#How to install java in windows 10
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

It's here! Our newest product - VOXEJI !
If you don't know, a shimeji is a program where a character roams around your computer screen (in this case, it's our lovely Vox)
If you already know how to download them, here's the link:
https://www.mediafire.com/file/mmcj5k9riqe3lph/Vox_Shimeji.zip/file
Otherwise, see below for install instructions!
You need:
Java
Windows 10 or 11 (may work on other OSes, not tested)
Instructions:
1. Click the link above, and hit download 2. Find Vox Shimeji.zip in your downloads > right click > extract all > extract 3. You should now have a file called Vox Shimeji - open it, then open the Vox folder 4. Double click shimeji-ee.jar or shimeji-ee.exe 5. His little Voxtek logo should appear at the bottom right of the screen. On Windows 11, it might be inside the little ^ menu 6. A moment later, he should fall onto the screen! Right click him for more options or just let him run around
Edit: If the icon appears but Vox doesn't, please try this download link instead! https://www.mediafire.com/file/dy5ric3qa07h9yd/Vox_V2.zip/file
If you encounter any trouble, message me and I'll help fix it!
448 notes
·
View notes
Text
Custom Disc Installation Guide for Hermitcraft Season 9
I've seen a lot of people struggle with specifically the custom discs, so I made a guide on how to install the mods! It was originally posted as a twitter thread, along with a guide on how to get the world download.
How to install the Custom Discs mod for Decked Out / Hermitcraft 9 world download. Note: I'm assuming you already have the world installed. If you don't know how to do that, you can follow my previous guide here.
1) Follow this link https://oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/#jdk17-windows…
2) Scroll down and download the "x64 Installer" (or whatever is more convenient for you).
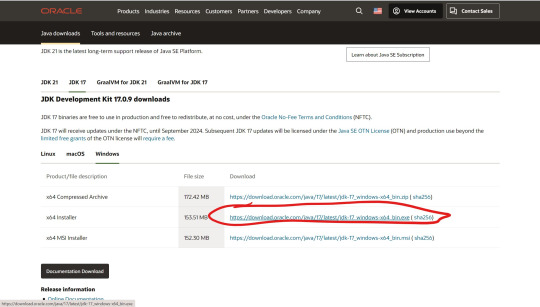
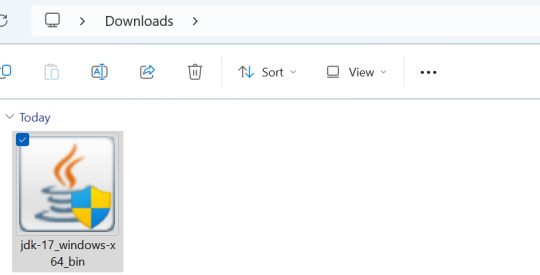
3) Open your Downloads folder and double click - you may need to right click and "Run as Administrator" if it's not working. Then, click Yes and install the program.
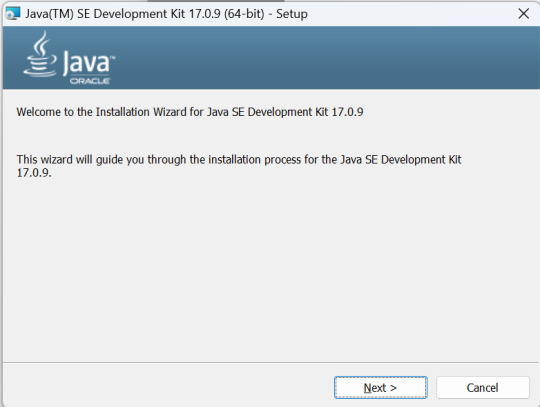
4) The installation software should then open. Just follow the instructions and press Next, Next, and then Close.
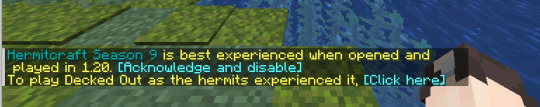
5) Open up the Hermitcraft world download. You may have seen the "To play Decked Out as the hermits experienced it..." message in chat. Click on "[Click here]".
6) Press the first link ("Hermitcraft runs on Fabric [link]")
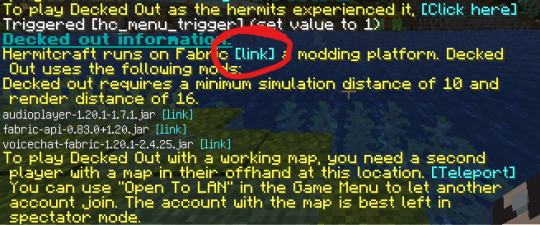
7) Press the download button, then Download for Windows

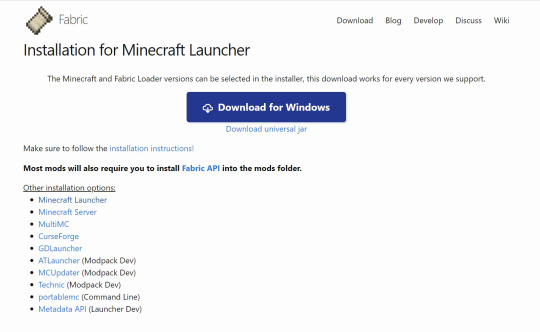
8) Double click the fabric-installer to open.

