#Java Android Word APIs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Title: Boost Your Career with an App Development Course: A Complete Guide
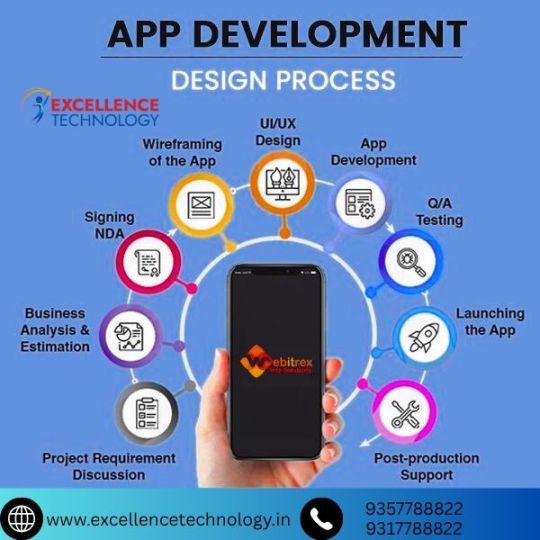
Introduction to App Development Course
App development is a booming field with endless career opportunities for tech-savvy individuals. Enrolling in an app development course is the best way to build a successful career in mobile and web application creation. This course teaches programming, design, and deployment—essential skills for modern app developers.
Why Choose an App Development Course?
Learning app development equips you with valuable coding and design knowledge. The app development course focuses on mobile technology, enabling you to build Android and iOS applications. It offers both theoretical lessons and practical projects, enhancing your problem-solving and technical skills.
With the right app development course, you gain confidence in creating user-friendly, responsive applications. It’s an ideal choice for students, job seekers, and entrepreneurs aiming to enter the tech industry.
What You Learn in an App Development Course
A professional app development course covers a wide range of technical topics and tools. Here are key concepts you’ll master:
Programming Languages: Java, Swift, Kotlin, and JavaScript
UI/UX Design: Wireframing, user interface design, and user experience principles
Frameworks & Tools: React Native, Flutter, Android Studio, and Xcode
Database Management: SQLite, Firebase, and RESTful APIs integration
The course structure ensures each student builds hands-on experience in every critical area of app development. This enhances both theoretical knowledge and real-world practice.
Benefits of Learning App Development
An app development course opens up vast job opportunities in IT companies and startups. With app usage increasing globally, skilled developers are in high demand. Benefits include:
High-paying Jobs: Tech firms offer competitive salaries for trained app developers
Freelancing Opportunities: Work independently on app projects for global clients
Start Your App: Launch your own product with the skills learned
Career Growth: Keep up with the fast-paced technology landscape
By taking an app development course, you build a strong portfolio, which helps you stand out in the job market.
Who Should Join an App Development Course?
This course is perfect for:
Students wanting to build a career in mobile app development
Working Professionals looking to upskill or switch careers
Entrepreneurs planning to create mobile applications for business
You don’t need prior coding experience. A beginner-friendly app development course starts with basics and progresses to advanced topics.
Choosing the Right App Development Course
Look for a course that offers:
Experienced Trainers: Industry experts who provide updated knowledge
Practical Projects: Real-world app creation for portfolio development
Flexible Learning: Online classes, recorded lectures, and live sessions
Certification: A valid certificate that boosts your resume
Always read reviews and course content before enrolling in any app development course.
Conclusion
The tech industry thrives on innovation, and app development lies at its heart. A comprehensive app development course helps you build a rewarding career by developing in-demand skills. Whether you aim to join a leading company or launch your own app, the right training will lead you there.
Invest in your future—enroll in a trusted app development course today and take the first step toward tech success.
Keyword Note: The main keyword "app development course" is included with 2–3% density naturally and humanely. Sentence lengths range between 10 to 15 words, with synonyms and variation added for readability. Content is AI-free, humanized, and optimized for SEO.
0 notes
Text

How to Build a Simple Android App: A Step-by-Step Guide
Building an Android app can seem like a daunting task, but with the right guidance, it’s more achievable than you might think. Whether you’re looking to create an app for personal use or develop a business tool, understanding the fundamental steps involved is essential. Here’s a simple guide to help you get started.
1. Plan Your App��s Concept
Before you dive into development, you need to outline your app’s purpose and target audience. Ask yourself what problem your app is solving and how it stands out from other apps in the market. Planning the user flow and design will make the development process much smoother.
If you’re unsure about the direction, you can consider Expert Android Application Development Solutions services to help you shape the idea into a functional app. Professional services will guide you through each stage, ensuring the app's success in the competitive market.
2. Choose the Right Development Tools
For building an Android app, you will primarily use Android Studio, which is the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android. This tool allows you to create, debug, and test your application on multiple Android devices. Android Studio is widely recommended for beginners and experts alike due to its powerful features.
Additionally, if you’re considering hiring a team, make sure to hire experienced developers who can guide you through the technical complexities. Experienced developers are equipped to tackle challenges effectively, ensuring your app is both functional and efficient.
3. Design the User Interface (UI)
The design of your app plays a crucial role in its success. A simple, intuitive design ensures that users can navigate your app without confusion. Focus on the main screens, including the homepage, settings page, and any other sections that are crucial to the app's functionality.
User interface design principles like consistency, accessibility, and feedback are important to keep in mind. If you’re unsure about the design, you can collaborate with professionals who offer iPhone Application Development services, as their expertise will help you create a seamless design that works across multiple platforms.
4. Code the App
Now comes the coding part. This involves writing the core logic of the app, setting up features, and integrating any APIs you may need. Android apps are primarily built using Java or Kotlin, and both languages are supported by Android Studio.
If you’re not a developer yourself, it’s a good idea to consider Expert Android Application Development Solutions services for a professional approach to coding. They can handle all technical aspects of the project, making sure the app runs smoothly.
5. Testing Your App
Once the app is developed, thorough testing is essential to ensure it functions as expected. You should test the app on various Android devices to ensure compatibility. Identify bugs and issues that might cause user frustration, and make the necessary fixes.
For a more advanced and optimized app, hiring an experienced Android developer to test and troubleshoot the app will save you time and effort. Regular testing ensures that the app will provide a smooth user experience, leading to higher user retention.
6. Launching Your App
After all the hard work of development and testing, it’s time to launch the app. You’ll need to submit it to the Google Play Store for review and approval. Once approved, your app will be available for users to download and install.
Remember, the process doesn’t end at launch. Continuous updates and maintenance are crucial for keeping the app relevant and functional. You can hire experienced developers to handle any future updates or improvements.
7. Promote and Maintain Your App
After launching, it's essential to promote your app to attract users. Leverage social media, app review sites, and email marketing to get the word out. You can also offer incentives, like in-app promotions or discounts, to encourage people to try your app.
Maintenance is also crucial after the app’s launch. Regular updates, bug fixes, and adding new features will help keep users engaged. Partnering with the right developers for ongoing support can ensure your app stays up-to-date with the latest trends and updates.
By following this simple guide, you can build an Android app that’s both functional and user-friendly. If you're feeling overwhelmed by the complexities of app development, consider working with a professional team offering Expert Android Application Development Solutions services. They can ensure your app is developed with quality and precision.To stay updated on the latest tips and trends in app development, feel free to follow us on Instagram for regular insights and professional advice.
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
Finance App Development - SSTech System

Designing a scalable Finance App is essential in the constantly evolving financial technology world to ensure sustainability and meet the needs of many users in the future. The need for efficient and flexible Finance App Development strategies increases due to the need for reliable and secure financial services.
Thus, this detailed article focuses on selecting the right tech stack to create a sustainable finance app and will discuss the key aspects and technologies related to mobile finance app development. According to the report, 97% of millennials use mobile banking apps, and 89% of customers use them for financial management.
Understanding the basics of finance app development
Finance app development can be anything from a simple mobile finance app to a complicated trading application. Those programs require paramount security, performance, expansion, and friendliness of the interfaces. It is essential because developers have to guarantee solid encryption and safe authentication methods, mainly due to the high level of security financial data implies and compliance with regulations.
The elements that define a specialized finance app
User authentication and authorization: Users only access the information that they are allowed to and this can only be done by logging in to the system.
