#Jessica Rosenworcel
Text
By Jessica Corbett
Common Dreams
Sept. 26, 2023
Open internet advocates across the United States celebrated on Tuesday as Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel announced her highly anticipated proposal to reestablish FCC oversight of broadband and restore net neutrality rules.
"We thank the FCC for moving swiftly to begin the process of reinstating net neutrality regulations," said ACLU senior policy counsel Jenna Leventoff. "The internet is our nation's primary marketplace of ideas—and it's critical that access to that marketplace is not controlled by the profit-seeking whims of powerful telecommunications giants."
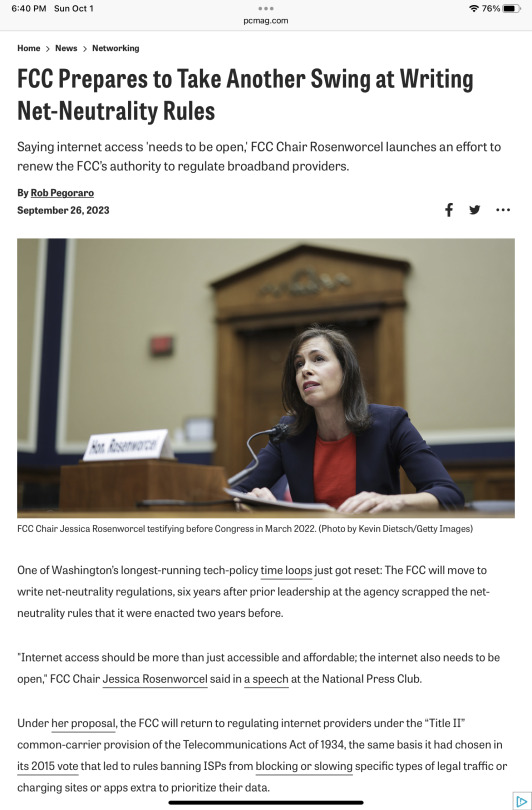
Rosenworcel—appointed to lead the commission by President Joe Biden—discussed the history of net neutrality and her new plan to treat broadband as a public utility in a speech at the National Press Club in Washington, D.C., which came on the heels of the U.S. Senate's recent confirmation of Anna Gomez to a long-vacant FCC seat.
Back in 2005, "the agency made clear that when it came to net neutrality, consumers should expect that their broadband providers would not block, throttle, or engage in paid prioritization of lawful internet traffic," she recalled. "In other words, your broadband provider had no business cutting off access to websites, slowing down internet services, and censoring online speech."
"Giant corporations and their lobbyists... will try every trick to block or delay the agency from restoring net neutrality."
After a decade of policymaking and litigation, net neutrality rules were finalized in 2015. However, a few years later—under former FCC Chair Ajit Pai, an appointee of ex-President Donald Trump—the commission caved to industry pressure and repealed them.
"The public backlash was overwhelming. People lit up our phone lines, clogged our email inboxes, and jammed our online comment system to express their disapproval," noted Rosenworcel, who was a commissioner at the time and opposed the repeal. "So today we begin a process to make this right."
The chair is proposing to reclassify broadband under Title II of the Communications Act, which "is the part of the law that gives the FCC clear authority to serve as a watchdog over the communications marketplace and look out for the public interest," she explained. "Title II took on special importance in the net neutrality debate because the courts have ruled that the FCC has clear authority to enforce open internet policies if broadband internet is classified as a Title II service."
"On issue after issue, reclassifying broadband as a Title II service would help the FCC serve the public interest more efficiently and effectively," she pointed out, detailing how it relates to public safety, national security, cybersecurity, network resilience and reliability, privacy, broadband deployment, and robotexts.
Rosenworcel intends to release the full text of the proposal on Thursday and hold a vote regarding whether to kick off rulemaking on October 19. While Brendan Carr, one of the two Republican commissioners, signaled his opposition to the Title II approach on Tuesday, Gomez's confirmation earlier this month gives Democrats a 3-2 majority at the FCC.
"Giant corporations and their lobbyists blocked President Biden from filling the final FCC seat for more than two years, and they will try every trick to block or delay the agency from restoring net neutrality now," Demand Progress communications director Maria Langholz warned Tuesday. "The commission must remain resolute and fully restore free and open internet protections to ensure broadband service providers like Comcast and Verizon treat all content equally."
