services, Netflix can stream content to millions of users simultaneously, without interruptions or performance issues.
6.2 Saudi Arabian Case Study
In Saudi Arabia, the ride-hailing app Careem has become a success story by utilizing cloud technology to scale its operations. Careem’s cloud-based infrastructure allows it to handle millions of rides across the region, ensuring a smooth experience for both drivers and passengers.
7. Future Trends in Cloud and Mobile App Development
The future of mobile app development will be shaped by emerging trends in cloud technology, with a focus on enhancing scalability and user experience.
7.1 AI and Machine Learning in Cloud
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming increasingly integrated into cloud services, offering predictive analytics, personalized experiences, and improved decision-making capabilities. These technologies will play a critical role in enhancing the scalability of mobile apps.
7.2 The Rise of Edge Computing
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source of data generation, is expected to revolutionize mobile app development. By reducing latency and improving real-time data processing, edge computing will enhance the scalability and performance of mobile apps.
8. Best Practices for Cloud Implementation
Successfully implementing cloud technology demands thorough planning and adherence to best practices, especially regarding scalability.
8.1 Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and compliance with local regulations is paramount when using cloud services. Developers should implement robust security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect app data.
8.2 Cost Management Strategies
Managing costs is a key concern for businesses using cloud services. By optimizing resource usage, leveraging cost management tools, and choosing the right pricing models, businesses can keep costs under control while scaling their apps.
9. Conclusion
Cloud technology has become essential for scalable mobile app development, offering the flexibility, efficiency, and resources needed to meet the demands of a growing user base. For businesses in Saudi Arabia, leveraging cloud services is key to staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market. By understanding the benefits and best practices associated with cloud technology, developers can create mobile apps that not only meet current demands but are also poised for future growth.
10. FAQs
Q1: What is cloud technology in mobile app development?Cloud technology involves utilizing remote servers accessed through the internet to store, manage, and process data. This enables mobile apps to scale efficiently and manage growing user demands.
Q2: Why is scalability important for mobile apps?Scalability ensures that a mobile app can handle an increasing number of users and transactions without compromising performance, which is crucial for maintaining a positive user experience.
Q3: How does cloud technology enhance app scalability?Cloud technology provides features like elasticity, auto-scaling, and load balancing, which allow mobile apps to scale dynamically in response to changing demand.
Q4: What are some challenges of traditional scaling methods? Traditional scaling methods, such as adding more physical servers, can be costly, time-consuming, and inflexible, making them less effective for modern mobile apps. Q5: What are the key considerations for developing custom mobile apps in Saudi Arabia? Developers should consider local market trends, user preferences, cultural nuances, and regulatory requirements, as well as ensuring their apps are scalable to handle growing demand.
#Cloud-based app development#Scalable mobile apps#Cloud computing in app development#Mobile app scalability#Cloud infrastructure for apps#App development in the cloud#Scalable application architecture#Cloud technology for developers#Mobile app performance with cloud#Cloud-native mobile apps#App development scalability solutions#Cloud services for app developers#Benefits of cloud for mobile apps#Cloud-enabled app growth#Cloud computing for scalable apps
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Growing Importance of Point Cloud Modeling Services

With Commercial Point Cloud Modeling Services, you can unlock the future! Create accurate 3D models from unprocessed data to spur creativity in design, engineering, and architecture. Our state-of-the-art equipment records every detail, guaranteeing efficiency and accuracy. Whether it's for building, remodeling, or inspection, our services produce top-notch models that improve choices and project results. Start now!
0 notes
Text
Going Over the Cloud: An Investigation into the Architecture of Cloud Solutions

Because the cloud offers unprecedented levels of size, flexibility, and accessibility, it has fundamentally altered the way we approach technology in the present digital era. As more and more businesses shift their infrastructure to the cloud, it is imperative that they understand the architecture of cloud solutions. Join me as we examine the core concepts, industry best practices, and transformative impacts on modern enterprises.
The Basics of Cloud Solution Architecture A well-designed architecture that balances dependability, performance, and cost-effectiveness is the foundation of any successful cloud deployment. Cloud solutions' architecture is made up of many different components, including networking, computing, storage, security, and scalability. By creating solutions that are tailored to the requirements of each workload, organizations can optimize return on investment and fully utilize the cloud.
Flexibility and Resilience in Design The flexibility of cloud computing to grow resources on-demand to meet varying workloads and guarantee flawless performance is one of its distinguishing characteristics. Cloud solution architecture create resilient systems that can endure failures and sustain uptime by utilizing fault-tolerant design principles, load balancing, and auto-scaling. Workloads can be distributed over several availability zones and regions to help enterprises increase fault tolerance and lessen the effect of outages.
