#Endpoint Detection and Response
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
《企業端點完美防禦》26-偵測與回應的迷思
EDR指的是端點偵測和回應(Endpoint Detection and Response, EDR),,是一種持續監控「端點」(桌上型電腦、筆記型電腦、手機、物聯網設備等)以緩解威脅的安全技術。 在《企業端點完美防禦》20-EDR小試牛刀:卡巴斯基端點偵測與回應優選版、與《企業端點完美防禦》22-綜觀全局:卡巴斯基反針對攻擊平台,我們看到了EDR的執行方法:收集端點資料、分析、加入偵測規則。雖然卡巴斯基把EDR分為優選版、和專家版,但差別在於優選版是針對端點可以偵測到的威脅進行調查,而專家版則是把端點上所有資料收集下來,經由機器學習分類為安全(綠色)、低危險性(灰色)、中危險性(黃色)、高危險性(紅色),系統管理員可以對每個事件進行調查。 然而,我們已經在網路上看到太多吹噓自己EDR有多強、在MITRE…
0 notes
Text
Trellix Acknowledged As Leading In IDC MarketScape: Modern Endpoint Security

Trellix, a leading cybersecurity firm specializing in extended detection and response (XDR), has achieved recognition as a Leader in the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Modern Endpoint Security for Midsize Businesses 2024 Vendor Assessment, complementing its earlier recognition in the Enterprises category. Trellix's cutting-edge Endpoint Security Suite, a crucial element of its AI-powered XDR platform, provides comprehensive protection, encompassing endpoint protection, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and forensic controls. This suite delivers a robust defense strategy, covering protection, detection, investigation, forensics, and remediation to minimize risks across the attack surface. Trellix's expansive portfolio allows customers to seamlessly expand to XDR from an endpoint security base and integrate native and third-party tools, facilitating adaptability in hybrid environments.
John Morgan, XDR General Manager at Trellix, underscores the imperative need for a modern endpoint security solution that surpasses traditional protection, incorporating detection, investigation, forensics, and remediation. Trellix's Endpoint Security Suite is relied upon by organizations of all sizes and industries to provide informed control over their endpoints, featuring AI-guided investigation, remediation, policy management, and world-class threat intelligence telemetry from millions of sensors worldwide. The IDC MarketScape recognizes Trellix as an excellent choice for midsize businesses with intricate environments and advanced cybersecurity requirements.
Read More - https://www.techdogs.com/tech-news/business-wire/trellix-named-a-leader-in-idc-marketscape-for-modern-endpoint-security-for-midsize-businesses
0 notes
Text
Cyber Security Services Company | Data Security Solutions

In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses increasingly rely on technology to store, process, and transmit sensitive data. As companies across industries harness the power of the internet, the need for robust cybersecurity services has never been more crucial. Data breaches and cyberattacks are growing threats from small startups to large corporations that can have devastating consequences. That’s where a cybersecurity company specializing in data protection services and cybersecurity management comes into play.
This blog explores the importance of cybersecurity management, the types of services offered by a cybersecurity services company, and how data protection services and endpoint security services can help businesses protect their sensitive information.
Understanding the Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
The digital transformation that businesses have undergone in recent years has revolutionized operations, providing significant benefits like improved efficiency, better customer engagement, and more streamlined processes. However, this transformation has also opened new doors for cybercriminals who exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks to steal data, launch attacks, and disrupt operations.
With data breaches and cyberattacks on the rise, organizations must safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, manipulation, and theft. Whether it’s customer data, intellectual property, or financial records, securing these assets is paramount to maintaining trust, compliance with regulations, and protecting brand reputation.
Cybersecurity solutions providers play a key role in defending organizations from these threats. Cybersecurity isn’t just a technical need—it’s a business priority that can help prevent costly disruptions, legal ramifications, and loss of customer confidence. This is where the role of a cybersecurity consulting firm becomes indispensable.
What Is a Cybersecurity Services Company?
A cybersecurity services company specializes in identifying, mitigating, and preventing cyber threats. They provide tailored solutions to ensure businesses’ information and infrastructure are well-protected from a wide range of security risks. These companies are essential partners in safeguarding businesses from cyberattacks and ensuring the security of sensitive data and systems.
Key Services Provided by a Cybersecurity Services Company

Cybersecurity companies offer a range of services designed to safeguard businesses from evolving threats. These services include:
Threat Detection & Prevention Services: Cybersecurity companies deploy advanced monitoring tools and techniques to detect vulnerabilities, anomalous activities, and potential threats before they cause harm. This includes setting up firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
Risk Management: Cybersecurity firms assess vulnerabilities and design strategies to safeguard businesses from both internal and external threats. A cyber risk management company helps ensure that businesses are prepared for any potential cyber risks.
Cybersecurity Audits & Assessments: Regular security audits and penetration testing are vital for identifying weaknesses in a company’s infrastructure. These audits ensure no part of the system remains unprotected.
Compliance Support: For businesses in regulated industries, cybersecurity compliance services help ensure adherence to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Companies in these industries can also benefit from IT security services companies that provide guidance and support for meeting compliance requirements.
Incident Response & Disaster Recovery: Even with robust security measures, breaches can still occur. Incident response services help businesses respond quickly and effectively to limit damage. Additionally, cybersecurity audit services and vulnerability assessment companies help identify and prevent potential attacks before they materialize.
Employee Training & Awareness: Cybersecurity management companies often provide training programs to raise awareness about phishing, password hygiene, and safe online behavior, reducing human error and improving security.
Types of Data Security Solutions Offered by Cybersecurity Companies

At the core of every cybersecurity service is data protection. Cybersecurity solutions providers offer several key solutions to help businesses secure their information:
Encryption: Encryption ensures that even if data is accessed by cybercriminals, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. Cloud security companies offer encryption solutions to protect data stored in the cloud, safeguarding sensitive information during transit and while at rest.
Access Control & Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) are implemented to ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Data protection services monitor data transfers and emails to prevent unauthorized sharing or leakage of confidential information.
Firewalls & Network Security: Firewalls act as the first line of defense by filtering traffic and blocking harmful activities. Network security services providers ensure that your network is properly configured with firewalls, VPNs, and network segmentation to protect data from external attacks.
Backup & Disaster Recovery: A comprehensive backup and recovery plan ensures that lost or compromised data can be restored with minimal disruption to business operations. Cloud security companies play a key role in providing reliable cloud-based backup and recovery services.
