#Iroquois confederacy
Text
❣️♀️Beloved Woman

Cherokee Beloved Woman Nancy Ward
Nancy Ward, or Nan'yehi (nan yay hee), is the most famous Cherokee Beloved Woman. The role of Beloved Woman, Ghigau (Ghee gah oo), was the highest a Cherokee woman could aspire to. A Ghigau had a voice and vote in General Council, leadership of the Woman's Council, the honor of preparing and serving the ceremonial Black Drink, the duty of ambassador of peace-negotiator, and the right to save the life of a prisoner already condemned to execution.
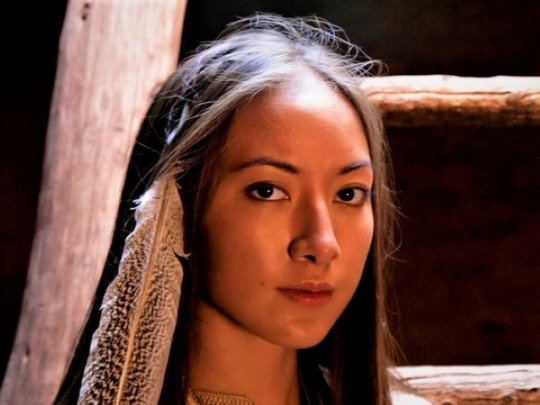

The Native American Cherokee
The word Cherokee is believed to have evolved from a Choctaw word meaning "Cave People." It was picked up and used by Europeans and eventually accepted and adopted by Cherokees. Traditionally, the people now known as Cherokee refer to themselves as aniyun-wiya, a name usually translated as "the Real People," sometimes "the Original People."
The Role of the Cherokee Woman
The Cherokee were matrilineal with a complex society structure. Clan kinship followed the mother's side of the family. The children grew up in the mother's house, and it was the duty of an uncle on the mother's side to teach the boys how to hunt, fish, and perform certain tribal duties. The women owned the houses and their furnishings. Marriages were carefully negotiated, but if a woman decided to divorce her spouse, she simply placed his belongings outside the house. Cherokee women also worked hard. They cared for the children, cooked, tended the house, tanned skins, wove baskets, and cultivated the fields. Men helped with some household chores like sewing, but they spent most of their time hunting.

Women in the Cherokee society were equal to men. This privilege led an Irishman named Adair who traded with the Cherokee from 1736-1743 to accuse the Cherokee of having a "petticoat government."

Princess Tsianina Red Feather
Tsianina Red Feather was not a "Princess." The Cherokee never had princesses. This is a concept based on European folktales and has no reality in Cherokee history and culture. Beloved women and high ranking women in a clan were treated with such reverence, that Europeans assumed they were some type of royalty.
Red Feather was born Florence Tsianina Evans on December 13,1882 in Eufallia (Oklahoma Territory) to Creek and Cherokee parents. All her 9 siblings were musical, but she was the one who stood out.
At age 14, she went to Denver to be trained to sing. There, she met the composer Charles Cadman and began touring with him at 16. She became a mezzo soprano virtuoso. While touring the United States, Canada, Paris and London, she wore native dress, braided her hair and wore a headband she beaded herself.

In 1918, she and Cadman debuted "Shanewis" (The Robin Woman) at the Metropolitan Opera; the cast received 22 curtain calls. Cadman based the opera on Native American stories told by Redfeather. Although this opera had many firsts, it became the first contemporary opera to be performed for a 2nd season at the Met.

The Robin Woman: Shanewis, 1918 - an opera in one act and two scenes by American composer Charles Cadman and Tsianina Redfeather Blackstone. Cadman called the work an "American opera."
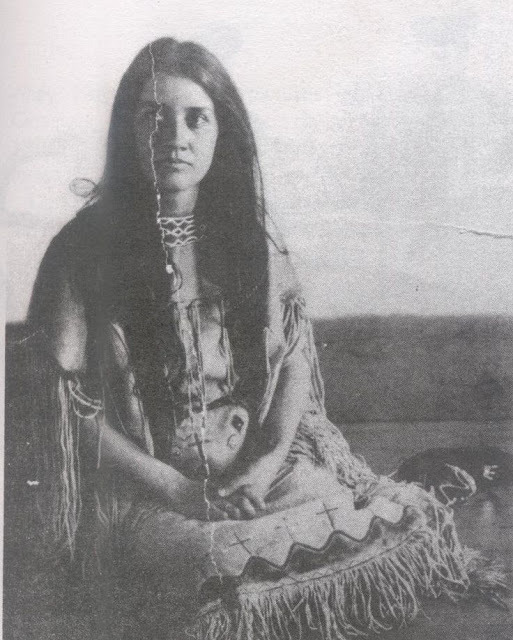

Photo is Miss Anna Trainor, who later became Mrs. Anna Bennett. She was only Cherokee on her mother's side, but because it was the woman's bloodlines that determined kinship, she was considered Cherokee.