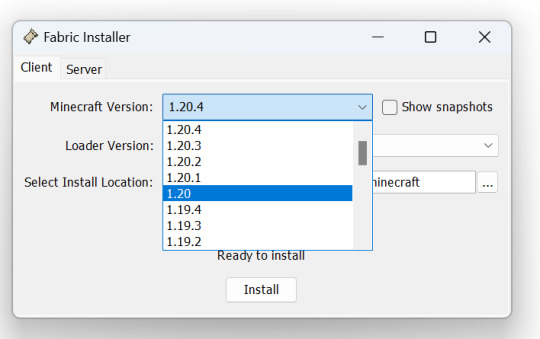
9) MAKE SURE THE VERSION IS 1.20! Leave everything else as their defaults. Make sure "Create Profile" is checked. Then, press "Install". - If you can't install, open your normal Minecraft launcher and run 1.20, then close Minecraft.
10) Go back to the Hermitcraft world and download the other three mods. Make sure you download all three of them!
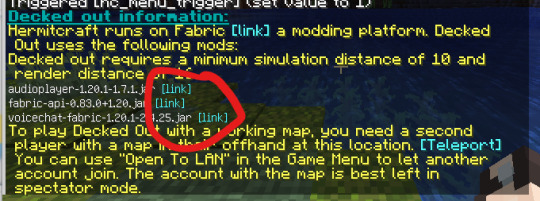
11) Open your Minecraft Launcher and go to Installations. You should see "fabric-loader-1.20". Hover over it and press the folder icon on the right hand side

12) Open the "mods" folder. If you don't have one, create a new folder and name it "mods" (no capitals or punctuation)
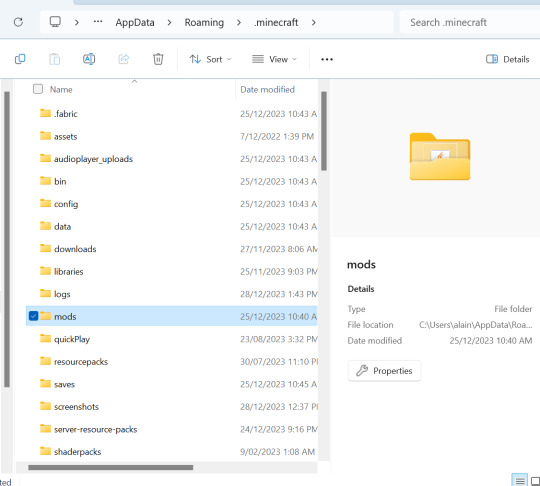
13) Drag and drop the three mods you just downloaded into the "mods" folder.
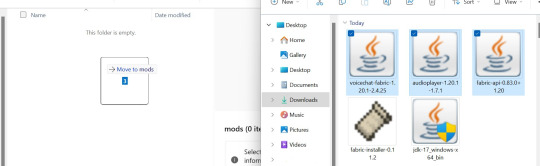
14) Close Minecraft, and then press "Play" on the Fabric installation

Open Singleplayer, and then your hermitcraft world, and everything should be in working order! To get to Decked Out, you can either visit by the Nether Hub (DO is East/Red 2), or teleport by: /tp -523 103 2171

If you have any issues, feel free to reblog / comment with your problem (with a screenshot of your issue if you have one) and I'll be happy to help.
Good luck, and happy running!
#istg it's an entirely different experience when you get the custom sounds working it's like. amazing#hermitcraft#hermitcraft season 9#hermitcraft world download#decked out 2#scarland#sorry for clogging the tags these are just the two most sound-based experiences i've seen people struggle with#strbylmn posts
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
I work for insane people
So… I started work a few months ago and...
I keep being impressed with corporations lowering my expectations.
Like. EVERY time I think "Surely, this is as incompetent as it gets".
The boss is nice, the workers are nice, every PERSON is great so far. But the firm is just… fucked in ways that makes it hard to not scream with laughter.
It is like working in the ministry of silly walks by Monty Python. Insane things are happening, and everyone just acts like it is normal.
A dude was stating to someone else near me, that despite the costumers saying they did not want it, his code that crashed the application once a day, was NECESSARY, because writing code without memory leaks in C is basically impossible. Like… I just have all these small moments of insanity. Completely disconnected from each-other
My boss showing me and the other 3 new hires the coffee room, where a big screen proudly shows that not a single software product have 100% code coverage… as in, not a single person in this entire building filled with software people knows how code coverage works. He then points out an empty bowl, and declares "Twice a week, there is a fruit event". By which he means, fresh fruit is provided, and people can just grab some…. just said by a alien who is pretending to be human. Badly.
He then explained that the 2 coffee machines in here makes bad coffee. He then takes us to the copy room, showing us that THIS is where the GOOD coffee machine is. Which only takes coffee beans from a SPECIFIC vendor (Is… is the coffee machine… sponsored????)
He briefly pets the Foosball table (Again, in the copy room), which is jammed up against the wall so you can only reach the controls on one side ( Because, again, it is a copy room, and there is not enough space for it ) and he exclaims "Ahhhh… Not enough people are using this"
Suggesting, that he is trying to promote the little known sport "Single-player Foosball">
I start setting up my work PC and... Whenever any of the developers in this place wants to install things on their PC's, including compilers and testing frameworks, they have to either use the "SOFTWARE CENTER" program, which installs it FOR you… or in 10% of the cases, fails, without giving you any context for why it did that, and no tools for fixing it. Is it missing a dependency? Not working with the OS? Who knows!