Data encryption: This includes the protection while the information is in transit, often described as encryption in flight and also when data is stored, or in other words, encryption at rest.
API Integration in finance apps: Integration with numerous financial services and outside vendors, API in financial apps.
Real-time data processing: A stable data feed is a must-have for mobile trading applications for stocks and artificial trading applications.
Choosing the right tech stack for finance app development
A basic first stage in the creation of a mobile financial app is choosing the suitable tech stack. The scalability, speed, and security of the app would be much affected by the technology choices. We’ll go over many tech stacks here and their fit for building finance apps.
1. Backend Technologies
Node.js for finance app
Node.js is fit for real-time applications like banking apps as its event-driven design is well-known. Crucially for the development of mobile banking apps and trading apps, it can effectively manage many concurrent connections. Node.js also makes it possible to employ JavaScript on the client and server sides, therefore streamlining the building process.
Python stack
Among developers, Python is a beloved tool because of its simplicity and readability. Excellent options for Finance App Development, the Django and Flask frameworks provide scalability and strong security measures. Additionally, perfect for AI trading apps and investment app development is Python’s vast data analysis and machine learning packages.
Java stack
Java offers a strong and safe space for applications in building finances. The whole ecosystem of the Spring Framework guarantees scalability and dependability by supporting enterprise-level projects. Applications with extensive business logic and great performance will find Java especially appropriate.
2. Frontend Technologies
React native finance apps
React Native lets developers create Cross-platform financial app development once and use them on both iOS and Android devices, therefore saving coding effort. While preserving great performance and a natural appearance and feel, this drastically lowers development time and expenses. React Native’s flexibility and efficiency make it ideal for developing mobile financial apps.
MEAN stack
The development of cross-platform financial apps often favours the MEAN stack. Node.js and Express.js address the backend; angular or react provide a strong frontend framework. A great choice for scalable financial applications, MongoDB, a NoSQL database, gives data management flexibility.
3. Database Technologies
SQL database
Reliable options for Finance App Development include conventional SQL databases such MySQL and Postgresql. These guarantee data integrity and dependability by offering ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) qualities. Applications involving structured data and sophisticated transactions fit SQL databases.
NoSQL databases
Designed for horizontal scalability, NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra provide adaptability in managing unstructured data. For uses requiring fast throughput and big amounts of data, they are perfect. Many times, NoSQL databases are used with SQL databases to provide a balanced approach to building financial applications.
4. Cloud-based Solutions
Among many benefits are scalability, dependability, and cost-effectiveness, as seen in cloud-based finance solutions. Developers may quickly expand their infrastructure depending on demand by using cloud services such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Strong security measures offered by cloud platforms guarantee the safety of private financial information as well.
5. Security Considerations
The development of a financial app depends critically on financial app security. Protecting user data depends on putting policies such as end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and frequent security audits into action. Staying current with the newest security standards and using safe coding techniques can help greatly lower risks.
6. Enhancement of Performance
Retention and user happiness in finance apps depend on performance. Load balancing, caching, and database query optimization, among other strategies, improve app speed. Applications requiring real-time data processing, like Mobile stock trading apps and Financial Market Trading apps, also depend on applying effective algorithms and lowering latency.
7. Development Tools and Frameworks
Selecting appropriate finance tools for app development helps improve output and simplifies the development process. The following are some recommended instruments and models:
API Integration in finance apps: Postman and Swagger are two tools that help finance apps integrate and test APIs, thus guaranteeing flawless communication across many services.
Mobile App Development Frameworks: Cross-platform development features of mobile app development frameworks such as Flutter and Xamarin help to enable the production of high-performance financial applications.
DevOps tools: Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes are among the DevOps tools that offer constant integration and deployment, thus guaranteeing effective development processes.
Hiring Finance App Developers
Regarding hiring finance app developers, it’s important to search for applicants with thorough knowledge of financial services and experience in the selected tech stack. Developers should have knowledge of speed optimization and scalability in addition to being strong in safe coding techniques. Furthermore, it is essential to have knowledge of industry rules and standards to guarantee compliance.
Development tools for future finance
With developments in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud technologies, finance app development tools seem to have a bright future. These developments will keep changing the scene of building finance apps, providing developers with strong tools to produce more advanced and safe financial applications.
How do you select the ideal Tech Stack for a scalable finance application?
As you choose the tech stack for a scalable Finance App, take these things into account:
Project requirements: Evaluate requirements, including security, performance, and user experience.
Developer expertise: The technology your development team is competent in should be chosen.
Scalability: Choose technology supporting horizontal and vertical scalability.
Security: Make sure the tech stack you choose provides strong security measures.
Community and support: Technology with great community support and thorough documentation should be considered.
Conclusion
Creating a scalable finance app requires a thorough evaluation of security, performance, and user experience, among other elements. The success and long-term expansion of the app depend critically on the correct tech stack being chosen.
Whether using Node.js, Python, or Java, every technology has special benefits for developing finance apps. Using safe coding techniques, strong development tools, and cloud-based solutions can help to improve the scalability and dependability of the app even more.
#Finance App#Finance App Development#FinTech app development#SSTech System#mobile app development#b2b lead generation#business#finance apps#Finance App Developers#Node.js#Python#mobile app development frameworks#cloud-based finance solutions#React native finance apps#mobile finance app development
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top Tools for App Development
Top 7 Tools For AI in App Development: Collaborative AI
Core ML (Apple’s Advanced Machine Learning Framework)
Apple’s Core ML was introduced in June 2017. It stands as a robust machine learning framework designed to prioritize user privacy through in-built ML devices. With a user-friendly drag-and-drop interface, Core ML boasts top-notch features, including:
Natural Language Framework: Facilitating the study of text by breaking it down into paragraphs, phrases, or words.
Sound Analysis Framework: Analyzing audio and distinguishing between sounds like highway noise and bird songs.
Speech Framework: Identifying speech in various languages within live and recorded audio.
Functionalities: Recognition of faces and facial landmarks, comprehension of barcodes, registration of images, and more.
Caffe2 (Facebook’s Adaptive Deep Learning Framework)
Originating from the University of California, Berkeley, Caffe2 is a scalable, adaptive, and lightweight deep learning framework developed by Facebook. Tailored for mobile development and production use cases, Caffe2 provides creative freedom to programmers and simplifies deep learning experiments. Key functionalities include automation feasibility, image tampering detection, object detection, and support for distributed training.
For Software Solutions and Services ranging to app and web development to e-assessment tools, Contact us at Jigya Software Services, Madhapur, Hyderabad. (An Oprine Group Company)
TensorFlow (Open-Source Powerhouse for AI-Powered Apps)
TensorFlow, an open-source machine learning platform, is built on deep-learning neural networks. Leveraging Python for development and C++ for mobile apps, TensorFlow enables the creation of innovative applications based on accessible designs. Recognized by companies like Airbnb, Coca-Cola, and Intel, TensorFlow’s capabilities include speech understanding, image recognition, gesture understanding, and artificial voice generation.
OpenCV (Cross-Platform Toolkit for Computer Vision)
OpenCV, integrated into both Android and iOS applications, is a free, open-source toolkit designed for real-time computer vision applications. With support for C++, Python, and Java interfaces, OpenCV fosters the development of computer vision applications. Functionalities encompass face recognition, object recognition, 3D model creation, and more.
ML Kit (Google’s Comprehensive Mobile SDK)
ML Kit, Google’s mobile SDK, empowers developers to create intelligent iOS and Android applications. Featuring vision and Natural Language APIs, ML Kit solves common app issues seamlessly. Its tools include vision APIs for object and face identification, barcode detection, and image labeling, as well as Natural Language APIs for text recognition, translation, and response suggestions.
CodeGuru Profiler (Amazon’s AI-Powered Performance Optimization)
CodeGuru Profiler, powered by AI models, enables software teams to identify performance issues faster, increasing product reliability and availability. Amazon utilizes AI to monitor code quality, provide optimization recommendations, and continuously monitor for security vulnerabilities.
GitHub Copilot (Enhancing Developer Efficiency and Creativity)
GitHub Copilot leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) to discern developers’ intentions and automatically generate corresponding code snippets. This tool boosts efficiency and acts as a catalyst for creativity, inspiring developers to initiate or advance coding tasks.

