#GAD65
Text
Now listening to this episode.
Diagnosis of DM: HgbA1c greater than or equal to 6.5%, fasting blood glucose level above 126 mg/dL, random blood glucose of 200 mg/dL or higher with symptoms . You have to repeat the number to make the diagnosis. I learned that if blood glucose is 200 mg/dL and you have symptoms, that's enough to make the diagnosis then and there.
Two hour oral glucose tolerance test - blood glucose above 200 mg/dL at 2 hours is diabetes; blood glucose 150 to 200 mg/dL is pre-diabetes.
Fatigue, weight loss, polyuria, polyphagia are common presenting symptoms.
Risk of type 1 diabetes is 1 in 500. But if you have a family member who has type 1 diabetes, it's increased to 1 in 50. It's 50% if you have an identical twin who has it.
You can also test the pt for thyroid disease, celiac disease. Antibodies for diabetes: glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) antibody and some form of islet cell antibody like ICA512 or IA2 anti-insulin antibody. Another antibody you could order is anti zinc transporter 8 antibody. Not having the antibodies doesn't exclude the diagnosis. If you have the zinc transporter 8 antibody, you lose islet cells 20% faster.
You can check C-peptide level. Pro-insulin has C-peptide on it. C-peptide gets cut off of pro-insulin, which then becomes active insulin. C-peptide is a marker of innate insulin production. If you have C-peptide, it means your body is producing insulin. If you have insulin in your body, but no C-peptide, it means you injected insulin and your body didn't make that insulin.
Screen for pts with DM1 for other autoimmune diseases such as celiac disease, thyroid disease, Addison disease, rheumatoid arthritis. They are also at risk for IBD. Thyroid disease + diabetes + Addison's disease = autoimmune polyglandular syndrome.
A baby less than 1 years old who has diabetes can present like she has sepsis. It could be DKA.
Pts can have neonatal diabetes. Pts who present at less than 6 months old should have genetic testing for autoimmune diseases.
Hemolytic uremic syndrome or other storage diseases (like hemochromatosis or cystinosis) can cause pancreatitis-induced insulin dependent diabetes.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a group of several conditions characterized by abnormally high blood sugar levels. It's genetic and mild. Pts with MODY have none of the antibodies associated with DM1 and don't need insulin.
Pts can present at any age with diabetes type 1. If it develops in older age, it takes longer to progress to the point where they need insulin. Sometimes they are misdiagnosed as having type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 DM tx: basal bolus insulin regimen = daily basal insulin bolus + meal time insulin injections. Most pts are not started on insulin pumps because insulin pumps can fail. Pts should start with insulin they inject themselves so that they know how to do this in case an insulin pump were to fail. Glargine, detemir, tresiba are long acting basal insulins.
You teach pts how to carb count and use pre-meal insulin. Can also give sliding scale insulin.
Avoid sugary beverages. Learn to count carbs. Do insulin to carb ratio. Low carb diet can help. But in pediatric pts, you can limit to 50 to 100 grams of carbs daily.
Pts should check blood glucose before meals abd at bedtime. They should check it at 2:00 a.m. in the beginning of treatment to ensure they don't become hypoglycemic in the middle of the night. Can also check blood sugar 2 hours after a meal to ensure that the meal time bolus is appropriate. Aim for blood glucose level between 80 and 150 mg/dL (but it ranges depending on the kid's age) and how recently they were diagnosed. You want 50% of blood glucose readings to be in that goal range. If less than 50% of blood sugars are in that goal range, then you have to adjust treatment regimen.
Use fasting blood glucose to titrate basal insulin. You can skip a meal and check blood glucose every 2 hours. If blood glucose rises 30 mg/dL or drops 30 mg/dL every 2 hours, then your basal insulin needs adjustment.
Type 1 DM - loss of 80% of pancreatic islet cells. When the pt starts receiving insulin, the remaining 20% of islet cells can start producing insulin. That may make it easier to control the diabetes initially. This is called "Honeymoon phase."
I googled it and found this:
In the period after a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, some people experience a ‘honeymoon’ phase. During the honeymoon the pancreas is still able to produce a significant amount of its own insulin. This helps to lower blood sugar levels and can reduce the amount of insulin you need to inject or pump.
Honeymoon phase can last up to 2 years or 3 years. This phase disappears. Blood glucose below 70 is low. Blood sugar should not be below 50 more than 2 times a week. If it occurs more often than that, you have to adjust their regimen. You want to avoid neuroglycopenia (low blood glucose in the brain). It can cause AMS and seizures. Sweating, palpitations, tremors are other symptoms of low blood glucose. Treat it by eating or drinking 15 grams of carbs, waiting 15 minutes, then rechecking blood glucose. If blood glucose is still low, give another 15 grams of carbs and check it again in 15 minutes. Glucose gel can be used or glucagon injection. Mini-dosing: 1 unit per year of age subcutaneous glucagon can be given.
Aerobic activity makes you absorb insulin. But if you don't have enough insulin, cells can't take it in. Kids with blood glucose above 350 mg/dL should not play sports. Increased activity increases sympathetic tone, which can increase blood glucose level.
If you've been very active during the day, your blood glucose can go low hours later, so for kids who play sports, they should check their blood glucose more frequently at end of day.
Illness can raise or lower glucose levels--stress can raise glucose and not eating can decrease it. Pts should still always take basal insulin when sick and should check blood sugars more frequently. You may need to avoid insulin boluses if your sugar is low.
NPO after midnight for pts who are going for surgery doesn't include cleat liquids. Diabetics can drink clear liquids up to 2 hours prior to surgery to treat low blood sugars. You can decrease these pts' basal insulin if necessary.
