#Difference Between Procedural and Object Oriented Programming
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Discover the key differences between procedural and object-oriented programming. Enhance your coding skills with our comprehensive guide and practical insights.
#Difference Between Procedural and Object Oriented Programming#procedural programming vs oop#procedural programming vs object oriented programming
0 notes
Text
Difference Between C and C++

Introduction
The difference between C and C++ is one of the most important topics for programmers to understand. C and C++ are two of the most popular programming languages, widely used for system programming, application development, and competitive coding. While they share many similarities, they have distinct differences that make each suitable for specific types of projects. At TCCI Computer Coaching Institute, we help students understand these differences to build a strong programming foundation.
What is C?
C is a procedural programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie in 1972. It is widely used for system programming, operating systems, embedded systems, and applications where performance and memory management are crucial.
Key Features of C:
Procedural Language: Follows a structured approach with functions.
Memory Management: Uses pointers and manual memory allocation.
Speed & Efficiency: Highly efficient for low-level programming.
No Object-Oriented Features: Lacks classes, objects, and inheritance.
What is C++?
C++ is an extension of C, developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in the early 1980s. It introduced Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), making it more powerful and flexible for large-scale applications, game development, and software engineering.
Key Features of C++:
Object-Oriented Programming: Supports classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction.
Multi-Paradigm Language: Supports both procedural and object-oriented programming.
Standard Template Library (STL): Provides built-in functions for efficient coding.
Better Code Reusability & Maintainability: Encourages modular programming.
Which One Should You Learn?
If you are a beginner in programming, learning C first helps you understand core programming concepts like memory management and algorithms.
If you want to work on modern applications, game development, or large-scale software, C++ is a better choice due to its object-oriented features.
At TCCI Computer Coaching Institute, we offer expert training in both C and C++, helping students and professionals master these languages with practical, real-world examples.
Join TCCI Today!
Learn C and C++ with Expert Trainers
Best Computer Coaching Institute in Ahmedabad
Hands-on Projects and Practical Learning
Location: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Get information from TCCI Computer Coaching Institute
#Difference Between C and C++#C vs C++#C and C++ comparison#Procedural vs Object-Oriented Programming#TCCI
0 notes
Text
How to Learn Python for Beginners: Tips and Resources

Python has become one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its simplicity and versatility. Whether you are a complete novice or someone looking to expand your programming skills, learning Python can open up a world of opportunities in fields such as web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more. This guide, "How to Learn Python for Beginners: Tips and Resources," aims to provide you with practical advice and valuable resources to kickstart your Python learning journey.
Understanding Python
Before diving into the learning process, it’s essential to understand what Python is and why it is so widely used. Python is an interpreted, high-level programming language that emphasizes code readability and simplicity. Its syntax is designed to be intuitive, making it an excellent choice for beginners. Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming, which allows developers to choose the best approach for their projects.
Setting Up Your Environment
The first step in learning Python is to set up your development environment. Here’s how to get started:
Install Python: Download the latest version of Python from the official website (https://www.python.org/downloads/). The installation process is straightforward, and you can choose to install additional tools like pip, which is a package manager for Python.
Choose an Integrated Development Environment (IDE): An IDE is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to programmers for software development. Popular IDEs for Python include:PyCharm: A powerful IDE specifically designed for Python development. Visual Studio Code: A lightweight and versatile code editor with excellent Python support. Jupyter Notebook: Ideal for data analysis and visualization, allowing you to create and share documents that contain live code.
Set Up a Virtual Environment: It’s a good practice to create a virtual environment for your Python projects. This allows you to manage dependencies and avoid conflicts between different projects. You can create a virtual environment using the following command:bashRunCopy code1python -m venv myenvActivate it with:On Windows: myenv\Scripts\activate On macOS/Linux: source myenv/bin/activate
Learning Resources
With your environment set up, it’s time to explore various resources to learn Python effectively. Here are some recommended resources:
Online Courses:Coursera: Offers courses like "Python for Everybody" by the University of Michigan, which is perfect for beginners. edX: Provides a range of Python courses from institutions like MIT and Harvard. Udemy: Features numerous Python courses, often at discounted prices, covering everything from basics to advanced topics.
Books:"Automate the Boring Stuff with Python" by Al Sweigart: A great book for beginners that focuses on practical applications of Python. "Python Crash Course" by Eric Matthes: A hands-on introduction to programming with Python, ideal for beginners. "Learn Python the Hard Way" by Zed A. Shaw: A popular book that emphasizes practice and repetition.
Interactive Platforms:Codecademy: Offers an interactive Python course that allows you to write code directly in your browser. LeetCode: A platform for practicing coding problems, which can help you improve your problem-solving skills in Python. HackerRank: Provides coding challenges and competitions to test your skills and learn from others.
YouTube Channels:Corey Schafer: Offers a series of Python tutorials that cover various topics in depth. Programming with Mosh: Provides beginner-friendly Python tutorials that are easy to follow. freeCodeCamp.org: Features comprehensive Python courses and tutorials for beginners.
Tips for Effective Learning
As you embark on your Python learning journey, consider the following tips to enhance your experience:
Practice Regularly: Consistency is key when learning a new programming language. Set aside time each day or week to practice coding. The more you code, the more comfortable you will become with Python.
Work on Projects: Apply what you learn by working on small projects. This could be anything from a simple calculator to a web scraper or a personal website. Projects help reinforce your knowledge and provide practical experience.
Join a Community: Engage with other learners and experienced developers by joining online communities such as Stack Overflow, Reddit (r/learnpython), or Python Discord servers. These platforms allow you to ask questions, share your progress, and learn from others.
Utilize Documentation: Familiarize yourself with the official Python documentation (https://docs.python.org/3/). It is a valuable resource that provides detailed information about Python’s features, libraries, and best practices.
Learn by Teaching: One of the best ways to solidify your understanding of a topic is to teach it to someone else. Consider writing blog posts, creating tutorials, or explaining concepts to friends or peers.
Stay Curious: Python is a vast language with numerous libraries and frameworks. Explore different areas such as web development (Django, Flask), data analysis (Pandas, NumPy), and machine learning (TensorFlow, scikit-learn) to find what interests you the most.
Conclusion
Learning Python can be an exciting and rewarding journey, especially for beginners. By setting up your environment, utilizing the right resources, and following effective learning strategies, you can build a strong foundation in Python programming. Remember that persistence and practice are essential to mastering any skill, so stay motivated and keep coding!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top Python Interview Questions and Answers to Crack Your Next Tech Interview

Python is one of the most in-demand programming languages for developers, data scientists, automation engineers, and AI specialists. If you're preparing for a Python-based role, reviewing commonly asked Python interview questions and answers is a smart move.
This blog covers essential questions and sample answers to help you prepare for technical interviews at both beginner and advanced levels.
📘 Looking for the full list of expert-level Q&A? 👉 Visit: Python Interview Questions and Answers – Freshy Blog
🔹 Basic Python Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Python?
Python is an interpreted, high-level programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It supports multiple programming paradigms including OOP, functional, and procedural styles.
2. What are Python's key features?
Easy-to-read syntax
Large standard library
Open-source and community-driven
Supports object-oriented and functional programming
Platform-independent
3. What are Python lists and tuples?
List: Mutable, allows changes
Tuple: Immutable, used for fixed collections
🔸 Intermediate Python Interview Questions and Answers
4. What is a dictionary in Python?
A dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs. It allows fast lookups.
my_dict = {"name": "Alice", "age": 30}
5. What is a Python decorator?
A decorator is a function that takes another function and extends its behavior without explicitly modifying it.
def decorator(func):
def wrapper():
print("Before")
func()
print("After")
return wrapper
🔹 Advanced Python Interview Questions and Answers
6. What is the difference between deep copy and shallow copy?
Shallow Copy: Copies the outer object; inner objects are still referenced.