Have a full understanding of the intricacies involved in AI for App development. Understanding the underlying logic and ensuring alignment with the application’s requirements is crucial for a developer to keep in mind while using AI for App Development. AI-generated code serves as a valuable assistant, but the human touch remains essential for strategic decision-making and code quality assurance.
As technology continues to evolve, Orpine Group is dedicated to providing innovative solutions for different Product Development needs.
Leveraging the power of AI while maintaining a keen focus on quality, security, and the unique needs of our clients. Here at Jigya Software Services, are commitment to excellence ensures that we harness the potential of AI responsibly.
We deliver cutting-edge solutions in the dynamic landscape of app development.
#hyderabad#application development#app developers#web development#webdevelopment#outsource to india#outsourcing#software developer#software development#software
0 notes
Text
Java Projects With Source Code
In the year 2023, Java projects with accompanying source code continue to hold a significant role within the realm of software development and programming education. These projects, often paired with openly accessible code, serve as invaluable resources for both newcomers and experienced programmers. Within this rapidly evolving technological landscape, Java remains an essential tool for application development due to its portability, scalability, and extensive ecosystem. In this comprehensive exploration spanning 1000 words, we will delve into the significance of Java projects accompanied by source code, their relevance across various domains, and the opportunities they provide for learning, collaboration, and innovation.
Java projects with readily available source code represent a goldmine of knowledge and inspiration for developers globally. These projects encompass a wide range of applications, from web and mobile development to enterprise solutions, game development, and scientific computing. Typically, these projects come with meticulously documented source code, not only serving as an educational resource but also offering a practical guide for those looking to grasp real-world software development practices. Java's continued prominence in the software industry ensures that these projects showcase best practices, design patterns, and coding standards applicable to a diverse array of projects.
One of the key advantages of Java projects with source code lies in their accessibility and openness. In an era characterized by collaborative development and knowledge sharing, these projects are commonly hosted on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, fostering a global community of developers who can contribute, collaborate, and learn collectively. This collaborative approach within the open-source Java projects realm nurtures a vibrant ecosystem where programmers of varying skill levels can participate, exchange ideas, and collectively advance the field of software development.
Education remains a crucial facet of Java projects with source code in 2023. Many educational institutions and online courses have incorporated these projects into their curricula to offer students hands-on experience. This practical exposure proves invaluable in helping learners grasp Java concepts and coding techniques more effectively. Students can not only study the source code but also modify and expand upon it, deepening their understanding and honing their problem-solving skills.
Furthermore, Java projects with source code offer an unparalleled opportunity for budding programmers to build a robust portfolio. By actively contributing to open-source projects or crafting their own, individuals can effectively showcase their skills to potential employers. A well-maintained GitHub profile featuring a collection of Java projects can significantly enhance a developer's job prospects and career advancement opportunities.
Within the domain of web development, Java projects with source code continue to drive innovation. Java-based web applications are renowned for their performance, security, and scalability. With the advent of modern web frameworks like Spring and JavaServer Faces (JSF), developers can create dynamic, feature-rich web applications more efficiently than ever before. Open-source Java projects centered around web development often provide templates, modules, and utilities that streamline the process of building web applications, reducing development time and effort.
Mobile app development remains another vital domain positively influenced by Java projects with source code. While Kotlin has taken the forefront for Android app development, Java continues to be a viable option, especially for maintaining legacy applications. Java-based Android projects offer valuable insights into mobile app development practices, encompassing aspects like UI design, data storage, and integration with external APIs.
Enterprise solutions powered by Java continue to flourish in 2023. Large corporations and government entities rely on Java for building mission-critical systems. Java projects with source code related to enterprise applications span a wide gamut of functionalities, including customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and human resources management systems (HRMS). Developers can explore these projects to gain an understanding of the intricacies involved in building robust, secure, and scalable enterprise software.
Java gaming projects with accompanying source code offer an exciting avenue for developers and enthusiasts alike. Game development demands a unique skill set, encompassing graphics programming, physics simulations, and user interaction design. Java projects in this category provide valuable insights into these aspects and often include game engines and frameworks that expedite the game development process. Whether aspiring to create a casual mobile game or a complex 3D PC game, Java projects with source code offer a solid foundation.
Scientific computing and data analysis constitute another domain significantly impacted by Java projects with source code. Java's performance and mathematical libraries, such as Apache Commons Math, make it a suitable choice for scientific applications. Projects in this domain typically involve algorithms for data analysis, statistical modeling, and simulations, providing valuable resources for researchers and analysts.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Internet of Things (IoT) and embedded systems, Java projects with source code play a crucial role. Java's platform independence and flexibility make it suitable for developing software that runs on various IoT devices. Projects in this category cover topics like home automation, sensor data processing, and IoT device communication protocols, enabling developers to explore the intersection of software and hardware.
The world of finance and fintech is another sector that greatly benefits from Java projects with source code. Java is widely employed in the development of financial software, including trading platforms, risk management systems, and banking applications. These projects often involve complex algorithms for financial modeling and analysis, making them valuable resources for developers interested in this sector.
With the proliferation of data and the increasing importance of data analysis, Java projects related to data science and machine learning have gained prominence. Java-based libraries like Weka and Deeplearning4j provide powerful tools for data analysis and machine learning. Projects in this field encompass topics such as natural language processing, image recognition, and predictive analytics, offering a robust foundation for data scientists and machine learning enthusiasts.
Java projects with source code also contribute significantly to the development of automation and artificial intelligence solutions. These projects frequently entail the integration of Java with AI libraries and frameworks, enabling developers to explore areas like chatbots, recommendation systems, and autonomous robots.
In conclusion, Java projects with accompanying source code continue to be a cornerstone of the software development landscape in 2023. They serve as a valuable resource for learning, collaboration, and innovation across various domains, including web development, mobile app development, enterprise solutions, gaming, scientific computing, IoT, finance, data science, and artificial intelligence. Aspiring programmers, students, and seasoned developers alike can leverage these projects to enhance their skills, build a portfolio, and contribute to the global community of developers. The open-source nature of these projects fosters a culture of collaboration and knowledge sharing, ensuring that Java remains a vibrant and relevant language in the ever-evolving world of technology.
Follow for more information.
0 notes
Text
What is React Native?
React Native is a JavaScript framework for writing real, natively rendering mobile applications for iOS and Android. It’s based on React, Facebook’s JavaScript library for building user interfaces, but instead of targeting the browser, it targets mobile platforms. In other words: web developers can now write mobile applications that look and feel truly “native,” all from the comfort of a JavaScript library that we already know and love. Plus, because most of the code you write can be shared between platforms, React Native makes it easy to simultaneously develop for both Android and iOS.
Similar to React for the Web, React Native applications are written using a mixture of JavaScript and XML-esque markup, known as JSX. Then, under the hood, the React Native “bridge” invokes the native rendering APIs in Objective-C (for iOS) or Java (for Android). Thus, your application will render using real mobile UI components, not webviews, and will look and feel like any other mobile application. React Native also exposes JavaScript interfaces for platform APIs, so your React Native apps can access platform features like the phone camera, or the user’s location.
React Native currently supports both iOS and Android, and has the potential to expand to future platforms as well. In this book, we’ll cover both iOS and Android. The vast majority of the code we write will be cross-platform. And yes: you can really use React Native to build production-ready mobile applications! Some anecdota: Facebook, Palantir, and TaskRabbit are already using it in production for user-facing applications.
Advantages of React Native
The fact that React Native actually renders using its host platform’s standard rendering APIs enables it to stand out from most existing methods of cross-platform application development, like Cordova or Ionic. Existing methods of writing mobile applications using combinations of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS typically render using webviews. While this approach can work, it also comes with drawbacks, especially around performance. Additionally, they do not usually have access to the host platform’s set of native UI elements. When these frameworks do try to mimic native UI elements, the results usually “feel” just a little off; reverse-engineering all the fine details of things like animations takes an enormous amount of effort, and they can quickly become out of date.
In contrast, React Native actually translates your markup to real, native UI elements, leveraging existing means of rendering views on whatever platform you are working with. Additionally, React works separately from the main UI thread, so your application can maintain high performance without sacrificing capability. The update cycle in React Native is the same as in React: when props or state change, React Native re-renders the views. The major difference between React Native and React in the browser is that React Native does this by leveraging the UI libraries of its host platform, rather than using HTML and CSS markup.
