#LMS implementation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
8 Common pitfalls when implementing learning management software
Implementing Learning Management Software (LMS) can revolutionize how an organization manages training and education. However, many organizations face common pitfalls during the implementation process that can undermine the effectiveness of the LMS. Understanding these pitfalls and planning accordingly can help ensure a smoother transition and better outcomes. Here are some common challenges and a checklist to help avoid them:
1. Inadequate Needs Analysis
Pitfall: Failing to thoroughly analyze the organization’s needs and objectives before selecting an LMS can lead to a poor fit.
Checklist:
Identify specific training needs and goals
Engage stakeholders from various departments
Assess existing systems and content
2. Lack of User Involvement
Pitfall: Not involving end-users (e.g., employees, instructors) in the selection and implementation process can lead to resistance and underutilization.
Checklist:
Gather feedback from potential users
Include users in testing phases
Provide training and support for all users
3. Insufficient Training and Support
Pitfall: Neglecting to provide adequate training and ongoing support can result in poor adoption and effective use of the LMS.
Checklist:
Develop comprehensive training materials
Offer initial and refresher training sessions
Set up a helpdesk or support team
4. Poor Integration with Existing Systems
Pitfall: Failing to ensure that the LMS integrates seamlessly with existing systems (e.g., HR software, content management systems) can lead to data silos and inefficiencies.
Checklist:
Evaluate integration capabilities of the LMS
Plan for data migration and system compatibility
Test integration thoroughly before full deployment
5. Ignoring Scalability and Flexibility
Pitfall: Choosing an LMS that doesn’t scale or adapt to changing needs can limit future growth and flexibility.
Checklist:
Assess the scalability of the LMS
Ensure it supports a range of learning formats
Review the vendor’s update and support policies
6. Overlooking Data Security and Compliance
Pitfall: Failing to address data security and compliance issues can lead to breaches and legal problems.
Checklist:
Verify the LMS complies with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, FERPA)
Implement robust security measures
Regularly review and update security protocols
7. Inadequate Evaluation and Feedback Mechanisms
Pitfall: Not having a system in place to evaluate the effectiveness of the LMS and gather feedback can result in missed opportunities for improvement.
Checklist:
Establish metrics for evaluating LMS success
Collect feedback from users regularly
Make adjustments based on feedback and performance data
8. Unrealistic Expectations and Goals
Pitfall: Setting unrealistic expectations for the LMS’s capabilities and benefits can lead to disappointment and dissatisfaction.
Checklist:
Set clear, achievable goals for the LMS implementation
Communicate expectations clearly to all stakeholders
Monitor progress and adjust goals as needed
By addressing these common pitfalls effectively, organizations can maximize the benefits of LMS, ensuring a successful implementation that drives learning and development outcomes.
#LMS implementation#LMS#Learning management software#content management systems#elearning solutions#custom elearning development services#elearning platform
1 note
·
View note
Text
LMS Support and Maintenance Best Practices: Ensuring a Seamless Learning Experience

As Learning Management Systems (LMS) become increasingly integral to educational and corporate environments, maintaining their optimal functionality is paramount. This article delineates best practices for LMS support and maintenance to ensure a seamless, uninterrupted learning experience.
I. Proactive Planning: The Backbone of Effective Maintenance
Adopting a proactive approach in planning LMS maintenance activities can prevent unforeseen issues and downtime.
1. Schedule Regular Updates and Patches
Set a routine schedule for installing updates and security patches, ideally during off-hours to minimize disruption.
2. Conduct Preventive Audits
Regularly assess the system for vulnerabilities and address them before they lead to problems.
II. User Support: Meeting the Needs of Your Learning Community
Addressing users’ needs and queries promptly is critical in maintaining a positive learning environment.
1. Create Comprehensive FAQs and Guides
Develop detailed documentation that users can refer to for common issues.
2. Establish a Help Desk or Support System
Provide a clear and easy way for users to report issues and seek help.
III. Monitoring and Optimization: Keeping an Eye on Performance
Continuously monitor your LMS to ensure that it performs at its best.