Protection of Data in the Cloud and Security by Design
As data thefts become more common, security becomes a top priority in cloud solution architecture. Architects include identity management, access controls, encryption, and monitoring into their designs using a multi-layered security strategy. By adhering to industry standards and best practices, such as the shared responsibility model and compliance frameworks, organizations may safeguard confidential information and guarantee regulatory compliance in the cloud.
Using Professional Services to Increase Productivity Cloud service providers offer a variety of managed services that streamline operations and reduce the stress of maintaining infrastructure. These services allow firms to focus on innovation instead of infrastructure maintenance. They include server less computing, machine learning, databases, and analytics. With cloud-native applications, architects may reduce costs, increase time-to-market, and optimize performance by selecting the right mix of managed services.
Cost control and ongoing optimization Cost optimization is essential since inefficient resource use can quickly drive up costs. Architects monitor resource utilization, analyze cost trends, and identify opportunities for optimization with the aid of tools and techniques. Businesses can cut waste and maximize their cloud computing expenses by using spot instances, reserved instances, and cost allocation tags.
Acknowledging Automation and DevOps Important elements of cloud solution design include automation and DevOps concepts, which enable companies to develop software more rapidly, reliably, and efficiently. Architects create pipelines for continuous integration, delivery, and deployment, which expedites the software development process and allows for rapid iterations. By provisioning and managing infrastructure programmatically with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and Configuration Management systems, teams may minimize human labor and guarantee consistency across environments.
Multiple-cloud and hybrid strategies In an increasingly interconnected world, many firms employ hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to leverage the benefits of many cloud providers in addition to on-premises infrastructure. Cloud solution architects have to design systems that seamlessly integrate several environments while ensuring interoperability, data consistency, and regulatory compliance. By implementing hybrid connection options like VPNs, Direct Connect, or ExpressRoute, organizations may develop hybrid cloud deployments that include the best aspects of both public and on-premises data centers. Analytics and Data Management Modern organizations depend on data because it fosters innovation and informed decision-making. Thanks to the advanced data management and analytics solutions developed by cloud solution architects, organizations can effortlessly gather, store, process, and analyze large volumes of data. By leveraging cloud-native data services like data warehouses, data lakes, and real-time analytics platforms, organizations may gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries and extract valuable insights. Architects implement data governance frameworks and privacy-enhancing technologies to ensure adherence to data protection rules and safeguard sensitive information.
Computing Without a Server Serverless computing, a significant shift in cloud architecture, frees organizations to focus on creating applications rather than maintaining infrastructure or managing servers. Cloud solution architects develop serverless programs using event-driven architectures and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions. By abstracting away the underlying infrastructure, serverless architectures offer unparalleled scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility, empowering companies to innovate swiftly and change course without incurring additional costs.
Conclusion As we come to the close of our investigation into cloud solution architecture, it is evident that the cloud is more than just a platform for technology; it is a force for innovation and transformation. By embracing the ideas of scalability, resilience, and security, and efficiency, organizations can take advantage of new opportunities, drive business expansion, and preserve their competitive edge in today's rapidly evolving digital market. Thus, to ensure success, remember to leverage cloud solution architecture when developing a new cloud-native application or initiating a cloud migration.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Real-World Application of Data Mesh with Databricks Lakehouse
Explore how a global reinsurance leader transformed its data systems with Data Mesh and Databricks Lakehouse for better operations and decision-making.
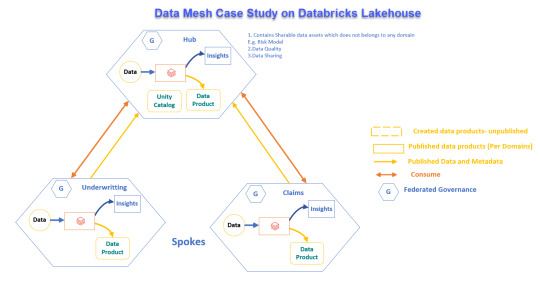
View On WordPress
#Advanced Analytics#Business Transformation#Cloud Solutions#Data Governance#Data management#Data Mesh#Data Scalability#Databricks Lakehouse#Delta Sharing#Enterprise Architecture#Reinsurance Industry
0 notes
Text
#cloud#cloud architecture#cloud computing#cloud hcm#cloud infrastructure#cloud solutions#cloud services
0 notes
Text
Digital Integration Solutions with Cloud-Based Architectural Design
W3 Partnership, founded in 2007, provides solutions and services that help organizations make sense of their digital applications and services through integrated platforms and patterns. SMEs in their respective fields, our in-house integration consultants are specialists in IBM and MuleSoft products, and our cloud consultants and developers are experts in AWS and Azure. We design, develop, manage, and monitor such platforms.