Vision, neurological, kidney problems, cardiovascular problems can occur as complications. If HgbA1c is persistently high over time, this can lead to the complications of diabetes. Check eyes yearly, check lipids yearly, check kidney function, urine albumin yearly. Glycosylation of cell proteins causes damage.
For toddlers, tolerate Hgba1c up to 8.5%. As they get older, aim for Hgba1c of 6.5%. It's hard to achieve that in type 1 DM. So 7.5% is not bad in a pt with type 1 DM.
Continuous glucose monitor checks blood glucose every 5 minutes or so. It's connected to the insulin pump, telling it to give more or less insulin based on the blood glucose trend. Pts still need to bolus themselves before meals.
There are diabetes camps where you can volunteer to learn more about diabetes.
From the post test:
Autoimmune thyroid disease is the most common autoimmune disorder associated with diabetes, occurring in 17–30% of patients with type 1 diabetes.
Key Point: It is important to check other autoimmune studies when first diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes. Screening for thyroid dysfunction and for celiac disease should be considered. Other conditions such as primary adrenal insufficiency, autoimmune hepatitis, autoimmune gastritis, dermatomyositis, and myasthenia gravis, occur more commonly in the population with T1DM than in the general pediatric population and should be assessed and monitored as clinically indicated.
Citation:
American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2020 Jan; 43(Supplement 1): S163-S182
International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD) guidelines recommend a target HbA1c of <7.5% for all pediatric patients with strong emphasis placed on individualizing glucose targets to promote normoglycemia while preventing severe or frequent hypoglycemia.
Key Point: Advise patients to aim for as low of an A1C as possible (<7.5%) while avoiding low sugars. Additionally, educate patients that the trend of A1C’s over time is more important than one specific value.
Citation:
Chiang, J. L., Maahs, D. M., Garvey, K. C., Hood, K. K., Laffel, L. M., Weinzimer, S. A., Wolfsdorf, J. I., & Schatz, D. (2018). Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes care, 41(9), 2026–2044. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci18-0023
Differentiating the specific type of Diabetes is important due to the differences in treatment and education for the patient. The presence of one or more of these antibodies confirms the diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes.
Key Point: It is helpful to order antibody studies to aid in the diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes, especially if it is difficult to distinguish from Type 2, MODY, etc. However, negative antibodies do not exclude a diagnosis of T1DM, but it should trigger a thought process of thinking this could be another or new form of disease that acts like T1DM but may not necessarily be T1DM.
Citation:
Mayer-Davis et al. (2018) IPSAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Definition, epidemiology and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatric Diabetes. 2018, 19(S27), 7-19.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
cw: death and illness
I haven't seen anyone talk about it on tumblr, so I'm bringing the bad news from twitter.
The voice actress behind Dead By Daylight's Unknown, Zoey Alexandria Wendorf has passed away on April 30th. After a long time battle with an autoimmune disorder, (GAD65 based Non-paraneoplastic Limbic Autoimmune Encephalitis and Stiff Person Syndrome). There wasn't long term cure, and the treatments she received had side effects she described as "absolutely horrendous", so a couple months ago she decided to permanently stop receiving them.
Unfortunately, that means her illness progressed much faster and today it has been announced in her obituary that Zoey passed away.
Rest in peace 💔
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is anyone here know how to properly read lab result because its confusing . Just got my GAD65 autoantibodies results back the normal value is 0.02 mine is 0.01 so who knows what is going on.... im pretty sure this and my high white blood cell count caused them to think i had lupus which i dont..... sooo yea wouldn't shock me if i was told that its type 1 because my great aunt had both types of diabetes pretty bad as well as other things, but other blood relatives have it or something similar....
#mod speaks#ally speaks#life update#adulting sucks#glucose levels#ted talks#help plz#blog#why does this keep happening
0 notes
Photo

The primary difference between type 1 and 2 diabetes has all to do with the cause. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) develops when the immune system takes out the cells of the pancreas that release insulin, which causes an insulin deficiency, a rise in blood sugar, and a need to supplement the insulin that is not being produced. T1D tends to occur in those who are younger, but I’ve also had conversations with many who are diagnosed later into their adulthood. For example, I was diagnosed at 23, and my grandmother at 18 years old. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) develops because of insulin resistance and tends to occur more in those older than 45. In insulin resistance, there is typically too much insulin, but we’re not able to use it. Since we can’t use the insulin we have, blood sugar rises, and lifestyle, supplements, or medications to reduce insulin resistance are commonly used. Both can be diagnosed with a high fasting blood sugar above 125 and an A1c above 6.4. The stereotyped diagnosis is typically made on weight. If someone is skinny, the common thought is they have T1D, and if overweight, T2D, but that’s not always the case. The true difference will be if the person is producing antibodies, like GAD65, ICA, IA-2A, ZnT8A, or IAA, which are all different antibodies towards aspects of insulin production. If one of those is positive, the person likely has type 1. While someone with T2D can’t develop T1D and vice versa, the longer someone has T1D or T2D and is living in a way that’s not supporting their health and blood sugars, the lines between the two start to blur. In other words, those with T1D start to become more insulin resistant and those with T2D may not produce as much insulin. There are certainly major differences between these forms, but at the end of the day, we all are working toward the same goal - to manage blood sugar! Have you heard of these differences before? https://www.instagram.com/p/CkL8eitOhCq/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
Kundakovic & Jaric 2017 - The Epigenetic Link between Prenatal Adverse Environments and Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Kundakovic & Jaric 2017 is a literature review on the interaction between disruptions of the prenatal environment and normal brain development at the nexus of alterations of the epigenetic machinery. Working on the observation that a complex interaction of genetic make-up, sex, and life-long environment determine final brain outcomes, Kundakovic & Jaric investigate the epigenome as a biological substrate of this connective web of factors.