Deep Copy: Copies all nested objects recursively.
7. Explain Python's Global Interpreter Lock (GIL).
GIL is a mutex that protects access to Python objects, preventing multiple threads from executing Python bytecode simultaneously in CPython.
🔍 More Covered in the Full Guide:
Exception handling and custom exceptions
Lambda functions and map/filter/reduce
File handling in Python
List comprehension vs generator expressions
Python 3.x updates and syntax changes
📘 Read them all in this full-length guide: 👉 https://www.freshyblog.com/python-interview-questions-and-answers/
✅ Tips to Crack Python Interviews
Practice writing code daily
Review OOP, exception handling, file I/O
Solve Python problems on LeetCode or HackerRank
Be prepared to explain your logic step-by-step
Final Thoughts
Whether you're a beginner or aiming for a senior developer position, reviewing these Python interview questions and answers will boost your confidence and interview performance.
🔗 Explore the full list with real-world examples and pro tips: 👉 https://www.freshyblog.com/python-interview-questions-and-answers/
#PythonInterviewQuestionsAndAnswers#PythonForBeginners#TechInterviewPrep#PythonJobs2025#LearnPython#BackendDeveloper#FreshyBlog#PythonTips#CrackTheInterview#CodingInterviewQuestions#pyhon
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Tech Careers: Benefits of Joining Python Classes in Pune
Introduction: The Growing Demand for Python Skills In recent years, Python has become one of the most sought-after programming languages across the globe. Its simplicity, flexibility, and wide range of applications make it ideal for beginners as well as professionals. From web development and data science to artificial intelligence and automation, Python is everywhere.
For learners based in Maharashtra, joining well-structured Python classes in Pune can be a strategic step. Pune has become a leading destination for technical education, offering access to quality learning resources and an active tech ecosystem.
What Makes Python Ideal for Beginners and Professionals? Python is known for its easy-to-read syntax, which closely resembles English. This feature makes it accessible to people from non-technical backgrounds. It also supports multiple programming paradigms — including object-oriented, functional, and procedural programming — allowing learners to explore different approaches to problem-solving.
In addition, Python has an extensive library of modules and frameworks, which speeds up development and expands its applications across industries.
Benefits of Enrolling in Python Classes in Pune Learning Python in a structured classroom or instructor-led environment can offer several advantages:
Foundational Knowledge: Classes often start from the basics, making them suitable for absolute beginners.
Hands-On Practice: Regular assignments and real-world projects help reinforce theoretical concepts.
Peer Learning: Interacting with classmates and sharing ideas often enhances understanding.
Guided Learning Path: An organized syllabus ensures that you progress logically from basics to advanced topics.
Python classes in Pune are generally designed to cater to different learning needs, including short-term crash courses, beginner-friendly batches, and advanced training programs.
Understanding the Scope of a Full Stack Python Course in Pune If you’re looking to become a full-fledged web developer, Python classes in Pune might be the right choice. These programs typically combine:
Front-End Technologies: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Back-End Frameworks: Django or Flask (Python-based)
Database Management: SQL or NoSQL
Development Tools: Git, GitHub, Docker (sometimes)
This integrated approach allows learners to build complete web applications and understand how all parts of a software project come together. Such comprehensive training can help bridge the gap between academic knowledge and industry requirements.
Career Opportunities After Learning Python Python is used in various domains, including:
Web development
Data analysis and visualization
Machine learning and AI
Cybersecurity
Automation and scripting
Game development
Having Python skills on your resume can open doors to roles like software developer, data analyst, back-end engineer, or automation tester.
Conclusion: Building a Strong Foundation in Tech Choosing the right learning path is essential to mastering any programming language. Enrolling in well-structured Python classes in Pune can provide the foundation and confidence you need to succeed. For those aiming to acquire full-stack development skills, a full stack python course in Pune offers a complete package that aligns with industry standards.
ITView Inspired Learning has emerged as a go-to resource for learners seeking a practical and industry-relevant approach to mastering Python. With structured modules and real-world projects, it supports students in becoming job-ready in today’s evolving tech landscape.
Regardless of your background, learning Python is a smart and strategic investment in your future.
0 notes
Text
Master Your Python Interview with These Essential Q&A Tips Python continues to dominate the tech industry, powering applications in fields ranging from web development to machine learning. Its simplicity and versatility make it a favorite among developers and employers alike. For candidates preparing for Python interviews, understanding the commonly asked questions and how to answer them effectively can be the key to landing your dream job. This guide covers essential Python interview questions and answers, categorized for beginners, intermediates, and experts. Let’s dive in! 1. Basic Python Interview Questions Q1: What is Python, and what are its key features? Answer: Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability and simplicity. Key features include: Easy syntax, similar to English. Dynamically typed (no need to declare variable types). Extensive standard libraries. Cross-platform compatibility. Supports multiple paradigms: object-oriented, procedural, and functional. Q2: What are Python’s data types? Answer: Python offers the following built-in data types: Numeric: int, float, complex Sequence: list, tuple, range Text: str Set: set, frozenset Mapping: dict Boolean: bool Binary: bytes, bytearray, memoryview Q3: Explain Python’s Global Interpreter Lock (GIL). Answer: The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) is a mutex that protects access to Python objects, preventing multiple native threads from executing Python bytecode simultaneously. This ensures thread safety but can limit multithreading performance in CPU-bound tasks. Q4: What are Python’s popular frameworks? Answer: Some popular Python frameworks include: Web Development: Django, Flask, FastAPI Data Science: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Pandas Automation: Selenium, Robot Framework 2. Intermediate Python Interview Questions Q5: What is the difference between shallow and deep copying? Answer: Shallow Copy: Creates a new object but inserts references to the original objects within it. Use copy.copy(). Deep Copy: Creates a new object and recursively copies all objects within it. Use copy.deepcopy(). Q6: What are Python decorators? Answer: Decorators are functions that modify the behavior of another function or method. They are applied using the @decorator_name syntax and are commonly used for: Logging Authentication Performance measurement Access control Example: def decorator(func): def wrapper(): print("Before function execution") func() print("After function execution") return wrapper @decorator def say_hello(): print("Hello!") say_hello() Q7: How is memory managed in Python? Answer: Python uses automatic memory management through: Reference Counting: Tracks the number of references to an object. Garbage Collection: Reclaims memory when objects are no longer in use. Memory Pools: Allocates memory blocks to improve efficiency. 3. Advanced Python Interview Questions Q8: Explain Python’s metaclasses. Answer: Metaclasses define how classes behave. They control class creation and are specified using the metaclass keyword in class definitions. Metaclasses are commonly used to: Enforce coding standards. Add methods or attributes dynamically. Perform validation during class creation. Q9: What are Python’s comprehensions? Answer: Comprehensions provide a concise way to create sequences. Types include: List Comprehension: [x for x in range(10)] Set Comprehension: x for x in range(10) Dictionary Comprehension: x: x**2 for x in range(10) Generator Expression: (x for x in range(10)) Q10: How can you optimize Python code? Answer: Use built-in functions and libraries. Apply list comprehensions instead of loops. Use generators for large datasets. Leverage caching with functools.lru_cache. Profile code using cProfile and optimize hotspots.