The title Ghigau also translates to "War Woman," and Nan'yehi (Nancy Ward) earned the title by taking up her husband's gun when he was slain in a battle against the Creeks and leading her people to victory. Another War Woman, Cuhtahlatah, won honor during the American Revolutionary period by leading Cherokee warriors to victory after her husband fell. She later joined in a vigorous war dance carrying her tomahawk and gun.
It was important to the Cherokee that their losses be compensated with the same number of prisoners, scalps, or lives. Woman led in the execution of prisoners. It was their right and responsibility as mothers. Women had the right to claim prisoners as slaves, adopt them as kin, or condemn them to death "with the wave of a swan's wing."
In the Cherokee society your Clan was your family. Children belonged to the entire Clan, and when orphaned were simply taken into a different household. Marriage within the clan was strictly forbidden, or pain of death. Marriages were often short term, and there was no punishment for divorce or adultery. Cherokee women were free to marry traders, surveyors, and soldiers, as well as their own tribesmen.

7 Cherokee Clans - L to R: 1.Wolf Clan 2.Long Hair Clan 3.Red Tail Hawk Clan 4.Blue Holly Clan 5.Deer Clan 6.Paint Clan 7.Wild Potato Clan
Cherokee girls learned by example how to be warriors and healers. They learned to weave baskets, tell stories, trade, and dance. They became mothers and wives, and learned their heritage. The Cherokee learned to adapt, and the women were the core of the Cherokee.


Other indigenous nations were were matrilineal. Women of the six nations Iroquois confederacy (Haudenosaunee) had a political voice on this land for at least 1,000 years.
The male chiefs who are the representatives of their clan in the confederacy of the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, and Tuscarora Nations are selected, held in office, and removed by women – the clan mothers. Founded on the shores of Onondaga Lake, this oldest continuing democracy in the world is based on a system of gender balance. The position of the chief is vested in the clan mother, who is the eyes and ears of the people, while the chief is her voice. Women were “the great power among the clan, as everywhere else,” Elizabeth Cady Stanton marveled. Lucretia Mott wrote about listening to “speeches of their chiefs, women as well as men” (clan mothers and chiefs) when she visited the Cattaraugus Seneca community during the summer of 1848 before Mott, with Stanton and Quaker friends, organized the Seneca Falls convention.
In other words, the Beloved and Haudenosaunee women influenced the Women's Suffrage Movement.
#original people#cherokee#native american#Beloved Woman#nancy ward#choctaw#Shanewis#clan#indigenous#women#katteuha#haudenosaunee woman#Iroquois confederacy#suffragette#women's suffrage#Elizabeth Cady Stanton#Lucretia Mott#Seneca Falls#clans#society#culture
227 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mohawk ironworkers who built the Chrysler Building, ca. 1930. For more on the Mohawks who built Manhattan's skyscrapers, see here.
Photo: Smithsonian Institution via the Daily Mail
#vintage New York#1930s#Mohawks#construction#construction workers#Chrysler Building#Native Americans#indigenous people#Iroquois Confederacy#Iroquois Confederation
142 notes
·
View notes
Text
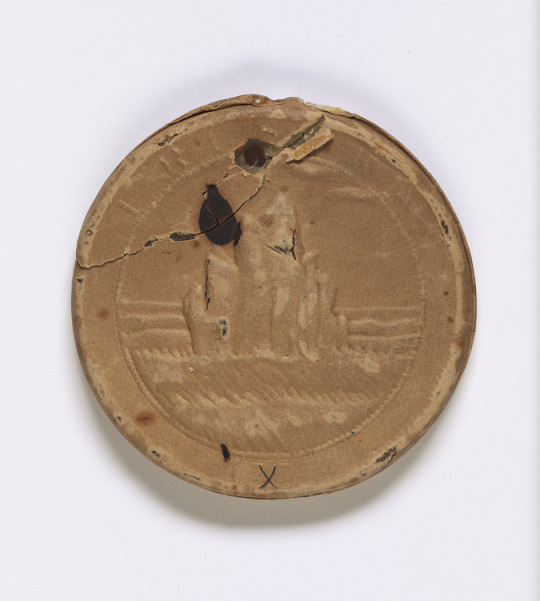




Ratified Indian Treaty 19A (first and last pages), April 11, 1793.
This treaty with the Six Nations (Seneca, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Mohawk, and Tuscarora) included this wax Great Seal of the State of New York.
Record Group 11: General Records of the United States Government
Series: Indian Treaties
Image description: A circular seal, just over three inches in diameter, made of wax covered with paper. Depicted in the center is a sun with a face, rising over hills. Below the hills is “EXCELSIOR”. Around the border of the seal is “THE GREAT SEAL OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK”. There is a hole through the seal at the top.
Image description: Reverse of the circular seal. In the center are spiky rocks jutting out of the water. There are letters at the top of the border, but it’s difficult to see what they say. At the bottom of the seal is an ink “X”. There is a hole through the seal at the top.