First, they describe the process of DNA methylation and its importance as an epigenetic mechanism. DNA methylation is a process that impacts the cytosine-guanine (CpG) connection at the position 5 cytosine in most cells and works by impeding the binding of transcription factors or inducing a repressive chromatin structure. They acknowledge the complexity of this process, noting that methylation happens at non-CpG sites in neuronal cells, that gene bodies are also subject to methylation, that other cytosine modifications, like Tet modifications, have been described, and that there is an effect on alternative splicing and higher-order chromatin structure.

They establish prenatal development as the most vulnerable period for epigenetic disruption, as it is contains the critical period for totipotency of the zygote as it becomes a blastocyst and the differentiation of the neural and glial progenitor cells relies on proper DNA methylation patterns. The remainder of the paper focuses on the method by which epigenetic changes at this crucial developmental stage produce outcomes in adulthood.
They present two possible models for problems in adult postmitotic neuronal cells. The first model maintains that DNA methylation patterns remain stable, but this is unlikely. The second model, which is ultimately embraced by Kundakovic & Jaric, states that it is malfunctions of the epigenetic machinery that is stable in postmitotic cells throughout life, not specific methylation patterns.
After establishing a general mode, Kundakovic & Jaric move to a discussion of specific evidence for this model in animal research.
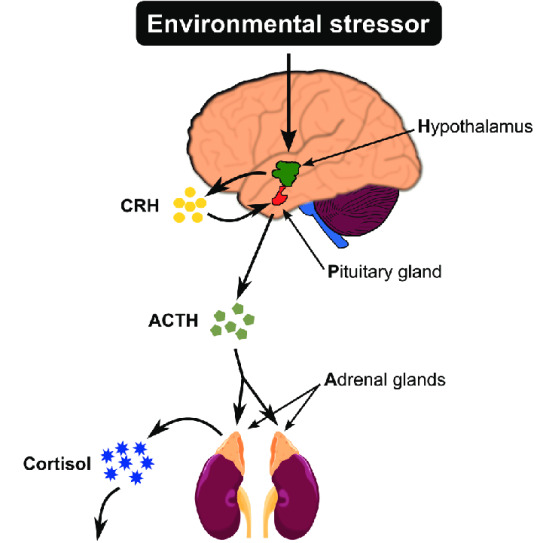
First, they discuss the association between maternal stress and SCZ, depression, anxiety, and autism, and the role of the HPA axis in all of these disorders. Glucocorticoid receptor gene Nr3c1 and corticotropin-releasing factor genes (Crf) are methylated in the hippocampus and amygdala respectively in males only with prenatal stress. In a study of restraint stress from gestation day (GD) 7 to GD21, offspring showed reduced cortical and hippocampal Bdnf mRNA expression and increased DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation at the BDNF regulatory region, as well as decreased histone acetylation in these regions. St-Cyr and McGowan showed that prenatal exposure to predator odor in the 2nd half of pregnancy made females show a higher stress response and decreased Bdnf expression in the hippocampus. Additional GABAergic gene changes were observed.

Toxicological exposure was covered next. Exposure to bisphenol A (BPA), used in many plastic products, produced lasting down-regulation of Bdnf gene expression in males, which led to memory deficits in young adult mice likely resulting from CREB transcription factor changes. Methylmercury exposure also reduced Bdnf expression at the hippocampal dentate gyrus, leading to depression in adulthood.

Viral infection is studied in animals in a controlled manner by injection into the mother’s body of a viral mimetic polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid, or a poly(I:C). Brain tissue is then harvested for study from 6-week-old offspring. Basil et al. found significant global DNA methylation specific to females and hypomethylation of the promoter Mecp2 in the hypothalamus, but did not link this to function. Labouesse et al. studied GD17 Poly(I:C) and observed Gad1 and Gad2 epigenetic changes in the form of reduced RNA expression. These two genes encode GABA-synthesizing enzymes GAD67 and GAD65. Richetto et al. demonstrated the functional relevance of methylation of promoter regions binding to GAD1 by studying GD9 and GD17 Poly(I:C) when he observed that GD9 changes resulted in more gnt signaling, while GD17 changes resulted in more GABAergic differentiation.

The final variable discussed in animal studies is drug use and abuse. Kundakovic & Jaric found that THC is linked to reduced expression of the DRD2 gene in the fetus at 20 weeks of gestation, impacting the movement of dopamine through the ventral tegmental - Nucleus Accumbens (NAc) pathway. Maternal cocaine use produced changes in DNMTs, epigenetic regulator, and global DNA methylation in hippocampal neurons in male and prepubertal mice. Kaminen-Ahole et al. found that maternal ethanol exposure from GD0.5 to GD8.5 increased the probability of hypermethylation and produced more mice offspring with agouti coats. Critically, these mice also displayed symptoms very similar to human Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS).
The discussion then moves to human studies. It is harder to study humans because human brain tissue cannot be directly studied in vivo, and researchers have to rely on epigenetic profiling of peripheral tissues: blood and buccal cells. For ethical reasons, it is also much more likely to encounter naturalistic observation paradigms than controlled laboratory experiments of prenatal adversities. Finally, the independent variables in these human studies are often not as clear and controlled as they are in animal studies.
