#Egypt Tours
Text
Image of the Milky Way over the Temple of Karnak in Egypt.
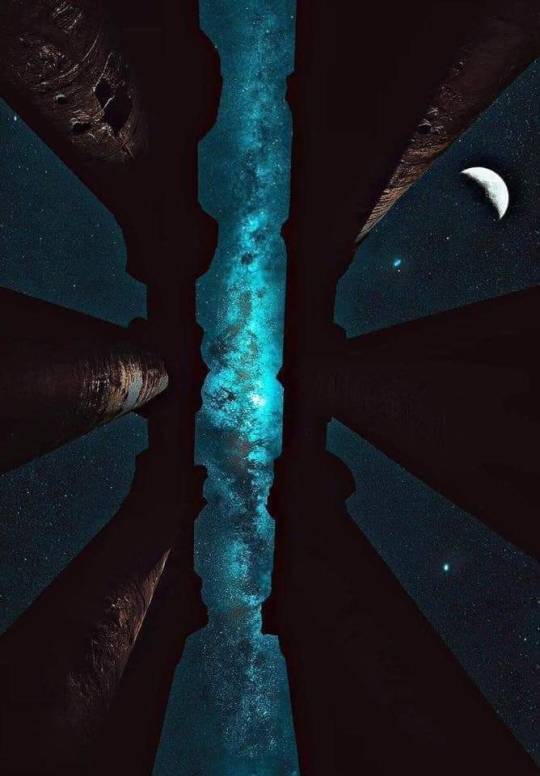

8K notes
·
View notes
Text


mood.
#why is he always falling bro HAHA#he’s such an idiot i want to make love to him#i miss steven grant#steven grant supremacy#steven grant x gender neutral reader#steven grant x y/n#steven grant x reader#steven grant#marc spector#marc spector x reader#jake lockley#jake lockely x reader#jake lockley imagine#and moonknight my sweet boy#moon knight mcu#egyptian god of the moon#moon boys#god of the moon#moon knight system#moon knight x reader#moon#konsu#ancient egypt#egypt#egyptian#egyptology#egypt tours#the prince of egypt#denial is a river in egypt#egypt travel
685 notes
·
View notes
Text


#spotify#tumblr fyp#fypage#quotes#arabian#cat#egyptology#ancient egypt#egypt#egypt tours#pharaohs#winter#soundcloud
350 notes
·
View notes
Text

Giza, Egypt, 1981 - Photo: Louie Psihoyos
#novos#meus#egypt#giza#egyptian#ancient egypt#ancient#pyramids#Louie Psihoyos#photografy#photo#africa#egyptology#egypt tours#1981#egypt history#desert#sahara
54 notes
·
View notes
Text

#ancient egypt#ancient#giza#egyptian#egyptology#pyramids#egypt tours#egypt#ancient history#history tag#archaeology#anthropology#world history#culture#history#cartography#map#library
194 notes
·
View notes
Text










Amazing 💜🔥
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
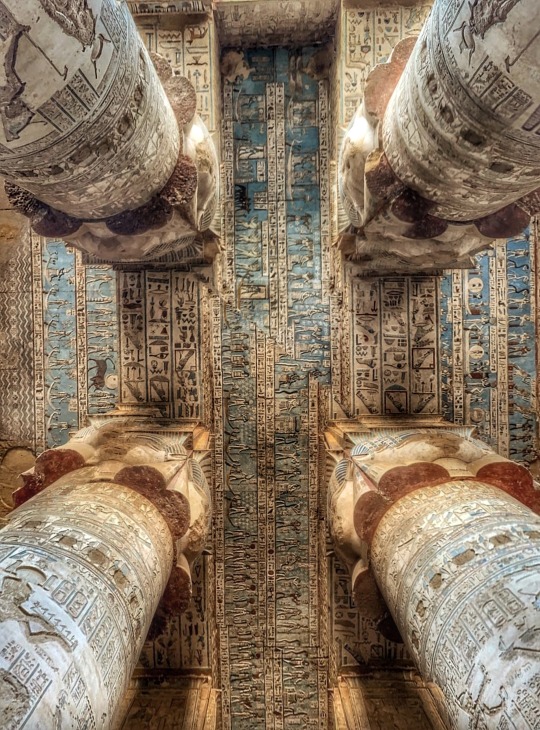

Dendera Temple Complex 3
#original photography#photographers on tumblr#travel photography#original artist#archeaology#ancient history#ancient architecture#ancient monument#egypt#egyptology#ancient egypt#egypt tours#ancient#hieroglyphs#antiquity#dendera temple complex
183 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cairo - Egypt
#egypt#egyptian_girl#egyptian#kemet#kemetic#مصر#loly945#مصريين#sunset#nile#nile river#natural#naturecore#nature photography#visit egypt#egyptian soul#egypt tours#cairo#cairo tours#boat#trees#trip#travel#east#middle east#palm trees#nature#sky
108 notes
·
View notes
Text