At W3 Partnership, we specialize in delivering integration connectivity as a service (iCaaS), cloud-based integration solutions, and middleware integration consultancy tailored to your unique needs. With decades of expertise, we empower businesses to streamline operations, eliminate silos, and drive innovation through hybrid integration platforms and advanced digital integration architecture services. Using advanced requirements analysis and digital integration architecture techniques, we collect all the necessary information to enable efficient stakeholder communication, ensuring a smooth transition from analysis to implementation.
Architecture Digital Integration
A data architecture called a Digital Integration Hub (DIH) separates the digital applications of the SoRs and compiles operational data into a low-latency data fabric. Organizations may connect to, integrate, and manage various software applications and systems using this architecture. To simplify data exchange and automate business processes, Architecture digital integration provides a central hub for managing the data flow between different systems. A digital integration hub supports modernization efforts by delivering a detached API layer that easily supports current online apps.
Digital Integration Solutions
An organization's digital transformation journey heavily depends on integrations to create a connected business. With the potent combination of innovative integration tools, intelligent methodologies, tried and tested templates, carefully designed organizational frameworks, and our knowledge and experience. Technology solutions known as "digital integration solutions" make it easier for digital systems, apps, and data sources to communicate and exchange data. They give firms a capacity to integrate many systems, optimize processes, and use data from various sources to make better decisions and provide better customer service.
Cloud-Based Integration
In today's digital-first business world, cloud-based integration serves as the cornerstone for tying together systems, data, and applications. Our cloud-based integration services at W3 Partnership effectively connect on-premises systems, cloud applications, and third-party solutions to form a cohesive digital ecosystem. Our solutions, built with agility, scalability, and security in mind, simplify IT, enhance data accuracy, and facilitate real-time data exchange, enabling your teams to make data-driven decisions more quickly. W3 Partnership's cloud-based integration strategy utilizes API-led connections and sophisticated integration platforms to help companies rapidly and affordably integrate apps. Our cloud-based integration services simplify the connection of marketing tools, CRM systems, ERP platforms, and data analytics applications while ensuring data accessibility and integrity.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Microsoft Azure Consulting Services
With Goognu's Microsoft Azure Consulting Services, we provide tailored solutions to meet your specific business requirements. Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, our experienced consultants will work closely with you to design and implement Azure strategies that align with your unique needs.
0 notes
Text
Karthik Ranganathan, Co-Founder and Co-CEO of Yugabyte – Interview Series
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/karthik-ranganathan-co-founder-and-co-ceo-of-yugabyte-interview-series/
Karthik Ranganathan, Co-Founder and Co-CEO of Yugabyte – Interview Series


Karthik Ranganathan is co-founder and co-CEO of Yugabyte, the company behind YugabyteDB, the open-source, high-performance distributed PostgreSQL database. Karthik is a seasoned data expert and former Facebook engineer who founded Yugabyte alongside two of his Facebook colleagues to revolutionize distributed databases.
What inspired you to co-found Yugabyte, and what gaps in the market did you see that led you to create YugabyteDB?
My co-founders, Kannan Muthukkaruppan, Mikhail Bautin, and I, founded Yugabyte in 2016. As former engineers at Meta (then called Facebook), we helped build popular databases including Apache Cassandra, HBase, and RocksDB – as well as running some of these databases as managed services for internal workloads.
We created YugabyteDB because we saw a gap in the market for cloud-native transactional databases for business-critical applications. We built YugabyteDB to cater to the needs of organizations transitioning from on-premises to cloud-native operations and combined the strengths of non-relational databases with the scalability and resilience of cloud-native architectures. While building Cassandra and HBase at Facebook (which was instrumental in addressing Facebook’s significant scaling needs), we saw the rise of microservices, containerization, high availability, geographic distribution, and Application Programming Interfaces (API). We also recognized the impact that open-source technologies have in advancing the industry.
People often think of the transactional database market as crowded. While this has traditionally been true, today Postgres has become the default API for cloud-native transactional databases. Increasingly, cloud-native databases are choosing to support the Postgres protocol, which has been ingrained into the fabric of YugabyteDB, making it the most Postgres-compatible database on the market. YugabyteDB retains the power and familiarity of PostgreSQL while evolving it to an enterprise-grade distributed database suitable for modern cloud-native applications. YugabyteDB allows enterprises to efficiently build and scale systems using familiar SQL models.
