#Financial Management Assignment Help
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
All Assignment Help is a comprehensive online platform provided by myassignmentspro.com. With All Assignment Help, students and professionals alike can access expert assistance and guidance for all their academic and professional needs. From essays to research papers to business reports, our team of experienced writers is here to help you succeed in your assignments. We understand the pressures of academia and are dedicated to providing top-notch quality work within tight deadlines. With All Assignment Help, you can trust that your assignments are in good hands and focus on other important aspects of your education or career.
#financial management assignment help#Architecture assignment help#mechanical engineering assignment help#All Assignment Help#history assignment help#macroeconomics assignment help#cipd assignment help#do my assignment#Help with my assignment#My assignment helper#mba financial management assignment help#online architecture assignment help#online mechanical engineering assignment help#all assignment help australia#online history assignment help#history assignment help online#best macroeconomics assignment help
0 notes
Text
Financial Management Assignment Help

Financial management is most likely the most important subject business, commerce, or finance students need to learn. It entails planning, organization, and control within the company. Financial management assignments can prove difficult as the student will be required to break down budgets, research investment opportunities, and interpret complex financial reports. Do not fret if you are having trouble with your assignment. The Tutors Help is available to provide top-notch financial management assignment help.
What Is Financial Management?
Financial management is all concerning careful and effective handling of money. It consists of making financial, budgeting, saving, expenditure, and investment decisions and assessing financial risk. Effective financial management is essential by every firm for growth and flourishing. Students understand how to create company finances, present financial statements, and analyze financial ratios.
But finance is not necessarily easy to understand, especially when tasks relate to numbers, calculations, and real-life situations of money. Therefore, most students require help to complete their assignments correctly and on time.
Issues Students Normally Face
Complex Formulae and Calculations: Finance assignments normally entail complex formulae like Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and cost of capital, which are not easy to grasp.
Shortcomings in Concept Clarity: Students will not be able to understand concepts such as capital budgeting, working capital, or financial statement analysis.
Constricted Timetables: Students are most likely given a number of assignments to submit at short time intervals, with no sufficient time for careful work.
Format and Referencing Complications: Financial tasks have strict format and referencing guidelines, unknown to the students.
How The Tutors Help Can Assist You
Here at The Tutors Help, we deliver quality financial management assignment help to simplify your student life. Our finance experts are thoroughly familiar with the subject and can help you achieve higher grades in your course work.
Why Choose Us?
Experts Qualified: Our teachers have good academic qualifications and real-time experience in finance.
Personalized Solutions: We have personalized and customized solutions as per your assignment requirements.
Original Plagiarism-Free Work: We offer original and research-based work so that you can obtain good grades.
Guaranteed Delivery: We respect your time and submit the work on or before the deadline given.
Student-Friendly Prices: Our services are affordable.
Easy Steps to Ask for Help
Send Us Your Assignment: Give us your topic, instructions, and deadline.
Quote Your Assignment: We will give you a reasonable quote for the assignment.
Get Professional Help: Our finance expert will complete your work and submit it perfectly.
Download and Authenticate: We will provide your completed assignment on time.
Conclusion
Financial management is a useful subject that educates you about money in business. But the assignments are difficult. If you are having trouble with your financial management assignment, The Tutors Help can help you.
With the assistance of ours, you are able to study effectively, complete assignments without any hassle, and achieve good marks. You don't need to worry anymore. Chat with The Tutors Help today and get the best assignment help in financial management at your doorstep!
thetutorshelp.com/financial-management-assignment-help.php
0 notes
Text

Save the key concepts, topics and shortcuts you must know in financial management. Get expert financial management assignment help to solve trickiest problems.
0 notes
Text
10 Helpful Examples of Cost-Benefit Analysis to Use in Financial Management Assignments
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is essential in financial management for evaluating the economic viability of projects and investments. For MBA students in financial management, understanding CBA is crucial as it helps in assessing both potential returns and associated costs, ensuring optimal resource allocation. CBA is a key method for determining the value of investments by comparing costs and benefits, aiding managers in deciding if a project is worthwhile. It provides a structured approach to evaluate economic, social, and environmental impacts, crucial in a competitive global economy.
However, students often find CBA challenging due to difficulties in quantifying intangible benefits and costs, the need for accurate data, and forecasting future cash flows. To overcome these challenges, many students seek help from financial management homework help, which offers expert guidance on CBA techniques, enhancing their ability to apply these concepts in real-world scenarios and preparing them for successful careers in financial management.
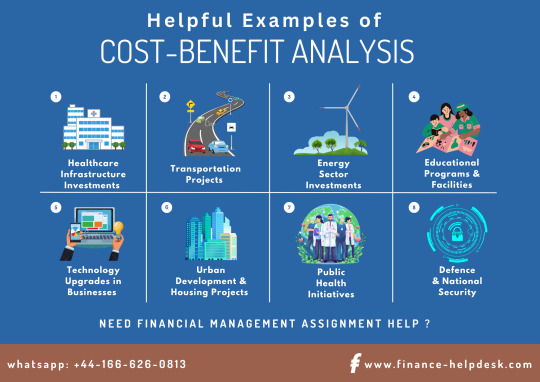
10 Real-World Examples of Cost-Benefit Analysis in Financial Management
Healthcare Infrastructure Investments
CBA has a significant importance in financial management of a country especially when used in investments in health infrastructure. For example, the establishment of a new hospital requires capital outlay such as land costs, construction and acquisition of equipment. However, the positive impacts include; increased accessibility to health services, increased employment, and overall improvement of welfare among the inhabitants.
One can cite example such as construction of the University Medical Center in New Orleans USA. The project, which cost approximately $1.2 billion, underwent a thorough CBA to justify its feasibility. The assessment included not only the direct costs and advantages but also the potential economic repercussions for the community. It further stated that the hospital would contribute more than $6 billion within a decade in terms of economic contribution and value.
Transportation Projects
CBA is also useful in transportation projects where organizations seek to know if constructing new highways or improving public transport is feasible. A recent example is High-Speed 2 (HS2) railway project in the UK that has faced numerous criticism due to its expenditures. The plan to build a network of linking the British capital to other key cities and towns in in the north has been subjected to extensive CBA.
The expenditure that is to be incurred for the completion of the HS2 project is almost £106 billion. Substantial benefits such as shorter travelling time, increased economic returns and reduction of congestion on the roads were presented in minutest detail. It is important to note that according to the CBA the investment would yield a return of approximately £2.30 for every £1 spent.
Energy Sector Investments
In the energy sector for instance, CBA is very essential for assessing prospective investments in projects in renewable power. For instance, the investment made with the intention of developing offshore wind farms in the UK entails enormous initial expenditures such as those that are incurred on turbines and connection to the grid. This resulted in some advantages such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy security, and long-term cost savings.
Hornsea One offshore wind farm which is one of the largest in the world, went through a rigorous CBA before its construction. The project which cost about £4.2 billion, proposed to yield numerous advantages, including available electricity to more than one million home and playing remarkable role in fulfilling the government renewable energy aspiration of the UK. The positive CBA results ensured that there was no cash crunch to fund the project and adequate political support.
Educational Programs and Facilities
CBA is used in education systems to determine the addition of more facilities or offering new programmes. An example is the spending on online learning solutions by universities across the USA and the UK in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic.
For instance, the University of California made certain improvements in the online education infrastructure. Investments were made towards software development, licensing, training of teachers. The advantages included the continuation of extending educational services during lock down and enhanced enrolment from remote student. The analysis of the case showed that the CBA provided a long-term advantage outweighing short-term expense.
Environmental Conservation Projects
CBA is also commonly used by the governments and NGOs to justify the funding for projects related to environment conservation. For instance, the attempt of restoring the Everglades in Florida, USA, required a huge capital of approximately $8 billion. A number of benefits were observed such as an increase in biological diversity, an increase in the quality of water and an increase in tourism.
The study established that the project would create benefits equivalent to $46 billion in fifty-year time frame, in relation to environment conservation. Such CBAs facilitates acquiring public and private funding in support of environmental projects.
Technology Upgrades in Businesses
Businesses often applies CBA when evaluating the financial feasibility of new technologies. The perfect example of this is the adoption of blockchain technology by numerous banks of UK to streamline their operations and minimize fraud.
The investment made in the technology of blockchain was made to covered the cost of development of the software, the cost of integration of the block chain software to the existing systems, and the cost of staff training. This resulted into decrease of transaction costs, increased security, and enhanced customer trust. The use of CBA indicated the technology would yield more than £1 billion within five years which garnered support to implement.
Urban Development and Housing Projects
Urban development projects, such as the construction of affordable housing, often require a thorough CBA to justify their economic and social benefits. The Crossrail project in London, UK, serves as an excellent example.
The improvement of transportation network within the city required about £18 billion throughout the course of the project. The benefits such as reduction of the time taken in traveling, increase in property value and employment opportunities were discussed. The CBA showed that the project would generate more than £42 billion in economic benefits, making such investment worthy and beneficial.
Public Health Initiatives
CBA is also widely used in public health interventions such as vaccination. For instance, the programme for mass vaccination against Covid-19 in the UK had to go through a stringent CBA evaluation.
This program, which cost billions of pounds, was aimed at vaccinating the entire population of adults. The advantages include decrease in healthcare cost, low mortality and the Economy revival. Using CBA, it was pointed out that the program would generate more than £100 billion in economic benefits by averting sickness and allowing for a faster return to pre-epidemic states.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Programs
CBA is used commonly by the companies to measure the efficiency of their CSR initiatives. For instance, the Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan, which looks at its strategies to lessen its negative impact on the environment and to create a positive social impact were done through CBA.
The advantages which included increased customer loyalty, reduction in operational expenses, and adherence to the laid down regulations were weighed against the expenses of practices like the conservation of water and sourcing sustainably. The CBA revealed that the program would generate a profit of more than €12 billion in ten years, helping Unilever to fulfill its sustainability mission.
Defence and National Security Projects
Proposed defense projects, for instance, the development of a new weapon also go through extensive CBA to meet the costs. One recent example is Britain’s investment in F-35 fighter jet.
The program which costs over £9 billion carries benefits such as improved national security, employment and technological development. Further, a CBA showed that the strategic and economic gains accruing from the program outweigh the costs of the investment decisively.
Common Challenges in Understanding Cost-Benefit Analysis
It should be noted that even though CBA is one of the foundational tools in financial management, MBA students can encounter issues with ideas herein. Some of the common issues include:
Quantifying Intangible Costs and Benefits: Valuing qualitative benefits like such as improved employee morale or environmental sustainability, can be difficult.
Data Collection and Accuracy: It is often difficult to acquire authentic data to present an accurate CBA.
Complex Calculations: The mathematical complexity of calculating net present values, internal rates of return, and conducting sensitivity analyses can be difficult for many students.
To overcome these challenges, engaging with our financial management assignment help service can be immensely beneficial.
Improve grades with Our Financial Management Assignment Help!
Stuck with difficult finance coursework or financial management assignments? We offer Financial Management Assignment Help service to make you excel in your academic performance and teaching. Specializing in Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA), we assist students in manageable financial decision in a simple manner.
Our USP
Our competitive advantage is offering easy to understand material that breaks down complex information into small digestible portions so that students grasp the important concepts related to CBA and other financial management concepts. We have a highly qualified team of individuals who have promising academic credentials and professional experience extending support to all students with their individual needs.
Beyond Cost-Benefit Analysis
Apart from CBA, we offer help in a wide range of financial management topics, including:
Capital Budgeting: Learn how to evaluate potential investments and projects to maximize returns.
Financial Statement Analysis: Understand how to interpret financial statements to assess a company’s performance.
Risk Management: Gain insights into identifying, analyzing, and mitigating financial risks.
Corporate Finance: Master the principles of managing a company’s financial activities.
What You Can Expect in Our Solutions
Every solution we provide is detailed and drafted with the finest detail in order to meet the specifications of your assignment. We provide the soft copies of the reference papers used along with excel files containing the computations. We ensure that only authentic data and figures are used to support the arguments in the solution. Our step-by-step approach not only helps in having a better understanding of the solution but help to secure decent grades.
Take the Leap Towards Excellence. Opt for our financial management assignment help and experience the improvement in your knowledge and overall performance in your course.
Also Read: How a Company Resolved an NPV vs IRR Conflict: A Financial Management Assignment Case Study
Helpful Resources and Textbooks
To further assist students in mastering CBA, here are some recommended textbooks and resources:
"Financial Management: Theory & Practice" by Eugene F. Brigham and Michael C. Ehrhardt
2. "Cost-Benefit Analysis: Concepts and Practice" by Anthony E. Boardman, David H. Greenberg, Aidan R. Vining, and David L. Weimer
0 notes
Text
Financial Management Assignment Help: Achieve Excellence in Finance Studies
Our financial management assignment help service provides expert guidance tailored to students navigating the complexities of finance. From budgeting and financial analysis to risk management and investment strategies, our seasoned professionals offer comprehensive support.
0 notes
Text
Financial Management Assignment Help - Expert Guidance & Assistance
Struggling with your financial management assignments? Get expert guidance and top-notch assistance with our professional financial management assignment help service. Boost your grades today!