Some programs cannot be installed like this though, because the SOFTWARE CENTER is not updated a lot. And when you want to install something the normal way… You get a popup, where you must provide a written explanation for why you need to have temporary admin rights to your own dang PC … you then submit that, and your screen will then be watched remotely by a worker from India, for a varied amount of time you are not told…
Or at least it says so. Maybe the Indian dude watching me is just an empty threat. Who knows. But they get to see me running absolutely… BONKERS .bat files
Like, I CHECKED them, and a good 80% of them calls a Power-Shell script in the folder above it, called "YES_OR_NO.ps1" which opens a windows 95 window informing you that DURING INSTALLATION YOU MAY NOT USE THE KEYBOARD OR MOUSE, AS IT MAY DISTURB THE SCRIPT THAT WILL INSTALL THE PROGRAM. A normal installation wizard then runs, except the developers are not trusted to click the buttons, and instead the script does it for you by moving and clicking the mouse.
All of this is documented. In markdown like reasonable people? Of course not! It is in ENHANCED markdown. Which is markdown in the same way javascript is java.
ENHANCED markdown requires browser and visual studio code extensions to be read. Completely missing the point of markdown being readable both raw and encoded… And sometimes word documents And sometimes power-point presentations left next to another bat file… this one calling the .exe file… right next to it…. I later found out is because the idea USED to be that all documentation MUST be made with Microsoft office tools.
I had to read the code of conduct today. And it was actually very well written.
I then watched a interactive animation telling me about the code of conduct… which it not only got a fact wrong about, it also broke it once.
I repeat. The introductory course in the code of conduct… broke the code of conduct'
After I watched that, and read the safety material…. which literally just said "Wear safety boots in the production floor"… I was then show the testing room.
I was lead to a different building, saying hello to the Vice CEO who was walking the other way, we walk into the production floor, ignored the fact that none of us have safety boots on, and walks into a room, with a 3*2 meter wide machine, several meters tall.
We edge around it, quietly hoping no one turns it on, since we would get slammed by it if they did, and walk down some stairs into the basement. Casually walk over a small river in the floor from a pipe that is leaking… what I really hope is water, and over to a shelf rack FILLED with the most MacGyver shit you ever did see.
Including, but not limited to, the 3D printed plastic block, with a piston that repeatedly smacking half a aluminum nameplate over the device it is testing. You see, it is a capacitance button, and it is testing it by simulating a human finger pressing it many thousands of times, a saws off antenna which is the end of a cable that is attached to it via a nice thick bolt, so it can send fake signals into it.
And of course the 24 volt, 5 amp system that is turning a circuit board on and off again, until it will crack.
We walk back out, remembering to step over the small river, which never even got a comment, and walk back to my department It is SO great. It is like working in the ministry of silly walks by Monty Python Like… Do I think I can bring value to this company? Like, making it better and more efficient? Yes. It would be hard not to!
And his is the largest pump manufacturer in the world! A super serious company with 4 billion dollars of revenue a year. And it is just… a NUTHOUSE
Like… NEVER believe the myth that corporations are competent.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Install
Looking for easy, step-by-step guides on how to install everything from software to home devices? Our "How to Install" blog provides clear, beginner-friendly instructions to help you get things up and running without the hassle. Whether you're setting up a new app, assembling tech gadgets, or configuring tools, we simplify the process for you. Each post is written with accuracy and user convenience in mind.
How to Install How to Install Printers Without CD How to Install Webcam Drivers How to Install SSH How to Install Pixelmon How to Install OptiFine How to Install Fabric How to Install Zend Framework with XAMPP on Windows How to Install Roblox on Chromebook How to Install Roblox Studio How to Install Firefox on Mac How to Install Firefox on Linux How to Install Firefox on Windows How to Install Java Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners How to Install Java on Mac Follow Full Process Ultimate Guide How to Install Java for Minecraft Easy Step Guide for How to Install VPN for Privacy How to Install VPN Server Virtual Private Network How to Install VPN on Router A Step-by-Step Guide : Complete Guide for How to Install Anaconda How to Install Anaconda on Linux Complete Guide How to Install Anaconda on Mac: A Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Anaconda on Ubuntu: A Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Anaconda on Windows How to Install npm A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners How to Install npm on Ubuntu Step-by-Step How to Install NVM on Ubuntu Tips, and Explanations How to Install npm on Windows Solve Common Issues How to Install NVM on Windows Troubleshooting Tips How to Install npm on Visual Studio Code How to Install Node.js on Your Machine How to Install Node.js on Linux Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Node.js on Mac Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Node Modules on Angular How to Install Node.js on Ubuntu The Latest Version How to Install Node.js on Windows Get started Full Method How to Install APK File on Your Android Device Complete Guide on How to Install APK on Android TV How to Install APK on Chromebook Step by Step Process How to Install APK on iOS A Comprehensive Guide How to Install IPA on iPhone A Complete Guide How to Install APK on Windows 10 Complete Guide How to Install Git A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners How to Install Git Bash A Complete Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Git on Visual Studio Code How to Install GitHub Simple Step-by-Step Process How to Install Git on Mac Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Git on Linux A Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Git on Ubuntu Step-by-Step Guide How to Install Git on Windows A Simple Guide How to Install Docker How to Install Docker on Linux How to Install Docker on Mac How to Install Docker Daemon Mac How to Install Docker on Ubuntu How to Install Docker Compose on Ubuntu 20.04 How to Install Docker Compose on Windows How to Install Docker on Windows How to Install WordPress How to Install WordPress on Ubuntu How to Install WordPress Plugins How to Install WordPress on Windows 10 How to Install Kodi on Firestick How to Install Exodus on Kodi How to Install The Crew on Kodi How to Install XAMPP on Mac
0 notes
Text
AOSP Architecture Explained: A Practical Guide for Android Developers
In this blog, we delve into the architecture of the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), breaking down each layer of the software stack. From the Linux Kernel to Applications, we explore the functionalities and responsibilities of each component. Whether you're customizing ROMs or developing hardware-specific solutions, understanding the AOSP architecture is crucial.