Kundakovic & Jaric discuss the Dutch Famine Study, which observed an increased risk of neural tube defects, schizoid personality disorders at age 18, and schizophrenia in adulthood for children of Dutch mothers eating as little as 500-1000kcal per day. The twin factors of malnutrition and maternal stress likely overlapped to reduce expression of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), as observed in children born during the famine when compared to their siblings born outside the famine. Other human studies considered included the impact of maternal stress and depression on glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 in the HPA axis, which predicts infant HPA reactivity at 3 months of age, and BPA exposure, implicated in aggressive behavior resulting from BDNF DNA methylation in boys.
In conclusion, Kundakovic & Jaric reiterate the importance of timing and dose of various prenatal factors, the need more female subjects to study numerous sex-specific epigenetic effects, the need for better correlations between blood and brain epigenome to aid future human studies, and the importance of tech advances - whole-genome bisulfite sequencing, ChIP-seq, and ATAC-seq - to allow profiling at the whole-genome level. With a focus on better methods and technological advances in the field comes better understanding of the epigenetic impact of prenatal factors, which would undoubtedly have massive clinical implications.
0 notes
Text
Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA) is autoimmune diabetes that begins in adulthood and does not need insulin for glycemic control at least in the first six months after diagnosis. It shares genetic, immunologic, and metabolic features with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM).
Once the diagnosis of LADA is made, non-pharmacological therapies including a diet with carbohydrate and calorie counting, exercise, and precautions to prevent complications similar to those employed in patients with T1DM and T2DM. Since LADA is a heterogeneous condition, pharmacological treatment has to be personalized to gain the maximum therapeutic advantage.
The two goals of pharmacological treatment are (1) to obtain good glycemic control and (2) to prevent or delay complications. Therapies that will preserve beta-cell function are a priority. Insulin has been the treatment of choice for LADA. Studies have shown preserved beta-cell function as evidenced by a maintained stimulated C-peptide response, normal HbA1C levels, and a decrease in autoantibody concentrations.[36]
Sulfonylureas are a poor choice for LADA. They deplete beta-cells of insulin as depicted by falling C-peptide levels, the persistence of antibodies, and the earlier progression to insulin.
Although metformin may help initially in glycemic control in patients with LADA with higher BMI, it alone cannot achieve the second and more important goal of preserving beta-cell function or delaying its destruction.
Thiazolidinediones have antiinflammatory effects on beta-cells and can prolong their survival and can be useful if used in the earlier stage in LADA. They can also be combined with insulin. Rosiglitazone is the only drug studied in LADA.[37] Unfortunately, the cardiovascular risks associated with this drug have extremely limited its use in the past decade. More long-term studies are warranted with other compounds in this class, like pioglitazone.
DPP4 inhibitors have shown promise alone or when combined with insulin in preserving beta-cell function in LADA. They affect metabolic control by prolonging levels of GLP1 and other peptides. Their primary action is to increase levels of GLP1, thereby suppressing glucagon and increasing insulin secretion after a glucose load by activating DPP4 receptors in the GI tract and brain. DPP4 receptors have also been identified on the surface of T lymphocytes, where they may affect immune regulation. This latter action may be of importance in slowing the beta-cell immune destruction in LADA. Thus far, these studies with DPP4 inhibitors have been either underpowered or not long-term. While this drug category has potential value, additional studies are needed before routinely recommending them for patients with LADA.[38][39][40][41][42]
A study using the GLP1 receptor agonist dulaglutide has shown reductions in HbA1C levels and improvement in beta-cell function in patients with LADA with results comparable to T2DM.[43]
The benefit from the addition of vitamin D to insulin or DPP4 inhibitors in improved glycemic control and preserving beta-cell function has been demonstrated in separate studies.[44][45]
Similarly, a Chinese herbal decoction combined with insulin has yielded positive results.[41]
SGLT2 inhibitors have not been well-studied in LADA. However, some case reports of euglycemic ketoacidosis have appeared. Therefore this category is not recommended.[46]
There are no studies with metformin alone in LADA, and with understandings of both the pathogenesis of LADA and the pharmacological profile of metformin, the latter has no role as a single agent for this condition.
The novel immunomodulating treatment with alum formulated recombinant human GAD65 by administering 3 injections of 4 mcg each into a lymph node in the groin along with daily oral vitamin D is in phase II of the GADinLADA trial. The study will evaluate the effects of the drug on the parameters of the beta-cell function for one year. This is based on the encouraging results from the DIAGNODE2 T1DM trial and the Diamyd LADA trial, which involved the injection of the GAD 65 formulation subcutaneously 20 mcg per dose for 2 doses one month apart. Several beneficial changes were noted in the immunological system. These included a shift of the GADA isotypes to IgG3/igG4, increased beneficial cytokines, increased FOXP3, and TGF beta, all favoring a Th2 lymphocyte response, more regulatory T lymphocytes, and downplay of activated T lymphocytes thereby promoting a state of immune tolerance. These beneficial effects were persistent even after four years.[47]
In some patients with obesity and DM, bariatric surgery (BS) is undertaken for weight loss and glycemic control. Some cases with presumed T2DM and obesity, in reality, have LADA. In such patients, BS causes successful weight loss, but inadequate glycemic control post-surgery and the remission of diabetes often seen in T2DM are absent in LADA confirming a progressive beta-cell failure. Patients with LADA have an increased post-operative risk of ketoacidosis and should be diligently watched. Some experts have even suggested screening for beta-cell function before BS to avoid disappointment with glycemic control in all obese patients with DM.