0 notes
Text
https://www.articlewood.com/assignment-help-uae-best-writing-service-providers/
#business management assignment help#financial management assignment help#financial management assignment#project management assignment help
0 notes
Text
Financial Management Assignment Help
Financial Management Assignment Help is a valuable resource for students studying finance-related subjects. The complexities of financial management require a deep understanding of concepts like budgeting, investment analysis, risk assessment, and capital structure. This assistance provides students with expert guidance and support to tackle challenging assignments.

0 notes
Text
Kviku a non-banking credit organization that offers online loans in spain. 🇪🇸
providing hassle-free online loans to meet your urgent financial needs.
Instant approved : Finance Apply now
Read more..

#financial#financial planning#finance management#business#credit score#financial freedom#personal loans#credit cards#finance assignment help#moto: spain 2024#madrid spain#philip ii of spain#spa in ajman#hws spain#spa in chennai#spain eurovision#spain football#spain hetalia#spain news#spain hws#spain art#spain 2023#spain#spain travel#spain visa#spain nt#spain without the s#spain women's national team#spain x reader#spainese
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Working Capital Optimization: Essential Help for Finance Assignments
Introduction: What is Working Capital?
Working capital constitutes a crucial principle in the field of finance, signifying the short-term liquidity position of a firm. It is defined as the difference between an organization's current assets—encompassing cash, inventory, and accounts receivable—and its current liabilities, including accounts payable and short-term debt. In essence, it denotes the financial resources available to the company to facilitate its daily operational needs. Effective working capital management ensures that a company can meet its operational needs and financial obligations, while also channeling available resources to facilitate growth in the company.
Every student or learner involved in finance studies or assignments particularly those that relate to working capital, must understand the factors that explain the working capital. Why? Working capital belongs to the most critical indicators of financial performance since they directly reflect the financial result, availability of funds for operations, and risks involved. Effective management of work capital can enhance or develop efficiency in the business hence enhancing the performance by the firm. For students, to understand these dynamics students are usually tasked to solve various numerical questions to gain insights into the practical financial operations of businesses.
By opting for finance assignment help, students can get to know more about the perspective of working capital optimization and other advanced techniques in the field. This means that one can seek working capital study assistance from professional experts, especially in complex working capital problems as opposed to what is found in textbooks and theories. This involves an opportunity for students to gain a greater understanding of the subject, hence exposing them to applicable strategies for succeeding in their assignments.