"Americans' internet experience should not be at the whims of corporate executives whose primary concerns are the pockets of their stakeholders and the corporations' bottom line," she added, also applauding the chair.
Free Press co-CEO Jessica J. González similarly praised Rosenworcel and stressed that "without Title II, broadband users are left vulnerable to discrimination, content throttling, dwindling competition, extortionate and monopolistic prices, billing fraud, and other shady behavior."
"As this proceeding gets under way, we will hear all manner of lies from the lobbyists and lawyers representing big phone and cable companies," she predicted. "They'll say anything and everything to avoid being held accountable. But broadband providers and their spin doctors are deeply out of touch with people across the political spectrum, who are fed up with high prices and unreliable services. These people demand a referee on the field to call fouls and issue penalties when broadband companies are being unfair."
Like Rosenworcel, in her Tuesday speech, González also highlighted that "one thing we learned from the Covid-19 pandemic is that broadband is essential infrastructure—it enables us to access education, employment, healthcare, and more."
That "more" includes civic engagement, as leaders at Common Cause noted Tuesday. Ishan Mehta, who directs the group's Media and Democracy Program, said that "the internet has fundamentally changed how people are civically engaged and is critical to participating in society today. It is the primary communications platform, a virtual public square, and has been a powerful organizing tool, allowing social justice movements to gain momentum and widespread support."
After the Trump-era repeal, Mehta explained, "we saw broadband providers throttle popular video streaming services, degrade video quality, forcing customers to pay higher prices for improved quality, offer service plans that favor their own services over competitors, and make hollow, voluntary, and unenforceable promises not to disconnect their customers during the pandemic."
Given how broadband providers have behaved, Michael Copps, a Common Cause special adviser and former FCC commissioner, said that "to allow a handful of monopoly-aspiring gatekeepers to control access to the internet is a direct threat to our democracy."
Rosenworcel's speech came a day after U.S. Sens. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) and Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) led over two dozen of their colleagues in sending a letter calling for the restoration of net neutrality protections. The pair said in a statement Tuesday that "broadband is not a luxury. It is an essential utility and it is imperative that the FCC's authority reflects the necessary nature of the internet in Americans' lives today."
"We need net neutrality so that small businesses are not shoved into online slow lanes, so that powerful social media companies cannot stifle competition, and so that users can always freely speak their minds on social media and advocate for the issues that are most important to them," they said. "We applaud Chairwoman Rosenworcel for her leadership and look forward to working with the FCC to ensure a just broadband future for everyone."
153 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weekly output: Threads forecast, net-neutrality reboot (x2)
The Nats closed out a 2023 season that proved less awful than I’d feared with a win in Atlanta, and I was listening to the game I read of the untimely passing of Red Sox legend Tim Wakefield (cancer can quit giving me reasons to hate it any goddamn time now). Sigh.
The bonus post this week for Patreon readers: notes on surviving eight weeks in a row of travel, a dubious achievement that eclipses…
View On WordPress
#Brendan Carr#broadband privacy#Elon Musk Twitter#FCC#Insider Intelligence#Jessica Rosenworcel#Las Vegas#MWC#MWC Las Vegas#net neutrality#Threads#Threads app#Title II
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
“I think our new threshold, frankly, should be 100Mbps. I think anything short of that shortchanges our children, our future, and our new digital economy.” That’s what FCC commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel argued nine years ago — now, it’s finally happening.
Today, the FCC has changed its definition of “broadband” to mean download speeds of 100 megabits per second and upload speeds of 20 megabits per second. It had been stuck at 25Mbps/3Mbps since 2015. As recently as 2021, outgoing FCC chairman Ajit Pai claimed we still didn’t need more than that.
...
The new definition was pushed through by the FCC’s Democratic majority, something it hasn’t had for the majority of President Biden’s term in office. The FCC spent years completely deadlocked without its full five commissioners, until Anna Gomez was finally confirmed by the Senate last September.
Anyway, vote blue, it actually fucking matters.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The U.S. Senate moved yesterday in a 55-43 vote to confirm Anna Gomez to the Federal Communications Commission. Her confirmation breaks a partisan deadlock at the agency that has been in place since the beginning of the Biden administration, when Commissioner Jessica Rosenworcel vacated her seat to become FCC chair. The commission now has a 3-2 Democratic majority.
With the new majority, many speculate that the FCC will push to bring back net neutrality, which President Joe Biden supports.