Source
1 note
·
View note
Link
Diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the inability of body to produce or respond to insulin a hormone required by body to burn glucose for energy. Type I Diabetes mellitus, also known as Insulin Dependent Diabetes mellitus is a most frequent chronic disease of childhood, afflicts 0.2-0.3% of human individuals due to auto immune destruction of insulin secreting pancreatic β cells. GAD65 is the major auto antigen in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IIDM). Thus, this project is aimed at expression of GAD65 in E. coli. GAD65 gene was cloned into pET-28a bacterial expression vector and expression was studied in BL21 DE3 cells. Different parameters of induction like isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), temperature, time interval were standardized. The recombinant clones induced with 2 μM of IPTG at 30oC for 4 h at flask level produced the protein upto 537μg/ml. Furthermore, the specificity of the purified recombinant protein was confirmed by western blot analysis using monoclonal antibodies. This work establishes a strategy in E. coli for the expression of GAD65 with optimized parameters.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Sistem Pre Order, Sudah Ada Pesanan 800 Ribu Kit
Komitmen Prof Dr drh Aulanni’am DES untuk menciptakan alat tes diabetes dini tak main-main. Setelah melewati riset puluhan tahun dan biaya besar, akhirnya ada karya anak bangsa yang akan membantu pasien diabetes yang selama ini hanya bisa dilayani dengan alat tes impor. Seperti apa proses penemuannya?
SANDRA DESI CAESARIA
Sebagai wakil rektor I Universitas Brawijaya (UB), Prof Dr drh Aulanni’am DES terbilang padat. Istirahat satu jam saja menjadi hal berharga bagi seorang pimpinan. Beruntung setelah membuat janjian, wartawan koran ini dipersilakan masuk di ruang kerjanya yang minimalis.
Tak terlihat raut lelah di wajah sang professor itu meski beberapa hari sebelumnya dia sedang berada di Jakarta. Yakni, untuk me-launching alat yang sudah mulai diproduksi bersama timnya itu.
Alat bernama Rapid Test GAD65 ini merupakan alat buatan dalam negeri pertama untuk tes diabetes dini yang telah dipatenkan dan siap diproduksi secara masal. Tentu ini bisa menjadi kabar gembira. Karena selama ini, untuk tes semacam ini, alatnya masih menggunakan buatan luar negeri.
”Selama ini problema orang yang ingin tes diabetes itu terkendala biaya. Sekali tes bisa Rp 1,8 juta dan berminggu-minggu baru tahu hasilnya,” tambahnya. Apalagi untuk bisa melakukan tes diabetes, darah pasien yang diambil sekitar 10 cc harus dikirim ke Laboratorium Singapore terlebih dahulu.
Tentu kesempatan tes diabetes sendiri akhirnya hanya bisa dilakukan oleh orang yang memiliki uang. Dengan Rapid Test GAD65, ada minimalisasi waktu. Darah yang diambil pun tak sampai 10 cc. ”Sekitar 30 menit sudah keliatan ada potensi diabetes atau tidak,” tambah Aulanni’am.
Dengan alat temuannya ini, deteksi dilakukan terhadap keberadaan autoantibodi GAD65 yang merupakan penanda dini kerusakan sel beta pankreas. Tes diambil dari serum darah dan langsung mendeteksi awal terjadinya autoimun diabetes. ”Tes ini bisa mendeteksi diabetes hingga diabetes mellitus (DM) hingga tipe 1 dan 1,5,” jelasnya.
Jika diproduksi dalam negeri, biayanya juga tidak sebesar alat dari luar negeri. ”Bisa saja pembayaran tesnya melalui Badan Penyelenggara Jaminan Sosial (BPJS), tapi itu kan kebijakan pemerintah kalau urusan itu,” kelakarnya.
Alat ini baru bisa dinikmati masyarakat sekitar tahun depan. Saat ini Rapid Test GAD65 sudah mengantongi sertifikat Produksi Alat Kesehatan serta Nomor Izin Edar Alat Kesehatan AKD dari Kementerian Kesehatan RI.
Nantinya, yang mendistribusikan dan menentukan harga alat ini adalah PT Bio Farma. ”Memang kerja samanya dengan Bio Farma. Karena membuat alat ini sangat mahal dan labnya sendiri, Bio Farma yang merancang,” tambahnya.
Aulanni’am kemudian menerawang, kembali ke masa-masa membuat Rapid Test ini. Awal mulanya, dia berkenalan dengan ahli diabetes Prof Djoko Wahono. Karena perkenalan itu, profesor yang mengenyam S-1-nya di Universitas Airlangga (Unair) Surabaya ini semakin tertantang melihat lebih dalam dunia autoimun.
”Di tahun 1998 apa 2000-an, awalnya meneliti mengenai enzim GAD65 di otak sapi. Selanjutnya, dipakai untuk publikasi Prof Djoko, lanjutlah memproduksi alat ini,” ujar sosok yang profesi kedokteran hewan-nya dituntaskan di Universitas Airlangga.
Profesor yang memiliki puluhan kucing ini, lalu mematenkan produknya pada 2008 dan dilanjutkan pada kerja sama antara UB dan PT Bio Farma pada 2013. Setidaknya, selama pembuatan alat ini, Aulanni’am menjadi ketua tim. ”Pak Presiden kebetulan ingin ada divisi pengembangan karya anak bangsa. Mungkin Bio Farma ada divisi itu. Yang produksi nanti Bio Farma,” tuturnya.
Saat ini per bulan sudah ada pesanan 800 ribu kit melalui sistem pre order (PO). Hanya, saat awal produk ini dibuat untuk pembeliannya sendiri for riset use only alias untuk kebutuhan penelitian. Alasannya, karena nomor registrasinya belum keluar. ”Belum ada izin dari Kemenkes dan data-data yang saya gunakan belum teregistrasi waktu itu,” jelas dia.
Saat ditanya harga, Prof Aul hanya tersenyum. ”Wah itu nanti menjadi urusan Bio Farma. Ya masih belum tertulis,” ujarnya. Targetnya, dari Bio Farma ada 10 juta kit yang dijual. Dia mengatakan, sempat kewalahan dengan pesanan Bio Farma.