Endpoint Security: With more employees working remotely, endpoint security services are becoming essential. Cybersecurity firms implement solutions to protect mobile devices, laptops, and tablets from threats.
Why Partner with a Cybersecurity Services Company?
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from the specialized expertise of a cybersecurity consulting firm. Here are some reasons why partnering with one is essential:
Expertise and Experience
Cybersecurity is a complex field requiring in-depth knowledge of emerging threats and security solutions. A cybersecurity services company brings years of experience and expertise to the table, ensuring best practices and cutting-edge tools are used to protect your data.
Cost Efficiency
Building an in-house cybersecurity team can be costly. By outsourcing to a cybersecurity solutions provider, businesses gain access to expert resources and advanced technologies without the need to invest in full-time staff.
Proactive Protection
Rather than waiting for a breach to occur, a cybersecurity management company helps you adopt a proactive approach by identifying and neutralizing potential threats before they can impact your business.
Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA can be challenging. A cybersecurity services company ensures your business complies with relevant data protection laws, avoiding legal complications and fines. These companies provide cybersecurity compliance services to meet the highest standards of data protection.
Business Continuity
Cybersecurity services also encompass disaster recovery planning, ensuring that your business can continue to operate smoothly after a cyber attack or natural disaster. Security operations center services ensure continuous monitoring, offering peace of mind that any security breaches are quickly detected and neutralized.
Conclusion: Protect Your Business with a Cybersecurity Services Company
As cyber threats continue to evolve, businesses must take proactive steps to protect their sensitive data and maintain customer trust. Partnering with a reputable cybersecurity consulting firm ensures that you have the right tools, expertise, and strategies in place to prevent cyberattacks, secure your data, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Whether it’s through penetration testing, endpoint security services, or incident response services, a cybersecurity services company plays a crucial role in keeping your data safe and your business running smoothly.
Investing in cybersecurity solutions today can help prevent significant financial and reputational damage in the future. Don't wait until it's too late—reach out to a trusted cybersecurity services company today to protect your data and your business's future.
#Cyber Security Services Company | Data Security Solutions#Cybersecurity Management Company#Managed Cyber Security Services#Cyber Security Company#Cyber Security Services#Endpoint Security Services#Cybersecurity Solutions Provider#Cyber Security Consulting Firm#Network Security Services#Cybersecurity Audit Services#IT Security Services Company#Cloud Security Company#Data Protection Services#Cybersecurity Compliance Services#Security Operations Center Services#Threat Detection Services#Penetration Testing Company#Incident Response Services#Vulnerability Assessment Company#Cyber Risk Management Company#Information Security Services
0 notes
Text
What is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)?

EDR is a cybersecurity solution that continuously monitors and responds to potential threats on endpoints (devices like laptops, smartphones, and servers). It involves real-time tracking, threat detection, and automated response to mitigate risks.
Why is EDR important for your business?
1. Enhanced Security: Detects and responds to threats quickly, reducing the risk of data breaches.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: Provides continuous oversight of all endpoints, ensuring threats are identified and dealt with promptly.
3. Automated Response: Automates threat responses, minimizing the impact on your operations and reducing downtime.
Investing in EDR helps protect your business from evolving cyber threats, ensuring your data and systems remain secure. Safeguard your business with advanced EDR solutions from Century Solutions Group. #CyberSecurity #EDR #CenturySolutionsGroup – www.centurygroup.net
1 note
·
View note
Text
Strategic Insights: Endpoint Detection and Response Market Poised for US$ 25 Billion in 2033
The endpoint detection and response market is estimated to be worth US$ 4.0 billion in 2024 and is projected to be valued at US$ 32.4 billion in 2034. Between 2024 and 2034, the industry is expected to register a CAGR of 23.2%. The rising concern for data security owing to the rising popularity of remote working is one of the major market drivers for endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions during the forecast period.
With the rising trend of remote working, there has been an increase in the threat of data breaches and malware attacks. This has been a growing concern for data security, as the devices can be stolen, lost, or hacked, potentially leading to a breach of sensitive corporate data.
The growth of the global endpoint detection and response market is driven by Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) trend as employees using their personal devices for work-related activities, which has become increasingly common in recent years. Thus the growing need for managing and securing these devices boost the demand for endpoint detection and response solutions in organization.
Get Exclusive Sample Copy of the Report: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-18568
EDR solutions are increasingly being integrated into larger security ecosystems, including SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platforms and other security tools. The increasing partnerships between EDR solution providers and other cybersecurity firms or industry-specific entities further drive innovation and market growth.
Key Takeaways from the Market Study
From 2019 to 2023, the endpoint detection and response market was valued at a CAGR of 19.3%
Based on solution, the software segment is expected to account for a share of 64.5% in 2024.
Global endpoint detection and response demand in China is predicted to account for a CAGR of 23.7% in 2024.
In the United States, the endpoint detection and response industry is expected to account for a CAGR of 21.1% in 2024.
Germany is projected to expand by a value CAGR of 22.7% between 2024 and 2034.
Endpoint detection and response market in Japan is anticipated to record a CAGR of 24.4% in 2024.
“ The growing number of cyber threats, along with the growing awareness of the importance of endpoint security in the overall cybersecurity posture, is anticipated to drive the market growth during the forecast period.” opines Sudip Saha, managing director at Future Market Insights (FMI) analyst.
Request Report Methodology: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/request-report-methodology/rep-gb-18568
Key Market Players
Bitdefender
Broadcom, Inc. Cisco Systems
CrowdStrike
ESET
FireEye
Fortinet
Kaspersky
McAfee
Microsoft Corporation
Competitive Landscape
Key players focus on organic growth strategies like product launches and approval. Collaborations and partnerships with key players and acquiring niche players are critical strategies followed by leading endpoint detection and response market.
Key Product Offerings
CrowdStrike k nown for its cloud-native Falcon platform, CrowdStrike provides endpoint security solutions that leverage AI and machine learning for threat detection and response. They focus on real-time visibility and prevention of threats across endpoints.
Carbon Black (VMware) acquired by VMware, offers EDR solutions designed to protect endpoints by continuously monitoring and analyzing endpoint activities. Their technology emphasizes behavior-based threat detection and response.
Symantec, now part of Broadcom, offers EDR capabilities through its Endpoint Security portfolio. Their solutions provide threat hunting, incident investigation, and response functionalities to secure endpoints against evolving threats.