Transcription:
1)
The People of the State of New York, by the Grace of God, Free and Independent: To all to
whom these presents shall come, Greeting Know ye that We having inspected the Records remaining in
our Secretary's Office do find there certain Indian Deeds recorded in Book of Indian Deeds commencing
in the year 1748 in the Words Characters and figures following, to wit, "To all to whom these presents
"shall come or may concern: Know ye that We Peter Ojistarare, Johan Jesry Towahangaraghkou, Rawhistoni,
"Paul Tewasgwadeghkow, John Skanondonagh of the wolf tribe, Peter Oneyanha, Joseph Kanaghsaterhon, Cornilius Okonyota, John Onontiyo, Nicholas Sagoyatokare of
"the Turtle Tribe; Lodowick Kaghsaweta, Paul Kanyatashayea and Peter Agwirontongwas of the Bear Tribe,
"Sachems and chief Warriors of the Oneyda and Tuscarara Nations, by and with the advice and consent and in
"the presence of the said Nations at a public Treaty held at Fort Herkimer in the county of the Montgomery with
"his Excellency George Clinton Esquire Governor of the State of New York and the other Commissioners of In-
"dian Affairs of the said State for the consideration of the sum of Eleven Thousand five hundred Dollars
"in Goods & Money to us in hand paid at and before [illegible] ensealing and delivery of these presents, the receipt whereof
"We do hereby acknowledge Have Given, Granted, Bargained and Sold, and by these presents Do fully freely and
"Absolutely Grant Bargain and Sell unto the People of the State of New York all that certain Tract of Land situate
"in the said State and on the West Side of the Line commonly called the Line of Property established at a
"Treaty held at Fort Stanwix in 1768, and on the North Side of the Pensylvania Line, Beginning at the
"Mouth of the Unadilla or Tianaderha River where the same empties into the Surquchanna River, thence up
"the said Unadilla or Tianaderha River ten Miles measured on a straight line, thence due West to the Chenen-
"go River, thence Southerly down the said Chenengo River to where it empties into the said Sasquchanna River
"& to the said Line called the Line of Property, thence along the said Line to the place of Beginning so as to comprehend
"all the Lands belonging to us the said Oneyda and Tuscarora Nations lying South of the said Line to be run from
"the said Unadilla or Teanaderha River to the Chenengo River and North of the Division Line between this State
"and the State of Pensylvania, Together with all Ways, Waters, Water courses, Rivers, Riverlets, Creeks and Streams
(of)
[page 2]
16.)
"Onaakaronton his x mark LS Tehoghweakaronto his x mark LS Kaghnunrayen his x mark LS Agwirontong-
"waghs his x mark LS Anonghsighraghtha his x mark LS Oniatariyoo his x mark LS Kaneyaggh his x mark
"LS Geo: Clinton LS Pierre Van Cortlandt LS Ezra L Hommedieu LS Abm Ten Broeck LS Peter Gansevoort-
"Junr. LS Richd. Varick LS Witnesses Present Sam Kirkland Missry. Interpreter John Lansing Junr. Jos.
"Brant, David Hill, John Tayler, Malachi Treat, Abm Hardenbergh, Peter Otsiequette, Aghwistonisk his x mark,
"Oneyanka his x mark, Coll. Honyery his [mark] mark, Oneida Chiefs. Onangaiekhon his x mark, Fhoghnawayen
"x Senekas. - Be it Remembered that on the Twenty fifth day of November in the year one thousand seven hundred and
"ninety one before me John Sloss Hobart one of the Justices of the Supreme Court of the State of New York came Samuel Kirkland,
"Clerk, Missionary and Interpreter to the Six Nations of Indians, who made oath that he was present and did see the Twenty
"-Eight Sachems, Chiefs and Warriors of the Onondaga Nation of Indians whose names are written opposite to their respec-
"tive Seals severally seal and deliver the within written Ratification as their Voluntary act and deed for the purposes and uses therein mentioned,
"he having previously thereto faithfully and truly interpreted the Contents of the same from the English into the Indian Language unto the said
"Sachems, Chiefs and Warriors in such a manner that it was fully understood by them and that he also saw the Commissioners on the part of the
"State of New York in the said Ratification Mentioned severally seal and deliver the same as their Voluntary act and deed for the purposes and
"uses therein mentioned, and that John Lansing Junr. and the Eleven other persons whose names are signed as Witnesses were present and did see
"the said parties Seal and deliver the said Ratification; and I having Examined the same and found no material alteration therein do al-
"low it to be recorded Jno. Sloss Hobart. The preceding Instrument refers to the Treaty recorded in pages 150 & which is dated the 12th.
"of September 1788, and is a true copy of the Original, Examined and compared therewith this 5th. day of April 1793 (the words "alias Land Car-
"rier" in page 170 being interlined) By me Robert Harpur D Secry."