This is very good news.
582 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Tuesday, New Hampshire attorney general John Formella said that a Texas-based telecom company was behind the reportedly AI-generated robocalls impersonating President Joe Biden that went out ahead of the state’s presidential primary last month.
At a press conference on Tuesday, Formella announced that he had identified Life Corporation and its owner, Walter Monk, as the source behind the thousands of calls and that his office issued a cease-and-desist letter to the company and had opened a criminal investigation into the matter. The Federal Communications Commission sent its own cease-and-desist letters to Life Corporation, as well as another Texas company, Lingo Telecom, the alleged voice service provider of the calls.
“Ensuring public confidence in the electoral process is vital,” Formella said at the Tuesday press conference. “We're providing this update and information today to assure the public that we take this seriously and that this is one of our most important priorities. We are also providing this update and information to send a strong message of deterrence to any person or entity who would attempt to undermine our elections through AI or other means.”
Formella said that anywhere from 5,000 to 25,000 of these robocalls were placed ahead of the New Hampshire primary that mimicked Biden and discouraged voters from voting. “Your vote makes a difference in November, not this Tuesday,” the robocall said.
In January, WIRED reported that two teams of researchers had determined that the call was created with voice-cloning software from the AI startup Eleven Labs. The company declined to take responsibility for the Biden clone, telling WIRED that it was “dedicated to preventing the misuse of audio AI tools.”
Last week, the FCC put out a new proposal to ban robocalls that use AI-generated voices by updating the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, a 1991 law that regulates telemarketers. The FCC has used the TCPA in the past to go after junk callers, including conservative activists Jacob Wohl and Jack Burkman. In 2021, the FCC fined the pair more than $5 million for violating the law after they placed calls threatening to release the personal information of voters if they voted by mail in the 2020 election.
“Consumers deserve to know that the person on the other end of the line is exactly who they claim to be,” FCC chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said in a statement on Tuesday.
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
For those of you that know me, I've always advocated for fair, equal and open internet as well as common carrier regulations for internet access in the USA. Today, we finally took a step back in the right direction.
After Ajit Pie repealed it, New Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel as of the 26th of Sept. 2023, put in place the Full Title: FCC Chairwoman Rosenworcel Proposes to Restore Net Neutrality Rules to Re-Establish the FCC's Authority Over Broadband Providers Under Title II
This is a HUGE win and means we have someone that actually understands and CARES about what this means.
https://www.fcc.gov/document/chairwoman-rosenworcel-proposes-restore-net-neutrality-rules
#lets go#net neutrality#gaming news#internet news#best news I've had all day#I'm so happy#lets fucking go
7 notes
·
View notes
Link
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Weekly output: competing with Google, FCC vs. TV ETFs
Seeing friends of mine on their way to Las Vegas or already there for Amazon’s AWS re.Invent conference makes me thankful that my schedule is devoid of business travel this week, even if solo travel for work can seem blissfully easy compared to family travel for Thanksgiving.
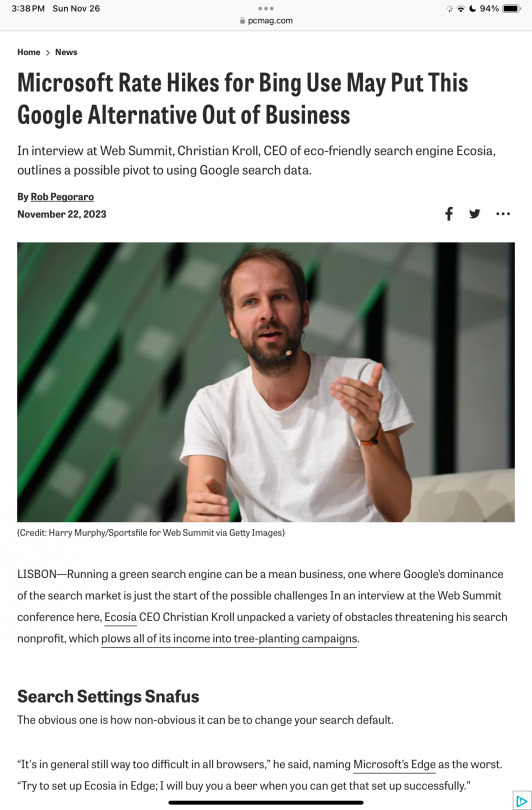
11/22/2023: Microsoft Rate Hikes for Bing Use May Put This Google Alternative Out of Business, PCMag
Ecosia CEO Christian…
View On WordPress
#Bing#Christian Kroll#early-termination fees#Ecosia#ETF#FCC#Google competition#Jessica Rosenworcel#pay TV#Thanksgiving#Web Summit
0 notes
Text
Excerpt:
AT&T, Verizon, Sprint, and T-Mobile allegedly provided location data to third parties without their users' consent, which is illegal.