Dalam proses riset menuju produksi alat tersebut, Prof Aul tidak bekerja sendirian. Sebagai ketua tim, dia dibantu lebih dari lima orang dalam meriset. Biaya risetnya juga tinggi, sekitar Rp 10 miliar. Untuk membantu mencapai target yang ditentukan, tim Biosains sudah meminta kepada rektor UB menambah pekerja outsourcing, terutama pada bagian packaging atau pengemasannya.
”Semoga produk awal ini bisa membanggakan sehingga penderita diabetes di Indonesia bisa berkurang. Karena sudah terdeteksi di awal sehingga bisa diatur pola makan dan gaya hidupnya agar tidak terkena diabetes. Produk ini bisa mendeteksi hingga 14 tahun ke depan,” pungkasnya.
Pewarta : *
Copy Editor : Dwi Lindawati
Penyunting : Ahmad Yani
Source : https://malangtoday.net/flash/nasional/sistem-pre-order-sudah-ada-pesanan-800-ribu-kit/
MalangTODAY
0 notes
Text
01.31.2017
True to my normal fashion, I made the update SUPER brief... 😂😂😂 #EveryDetailMatters If there is one thing I’ve learned in almost 28 years of life, it’s how to find the faintest sparkle of silver in the darkest black clouds. To some, the news I learned today will be read as bad news, but worry not! This is, indeed, good news! I haven’t yet received the official interpretation of the results, but I am confident in the knowledge I have from listening to Dr.Cline at the Cleveland Clinic and as always, researching everything myself. I have another autoimmune disorder. Let the huge, resounding, “Huh? How is this good?” be heard. When meeting with Dr.Cline last week, he made a rather bold statement. “I think it’s less of your stomach and more of your small intestine causing the motility problem. Also, the GI tract paralysis isn’t the illness, but a symptom of another autoimmune disorder.” What!? NO. That was the initial thought, but as we drove home last Wednesday, it dawned on me that this was good…VERY good. If we treat the actual problem, perhaps the symptoms will resolve. Do you follow this? We can treat an autoimmune disorder/disease when we know what it is. Like Crohn’s Disease, if properly treated, it can go into remission. So, what if we treat this underlying disorder properly and my digestive system follows suit and begins to function again?! What if, like Crohn’s Disease, I just have periods of relapse and remission!? What if these remission periods occur simultaneously and I’m able to eat again….not just anything…PIZZA!?!!?🍕🍕🍕 How do I know that this may be the answer? Dr.Cline ordered so many blood tests that the nurse at the infusion clinic was careful to measure everything just right since I'm running low on RBCs & HGB right now. The one test that he specifically talked about, Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase (GAD65), was the one he was curious to see. This number would, as he said, determine the autoimmune theory. These antibodies are also present in people with diabetes, but I am not diabetic or "pre-diabetic". The reference range for this specific test should be less than 5. I learned today that mine is 77.1. Yep. Seventy seven point one. 😳 If I'm correct, I will ultimately be diagnosed with generalized autoimmune dysautonomia. The course of treatment, I believe, will not be too far from what I'm already doing. For the Crohn's Disease, I'm currently receiving ivig every other week, dosed according to ideal body weight. My understanding is that my dose will be bumped to 400mg/kg weekly. Initially, we set this to only be a 12 week course, but given the new info, I assume this will be a long-term change. The challenge will be insurance, per usual. I've got this, though. In the words of Pat Benatar, "Put up your dukes! Let's get down to it!" Typically, I would say that I KNOW I'm right because I do actually know a thing or two about this stuff, but I am not familiar with much of what was ordered. (If you know me, you know I don't like to admit I'm capable of mistakes.😜)I've been reading up on everything today & I'm feeling confident that we have found the potential source of the problem. I spoke with the nurse in Cleveland this afternoon & she informed me that some of the tests ordered will take up to a month to receive results. It's still a waiting game, but some primary pieces of the puzzle are starting to fall into place! Thank you for the prayers, love, support, & all that good stuff! The best part of my day was telling the people dearest to me this news. The first person was my aunt Lisa. ❤ ...& now you know. I am so very hopeful!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings of 36 Adult Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Related Articles
Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings of 36 Adult Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Brain Sci. 2020 Jun 08;10(6):
Authors: Runge K, Tebartz van Elst L, Maier S, Nickel K, Denzel D, Matysik M, Kuzior H, Robinson T, Blank T, Dersch R, Domschke K, Endres D
Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties with social interaction, repetitive behavior, and additional features, such as special interests. Its precise etiology is unclear. Recently, immunological mechanisms, such as maternal autoantibodies/infections, have increasingly been the subject of discussion. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) investigations play a decisive role in the detection of immunological processes in the brain. This study therefore retrospectively analyzed the CSF findings of adult patients with ASD. CSF basic measures (white blood cell count, total protein, albumin quotient, immunoglobulin G (IgG) index, and oligoclonal bands) and various antineuronal antibody findings of 36 adult patients with ASD, who had received lumbar puncture, were compared with an earlier described mentally healthy control group of 39 patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. CSF protein concentrations and albumin quotients of patients with ASD were significantly higher as compared to controls (age corrected: p = 0.003 and p = 0.004, respectively); 17% of the patients with ASD showed increased albumin quotients. After correction for age and gender, the group effect for total protein remained significant (p = 0.041) and showed a tendency for albumin quotient (p = 0.079). In the CSF of two ASD patients, an intrathecal synthesis of anti-glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) antibodies was found. In total, more of the ASD patients (44%) presented abnormal findings in CSF basic diagnostics compared to controls (18%; p = 0.013). A subgroup of the patients with adult ASD showed indication of a blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and two patients displayed an intrathecal synthesis of anti-GAD65 antibodies; thus, the role of these antibodies in patients with ASD should be further investigated. The results of the study are limited by its retrospective and open design. The group differences in blood-brain barrier markers could be influenced by a different gender distribution between ASD patients and controls.