How did your experiences at Facebook influence your vision for the company?
In 2007, I was considering whether to join a small but growing company–Facebook. At the time, the site had about 30 to 40 million users. I thought it might double in size, but I couldn’t have been more wrong! During my over five years at Facebook, the user base grew to 2 billion. What attracted me to the company was its culture of innovation and boldness, encouraging people to “fail fast” to catalyze innovation.
Facebook grew so large that the technical and intellectual challenges I craved were no longer present. For many years I had aspired to start my own company and tackle problems facing the common user–this led me to co-create Yugabyte.
Our mission is to simplify cloud-native applications, focusing on three essential features crucial for modern development:
First, applications must be continuously available, ensuring uptime regardless of backups or failures, especially when running on commodity hardware in the cloud.
Second, the ability to scale on demand is crucial, allowing developers to build and release quickly without the delay of ordering hardware.
Third, with numerous data centers now easily accessible, replicating data across regions becomes vital for reliability and performance.
These three elements empower developers by providing the agility and freedom they need to innovate, without being constrained by infrastructure limitations.
Could you share the journey from Yugabyte’s inception in 2016 to its current status as a leader in distributed SQL databases? What were some key milestones?
At Facebook, I often talked with developers who needed specific features, like secondary indexes on SQL databases or occasional multi-node transactions. Unfortunately, the answer was usually “no,” because existing systems weren’t designed for those requirements.
Today, we are experiencing a shift towards cloud-native transactional applications that need to address scale and availability. Traditional databases simply can’t meet these needs. Modern businesses require relational databases that operate in the cloud and offer the three essential features: high availability, scalability, and geographic distribution, while still supporting SQL capabilities. These are the pillars on which we built YugabyteDB and the database challenges we’re focused on solving.
In February 2016, the founders began developing YugabyteDB, a global-scale distributed SQL database designed for cloud-native transactional applications. In July 2019, we made an unprecedented announcement and released our previously commercial features as open source. This reaffirmed our commitment to open-source principles and officially launched YugabyteDB as a fully open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) under an Apache 2.0 license.
The latest version of YugabyteDB (unveiled in September) features enhanced Postgres compatibility. It includes an Adaptive Cost-Based Optimizer (CBO) that optimizes query plans for large-scale, multi-region applications, and Smart Data Distribution that automatically determines whether to store tables together for lower latency, or to shard and distribute data for greater scalability. These enhancements allow developers to run their PostgreSQL applications on YugabyteDB efficiently and scale without the need for trade-offs or complex migrations.
YugabyteDB is known for its compatibility with PostgreSQL and its Cassandra-inspired API. How does this multi-API approach benefit developers and enterprises?
YugabyteDB’s multi-API approach benefits developers and enterprises by combining the strengths of a high-performance SQL database with the flexibility needed for global, internet-scale applications.
It supports scale-out RDBMS and high-volume Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) workloads, while maintaining low query latency and exceptional resilience. Compatibility with PostgreSQL allows for seamless lift-and-shift modernization of existing Postgres applications, requiring minimal changes.
In the latest version of the distributed database platform, released in September 2024, features like the Adaptive CBO and Smart Data Distribution enhance performance by optimizing query plans and automatically managing data placement. This allows developers to achieve low latency and high scalability without compromise, making YugabyteDB ideal for rapidly growing, cloud-native applications that require reliable data management.
AI is increasingly being integrated into database systems. How is Yugabyte leveraging AI to enhance the performance, scalability, and security of its SQL systems?
We are leveraging AI to enhance our distributed SQL database by addressing performance and migration challenges. Our upcoming Performance Copilot, an enhancement to our Performance Advisor, will simplify troubleshooting by analyzing query patterns, detecting anomalies, and providing real-time recommendations to troubleshoot database performance issues.
We are also integrating AI into YugabyteDB Voyager, our database migration tool that simplifies migrations from PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, and other cloud databases to YugabyteDB. We aim to streamline transitions from legacy systems by automating schema conversion, SQL translation, and data transformation, with proactive compatibility checks. These innovations focus on making YugabyteDB smarter, more efficient, and easier for modern, distributed applications to use.
What are the key advantages of using an open-source SQL system like YugabyteDB in cloud-native applications compared to traditional proprietary databases?
Transparency, flexibility, and robust community support are key advantages when using an open-source SQL system like YugabyteDB in cloud-native applications. When we launched YugabyteDB, we recognized the skepticism surrounding open-source models. We engaged with users, who expressed a strong preference for a fully open database to trust with their critical data.