Working Capital Optimization: Issue Diagnosis in Details
Working capital optimization can be defined as the means and methods that are used in the management of the short-term assets and liabilities of a business with the aim of ensuring the operations of the firm are done in the most efficient and profitable manner. This also means that there is a fine line to be drawn between the need for liquid assets to meet short-term obligations and bringing down capital expenses.
As regards finance students, it may appear that working capital optimization is quite simple and quite basic as a subject however in a real sense, it is quite an elaborate and complicated subject that can make or break a business. In this regard, we shall look at why working capital optimization is important, how the companies achieve these goals and real cases where companies have demonstrated a working capital optimization impact.
Why Optimize Working Capital?
It is quite evident that working capital management is of great importance for all businesses as it influences many key performance metrics:
Liquidity: Sufficient working capital ensures that the company can perform its short-term obligations in terms of paying off suppliers and employees.
Profitability: Proper working capital management will minimize the capital cost incurred, therefore increasing cash flows available for financing growth and innovation.
Operational Performance: Focused and disciplined working capital management enables businesses to operate more efficiently, decrease waste, and enhance stock control.
Risk Management: Working capital management in a business alleviates the operational risk exposure – Supply Chain risks, economic downturns, and other surprises that a business may experience.
For students, such a study helps to understand the rationale behind the varying impacts of the financial decisions made in a company on its various operations.
Ways on how Working Capital can be Improved
There are various strategies that can be recommended for companies that require improvement of the working capital. These strategies are aimed at ensuring that companies maintain adequate amounts of cash, increase cash inflows, and reduce cash outflows that are unnecessary in the first place.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is one of the key components of working capital management. A firm can enhance its liquidity profile by lowering the total stock holding of unsold products by minimizing excess stocks.
Methods such as JIT manufacturing systems, where products are sourced and produced only when needed. This approach helps companies save on stockholding expenditure and overproduction.
Example: Toyota was able to change the face of the auto industry with the implementation of the manufacturing system called Just In Time (JIT), giving the extra edge of efficiency coupled with a reduction in working capital requirements.
Accounts Receivable Management
Customers paying their bills within the set timeframe is very important. For further optimization of receivables, some credit control measures are often applied such as allowing discounts for early payments or limiting credit for customers with a history of poor payments.
Another approach known as factoring helps in supplementing working capital. This involves receivables sold to a third party thus providing cash flow in a shorter time frame.
Case Study: In its attempt to improve cash flow, General Electric in the year, 2009 commenced sales of parts of its receivables and created 2 billion in capital within a year leading the firm to focus more on growth and investment avenues.
Accounts Payable Management
The payable side is much more interesting. This is about optimizing for the longest period before making any payment ta the supplier without jeopardizing any existing credit or relationships. Cash flow may be enhanced if payment terms can be adjusted without any serious penalty for longer terms.
Purchasers may utilize the assisted financial program to make early payments to their suppliers through financial institutions, while the purchaser gets extended terms to preserve working capital.
Example: Walmart has entered into extended payment terms with its suppliers to preserve its working capital for longer terms.
Cash Management
Firms need to ensure that there is an optimal cash reserve committed to the working capital requirements and also minimize cash that is idle earning no returns.
Firms utilize sweeping mechanisms, in which the excess cash is transferred to an interest-bearing account thereby making returns out of excess cash and at the same time preserving liquidity.
Example: Microsoft is well known for its cash management practices. The world’s biggest computer software company has for many years managed to keep positive working capital instead of spending it on many things and maintains generous cash reserves for investments, buying back stock, and paying dividends.
The Role of Working Capital Management
The effect of working capital optimization is not limited to the enhancement of liquidity and cash flow alone. This is capable of reinventing the potential of a company for growth and competitiveness within the industry.
Better Financial Condition: Reduction in the amounts tied up in working capital positively impacts the company's operating cycle and the balance sheet. Improvement in some of the operational ratios such as current and quick ratios is also observed. This subsequently increases the creditworthiness and the cost of borrowing reduces.
Secure Superior Position: Efficient working capital allows organizations to respond to changes in the market more effectively. For instance, they will be able to take advantage of bulk buying discounts and invest in new opportunities more quickly than its competitors.
Recovery from Impacts: When the economy is going through difficult times, the likelihood of companies that strategically manage their working capital to manage disruptions. For instance, during the most recent period when the majority of the companies were in a cash liquidity crisis due to covid19 pandemic, companies that effectively managed cash flows survived.
Long-Term Development: Firms can free up cash from operational efficiency which then allows them to seek more growth opportunities like R&D, marketing, or expansion. Optimization of working capital, therefore, becomes the initial move towards the attainment of competitive advantage in due time.
Case Example: Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is probably the most referenced case when it comes to the optimization of working capital. This has been made possible because of the peculiarities in the businesses of Apple-it is able to maintain working capital which is negative by collecting money from customers before it pays suppliers. This offers the company a huge liquidity edge and a key reason behind its financial performance.
Due to Apple’s excellent supply chain management processes and beneficial contractual payment agreements with suppliers, the company does not require additional working capital. Such a strategy releases massive amounts of cash flow, which Apple has invested in R&D, advertising, and acquisitions. As a result, Apple has grown and become a market leader.
Expert Finance Assignment Help for MBA Students
Our finance assignment assistance service is primarily directed toward MBA students who are having a tough time comprehending and practicing difficult areas such as working capital management. We offer detailed, individualized help to students in dealing with difficult assignments, case studies, and analysis.
As for complicated financial topics including working capital optimization, our company employs seasoned financial specialists with expertise in sophisticated techniques on liquidity, cash flow, and operational efficiency management. We break down these concepts into simple steps for students to facilitate their understanding of the theory and practical aspects of the problem. Our aim is not only to assist the learners in solving practical problems but help them learn how and when to utilize these techniques when they face real financial problems.
How Our Service Makes Complex Financing Problems Simple
We use a combination of visuals, like flowcharts and financial models in order to simplify difficulties in complicated financial problems. By demonstrating the relation between the problem to its financial theory, we make sure that students never miss any important aspect of the solution. We offer tailored solutions for case studies and give in-depth information on different working capital strategies used by top companies. This helps students understand how to use these strategies in their studies.
More Sophisticated Techniques and Wider Scope
We introduce students to new and improved methods that they can adopt in solving questions that go beyond the basics of financial management. Among those advanced techniques include; modeling of dynamic working capital, cash conversion optimization, and enhancing working capital with financial technologies.
Apart from working capital optimization, we also offer finance assignment assistance in a wide range of subjects including but not limited to:
Corporate Finance
Risk Management
Investment Analysis
Financial Statement Analysis
Capital Budgeting
Mergers & Acquisitions
Benefits for MBA Students:
Many students ask the question: “Why should I choose your service?” The explanation is that they not only get custom-made solutions that enable them to complete their tasks in due time but also enhance their grasp of contemporary financial principles. Our specialists always give new ideas to the students to enable them to apply in their coursework assignments for top grades.
Conclusion:
Working capital management is an important aspect of financial management. This influences liquidity and profitability as well as risk factors. Students studying finance must learn the concepts to have a deeper understanding of the practical issues of business functioning. By opting for our service and getting help with finance assignments, students can learn from experts and understand important topics better. We provide sample problems, case studies, textbooks, and research papers to help students complete their assignments confidently and clearly.
Textbooks and References for Students
For students who want to undertake deeper studies in the area of working capital optimization, the is a selection of relevant textbooks and some research papers that lay a good base.
One such textbook is “Financial Management: Theory and Practice” by Eugene F. Brigham & Michael C. Ehrhardt.– This particular book attempts to explain the fundamentals of why decisions are made financially with reasonable chapters on working capital management.
Corporate Finance Jonathan Berk and Peter DeMarz– A commonly recommended textbook, which considers some of the working capital management aspects among other principles of financial management.
#Financial analysis homework help#Help with finance projects#Personal finance assignment assistance#Financial management homework help#Online finance tutoring services#Finance case study assistance#International finance assignment help#Accounting and finance assignment help#Financial modeling assignment support
0 notes
Text
Timely, Accurate, and Affordable History Assignment Help – Only at MyAssignmentsPro.com!
History is one of the most intriguing academic disciplines. It offers a window into the past, helping us understand the evolution of societies, cultures, economies, and governments. But as fascinating as history is, writing assignments on it can be daunting. From memorizing dates and analyzing historical contexts to constructing arguments and referencing sources correctly—history assignments demand both time and precision.
If you’re a student struggling with tight deadlines, complex topics, or the pressure to maintain high academic standards, MyAssignmentsPro.com is your reliable partner. We offer timely, accurate, and affordable online history assignment help tailored to students across all educational levels. Whether you’re tackling high school history or advanced university-level research, our expert team is here to help you succeed.
Why History Assignments Can Be Challenging
History assignments are not just about retelling events. They require a strong understanding of cause-and-effect relationships, historical debates, primary sources, and critical interpretation. Here are a few reasons students often seek help:
Complex Topics: Subjects like the French Revolution, World Wars, Cold War politics, ancient civilizations, and post-colonial history require deep knowledge and analytical skills.
Time Constraints: Balancing multiple courses, jobs, or personal responsibilities often makes it hard to meet deadlines.
Referencing Issues: History assignments often require detailed citations from primary and secondary sources using styles like Chicago, Harvard, APA, or MLA
Language Barriers: For international students, understanding historical texts and writing clear, concise arguments in English can be a struggle.
That’s where MyAssignmentsPro.com makes a difference.

What Makes MyAssignmentsPro.com the Best Choice?
At MyAssignmentsPro.com, we combine academic excellence with student-friendly services to provide unmatched support. Here’s how we help you ace your history assignments:
1. Expert History Scholars
Our team consists of professional academic writers with degrees in history, political science, and related fields. Whether you need help with ancient civilizations, European monarchies, African history, or modern political movements, we assign your work to someone who truly understands the topic and academic expectations.
2. Customized Solutions for Every Topic
We don’t believe in one-size-fits-all solutions. Every history assignment we deliver is:
Custom-written from scratch
Aligned with your syllabus and instructions
Properly structured with arguments, analysis, and evidence
Backed by credible sources and references
From essays and reports to research papers and case studies, we handle it all with care.
3. Timely Delivery – No Matter the Deadline
Missed deadlines can mean lost grades. At MyAssignmentsPro.com, we understand the urgency of academic timelines. Our experts work efficiently to ensure you get your history assignment:
Well before the due date
With time to review and request changes if needed
Without compromising on quality
Even if your submission is just a few hours away, we’ve got your back.
4. 100% Original, Plagiarism-Free Work
We take academic integrity seriously. Every history assignment we deliver is:
Written from scratch
Checked through plagiarism detection software
Accompanied by proper citations and referencing
Tailored to reflect your voice and style (if requested)
You can submit your work confidently, knowing it's completely authentic.
5. Affordable for Every Student
We know students often work within tight budgets. That’s why our pricing is:
Transparent – no hidden fees
Flexible – with discounts for bulk orders and returning clients
Affordable – so you don’t have to break the bank for quality academic help
Our goal is to make academic support accessible to everyone.
6. 24/7 Customer Support
Got a late-night question or a sudden update from your professor? No problem. Our customer service team is available 24/7 to:
Answer your queries
Provide updates on your order
Assist with revisions or urgent requests
Help you place new orders with ease
Studying history helps us understand how our present world came to be. But writing about it effectively takes skill, time, and research. If you’re overwhelmed with deadlines, confused by complex topics, or just aiming for better grades, MyAssignmentsPro.com is here to help.
With a focus on timeliness, accuracy, and affordability, we’re committed to being your most trusted academic partner. Let us take the stress out of your history assignments so you can focus on what matters most—learning and succeeding.
#financial management assignment help#Architecture assignment help#mechanical engineering assignment help#All Assignment Help#history assignment help#macroeconomics assignment help#cipd assignment help#do my assignment#Help with my assignment#My assignment helper#mba financial management assignment help#online architecture assignment help#online mechanical engineering assignment help#all assignment help australia#online history assignment help#history assignment help online#best macroeconomics assignment help
0 notes
Text