PMID: 32521749 [PubMed]
via pubmed: autism https://ift.tt/3fkCARc
0 notes
Text
Total triterpenes extracted from P. cocos possessed potential antiepileptic properties.
PMID: Pharm Biol. 2016 Nov ;54(11):2528-2535. Epub 2016 May 9. PMID: 27159135 Abstract Title: Antiepileptic activity of total triterpenes isolated from Poria cocos is mediated by suppression of aspartic and glutamic acids in the brain. Abstract: CONTEXT: Triterpenes from Poria cocos Wolf (Polyporaceae) have been used to treat various diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. However, the antiepileptic effects and mechanism are not fully understood.OBJECTIVE: The objective of this study is to investigate the antiepileptic properties of total triterpenes (TTP) from the whole P. cocos.MATERIALS AND METHODS: The ethanol extract TTP was identified by HPLC fingerprint analysis. Male ICR mice were gavaged (i.g.) with TTP (5, 20, 80 or 160 mg/kg) or reference drugs twice a day for 7 d. Antiepileptic activities of TTP were evaluated by maximal electroshock (MES)- and pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures in mice for 30 and 60 min, respectively. Locomotor activity and Rota-rod tests were performed for 60 min and 5 min, respectively. The levels of glutamic acid (Glu), aspartic acid (Asp), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine (Gly) in convulsive mice were estimated. The chronic epileptic model of Wistar rats was built to measure expressions of glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) and GABAin rat brain after TTP treatment.RESULTS: The LCof TTP (i.g.) was above 6 g/kg. TTP (5-160 mg/kg) protected mice against MES- and PTZ-induced convulsions at 65.0% and 62.5%, respectively, but have no effect on rota-rod treadmill; TTP (20-160 mg/kg) significantly reduced the locomotor activities, shortened the onset of pentobarbital sodium-induced sleep; TTP decreased Glu and Asp levels in convulsive mice, but increased the GAD65 and GABAexpressions in chronic epileptic rats at doses usage.DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: TTP extracted from P. cocos possessed potential antiepileptic properties and is a candidate for further antiepileptic drug development.
read more
0 notes
Text
Alat Pendeteksi Potensi Diabetes Melitus
Alat Pendeteksi Potensi Diabetes Melitus
Setelah melakukan riset panjang sejak 1998, periset Universitas Brawijaya Malang, Jawa Timur meluncurkan alat Biosains Rapid Test GAD65 untuk mengetahui potensi diabetes melitus pada tubuh manusia.
(more…)
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Cancers : les inhibiteurs de checkpoint associés à des complications neurologiques rares mais potentielles graves
Les immunothérapies par inhibiteurs de checkpoint dans le traitement de cancers sont associées à des complications neurologiques rares mais potentiellement graves, comme des neuropathies, des troubles neuromusculaires et des encéphalopathies, selon plusieurs communications faites au congrès de l'American Academy of Neurology (AAN) la semaine dernière à Philadelphie.
L'usage croissant des immunothérapies dans le traitement des cancers souligne l'importance de diagnostiquer rapidement et précisément les effets indésirables associés, notamment neurologiques car ils peuvent avoir des présentations atypiques, indiquent Divyanshu Dubey de la Mayo Clinic à Rochester et ses collègues du Massachusetts General Hospital à Boston dans le résumé de leur communication orale.
Dans leur étude, ils ont voulu décrire le spectre clinique, la prise en charge et l'évolution des effets indésirables neurologiques associés aux inhibiteurs de checkpoint à partir du registre des patients pris en charge au Massachusetts General Hospital entre 2011 et 2017.
Parmi 1.851 patients, 28 ont développé des effets indésirables neurologiques de grade 3 (interférant avec les activités de la vie quotidienne comme la toilette) ou de grade 4 (menaçant le pronostic vital et nécessitant une intervention urgente), soit un taux de 1,5%.
Ces patients étaient traités par inhibiteur de checkpoint pour un mélanome (21 patients), un adénocarcinome (5 patients), un carcinome rénal (1 patient) et un lymphome de Hodgkin (1 patient).
Le taux des effets indésirables neurologiques était significativement plus élevé avec les anti-CTLA-4 seuls (2,8%) ou en association avec un anti-PD-1 (2,7%) par rapport à un anti-PD-1 en monothérapie (0,8%). La plupart des effets indésirables (68%) sont survenus au cours des cycles 1 à 4 de traitement.
Des troubles à médiation immunitaire touchant le système nerveux central ont concerné 9 patients dont 3 avaient aussi des neuropathies périphériques à médiation immunitaire et un autre, une myosite. Des neuropathies immuno-médiées et des myosites avec ou sans troubles de la fonction neuromusculaires ont été retrouvées chez respectivement 13 et 10 patients.
L'administration de corticoïdes par voie orale ou intraveineuse était associée à une évolution favorable (76% vs 24% sans corticoïdes).
Sept patients ont présenté une récidive de leurs troubles neurologiques, le plus souvent en raison d'un nouveau cycle de traitement (86% vs 14% sans nouveau traitement).
Dans une autre communication orale, Lauren Reoma du National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS, dépendant des NIH américains) et ses collègues ont rapporté 16 effets indésirables neurologiques survenus chez 11 patients traités par inhibiteur de checkpoint pour des cancers génito-urinaires métastatiques ou des cancers du poumon non à petites cellules.