The Android Open Source Project (AOSP) serves as the foundation for the Android operating system, offering a comprehensive software stack that enables developers to create a consistent user experience across various devices. Understanding the AOSP architecture is essential for developers aiming to build custom Android builds or integrate deeply with system components.
Overview of the AOSP Software Stack
The AOSP software stack is organized into several layers, each responsible for specific functionalities:
Linux Kernel: At the base, the Linux Kernel manages core system services such as process management, memory management, and hardware drivers. It acts as an abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack.
Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL): HAL provides standard interfaces that expose device hardware capabilities to the higher-level Java API framework. This allows Android to be agnostic about lower-level driver implementations.
System Services and Daemons: These are background processes that provide core system functionalities like power management, telephony, and media playback. They facilitate communication between the HAL and the Android Runtime.
Android Runtime (ART): ART is the managed runtime used by applications and some system services. It includes a set of core libraries and handles tasks like memory management, garbage collection, and bytecode execution.
System APIs: These APIs provide the necessary interfaces for applications to interact with the underlying hardware and system services, enabling functionalities like location services, telephony, and sensor management.
Android Framework: The framework offers a rich set of APIs that developers use to build applications. It includes components like Activity Manager, Window Manager, and Content Providers, which manage the user interface and application resources.
Applications: At the top layer, applications include both native apps provided by the device manufacturer and third-party apps installed by users. These apps interact with the Android Framework to perform their functions.
Importance for Developers
Understanding the AOSP architecture is vital for several reasons:
Customization: For developers building custom ROMs or tailoring Android for specific hardware, knowledge of each layer allows for effective customization and optimization.
Performance Optimization: Identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks requires a deep understanding of how different layers interact and where potential issues may arise.
Scalability: Proper utilization of the Android Framework and System APIs ensures that applications are scalable and maintain compatibility across various devices and Android versions.
Security: Awareness of the interactions between privileged and system-level components is crucial for developing secure applications and protecting user data.
Conclusion
The AOSP software stack is a meticulously designed architecture that harmonizes hardware and software components to deliver a seamless user experience. For developers, mastering this architecture is key to unlocking the full potential of Android, whether it's for application development, system customization, or hardware integration.
If you're looking to leverage AOSP for your projects, consider partnering with industry leaders like Silicon Signals. Recognized among the top 10 BSP and AOSP service companies, Silicon Signals offers expert services in Android BSP development, custom Android solutions, and more. Their team excels in delivering tailored solutions that meet the evolving demands of the industry. Silicon Signals
Ready to bring your Android project to life? Reach out to Silicon Signals at [email protected] for a free consultation.
#embeddedtechnology#embeddedsoftware#embeddedsystems#linux kernel#androidbsp#linuxdebugging#android#aosp#androidopensource
0 notes
Text
Difference Between Java and JavaScript
When it comes to programming, Java and JavaScript are two of the most widely used languages. Despite their similar names, they are quite different in terms of functionality, usage, and even underlying principles. This often leads to confusion among beginners who may assume that the two technologies are related. However, understanding the differences between Java and JavaScript can give developers the clarity they need to decide which tool is best suited for their specific needs.
In this blog, we will explore the key differences between Java and JavaScript by discussing their features, syntax, platforms, and use cases. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of when and why to use each of these languages.
1. What is Java?
Java is a powerful, object-oriented programming (OOP) language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). It was first released in 1995 and is designed to be a platform-independent language that allows developers to "write once, run anywhere." This means that Java code can be written on one platform (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux) and run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) installed. The JVM translates the compiled Java bytecode into machine-specific code, making it platform-independent.
Java is primarily used for developing standalone applications, large enterprise systems, Android applications, and server-side applications. It’s known for its stability, scalability, and performance.
2. What is JavaScript?
JavaScript, on the other hand, is a lightweight, interpreted scripting language that was created for web development. Originally designed to run in web browsers, it allows developers to create dynamic and interactive elements on websites. JavaScript was created by Brendan Eich at Netscape Communications in 1995 and has since evolved into one of the most important languages in web development.
JavaScript is a client-side language, which means it runs in the browser, but it can also be used on the server side through Node.js. Unlike Java, JavaScript is not a strictly object-oriented language; it supports multiple programming paradigms such as procedural, functional, and event-driven programming.
3. Syntax Differences Between Java and JavaScript
One of the most noticeable differences between Java and JavaScript lies in their syntax. While they may share some similar constructs (like curly braces for code blocks), the syntax rules and programming paradigms they follow are quite different.
Java is a statically-typed language, meaning that you must declare the type of variable before using it. For example:javaCopyint number = 10; String message = "Hello, World!"; The types (like int and String) must be specified and can’t be changed once the variable is declared.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is dynamically typed. This means you do not have to specify the type of the variable before using it, and the type can change as the program runs. For example:javascriptCopylet number = 10; let message = "Hello, World!"; Here, the type of number and message is determined dynamically at runtime.
4. Compiling vs. Interpreting
Another significant difference between Java and JavaScript is how they are executed.
Java is a compiled language. This means that Java code is first written and then compiled into bytecode by a Java compiler. The bytecode is platform-independent and can be run on any device that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This provides portability and allows Java applications to run across different systems without modification.Steps in Java Execution:
Write Java source code (.java file).
Compile the code using a Java compiler, which converts it into bytecode (.class file).