~~~~~~~~
All which WE have caused to be Exemplified by these Presents: In Testimony whereof
We have caused these our Letters to be made patent and the Great Seal of our said State to be hereunto affixed Witness
our Trusty and well beloved George Clinton Esquire Governor of our said State General and Commander in chief
of all the Militia and Admiral of the Navy of the same, at our City of New York; this Eleventh day of April in the year of
our Lord one thousand seven hundred and Ninety-Three, and in the Seventeenth year of our Independence.~
#archivesgov#April 11#1793#1700s#Early America#Native American history#American Indian history#Indigenous American history#Iroquois Confederacy#Seneca#Cayuga#Onondaga#Oneida#Mohawk#Tuscarora#New York#Indian treaties
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
#w. michael gear and kathleen o'neal gear#people of the longhouse#people series#Iroquois confederacy#native history#American history
0 notes
Text
Over on the Substack, we're talking 'bout flags!
(If you like what you read, SUBSCRIBE TODAY!)
0 notes
Text
Watch "Northeast Region | US History to 1865 | Study Hall" on YouTube
youtube
0 notes
Text
A Swiss museum has returned two sacred artifacts to the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) confederacy.
The objects — a medicine mask and turtle rattle — had been in the possession of the Geneva Museum of Ethnography (MEG) for nearly 200 years.
Mohawk elder and activist Kenneth Deer was one of three men sent to retrieve the objects.
He says he was "surprised and thankful" for the museum's co-operation and called the MEG "progressive" for returning the objects without conditions or complications.
The museum held a ceremony in Geneva on Feb. 7 to mark the first time that the MEG returned a sacred object to its rightful owners. [...]
Continue Reading.
Tagging: @politicsofcanada
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

The Keepers of the Eastern Door by Robert Griffing, portraying two Mohawk warriors in the mid-eighteenth century. The Mohawk were the easternmost tribe of the powerful Iroquois Confederacy, an alliance closely involved in the Seven Years War and the American Revolution (usually fighting alongside the British). Always loved Griffing's artwork, especially his pieces depicting eighteenth c. highlanders and Native Americans.
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
a fun language thing
I'm learning Kanien'kehá (Mohawk) and the way to ask "how are you" is "Skennon'kó:wa ken?" Which means "Do you carry the great peace?"
Which apparently originates from when the peacemaker joined the nations of the Iroquois Confederacy under the Great Law of peace (Kaianere'kó:wa)
66 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Twelve Famous Native American Women
Native American women are traditionally held in high regard among the diverse nations, whether a given people are matrilineal or patrilineal. Traditionally, women were not only responsible for raising children and caring for the home but also planted and harvested the crops, built the homes, and engaged in trade, as well as having a voice in government.
The history of the women of the Native peoples of North America attests to their full participation in the community whether as elders and "medicine women" or as skilled agriculturalists and merchants and, in some cases, even warriors. Although hunting and warfare were traditionally the provenance of males, some women became famous for their courage and skill in battle. These women, as well as others in the arts and sciences, are often overlooked because they do not fit the paradigm of what has been accepted as American history.
Pocahontas and Sacagawea are usually the only North American Native women that non-Natives have heard of, but even their narratives have been obscured by legend and half-truths. Many other Native American women have simply been ignored, and among them are most of those listed below. These women, and the nations they were citizens of, include:
Jigonhsasee – Iroquois
Pocahontas – Powhattan
Weetamoo – Wampanoag
Glory-of-the-Morning – Ho-Chunk/Winnebago
Sacagawea – Shoshone
Old-Lady-Grieves-the-Enemy – Pawnee
Pine Leaf/Woman Chief – Crow
Lozen – Apache
Buffalo Calf Road Woman – Cheyenne
Thocmentony/Sarah Winnemucca – Paiute
Susan La Flesche Picotte – Omaha
Molly Spotted Elk/Mary Alice Nelson – Penobscot
There are many others who do not appear here because they are more widely known, such as the Yankton Dakota activist, musician, and writer, Zitkala-Sa (l. 1876-1938) or the Cheyenne warrior Mochi ("Buffalo Calf", l. c. 1841-1881). Modern-day figures are also omitted but deserve mention, such as the activist Isabella Aiukli Cornell of the Choctaw nation, who drew national attention in 2018 with her red prom dress designed to call attention to the many missing and murdered indigenous women across North America, and poet/activist Suzan Shown Harjo of the Muscogee/Southern Cheyenne nation. There are many more, like these two, who have devoted themselves to raising awareness of the challenges facing Native Americans and continue the same struggle, in various ways, as the women of the past.
Jigonhsasee (l. c. 1142 or 15th century)
According to Iroquois lore, Jigonhsasee (Jikonhsaseh, Jikonsase) was integral to the origins of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Confederacy dated to either the 12th or 15th century. She was an Iroquoian whose home was along the central path used by warriors going to and from battle and became well-known for the hospitality and wise counsel she offered them. The Great Peacemaker (Deganawida) chose her to help him form the Iroquois Confederacy, based on the model of a family living together in one longhouse, and, along with Hiawatha, this vision became a reality. Jigonhsasee became known as the 'Mother of Nations' and established the policy of women choosing the chiefs of the council in the interests of peace, instead of war. The American women's suffrage movement of the 19th century called attention to the freedom and rights of Native American women, notably those of the Iroquois Confederacy, in arguing for those same rights for themselves.
Continue reading...
63 notes
·
View notes
Photo



1940.