Ces effets indésirables sont survenus dans un délai médian de 4,4 mois (entre 0,5 et 12 mois); ils étaient de grade 3 pour 5 sur les 16 cas, de grade 2 pour 8 et de grade 1 pour les deux derniers (un cas non renseigné). Sur ces 16 cas, 13 ont été considérés en lien avec le traitement de manière possible, probable ou définitive.
Parmi les 7 cas considérés comme des effets indésirables certains, 5 sont survenus avec une combinaison thérapeutique, observent les auteurs.
Parmi ces troubles, les chercheurs citent notamment un patient recevant du nivolumab (Opdivo*, Bristol-Myers Squibb et de l'ipilimumab (Yervoy*, BMS) a développé une encéphalite limbique auto-immune à l'IRM avec une pléïocytose lymphocytaire et une paralysie progressive du sixième nerf crânien; un autre sous nivolumab a développé une méningite aseptique avec un léger signal leptoméningée à l'IRM et une pléïocytose lymphocytaire; un autre encore a développé des infarctus emboliques centraux sous CV301 (Bavarian Nordic), une immunothérapie anti-CEA et MUC1 associée au nivolumab; un patient sous durvalumab (Imfinzi*, AstraZeneca) + olaparib (Lynparza*, AstraZeneca/Merck & Co).
Sur ces 11 patients, 5 ont dû arrêter le traitement.
Dans un poster, une équipe de la faculté de médecine Yale à New Haven rapporte une analyse rétrospective de 18 cas, avec une incidence plus élevée des effets indésirables neurologiques chez les patients sous combinaison thérapeutique.
Dans cette cohorte, l'inhibiteur de checkpoint a été arrêté pour tous les patients, 16 ont répondu à un traitement par corticostéroïdes et 9 ont reçu d'autres traitements (immunoglobulines, hormones). Cinq patients ont totalement récupéré, 11 de manière partielle et deux autres ont conservé des séquelles, selon le résumé.
Des encéphalopathies, des symptômes oculaires
Parmi les autres posters présentés figurent également une série de cas d'encéphalopathie et un cas d'encéphalite limbique avec en particulier l'association ipilimumab + nivolumab.
Dans le résumé de leur poster, une équipe de l'université du Nebraska à Omaha rapporte 5 cas d'encéphalopathie chez des patients traités par nivolumab, ipilimumab ou pembrolizumab (Keytruda*, Merck & Co). Ils ont développé un état confusionnel, des convulsions ou une dyskinésie dans un délai de 13 jours en moyenne (entre 3 et 27 jours) après l'initiation du traitement.
L'imagerie cérébrale n'était pas parlante alors que l'électro-encéphalogramme (EEG) mettait en évidence un ralentissement généralisé de l'activité cérébrale. Tous les patients se sont par la suite détériorés et son décédés, notamment deux qui avaient montré une amélioration transitoire après corticothérapie.
Le cas décrit sous ipilimumab + nivolumab serait le premier cas d'encéphalite limbique auto-immune à anticorps anti-GAD65 (dirigés contre le récepteur du glutamate décarboxylase), à la connaissance des chercheurs de l'University of South Florida et Moffitt Cancer Center à Tampa.
Cette femme de 36 ans a développé des troubles cognitifs après son troisième cycle de traitement, un ralentissement des fréquences delta à l'EEG et un taux élevé d'anti-GAD65 à la ponction lombaire. Elle a été traitée avec succès par immunoglobulines par intraveineuse (IgIV) puis échange plasmatique.
Des chercheurs de Cleveland rapportent dans un poster une série de 4 cas de symptômes oculaires parmi les divers troubles neurologiques pouvant survenir avec des inhibiteurs de checkpoint. Trois de ces patients avaient aussi une dyspnée, une dysphagie ou une faiblesse proximale.
Parfois ces symptômes oculaires représentent parfois un trouble de la jonction neuromusculaire mais peuvent aussi correspondre, comme dans ces 4 cas, à une myosite, une neuropathie démyélinisante ou une métastase au niveau de l'orbite, ce qui implique une prise en charge adaptée, selon le résumé du poster.
Parmi les autres cas et séries rapportés figurent par ailleurs des myéloradiculonévrites, des polyradiculoneuropathies, des myopathies, des myosites, des myasthénies ainsi que des syndromes paranéoplasiques.
0 notes
Text
Kit Diagnostik Diabetes Melitus Siap Di Produksi Masal
Kit Diagnostik Diabetes Melitus Siap Di Produksi Masal
Kit Diagnostik Diabetes Melitus Siap Di Produksi Masal Kit Diagnostik DiabetesMelitus GAD65, merupakan salah satu produk unggulan dari laboratorium Biosains Universitas Brawijaya Malang tengah memasuki izin produksi dan izin edar. “Produksi kita sudah siap tinggal perizinannya,” kata Ketua Tim Peneliti Prof. Dr. Aulanni’am, DVM, DES. yang juga Dekan Fakultas Kedokteran Hewan dirilis Humas…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
One of my coresidents sent this in a group message:
DM Type I testing:
Pancreatic autoantibodies:
GAD65 (glutamic acid decarboxylase 65),
IA2 (the 40K fragment of tyrosine phosphatase),
insulin,
ZnT8 (zinc transporter 8)
Insulin/c-peptide testing
T1DM, levels of fasting insulin and C-peptide are inappropriately low relative to the concomitant plasma glucose concentration (ie, low or in the normal range despite hyperglycemia). By contrast, high fasting insulin and C-peptide levels suggest T2DM.
Per UTD
1 note
·
View note