Buy this Exclusive Report: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/checkout/18568
Market Segmentation
Solution:
Software
Service
Professional Services
Managed Services
Endpoint Device:
Network Devices and Servers
Mobile Devices
Point Of Sale (POS) Devices
Others
Deployment:
Cloud
On-premise
Enterprise Size:
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
Large Enterprises
Vertical:
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Government and Defence
Retail and E-commerce
IT and Telecom
Energy and Utilities
Manufacturing
Others
Region:
North America
Latin America
Western Europe
Eastern Europe
South Asia and Pacific
East Asia
Middle East and Africa
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Antivirus Software: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, where our lives are intricately intertwined with technology, safeguarding our digital assets has become paramount. With the proliferation of cyber threats, antivirus software stands as a crucial line of defense against malware, viruses, ransomware, and other malicious entities lurking online. However, the abundance of antivirus options can be overwhelming, making it…

View On WordPress
#A#Advanced Behavioral Analysis Software#Advanced Threat Detection#Antivirus#Antivirus Software#Automated Security Incident Response#Cloud Security Solutions#Cloud-Based Endpoint Security Platform#Comprehensive Data Protection Suite#Continuous Vulnerability Assessment#Cyber Defense#Cybersecurity#Cybersecurity Awareness Training#Data Encryption Software#Data Protection#Defense#Encryption#Endpoint Protection Suite#Endpoint Security#Firewall#Firewall Protection#Identity Theft#Identity Theft Prevention#Integrated Firewall Protection Mechanism#Internet Security Software#Malware#Malware Detection#Malware Removal Tool#Mobile Device Management#Multi-Layered Malware Defense System
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
Endpoint Detection and Response Market Report: Challenges and Opportunities
The global endpoint detection and response market size is expected to reach USD 16.89 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 24.9% from 2023 to 2030, according to a recent report by Grand View Research, Inc. The market for endpoint detection and response (EDR) is expected to continue its growth in the coming years due to the increasing adoption of servers, network devices, and mobile devices in the workplace and the need to secure and manage them.
Furthermore, the growing demand for cloud-based EDR solutions across BFSI and IT & telecom industries has fueled the demand for the market. Moreover, the ongoing trend of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) has led to an increase in the number of personal devices that need to be managed and secured within an organization.
Gain deeper insights on the MLOps Market market and receive your free copy with TOC now @: Endpoint Detection And Response (EDR) Market Report
EDR solutions use innovative threat intelligence, machine learning, and behavioral analysis algorithms that detect threats and suspicious activities leading to security breaches. These solutions are designed to detect real-time potential threats on endpoint devices such as servers, memory devices, mobile devices, and other point-of-sale devices, thereby helping the organization enhance its security posture through the rapid response capability.
As more organizations adopt BYOD policies or provide employees with company-owned devices, the demand for EDR solutions is expected to continue to grow, boosting the endpoint detection & response (EDR) market growth. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted the work culture globally, compelling offices to adopt a work-from-home environment, where the need for EDR solutions has increased, in order to secure and manage employee devices outside the organization's network perimeter. However, the high costs of implementation, operation, and maintenance of EDR solutions among small- & medium-sized enterprises are anticipated to hamper the market growth. The cost of implementing EDR solutions varies, depending on the size of the enterprise, endpoint devices, and the pricing model of the vendor. Additionally, these solutions require additional hardware and software components that further enhance the overall deployment cost
#Endpoint Detection And Response Market Size & Share#Global Endpoint Detection And Response Market#Endpoint Detection And Response Market Latest Trends#Endpoint Detection And Response Market Growth Forecast#COVID-19 Impacts On Endpoint Detection And Response Market#Endpoint Detection And Response Market Revenue Value
0 notes
Text
Prevention Techniques for Top 10 Common Cyber Attacks

In the ever-escalating war against cybercriminals, staying informed about the most common attack vectors is half the battle. The other half is implementing robust prevention techniques. As we navigate 2025, the threat landscape continues to evolve, but many foundational attack methods remain prevalent due to their effectiveness.
Here's a breakdown of the top 10 common cyber attacks and the essential prevention techniques to keep you and your organization secure.
1. Phishing & Smishing (SMS Phishing)
The Attack: Attackers impersonate trusted entities (banks, colleagues, popular services) via email or text messages to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, clicking malicious links, or downloading malware. Modern phishing often uses AI to generate hyper-realistic content.
Prevention Techniques:
Vigilant User Education: Train employees to scrutinize sender email addresses, hover over links to check destinations, and be suspicious of urgent or generic requests. Conduct regular simulated phishing tests.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Even if credentials are stolen, MFA can block unauthorized access. Enforce it widely.
Email & SMS Security Solutions: Deploy advanced email filters (e.g., Microsoft Defender for Office 365, secure email gateways) that scan for suspicious patterns, attachments, and URLs. Forward suspicious texts to 7726 (SPAM).
DMARC, SPF, DKIM: Implement these email authentication protocols to prevent email spoofing of your own domain.
2. Malware (Viruses, Worms, Trojans)
The Attack: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Malware can be delivered via downloads, malicious websites ("drive-by" attacks), or attachments.
Prevention Techniques:
Antivirus/Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Install and keep robust antivirus and EDR solutions updated on all devices.
Regular Software Updates: Patch operating systems, applications, and browsers promptly to close security loopholes that malware exploits.
Firewalls: Use network and host-based firewalls to control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Download Caution: Only download software and files from trusted, official sources. Scan all downloads before opening.
3. Ransomware
The Attack: A type of malware that encrypts a victim's files or locks their system, demanding a ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) for decryption or restoration of access. It often enters via phishing or exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities.
Prevention Techniques:
Robust Backups: Implement a 3-2-1 backup strategy (3 copies, on 2 different media, with 1 copy off-site and isolated/immutable). Regularly test recovery.
MFA & Strong Passwords: Crucial for protecting remote access services (like RDP) often targeted by ransomware operators.
Vulnerability Management: Continuously scan for and patch vulnerabilities, especially on internet-facing systems.
Network Segmentation: Divide your network into isolated segments to prevent ransomware from spreading laterally if it gains a foothold.
Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about ransomware's common entry points (phishing).
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
The Attack: Overwhelming a target server, service, or network with a flood of internet traffic from multiple compromised computer systems (a botnet), aiming to disrupt normal operations and make services unavailable.