Python Coding Challenges for Interviews Challenge 1: Reverse a String Write a function to reverse a string without using built-in functions. def reverse_string(s): result = "" for char in s: result = char + result return result Challenge 2: FizzBuzz Problem Print numbers from 1 to 100. For multiples of 3, print “Fizz”; for multiples of 5, print “Buzz”; for multiples of both, print “FizzBuzz”. for i in range(1, 101): if i % 3 == 0 and i % 5 == 0: print("FizzBuzz") elif i % 3 == 0: print("Fizz") elif i % 5 == 0: print("Buzz") else: print(i) Challenge 3: Find Duplicates in a List Write a function to find duplicate elements in a list. def find_duplicates(lst): seen = set() duplicates = set() for item in lst: if item in seen: duplicates.add(item) else: seen.add(item) return list(duplicates) Conclusion Preparing for a Python interview requires a mix of theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice. The questions above cover a wide range of topics, ensuring you are well-equipped for technical discussions. Remember, employers value problem-solving skills and clear communication as much as technical proficiency. Practice consistently, and you’ll be ready to ace that Python interview!
0 notes
Text
Difference Between Java and JavaScript
When it comes to programming, Java and JavaScript are two of the most widely used languages. Despite their similar names, they are quite different in terms of functionality, usage, and even underlying principles. This often leads to confusion among beginners who may assume that the two technologies are related. However, understanding the differences between Java and JavaScript can give developers the clarity they need to decide which tool is best suited for their specific needs.
In this blog, we will explore the key differences between Java and JavaScript by discussing their features, syntax, platforms, and use cases. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of when and why to use each of these languages.
1. What is Java?
Java is a powerful, object-oriented programming (OOP) language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). It was first released in 1995 and is designed to be a platform-independent language that allows developers to "write once, run anywhere." This means that Java code can be written on one platform (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux) and run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) installed. The JVM translates the compiled Java bytecode into machine-specific code, making it platform-independent.
Java is primarily used for developing standalone applications, large enterprise systems, Android applications, and server-side applications. It’s known for its stability, scalability, and performance.
2. What is JavaScript?
JavaScript, on the other hand, is a lightweight, interpreted scripting language that was created for web development. Originally designed to run in web browsers, it allows developers to create dynamic and interactive elements on websites. JavaScript was created by Brendan Eich at Netscape Communications in 1995 and has since evolved into one of the most important languages in web development.
JavaScript is a client-side language, which means it runs in the browser, but it can also be used on the server side through Node.js. Unlike Java, JavaScript is not a strictly object-oriented language; it supports multiple programming paradigms such as procedural, functional, and event-driven programming.
3. Syntax Differences Between Java and JavaScript
One of the most noticeable differences between Java and JavaScript lies in their syntax. While they may share some similar constructs (like curly braces for code blocks), the syntax rules and programming paradigms they follow are quite different.
Java is a statically-typed language, meaning that you must declare the type of variable before using it. For example:javaCopyint number = 10; String message = "Hello, World!"; The types (like int and String) must be specified and can’t be changed once the variable is declared.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is dynamically typed. This means you do not have to specify the type of the variable before using it, and the type can change as the program runs. For example:javascriptCopylet number = 10; let message = "Hello, World!"; Here, the type of number and message is determined dynamically at runtime.
4. Compiling vs. Interpreting
Another significant difference between Java and JavaScript is how they are executed.
Java is a compiled language. This means that Java code is first written and then compiled into bytecode by a Java compiler. The bytecode is platform-independent and can be run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This provides portability and allows Java applications to run across different systems without modification.Steps in Java Execution:
Write Java source code (.java file).
Compile the code using a Java compiler, which converts it into bytecode (.class file).
The bytecode is then executed by the JVM.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is an interpreted language, which means the code is executed line-by-line by an interpreter (usually within a web browser). The JavaScript engine in a browser reads the JavaScript code, interprets it, and executes it in real-time.Steps in JavaScript Execution:
Write JavaScript code (.js file).
The code is directly interpreted and executed by a web browser or JavaScript runtime environment like Node.js.
5. Execution Environment
Java and JavaScript also differ greatly in terms of their execution environments:
Java is typically used for building standalone applications that run on the JVM. These applications can be anything from mobile apps (Android) to large-scale enterprise applications or even desktop software.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is designed for web development. It is mostly used to create dynamic web pages, handle user interactions, and perform client-side tasks. JavaScript code runs within a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) and can also run on the server side through Node.js.
6. Object-Oriented vs. Multi-Paradigm
Java is primarily an object-oriented programming (OOP) language, which means it is based on the principles of encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Java focuses heavily on classes and objects, and most Java programs are organized around these core concepts.
JavaScript, however, is a multi-paradigm language. While it can support object-oriented programming (OOP) through prototypes, it also supports functional programming and event-driven programming. JavaScript uses prototypes for inheritance rather than classes (though modern JavaScript has introduced classes, they are syntactic sugar over prototypes).
7. Memory Management
Both Java and JavaScript have automatic memory management, but they handle it differently:
Java uses garbage collection to automatically manage memory. The JVM’s garbage collector automatically frees up memory that is no longer in use. Java also allows developers to manually control memory management through various memory allocation techniques.
JavaScript also uses garbage collection for memory management, but since JavaScript runs in a single-threaded environment (in the browser), memory management is typically more lightweight and less complex compared to Java.
8. Use Cases
The primary use cases for each language highlight their distinct roles in the software development landscape.
Java:
Enterprise Applications: Java is often used in large-scale business systems due to its scalability, robustness, and extensive libraries.
Mobile Development: Java is the official language for Android app development.
Backend Systems: Java powers many server-side applications, particularly in environments that require high performance.
Embedded Systems: Java is used in various embedded systems due to its portability and efficiency.
JavaScript:
Web Development: JavaScript is essential for front-end web development, enabling dynamic and interactive web pages.
Backend Development: With the rise of Node.js, JavaScript can also be used on the server side to build web servers and APIs.
Mobile Apps: JavaScript frameworks like React Native and Ionic allow developers to create mobile applications for both iOS and Android.
Game Development: JavaScript is increasingly used in building browser-based games or game engines like Phaser.js.
9. Performance
Performance is another area where Java and JavaScript differ significantly.
Java generally performs better in comparison to JavaScript because it is a compiled language. The compiled bytecode is optimized by the JVM and can be executed more efficiently. Java is well-suited for large-scale applications that require high performance.
JavaScript is typically slower than Java due to its interpreted nature and the overhead involved in real-time interpretation. However, JavaScript has made significant strides in performance, especially with modern engines like V8 (used in Google Chrome and Node.js), which optimize execution.
10. Learning Curve
Java can be more difficult to learn for beginners because it’s a statically-typed language with a focus on OOP principles. The syntax and structure are more complex, and it requires understanding various programming concepts such as classes, interfaces, and inheritance.
JavaScript is often considered easier to learn, especially for web developers, because it is dynamically typed and has a simpler syntax. Additionally, JavaScript is very forgiving with variable types, making it easier to experiment with code.
Conclusion
While Java and JavaScript have similar names, they are fundamentally different languages with different uses, execution models, and ecosystems. Java is a versatile, platform-independent, and high-performance language primarily used for backend applications, mobile development, and large-scale enterprise solutions. JavaScript, on the other hand, is a lightweight, interpreted language that powers the dynamic, interactive elements of the web.
Choosing between Java and JavaScript depends on the specific needs of your project. If you are working on a web-based application or interactive front-end elements, JavaScript will be the way to go. If you are building complex back-end systems, enterprise software, or mobile apps, Java might be more appropriate. Both languages are crucial in their own domains, and mastering them can open up a world of development opportunities.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to BMW and Mazda Car Keys: Technology, Features, and Maintenance
.