The Indian Defense League staged a protest in December 1940 at the US-Canada border, which had been carved through pre-existing Indigenous nations, bisecting the Iroquois Confederacy.
At the time of this protest, the US government was planning on changing federal classifications of Indigineous people to foreign aliens.
Tribal leaders held a sign that read, “WE DID NOT FINGERPRINT THE PILGRIMS WHEN THEY ARRIVED IN OUR OWN NATIVE AMERICA.”
172 notes
·
View notes
Text


[New York, 1746 – First meeting ]
In 1744, King George's War was fought between the British, the British-American forces in the colonies and the Iroquois Confederacy against the French and the Wabanaki Confederacy of New France. Part of the Austrian War of Succession, it was fought mainly in New York and the Massachusetts bay. The battle meant tremendous losses for the colonies, with an estimated loss of 8% of the male population in Massachusetts. The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the war in 1748, returning colonial borders back to how they were before the war. Three years later however, the town of Louisbourg was returned to France in exchange for the city of Madras (renamed to Chennai in 1996) in India. This city was captured by the French in September 1746 from the British, thus the "exchange". This angered New Englanders, who provided funding and personnel. The British paid Massachusetts £180,000 (roughly £32,281,486.29 in 2022), which the province then used to retire their currency.
[ Disclaimer : I am not, nor do I claim to be any expert on anything. I am constantly learning, so this post and others like it are subject to retcons and the like. Appropriate warnings will be given as I go. Also, please note that this, whilst based on history, is still a work of fiction. I do not condone nor support generally morally reprehensible things directly mentioned or alluded to on these. ]
1746 was more or less the midpoint of this war (with France launching a major expedition to recapture Louisbourg, the previous figures for Massachusetts losses being from 1745-46, etc.) and so the idea was for Susannah to act as the crown's (and by extension, Arthur's) eyes and ears to the colonies in direct response to the growing unrest. Alfred up until this point had been a loyal and steadfast son and subject, despite his eternal curiosity leading him to consume more and more literature that directly put old beliefs into question. Though he was not initially aware of Susannah's double allegiances, Alfred was aware of the formal, employer-employee arrangement between himself and Susannah. Despite that, his warm personality and similar wavelength of interests allowed him to easily breach the gap between 'acquaintance' and 'friend'. His father was often entire oceans away and this is the first time he met someone whom he could get attached to without fearing their mortality (see: humans Alfred had befriended throughout the years) or any perceived double national interests. The exchange of Louisbourg for Madras had been one of the many events that would plant the idea that his father was not entirely devoted to him in Alfred's mind. His conflicting feelings about the exchange and his place in the empire allowed him to open himself up to befriending Susannah, perhaps thinking that if he behaved well and treated who was essentially a bureaucratic extension of his Lord Father's presence well, perhaps he could earn his favor again.
Susannah on the other hand, was caught off guard by his lack of formality and had even found him to be somewhat "uncultured" in the beginning. The mainland British had mixed feelings about the colonists, but many of them held prejudices and saw them as "uncouth". As Suzie's household had mainly been attendants and tutors brought in from Britain, she shared their beliefs throughout her childhood. But slowly, as Suzie began to spend more time with Alfred, she warmed up to him, happy for the chance to finally be taken seriously instead of waved off for her more intellectual pursuits. Susannah was born in the colonies. But due to her ancestor, Sir Wilfred Knightley, whose affection and counsel she received growing up, her family has and continues to hold deep ties to the crown. Her beliefs and viewpoints were shaped simultaneously by her birthplace and her family's values. Though they were seen as upstarts in Britain, the Knightleys were an esteemed family in the colonies. She interacted with a lot of people from the mainland, a lot of important family friends and other acquaintances, but she'd also spent a lot of time talking to and mingling with colonists, both ranking ones and average, everyday people. To reflect the attitudes of many colonists, Susannah identified as a loyalist up until the middle of the Revolution.
[ commissions open | do not repost ] ocs by sunnysssol
#hetalia#aph america x oc#aph america#aph england#hetalia oc#hws assistantverse#oc: susannah knightley#oc: wilfred knightley#re: amesuzie [ canon timeline ]#[ 18th century ]#cc: alfred f jones#cc: arthur kirkland
89 notes
·
View notes
Note
The Biden administration is removing William Penn from Philadelphia.
New plans by the National Park Service to renovate Old City’s Welcome Park include removing the centerpiece statue of William Penn permanently and redesigning the park to highlight Native American history — a move that has angered Pennsylvania’s Republican leadership.
The plan is a major shift, considering that the park was built on the site of Penn’s home, the Slate Roof House, and is named for the ship, Welcome, that transported him from England. Penn actually landed first in 1682 near the intersection of the Delaware River and Chester Creek in Chester.
Welcome Park is part of Independence National Historical Park and was completed in 1982 on designs by Venturi, Scott Brown and Associates to commemorate the 300th anniversary of Penn’s arrival.
The wide-open park across from the former site of City Tavern aims to tell the story of Penn’s vision for the city. Although a lesser-known area of Independence Park, it provides visitors with an overview of the city layout and history of Penn’s landing. The Penn statue includes a farewell ode to Philadelphia, imparting “what love, what care, what service, what travail have there been to bring thee forth.”