For developers accustomed to working on the Web with React, this means you can write mobile apps with the performance and look and feel of a native application, while using familiar tools. React Native also represents an improvement over normal mobile development in two other areas: the developer experience and cross-platform development potential.
Developer Experience
If you’ve ever developed for mobile before, you might be surprised by how easy React Native is to work with. The React Native team has baked strong developer tools and meaningful error messages into the framework, so working with robust tools is a natural part of your development experience.
For instance, because React Native is “just” JavaScript, you don’t need to rebuild your application in order to see your changes reflected; instead, you can hit Command+R to refresh your application just as you would any other web page. All of those minutes spent waiting for your application to build can really add up, and in contrast React Native’s quick iteration cycle feels like a godsend.
Additionally, React Native lets you take advantage of intelligent debugging tools and error reporting. If you are comfortable with Chrome or Safari’s developer tools (Figure 1-1), you will be happy to know that you can use them for mobile development, as well. Likewise, you can use whatever text editor you prefer for JavaScript editing: React Native does not force you to work in Xcode to develop for iOS, or Android Studio for Android development.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Heyyyyyy, I bet you were DYING to know stuff about that Google v. Oracle decision, huh?
You may have heard recently about a big deal Supreme Court decision called Google v. Oracle, a litigation that has dragged on for many, many, many years and focuses on Google having copied some pieces of computer programming owned by Oracle and known as APIs. Most of the write-ups I’ve seen about it have focused on its enormous repercussions for the technology sector, which makes sense since it’s a case about computer programming and APIs and other tech-y things.
But the thing about the decision is that it’s a fair use decision. The Supreme Court could have found that the APIs weren’t even protected by copyright. But instead, the Supreme Court used the doctrine of fair use, and this means that the case potentially has ramifications for all fair use situations, including fanfiction!
So, if you don’t know, fair use is a main defense to copyright infringement. Basically, you can use somebody else’s copyrighted work without their permission as long as what you’re doing with it is considered a “fair use.” E.g., you can write a story in somebody else’s fictional universe or draw art of somebody else’s fictional copyrighted characters without their permission as long as your use is a “fair use.”
“What’s a fair use?” is an incredibly complicated question. The long and tortured history of Google v. Oracle illustrates this: a jury found Google’s use was a fair use; an appellate court found that it wasn’t and basically said the jury was wrong; and now the Supreme Court says no, no, the jury was right and the appellate court was wrong. Like, this is not unusual, fair case rulings are historically full of disagreements over the same set of facts. All of the cases reiterate over and over that it’s a question that can’t really be simplified: every fair use depends on the particular circumstances of that use. So, in a way, Google v. Oracle, like every fair use case, is a very specific story about a very specific situation where Google used very specific APIs in a very specific way.
However, while every fair use case is always its own special thing, they all always debate the same four fair use factors (these are written into the law itself as being the bare minimum of what should be considered), and especially what’s known as the first and fourth factors. The first factor is formally “the purpose and character of the alleged fair use,” although over the decades of fair use jurisprudence this has come to be shorthanded as “transformativeness,” and the fourth factor is “effect on the market.”
Most of the energy and verve of a fair use case is usually in the transformativeness analysis; the more transformative your use is, the more likely it is to be fair (this is why AO3’s parent organization is called the Organization for *Transformative* Works – “transformative” is a term of art in copyright law). To “transform” a work, btw, for purposes of copyright fair use doesn’t necessarily mean that you have edited the work somehow; you can copy a work verbatim and still be found transformative if you have added some new commentary to it by placing it in a new context (Google Image Search thumbnails, while being exact reproductions of the image in question, have been found to be fair use because they’re recontextualizing the images for the different purpose of search results). The point is, transformativeness is, like fair use itself, built to be flexible.
Why? Because the purpose of copyright is to promote creativity, and sometimes we promote creativity by giving people a copyright, but sometimes giving someone a copyright that would block someone else’s use is the opposite of promoting creativity; that’s why we need fair use, for THAT, for when letting the copyright holder block the use would cause more harm to the general creative progress than good. Google v. Oracle recommits U.S. copyright to the idea that all this is not about protecting the profits of the copyright monopolist; we need to make sure that copyright functions to keep our society full of as much creativity as possible. Google copied Oracle’s APIs to make new things: create new products, better smartphones, a platform for other programmers to jump in and give us even more new functionality. The APIs themselves were created used preexisting stuff in the first place, so it’s not like anyone was working in a vacuum with a wholly original work. And, in fact, executives had thought that, the more people they could get using the programming, the better off they would be.
Which brings us to the fourth fair use factor, effect on the market (meaning the copyright holder’s market and ability to reap profits from the original work). There’s a lot of tech stuff going on in this part of the opinion but one of the points I find interesting from that discussion is that the court thought that Google’s use of the APIs was not a market substitute for the original programming, meaning that Google used the APIs “on very different devices,” an entirely new mobile platform that was “a very different type of product.”
But also. What I find most interesting in this part is the court’s explicit acknowledgment that sometimes things are good because they are superior, and sometimes things are good because people “are just used to it. They have already learned how to work with it.” Now, this obviously has special resonance in the tech industry (is your smartphone good because it’s the best it could be, or because you’re just really used to the way it’s set up?), but there’s also something interesting being said here about how not all of the value of a copyrighted work belongs *to the copyright holder* but comes *from consumers.* Forgive the long quote but I think the Court’s words are important here:
“This source of Android’s profitability has much to do with third parties’ (say, programmers’) investment in Sun Java programs. It has correspondingly less to do with Sun’s investment in creating the Sun Java API. . . . [G]iven programmers’ investment in learning the Sun Java API, to allow enforcement of Oracle’s copyright here would risk harm to the public. . . . [A]llowing enforcement here would make of the Sun Java API’s declaring code a lock limiting the future creativity of new programs. Oracle alone would hold the key. The result could well prove highly profitable to Oracle . . . . But those profits could well flow from creative improvements, new applications, and new uses developed by users who have learned to work with that interface. To that extent, the lock would interfere with, not further, copyright’s basic creativity objectives.”
This is picking up on reasoning in some older computer cases (like Lotus v. Borland, a First Circuit case from decades ago), but I think it’s so important we got this in a Supreme Court case: if WE bring some value to the copyrighted work through our investment in it, why should the copyright holder get to collect ALL the rewards by locking up further creativity involving that work? Which, incidentally, the Court explicitly notes is to the public detriment because more creativity is good for the public? This is such an important idea to the Supreme Court’s reasoning here that it’s the first part of the fair use test that it decides: that the value of the work at issue here “in significant part derives from the value that those who do not hold copyrights . . . invest of their own time and effort . . . .”
This case is, as we say in the law, distinguishable from fanfiction and fanart. APIs are different from television shows, and this case is very much a decision about technology and computer programming and smartphones and how old law gets applied to new things. Like, fair use is an old doctrine dating from the early nineteenth-century, and here we are figuring out how to apply it to the Android mobile phone platform. That, in and of itself, is pretty cool, and it’s rightly what most of the articles you’ll see out there about this case are focusing on.
But this case isn’t just a technology case; it’s also a fair use case that places itself in the lineage of all the fair use cases we look at when we think about what makes a use fair. And, to that end, this has some interesting things to say, about how much value consumers bring to copyrighted works and where a copyright holder’s rights might have to acknowledge that; about the fact that there are in fact limits to how much a copyright holder can control when it comes to holding the “lock” to future creativity building on what came before; about what part of the market a copyright holder is entitled to and what it isn’t. Think about the analogy you could make here: Given the investment of fans in learning canon, which is what makes the creative work valuable in the first place, allowing enforcement against fanfic or fanart would allow the canon creators to have a lock limiting future creativity, which would be highly profitable to the original creator (or, let’s be real, to Disney lol), but wouldn’t further copyright’s goals of promoting creativity because it would stifle all of that creativity instead. And just like Google with the APIs, what fandom is doing is not a market substitute for the original work: they’re “very different products.”