Outline:
1. Introduction
Brief introduction to the evolution of car keys
Importance of car keys in modern automotive technology
The need for a comparison of BMW and Mazda car keys
2. Understanding BMW Car Keys
Overview of BMW car key types
Traditional Keys
Keyless Entry Fobs
Display Keys mazda key
Digital Keys (BMW Digital Key)
Advanced Features of BMW Car Keys
Comfort Access
Personalized Settings

Security & Anti-Theft Technology
Key Technology in BMW: RFID, NFC, and Battery Life
Explanation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near-Field Communication (NFC)
Battery and Range Considerations for BMW car keys
3. Understanding Mazda Car Keys
Overview of Mazda car key types
Traditional Keys
Keyless Entry Fobs
Mazda Digital Key (MyMazda app)
Key Features of Mazda Car Keys
Remote Control Features
Push-Button Start
Mazda Connect System Integration
Mazda Key Technology: Infrared, Bluetooth, and App Integration
How infrared and Bluetooth work in Mazda car keys
Benefits of Mazda's smartphone integration for remote access and monitoring
4. Key Challenges and Solutions for BMW and Mazda Car Keys
How to Replace Lost or Damaged Keys
BMW: Authorized dealer replacement process
Mazda: Replacement through dealers and MyMazda app
Programming New Keys
BMW Key Coding Process
Mazda Key Programming Tutorial
Battery Replacement Tips
BMW and Mazda Battery Life & Replacement Procedure
Tools and steps involved
5. Security Features and Best Practices
BMW Security Features
Key encryption and anti-theft protection
Preventing signal jamming or relay attacks
Mazda Security Features
Signal blocking, anti-theft alarms
Preventive steps for enhancing key security
Key Maintenance Best Practices
Cleaning, care, and safe handling of keys
Updating key systems and ensuring firmware compatibility
6. Advanced Strategies: Maximizing the Potential of BMW and Mazda Car Keys
How to Pair and Use Digital Keys for Both Brands
Step-by-step instructions for BMW Digital Key setup
How to connect the Mazda Digital Key through MyMazda app
DIY Repairs and Programming
Tools for advanced users
When to seek professional help
Integration with Smart Home Systems
BMW’s compatibility with Alexa, Google Home
Mazda’s Smart App for automation
7. Conclusion
Recap of key differences between BMW and Mazda car keys
Tips for maintaining key longevity and security
The future of car key technology: What’s next for BMW and Mazda owners?
Topic Strategy:
Educational Approach: Focus on educating readers by offering a comparison of BMW and Mazda car keys, their technologies, functionalities, and maintenance. This will benefit car owners by helping them better understand and manage their keys.
Solution-Oriented: Provide practical solutions to common challenges like key replacement, programming, and battery maintenance. Offer easy-to-follow tutorials, which will enhance user experience and reduce the frustration of dealing with key issues.
Incorporate Technological Insight: Explain the advanced technologies such as RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth used in both BMW and Mazda car keys. This allows readers to appreciate the innovation behind their vehicle's key systems.
Security-Focused: Dedicate a section to security features and preventive measures, helping readers understand how to protect their vehicle from unauthorized access and potential theft.
Forward-Thinking: Address future trends, such as smartphone integration and smart home system compatibility, and how they will shape the user experience for BMW and Mazda owners.
Introduction Draft (for a 2500-word article):
Modern car keys have come a long way from their humble beginnings. What was once just a metal object used to turn an ignition is now a sophisticated device that plays a critical role in the safety, convenience, and overall functionality of a vehicle. This is especially true for brands like BMW and Mazda, which have integrated advanced technology into their car key systems to enhance the user experience.
BMW and Mazda, two renowned automotive manufacturers, offer a variety of key types and technologies that go beyond simple locking and unlocking. From digital keys that allow smartphone integration to keyless entry systems that make getting into your car as easy as a touch of a button, these brands have mastered convenience, security, and innovation. However, with these advances come new challenges—key replacement, programming, and security issues—that require a deeper understanding of the systems involved.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything there is to know about BMW and Mazda car keys. From their types and features to advanced technology and troubleshooting tips, this article will help you get the most out of your vehicle’s key system while ensuring maximum security and longevity.
Let me know if you need further sections drafted or modifications to the approach!
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to BMW and Mazda Car Keys: Technology, Features, and Maintenance
Outline:
1. Introduction
Brief introduction to the evolution of car keys
Importance of car keys in modern automotive technology
The need for a comparison of BMW and Mazda car keys
2. Understanding BMW Car Keys
Overview of BMW car key types
Traditional Keys
Keyless Entry Fobs
Display Keys mazda key
Digital Keys (BMW Digital Key)
Advanced Features of BMW Car Keys
Comfort Access

Personalized Settings
Security & Anti-Theft Technology
Key Technology in BMW: RFID, NFC, and Battery Life
Explanation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near-Field Communication (NFC)
Battery and Range Considerations for BMW car keys
3. Understanding Mazda Car Keys
Overview of Mazda car key types
Traditional Keys
Keyless Entry Fobs
Mazda Digital Key (MyMazda app)
Key Features of Mazda Car Keys
Remote Control Features
Push-Button Start
Mazda Connect System Integration
Mazda Key Technology: Infrared, Bluetooth, and App Integration
How infrared and Bluetooth work in Mazda car keys
Benefits of Mazda's smartphone integration for remote access and monitoring
4. Key Challenges and Solutions for BMW and Mazda Car Keys
How to Replace Lost or Damaged Keys
BMW: Authorized dealer replacement process
Mazda: Replacement through dealers and MyMazda app
Programming New Keys
BMW Key Coding Process
Mazda Key Programming Tutorial
Battery Replacement Tips
BMW and Mazda Battery Life & Replacement Procedure
Tools and steps involved
5. Security Features and Best Practices
BMW Security Features
Key encryption and anti-theft protection
Preventing signal jamming or relay attacks
Mazda Security Features
Signal blocking, anti-theft alarms
Preventive steps for enhancing key security
Key Maintenance Best Practices
Cleaning, care, and safe handling of keys
Updating key systems and ensuring firmware compatibility
6. Advanced Strategies: Maximizing the Potential of BMW and Mazda Car Keys
How to Pair and Use Digital Keys for Both Brands
Step-by-step instructions for BMW Digital Key setup
How to connect the Mazda Digital Key through MyMazda app
DIY Repairs and Programming
Tools for advanced users
When to seek professional help
Integration with Smart Home Systems
BMW’s compatibility with Alexa, Google Home
Mazda’s Smart App for automation
7. Conclusion
Recap of key differences between BMW and Mazda car keys
Tips for maintaining key longevity and security
The future of car key technology: What’s next for BMW and Mazda owners?
Topic Strategy:
Educational Approach: Focus on educating readers by offering a comparison of BMW and Mazda car keys, their technologies, functionalities, and maintenance. This will benefit car owners by helping them better understand and manage their keys.
Solution-Oriented: Provide practical solutions to common challenges like key replacement, programming, and battery maintenance. Offer easy-to-follow tutorials, which will enhance user experience and reduce the frustration of dealing with key issues.
Incorporate Technological Insight: Explain the advanced technologies such as RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth used in both BMW and Mazda car keys. This allows readers to appreciate the innovation behind their vehicle's key systems.
Security-Focused: Dedicate a section to security features and preventive measures, helping readers understand how to protect their vehicle from unauthorized access and potential theft.