Amun Ra Temple, Egypt | 9.13.18
34 notes
·
View notes
Text




Marsa Matruh, Egypt.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
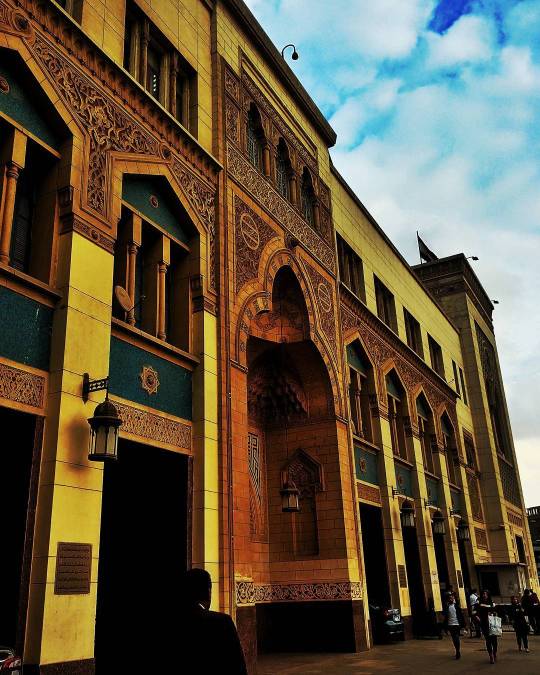


محطة مصر.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text


#egyptology#egyptian#egypt tours#egypt#pharaohs#EGYPTIAN Civilization#spotify#tumblr fyp#winter#fypage#quotes#arabian#pins#pinterest#god anubis
161 notes
·
View notes
Text





المومياء الوحيدة التي لم يجرؤ العلماء ورفضوا نزع الكتان عنها، لأنه لا يوجد إنسان ولا تكنولوجيا في العالم بأسره يمكنها إعادته كما كان ..
مومياء "باشيري" لم يجرؤ كل علماء المصريات على نزع اللفائف الكتانية عنها لصعوبة إعادته الى هيئته الأصلية الأولى وبنفس الدقة، فباتت كل المومياوات المكتشفة معروفة تفاصيلها وقصصها إلا هاته .
The only mummy that scientists did not dare to remove linen from, because there is no human or technology in the entire world that can restore it as it was.
The mummy of "Bashiri" did not dare all Egyptologists to remove the linen scrolls from it because of the difficulty of returning it to its original form and with the same accuracy, so all the mummies discovered are known their details and stories except these.
#vintage#ancient#lovely#egypt#egyptian#ancient egypt#egyptology#gods of egypt#i love you#movie quotes#ancient ruins#ancient history#history#historical#egyptian gods#egypt tours#godness#gods
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
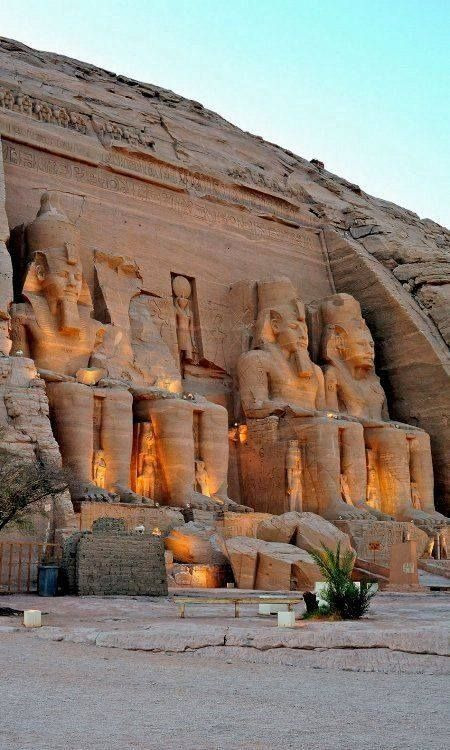

#abu simbel#egyptian#aesthetic#ancient#giza#egyptology#pyramids#egypt tours#ancient egypt#egypt#historic#language tag#artifacts#na fila#history tag#history#histoire#monument#love#gif#tumblr#halloween#quotes#spooky#fall#pink#flowers
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Queen's Pets
#art#artist#artsy#artwork#arte#illustration#blackartistsmatter#egyptian#ancient egypt#egyptology#egypt#egypt tours#pinupgirl#pin up model#pinup#cheetah#pets
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
๋࣭ ⭑⚝ The Rise and Fall of Ancient Egyptian Civilization๋࣭ ⭑⚝

hey guys im back AND late but here was a very long and slightly complicated one enjoy :D