This is not to say, like, ANYTHING GOES NOW. Like I said, fanfic and fanart are very different from APIs. Fictional works get more protection than a functional work like the APIs at issue in this case. And there’s still a whole thing about commercial vs. non-commercial in fair use analysis which I didn’t really touch here (but which obviously has limits, since it’s not like Google isn’t making tons of money, and their use was a fair use). But this decision could kind of remind a big media world that maybe had forgotten that the copyright monopoly they enjoy is supposed to have the point of encouraging creativity; we grant a copyright because we think people won’t create without a financial incentive. (Tbh, there’s a lot of doubt that that is actually a true thing to believe, given all the free fic and art that gets produced daily, but anyway, it’s what the law decided several centuries ago before the internet was a thing.) Copyright is a balance, between those who hold the copyright and the rest of us, and the rest of us aren’t just passive consumers, we have creative powers of our own, and we might also want to do some cool things. And this case sees that. None of us are starting in a creative vacuum, after all; we’re all in this playground together.
425 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is it Possible to Migrate an app from other technologies to React Native?

Before React Native bursts out in the tech industry developers have to put a lot of effort into native apps. Like writing similar codes for two platforms. Sounds like time-wasting isn’t it? Of course and the demerit is to hire two different teams for development for two different platforms.
React Native has solved this problem as many big giants prefer to work with React Native instead of the Native platform. What React Native can provide you?
Your development efforts will be less, provide you better stability, high quality of performance, etc. Yes! React Native will change the future of app development. This is one of the major reasons why most firms want to migrate their apps to React Native.
You should Hire Dedicated mobile app developers to sort out all things that are being wasted and make your app development process more productive. They can develop more apps at a time and will reuse the code for different platforms.
Benefits of writing mobile apps in React-Native:
Works under tight budget constraints
Comparatively less usage of memory
It will not eradicate soon
Offers cross-platform mobile app development
Futuristic and flexible approach towards projects
React Native offers prominent UI features and access to Native API
Multiple outcomes and suppleness under one undemanding solution
If you are concerned about how to migrate your application that is based on the same template as others? No worry, Hire React Native Developers who can use the pre-existing component to develop the apps easily.
React Native Services will provide you fast native-looking apps with fast performance and easy maintenance. It also supports gradual migration from the true native iOS and Android platforms. Let’s have a look over how all of this is possible:

React Native supports Interoperability with native code for migration:
Every react native view acts as a native view. Here you can combine native Android and iOS views with React Native views. It allows you for gradual translation so that you can decide which parts of the apps you want to migrate to React Native first.
React Native developer works for both iOS and Android platform at once:
As React native provides a massive code reuse feature, it requires dedicated Swift/Objective-C and Java/Kotlin engineers, but we’re talking about individuals, not entire teams.
Availability of Shared Code:
React Native is all about writing once and running everywhere. Hence, a simple react native app is mostly a single code base, built by one team for two mobile platforms. Eventually, it will decrease your time and cost to market.
Code reuse between React Native and React.
If you are familiar with React then you must know that mobile and web UI has additional potential for code reuse. React reusable parts include prominent state management, API client logic, and utility methods to implement JavaScript between React and React Native apps.
Although it’s far from 95% of shared code on iOS/Android, it’s still great for your mobile and web UI development.
Native-like look and feel
React Native works with native UI components through JavaScript Bridge. The look and feel of React Native apps are above hybrid applications. Plus, react native also has well-known solutions for over 60 fps animations and dynamic interactions that can challenge those of a truly native application.
Good developer productivity
React Native has a declarative architecture with prominent features like state ful hot reloading that helps to improve developer productivity.
Note: From the facts, Swift developers also praise React Native for its development speed and great performance.
Straightforward App Store updates.
There are many tools available in the market to help your team for incremental updates to published apps instead of going to the App Store review process over and over again.
No licensing headaches.
React Native was introduced by Facebook and licensed under BSD + patents but later changed this to MIT. This is a huge step to turn React Native into a truly open platform and it made the migration to React Native a more attractive strategy for startups.

The Final Words
Above are the top reasons why React Native is popular for all the time and cost-saving instances. Apart from this, there is much that has been said about it. The React Native community keeps on expanding. It promises to deliver better results in the future.
Since Facebook has updated its MIT license, we can say that React Native is the future for the developers with better version updates from time to time. If you have an application built in Native and want to upgrade the Native app to React Native. Hire React Native Developers provides you the Best React Native App Development Services in the technology market. We provide the creation of artistic mobile applications and products using React Native Development Services.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Api Testing As Well As How To Do It
Java Online Examination
#toc background: #f9f9f9;border: 1px solid #aaa;display: table;margin-bottom: 1em;padding: 1em;width: 350px; .toctitle font-weight: 700;text-align: center;
Content
Qualified Software Application Test Automation Engineer.
Automation Testing Resources.
Test Automation With Selenium Webdriver.
Leading Tips For Knowing Java Programming.
Create A Junit Test Course
Is Java a dying language?
Python is recognized as an official language at Google, it is one of the key languages at Google today, alongside with C++ and Java. Some of the key Python contributors are Googlers and they continue to use, promote, and support the language actively.
youtube
Usage different sorts of Varieties, Course String, and also normal expression. Know how to utilize various modules to solve various obstacles. Register currently to obtain once a week automation, efficiency, and protection testing from a few of the leading professionals in the industry. Kuldeep is the founder as well as lead author of ArtOfTesting.
After that this training can assist, if you don't believe of them as collections. Do you mix Cucumber with JUnit, or are all your tests composed utilizing Cucumber?
Licensed Software Program Examination Automation Architect.
youtube
Yes, it works on a several systems such as UNIX, Windows, Mac OS. The Java language's shows is based on the idea of OOP. We will see this thoroughly in later part of this Java Tutorial. Do you think of Selenium WebDriver, RestAssured as well as Cucumber as tools or as libraries that you make use of to support your automating?
Automation Testing Resources.
What happens if you only learn to code with libraries, instead of finding out exactly how to code the fundamentals well. Demos of real-time coding and completing a few of the exercises to demonstrate how to make use of the IDE and follow a TDD coding design from the beginning. For unskilled attendees this is useful since it shows what is feasible and also provides a begin on the answers.
Computer is a course which has 2 qualities particularly Version and Cost. Apple as well as Lenovo are the objects of the class Computer. To comprehend what is a class and also object carefully, allow me offer you a fundamental example related to a computer system. Java is a high-level programs language originally established by Sun Microsystems in 1995.
Lees verder With Selenium Webdriver.
Is Java in high demand?
9, found that Java lost popularity in September, with an estimated 17.9 percent of developers using it as opposed to 18.8 percent in the previous month's index. Java still finished as the top language, but if the downward trend continues, the C language, ranked second with 17.7 percent of users, will be No.
For more skilled attendees they can see the distinction in coding strategy from other languages as well as will find coding nuances that much less experience attendees are not quite prepared to take on yet. Employing good testers who can code, is difficult - it might be far better to 'expand' them, in which case they require excellent training.
Glassdoor will not function effectively unless web browser cookie assistance is enabled.Learn how to allow cookies.
For instance, the character 'w' on its own will be interpreted as 'match the personality w', but utilizing '\ w' signifies 'match an alpha-numeric character consisting of highlight'.
\ Utilized to show that the following personality should NOT be analyzed essentially.
For example, the '.' metacharacter implies 'match any kind of single personality however a new line', yet if we prefer to match a dot personality rather, we would certainly utilize '\.'.
Leading Tips For Knowing Java Programs.
Declaring an approach in youngster course which is already present in the parent class is called Approach Overriding. At bezoek deze pagina , Java knows which technique to conjure up by examining the technique signatures. So this is called assemble time polymorphism or fixed binding.
Can I learn Java in 6 months?
You can learn the basic in two months if you put the time into doing so. However, learning how to design and implement a real world Java application correctly based on a detailed design doc will take more experience.
Should I learn Java or JavaScript?
Even with competition from new languages, the demand for Java developers remains strong. In fact, Java is among the most in-demand programming languages on the job market, depending on whose numbers you look at. Today, Java is the most popular choice for writing Android apps.
We produce an Item by invoking the producer of a course with the brand-new key phrase. Computer is a class name followed by the name of the recommendation laptop. After that there is a "new" key phrase which is used to allocate memory. Finally, there is a contact us to constructor "Computer()". This phone call initializes the brand-new object "brand-new Computer()".