The bytecode is then executed by the JVM.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is an interpreted language, which means the code is executed line-by-line by an interpreter (usually within a web browser). The JavaScript engine in a browser reads the JavaScript code, interprets it, and executes it in real-time.Steps in JavaScript Execution:
Write JavaScript code (.js file).
The code is directly interpreted and executed by a web browser or JavaScript runtime environment like Node.js.
5. Execution Environment
Java and JavaScript also differ greatly in terms of their execution environments:
Java is typically used for building standalone applications that run on the JVM. These applications can be anything from mobile apps (Android) to large-scale enterprise applications or even desktop software.
JavaScript, on the other hand, is designed for web development. It is mostly used to create dynamic web pages, handle user interactions, and perform client-side tasks. JavaScript code runs within a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) and can also run on the server side through Node.js.
6. Object-Oriented vs. Multi-Paradigm
Java is primarily an object-oriented programming (OOP) language, which means it is based on the principles of encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. Java focuses heavily on classes and objects, and most Java programs are organized around these core concepts.
JavaScript, however, is a multi-paradigm language. While it can support object-oriented programming (OOP) through prototypes, it also supports functional programming and event-driven programming. JavaScript uses prototypes for inheritance rather than classes (though modern JavaScript has introduced classes, they are syntactic sugar over prototypes).
7. Memory Management
Both Java and JavaScript have automatic memory management, but they handle it differently:
Java uses garbage collection to automatically manage memory. The JVM’s garbage collector automatically frees up memory that is no longer in use. Java also allows developers to manually control memory management through various memory allocation techniques.
JavaScript also uses garbage collection for memory management, but since JavaScript runs in a single-threaded environment (in the browser), memory management is typically more lightweight and less complex compared to Java.
8. Use Cases
The primary use cases for each language highlight their distinct roles in the software development landscape.
Java:
Enterprise Applications: Java is often used in large-scale business systems due to its scalability, robustness, and extensive libraries.
Mobile Development: Java is the official language for Android app development.
Backend Systems: Java powers many server-side applications, particularly in environments that require high performance.
Embedded Systems: Java is used in various embedded systems due to its portability and efficiency.
JavaScript:
Web Development: JavaScript is essential for front-end web development, enabling dynamic and interactive web pages.
Backend Development: With the rise of Node.js, JavaScript can also be used on the server side to build web servers and APIs.
Mobile Apps: JavaScript frameworks like React Native and Ionic allow developers to create mobile applications for both iOS and Android.
Game Development: JavaScript is increasingly used in building browser-based games or game engines like Phaser.js.
9. Performance
Performance is another area where Java and JavaScript differ significantly.
Java generally performs better in comparison to JavaScript because it is a compiled language. The compiled bytecode is optimized by the JVM and can be executed more efficiently. Java is well-suited for large-scale applications that require high performance.
JavaScript is typically slower than Java due to its interpreted nature and the overhead involved in real-time interpretation. However, JavaScript has made significant strides in performance, especially with modern engines like V8 (used in Google Chrome and Node.js), which optimize execution.
10. Learning Curve
Java can be more difficult to learn for beginners because it’s a statically-typed language with a focus on OOP principles. The syntax and structure are more complex, and it requires understanding various programming concepts such as classes, interfaces, and inheritance.
JavaScript is often considered easier to learn, especially for web developers, because it is dynamically typed and has a simpler syntax. Additionally, JavaScript is very forgiving with variable types, making it easier to experiment with code.
Conclusion
While Java and JavaScript have similar names, they are fundamentally different languages with different uses, execution models, and ecosystems. Java is a versatile, platform-independent, and high-performance language primarily used for backend applications, mobile development, and large-scale enterprise solutions. JavaScript, on the other hand, is a lightweight, interpreted language that powers the dynamic, interactive elements of the web.
Choosing between Java and JavaScript depends on the specific needs of your project. If you are working on a web-based application or interactive front-end elements, JavaScript will be the way to go. If you are building complex back-end systems, enterprise software, or mobile apps, Java might be more appropriate. Both languages are crucial in their own domains, and mastering them can open up a world of development opportunities.
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Timeline for Learning Selenium: From Beginner to Pro
Selenium is one of the most sought-after tools for web automation testing, making it a valuable skill for software testers and developers. Whether you’re starting from scratch or looking to enhance your existing knowledge, this timeline will guide you from a beginner to a Selenium pro. By following this structured approach, you’ll gain proficiency in Selenium within a realistic time frame. If you want to advance your career at the Selenium Course in Pune, you need to take a systematic approach and join up for a course that best suits your interests and will greatly expand your learning path.

Week 1: Lay the Foundation
Days 1–2: Learn the Basics Before diving into Selenium, ensure you have a solid understanding of:
Programming Fundamentals: Focus on Python, Java, or C#. Python is often the easiest for beginners. For those looking to excel in Selenium, Selenium Online Course is highly suggested. Look for classes that align with your preferred programming language and learning approach.
HTML, CSS, and DOM: Understand how web pages are structured, including tags, attributes, and the DOM.
If you’re entirely new to programming or web technologies, spend a few extra days mastering these essentials.
Days 3–7: Setting Up and Exploring Selenium
Install Selenium: Set up Selenium WebDriver and a browser driver like ChromeDriver.
First Script: Write your first script to open a webpage and automate basic tasks like clicking buttons and filling forms.
Locators: Master identifying web elements using locators like id, name, class, XPath, and CSS Selectors.
Waits: Understand implicit and explicit waits to handle page load times.
By the end of Week 1, you should be comfortable with basic web automation tasks.