Forward-Thinking: Address future trends, such as smartphone integration and smart home system compatibility, and how they will shape the user experience for BMW and Mazda owners.
Introduction Draft (for a 2500-word article):
Modern car keys have come a long way from their humble beginnings. What was once just a metal object used to turn an ignition is now a sophisticated device that plays a critical role in the safety, convenience, and overall functionality of a vehicle. This is especially true for brands like BMW and Mazda, which have integrated advanced technology into their car key systems to enhance the user experience.
BMW and Mazda, two renowned automotive manufacturers, offer a variety of key types and technologies that go beyond simple locking and unlocking. From digital keys that allow smartphone integration to keyless entry systems that make getting into your car as easy as a touch of a button, these brands have mastered convenience, security, and innovation. However, with these advances come new challenges—key replacement, programming, and security issues—that require a deeper understanding of the systems involved.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything there is to know about BMW and Mazda car keys. From their types and features to advanced technology and troubleshooting tips, this article will help you get the most out of your vehicle’s key system while ensuring maximum security and longevity.
Let me know if you need further sections drafted or modifications to the approach!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Which one better c or c++?

The choice between C and C++ depends on the context and specific needs of your project. Here’s a comparison to help you decide which language might be better suited for your needs:
C
**Advantages:**
**Simplicity**:
- C has a simpler syntax and fewer concepts to learn, making it easier for beginners to pick up.
**Performance**:
- C code can be highly optimized and is often used in systems programming, embedded systems, and high-performance computing.
**Low-Level Programming**:
- Offers low-level access to memory and hardware, which is ideal for developing operating systems, drivers, and other hardware-related software.
**Wide Usage**:
- C is widely used in legacy systems, and there is a vast amount of existing code and libraries.
**Disadvantages:**
**Lack of Object-Oriented Features**:
- C does not support object-oriented programming (OOP), which can make code organization and reuse more challenging.
**Manual Memory Management**:
- Requires explicit management of memory allocation and deallocation, increasing the risk of memory leaks and pointer errors.
C++
**Advantages:**
**Object-Oriented Programming**:
- Supports OOP, which helps in designing modular and reusable code. Concepts like classes, inheritance, and polymorphism are fundamental to C++.
**Standard Template Library (STL)**:
- Provides a rich set of template classes and functions for data structures and algorithms, reducing the need to write boilerplate code.
**Modern Features**:
- Includes modern programming features like auto memory management, lambda expressions, smart pointers, and more, making development faster and safer.
**Backwards Compatibility**:
- C++ is largely compatible with C, allowing C code to be integrated into C++ projects.
**Disadvantages:**
**Complexity**:
- The language is more complex due to its extensive feature set, which can lead to steeper learning curves and potentially more difficult debugging.
**Performance Overhead**:
- While C++ can be highly optimized, certain features (like polymorphism and exceptions) can introduce some performance overhead compared to C.
When to Use C
- **System-Level Programming**: Operating systems, embedded systems, and real-time systems.
- **Performance-Critical Applications**: High-performance computing where low-level hardware control is required.
- **Learning Fundamentals**: Learning fundamental programming concepts, memory management, and procedural programming.
When to Use C++
- **Large-Scale Software Development**: Applications that benefit from OOP such as GUI applications, games, and complex simulations.
- **Standard Libraries**: Projects that can leverage the STL for efficient data handling and algorithms.
- **Modern Development Practices**: When modern programming features and paradigms can enhance productivity and code safety.
In summary, choose C for simpler, performance-critical, or low-level programming tasks. Choose C++ if you need object-oriented features, richer standard libraries, or are developing larger and more complex software projects.
TCCI Computer classes provide the best training in online computer courses through different learning methods/media located in Bopal Ahmedabad and ISCON Ambli Road in Ahmedabad.
For More Information:
Call us @ +91 98256 18292
Visit us @ http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
#learn c language in Iscon Ambli Road-Ahmedabad#learn c language in bopal-Ahmedabad#learn c++ language in Iscon Ambli Road-Ahmedabad#learn c++ language in bopal-Ahmedabad#computer class in Iscon Ambli Road-Ahmedabad
0 notes
Text
The Comprehensive Guide to Onboarding Management.

Effective onboarding management is essential for integrating new employees into an organization, ensuring they feel welcomed, valued, and prepared to contribute to their fullest potential. This comprehensive guide delves into the importance, process, best practices, and benefits of onboarding management, providing valuable insights for HR professionals and managers alike.
Understanding Onboarding Management
What is Onboarding?
Onboarding is the process of integrating new employees into an organization and its culture, providing them with the necessary tools, resources, and knowledge to become effective and productive members of the team. This process extends beyond mere orientation and encompasses everything from initial paperwork to ongoing training and support.
The Importance of Effective Onboarding
Effective onboarding is crucial for several reasons. It helps new hires acclimate to the company culture, reduces time to productivity, enhances employee engagement, and lowers turnover rates. A well-structured onboarding process ensures that new employees are well-informed, motivated, and aligned with the organization’s goals and values.
The Onboarding Process
Pre-boarding
Pre-boarding occurs between the acceptance of the job offer and the employee’s first day. During this phase, organizations can send welcome emails, provide access to online portals for paperwork, and share information about the company culture and team structure. This helps new hires feel connected and reduces first-day jitters.
Orientation
Orientation is the initial phase of onboarding, typically occurring on the first day or week. It involves introducing new employees to the company’s mission, values, policies, and procedures. Orientation sessions often include tours of the workplace, introductions to team members, and training on essential tools and systems.
Training and Development
Training is a critical component of onboarding sellers, ensuring that new employees have the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their roles effectively. This includes job-specific training, as well as education on company-wide systems and processes. Ongoing development opportunities should also be provided to support continuous learning and growth.
Social Integration
Social integration involves helping new employees build relationships within the organization. This can be facilitated through team-building activities, mentorship programs, and informal social gatherings. Fostering a sense of belonging and camaraderie is essential for employee engagement and retention.
Performance Management
During the onboarding process, it’s important to set clear performance expectations and provide regular feedback. New employees should understand their goals and how their contributions align with the organization’s objectives. Regular check-ins and performance reviews help track progress and address any challenges early on.
Best Practices for Onboarding Management
Personalize the Experience
Each new hire is unique, and personalizing the onboarding experience can make a significant impact. Tailor the onboarding process to address the specific needs, preferences, and backgrounds of individual employees. This might include customizing training programs, offering flexible schedules, or providing resources that cater to different learning styles.
Utilize Technology
Leveraging technology can streamline the onboarding process and enhance the overall experience. Online platforms and software can automate administrative tasks, provide access to training materials, and facilitate communication between new hires and their teams. Virtual onboarding tools are especially valuable for remote employees, ensuring they feel connected and supported.
Assign a Buddy or Mentor
Pairing new employees with a buddy or mentor can provide additional support and guidance during the onboarding process. A buddy or mentor can answer questions, offer insights into company culture, and help new hires navigate their roles. This relationship fosters a sense of belonging and can accelerate the integration process.
Communicate Clearly and Consistently
Effective communication is key to a successful onboarding process. Ensure that new hires receive clear and consistent information throughout the process. This includes providing detailed instructions for completing tasks, setting expectations, and offering regular updates on their progress. Open lines of communication help new employees feel supported and informed.
Measure and Evaluate
Regularly measure and evaluate the effectiveness of your onboarding program to identify areas for improvement. Gather feedback from new hires through surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Analyze key metrics, such as time to productivity, employee engagement, and retention rates, to assess the impact of your onboarding efforts. Use this data to make informed adjustments and enhance the onboarding experience.