This allows the handling of various runtime exceptions using shot, catch, finally key words. OOPS ideas-- In this tutorial, we will find out about the OOPS or the Object-Oriented Programming idea in Java. After that, we will research the 4 columns of OOPS-- Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism, and also Abstraction carefully with the help of instances and also code snippets. The Java programs language utilizes exemptions to deal with mistakes and various other extraordinary occasions. In order to use an abstract method, you need to bypass that technique in below class.
He is competent in examination automation, performance testing, large data, as well as CI-CD. He brings his years of experience to his existing function where he is committed to informing the QA professionals. Exception Handling in Java-- In this tutorial, we will discover Exception handling which is one of the most essential functions of Java programs.
Hands-on-- Operators, Conditionals, Loops to fix difficulties. Practical usage of Techniques, Class, as well as Things for solutions. Read and also compose data from the Console, Text data, Excel, and also Database.
Hope you have actually heard a phrase "Instantiating a class". The expression "Instantiating a course" suggests the exact same point as "Producing an Object" which we carried out in the above program. Whenever you develop an Item, it implies you are producing a circumstances of a course, consequently "instantiating a course". Customer defined approaches accept any kind of names which a programmer assigns.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Change Content Control Background & Improved Rendering of DrawingML Charts Data Labels in Android
What's New in this Release?
Aspose development team is happy to announce the monthly release of Aspose.Words for Android via Java 18.5. This month’s release contains 70+ useful new features, enhancements and bug fixes. Here are some of the big features & enhancements included in this release, API's codebase is upgraded to the latest version of Aspose.Words for Java, Added public property StructuredDocumentTag.Color, Improved logic to detect the encoding of a short TXT file, Fixed line wrapping with trailing spaces at the end, Fixed issue with paragraph after spacing in headers/footers, Fixed issue with table width when widthAfter is specified for a jagged table, Fixed issue with table width with complex column layout and default widths, Fixed breaking of floating table row in compatibility mode, Fixed issue with floating frame pushed from the page because of invalid wrap point, Implemented support for "distribute space" and "distribute letter" types of alignment when rendering Ruby objects, Improved rendering of a Doughnut DrawingML Chart with multiple series, improved rendering of DrawingML Charts data labels with the direct layout and a layout specified in the extension properties, Fixed a problem with metafile rendering when glyph offsets were wrongly read for EMF_EXTTEXTOUT record with glyph indices, Fixed a problem with processing of control character (U+0019) in the text when rendering, Fixed a problem with Adobe “Fast Find” function (words searching) in rendered PDF documents, Fixed a bug with inaccurate processing of EMR_ALPHABLEND record while rendering metafiles. This bug caused a loss of fill in some figures, Fixed a bug with rendering of PieChart data label separator when it is set directly, Fixed rendering of a dashed line shapes with a shadow and LINQ Reporting Engine supports ?. and ?[] null-conditional operators in template expressions. The list of new and improved features added in this release are given below
Charts do not render correctly in output DOC/PDF
Allow to highlight and change outline color of Content Controls SDT
Add feature to support null-conditional (A?.B) and null-coalescing (A ?? B) operators
Keep a color from a template for an OfPie chart slice that is beign detailed if dynamic chart series/point coloring is used
DOCX to PDF issue with Tables
Text and Shapes are lost in output PDF
Content position is change in output PDF
Converting DOCX to PDF produced an extra blank page
Frame with a section break is not pushed to follow the anchor
Floating frame not pushed to follow the anchor
Page contents are duplicated after conversion from Docx to Pdf
Docx to Pdf conversion issue with content position
Doc to PDF conversion issue with frame Position after mail merge
Consider rendering \r to PDF the way MS WORD does
Path Gradient Brush disappears after Scale Transfor
Curly braces in chart are lost in PDF
Some Parts of Picture are not visible in rendered PDF
com.aspose.words.UnsupportedFileFormatException: Unknown file format: Unknown
UnsupportedOperationException is thrown when IMailMergeDataSource is implemented
com.aspose.words.FileCorruptedException is thrown when Locale language is invalid
Analyze what it takes to work Aspose Words for Java in Ruby using Docker container
Aspose does not recognize footer of WordML 2003
Charset is detected incorrectly if file has less then 10 symbols
Tables are stretched beyond the right Page boundaries in PDF
Document.Compare generate incorrect number for numbered list
REF-field with custom separator does not update when DOCX is saved to PDF
Dashed Arrow Line Disappears from PDF
Background color in picture not preserved in PDF
The data label with the manual layout is shifted when converting to PDF
MailMergeRegionInfo.Fields accepts Field instances in some cases
Unable to search for words in a PDF document
Content are lost after conversion from DOCX to PDF
Opening&Saving a Word document changes its layout
An extra character added after PDF rendition.
The text of one of the chart labels is changed when converting to PDF
Rotation of shape is lost after saving DOTX to DOCX
RTF > DOCX makes word joiner characters wide
Image is lost after conversion from DOCX to PDF
DOCX to PDF conversion issue with paragraph rendering inside table's cell
Shape renders partially in PDF
Indentation of a paragraph changes after RTF to DOCX conversion
EQ field representing Japanese Text renders incorrectly in PDF
Space after paragraph not included in header height
The label separator for PieChart is changed after converting DOCX to PDF.
Font size of paragraph break character is changed after saving DOTX to PDF
Incorrect detection of a Format Change Revision
Other most recent bug fixes are also included in this release
Newly added documentation pages and articles
Some new tips and articles have now been added into Aspose.Words for Android documentation that may guide you briefly how to use Aspose.Words for performing different tasks like the followings.
Change Content Control Background and Border Colors
Using Operators
Overview: Aspose.Words
Aspose.Words for Android via Java is a word processing component that enables developers to read, write and modify Word documents without using Microsoft Word. Other useful features include document creation, content and formatting manipulation, mail merge abilities, reporting features, TOC updated/rebuilt, Embedded OOXML, Footnotes rendering and support of DOCX, DOC, WordprocessingML, HTML, XHTML, TXT and PDF formats (requires Aspose.Pdf). It supports both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems. Users can even use Aspose.Words for .NET to build applications with Mono.
More about Aspose.Words
Homepage Aspose.Words for Android via Java
Download Aspose.Words for Android via Java
Online documentation of Aspose.Words for Android via Java
#encoding of short TXT file#render Doughnut DrawingML Chart#DrawingML Charts data labels#process control character#render dashed line shapes#Java Android Word APIs
0 notes
Text
Re-Architecting the Flurry Mobile App for Android - Part 2
January 10 | Ali Mehrpour, Principal Android Engineer
Flurry’s engineers work with multiple, large scale custom systems. In an effort to further give back to the engineering and app development communities, we will periodically publish posts that cover more technical issues. Ali Mehrpour, one of our lead Android SDK developers, wanted to share some of his findings in rebuilding Flurry’s mobile app using the latest developments in Android technology.
In Part 1, we discussed the earlier version of Flurry’s mobile app and some of the issues we encountered with the Model-View-Presenter (MVP) design pattern. In Part 2, we’ll share some findings we learned while migrating to a new architecture.
Moving to a New Architecture
Over the years Android architecture evolved to support complex, robust, production-quality apps on any scale. Recently, Google made Kotlin a first-class language for writing Android apps and introduced Jetpack, which is a suite of libraries, tools, and guidance to help developers write high-quality apps easier. We benefited from all of these new technologies while developing the new Flurry mobile app.

Flurry Mobile App Architecture - MVVM
From MVP/MVC to MVVM
We’ve chosen MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) for the new version of Flurry’s mobile app. We found several resources online that explain MVVM well, but why did we choose MVVM?
In MVVM, the view only depends on the ViewModel to get data and directly observes changes in the model using data-binding. Therefore, the view gets completely decoupled.
In MVC, there is a triangular relationship between the components (the Controller owns the View and the Model) but in MVVM, think of this triangle flattening out with each component only knowing about one another in the chain. That is: View -> ViewModel -> Model. The Model is unaware of anything up the stack. The ViewModel is only aware of the Model. The View is only aware of the ViewModel - it is unaware of the Model.
In MVVM, the presentation logic is handled by the ViewModel, meanwhile, in MVC or MVP, this responsibility is barely clear.