Prevention Techniques:
DDoS Protection Services: Utilize specialized DDoS mitigation services (e.g., Cloudflare, Akamai) that can absorb and filter malicious traffic.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute traffic and cache content, helping to absorb some attack volume and improve resilience.
Rate Limiting: Configure servers and network devices to limit the number of requests they will accept from a single IP address or source over a given time.
Network Redundancy: Ensure your infrastructure has redundant systems and sufficient bandwidth to handle traffic spikes.
5. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
The Attack: An attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. This often happens over unsecured Wi-Fi.
Prevention Techniques:
Always Use HTTPS: Ensure websites you visit use HTTPS (look for the padlock icon in the browser address bar) to encrypt communication.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Tasks: Refrain from accessing banking, email, or other sensitive accounts over unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
Use VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, creating a secure tunnel even over public networks.
Strong Authentication: Implement MFA and passwordless authentication to mitigate credential theft even if traffic is intercepted.
6. SQL Injection (SQLi)
The Attack: An attacker injects malicious SQL code into input fields of a web application to manipulate the database, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data theft, or data corruption.
Prevention Techniques (primarily for developers):
Prepared Statements & Parameterized Queries: The most effective defense. Treat user input as data, not executable code.
Input Validation & Sanitization: Validate and sanitize all user input on both the client and server sides to ensure it conforms to expected formats and removes malicious characters.
Least Privilege: Grant database accounts only the minimum necessary privileges required for their function.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): WAFs can detect and block common web-based attacks like SQLi.
7. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
The Attack: Attackers inject malicious client-side scripts (e.g., JavaScript) into web pages viewed by other users. This can lead to session hijacking, defacement of websites, or redirection to malicious sites.
Prevention Techniques (primarily for developers):
Output Encoding/Escaping: Properly encode or escape all user-supplied data before rendering it in HTML to prevent it from being interpreted as executable code.
Input Validation: Validate user input to ensure it doesn't contain malicious scripts.
Content Security Policy (CSP): Implement a CSP to restrict which sources are allowed to execute scripts on your website.
Sanitize HTML: If your application allows users to input HTML, use robust libraries to sanitize it and remove dangerous tags/attributes.
8. Zero-Day Exploits
The Attack: Exploits that target newly discovered software vulnerabilities for which a patch is not yet available. They are extremely dangerous because there's no immediate defense.
Prevention Techniques:
Layered Security (Defense-in-Depth): Rely on multiple security controls (firewalls, EDR, IDS/IPS, network segmentation) so if one fails, others can still detect or contain the attack.
Behavioral Analysis: Use security tools (like EDR, UEBA) that monitor for anomalous behavior, even if the specific exploit is unknown.
Application Whitelisting: Allow only approved applications to run on your systems, preventing unauthorized or malicious executables.
Rapid Patch Management: While a patch doesn't exist initially, be prepared to deploy it immediately once released.
9. Insider Threats
The Attack: A security breach or data loss caused by a person with authorized access to an organization's systems and data, whether malicious or accidental.
Prevention Techniques:
Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP): Grant users only the minimum access necessary to perform their job functions.
User Behavior Analytics (UBA/UEBA): Monitor user activity for anomalous behaviors (e.g., accessing unusual files, working outside normal hours).
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization's controlled environment.
Employee Training: Educate employees on security policies, data handling best practices, and recognizing social engineering.
Offboarding Procedures: Have strict procedures for revoking access immediately when an employee leaves.
10. Brute Force & Credential Stuffing
The Attack:
Brute Force: Systematically trying every possible combination of characters until the correct password or encryption key is found.
Credential Stuffing: Using lists of stolen usernames and passwords (from previous breaches) to try and log into accounts on other services.
Prevention Techniques:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): The most effective defense, as attackers need a second factor beyond just the password.
Strong Password Policies: Enforce complex, unique passwords that are difficult to guess.
Account Lockout Mechanisms: Implement policies that temporarily lock accounts after a certain number of failed login attempts.
Rate Limiting: Restrict the number of login attempts from a single IP address over a period.
CAPTCHA Challenges: Introduce CAPTCHAs or other challenge-response mechanisms during login to differentiate humans from bots.
Threat Intelligence: Monitor dark web forums for compromised credentials and prompt affected users to reset their passwords.
By proactively addressing these common attack vectors with a layered and comprehensive security strategy, individuals and organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses and foster a more secure digital environment. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and make cybersecurity a continuous priority.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
CrowdStruck
By Edward Zitron • 19 Jul 2024 View in browser
Soundtrack: EL-P - Tasmanian Pain Coaster (feat. Omar Rodriguez-Lopez & Cedric Bixler-Zavala)
When I first began writing this newsletter, I didn't really have a goal, or a "theme," or anything that could neatly characterize what I was going to write about other than that I was on the computer and that I was typing words.
As it grew, I wrote the Rot Economy, and the Shareholder Supremacy, and many other pieces that speak to a larger problem in the tech industry — a complete misalignment in the incentives of most of the major tech companies, which have become less about building new technologies and selling them to people and more about capturing monopolies and gearing organizations to extract things through them.
Every problem you see is a result of a tech industry — from the people funding the earliest startups to the trillion-dollar juggernauts that dominate our lives — that is no longer focused on the creation of technology with a purpose, and organizations driven toward a purpose. Everything is about expressing growth, about showing how you will dominate an industry rather than serve it, about providing metrics that speak to the paradoxical notion that you'll grow forever without any consideration of how you'll live forever. Legacies are now subordinate to monopolies, current customers are subordinate to new customers, and "products" are considered a means to introduce a customer to a form of parasite designed to punish the user for even considering moving to competitor.
What's happened today with Crowdstrike is completely unprecedented (and I'll get to why shortly), and on the scale of the much-feared Y2K bug that threatened to ground the entirety of the world's computer-based infrastructure once the Year 2000 began.
You'll note that I didn't write "over-hyped" or anything dismissive of Y2K's scale, because Y2K was a huge, society-threatening calamity waiting to happen, and said calamity was averted through a remarkable, $500 billion industrial effort that took a decade to manifest because the seriousness of such a significant single point of failure would have likely crippled governments, banks and airlines.
People laughed when nothing happened on January 1 2000, assuming that all that money and time had been wasted, rather than being grateful that an infrastructural weakness was taken seriously, that a single point of failure was identified, and that a crisis was averted by investing in stopping bad stuff happening before it does.