Benefits of Effective Onboarding Management
Increased Employee Engagement
Effective onboarding fosters a positive first impression, helping new employees feel valued and motivated. Employees who are engaged are more likely to be creative, productive, and dedicated to the success of the company. A well-structured onboarding program sets the stage for long-term engagement and job satisfaction.
Improved Retention Rates
A comprehensive onboarding process can significantly reduce employee turnover. When new hires feel welcomed, supported, and prepared, they are more likely to stay with the organization. High retention rates reduce the costs associated with recruiting and training new employees and contribute to a stable and experienced workforce.
Faster Time to Productivity
Effective onboarding accelerates the time it takes for new employees to become fully productive. By providing the necessary training, resources, and support from the outset, organizations can ensure that new hires are equipped to perform their roles efficiently. This leads to quicker integration and a more immediate impact on organizational goals.
Enhanced Company Culture
A strong onboarding process reinforces the company’s culture and values. By clearly communicating expectations and fostering a sense of community, organizations can build a cohesive and inclusive work environment. New employees who understand and embrace the company culture are more likely to contribute positively to the workplace.
Positive Employer Brand
A reputation for excellent onboarding can enhance an organization’s employer brand. When new hires have a positive onboarding experience, they are more likely to share their impressions with others, both within and outside the organization. This can attract top talent, improve recruitment efforts, and strengthen the overall brand image.
Conclusion
Onboarding management in Delhi is a critical component of the employee lifecycle, impacting engagement, retention, and overall organizational success. By understanding the importance of onboarding, implementing best practices, and continuously evaluating the process, organizations can create a welcoming and supportive environment for new hires. Effective onboarding not only benefits individual employees but also contributes to a positive and productive workplace, driving long-term success for the organization.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hire Dedicated Flutter App Developers In India (Within 24 Hours)
For your project, are you going to hire dedicated flutter app developer ? We have put together a list of the most important questions you should ask potential Flutter developers before hiring them for your project in order to help you choose the best one.

Flutter: What Is It?
Flutter is a UI-based tool for making mobile apps. It uses only one programming language and codebase; you can use Flutter to build native mobile apps. With the correct skill sets, one can write attractive and quick mobile apps with Flutter. The Flutter work was created by Google, and the source code is available. While Flutter uses the Flutter Dart language for development, it is not a language in and of itself. Using it, you can write code for iOS and Android. Mobile 2D applications are the best candidates for this optimization.
What Benefits Does Utilizing Flutter Offer?
When building mobile applications, Flutter offer following benefits:-
Cut down on the amount of code—Flutter's hot reload function contributes to better speed. To speed up app development, the application is written in C/C++ code, which is as near to machine code as feasible. Flutter's widget availability and usage of reused code cut down on the amount of time spent developing.
Cross-Platform development: To save the development team time and effort, Flutter code may be applied to several platforms.
Live and Hot Reloading: It facilitates easier and quicker code writing. When a modification is made, the code may be readily altered.
Flutter code is as similar to machine code as possible, so it functions just like a native program. This lowers the mistakes brought on by code interpretation. The programmed applications are quick and simple to use, and they operate in a native environment. So hire best flutter app developer in India.
What are FlutterFlow's shortcomings, in your opinion? Although FlutterFlow works well for most UI designs, implementing more complicated animations directly in the visual editor might take a lot of work. Additionally, additional human intervention outside of FlutterFlow may be necessary to run really large-scale projects with several screens and intricate state management.
How do you manage version control and collaboration in Flutterflow projects?
Could you describe the FlutterFlow theme and style management system? FlutterFlow's design framework enables us to specify and use themes and styles across the application. To guarantee design uniformity across all screens and components, we established global themes for font, color, and space.
Have you used FlutterFlow with Flutter plugins? What method do you use to integrate them? Yes, we use FlutterFlow with Flutter plugins quite a bit. When integrating plugins, we use the same procedure as for typical Flutter development. Our team uses the plugin APIs directly in FlutterFlow's code editor and add dependencies to Pubspec. yaml.
Which techniques do you use for FlutterFlow app speed optimization? We use const constructors wherever feasible, monitor widget tree efficiency, and utilize FlutterFlow's built-in performance analysis tools to find and fix performance bottlenecks and maximize performance. We also use lazy loading strategies for displays with a lot of data.
In Flutter, What are Flutter Packages And Plugins?
In Flutter and Flutter object-oriented languages, packages are collections of related classes, interfaces, and sub-packages. Packages and plugins are employed throughout development to lessen the coder's work. To save coding work, the developer may use packages and plugins rather than writing the code from scratch for everything.
There is little difference between plugins and packages. Packages are brand-new parts of Dart code written in the language. In contrast, plugins use native code to provide additional functionality. Even though there is a little difference, the two names are sometimes used interchangeably.
What programming language is Dart? Give a thorough explanation.
Without the Dart programming language Flutter’s syntax is relatively close to that of the C language. Dart programming language features include:
Because Dart is declarative and programmatic, developers can and quickly comprehend and visualize the layout.
Dart supports basic programming ideas like classes, interfaces, and functions, as well as data structure replicating collections like arrays, generics, and optional typing.
Several times quicker than JavaScript, Dart code operates.
Ahead-of-time (AOT) and just-in-time (JIT) compilers are used by the Dart virtual machine (VM) to improve performance and shorten code execution times.
Developers of Flutter: Accountability
If you want to engage a Flutter app developer for your company, this section will detail their responsibilities.
Creation of Flutter on Flutter platforms using Flutter may create applications for a range of devices, such as:
Flutter While Travelling
Developing specialized experiences for iOS and Android consumers is the duty of Flutter mobile app developers. Flutter is a fantastic choice for cross-platform mobile applications.
Futter on the Internet - You can develop fast, attractive, and highly interactive webpages and web apps using Flutter. In addition to mobile apps, developers also work on desktop applications. They use a single codebase to target several operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS, and Linux, removing the need to change the code for each OS.
System Embedded Flutter
It can be used to construct hardware device interfaces for mobile and online platforms. It provides strong interaction with components developed in different languages, a clean interface, and portable code.
Conclusion
There are important differences between internal hiring and outsourcing. Naturally, many companies prefer hiring engineers in-house. However, because of the need for more technical talent in the market, the lengthy recruiting and on boarding process, and the need to manage, provide, and support engineers to assure retention, businesses usually outsource their development to near shore or offshore engineering suppliers. Hire top flutter app developer in India.
#top mobile app development company#top mobile app developers#mobile app development#hire flutter app developers
0 notes
Text
Exploring Business Process Management (BPM) Applications
Business process management (BPM) finds widespread application across various departments within organizations, aiming to enhance efficiency and streamline workflows. Let's delve into examples of how BPM is harnessed to achieve key business objectives across different functional areas:

Human Resources (HR)
BPM software plays a pivotal role in optimizing HR processes. For instance, it simplifies timesheet reviews and accelerates the onboarding of new hires by automating and orchestrating the multitude of steps involved in these processes. Automation of document-centric HR tasks reduces reliance on paper forms, promoting efficiency and sustainability throughout the company.
Finance
In finance departments, BPM tools facilitate the handling of diverse documentation arising from system-centric and human-centric processes. Finance teams deal with a significant volume of emails and paper forms related to internal and external financial processes. BPM platforms expedite the processing of employee travel requests and streamline purchasing procedures, enhancing operational agility and compliance.