“Our communications providers have access to some of the most sensitive information about us," said FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel in a statement. "These carriers failed to protect the information entrusted to them. Here, we are talking about some of the most sensitive data in their possession: customers’ real-time location information, revealing where they go and who they are.”
0 notes
Text
(LATimes) Michael Hiltzik: The revival of network neutrality - Los Angeles Times

Federal Communications Commission Chair Jessica Rosenworcel shepherded a restoration of network neutrality at the FCC.
(Jonathan Newton / Pool)
In the midst of its battle to extinguish the Mendocino Complex wildfire in 2018, the Santa Clara County Fire Department discovered that its internet connection provider, Verizon, had throttled their data flow virtually down to zero, cutting off communications for firefighters in the field. One firefighter died in the blaze and four were injured.
Verizon refused to restore service until the fire department signed up for a new account that more than doubled its bill.
That episode has long been Exhibit A in favor of restoring the Federal Communications Commission’s authority to regulate broadband internet service, which the FCC abdicated in 2017, during the Trump administration.
This is an industry that requires a lot of scrutiny.
— Craig Aaron, Free Press, on the internet service industry
Now that era is over. On Thursday, the FCC — now operating with a Democratic majority — reclaimed its regulatory oversight of broadband via an order that passed on party lines, 3-2.
The commission’s action could scarcely be more timely.
“Four years ago,” FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel observed Thursday as the commission prepared to vote, “the pandemic changed life as we know it. ... Much of work, school and healthcare migrated to the internet. ... It became clear that no matter who you are or where you live, you need broadband to have a fair shot at digital age success. It went from ‘nice to have’ to ‘need to have.’ ”
Yet the commission in 2017 had thrown away its own ability to supervise this essential service. By categorizing broadband services as “information services,” it relinquished its right to address consumer complaints about crummy service, or even collect data on outages. It couldn’t prevent big internet service providers such as Comcast from favoring their own content or websites over competitors by degrading the rivals’ signals when they reached their subscribers’ homes.
“We fixed that today,” Rosenworcel said.
The issue the FCC addressed Thursday is most often viewed in the context of “network neutrality.” This core principle of the open internet means simply that internet service providers can’t discriminate among content providers trying to reach your home or business online — they can’t block websites or services, or degrade their signal, slow their traffic or, conversely, provide a better traffic lane for some rather than others.
The principle is important because their control of the information highways and byways gives ISPs tremendous power, especially if they control the last mile of access to end users, as do cable operators such as Comcast and telecommunications firms such as Verizon. If they use that power to favor their own content or content providers that pay them for a fast lane, it’s consumers who suffer.
Net neutrality has been a partisan football for more than two decades, or ever since high-speed broadband connections began to supplant dial-up modems.
In legal terms, the battle has been over the classification of broadband under the Communications Act of 1934 — as Title I “information services” or Title II “telecommunications.” The FCC has no jurisdiction over Title I services, but great authority over those classified by Title II as common carriers.
The key inflection point came in 2002, when a GOP-majority FCC under George W. Bush classified cable internet services as Title I. In effect, the commission stripped itself of its authority to regulate the nascent industry. (Then-FCC Chair Michael Powell subsequently became the chief Washington lobbyist for the cable industry, big surprise.)
Not until 2015 was the error rectified, at the urging of President Obama. Broadband was reclassified under Title II; then-FCC Chair Tom Wheeler was explicit about using the restored authority to enforce network neutrality.
But that regulatory regime lasted only until 2017, when a reconstituted FCC, chaired by a former Verizon executive Ajit Pai, reclassified broadband again as Title I in deference to President Trump’s deregulatory campaign. The big ISPs would have geared up to take advantage of the new regime, had not California and other states stepped into the void by enacting their own net neutrality laws.