Ancient Egypt, one of the most iconic civilizations in history, thrived for over three millennia, leaving an indelible mark on human culture, art, and governance. Its history is a tapestry of great achievements and inevitable decline, shaped by its geographic advantages, complex social structure, and interactions with neighboring powers.
The Geographic Foundation of Egyptian Civilization
The Nile River was the foundation of Ancient Egypt's prosperity. Flowing northward through an arid desert, the Nile created a fertile strip of land that was ideal for agriculture. The river's annual inundation deposited nutrient-rich silt onto the land, enabling the Egyptians to grow abundant crops, which in turn supported a growing population and the development of a complex society.
Geography played a crucial role in the development of a unified Egyptian state. The Nile served as a natural highway, facilitating communication and trade between Upper and Lower Egypt. This unity was essential for the centralized control that characterized Ancient Egyptian governance. Moreover, the deserts to the east and west, and the cataracts of the Nile to the south, provided natural barriers that protected Egypt from invasions, allowing the civilization to flourish relatively undisturbed by external threats.
The Unification of Egypt and the Early Dynastic Period
Around 3100 BCE, King Narmer (often identified as Menes) achieved the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, marking the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period (c. 3100–2686 BCE). This unification was a critical moment in Egyptian history, laying the groundwork for the centralized state that would dominate the region for centuries.
During this period, the pharaoh emerged as both a political and religious leader, considered a divine ruler responsible for maintaining Ma'at, the cosmic order. The early pharaohs established a bureaucratic system that allowed them to administer the state efficiently, collect taxes, and organize large-scale construction projects. The development of hieroglyphic writing during this time enabled the recording of official decrees, religious texts, and monumental inscriptions, further solidifying the authority of the pharaohs.
The Old Kingdom: The Age of the Pyramids
The Old Kingdom (c. 2686–2181 BCE), often referred to as the "Age of the Pyramids," saw the construction of some of the most enduring symbols of Ancient Egypt. The most famous of these is the Great Pyramid of Giza, built during the reign of Pharaoh Khufu (c. 2589–2566 BCE). This period was characterized by the centralization of power in the hands of the pharaoh, who was regarded as a living god responsible for the well-being of the state.
The economy of the Old Kingdom was based on a redistributive system, where the surplus from agriculture was collected by the state and used to fund massive construction projects, support the bureaucracy, and maintain the military. This system allowed the pharaohs to command vast resources, which were used to build monumental structures that symbolized their divine authority and ensured their legacy.
However, the immense resources required for these projects eventually strained the economy. By the end of the Sixth Dynasty, around 2181 BCE, the centralized power of the pharaohs began to decline. Low Nile floods, combined with the growing power of regional governors (nomarchs), led to a weakening of central authority and the collapse of the Old Kingdom, ushering in the First Intermediate Period.
The First Intermediate Period: A Time of Fragmentation
The First Intermediate Period (c. 2181–2055 BCE) was marked by political fragmentation and social instability. With the collapse of the Old Kingdom, Egypt split into several smaller, competing regions, each ruled by local leaders. This period is often described as a "dark age" in Egyptian history, characterized by a decline in monumental building, cultural achievements, and central authority.
Despite the challenges of this period, the resilience of Egyptian society eventually led to the reunification of the country. The rulers of Thebes, in Upper Egypt, gradually gained power and, by the end of the Eleventh Dynasty, succeeded in reuniting Egypt under the leadership of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II. This marked the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, a period of renewed stability and prosperity.
The Middle Kingdom: A Period of Renewal
The Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BCE) is often regarded as a renaissance period in Egyptian history. The pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom focused on consolidating their power, reforming the administration, and expanding Egypt's influence beyond its traditional borders.
One of the most significant achievements of the Middle Kingdom was the expansion of Egypt's borders into Nubia, a region rich in gold and other valuable resources. The Egyptians established a series of fortresses along the Nile in Nubia, securing control over the region and ensuring a steady supply of resources for the state. The Middle Kingdom also saw increased trade with the Levant and other regions, bringing in goods such as cedarwood, lapis lazuli, and silver.
The literature of the Middle Kingdom reflects a more introspective and realistic view of life compared to the Old Kingdom. Works such as the "Tale of Sinuhe" and the "Instructions of Amenemhat" emphasize themes of loyalty, morality, and the responsibilities of the pharaoh to his people. The concept of Ma'at continued to be central to Egyptian thought, but there was also a growing recognition of the complexities and challenges of maintaining order in the world.