Now, the National Park Service wants to rehabilitate the park in time for the 250th birthday celebration of America in 2026. The park on Second Street between Chestnut and Walnut Streets has fallen into disrepair with rows of broken granite floor.
Representatives for the National Park Service could not be reached for comment Monday. They are seeking public comment on the proposal, according to their website.
Plans announced Friday call for “an expanded interpretation of the Native American history of Philadelphia” in consultation with Indigenous nations of the Haudenosaunee, Delaware Nation, Delaware Tribe of Indians, Shawnee Tribe, and the Eastern Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma.
Designs would keep some parts of the current park, including the original Philadelphia street grid, but the “Penn statue and Slate Roof House model will be removed and not reinstalled,” according to the plans.
Republican outcry
“The decision by President Biden and his administration to try and cancel William Penn out of whole cloth is another sad example of the left in this country scraping the bottom of the barrel of woke-ism to advance an extreme ideology and a nonsensical view of history,” Pennsylvania House Republican Leader Bryan Cutler (R., Lancaster) said in a statement.
Cutler said the treaty signed by Penn with Native Americans was historical and with “mutual respect shown between Penn and Native tribes.”
“This issue is also deeply personal to me,” Cutler said. “The first Cutlers came to Pennsylvania in 1685 on the ship Rebekah, not long after Penn’s arrival in 1682. They came to Pennsylvania because they were Quakers who shared Penn’s view of religious tolerance and peace.”
Cutler said removing the statue creates an “absurd and revisionist view of our state’s history.” He said he plans to introduce a resolution honoring William Penn and “encouraging” the National Park Service to halt the plan.
Pennsylvania State Sen. Scott Martin (R., Berks) and chair of the Senate Appropriations Committee, on social media called the plan “absolutely disgraceful.”
Native Americans
Welcome Park, though not necessarily the statue of Penn, has also been the site of some resentment among Native Americans. The plot had been given to the Haudenosaunee (Six Nations from the Iroquois Confederacy) in January 1755 by John Penn, William Penn’s grandson. In the 1700s, Native American groups often visited Philadelphia for diplomatic and trade meetings. They sometimes numbered in the hundreds and visited so frequently that John Penn asked the Provincial Council of Philadelphia to consider setting aside a piece of land for these gatherings. The delegations often refused to negotiate treaties until they could stand on their own ground and build a council fire.
A 2020 Inquirer article chronicled a trip by six women from the Iroquois Confederacy in upstate New York to reconnect with the patch of tribal land on the site of Welcome Park.
“I anticipated a park in a natural pristine state. Like any other park, it would have trees, grass, water,” said Louise McDonald (Native name Wa’kerakátste), a Mohawk Bear Clan Mother from Akwesasne, N.Y. “I was frozen for a minute because I felt it had been choked and that it wasn’t a true representation of the original intentions of the space. It just seemed to be purposely buried with a cover-up narrative. There certainly seems to be a feeling of erasure intended to remove any spirit that would imply that we were once there.”
Penn in Philly
William Penn’s likenesses will still remain in Philly. The statue of Penn atop City Hall is a landmark, visible from many parts of the city.
And there is another Penn statue at Penn Treaty Park off North Delaware Avenue at the corner of East Columbia Avenue and Beach Street. Legend says Penn and a local Lenape clan made a peace agreement under an elm tree. The original “treaty elm” has long been replaced, but the park contains an obelisk and plaque memorializing the agreement, as well as a statue of Penn.
The discussion of the Penn statue’s removal is not the first time in recent years that Philadelphia has seen a struggle over statues.
The statue of Frank L. Rizzo, the late mayor and police commissioner, was ordered removed from in front of the Municipal Services Building in 2020 by then-Mayor Jim Kenney amid sweeping protests after the murder of George Floyd. Also in recent years, people have petitioned to have the Christopher Columbus statue in Marconi Plaza removed, though it still remains.
_______________________________________
Time to start finding problematic people the folks on the left like and tearing monuments to them down, maybe Fredrick Douglas was sexist, we already know MLK was a Zionist that should count against him for some people, know who else was a Zionist

Wonder where the "Ruth Sent Us" group is now.......
Maybe we find something bad Harriet Tubman did and start to disqualify her, she may have been mean to native Americans or something.
Given enough time they're going to find something wrong with everyone that has a statue eventually.
Start with every single statue and bust of karl marx
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
saw some tags on a reblog i did but yes, iroquois is a derogatory term. it's a french bastardization of (i believe) the algonquin word for "snake." the term is used to describe member tribes of the haudenosaunee (approximate pronunciation ho-di-no-SHO-ni) confederacy in the capital region of the us and up into canada, which include:
Mohawk / Kanienʼkehá꞉ka (approximate pronunciation "gah-nyen-geh-hah-ga") - “People of the Flint."
Also referred to as the “Keepers of the Eastern Door” because they are the nation furthest to the east in the Confederacy. (alix note: mohawk communities are predominantly in canada but there are bands in northern new york as well.)