Order your financial management assignment help online in Australia. Call our expert writers by Request Call Back
0 notes
Text
GAAP vs IFRS

Decoding US Accounting Rules: GAAP vs IFRS | Expert Insights in 2024
Navigate the GAAP vs IFRS debate in US Accounting effortlessly. Gain expert insights, make sense of regulations. Your guide to financial clarity.
The evolving landscape of accounting standards unfolds a nuanced debate between the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and the International Financial Reporting Standards. These two frameworks, while sharing a common goal of transparent financial reporting, diverge in their approaches, giving rise to a multifaceted discourse with far-reaching implications for the financial world.

1. Introduction
The evolution of accounting standards has witnessed the crystallization of two dominant frameworks – General Accounting Accepted Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards. In the labyrinth of financial reporting, companies grapple with choosing between these standards, each with its unique history, principles, and global relevance. The debate surrounding GAAP vs IFRS is not a mere academic exercise but a pivotal consideration with implications for investment decisions, legal compliance, and the global financial landscape.
1.1. Evolution of Accounting Standards
The journey of accounting standards traces back to the aftermath of the 1929 stock market crash when the need for standardized, transparent financial reporting became glaringly apparent. What emerged were the General Accounting Accepted Principles, designed to restore investor confidence by providing a reliable framework for financial statements. Over time, GAAP has become deeply embedded in the U.S. financial system, shaping the way companies communicate their financial health.
On the global stage, the International Financial Reporting Standards evolved as a response to the growing interconnectedness of economies. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) took the reins in developing IFRS, aiming for a standardized global language of financial reporting. This set the stage for a two-pronged approach to financial reporting standards – General Accounting Accepted Principles dominating in the U.S. and International Financial Reporting Standards gaining traction internationally.
1.2. The Crucial Role of GAAP and IFRS
GAAP stands as the bedrock of accounting standards in the United States, overseen by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Its principles, rooted in historical cost, revenue recognition, and matching, provide stability and a familiar structure for U.S. businesses. On the other hand, IFRS, under the stewardship of the IASB, operates as a global player, emphasizing fair value, substance over form, and materiality.
The significance of General Accounting Accepted Principles lies in its historical context and its alignment with the unique needs of the U.S. business environment. Its principles have served as a guiding light for American companies, offering a consistent framework for financial reporting. International Financial Reporting Standards, with its global perspective, caters to the interconnectedness of today’s businesses, providing a common language for multinational corporations.
1.3. Navigating the GAAP vs IFRS Dilemma
The choice between General Accounting Accepted Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Companies grapple with a complex decision-making process, considering factors such as their geographical reach, industry nuances, and investor preferences. This debate is not isolated to boardrooms; it resonates in financial markets, legal proceedings, and regulatory landscapes, shaping the very fabric of financial reporting practices.
2. Understanding GAAP
2.1. The Foundation of GAAP
a. Historical Roots and Evolution
GAAP’s roots delve deep into the need for a standardized accounting framework post the 1929 stock market crash. FASB emerged as a response to the chaos that ensued, charged with the responsibility of establishing and improving financial accounting and reporting standards. The journey of GAAP has been one of continuous evolution, adapting to the changing business landscape and regulatory requirements.
b. FASB’s Ongoing Influence
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) stands as the guardian of GAAP, playing a pivotal role in setting and refining accounting standards. FASB’s mission goes beyond rule-making; it seeks to improve financial reporting, providing transparency and relevance in financial statements. The ongoing influence of FASB ensures that GAAP remains adaptive and responsive to the dynamic nature of business transactions.
2.2. Core Principles Anchoring GAAP
a. Embracing the Historical Cost Principle
One of the cornerstones of GAAP is the historical cost principle, dictating that assets should be recorded at their original cost. This principle provides stability and reliability in financial statements, allowing users to assess the financial health of a company based on the actual cost of its assets at the time of acquisition. While critics argue that this approach may not reflect current market values, proponents emphasize the prudence and consistency it offers.
b. Revenue Recognition as a Cornerstone
GAAP’s approach to revenue recognition centers on the realization and earned criteria. Revenue is recognized when it is realized or realizable and earned. This conservative approach ensures that revenue is not prematurely recognized, aligning with the matching principle. While this method may defer recognizing revenue until later stages in the sales cycle, it safeguards against potential overstatement and presents a cautious picture to investors.
c. The Significance of the Matching Principle
The matching principle is a guiding force in GAAP, emphasizing the alignment of expenses with the revenue they generate. This principle ensures that the costs associated with generating revenue are recognized in the same period as the revenue itself, presenting a more accurate portrayal of a company’s profitability. While adhering to the matching principle might result in lower reported profits during high-revenue periods, it provides a more realistic long-term view.
2.3. Scrutinizing Criticisms and Recognizing Limitations
a. Rigidity vs. Stability
One common criticism leveled against GAAP is its perceived rigidity, particularly regarding the historical cost principle. Critics argue that this approach may not capture the true economic value of assets, especially in industries with rapidly changing market conditions. However, proponents assert that this rigidity provides stability and consistency, allowing for easier comparison across periods and industries.
b. The Balancing Act of Revenue Recognition
The conservative approach to revenue recognition in GAAP has faced scrutiny for potentially understating a company’s immediate financial performance. Critics argue that this caution may not be reflective of a company’s true economic position, especially in industries where revenue realization is instantaneous. However, the balancing act lies in mitigating the risk of premature revenue recognition, ensuring financial statements maintain integrity and accuracy.
c. Challenges in Adhering to the Matching Principle
While the matching principle aligns expenses with revenue, critics contend that it introduces complexities in determining the direct association between costs and specific revenue streams. This challenge becomes more pronounced in industries with diverse revenue sources. Despite these challenges, adhering to the matching principle remains integral in presenting a holistic view of a company’s financial health, helping investors make informed decisions.
3. Embracing IFRS
3.1. IFRS: A Global Framework
a. The Rise of International Financial Reporting Standards
The emergence of IFRS marks a significant shift towards a globalized approach to financial reporting. As businesses expanded internationally, the need for a common accounting language became evident. IFRS, under the stewardship of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), rose to prominence as a framework that transcends borders, providing a standardized set of principles for companies operating on the world stage.
b. IASB’s Pivotal Role in Shaping IFRS
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) shoulders the responsibility of developing and maintaining IFRS. Unlike GAAP, IFRS operates under a principles-based approach, focusing on broad principles rather than detailed rules. This flexibility allows for easier adaptation to diverse business environments, making IFRS an attractive choice for multinational corporations seeking a harmonized approach to financial reporting.
3.2. Unpacking Core Principles of IFRS
a. Fair Value Measurement: A Paradigm Shift
One of the fundamental differences between GAAP and IFRS lies in the approach to asset valuation. While GAAP predominantly adheres to the historical cost principle, IFRS leans towards fair value measurement. Fair value reflects the current market value of assets, providing a more dynamic and responsive perspective. Critics argue that fair value introduces volatility, but proponents emphasize its relevance in capturing real-time economic conditions.
b. Substance Over Form: Emphasizing Economic Reality
In IFRS, the substance of transactions takes precedence over their legal form. This principle ensures that financial statements reflect the economic reality of transactions, promoting transparency and accuracy. While this approach aligns with the overarching goal of providing relevant information to users, it requires careful judgment and interpretation, potentially introducing subjectivity in financial reporting.
c. Materiality’s Role in Flexibility
IFRS introduces greater flexibility in materiality judgments compared to GAAP. Materiality refers to the threshold at which information becomes relevant to users. The more flexible stance in IFRS allows entities to exercise judgment in determining what information is material, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors. This flexibility, while enhancing the adaptability of IFRS, also raises concerns about potential inconsistencies in financial reporting.
3.3. Weighing Advantages and Drawbacks
a. IFRS Flexibility: A Double-Edged Sword
The flexibility embedded in IFRS is both its strength and weakness. Proponents argue that this adaptability makes IFRS suitable for diverse business environments, allowing for easier integration with various industries and legal systems. However, critics contend that this very flexibility can lead to inconsistencies and a lack of comparability, challenging the reliability of financial statements for investors and stakeholders.
b. Global Appeal vs. Application Challenges
The global nature of IFRS makes it an attractive choice for multinational companies aiming for consistency in financial reporting across borders. The common language of IFRS facilitates international transactions and fosters a seamless global financial landscape. However, the application of IFRS can pose challenges in jurisdictions with varying legal and regulatory frameworks, potentially leading to complexities in implementation and interpretation.