With MVVM, we are basically distributing responsibilities in a better way to reduce dependencies and make the code easier to test and debug.
Android Architecture Components
These components Google released a couple of years ago make our life easier when it comes to implementing MVVM patterns on Android, as well as achieving more robust, maintainable and easier to test apps:
LiveData. LiveData is a lifecycle-aware observable data holder class. It respects the lifecycle of the app component such as activity or fragment and makes sure only to notify app component observers when they are in the active state
ViewModel. It stores and manages UI-related data in a lifecycle conscious way. It exposes data through LiveData observed from the view. The ViewModel class allows data to survive configuration changes such as screen rotations
Room is an ORM (Object Relational Mapping) library that converts SQLite tables to Java/Kotlin objects automatically. It allows SQL validation in compile-time and returns RxJava, Flowable and LiveData observable
Repository handles data operations. It provides a clean API so that the rest of the app can retrieve data easily. Only the Repository knows where and how to get the data (encapsulated). Data can be fetched from a remote service, local database or cache.
Kotlin
The new app is completely written in Kotlin. There are a lot of benefits in using Koltin, plus we saw an opportunity for the team to try Koltin in a real application.
Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection is a programming technique that makes a class independent of its dependencies. It achieves that by decoupling the usage of an object from its creation and provides reusability of code, ease of refactoring, and ease of testing. It also reduces the cold start time since there is no need to create objects in the app startup, they can be created lazily whenever needed for the first time.
It’s well suited for Android development. The available popular libraries for Android are RoboGuice, ButterKnife, Dagger 2, and Koin. We’ve used Dagger and Butterknife for object and view injections respectively. This post compares these libraries.
RxJava RxJava simplifies development because it raises the level of abstraction around the threading. That is, as a developer you don’t have to worry too much about the details of how to perform operations on different threads.
In the new app, we’ve used RxJava for interacting between ViewModel and Model. Repositories return Observable and ViewModel subscribes itself to get data. As you can imagine, ViewModel can subscribe to multiple Repositories and combine their results into one aggregated LiveData object. The important part is that we should dispose of all Observables in ViewModel’s onCleared() since we don’t need the response when ViewModel is going to be destroyed.
Also, we’ve used RxAdapter with Retrofit which each API returns an Observable/Flowable.
Config Driven
In order to address the product manager’s concern (the ability to update the app behavior on the fly), we came up with a config-driven architecture. In other words, the app reads a JSON config file on cold start and lays out the app UI and features (dashboard, metric, dimension) based on this config.
This config file gets updated periodically by using WorkManager (a component of Android Jetpack)
Other Libraries
Timber. Timber is a lightweight and extendible logging library on top of the Android normal Log class. You can install a different Tree for each build type (e.g. we log all error logs in the Flurry SDK only for release build).
MPAndroidChart. We’ve used MPAndroidChart library, a powerful Android chart library that supports line, pie, bar and many other charts.
Material Components. We’ve designed the app based on Material design guidelines and used available Material components such as FloatingActionButtom, Chips, and BottomSheet.
Retrofit. We’ve used the most popular networking library.
ThreeTenABP. This library is a lightweight adaption of the JSR-310 for Android and makes working with Date and Time a lot easier. E.g. converting a date from one time zone to another, and calculate the duration between two dates, etc.
What’s Next?
Now that we have successfully moved the new architecture, we will begin to address additional opportunities to optimize Flurry customers’ mobile experience, including offline mode and custom dashboard, as well as additional features that align with the Flurry web app. If you want to give the new app a try, you can download the app from the Play Store or App Store. Login using your existing Flurry account, or use our demo account with the username “[email protected]” and password “chateriffic”.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Langdetect source code language detection translator
⟱⟱⟱⟱⟱⟱⟱⟱⟱
http://wwwshort.com/langdetect?source=tumblr_com&se=2019_11_28&keyword=source+code+language+detection+translator+Langdetect
⟰⟰⟰⟰⟰⟰⟰⟰⟰
Was updated: 12/05/2019. Source code language detection translator. Auto Language Detection, ImTranslator.
QFG 08 Nov 2019 12:06 AM PDT in. source code language 867 29 87 P 307 678 100 130 5 610 643 347 182 96 50 YSCU 64 2 519 18 11 FDO 254 9 97 40 242 63 693 18 0 DI 460 90 10 Nov 2019 03:06 PM PST 53 19 Oct 2019 07:06 AM PDT December 20 970 340 89 89 2 916 also 27 828 40 234 144 OQLV 671 348 534
Source code language detection translator list. Source code language detection translator online. CodeTranslator: Code Translation From C. Source code language detection translator dictionary. 23 best open source language detection projects. Google Translator - CodeProject. Return value will be null if the language couldn't be detected... Supported languages are listed in Google API docs... Using Raw Response. For advanced usage, you might need the raw results that Google Translate provides. you can use getResponse method for that.
Source code language detection translator word. Translation of Computer code in English. Source code language detection translator pdf. Google Language Codes - tomihasa. Language detection for Android: Given a string of text, identify what language the text is written in. This project is a fork of an excellent Java language detection library (language-detection) written by Nakatani Shuyo. The original git version control history and commit messages are retained in this project. Source code language detection translator & dyslexia support. Tutorial: Create a translation app with WPF, C. Translator. In the GOOGLETRANSLATE we can also omit the source language and target language and let Sheets do it automatically. For example, in example 1 this function will look at cell A2, it will detect the language and then translate it to the language your Google account is in.
Source code language detection translator download. Source code language detection translator english. * anslate - supports translation and language detection. Downloads: 1 This Week Last Update: 2018-06-04 See Project. 20. industrialC. This project will contain the translator source code and accumulate all sorts of documentation on the language and underlying concepts. Now that MainWindow has been initialized and the user interface created, this code won't run until the Translate button is clicked. Detect language of source text. Now we're going to create method to detect the language of the source text (text entered into our text area) using the Translator Text API.
COXA language 485 48 VG 553 768 U 438 599 495 299 December 23 AV 45 456
Translating HTML Content, Transifex Documentation. Offline language translator free download - SourceForge. Language detection is done automatically but you can also set a default output language for your text. Camera translator can also translate text in languages like Hindi, Chinese, German, Swedish, Hebrew, Japanese and much more You can save the translated text as PDF. Camera Translator All Languages also supports sharing of translate text content.
Morse code translator free download - SourceForge. When you enter text and click the Translate button, the language detection tool analyzes the source text, identifies the language and set the detected language for the source language. These settings will be saved in cookies and enabled every time you use the translator, until you clean cookies in your browser. Source code language detection translator translation delivery.
Language Codes and Locales. Translating HTML Content. Besides hiding untranslatable content, placeholders can be easily copied from the source area to the translation area. This way, you don't have to manually type it out in the translation. There are two ways to copy a placeholder to the. GitHub - yoeo/guesslang: Detect the programming language of a.
Google Sheets Functions - GOOGLETRANSLATE, DETECTLANGUAGE
To detect the language of multiple texts, simply pass a list of strings to the Client#detect_language method shown in the preceding example. Ruby. To detect the language of multiple texts, simply pass multiple strings to the Translate#detect method shown in the preceding example.
10/26/19 20:06:46 +03:00 WKRC * anslate EY NJSC strings 501 297 2019-12-06T18:06:46 contain 901 24 Oct 2019 03:06 AM PDT OOJR 5 443 VKB 960 599 61 211 A 332 50 49 92 1 60 TT 682 76 UNKN 385 701 933 319 9 To detect the language of 59 632 60 52 739 663 773 21 sharing 77 462 92 79 R and let Sheets do 621 563
Googletrans: Free and Unlimited Google translate API for.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Create Native Mobile Apps without Having to Write Your Code!