We initially ran on an open-core model, but rapidly realized it needed to be a completely open solution. Developers increasingly turn to PostgreSQL as a logical Oracle alternative, but PostgreSQL was not built for dynamic cloud platforms. YugabyteDB fills this gap by supporting PostgreSQL’s feature depth for modern cloud infrastructures. By being 100% open source, we remove roadblocks to adoption.
This makes us very attractive to developers building business-critical applications and to operations engineers running them on cloud-native platforms. Our focus is on creating a database that is not only open, but also easy to use and compatible with PostgreSQL, which remains a developer favorite due to its mature feature set and powerful extensions.
The demand for scalable and adaptable SQL solutions is growing. What trends are you observing in the enterprise database market, and how is Yugabyte positioned to meet these demands?
Larger scale in enterprise databases often leads to increased failure rates, especially as organizations deal with expanded footprints and higher data volumes. Key trends shaping the database landscape include the adoption of DBaaS, and a shift back from public cloud to private cloud environments. Additionally, the integration of generative AI brings opportunities and challenges, requiring automation and performance optimization to manage the growing data load.
Organizations are increasingly turning to DBaaS to streamline operations, despite initial concerns about control and security. This approach improves efficiency across various infrastructures, while the focus on private cloud solutions helps businesses reduce costs and enhance scalability for their workloads.
YugabyteDB addresses these evolving demands by combining the strengths of relational databases with the scalability of cloud-native architectures. Features like Smart Data Distribution and an Adaptive CBO, enhance performance and support a large number of database objects. This makes it a competitive choice for running a wide range of applications.
Furthermore, YugabyteDB allows enterprises to migrate their PostgreSQL applications while maintaining similar performance levels, crucial for modern workloads. Our commitment to open-source development encourages community involvement and provides flexibility for customers who want to avoid vendor lock-in.
With the rise of edge computing and IoT, how does YugabyteDB address the challenges posed by these technologies, particularly regarding data distribution and latency?
YugabyteDB’s distributed SQL architecture is designed to meet the challenges posed by the rise of edge computing and IoT by providing a scalable and resilient data layer that can operate seamlessly in both cloud and edge contexts. Its ability to automatically shard and replicate data ensures efficient distribution, enabling quick access and real-time processing. This minimizes latency, allowing applications to respond swiftly to user interactions and data changes.
By offering the flexibility to adapt configurations based on specific application requirements, YugabyteDB ensures that enterprises can effectively manage their data needs as they evolve in an increasingly decentralized landscape.
As Co-CEO, how do you balance the dual roles of leading technological innovation and managing company growth?
Our company aims to simplify cloud-native applications, compelling me to stay on top of technology trends, such as generative AI and context switches. Following innovation demands curiosity, a desire to make an impact, and a commitment to continuous learning.
Balancing technological innovation and company growth is fundamentally about scaling–whether it’s scaling systems or scaling impact. In distributed databases, we focus on building technologies that scale performance, handle massive workloads, and ensure high availability across a global infrastructure. Similarly, scaling Yugabyte means growing our customer base, enhancing community engagement, and expanding our ecosystem–while maintaining operational excellence.
All this requires a disciplined approach to performance and efficiency.
Technically, we optimize query execution, reduce latency, and improve system throughput; organizationally, we streamline processes, scale teams, and enhance cross-functional collaboration. In both cases, success comes from empowering teams with the right tools, insights, and processes to make smart, data-driven decisions.
How do you see the role of distributed SQL databases evolving in the next 5-10 years, particularly in the context of AI and machine learning?
In the next few years, distributed SQL databases will evolve to handle complex data analysis, enabling users to make predictions and detect anomalies with minimal technical expertise. There is an immense amount of database specialization in the context of AI and machine learning, but that is not sustainable. Databases will need to evolve to meet the demands of AI. This is why we’re iterating and enhancing capabilities on top of pgvector, ensuring developers can use Yugabyte for their AI database needs.
Additionally, we can expect an ongoing commitment to open source in AI development. Five years ago, we made YugabyteDB fully open source under the Apache 2.0 license, reinforcing our dedication to an open-source framework and proactively building our open-source community.
Thank you for all of your detailed responses, readers who wish to learn more should visit YugabyteDB.
#2024#adoption#ai#AI development#Analysis#anomalies#Apache#Apache 2.0 license#API#applications#approach#architecture#automation#backups#billion#Building#Business#CEO#Cloud#cloud solutions#Cloud-Native#Collaboration#Community#compromise#computing#containerization#continuous#curiosity#data#data analysis
0 notes