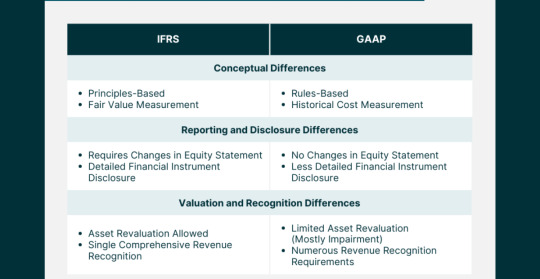
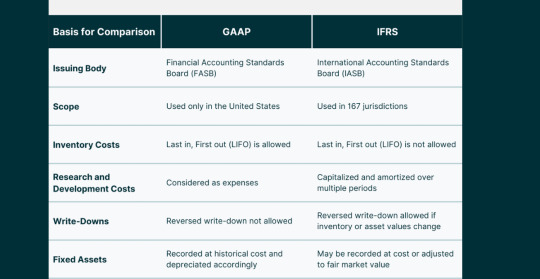
4. Key Differences Between GAAP and IFRS
4.1. Delving into Variances
a. Revenue Recognition: The GAAP-IFRS Divergence
One of the pivotal differences between GAAP and IFRS lies in the recognition of revenue. While both frameworks aim to depict the economic reality of transactions, their approaches diverge in certain key aspects. GAAP tends to be more prescriptive, providing specific guidelines for various industries, whereas IFRS adopts a broader principles-based approach, allowing entities more room for interpretation.
b. Inventory Valuation: Differing Approaches
The treatment of inventory valuation varies significantly between GAAP and IFRS. GAAP typically follows a specific set of rules for valuing inventory, such as the Last In, First Out (LIFO) or First In, First Out (FIFO) methods. In contrast, IFRS permits the use of various methods, including FIFO and weighted average, offering companies more flexibility in choosing an approach that aligns with their specific business dynamics
c. Consolidation Methods: Navigating Complexity
Consolidation methods, particularly in the context of subsidiaries and investments, showcase differences between GAAP and IFRS. GAAP often employs a more rule-based approach, specifying conditions for consolidation. In contrast, IFRS focuses on a principles-based approach, considering the substance of relationships rather than relying on rigid criteria. This variance introduces nuances in financial reporting, influencing how companies present their financial position and performance.
4.2. The Impact on Financial Statements
a. Shaping Investor Perception
The differences in revenue recognition, inventory valuation, and consolidation methods contribute to variations in financial statements produced under GAAP and IFRS. Investors, as key stakeholders, must navigate these differences to gain an accurate understanding of a company’s financial health. The choice between GAAP and IFRS significantly shapes investor perception, influencing investment decisions and risk assessments.
b. Decision-Making Dynamics
Companies, in choosing between GAAP and IFRS, must consider the implications on decision-making dynamics. The framework adopted affects how financial information is presented, potentially influencing strategic decisions, mergers and acquisitions, and capital-raising activities. Understanding the impact of these frameworks on decision-making is crucial for entities operating in dynamic and competitive business environments.
4.3. Global Adoption Trends: A Comparative Analysis
The adoption trends of GAAP and IFRS provide insights into the global dynamics of financial reporting standards. While GAAP maintains dominance within the United States, IFRS has gained traction in numerous jurisdictions worldwide. Understanding the factors influencing these trends, such as regulatory requirements, investor preferences, and global market integration, sheds light on the evolving landscape of accounting standards.
“Accounting isn’t just about profits and losses; it’s about sculpting the financial soul of a company.” Michael Johnson

5. The Evolution of Accounting Standards
5.1. GAAP’s Historical Odyssey
a. Post-1929: A Catalyst for Change
The stock market crash of 1929 served as a catalyst for rethinking the approach to financial reporting. The chaos that ensued prompted the establishment of standardized accounting principles, laying the foundation for what would later become GAAP. The primary goal was to restore investor confidence by providing a reliable framework for financial statements, reducing uncertainty and fostering stability in financial markets.
b. Amendments and Updates: Shaping GAAP’s Trajectory
GAAP’s journey has not been static; it has evolved through amendments and updates to address emerging challenges and align with changing business dynamics. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) plays a pivotal role in shaping GAAP, ensuring that it remains relevant, transparent, and responsive to the needs of companies and investors. The ongoing commitment to refinement reflects a dedication to maintaining the integrity of financial reporting.
5.2. Internationalization Efforts
a. Pioneering Attempts at Global Standardization
As globalization gained momentum, so did the recognition of the need for global accounting standards. Efforts were made to align U.S. GAAP with international standards, but achieving a universal standard proved challenging. The push for global standardization gained traction with the rise of IFRS, offering a framework that transcends national boundaries and facilitates consistency in financial reporting for multinational corporations.
b. The Challenge of Aligning U.S. Standards Globally
While the concept of global accounting standards gained support, aligning U.S. GAAP with international standards presented formidable challenges. The unique legal, regulatory, and cultural landscape in the United States posed hurdles to seamless integration. Despite these challenges, the pursuit of convergence and harmonization continued, reflecting the recognition of the interconnectedness of global economies.
5.3. Convergence Initiatives
a. The Ongoing Pursuit of Harmonization
Convergence initiatives aimed at harmonizing GAAP and IFRS gained prominence in the early 21st century. The objective was to reduce disparities between the two frameworks, fostering a more standardized global approach to financial reporting. While full convergence remained elusive, progress was made in aligning specific standards, reflecting a commitment to minimizing inconsistencies and facilitating ease of comparison for investors and stakeholders.
b. Prospects and Hurdles in a Unified Global Standard
The prospects of a unified global accounting standard remain a tantalizing goal, promising enhanced comparability and consistency in financial reporting. However, hurdles such as divergent national interests, legal complexities, and varying levels of standard-setting infrastructure continue to challenge the realization of this vision. Navigating these obstacles requires ongoing collaboration and a commitment to the overarching goal of global financial transparency.

6. Regulatory Bodies Influencing GAAP
6.1. FASB’s Pivotal Role
a. GAAP’s Guardian: The FASB Mandate
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) stands as the guardian of GAAP, wielding influence over the development and refinement of accounting standards. FASB’s mandate goes beyond rule-making; it encompasses a commitment to improving financial reporting, ensuring that standards are not only relevant but also responsive to the evolving needs of businesses and investors.
b. FASB’s Mission in Financial Reporting Improvement
FASB’s mission revolves around the improvement of financial reporting through the development of high-quality accounting standards. The board operates under a due process system, seeking input from various stakeholders, including investors, auditors, and preparers of financial statements. This collaborative approach ensures that GAAP remains a robust and adaptive framework that reflects the intricacies of modern business transactions.
6.2. SEC’s Watchful Eye
a. SEC’s Authority in Recognizing GAAP Standards
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a crucial role in the oversight of financial reporting in the United States. While the FASB sets accounting standards, the SEC has the authority to recognize and prescribe the principles used in the preparation of financial statements for publicly traded companies. This dual-layered system ensures a balance between industry expertise and regulatory oversight in shaping GAAP.
b. SEC’s Contributions to Financial Transparency
The SEC’s contributions to financial transparency extend beyond its recognition of GAAP standards. The commission actively engages in rule-making and enforcement to ensure that companies adhere to accounting principles and provide accurate and timely financial information to investors. The synergy between the SEC and FASB reinforces the integrity of financial reporting in the U.S. capital markets.
6.3. AICPA’s Industry Impact
a. AICPA: Nurturing Professional Standards
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) plays a vital role in shaping professional standards within the accounting industry. While not directly involved in setting GAAP, the AICPA contributes to the development of ethical and professional standards that guide the conduct of accountants. This commitment to excellence enhances the credibility of financial reporting, reinforcing the trust that stakeholders place in GAAP.
b. Industry-Wide Compliance through AICPA Guidance
The AICPA’s influence extends beyond standards development to encompass industry-wide compliance. The organization provides guidance on best practices, ethical considerations, and emerging issues within the accounting profession. This guidance ensures a cohesive and ethical approach to financial reporting, aligning with the principles embedded in GAAP and contributing to the overall reliability of financial statements.