The Middle Kingdom pharaohs undertook large-scale irrigation projects to improve agricultural productivity and prevent the famine that had plagued the late Old Kingdom. These projects included the construction of canals and reservoirs to control the Nile's flooding and to ensure a stable water supply for agriculture. The increased agricultural productivity contributed to the prosperity of the Middle Kingdom and supported the growth of a more complex and stratified society.
The Second Intermediate Period and the Rise of the New Kingdom
The decline of the Middle Kingdom led to the Second Intermediate Period (c. 1650–1550 BCE), a time of political instability and foreign invasions. The Hyksos, a group of Asiatic people, established themselves as rulers in Lower Egypt, introducing new technologies such as the horse-drawn chariot and composite bow. Meanwhile, native Egyptian rulers maintained power in Thebes, leading to a divided Egypt.
Eventually, the Theban rulers mounted a successful campaign to expel the Hyksos, leading to the reunification of Egypt under Ahmose I and the beginning of the New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BCE). This period is often referred to as the "Empire Period" due to Egypt's expansion and dominance over neighboring regions, including Nubia, the Levant, and parts of the Near East.
The New Kingdom pharaohs, such as Thutmose III, Hatshepsut, and Ramses II, expanded Egypt's borders through military campaigns and diplomatic alliances. The empire's wealth was further bolstered by tribute from conquered territories and extensive trade networks. The period also saw a resurgence in monumental building projects, with the construction of massive temples, such as those at Karnak and Luxor, and the rock-cut temples at Abu Simbel.
Religion played a central role in the New Kingdom, with the pharaohs increasingly emphasizing their divine status and their connection to the gods. The worship of the sun god Amun-Ra became particularly prominent, and the pharaohs were often depicted as the "son of Ra," chosen to rule by divine mandate. The New Kingdom also saw the rise of the powerful priesthood of Amun, which would later become a significant political force in its own right.
However, the immense costs of maintaining an empire, both in terms of resources and military commitments, gradually weakened the state. The death of Ramses II in 1213 BCE marked the beginning of a slow decline, as his successors struggled to maintain the empire's vast territories. Internal strife, including power struggles among the nobility and challenges to the authority of the pharaoh, further destabilized the kingdom.
The Decline and Fall of Ancient Egypt
The decline of Egypt accelerated during the Third Intermediate Period (c. 1070–664 BCE), a time characterized by political fragmentation and foreign invasions. The once-unified kingdom split into multiple smaller states, with the Libyans and Nubians establishing their own dynasties in different regions of Egypt. The arrival of the Sea Peoples, a confederation of naval raiders who caused widespread destruction throughout the Eastern Mediterranean, further strained Egypt's resources and military capabilities.
Despite these challenges, Egypt experienced a brief resurgence during the Late Period (c. 664–332 BCE) under the Saite dynasty, particularly under Pharaoh Psamtik I, who reasserted control over the country and repelled foreign invaders. The Saites focused on reviving the cultural and religious traditions of the past, as well as rebuilding the country's economy. However, this revival was short-lived, as Egypt was increasingly drawn into the conflicts of the larger Mediterranean world.
In 525 BCE, Egypt was conquered by the Persian Empire under Cambyses II, becoming a satrapy within the larger Achaemenid Empire. Although Egypt regained its independence briefly during the 28th to 30th Dynasties, it was finally and irrevocably absorbed into the Macedonian Empire following the conquest by Alexander the Great in 332 BCE. The subsequent Ptolemaic Period (305–30 BCE) represented a fusion of Greek and Egyptian cultures, but it was clear that the era of native Egyptian rule had come to an end.
The death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BCE and the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire marked the final chapter in the long and storied history of ancient Egyptian civilization. The fall of Egypt was not simply the result of external conquest, but also the culmination of centuries of internal decay, economic decline, and the gradual loss of autonomy in the face of rising foreign powers.
The rise and fall of ancient Egypt is a testament to the complex interplay of geography, governance, culture, and external forces in shaping the destiny of a civilization. From its origins along the life-giving Nile to its zenith as a powerful empire and its eventual decline, Egypt's history offers valuable insights into the factors that sustain and undermine civilizations. The legacy of ancient Egypt, preserved in its monuments, art, and written records, continues to influence and inspire the modern world. The civilization's story serves as both a cautionary tale and a reminder of the enduring achievements of human ingenuity and resilience.

guys i get my gcse results on thursday help
#history#dark aesthetic#dark academia#literature#egypt#ancient egypt#egyptian#egyptology#egypt tours#ancient history
8 notes
·
View notes