Oneida / Onyota’a:ká (approximate pronunciation "oh-nyo-DA-aw-GA") - “People of the Standing Stone” (there are two Oneida nations in the US, one in NY, one in Wisconsin, because of,,,y'know. displacement.)
Onondaga / Onöñda’gegá’ (approximately pronounced "ohnen-DA-geh-GA") - “People of the Hills.”
Also referred to as the “Keepers of the Central Fire” because they were the center and capital of the Confederacy
Cayuga / Gayogo̱hó꞉nǫ' (approximately pronounced "guy-yo-KO-no") - “People of the Great Swamp”
Seneca / Onöndawá'ga (approximately pronounced "Oh-nown-da-WA-gah") - “People of the Great Hill.”
Also known as the “Keepers to the Western Door” because they are the nation furthest to the west in the Confederacy
Tuscarora / Skarù:ręˀ (approximately pronounced "ska-ruh-reh") - “The Shirt Wearing People" or "the hemp gatherers"
In 1722, the Tuscarora moved from North Carolina to the Haudenosaunee area to seek refuge and they were invited to join the Confederacy
all nations in the confederacy are still extant and all (to the best of my knowledge) have programs to keep their languages alive; i've linked to the govt websites for each nation.
just like...as a general rule of thumb if something sounds french (or european, tbh) and it's being applied to indigenous peoples of the americas it's safe to assume it's probably not the right word to use. (exceptions exist: the st croix band of ojibwe, etc.) rule of thumb is double check and you can do this very easily by searching "[name of nation] tribal government website" to see what names and terms are acceptable.
(i keep forgetting to put this on posts but yeah, i'm white. i grew up in haudenosaunee territory, i work in indian law [canadians don't fight me, that's the legal term in the us, i don't like it either], and this is basic 101 stuff that every settler in the us needs to fuckin know.)
eta: this should also be obvious but if a mohawk, tuscarora, seneca, cayuga, onondaga, or oneida person self-describes as iroqouis, leave them the fuck alone. same rule of thumb as a lesbian self-describing as dyke. as a lesbian, i get to reclaim that word. as a white person, i do not get to reclaim iroquois. it's that simple.
30 notes
·
View notes
Note
When I was a kid, I heard not to call indigenous people Eskimo because it's derogatory. It means something to the effect of "eater of raw meat". "Inuit" was recommended instead.
As an adult, I've heard that they'd prefer Eskimo to Inuit because the former is a general term, whereas the latter is a specific tribe (and they hate getting confused with other tribes).
Inuit and Ojibwe are two tribes I've heard associated with Canada. I'd be interested in whatever other info (if any) you could dump on me.
Eskimo actually comes from the French word esquimaux, meaning one who nets snowshoes.
You are correct, Inuit is not the preferred term, while one group does use the term the hundreds of others do not.
To list a few terms used by the tribes aside from Inuit there is Inuvialuit, Inuinnaat, Inupiat, Yupiit, Cupiit, Yupiget, Yupik, and Sugpiat, but they can all be grouped under the term Eskimo as despite their varying cultures and traditions, all use snowshoes.
The Ojibwe live in both the United States and Canada and occupy land around the entire Great Lakes, including in Minnesota, North Dakota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and Ontario.
It'll be hard to name all of the tribes in Canada off the top of my head...
There are more than 630 tribal communities in Canada, which represent more than 50 Nations and 50 languages, but from the top of my head I can name the;
The Cree are one of the largest tribes in Canada. Their territory covers a vast area of Western Canada from the Hudson-James Bay region to the foot of the Rocky Mountains, and in Alberta between the North banks of the North Saskatchewan River to Fort Chipewyan.
The Dene have historically inhabited central and northwestern Canada in an area known as Denendeh, meaning “the Creator's Spirit flows through this Land” or “Land of the People.” This region includes the Mackenzie River Valley and the Barren Grounds in the Northwest Territories.
The Haida People have occupied Haida Gwaii since time immemorial. Their traditional territory encompasses parts of southern Alaska, the archipelago of Haida Gwaii and its surrounding waters.
The Niitsitapi, also known as the Blackfoot or Blackfeet Indians, reside in the Great Plains of Montana and the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Originally, only one of the Niitsitapi tribes was called Blackfoot or Siksika.
The majority of Métis live in the western provinces and Ontario, they are the product of tribal marriages with the French, they were rejected by both the tribes and the French and so formed their own tribe.
The Mohawk people are the most easterly section of the Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River.
The Nootka are a people who live on what is now the southwest coast of Vancouver Island, and on Cape Flattery, and the northwest tip of the state of Washington.
The Huron-Wendat are one of Québec's most urbanized Indigenous nations. Their cousins the Wyandot moved to Michigan, Ohio, Kansas, and Oklahoma.
Mi'kmaq communities are located predominantly in Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, but with a significant presence in Quebec, Newfoundland, Maine and the Boston area.
The Nuxalk people call themselves the Nuxalkmc. Traditional Nuxalk territory is the central coast of British Columbia, from the mouth of the Bella Coola River inland along the Bella Coola Valley and nearby inlets and channels.