7. International Bodies Shaping IFRS
7.1. IASB’s Global Mandate
a. IASB’s Significance in IFRS Development
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) holds a central role in the development and maintenance of IFRS. Unlike the FASB’s role in the U.S., the IASB operates on a global scale, aiming to set accounting standards that are applicable and relevant to entities worldwide. The IASB’s commitment to a principles-based approach reflects its recognition of the diverse needs of global businesses.
b. A Global Perspective in Standard Setting
The IASB’s global perspective is intrinsic to its standard-setting process. The board considers input from various regions, industries, and stakeholders, ensuring that IFRS reflects the nuances of international business. The principles-based approach allows for adaptability, catering to the diverse legal, economic, and cultural landscapes in which entities operate globally.
7.2. IFRIC’s Interpretative Role
a. Navigating Grey Areas: IFRIC’s Guidance
The International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC) plays a crucial role in navigating interpretative challenges within IFRS. Given the principles-based nature of IFRS, grey areas may arise, requiring clarification and guidance. IFRIC addresses these challenges by providing interpretations and guidance, ensuring consistent application of IFRS standards across diverse industries and jurisdictions.
b. Consistent Application of IFRS Standards
Consistency in the application of IFRS standards is paramount to ensuring comparability and reliability in financial reporting. IFRIC’s interpretative role contributes to this objective by offering guidance on ambiguous or complex issues. This commitment to clarity and consistency aligns with the overarching goal of IFRS – to provide a common language for financial reporting that transcends geographical and industry-specific boundaries.
7.3. Monitoring Board’s Oversight
a. Ensuring Independence in Standard Setting
The Monitoring Board plays a crucial oversight role in ensuring the independence and effectiveness of the IFRS Foundation, which houses the IASB. Independence is a cornerstone of credible standard-setting, and the Monitoring Board’s role is to safeguard the integrity of the standard-setting process. This commitment to independence reinforces the trust that global stakeholders place in IFRS as a reliable and unbiased framework.
b. The Role of the Monitoring Board in IFRS Integrity
The Monitoring Board’s vigilance extends beyond independence to the broader integrity of the IFRS framework. By overseeing the activities of the IFRS Foundation and IASB, the Monitoring Board contributes to the credibility of IFRS as a global accounting standard. This oversight ensures that IFRS continues to meet the evolving needs of global financial markets and remains a trusted framework for transparent financial reporting.

8. Impact on Financial Reporting
8.1. Side-by-Side Comparison
a. Financial Statement Variances: GAAP vs IFRS
A side-by-side comparison of financial statements prepared under GAAP and IFRS reveals variances arising from differences in principles, approaches, and interpretations. These variances extend to revenue recognition, asset valuation, and consolidation methods, influencing the reported financial position and performance of entities. Investors and analysts must navigate these differences to glean accurate insights into a company’s financial health.
b. Interpretation Challenges for Investors
Investors face interpretation challenges when analyzing financial statements prepared under different frameworks. Understanding the nuances of GAAP and IFRS differences is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The ability to discern how specific accounting choices impact financial metrics empowers investors to evaluate risks, assess potential returns, and navigate the complexities of the global investment landscape.
8.2. Revenue Recognition Dynamics
a. The Nuances of Revenue Recognition
The nuances of revenue recognition under GAAP and IFRS reflect the underlying philosophies of each framework. GAAP, with its prescriptive guidelines, provides specific criteria for recognizing revenue in various industries. In contrast, IFRS adopts a broader approach, emphasizing the substance of transactions over rigid rules. Navigating these nuances requires a deep understanding of industry dynamics and the specific requirements of each framework.
b. Implications for Investor Decision-Making
The implications of revenue recognition dynamics extend to investor decision-making. Differences in when and how revenue is recognized can influence perceptions of a company’s immediate financial performance. Investors must factor in these nuances to make informed decisions, considering the impact on key financial metrics such as earnings per share, profit margins, and return on investment.
8.3. Asset Valuation Approaches
a. Valuation Philosophies: Fair Value vs. Historical Cost
The variance in asset valuation philosophies between GAAP and IFRS introduces complexities in financial reporting. GAAP’s adherence to historical cost provides stability and consistency, albeit potentially understating the current market value of assets. In contrast, IFRS’s emphasis on fair value introduces a more dynamic and responsive approach to asset valuation. Companies must navigate the trade-offs between stability and accuracy in presenting their financial position.
b. Balancing Accuracy and Stability in Asset Reporting
Balancing accuracy and stability in asset reporting requires careful consideration of the trade-offs between fair value and historical cost. Companies must weigh the benefits of presenting current market values against the potential volatility introduced by fair value measurements. Striking the right balance ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the economic reality of a company’s assets while providing stakeholders with a stable and reliable foundation for decision-making.

9. Challenges in Adoption
9.1. Corporate Resistance Factors
a. Unpacking Corporate Hesitations
The decision to adopt new accounting standards, whether transitioning from GAAP to IFRS or vice versa, is met with corporate hesitations. Companies fear the potential disruptions, costs, and uncertainties associated with the transition. Understanding these resistance factors is essential for regulatory bodies, standard-setters, and industry stakeholders to develop strategies that facilitate smoother adoptions and ensure widespread compliance.
b. Overcoming Corporate Resistance Challenges
Overcoming corporate resistance challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Clear communication on the benefits of the new standards, comprehensive training programs, and support mechanisms can alleviate concerns. Regulators and standard-setters must collaborate with industry representatives to address specific challenges faced by different sectors, fostering a cooperative environment conducive to successful adoptions.
9.2. Implementation Costs
a. Financial and Operational Impacts
The implementation of new accounting standards incurs financial and operational impacts for companies. Costs associated with staff training, system upgrades, and adjustments to internal processes contribute to the overall financial burden. Companies must carefully assess these costs and develop comprehensive implementation plans to mitigate disruptions and ensure a seamless transition to the new standards.
b. Strategies for Mitigating Implementation Costs
Strategies for mitigating implementation costs involve proactive planning, phased adoption approaches, and leveraging technology. Companies can benefit from engaging with industry peers that have successfully navigated similar transitions, learning from best practices and challenges. Collaboration between standard-setters, regulatory bodies, and industry associations plays a crucial role in developing strategies that balance the need for improved standards with the practicalities of implementation.
9.3. Training and Skill Gaps
a. The Need for Specialized Training
The adoption of new accounting standards introduces the need for specialized training to ensure that professionals possess the skills required for compliance. Training programs must address the nuances of the new standards, focusing on changes in accounting principles, reporting requirements, and the application of new methodologies. Bridging skill gaps is crucial for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of financial reporting.
b. Collaborative Approaches to Skill Development
Collaborative approaches to skill development involve partnerships between educational institutions, professional organizations, and industry players. The goal is to create comprehensive training programs that equip professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary for successful compliance. Standard-setters and regulators can play a pivotal role in promoting and endorsing such collaborative initiatives, fostering a culture of continuous learning within the accounting profession.

10. Legal Implications for Corporations
10.1. Legal Challenges in GAAP Compliance
a. Litigation Risks in GAAP Adherence
The legal challenges associated with GAAP compliance include litigation risks arising from alleged non-compliance. Companies adhering to GAAP must navigate the complexities of the legal landscape, ensuring that their financial statements withstand scrutiny. Implementing robust internal controls, engaging in transparent communication, and staying abreast of legal developments are essential strategies for mitigating litigation risks.
b. Strategies for Legal Compliance in GAAP
Strategies for legal compliance in GAAP involve proactive measures to minimize litigation risks. This includes fostering a culture of compliance within the organization, conducting regular internal audits, and seeking legal counsel to ensure alignment with evolving regulations. Companies that prioritize legal compliance contribute to the overall stability and trustworthiness of the financial reporting ecosystem.
10.2. Legal Battles in IFRS Adoption
a. Navigating Legal Challenges in IFRS Transition
The transition to IFRS introduces legal battles that companies must navigate effectively. Disputes may arise over interpretations of IFRS standards, potentially leading to litigation. Companies must engage in comprehensive risk assessments, understanding the legal implications of IFRS adoption, and implementing measures to mitigate potential legal challenges.
b. Legal Safeguards for Companies Adopting IFRS
Legal safeguards for companies adopting IFRS involve proactive steps to minimize legal risks. This includes engaging legal experts in the transition process, conducting impact assessments, and implementing robust governance structures. Companies that prioritize legal safeguards position themselves to navigate the complexities of IFRS adoption with resilience and integrity.
10.3. Risk Mitigation Strategies
a. Legal Safeguards: Mitigating Risks in Regulatory Compliance
Legal safeguards play a pivotal role in mitigating risks associated with regulatory compliance. Companies must implement effective risk management strategies, including regular legal audits, compliance training, and a responsive approach to legal developments. A proactive stance towards legal safeguards enhances a company’s ability to navigate the intricate landscape of financial reporting standards.
b. Strategies for Minimizing Legal Challenges in Reporting Standards
Strategies for minimizing legal challenges in reporting standards involve a holistic approach to risk management. This includes collaboration with legal professionals, staying informed about evolving regulations, and fostering a culture of compliance within the organization. Companies that prioritize these strategies not only mitigate legal challenges but also contribute to the overall reliability and credibility of financial reporting standards.