Sales
BPM applications are instrumental in enhancing sales operations by coordinating the exchange of sales quotes and invoices. By automating sales cycle processes and workflows, BPM tools contribute to shortening sales cycles and optimizing overall sales performance.
Diverse Types of BPM Technologies
BPM software encompasses a suite of technologies designed to automate and optimize business processes:
Process Mining Tools: These tools enable the discovery, representation, and analysis of tasks driving business processes, providing insights for process improvement.
BPMN Tools: Used for diagramming and visual representation of business processes, facilitating communication and understanding of workflows.
Workflow Engines: Automate task flows within business processes, supporting workflow management and ensuring seamless execution.
Business Rules Engines (BREs): Enable end-users to modify business rules without programming intervention, fostering flexibility and adaptability in process management.
Recent Developments in BPM Software
Recent advancements in BPM software reflect a shift towards more intelligent and collaborative process automation:
iBPMS (Intelligent BPMS): Leveraging advanced technologies like real-time analytics, machine learning, and complex event processing, iBPMS solutions enable data-driven and dynamic process automation. They also integrate advanced social and collaboration capabilities.
LCNC (Low-Code/No-Code) Technology: The increasing adoption of LCNC technology empowers business analysts and users to model and optimize business processes without extensive coding expertise, fostering collaboration between business and IT teams.
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) vs. BPM: While RPA and BPM were once perceived as competitors, they now operate synergistically. RPA automates discrete, repetitive tasks, complementing BPM's broader process improvement objectives.
BPM as a Discipline
It's essential to understand that BPM is not solely about technology; it embodies a comprehensive approach to process improvement rooted in methodologies like Six Sigma, total quality management, and lean management. BPM advocates emphasize its dual nature as both a technical discipline and a strategic mindset. Successful BPM adoption hinges on organizations recognizing the value of process-oriented approaches to achieving business goals and embracing a culture of continuous improvement.
youtube
In conclusion, BPM applications span diverse organizational functions, leveraging advanced technologies to optimize processes, enhance collaboration, and drive operational excellence. The evolution of BPM software reflects a shift towards intelligent, data-driven process automation, empowering organizations to achieve agility and efficiency in a dynamic business environment.
SITES WE SUPPORT
BPM Process Tools - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
What are the differences in power between C and other programming languages such as Java, C#, .NET, and PHP?
C is a powerful programming language known for its efficiency, low-level control, and versatility. Here are some key differences in power between C and other programming languages like Java, C#, .NET, and PHP:
Low-Level Control: C provides direct access to memory and hardware, allowing developers to write code that interacts closely with system resources. This level of control makes C suitable for systems programming, embedded systems, device drivers, and performance-critical applications where efficiency and precise memory management are paramount. In contrast, higher-level languages like Java, C#, and .NET abstract away low-level details, offering more safety and ease of use but sacrificing some degree of control.
Portability: C code can be compiled to run on a wide range of platforms, from embedded devices to mainframe computers, making it highly portable. However, portability often requires manual adaptation of code to different platforms, as C does not provide built-in platform-independent abstractions like Java's bytecode or .NET's Common Language Runtime (CLR). Java, C#, and .NET, on the other hand, are designed with platform independence in mind, allowing code to run on any platform with a compatible runtime environment.
Memory Management: C requires manual memory management, with developers responsible for allocating and freeing memory explicitly using functions like malloc() and free(). While this level of control can lead to efficient memory usage and performance optimizations, it also increases the risk of memory leaks, dangling pointers, and buffer overflows if not managed carefully. Higher-level languages like Java, C#, and .NET use automatic memory management (garbage collection) to handle memory allocation and deallocation automatically, reducing the risk of memory-related errors but potentially introducing overhead and runtime performance penalties.
Language Features: C is a relatively simple and minimalistic language, with a small number of built-in features and a focus on procedural programming and low-level constructs. In contrast, languages like Java, C#, and .NET offer richer sets of built-in libraries, frameworks, and language features for object-oriented programming, functional programming, concurrency, and web development. PHP is specifically designed for web development, with features tailored to server-side scripting, database interaction, and dynamic web content generation.
In summary, while C is a powerful and efficient language suitable for low-level system programming and performance-critical applications, it requires more manual management and expertise compared to higher-level languages like Java, C#, .NET, and PHP, which offer greater abstraction, ease of use, and platform independence at the cost of some control and performance optimization capabilities. The choice of language depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the project, the target platform, developer expertise, and trade-offs between control, ease of use, and performance.
0 notes
Text
Top 20 Programming Languages You Should Learn in 2024

Imagine yourself commanding machines with words, creating very complex systems that can come to life through your spoken word and develop complete digital worlds. No, we are not talking about science fiction but programming in our daily lives.
Programming languages are just like the normal languages we use to communicate with computers; they enable us to instruct this sophisticated machinery on what it should do and how it should do that.
However, for novices, this programming world looks terrifying, full of enigmatic icons and strange expressions. Do not despair! Your map awaits you so that you can know and select even equipment for your own superpowers of software development. So, let’s get ready for this thrilling ride together!
What is a programming language?
Programming languages may seem intricate, but essentially they are just tools we employ in speaking to computers. We speak English to give commands to our fellow human beings, likewise, a programming language is used to pass instruction codes to a computer. In each language, there are its own rules as well as symbols, just like my language grammar works.

Think of it like writing recipes. With instructions and ingredients (data), you create delicious dishes (programs). Programming languages follow similar principles, using instructions and data to create digital applications, websites, and more.
Here’s a breakdown:
Human languages: we use English, Spanish, etc. to tell others what we want.
Programming languages: we use Python, Java, etc. to tell computers what we want them to do.
Programming languages can be:
Structured: they have rules and syntax to ensure clarity and avoid confusion.
Precise: each instruction needs to be exact, as computers understand things literally.
Versatile: different languages have different strengths, making them suitable for different tasks.
Translatable: while computers have their own language, programming languages act as translators, converting our instructions into something the computer can understand.
In short, programming languages are communication tools that bridge the gap between our ideas and the digital world. They open doors to exciting possibilities, allowing us to bring our creations to life!
Major types of programming languages
The world of programming languages is vast and diverse, each with its own strengths and quirks. Let’s explore some major types to give you a better understanding:
Procedural
Imagine a recipe with clear steps. Procedural languages, like C, Pascal, and FORTRAN, follow a similar approach. They break down tasks into a sequence of instructions, one after the other, like a chef following a recipe.
Example: In C, you might write code to calculate the area of a circle: float radius = 5.0; float area = 3.14159 * radius * radius; printf(“The area of the circle is: %.2f\n”, area);

Functional
Think of building blocks snapping together. Functional languages, like Haskell, Clojure, and Lisp, focus on independent functions (like blocks) that solve smaller problems. These functions can be combined to create larger programs, similar to building a complex structure with individual pieces.
Example: In Haskell, you could define a function to calculate the factorial of a number and use it later in your program: factorial n = if n == 0 then 1 else n * factorial (n-1)
Object-oriented
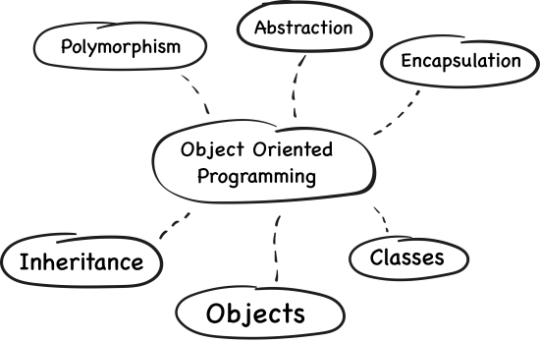
Imagine objects with their own properties and abilities. Object-oriented languages, like Java, Python, C++, and Ruby, model real-world objects. You create “objects” with data (properties) and functions (abilities) that interact with each other, making code more organized and reusable.