Week 2: Building on the Basics
Days 8–10: Interacting with Advanced Elements
Automate dropdowns, checkboxes, and radio buttons.
Handle pop-ups and alerts with Selenium.
Days 11–13: Navigating Frames and Windows
Learn how to switch between iframes and browser windows or tabs.
Practice using real-world websites with multiple frames and pop-ups.
Day 14: Data-Driven Testing
Integrate data-driven techniques to test multiple scenarios by reading data from files like Excel or CSV.
By the end of Week 2, you’ll be skilled at handling complex elements and data-driven testing.
Week 3: Tackling Real-World Scenarios
Days 15–17: Organize Code with POM
Implement the Page Object Model (POM) to make your test scripts reusable, modular, and easy to maintain.
Days 18–20: Work with Testing Frameworks
Combine Selenium with frameworks like TestNG (Java) or pytest (Python).
Learn how to create, organize, and run test suites efficiently.
Day 21: Handling Dynamic Elements
Develop strategies to manage dynamic web elements, such as those with frequently changing IDs or classes.
By the end of Week 3, you’ll be able to write clean, scalable, and efficient test scripts for real-world applications.
Week 4: Mastering Advanced Concepts
Days 22–24: Advanced Selenium Features
Explore headless browser testing to execute tests without a visible browser.
Learn how to run parallel tests to save time.
Days 25–27: Integration with CI/CD Tools
Set up Selenium with tools like Jenkins for continuous integration and delivery.
Automate test execution as part of your CI/CD pipeline.
Days 28–29: Distributed Testing with Selenium Grid
Set up Selenium Grid to run tests on multiple browsers and platforms simultaneously.
Day 30: Final Project
Choose a real-world application and create a comprehensive test suite. Use advanced techniques like POM, data-driven testing, and CI/CD integration.
Pro Tips for Success
Practice Daily: Dedicate 2–3 hours each day to coding and practicing on real websites.
Focus on Hands-On Learning: Write scripts regularly to strengthen your understanding.
Leverage Community Resources: Join forums and Selenium groups to troubleshoot and learn from others.
Stay Consistent: Stick to the timeline, even if progress feels slow.

Learning Selenium is an exciting journey that can significantly boost your career prospects. This timeline gives you a structured approach to mastering Selenium in just four weeks. From understanding the basics to handling advanced scenarios, you’ll be equipped to take on real-world web automation projects with confidence.
So, start today, follow this timeline, and watch yourself grow from a beginner to a Selenium pro in no time!
0 notes
Text
Selenium: Key Points to Learn
Selenium is a powerful tool for automating web applications for testing purposes, but it can also be used for web scraping and automating repetitive web-based tasks. For those keen to excel in Selenium, enrolling in a Selenium course in Pune can be highly advantageous. Such a program provides a unique opportunity to acquire comprehensive knowledge and practical skills crucial for mastering Selenium. To effectively learn and use Selenium, here are the key points to focus on:

1. Understanding Selenium and Its Components
Selenium WebDriver: The core component that drives the browser.
Selenium IDE: A browser extension for record-and-playback of interactions.
Selenium Grid: A tool to run tests on different machines and browsers in parallel.
2. Setting Up the Environment
Install WebDriver: Download the WebDriver for the browser you intend to automate (e.g., ChromeDriver for Google Chrome).
Configure IDE: If using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse, IntelliJ, or VSCode, ensure it's set up with necessary plugins.
3. Programming Languages
Language Support: Selenium supports multiple programming languages including Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript.
Learning Basics: Have a good grasp of the basics of the programming language you'll use with Selenium.
4. Basic Selenium Commands
Navigation: Learn how to navigate to URLs and interact with browser history.
Locators: Master different locators (ID, Name, Class Name, Tag Name, CSS Selector, XPath) to find elements on a web page.
Actions: Perform actions like click, sendKeys (for typing), and others like drag and drop.

5. Advanced Interactions
Waits: Implement implicit and explicit waits to handle dynamic web content.
Frames and Windows: Handle frames, windows, and alerts effectively.
Keyboard and Mouse Events: Use Actions class for complex user interactions like double-click, right-click, and hover.
6. Page Object Model (POM)
Design Pattern: Use POM to create an object repository for web elements, enhancing test maintenance and reducing code duplication.
Implementation: Structure your project to include page classes and test classes.
7. Test Framework Integration
JUnit/TestNG: Integrate Selenium with testing frameworks like JUnit or TestNG for better test structure, reporting, and annotations.
Assertions: Use assertions to validate test outcomes.
8. Handling Web Elements
Dynamic Elements: Learn strategies to interact with elements that change dynamically.
Dropdowns, Checkboxes, and Radio Buttons: Work with common form elements effectively.
9. Error Handling and Debugging
Exception Handling: Implement try-catch blocks to handle exceptions.
Logs and Reports: Utilize logging frameworks and create detailed test reports. Enrolling in a top-rated Selenium course online can unleash the full power of Selenium, offering individuals a deeper understanding of its intricacies.
10. Selenium Grid
Parallel Execution: Set up Selenium Grid to run tests across multiple environments simultaneously.
Configuration: Understand hub and node configuration and how to set up and tear down the Grid.
11. Best Practices
Clean Code: Write readable, maintainable, and reusable code.
Modular Approach: Break tests into smaller, manageable units.
Continuous Integration: Integrate Selenium tests with CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins.
12. Community and Resources
Documentation: Regularly consult the official Selenium documentation.
Community Forums: Engage with the Selenium community through forums, Stack Overflow, and GitHub.