11. Investor Perspectives
11.1. Investor Preferences
a. Surveying Investor Preferences: GAAP or IFRS?
Understanding investor preferences is crucial in the GAAP vs. IFRS discourse. Surveys play a valuable role in gauging investor sentiment and preferences regarding financial reporting standards. The insights gleaned from such surveys inform standard-setters, regulators, and companies in aligning financial reporting practices with investor expectations.
b. Implications of Investor Preferences on Reporting Standards
The implications of investor preferences on reporting standards are far-reaching. Companies that align with investor preferences enhance transparency and communication, fostering trust and confidence. Standard-setters and regulators, informed by investor feedback, can shape standards that not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to the information needs of investors in a dynamic and competitive market.
11.2. Impact on Investment Decision-Making
a. Investor Decision Dynamics: GAAP vs IFRS
Investor decision dynamics are influenced by the choice between GAAP and IFRS. Differences in financial reporting standards can impact the comparability of financial statements, influencing investment decisions. Investors must consider the implications of these standards on key metrics, risk assessments, and overall financial analysis to make informed and strategic investment decisions.
b. Strategic Impacts on Investment Choices
The strategic impacts of financial reporting standards on investment choices go beyond compliance. Companies that recognize the link between transparent financial reporting and investor confidence gain a strategic advantage. Similarly, investors who factor in the nuances of GAAP and IFRS differences in their decision-making processes navigate the complexities of the investment landscape more effectively.
11.3. Investor Education Initiatives
a. The Imperative of Investor Education
The imperative of investor education underscores the need for initiatives that enhance investor understanding of financial reporting standards. Educational programs, informational resources, and collaborative efforts between financial institutions and regulatory bodies contribute to a more informed investor community. An educated investor base not only demands higher standards of transparency but also actively participates in shaping the future trajectory of financial reporting.
b. Educating Investors on GAAP vs IFRS Implications
Educating investors on GAAP vs. IFRS implications involves demystifying the complexities of these frameworks. Providing accessible information, conducting investor workshops, and leveraging digital platforms for educational outreach are essential components. Investors empowered with a deeper understanding of financial reporting standards contribute to market efficiency and hold companies accountable for transparent and reliable reporting.

12. Ethical Considerations
12.1. Ethical Dimensions in Financial Reporting
a. Ethics in Financial Reporting Standards
Ethical considerations are integral to the formulation and adherence to financial reporting standards. The principles of integrity, objectivity, and transparency underpin ethical financial reporting. Standard-setters, regulators, and companies must navigate ethical dimensions to ensure that financial reporting serves the interests of investors and the broader public.
b. Upholding Integrity and Objectivity in Reporting
Upholding integrity and objectivity in reporting requires a commitment to ethical conduct. Companies must prioritize accurate representation over short-term gains, fostering a culture that values transparency. Regulators play a crucial role in setting the ethical tone, emphasizing the importance of unbiased and principled financial reporting in maintaining the integrity of capital markets.
12.2. Ethical Challenges for Accountants
a. Common Ethical Dilemmas in GAAP and IFRS
Accountants face common ethical dilemmas in navigating the intricacies of GAAP and IFRS. Issues such as revenue recognition, asset valuation, and disclosure requirements present challenges where ethical considerations intersect with professional responsibilities. Accountants must navigate these dilemmas with a commitment to ethical conduct, considering the broader impact on stakeholders and financial markets.
b. Navigating Ethical Challenges in Reporting Standards
Navigating ethical challenges in reporting standards involves equipping accountants with the tools and guidance needed for principled decision-making. Ongoing professional development, ethical training programs, and mentorship initiatives contribute to a culture of ethical awareness within the accounting profession. Companies, in turn, benefit from the assurance that financial reporting is not only compliant but also aligns with the highest ethical standards.
12.3. Regulatory Measures for Integrity
a. Regulatory Safeguards: Ensuring Ethical Conduct
Regulatory safeguards play a crucial role in ensuring ethical conduct in financial reporting. Regulatory bodies must establish and enforce ethical standards, conduct regular audits, and impose sanctions for non-compliance. A robust regulatory framework promotes integrity in financial reporting, reinforcing public trust in the accuracy and reliability of financial statements.
b. Maintaining the Integrity of Financial Reporting Standards
Maintaining the integrity of financial reporting standards requires a collaborative effort between regulators, standard-setters, and industry stakeholders. Periodic reviews, stakeholder consultations, and responsiveness to emerging ethical challenges contribute to the ongoing refinement of standards. The commitment to upholding ethical principles ensures that financial reporting continues to serve as a cornerstone of trust in the global business landscape.

13. Future Trajectories
13.1. The Evolution of Reporting Standards
a. Anticipating Future Changes
Anticipating future changes in reporting standards involves considering the dynamic nature of global business, technological advancements, and shifts in investor expectations. Standard-setters must adopt a forward-looking approach, engaging in scenario planning and staying attuned to emerging trends. The ability to anticipate future changes ensures that reporting standards remain relevant and adaptive to the evolving needs of the business environment.
b. Technological Innovations and Reporting
Technological innovations are poised to shape the future trajectory of reporting standards. The integration of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics introduces opportunities for enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and transparency in financial reporting. Standard-setters and companies must embrace these innovations responsibly, balancing the benefits of technology with the imperative of maintaining ethical and transparent financial practices.
13.2. Convergence vs. Divergence
a. Assessing Convergence Prospects
The prospects of convergence between GAAP and IFRS continue to be a topic of consideration. While convergence offers the promise of a more standardized global approach, challenges such as differing legal frameworks and regulatory philosophies persist. Assessing convergence prospects involves a nuanced examination of global trends, regulatory developments, and ongoing efforts by standard-setters to bridge divergences.
b. Navigating Divergences in Global Standards
Navigating divergences in global standards requires a pragmatic approach that acknowledges the unique needs of individual jurisdictions. The coexistence of multiple standards necessitates effective communication, education, and cross-border collaboration. Standard-setters can play a pivotal role in facilitating harmonization efforts, fostering a global financial reporting landscape that balances convergence with the flexibility needed to accommodate diverse economic and regulatory environments.
13.3. Sustainable Reporting Paradigms
a. The Rise of Sustainable Reporting
The rise of sustainable reporting reflects a paradigm shift in the broader understanding of corporate performance. Investors, regulators, and the public increasingly recognize the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Future reporting standards are likely to integrate sustainable reporting paradigms, providing a more comprehensive view of a company’s long-term value creation and societal impact.
b. Integrating ESG Metrics into Reporting Standards
Integrating ESG metrics into reporting standards requires a collaborative effort between standard-setters, regulators, and industry stakeholders. The development of clear guidelines, standardized metrics, and transparent disclosure requirements enhances the credibility of sustainable reporting. Companies embracing ESG considerations in their financial reporting contribute to a more informed and responsible investment landscape.

14. Conclusion
Financial reporting standards, whether grounded in GAAP or IFRS, serve as the bedrock of transparency, trust, and accountability in the global business landscape. The evolution of these standards reflects a journey of adaptation to changing business dynamics, regulatory landscapes, and investor expectations. While GAAP and IFRS diverge in certain philosophies and approaches, they share a common goal – to provide reliable and relevant information for decision-making.
As we navigate the complexities of GAAP vs. IFRS, it is imperative to recognize the strengths and limitations of each framework. GAAP, with its historical cost emphasis and rule-based approach, offers stability and comparability. In contrast, IFRS, operating under a principles-based approach, provides flexibility and a global perspective. Understanding the variances in revenue recognition, asset valuation, and consolidation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and companies alike.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of reporting standards involves a delicate balance – between convergence and divergence, between technological innovation and ethical considerations, and between traditional financial metrics and sustainable reporting paradigms. The future holds the promise of more standardized, adaptive, and responsible reporting standards that cater to the diverse needs of a dynamic global economy.
In conclusion, as the landscape of financial reporting continues to evolve, stakeholders must remain vigilant, adaptive, and collaborative. Whether one adheres to GAAP or IFRS, the shared commitment to integrity, transparency, and accountability ensures that financial reporting remains a cornerstone of trust in the interconnected world of business and finance.