As we speak, millions — or even hundreds of millions — of different Windows-based computers are now stuck in a doom-loop, repeatedly showing users the famed "Blue Screen of Death" thanks to a single point of failure in a company called Crowdstrike, the developer of a globally-adopted cyber-security product designed, ironically, to prevent the kinds of disruption that we’ve witnessed today. And for reasons we’ll get to shortly, this nightmare is going to drag on for several days (if not weeks) to come.
The product — called Crowdstrike Falcon Sensor — is an EDR system (which stands for Endpoint Detection and Response). If you aren’t a security professional and your eyes have glazed over, I’ll keep this brief. An EDR system is designed to identify hacking attempts, remediate them, and prevent them. They’re big, sophisticated, and complicated products, and they do a lot of things that’s hard to build with the standard tools available to Windows developers.
And so, to make Falcon Sensor work, Crowdstrike had to build its own kernel driver. Now, kernel drivers operate at the lowest level of the computer. They have the highest possible permissions, but they operate with the fewest amount of guardrails. If you’ve ever built your own computer — or you remember what computers were like in the dark days of Windows 98 — you know that a single faulty kernel driver can wreak havoc on the stability of your system.
The problem here is that Crowdstrike pushed out an evidently broken kernel driver that locked whatever system that installed it in a permanent boot loop. The system would start loading Windows, encounter a fatal error, and reboot. And reboot. Again and again. It, in essence, rendered those machines useless.
It's convenient to blame Crowdstrike here, and perhaps that's fair. This should not have happened. On a basic level, whenever you write (or update) a kernel driver, you need to know it’s actually robust and won’t shit the bed immediately. Regrettably, Crowdstrike seemingly borrowed Boeing’s approach to quality control, except instead of building planes where the doors fly off at the most inopportune times (specifically, when you’re cruising at 35,000ft), it released a piece of software that blew up the transportation and banking sectors, to name just a few.
It created a global IT outage that has grounded flights and broken banking services. It took down the BBC’s flagship kids TV channel, infuriating parents across the British Isles, as well as Sky News, which, when it was able to resume live broadcasts, was forced to do so without graphics. In essence, it was forced back to the 1950s — giving it an aesthetic that matches the politics of its owner, Rupert Murdoch. By no means is this an exhaustive list of those affected, either.
The scale and disruption caused by this incident is unlike anything we’ve ever seen before. Previous incidents — particularly rival ransomware outbreaks, like Wannacry — simply can’t compare to this, especially when we’re looking at the disruption and the sheer scale of the problem.
Still, if your day was ruined by this outage, at least spare a thought for those who’ll have to actually fix it. Because those machines affected are now locked in a perpetual boot loop, it’s not like Crowdstrike can release a software patch and call it a day. Undoing this update requires some users to have to individually go to each computer, loading up safe mode (a limited version of Windows with most non-essential software and drivers disabled), and manually removing the faulty code. And if you’ve encrypted your computer, that process gets a lot harder. Servers running on cloud services like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure — you know, the way most of the internet's infrastructure works — require an entirely separate series of actions.
If you’re on a small IT team and you’re supporting hundreds of workstations across several far-flung locations — which isn’t unusual, especially in sectors like retail and social care — you’re especially fucked. Say goodbye to your weekend. Your evenings. Say goodbye to your spouse and kids. You won’t be seeing them for a while. Your life will be driving from site to site, applying the fix and moving on. Forget about sleeping in your own bed, or eating a meal that wasn’t bought from a fast food restaurant. Good luck, godspeed, and God bless. I do not envy you.
The significance of this failure — which isn't a breach, by the way, and in many respects is far worse, at least in the disruption caused — is not in its damage to individual users, but to the amount of technical infrastructure that runs on Windows, and that so much of our global infrastructure relies on automated enterprise software that, when it goes wrong, breaks everything.
It isn't about the number of computers, but the amount of them that underpin things like the security checkpoints or systems that run airlines, or at banks, or hospitals, all running as much automated software as possible so that costs can be kept down.
The problem here is systemic — that there is a company that the majority of people affected by this outage had no idea existed until today that Microsoft trusted to the extent that they were able to push an update that broke the back of a huge chunk of the world's digital infrastructure.
Microsoft, as a company, instead of building the kind of rigorous security protocols that would, say, rigorously test something that connects to what seems to be a huge proportion of Windows computers. Microsoft, in particular, really screwed up here. As pointed out by Wired, the company vets and cryptographically signs all kernel drivers — which is sensible and good, because kernel drivers have an incredible amount of access, and thus can be used to inflict serious harm — with this testing process usually taking several weeks.
How then did this slip through its fingers? For this to have happened, two companies needed to screw up epically. And boy, they did.
What we're seeing today isn't just a major fuckup, but the first of what will be many systematic failures — some small, some potentially larger — that are the natural byproduct of the growth-at-all-costs ecosystem where any attempt to save money by outsourcing major systems is one that simply must be taken to please the shareholder.
The problem with the digitization of society — or, more specifically, the automation of once-manual tasks — is that it introduces a single point of failure. Or, rather, multiple single points of failure. Our world, our lifestyle and our economy, is dependent on automation and computerization, with these systems, in turn, dependent on other systems to work. And if one of those systems breaks, the effects ricochet outwards, like ripples when you cast a rock into a lake.
Today’s Crowdstrike cock-up is just the latest example of this, but it isn’t the only one. Remember the SolarWinds hack in 2020, when Russian state-linked hackers gained access to an estimated 18,000 companies and public sector organizations — including NATO, the European Parliament, the US Treasury Department, and the UK’s National Health Service — by compromising just one service — SolarWinds Orion?
Remember when Okta — a company that makes software that handles authentication for a bunch of websites, governments, and businesses — got hacked in 2023, and then lied about the scale of the breach? And then do you remember how those hackers leapfrogged from Okta to a bunch of other companies, most notably Cloudflare, which provides CDN and DDOS protection services for pretty much the entire internet?
That whole John Donne quote — “No man is an island” — is especially true when we’re talking about tech, because when you scratch beneath the surface, every system that looks like it’s independent is actually heavily, heavily dependent on services and software provided by a very small number of companies, many of whom are not particularly good.