Tutorials and Courses: Leverage online tutorials, courses, and webinars for continuous learning.
Conclusion
Learning Selenium is a journey that involves understanding its core components, setting up the environment, mastering basic and advanced commands, implementing design patterns like POM, integrating with test frameworks, and following best practices. By focusing on these key areas, you can become proficient in automating web testing and other web-related tasks using Selenium. Happy testing!
0 notes
Text
Top 50 Python Interview Questions
Top 50 Python Interview Questions: Mastering Python for Automation Testing
Python has become a go-to language for many software testing, especially in the realm of automation testing. With its simple syntax, readability, and vast community support, Python is an excellent choice for those looking to dive into automation testing using tools like Selenium WebDriver. In this article, we'll explore the top 50 Python interview questions, specifically tailored for those interested in automation testing.
Table of Contents
Sr#
Headings
1
Introduction to Python for Automation Testing
2
Python Basics
3
Data Structures
4
Control Flow
5
Functions and Modules
6
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
7
Exception Handling
8
File Handling
9
Regular Expressions
10
Python Libraries for Automation Testing
11
Selenium WebDriver Basics
12
Locators in Selenium WebDriver
13
Waits in Selenium WebDriver
14
Handling Dropdowns and Alerts in Selenium
15
Page Object Model (POM) in Selenium WebDriver
Introduction to Python for Automation Testing
Automation with Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in the field of automation testing due to its simplicity and readability. It provides a rich set of libraries and frameworks that make automation testing efficient and effective. Python's integration with Selenium WebDriver, a popular tool for web application testing, makes it a preferred choice for many automation testers.
Python Basics
What is Python? - Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It is widely used in various applications, including web development, data science, and automation testing.
How is Python different from other programming languages? - Python emphasizes code readability and simplicity, making it easier to write and understand compared to other languages like Java or C++.
What are the key features of Python? - Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. It has a comprehensive standard library and supports third-party libraries for various purposes.
How do you install Python? - Python can be installed from the official Python website (python.org) or using package managers like pip. It is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
What are Python variables? - Variables in Python are used to store data values. Unlike other programming languages, Python variables do not require explicit declaration or data type specification.
Data Structures
What are data structures in Python? - Data structures are used to store and organize data in a computer's memory. Python provides several built-in data structures, including lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets.
What is a list in Python? - A list is a collection of items that are ordered and mutable. Lists are created using square brackets and can contain elements of different data types.
How do you access elements in a list? - Elements in a list can be accessed using index values. Indexing in Python starts from 0, so the first element of a list has an index of 0.
What is a tuple in Python? - A tuple is similar to a list but is immutable, meaning its elements cannot be changed once it is created. Tuples are created using parentheses.
How do you iterate over a dictionary in Python? - You can iterate over a dictionary using a for loop. By default, the loop iterates over the keys of the dictionary, but you can also iterate over the values or key-value pairs.
Control Flow
What is control flow in Python? - Control flow refers to the order in which statements are executed in a program. Python provides several control flow statements, including if-elif-else statements, for loops, and while loops.
How does the if statement work in Python? - The if statement is used to execute a block of code only if a certain condition is true. It can be followed by optional elif and else statements to handle multiple conditions.
What is a for loop in Python? - A for loop is used to iterate over a sequence of elements, such as a list or tuple. It repeatedly executes a block of code for each element in the sequence.
How does the while loop work in Python? - The while loop repeatedly executes a block of code as long as a specified condition is true. It is used when the number of iterations is not known before the loop starts.
What is the difference between break and continue statements in Python? - The break statement is used to exit a loop prematurely, while the continue statement is used to skip the rest of the code in a loop for the current iteration.
Functions and Modules
What are functions in Python? - Functions are blocks of reusable code that perform a specific task. They help in modularizing code and making it more organized and readable.
How do you define a function in Python? - Functions in Python are defined using the def keyword followed by the function name and parentheses containing any parameters. The function body is indented.
What is a module in Python? - A module is a file containing Python code that defines functions, classes, and variables. It allows you to organize your Python code into reusable components.
How do you import a module in Python? - You can import a module using the import keyword followed by the module name. You can also use the from...import statement to import specific functions or variables from a module.
What is the difference between local and global variables in Python? - Local variables are defined inside a function and are only accessible within that function, while global variables are defined outside any function and are accessible throughout the program.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
What is object-oriented programming (OOP)? - OOP is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects," which can contain data in the form of attributes and code in the form of methods. Python supports OOP principles such as encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
How do you define a class in Python? - A class in Python is defined using the class keyword followed by the class name and a colon. It can contain attributes (variables) and methods (functions).
What is inheritance in Python? - Inheritance is a mechanism where a new class can inherit attributes and methods from an existing class. It allows for code reuse and the creation of a hierarchy of classes.
What is encapsulation in Python? - Encapsulation is the concept of restricting access to certain parts of an object, typically the internal data. In Python, encapsulation is achieved using private variables and methods.
What is polymorphism in Python? - Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on different forms or behaviors simplicity and readability.
How do you comment in Python? - Comments in Python start with a hash (#) symbol and continue until the end of the line.
What are the basic data types in Python? - Python has several basic data types, including integers, floats, strings, booleans, and NoneType.
How do you define a variable in Python? - Variables in Python are defined using the assignment operator (=).
What is a tuple in Python? - A tuple is an immutable collection of elements, typically used to store related data.
Data Structures
What is a list in Python? - A list is a mutable collection of elements, enclosed in square brackets ([]), and can contain elements of different data types.
How do you access elements in a list? - Elements in a list can be accessed using their index, starting from 0.