A federal appeals court upheld California’s law, the most far-reaching of the state statutes, in 2022. And although the FCC’s action could theoretically preempt the state law, “what the FCC is doing is perfectly in line with what California did,” says Craig Aaron, co-CEO of the consumer advocacy organization Free Press.
The key distinction, Aaron told me, is that the FCC’s initiative goes well beyond the issue of net neutrality — it establishes a single federal standard for broadband and reclaims its authority over the technology more generally, in ways that “safeguard national security, advance public safety, protect consumers and facilitate broadband deployment,” in the commission’s own words.
Although Verizon’s actions in the 2018 wildfire case did not violate the net neutrality principle, for instance, the FCC’s restored regulatory authority might have enabled it to set forth rules governing the provision of services when public safety is at stake that might have prevented Verizon from throttling the Santa Clara Fire Department’s connection in the first place.
Until Thursday, the state laws functioned as bulwarks against net neutrality abuses by ISPs. “California helped discourage companies from trying things,” Aaron says. Indeed, provisions of the California law are explicit enough that state regulators haven’t had to bring a single enforcement case. “It’s been mostly prophylactic,” he says — “telling the industry what it can and can’t do. But it’s important to have set down the rules of the road.”
None of this means that the partisan battle over broadband regulation is over. Both Republican FCC commissioners voted against the initiative Thursday. A recrudescence of Trumpism after the November election could bring a deregulation-minded GOP majority back into power at the FCC.
Indeed, in a lengthy dissenting statement, Brendan Carr, one of the commission’s Republican members, repeated all the conventional conservative arguments presented to justify the repeal of network neutrality in 2017. Carr painted the 2015 restoration of net neutrality as a liberal plot — “a matter of civic religion for activists on the left.”
He asserted that the FCC was then goaded into action by President Obama, who was outspoken on the need for reclassification and browbeat Wheeler into going along. Leftists, he said, “demand that the FCC go full-Title II whenever a Democrat is president.”
Carr also depicted network neutrality as a drag on profits and innovation in the broadband sector. “Broadband investment slowed down after the FCC imposed Title II in 2015,” he said, “and it picked up again after we restored Title 1 in 2017.”
Carr chose his time frame very carefully. Examine the longer period in which net neutrality has been debated at the FCC, and one finds that broadband investment crashed after a Republican-led FCC reclassified broadband as an information service in 2002, falling to $57 billion in 2003 from $111.5 billion in 2001.
Investment did decline between 2015, when net neutrality rules were reinstated, and 2017, when they were rescinded — by a minuscule 0.8%. It hasn’t been especially robust since then — as of 2002 it was still running at only about 92% of what it had been two decades earlier.
As the FCC observed in Thursday’s order, “regulation is but one of several factors that drive investment and innovation in the telecommunications and digital media markets.”
The commission cited consumer demand and the arrival of new technologies, among others. Strong, consistent regulation, moreover, opens the path for new competitors with new ideas and innovations — and can bring prices down for users in the process.
The truth is that network neutrality has been heavily favored by the public, in part because examples of ISPs abusing their power were not hard to find. In 2007, Comcast was caught degrading traffic from the file-sharing service BitTorrent, which held contracts to distribute licensed content from Hollywood studios and other sources in direct competition with Comcast’s pay-TV business.
In 2010, Santa Monica-based Tennis Channel complained to the FCC that Comcast kept it isolated on a little-watched sports tier while giving much better placement to the Golf Channel and Versus, two channels that compete with it for advertising, and which Comcast happened to own. The FCC sided with the Tennis Channel but was overruled by federal court.
Even barring a change at the White House, the need for vigilant enforcement will never go away; ISPs will always be looking for business models and manipulative practices that could challenge the FCC’s oversight capabilities, especially as cable and telecommunications companies consolidate into bigger and richer enterprises and combine content providers with their internet delivery services.
“This is an industry,” Aaron says, “that requires a lot of scrutiny.”
#long post#refrigerator magnet#michael hiltzik#net neutrality#internet#utility#fcc#better than four years ago#politics#republicans#internet is a utility
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
AI-generated voices in robocalls can deceive voters. The FCC just made them illegal (AP News)
NEW YORK (AP) — The Federal Communications Commission on Thursday outlawed robocalls that contain voices generated by artificial intelligence, a decision that sends a clear message that exploiting the technology to scam people and mislead voters won’t be tolerated.