This is as much a cultural failing as it is a technological one, the result of management geared toward value extraction — building systems that build monopolies by attaching themselves to other monopolies. Crowdstrike went public in 2019, and immediately popped on its first day of trading thanks to Wall Street's appreciation of Crowdstrike moving away from a focused approach to serving large enterprise clients, building products for small and medium-sized businesses by selling through channel partners — in effect outsourcing both product sales and the relationship with a client that would tailor a business' solution to a particular need.
Crowdstrike's culture also appears to fucking suck. A recent Glassdoor entry referred to Crowdstrike as "great tech [with] terrible culture" with no work life balance, with "leadership that does not care about employee well being." Another from June claimed that Crowdstrike was "changing culture for the street,” with KPIs (as in metrics related to your “success” at the company) “driving behavior more than building relationships” with a serious lack of experience in the public sector in senior management. Others complain of micromanagement, with one claiming that “management is the biggest issue,” with managers “ask[ing] way too much of you…and it doesn’t matter if you do what they ask since they’re not even around to check on you,” and another saying that “management are arrogant” and need to “stop lying to the market on product capability.”
While I can’t say for sure, I’d imagine an organization with such powerful signs of growth-at-all-costs thinking — a place where you “have to get used to the pressure” that’s a “clique that you’re not in” — likely isn’t giving its quality assurance teams the time and space to make sure that there aren’t any Kaiju-level security threats baked into an update. And that assumes it actually has a significant QA team in-house, and hasn’t just (as with many companies) outsourced the work to a “bodyshop” like Wipro or Infosys or Tata.
And don’t think I’m letting Microsoft off the hook, either. Assuming the kernel driver testing roles are still being done in-house, do you think that these testers — who have likely seen their friends laid off at a time when the company was highly profitable, and denied raises when their well-fed CEO took home hundreds of millions of dollars for doing a job he’s eminenly bad at — are motivated to do their best work?
And this is the culture that’s poisoned almost the entirety of Silicon Valley. What we’re seeing is the societal cost of moving fast and breaking things, of Marc Andreessen considering “risk management the enemy,” of hiring and firing tens of thousands of people to please Wall Street, of seeking as many possible ways to make as much money as possible to show shareholders that you’ll grow, even if doing so means growing at a pace that makes it impossible to sustain organizational and cultural stability. When you aren’t intentional in the people you hire, the people you fire, the things you build and the way that they’re deployed, you’re going to lose the people that understand the problems they’re solving, and thus lack the organizational ability to understand the ways that they might be solved in the future.
This is dangerous, and also a dark warning for the future. Do you think that Facebook, or Microsoft, or Google — all of whom have laid off over 10,000 people in the last year — have done so in a conscientious way that means that the people left understand how their systems run and their inherent issues? Do you think that the management-types obsessed with the unsustainable AI boom are investing heavily in making sure their organizations are rigorously protected against, say, one bad line of code? Do they even know who wrote the code of their current systems? Is that person still there? If not, is that person at least contracted to make sure that something nuanced about the system in question isn’t mistakenly removed?
They’re not. They’re not there anymore. Only a few months ago Google laid off 200 employees from the core of its organization, outsourcing their roles to Mexico and India in a cost-cutting measure the quarter after the company made over $23 billion in profit. Silicon Valley — and big tech writ large — is not built to protect against situations like the one we’re seeing today,because their culture is cancerous. It valuesrowth at all costs, with no respect for the human capital that empowers organizations or the value of building rigorous, quality-focused products.
This is just the beginning. Big tech is in the throes of perdition, teetering over the edge of the abyss, finally paying the harsh cost of building systems as fast as possible. This isn’t simply moving fast or breaking things, but doing so without any regard for the speed at which you’re doing so and firing the people that broke them, the people who know what’s broken, and possibly the people that know how to fix them.
And it’s not just tech! Boeing — a company I’ve already shat on in this post, and one I’ll likely return to in future newsletters, largely because it exemplifies the short-sightedness of today’s managerial class — has, over the past 20 years or so, span off huge parts of the company (parts that, at one point, were vitally important) into separate companies, laid off thousands of employees at a time, and outsourced software dev work to $9-an-hour bodyshop engineers. It hollowed itself out until there was nothing left.
And tell me, knowing what you know about Boeing today, would you rather get into a 737 Max or an Airbus A320neo? Enough said.
As these organizations push their engineers harder, said engineers will turn to AI-generated code, poisoning codebases with insecure and buggy code as companies shed staff to keep up with Wall Street’s demands in ways that I’m not sure people are capable of understanding. The companies that run the critical parts of our digital lives do not invest in maintenance or infrastructure with the intentionality that’s required to prevent the kinds of massive systemic failures you see today, and I need you all to be ready for this to happen again.
This is the cost of the Rot Economy — systems used by billions of people held up by flimsy cultures and brittle infrastructure maintained with the diligence of an absentee parent. This is the cost of arrogance, of rewarding managerial malpractice, of promoting speed over safety and profit over people.
Every single major tech organization should see today as a wakeup call — a time to reevaluate the fundamental infrastructure behind every single tech stack.
What I fear is that they’ll simply see it as someone else’s problem - which is exactly how we got here in the first place.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
**Outsourcing vs. In-House IT: Finding the Right Balance for SMBs in New York’s Competitive Market**
Introduction
In this day’s all of a sudden evolving technological landscape, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in New York face a imperative resolution: should still they outsource their IT necessities or build an in-dwelling team? This query is awfully urgent in a competitive marketplace where effectivity, defense, and suppleness are non-negotiable. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft have set top ideas for IT functions, and SMBs ought to determine how you can preserve tempo.
" style="max-width:500px;height:auto;">
youtube
This article dives deep into the nuances of outsourcing vs. in-house IT that can assist you discover the top balance on your enterprise. We'll explore all the things from rate implications and useful resource management to cybersecurity measures and compliance with specifications like NIST, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Outsourcing vs. In-House IT: Finding the Right Balance for SMBs in New York’s Competitive Market Understanding IT Needs Assessing Your Business Requirements
Before diving into outsourcing versus building an in-house team, it’s fundamental to assess your one of a kind IT requirements. Are you broadly speaking centred on guaranteeing sturdy network infrastructure? Or do you desire specialized talent like cybersecurity or cloud expertise?