What is a dictionary in Python? - A dictionary is a collection of key-value pairs, enclosed in curly braces ({}), and is mutable.
How do you iterate over a dictionary in Python? - You can iterate over a dictionary using a for loop, accessing the keys or values of each key-value pair.
What is a set in Python? - A set is an unordered collection of unique elements, enclosed in curly braces ({}).
Control Flow
What are the different types of loops in Python? - Python supports for loops and while loops for iteration.
How do you use conditional statements in Python? - Python uses if, elif, and else keywords for conditional statements.
What is the difference between break and continue statements? - The break statement terminates the loop, while the continue statement skips the current iteration and continues with the next iteration.
Functions and Modules
What is a function in Python? - A function is a block of reusable code that performs a specific task.
How do you define a function in Python? - Functions in Python are defined using the def keyword, followed by the function name and parameters.
What is a module in Python? - A module is a file containing Python code, which can define functions, classes, and variables.
How do you import a module in Python? - You can import a module using the import keyword, followed by the module name.
What is the difference between local and global variables? - Local variables are defined inside a function and are only accessible within that function, while global variables are defined outside any function and can be accessed throughout the program.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
What is OOP? - Object-Oriented Programming is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects," which can contain data in the form of attributes and code in the form of methods.
What is a class in Python? - A class is a blueprint for creating objects, which defines the properties and behaviors of those objects.
How do you create a class in Python? - Classes in Python are created using the class keyword, followed by the class name and a colon (:).
What is an object in Python? - An object is an instance of a class, which has its own unique identity, state, and behavior.
What is inheritance in Python? - Inheritance is a mechanism where a new class derives attributes and methods from an existing class.
Exception Handling
What is exception handling in Python? - Exception handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors or exceptions that occur during the execution of a program.
How do you use try-except blocks in Python? - You can use try-except blocks to catch and handle exceptions in Python.
What is the purpose of the finally block? - The finally block is used to execute code that should always run, whether or not an exception occurs.
File Handling
How do you open a file in Python? - You can open a file in Python using the open() function, specifying the file path and mode (read, write, append, etc.).
What is the difference between read() and readlines() methods? - The read() method reads the entire file contents as a single string, while the readlines() method reads the file line by line and returns a list of lines.
Regular Expressions
What are regular expressions (regex)? - Regular expressions are sequences of characters that define a search pattern, used for pattern matching within strings.
How do you use regular expressions in Automation Testing with Python ? - Python's re module provides functions and methods for working with regular expressions.
Python Libraries for Automation Testing
What is Selenium WebDriver? - Selenium WebDriver is a tool for automating web application testing, providing a programming interface for interacting with web elements.
How do you install Selenium WebDriver in Python? - You can install Selenium WebDriver using the pip package manager: pip install selenium.
What are the key features of Selenium WebDriver? - Selenium WebDriver supports various programming languages (including Python), multiple browsers, and parallel test execution.
Selenium WebDriver Basics
How do you create a WebDriver instance in selenium with python ? - You can create a WebDriver instance in Python using the webdriver module.
What are the different WebDriver methods for locating elements? - Selenium provides various methods for locating elements on a web page, such as find_element_by_id(), find_element_by_xpath(), etc.
Locators in Selenium WebDriver
What are locators in Selenium WebDriver? - Locators are used to identify and locate web elements on a web page, such as IDs, class names, XPath, etc.
How do you use XPath in Selenium WebDriver? - XPath is a language for navigating XML documents and is commonly used in Selenium WebDriver for locating web elements.
Waits in Selenium WebDriver
What are waits in Selenium WebDriver? - Waits are used to pause the execution of a test script for a certain amount of time or until a specific condition is met.
What are the different types of waits in Selenium WebDriver? - Selenium WebDriver supports implicit waits, explicit waits, and fluent waits.
Handling Dropdowns and Alerts in Selenium
How do you select an option from a dropdown menu in Selenium WebDriver? - You can use the Select class in Selenium WebDriver to interact with dropdown menus.
What are alerts in Selenium WebDriver? - Alerts are popup windows that appear during the execution of a test script, requiring user interaction.
Page Object Model (POM) in Selenium WebDriver
What is the Page Object Model (POM) in Selenium WebDriver? - The Page Object Model is a design pattern for organizing web elements and their interactions into reusable components.
How do you implement the Page Object Model in Selenium WebDriver? - You can create separate classes for each web page, defining locators and methods to interact with the page elements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Python for automation testing, especially with Selenium WebDriver, requires a solid understanding of python for automation testing fundamentals, object-oriented programming, and Selenium WebDriver basics. By familiarizing yourself with the top 50 Python interview questions outlined in this article, you'll be well-equipped to tackle automation testing challenges and excel in your career.
FAQs
What is Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium WebDriver is a tool for python automation testing web application testing, providing a programming interface for interacting with web elements.
How do you install Selenium WebDriver in Python?
You can install Selenium WebDriver using the pip package manager: pip install selenium.
What are locators in Selenium WebDriver?
Locators are used to identify and locate web elements on a web page, such as IDs, class names, XPath, etc.
What is the Page Object Model (POM) in Selenium WebDriver?
The Page Object Model is a design pattern for organizing web elements and their interactions into reusable components.
How do you handle alerts in Selenium WebDriver?
Alerts in Selenium WebDriver can be handled using the switch_to.alert method, which allows you to accept, dismiss, or get text from an alert.
By mastering these Python interview questions, you'll not only be well-prepared for interviews but also enhance your skills as an automation tester.
#Automation Testing with Python
0 notes