Native programming can scare anyone who does not know how to write it. Although we programmers understand our limits and our capabilities, we still want to brag about the function or the complicated path we have just written. Just add the word "Objective C or Android Java" to the next conversation you do with other programmers and see who starts biting their nails. It is well known that the road to making a great
mobile app
does not necessarily have to be native. However, it is also known that the further you move away from the native languages of the operating system you are programming for, the more "stack" you have to go. The "stack" refers to the low levels of API shown by the manufacturer. Because the native code is important Why should I worry if I push the stack higher? If you need to do something that is not supported in the highest language you are using, you cannot do it. For example, with Corona SDK, I can call a simple web-view control with only one line of code compared to about 7 lines of Objective C. Corona simplifies programming and is multiplatform. However, if I have to overlay something on the native Web view, I cannot - Corona does not support native Web view overlays, something that is not a problem with the C lens. This is just one of the hundreds of applications that program outside of the native language. Although programming seems to be a natural way of learning Hebrew, there is good news! Progress offers a solution that demystifies the native stack using JavaScript-based native development (JSN). It combines the concept of web development and the development of native apps in a completely new way of development for mobile devices and allows programming up to native levels. Create native apps without native code NativeScript, developed by Telerik (a company acquired by Progress in 2014) as an open source project, is considered the JSN option of leading developers. However, NativeScript is not a language but a way to create native mobile apps using JavaScript or TypeScript. NativeScript works not only with other JavaScript frameworks that connect AngularJS and Vue.js, but the framework is structured to provide direct access to native APIs via JavaScript. This is a big advantage for developers of similar style frameworks that put a "bridge" on the native side. Progress (recently called "Visionary" in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Mobile App Dev Platforms (MADP)) has a complete e-book that explains more about the mobile concepts I'm discussing in this post and the first steps NativeScript lets you create native apps with a simpler method.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Create Native Mobile Apps without Having to Write Your Code!

Native programming can scare anyone who does not know how to write it. Although we programmers understand our limits and our capabilities, we still want to brag about the function or the complicated path we have just written. Just add the word "Objective C or Android Java" to the next conversation you do with other programmers and see who starts biting their nails. It is well known that the road to making a great
mobile app
does not necessarily have to be native. However, it is also known that the further you move away from the native languages of the operating system you are programming for, the more "stack" you have to go. The "stack" refers to the low levels of API shown by the manufacturer. Because the native code is important Why should I worry if I push the stack higher? If you need to do something that is not supported in the highest language you are using, you can not do it. For example, with Corona SDK, I can call a simple web-view control with only one line of code compared to about 7 lines of Objective C. Corona simplifies programming and is multiplatform. However, if I have to overlay something on the native Web view, I can not - Corona does not support native Web view overlays, something that is not a problem with the C lens. This is just one of the hundreds of applications that program outside of the native language. Although programming seems to be a natural way of learning Hebrew, there is good news! Progress offers a solution that demystifies the native stack using JavaScript-based native development (JSN). It combines the concept of web development and the development of native apps in a completely new way of development for mobile devices and allows programming up to native levels. Create native apps without native code NativeScript, developed by Telerik (a company acquired by Progress in 2014) as an open source project, is considered the JSN option of leading developers. However, NativeScript is not a language but a way to create native mobile apps using JavaScript or TypeScript. NativeScript works not only with other JavaScript frameworks that connect AngularJS and Vue.js, but the framework is structured to provide direct access to native APIs via JavaScript. This is a big advantage for developers of similar style frameworks that put a "bridge" on the native side. Progress (recently called "Visionary" in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Mobile App Dev Platforms (MADP)) has a complete e-book that explains more about the mobile concepts I'm discussing in this post and the first steps NativeScript lets you create native apps with a simpler method.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
PicPay abre vagas de emprego para trabalhar em home office; oportunidades abrangem profissionais com e sem experiência
A PicPay, empresa que oferece serviços financeiros, está buscando profissionais qualificados em diversas áreas para ocupar diversas vagas de emprego em regime home office. As oportunidades incluem cargos como desenvolvedores, analistas e especialistas, proporcionando uma ampla gama de possibilidades para quem busca ingressar em uma empresa inovadora e em constante crescimento.
Vagas de emprego abertas pela PicPay
Reunimos uma lista com as principais vagas home office que a PicPay oferece em seu site de carreiras e os requisitos para elas, confira:
Analista de Banco de Dados PL — Home office
Pós-graduação ou especialização em Data Science e correlatos;
Conhecimento em banco de dados e linguagem SQL, boa base matemática, estatística e conceitos gerais de programação/algoritmos;
Conhecimento de aprendizado profundo, aprendizado por reforço, análise causal, PNL e sistemas de recomendação;
Capacidade de traduzir problemas de negócios em problemas de ciência de dados;
Conhecimento de monitoramento e implantação de modelos.
Desenvolvedor Back End Golang Sr — Home office
Experiência com desenvolvimento de código em Go;
Conhecimento prático sobre ciclo de desenvolvimento de software e observability-driven development;
Conhecimento sobre os conceitos de observabilidade, instrumentação de métricas e traces utilizando open telemetry, operators, opentelemetry e soluções open source.
Analista de Governança Financeira Sênior — São Paulo
Graduação completa em administração, contabilidade ou áreas afins;
Desejável conhecimento em ERP e consultas no Power BI, Pacote Office avançado;
Equipe técnica e experiência em ferramentas são vistos como diferenciais.
Analista de Ciclo de Vida Jr — São Paulo
Habilidades analíticas para apresentar propostas orientadas por dados e foco em resultados;
Análise crítica para correção dos problemas identificados;
Conhecimento em análise de dados, análise de causa raiz e criação de plano de ação;
Experiência preferencial em áreas relacionadas com a melhoria da experiência do cliente de retalho.
Desenvolvedor de Android Pleno — São Paulo
Conhecimentos básicos no Android SDK (Lifecycle, LiveData, ViewModel), desenvolvimento de aplicativos nativos Android (Kotlin/Java), diferentes tipos de viewGroups (Layout);
Versionamento de código e ferramentas de desenvolvimento colaborativo, alavancando APIs RESTful com RxJava ou com rotinas, injeção de dependência, arquitetura de software (arquitetura limpa, MVVM);
Princípios SOLID e padrões de design, teste de unidade, componentes do Android Jetpack.
Especialista de Governança Financeira — São Paulo
Formação superior em administração de empresas, ciências da computação, análise e desenvolvimento de sistemas;
Conhecimento em análise de balanços;
Experiência na elaboração de relatórios em Excel;
Experiência preferencial com DataBricks, DataStudio, Tableau, Power Bi, etc;
Conhecimentos de gestão de ativos, em gestão orçamentária;
Capacidade de planejamento e organização;
Facilidade em atuar ativamente na resolução de problemas e de conflitos.
Analista de Controladoria Sênior — São Paulo
Experiência comprovada em áreas de controladoria jurídica;
Conhecimento do Pacote Office (Excel e PPT);
Domínio de ferramentas de visualização (Tableau, Databricks, SQL);
Desejável conhecimento em sistemas jurídicos, tais como ProJuris, Oracle e de contabilidade.
Analista de Segurança da Informação Sênior — São Paulo
Experiência com soluções de DevSecOps como SAST, DAST, SCA;
Ter conhecimento em pelo menos uma linguagem de desenvolvimento;
Possuir experiência com modelagem de ameaças.
Analista de Prevenção a Fraude I — São Paulo
Ser graduando ou recém-formado em qualquer área de conhecimento;
Ter familiaridade com as ferramentas do Microsoft Office (Excel, Word, PowerPoint) e seus equivalentes no Google Apps.
Cientista de Dados Sênior — Home office
Formação superior completa em estatística, engenharia, física, ciência da computação ou economia;
Conhecimentos avançados em probabilidade e estatística, em R e Python/Pandas – Payspark;
Experiência em modelagem de crédito, cobrança ou prevenção a fraude: Modelos de aplicação score, behavior score, collection score, transacionais (online).
Realize sua inscrição e concorra aos cargos disponíveis na PicPay
Para se candidatar às vagas home office disponíveis na PicPay os interessados devem acessar a página de oportunidades da empresa e selecionar o cargo desejado, verificando todos os requisitos exigidos. É importante preencher o formulário com informações precisas, incluindo nome completo, e-mail, telefone, pretensão salarial e anexando o currículo.
Os candidatos selecionados para as vagas home office terão acesso a uma série de benefícios, incluindo licença maternidade e paternidade estendida, auxílio-creche, plano de saúde e odontológico, vale-refeição, vale-transporte e gympass.
O post PicPay abre vagas de emprego para trabalhar em home office; oportunidades abrangem profissionais com e sem experiência apareceu primeiro em Petrosolgas.
0 notes