The unanimous ruling targets robocalls made with AI voice-cloning tools under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, a 1991 law restricting junk calls that use artificial and prerecorded voice messages.
The announcement comes as New Hampshire authorities are advancing their investigation into AI-generated robocalls that mimicked President Joe Biden’s voice to discourage people from voting in the state’s first-in-the-nation primary last month.
Effective immediately, the regulation empowers the FCC to fine companies that use AI voices in their calls or block the service providers that carry them. It also opens the door for call recipients to file lawsuits and gives state attorneys general a new mechanism to crack down on violators, according to the FCC.
The agency’s chairwoman, Jessica Rosenworcel, said bad actors have been using AI-generated voices in robocalls to misinform voters, impersonate celebrities and extort family members.
Read more
0 notes
Text
The Federal Communications Commission this week voted to raise its internet speed benchmark for the first time since January 2015, concluding that modern broadband service should provide at least 100 Mbps download speeds and 20 Mbps upload speeds.
An FCC press release after Thursday's 3-2 vote said the 100 Mbps/20 Mbps benchmark “is based on the standards now used in multiple federal and state programs,” such as those used to distribute funding to expand networks. The new benchmark also reflects “consumer usage patterns, and what is actually available from and marketed by internet service providers,” the FCC said.
The previous standard of 25 Mbps downstream and 3 Mbps upstream lasted through the entire Donald Trump era and most of President Biden’s term. There has been a clear partisan divide on the speed standard, with Democrats pushing for a higher benchmark and Republicans arguing that it shouldn't be raised.
The standard is partly symbolic but can indirectly impact potential FCC regulations. The FCC is required under US law to regularly evaluate whether "advanced telecommunications capability is being deployed to all Americans in a reasonable and timely fashion" and to "take immediate action to accelerate deployment" and promote competition if current deployment is not "reasonable and timely."
With a higher speed standard, the FCC is more likely to conclude that broadband providers aren't moving toward universal deployment fast enough and to take regulatory actions in response. During the Trump era, FCC chair Ajit Pai's Republican majority ruled that 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload speeds should still count as "advanced telecommunications capability," and concluded that the telecom industry was doing enough to extend advanced telecom service to all Americans.
2-2 Deadlock Delayed Benchmark Increase
Democrat Jessica Rosenworcel has been the FCC chair since 2021 and was calling for a speed increase even before being promoted to the commission's top spot. Rosenworcel formally proposed the 100 Mbps/20 Mbps standard in July 2022, but the FCC had a 2-2 partisan deadlock at the time and the 25 Mbps/3 Mbps standard stayed in place a while longer.
Biden's first nominee to fill an empty FCC seat was stonewalled by the Senate, but Democrats finally got a 3-2 majority when Biden's second pick was confirmed in September 2023. Thursday's 3-2 party-line vote approved the 100 Mbps/20 Mbps standard and a report concluding "that advanced telecommunications capability is not being deployed in a reasonable and timely fashion," the FCC said in its press release.
That conclusion is "based on the total number of Americans, Americans in rural areas, and people living on Tribal lands who lack access to such capability, and the fact that these gaps in deployment are not closing rapidly enough," the press release said. Based on data from December 2022, the FCC said that fixed broadband service (excluding satellite) "has not been physically deployed to approximately 24 million Americans, including almost 28 percent of Americans in rural areas, and more than 23 percent of people living on Tribal lands."
A draft of the FCC report was released before the meeting. "Based on our evaluation of available data, we can no longer conclude that broadband at speeds of 25/3 Mbps—the fixed benchmark established in 2015 and relied on in the last seven reports—supports 'advanced' functions," the report said. "We find that having 'advanced telecommunications capability' for fixed broadband service requires access to download speeds of at least 100 Mbps and upload speeds of at least 20 Mbps. The record overwhelmingly supports increasing the fixed speed benchmark in this manner."
The report also sets a "long-term speed goal" of 1 Gbps download speeds paired with 500 Mbps upload speeds. The FCC said it intends to use this speed goal “as a guidepost for evaluating our efforts to encourage deployment.”
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Time to outlaw AI-generated robocalls in UK.
AI-generated robocalls: The recent decision by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to outlaw AI-generated robocalls carries significant implications for the upcoming UK election and necessitates proactive measures from political campaigners.
Announced by FCC Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel, the ban on AI-generated voices in robocalls aims to curb the exploitation of vulnerable…

View On WordPress
0 notes