Identify Core Competencies: What features of IT are major in your operations? Evaluate Current Capabilities: Do you might have existing team whose abilities may well be leveraged? Determine Future Needs: As your industry grows, what further features may you require? Common IT Challenges Faced with the aid of SMBs
Many SMBs stumble upon identical demanding situations whilst coping with their understanding science:
Limited budgets prohibit hiring gifted specialists. The want for really expert expertise routinely results in hiring difficulties. Cybersecurity threats have become increasingly more advanced.
Understanding these challenges is step one closer to making an instructed https://ameblo.jp/remingtonzqpr790/entry-12897681595.html determination approximately regardless of whether to outsource or take care of an in-area crew.
The Pros and Cons of Outsourcing Benefits of Outsourcing IT Services
Outsourcing has emerged as a doable alternative for lots SMBs trying to handle bills even as preserving top of the range provider. Here are a few compelling advantages:
Cost Efficiency: By outsourcing, establishments can store cost on salaries, merits, and overhead quotes linked to asserting an in-space group. Access to Expertise: Many outsourced vendors concentrate on a number fields inclusive of controlled detection and reaction or endpoint detection and response. Scalability: Outsourced ideas enable establishments to swiftly scale their IT competencies up or down centered on demand. Potential Drawbacks of Outsourcing
However, outsourcing isn't very without its challenges:
Loss of Control: Handing over duties way much less direct manage over methods. Communication Barriers: Working with assorted time zones or cultures can result in misunderstandings.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Complete Cybersecurity & Data Protection Services
Act now with expert cybersecurity management and 24/7 monitoring. Let us shield your business with next-gen data security solutions.
Protect your data and defend against threats with expert cybersecurity solutions. From risk assessments to endpoint protection, we help businesses stay secure, compliant, and operational. Prevent costly breaches before they happen. Contact us now for a free consultation and secure your digital future with trusted cybersecurity professionals.
#Cyber Security Services Company | Data Security Solutions#Cybersecurity Management Company#Managed Cyber Security Services#Cyber Security Company#Cyber Security Services#Endpoint Security Services#Cybersecurity Solutions Provider#Cyber Security Consulting Firm#Network Security Services#Cybersecurity Audit Services#IT Security Services Company#Cloud Security Company#Data Protection Services#Cybersecurity Compliance Services#Security Operations Center Services#Threat Detection Services#Penetration Testing Company#Incident Response Services#Vulnerability Assessment Company#Cyber Risk Management Company#Information Security Services
0 notes
Text
Protect Your Laravel APIs: Common Vulnerabilities and Fixes
API Vulnerabilities in Laravel: What You Need to Know
As web applications evolve, securing APIs becomes a critical aspect of overall cybersecurity. Laravel, being one of the most popular PHP frameworks, provides many features to help developers create robust APIs. However, like any software, APIs in Laravel are susceptible to certain vulnerabilities that can leave your system open to attack.

In this blog post, we’ll explore common API vulnerabilities in Laravel and how you can address them, using practical coding examples. Additionally, we’ll introduce our free Website Security Scanner tool, which can help you assess and protect your web applications.
Common API Vulnerabilities in Laravel
Laravel APIs, like any other API, can suffer from common security vulnerabilities if not properly secured. Some of these vulnerabilities include:
>> SQL Injection SQL injection attacks occur when an attacker is able to manipulate an SQL query to execute arbitrary code. If a Laravel API fails to properly sanitize user inputs, this type of vulnerability can be exploited.
Example Vulnerability:
$user = DB::select("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" . $request->input('username') . "'");
Solution: Laravel’s query builder automatically escapes parameters, preventing SQL injection. Use the query builder or Eloquent ORM like this:
$user = DB::table('users')->where('username', $request->input('username'))->first();
>> Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) XSS attacks happen when an attacker injects malicious scripts into web pages, which can then be executed in the browser of a user who views the page.
Example Vulnerability:
return response()->json(['message' => $request->input('message')]);
Solution: Always sanitize user input and escape any dynamic content. Laravel provides built-in XSS protection by escaping data before rendering it in views:
return response()->json(['message' => e($request->input('message'))]);
>> Improper Authentication and Authorization Without proper authentication, unauthorized users may gain access to sensitive data. Similarly, improper authorization can allow unauthorized users to perform actions they shouldn't be able to.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
Solution: Always use Laravel’s built-in authentication middleware to protect sensitive routes:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->post('update-profile', 'UserController@updateProfile');
>> Insecure API Endpoints Exposing too many endpoints or sensitive data can create a security risk. It’s important to limit access to API routes and use proper HTTP methods for each action.
Example Vulnerability:
Route::get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
Solution: Restrict sensitive routes to authenticated users and use proper HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE:
Route::middleware('auth:api')->get('user-details', 'UserController@getUserDetails');
How to Use Our Free Website Security Checker Tool
If you're unsure about the security posture of your Laravel API or any other web application, we offer a free Website Security Checker tool. This tool allows you to perform an automatic security scan on your website to detect vulnerabilities, including API security flaws.
Step 1: Visit our free Website Security Checker at https://free.pentesttesting.com. Step 2: Enter your website URL and click "Start Test". Step 3: Review the comprehensive vulnerability assessment report to identify areas that need attention.
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools.
Example Report: Vulnerability Assessment
Once the scan is completed, you'll receive a detailed report that highlights any vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection risks, XSS vulnerabilities, and issues with authentication. This will help you take immediate action to secure your API endpoints.
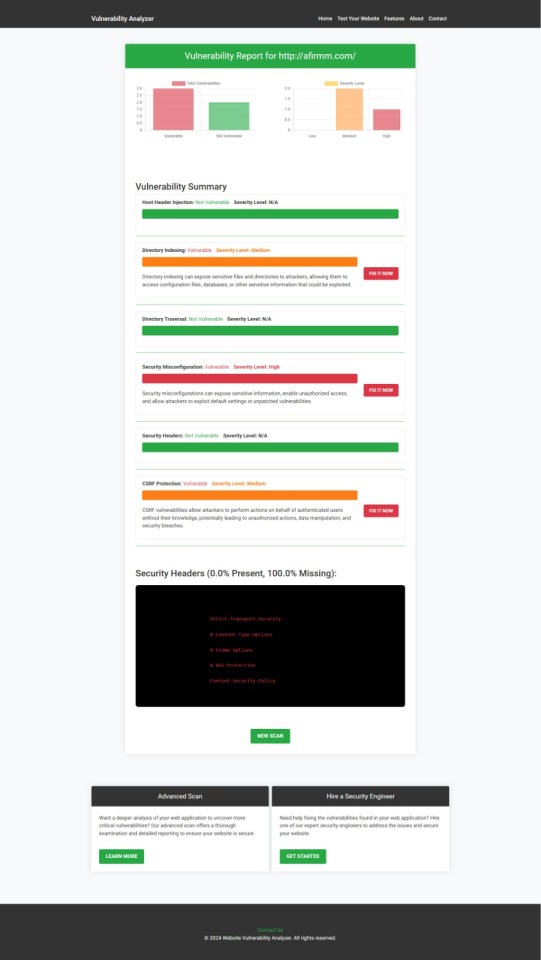
An example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool provides insights into possible vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Strengthen Your API Security Today
API vulnerabilities in Laravel are common, but with the right precautions and coding practices, you can protect your web application. Make sure to always sanitize user input, implement strong authentication mechanisms, and use proper route protection. Additionally, take advantage of our tool to check Website vulnerability to ensure your Laravel APIs remain secure.