Example: In Python, you could create a “Car” object with attributes like color and speed, and methods like accelerate and brake.
Scripting
Think of quick notes or shortcuts. Scripting languages, like Python, Perl, and Bash, are often used for automating tasks or small programs. They are generally easier to learn and use than other languages, making them good for beginners or quick fixes.
Example: In Python, you could write a script to automate downloading files from the internet.
Logic
Imagine solving a puzzle with clues. Logic languages, like Prolog, use logical rules and relationships to solve problems. They are often used in artificial intelligence and expert systems, where reasoning and deduction are important.
Example: In Prolog, you could write code to determine if a given word is a palindrome (reads the same backward and forward).
Imperative
Imagine directly controlling a machine. Imperative languages, like C and C++, give programmers precise control over how the computer executes instructions. They are often used for system programming and tasks requiring fine-grained control.
Example: In C, you could directly manipulate memory addresses and perform low-level operations on the computer hardware.
Top programming languages in 2024
Programming is a constantly evolving niche, with new technologies and trends shaping the landscape. So, what languages are at the forefront in 2024? To answer that, let’s take a pulse of the industry.
Current trends
Data science & AI: the ever-growing demand for data analysis and artificial intelligence fuels the popularity of languages like Python, R, and Scala.
Cloud computing: as businesses migrate to the cloud, languages like Go and JavaScript (Node.js) are in high demand for scalable and efficient cloud applications.
Mobile development: the ubiquitous presence of smartphones keeps languages like Kotlin (Android) and Swift (iOS) relevant for building engaging mobile apps.
Security: with rising cyber threats, secure coding practices and languages like Rust are gaining traction.
Now, let’s dive into some of the most sought-after languages in 2024, keeping these trends and demands in mind.

Machine code languages on colorful elements – Programming concept
C and C++
C and C++ are powerful, low-level programming languages known for their speed and efficiency. C is often used for system programming, while C++ adds object-oriented features. Both languages are widely used in operating systems, game development, and embedded systems.
C#
Developed by Microsoft, C# is a versatile language used for building a variety of applications, including desktop, web, and mobile apps. It combines the power of C++ with the simplicity of Java, making it popular among developers.
CSS
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a language used to style web pages written in HTML. It allows developers to control the layout, fonts, colors, and other visual aspects of a website, enhancing the user experience.
Go
Go, also known as Golang, is a statically typed, compiled language developed by Google. It emphasizes simplicity, efficiency, and concurrency, making it ideal for building scalable web services and distributed systems.
HTML
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the standard language for creating web pages and web applications. It defines the structure and content of a webpage, including text, images, and links.
Java
Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language known for its portability and versatility. It is used for building a wide range of applications, from enterprise software to mobile apps and games.
Javascript
Javascript is a dynamic, interpreted language primarily used for client-side web development. It enables interactive web pages by adding behavior and interactivity to HTML and CSS.
Kotlin
Kotlin is a modern, statically typed language developed by JetBrains and officially supported for Android app development by Google. It offers concise syntax, null safety, and interoperability with Java, making it a popular choice for Android developers.
Matlab
Matlab is a high-level programming language and interactive environment designed for numerical computation, data analysis, and visualization. It is widely used in engineering, science, and mathematics.
NoSQL
NoSQL is not a specific programming language but rather a category of databases that do not use the traditional relational database model. NoSQL databases offer flexible schema design and are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured data.
Perl
Perl is a versatile, interpreted language known for its powerful text-processing capabilities. It is commonly used for system administration, web development, and network programming.
PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting language used for web development and building dynamic web pages. It is widely used in conjunction with HTML to create interactive websites and web applications.
Python
Python is a high-level, interpreted language known for its simplicity and readability. It is used for a wide range of applications, including web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and scientific computing.
R
R is a programming language and environment specifically designed for statistical computing and graphics. It is widely used in data analysis, statistical modeling, and visualization.
Ruby
Ruby is a dynamic, object-oriented language known for its simplicity and productivity. It is often used for web development, particularly with the Ruby on Rails framework, which emphasizes convention over configuration.
Rust
Rust is a systems programming language developed by Mozilla known for its focus on safety, performance, and concurrency. It is designed to prevent common programming errors such as null pointer dereferencing and memory leaks.
Scala
Scala is a statically typed language that combines object-oriented and functional programming paradigms. It runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and is used for building scalable, high-performance applications.
SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a domain-specific language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. It is used to query, insert, update, and delete data from databases.
Swift
Swift is a powerful, open-source programming language developed by Apple for building iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS applications. It offers modern syntax, safety features, and performance optimizations.
TypeScript
TypeScript is a superset of Javascript that adds static typing and other features to the language. It is designed to improve the development experience and scalability of large Javascript projects.
Conclusion
Remember, the programming world is a vast and exciting landscape. While this guide has highlighted some popular languages, the perfect one awaits you based on your unique interests and goals.
Interesting headings:
Affiliate marketing case studies
Bonuses
Reviews
0 notes
Text

Python and JavaScript are both popular programming languages, but they have different purposes, features, and use cases. Here are some key differences between Python and JavaScript:
Type:
Python is a dynamically typed language, meaning variable types are determined at runtime. It is strongly typed, meaning type errors are caught during runtime.
JavaScript is also dynamically typed but is weakly typed, meaning it performs automatic type conversion during operations, which can sometimes lead to unexpected results.
Execution Environment:
Python is typically used for server-side development, scripting, data analysis, machine learning, and scientific computing. It's commonly used with frameworks like Django and Flask for web development.
JavaScript is primarily known as a client-side scripting language for web development, but it's also used for server-side development (Node.js), mobile app development (React Native), desktop app development (Electron), and game development (using libraries like Phaser or frameworks like Unity).
Syntax:
Python emphasizes readability and uses indentation (whitespace) to define code blocks. It uses a clear, concise syntax that resembles pseudo-code, making it beginner-friendly.
JavaScript syntax is influenced by C-style languages and uses curly braces {} to define code blocks. It's more flexible in terms of syntax and allows for various programming paradigms, including procedural, functional, and object-oriented programming.
Concurrency:
Python traditionally has a Global Interpreter Lock (GIL), which restricts multithreading within a single process. This can limit the performance of CPU-bound tasks.
JavaScript is single-threaded but asynchronous by nature, leveraging features like callbacks, Promises, and async/await to handle concurrent operations without blocking the main thread. In Node.js, it utilizes event-driven, non-blocking I/O to handle multiple requests efficiently.
Community and Ecosystem:
Python has a strong community with extensive libraries and frameworks for various domains, including web development (Django, Flask), data science (NumPy, Pandas), machine learning (TensorFlow, PyTorch), and more.
JavaScript also boasts a large and active community with a vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. Popular front-end frameworks/libraries include React, Angular, and Vue.js, while for back-end development, Express.js (Node.js) and NestJS are widely used.
Runtime Environment:
Python code is executed by the Python interpreter, available on various platforms.
JavaScript code is executed by the JavaScript engine, which is built into web browsers for client-side execution and available through runtime environments like Node.js for server-side execution.
In summary, while both Python and JavaScript are versatile languages, they have different strengths and are often used in different domains. Python excels in data analysis, scientific computing, and server-side development, while JavaScript is primarily associated with web development but has expanded into various other domains with the advent of Node.js and other frameworks.
0 notes