Also, the Canadian Ojibwe tribes are the same as the American Chippewa tribes, like I mean they are the exact same tribe just called different names.
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Peacemaking Protocol
Olan Leimomi Morgan, NARF Law Clerk
August 2, 2016
What are some of the peacemaking protocols of the Haudenosaunee people?
The Haudenosaunee utilize their founding constitution, Gayanesshagowa, to successfully implement their traditional peacemaking protocols. Among these protocols, the condolence ceremony assists adversaries in acknowledging each other’s humanity, losses, and sacrifices during disputes, creating a safe space for productive discussions.
Brief Haudenosaunee History
The Haudenosaunee, also known as the Iroquois, is a confederacy of six tribal nations that came together through the efforts of Dekanawida, also known as the Peacemaker. The founding constitution of the Haudenosaunee is known as the Gayanesshagowa (gaya-ness-HAgowa), or the Great Law of Peace. A full rendering of the Gayanesshagowa takes several days to convey, telling of “the ways in which the Peacemaker’s teachings emphasized the power of Reason, not force, to assure certain principles.” The Gayanesshagowa essentially “provides the Haudenosaunee people with instructions on how to treat others, directs them on how to maintain a democratic society, and expresses how Reason must prevail in order to preserve peace.” In Haudenosaunee stories, a boy was born into a world of continuous waring between tribes. His destiny was to address the issues of continuous warfare, and he became known as Dekanawida or the Peacemaker. Dekanawida travels among the people, “combing their hair” with the intention of “untangling old traumas that stand in the way of peace.” The peacemaking process runs on the people’s will and agreement to the government. Dekanawida established two houses of elder brothers (Mohawks, Onondagas, Senecas) and younger brothers (Cayugas, Oneidas, and later Tuskaroras).
Under Dekanawida’s leadership, the Haudenosaunee people created a protocol for bringing enemies together “under a temporary truce.” Dekanawida planted a white pine tree, known as the Great Tree of Peace, explaining that this tree had “four, white roots of truth that reach in the four, cardinal directions of the earth.” He explained further that “[t]hose people who had no place to go could follow the root back to its source and come under the shelter of the great law of peace.” He instilled the idea of disarmament, uprooting the tree and commanding all to come forward and throw their weapons of war into the unearthed hole. Depictions of the Great Tree of Peace often include a war club, arrow, or hatchet underneath the tree; hence the well-known phrase for ending conflict: “burying the hatchet.” The Peacemaker also gave Haudenosaunee women the responsibility to choose and oversee the leaders of the community, reserving the power to remove those unworthy of such leadership. The protocols and practices in the Gayenesshaqowa “were in place for generations prior to European arrival,” allowing the Haudenosaunee Confederacy to establish “expansive, prosperous communities across today’s state of New York.” The Haudenosaunee negotiated with English colonists at least since the late seventeenth century using Gayanesshagowa protocols and principles.
Peacemaking Protocol
The goal of Haudenosaunee peacemaking protocol is to address each party’s conditions for reaching a truce. The initial goal is to stop the warfare. The Haudenosaunee believe that the truce itself does not ensure peace, although it symbolizes the start of peaceful negotiations as time goes on. The peacemaking protocol is mainly about the process as opposed to the outcome, because the Haudenosaunee assume that the process of maintaining peaceful relations will never end. They accept that the process is ongoing, and instead of seeking closure, the larger purpose of a peacemaking meeting is to serve as a reminder of the continuing progress between affected parties.
Peacemaking Principles
Undoubtedly, one of the principles in Gayanesshagowa protocols is peace or disarmament, signified by the parties burying their weapons beneath the Great Tree of Peace. This practice is entirely symbolic since each party could either buy or make more weapons. Nonetheless, the burying of the weapons represents that the parties agree to no longer using their weapons against each other. The burying of weapons also signifies that talking through negotiations is superior to violence. Another principle is “equity, justice for the people,” and another is unity, summarized by the statement, “[w]e are now going to put our minds together to create peace.” Other principles include righteousness and health.
The overarching purpose of all these principles is to peacefully cooperate in order to create an appropriate outcome that benefits all sides. The principles focus on building a better world for future generations, known as the “politics of abundance.” The politics of abundance means “to always be respectful of the natural world and to have ceremonies” to ensure a healthy world for future generations. This idea contrasts with “politics of scarcity,” referencing political action taken only in response to the scarcity of resources. For tackling the war on terror, Haudenosaunee Great Law advocates for progressive pragmatism, barring idealism and vilification from negotiations to reach desirable outcomes agreed upon by all.
In conclusion, the Haudenosaunee continue to utilize their founding constitution, Gayanesshagowa, to successfully implement their traditional peacemaking protocols. Integral to these protocols, the condolence ceremony serves to ease the pain of grieving community members and establish a clear space for productive peacemaking. The principles and practices of this deep-rooted, nonviolent confederacy could be further utilized by other native peoples to facilitate peaceful negotiations and healing.
(continue reading)
20 notes
·
View notes