For more information on securing your Laravel applications try our Website Security Checker.
#cyber security#cybersecurity#data security#pentesting#security#the security breach show#laravel#php#api
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cynthia Kayle Shares Key Strategies for Effective Threat Mitigation

Introduction
Threat mitigation is an essential aspect of any organization’s security strategy. While the identification of emerging threats is crucial, organizations must also develop robust mitigation strategies to prevent potential risks from escalating into major incidents. Effective threat mitigation requires a comprehensive approach, blending proactive measures, real-time response, and long-term security strategies to reduce vulnerabilities across all operational areas.
This article explores key strategies for effective threat mitigation, offering actionable steps for organizations to safeguard their operations, personnel, and reputation from potential harm.
1. Establish a Risk Management Framework
A strong risk management framework serves as the foundation for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks in an organized and structured manner. This framework should integrate security, compliance, and operational requirements, ensuring that all potential threats are addressed at the organizational level.
Actionable Steps:
Create a Risk Management Team: Assemble a dedicated team to assess, identify, and respond to risks across the organization. This team should include experts from security, IT, legal, and compliance.
Develop a Risk Register: Maintain a comprehensive risk register that tracks all identified threats, their potential impact, likelihood, and mitigation strategies. This register should be continuously updated as new risks emerge.
Prioritize Risks Based on Impact: Use risk assessment tools to evaluate the severity of each risk and prioritize mitigation efforts accordingly. Focus on threats with the highest potential impact on business continuity.
Reference:
Full URL: https://www.iso.org/iso-31000-risk-management.html
2. Implement Security Best Practices and Policies
Establishing security policies and best practices helps to create a standardized approach to threat mitigation. These policies should cover everything from data protection to physical security, and should be enforced across the organization to ensure consistency.
Actionable Steps:
Develop Comprehensive Security Policies: Draft detailed security policies covering access controls, incident response, cybersecurity, and physical security. Ensure these policies are aligned with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Enforce Compliance: Regularly conduct audits to ensure that policies are being followed. Implement training programs for employees to keep them informed about security policies and their role in risk mitigation.
Review and Update Policies: Conduct regular reviews of security policies to account for new threats, emerging technologies, and regulatory changes. Update policies as necessary to stay ahead of evolving risks.
Reference:
Full URL: https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
3. Leverage Technology for Threat Detection and Response
Technology plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating threats quickly and efficiently. From advanced monitoring systems to AI-driven analytics, technology can significantly improve the effectiveness of your threat mitigation strategies.
Actionable Steps:
Invest in Threat Detection Tools: Use advanced tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and firewalls to monitor your network in real-time and detect potential threats as they arise.
Leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI): Implement AI-powered tools such as Darktrace or Vectra AI that can automatically detect anomalous behavior and mitigate threats before they escalate.
Deploy Automated Response Systems: Set up automated incident response systems that can take immediate action when a threat is detected, such as isolating infected systems, blocking suspicious IP addresses, or initiating alerts.
Reference:
Full URL: https://www.darktrace.com
Full URL: https://www.vectra.ai
4. Foster a Culture of Security Awareness
Emerging threats often stem from human error or lack of awareness within the organization. To mitigate this, building a security-aware culture is crucial. Employees must be educated on recognizing suspicious activity and adhering to security protocols.
Actionable Steps:
Conduct Regular Security Training: Provide ongoing training sessions for employees, covering topics such as phishing prevention, data protection, and password security.
Simulate Real-Life Scenarios: Run security awareness drills to simulate common attack scenarios like phishing emails or data breaches. This will help employees recognize and respond to threats effectively.
Encourage Reporting: Create a clear process for employees to report suspicious activity or potential security breaches. Ensure that they feel empowered to speak up without fear of repercussions.
Reference:
Full URL: https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-skills-training/
5. Establish Incident Response and Recovery Plans
A well-defined incident response plan (IRP) is crucial for quickly addressing and mitigating the impact of a security breach or attack. Equally important is having a recovery plan to restore operations and minimize downtime.
Actionable Steps:
Develop an Incident Response Plan (IRP): Outline clear steps for responding to various types of security incidents, including data breaches, malware infections, and physical security threats. Include protocols for containment, investigation, and recovery.
Test and Update the IRP Regularly: Conduct regular simulations and tabletop exercises to test the effectiveness of the IRP. Update the plan as necessary to account for new threats and organizational changes.
Create a Business Continuity Plan (BCP): Develop a business continuity plan that includes disaster recovery procedures and ensures the organization can continue operating in the event of a major security incident.
Reference:
Full URL: https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-61/rev-2/final
Conclusion
Effective threat mitigation requires a holistic approach that integrates risk management, advanced technology, employee awareness, and well-defined response plans. By employing these strategies, organizations can proactively address threats, reducing the potential for damage and ensuring business continuity in the face of security challenges.
Adopting these measures will enhance your organization's ability to not only identify emerging threats but also effectively mitigate them before they escalate into larger problems.
References:
Full URL: https://www.iso.org/iso-31000-risk-management.html
Full URL: https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
Full URL: https://www.darktrace.com
Full URL: https://www.vectra.ai
Full URL: https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-skills-training/
Full URL: https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-61/rev-2/final
#cynthia kayle#RiskMitigation#SecurityExpert#ThreatManagement#CommunityProtection#CrisisManagement#StrategicSecurity#SafetyPrograms#IntelligenceDriven#SecurityConsulting
1 note
·
View note