#cfo#banking#accounting#finance#investment#personal finance#international finance assignment help service#financial management#financial markets#financial modeling#financial planning#financial dominance#financial services#financial literacy#financial drain#management#business#entrepreneur
0 notes
Text
Foundations of Financial Management 17th edition by Stanley Block, Geoffrey Hirt, Bartley Danielsen PDF

#college#student#studies#study motivation#studyblr#university#studyspo#books and reading#textbook#financial management#finance#strategic management assignment help#economy#books & libraries#bookblr#booklr#books#book quotes#reading#booklover#bookworm#exam help#exam season#exam study#exam prep#exa#dark academia#light academia
0 notes
Text
How a Company Resolved an NPV vs IRR Conflict: A Financial Management Assignment Case Study
In corporate finance, handling conflicts between Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is essential. Both metrics are vital for assessing projects, making investment decisions, and create financial strategies. This post analyzes a case where a company faced a conflict between NPV and IRR and successfully resolved it. We will go through the methods, analysis, and decision-making that led to a positive result. Additionally, we will discuss how students can tackle similar cases in their studies by seeking financial management assignment help from renowned experts online.

Case Introduction
A company is focusing on two investment projects that have equal initial costs but different cash flow patterns. The NPV method provides better result for one project, while the second method, IRR is preferential for the other project. What could cause such a conflict and how should the company decide on the projects to be undertaken? We should go into more details on the case and its potential recommendations.
NPV as a Metric for Decision Making
NPV is one of the most basic financial metric that measures if an investment is profitable or not by calculation the difference of cash inflows and outflows. Any investment whose NPV is more than zero is deemed to be profitable since such investment is expected to generate more cash than the cash that it spends. NPV is widely used because it incorporates the time value of money to aid in presenting the future profitability of an investment.
IRR and Its Significance
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is another important measure employed in project appraisal process. It refers the interest rate from an investment that makes the NPV equal to zero. Thus, IRR is the growth rate that is anticipated to be earned on the investment. This is because a project with an IRR greater than the firm’s required rate of return is normally considered acceptable. IRR is mostly preferred for its simplicity, and it is much easier to understand when expressed in percentages.
The Conflict Between NPV and IRR
NPV and IRR are two different methods of evaluating the profitability of an investment and the disagreement between these two methods occurs where one is suggestive of a project being profitable while the other is not. This is more likely to happen where there are non-conventional cash flows, or where there could be several cycles of cash inflow and outflows. For instance, there may be a situation in which a project may yield a high IRR but may have a low NPV and hence confusing.
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
Background of the Conflict
Currently, the decision makers who are part of the XYZ Corporation, an automotive manufacturing firm, encountered the NPV-IRR conflict in assessing a new line of electric vehicle production. High initial costs were invested and further several years of negative operating cash flows due to R & D expenditure were incurred. But the company expected a large amount of money to flow in once the production line was established.
Initial Analysis
XYZ Corporation has a dedicated financial management team that carefully evaluated the NPV and the IRR of this project. When applying the NPV formula at a discount rate of $10%, the result was a negative value of -$2 million. On the other hand, the IRR for the project was estimated to be 15% which is higher than the required rate of return of the company. This was due to conflicting conclusions being offered by both decisions, thus leading to heated discussions among board members.
While analyzing the case some of the executives also claimed that it had high IRR and thus, could be a good investment for the company while some others observed that NPV was negative, and thus, this proposal should not be accepted by the company. The CFO also pointed out the significance time value of money and how this will affect the total cash flow.
Resolution Strategy
Sensitivity Analysis: In order to solve this problem, the financial team’s decision was to run sensitivity analysis to analyze the effect of various key assumptions. They analyzed various cases and factors like the cost of production, demand, and the discount rate. This assessment pointed out that a slight alteration of the market conditions could influence the project’s NPV and IRR drastically.
Comparative Metrics Evaluation: The team also reviewed a few other metrics, one of which included the Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR). It overcomes the limitations of IRR. MIRR includes the cost of capital and, in that way, is much more effective in reflecting the profitability of an investment. Calculating MIRR, the team found it to be more reasonable with the results from NPV and hence providing a clearer view of the potential of the project.
Decision Framework: To make a well-informed decision, XYZ Corporation adopted a multi-criteria decision framework. This approach considered not only NPV and IRR but also other factors such as strategic alignment, market trends, and risk assessment. By integrating qualitative and quantitative analysis, the company was able to balance the conflicting signals and arrive at a comprehensive decision.
Final Decision: After thorough analysis, the board came to a consensus that it was appropriate to go ahead with the production line of electric vehicles. They understood the need for the car maker to penetrate the market and the long-term gains that would be realized. However, they also put other precautionary measures such as management of risks, phased investments and constantly assessing the market conditions.
Implementing the Project
Phased Investment Approach: With this approach, XYZ Corporation minimized the financial risk. Under this approach, a project is first broken down into small, manageable phases each having specific milestones to be met. There would be an assessment of the performance of each phase, and based on that, they were permitted to go to the next level. This has allowed the company to bring real-time data and market feedback into the equation and make adequate changes in the process.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: In the whole project implementation, risk management was essential. The key risks identified by the company included technological challenges, changes in regulation, and market competition. It developed contingency plans for each so if required, potential issues could be worked out without leading to derailment of the entire project.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: XYZ Corporation had therefore put in place an evaluation mechanism that would continuously monitor the project. Regular performance appraisals and financial review were made to ensure that the project remained on track with the company's strategic plans. This proactive approach would enable the company to respond to any deviation immediately and make appropriate informed decisions.
Financial Management Assignment Help: Empowering Students to Master Case Studies
Solving problems in financial management in the modern context is not an easy task for students anymore, especially when they are exposed to diverse business problems linked to case studies. Asking for professional help greatly improves knowledge and concept building skills. Here is how taking case study help from financial management tutor help services can benefit students:
Benefits of Case Study Help
1. Understanding the Nuances of Case Studies: Case studies require a deep dive into real-world scenarios, necessitating a thorough understanding of various financial metrics and decision-making processes. Professional expert guides students through the nuances of case studies, helping them identify key issues, evaluate financial data, and apply theoretical knowledge practically.
2. Grasping Basic Concepts of NPV and IRR: Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) are some of the most basic tools in financial management. These basic concepts play an important role in the appraisal of investment projects and the settlement of the NPV/IRR conflict.
3. Applying Sensitivity Analysis: Sensitivity analysis is one of the techniques in the field of financial management which assess the variables that affect project’s outcome. By opting for expert help in sensitivity analysis, students strengthen their knowledge of risk assessment and decision-making.
Check out our viewpoint on How To Interpret Sensitivity Analysis Results In Financial Management Assignments
Recommended Textbooks
For students looking to deepen their understanding, the following textbooks are highly recommended:
"Principles of Corporate Finance" by Richard A. Brealey, Stewart C. Myers, and Franklin Allen.
"Financial Management: Theory & Practice" by Eugene F. Brigham and Michael C. Ehrhardt.
"Corporate Finance" by Jonathan Berk and Peter DeMarzo.
These textbooks offer comprehensive coverage of financial management principles, including detailed explanations of NPV, IRR, and sensitivity analysis.
FAQs
What is financial management assignment help?
Financial management homework assistance allows students to learn different kinds of complex case studies faster and more effectively from experts. It improves their understanding of the key concepts and improving analytical skills.
How does professional help improve understanding of NPV and IRR?
Expert assistance provides clear explanations and uses concrete examples and cases to explain to students why, how, when and at what NPV and IRR financial decisions are made.
What is the role of sensitivity analysis in financial management?
Sensitivity analysis also determines the changes within key variables and the corresponding effects on projects to evaluate the risks and make right decisions. It is useful where net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR) are in a conflicting state.
Which textbooks can students refer to for financial management concepts?
Students can refer to "Principles of Corporate Finance" by Brealey, Myers, and Allen, "Financial Management: Theory & Practice" by Brigham and Ehrhardt, and "Corporate Finance" by Berk and DeMarzo for comprehensive coverage of financial management concepts.
Why should students seek help with financial management case studies?
Asking for financial management assignment help allows students to comprehend the intricacies of the cases, learn practical implementation of the theories learnt in class and most importantly sharpen their analytical tools for making informed business decisions.
Conclusion
It is important to understand that NPV and IRR are two fundamentally different tools used to make cash flow evaluations. Thus, the solution of the conflict between them must be based on the most holistic and scientific approach to monetary evaluation. With the right professional financial management assignment help, a student is able to understand the various issues, analysis, and subsequently perform excellently in this course and the future career in finance.
0 notes
Text
Financial Management Assignment Help: Achieve Excellence in Finance Studies
Our financial management assignment help service provides expert guidance tailored to students navigating the complexities of finance. From budgeting and financial analysis to risk management and investment strategies, our seasoned professionals offer comprehensive support.
0 notes