1. Track System Load and Performance Metrics
Regularly review server load, response times, and other performance indicators.
2. Optimize for Scalability
Ensure that your LMS can efficiently handle increases in user numbers and content volume.
IV. Backup and Disaster Recovery: Preparing for the Unexpected
In the event of a catastrophic failure, having a robust backup and disaster recovery plan is invaluable.
1. Regular, Automated Backups
Set up automatic backups of your LMS data at frequent intervals.
2. Test and Update Recovery Procedures
Regularly test your recovery procedures to ensure they are effective and up to date.
V. Training and Continuous Learning for Support Staff
Equipping your support staff with the latest knowledge and skills is essential for effective LMS maintenance.
Regular Training Sessions
Conduct training sessions for staff to update them on new features or best practices.
Encourage Professional Development
Support staff in obtaining certifications and attending industry seminars.
VI. Feedback Loop: Listening to Your User Base
Actively collecting and acting upon feedback from users is essential for continuous improvement.
1. Conduct Surveys and Collect Feedback
Regularly solicit feedback from users regarding their experience with the LMS.
2. Implement Changes Based on Feedback
Use the feedback to make informed decisions about updates and improvements.
VII. Security Measures: Safeguarding Your LMS
With the sensitive data handled by an LMS, security is a paramount concern.
1. Regular Security Audits
Conduct comprehensive audits to identify potential vulnerabilities.
2. Implement Best Practices in Data Security
Follow industry standards for encryption, authentication, and authorization.
VIII. Documenting and Reporting: Keeping Records for Accountability and Improvement
Maintaining detailed records of maintenance activities and issues encountered can inform future actions.
1. Maintain Logs of All Support Requests and Resolutions
Detailed records can help identify recurring issues and effective solutions.
2. Generate Regular Reports
Use data to create reports that analyze performance and areas for improvement.
IX. Keeping Up with Industry Trends and Innovations
The world of e-learning is dynamic. Stay informed about industry trends and integrate meaningful updates into your LMS.
X. Cost Management: Efficiently Allocating Resources
Balancing the budget while ensuring top-tier support and maintenance is an art.
1. Regularly Review Vendor Contracts and Costs
Ensure you are getting the best value from your LMS provider and related services.
2. Optimize Staffing
Efficiently manage your support staff schedules and workload.
Conclusion: A Commitment to Excellence in LMS Support and Maintenance
LMS support and maintenance are not one-time activities but ongoing commitments. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can ensure that their LMS remains a robust, secure, and effective tool for learning. It’s not just about keeping the system up and running; it’s about optimizing the learning experience for all users.
With conscientious attention to support and maintenance, an LMS becomes more than a platform—it becomes a cornerstone of an enriching, engaging, and empowering educational experience. Whether for a small organization or a large institution, these best practices lay the foundation for success in the long term, making learning seamless and rewarding for everyone involved.
#Implementing an LMS best practices#seamless learning experiences#learning management system#seamless LMS experience#How to implement a learning Management system
0 notes
Note
What are some of the coolest computer chips ever, in your opinion?
Hmm. There are a lot of chips, and a lot of different things you could call a Computer Chip. Here's a few that come to mind as "interesting" or "important", or, if I can figure out what that means, "cool".
If your favourite chip is not on here honestly it probably deserves to be and I either forgot or I classified it more under "general IC's" instead of "computer chips" (e.g. 555, LM, 4000, 7000 series chips, those last three each capable of filling a book on their own). The 6502 is not here because I do not know much about the 6502, I was neither an Apple nor a BBC Micro type of kid. I am also not 70 years old so as much as I love the DEC Alphas, I have never so much as breathed on one.
Disclaimer for writing this mostly out of my head and/or ass at one in the morning, do not use any of this as a source in an argument without checking.
Intel 3101
So I mean, obvious shout, the Intel 3101, a 64-bit chip from 1969, and Intel's first ever product. You may look at that, and go, "wow, 64-bit computing in 1969? That's really early" and I will laugh heartily and say no, that's not 64-bit computing, that is 64 bits of SRAM memory.
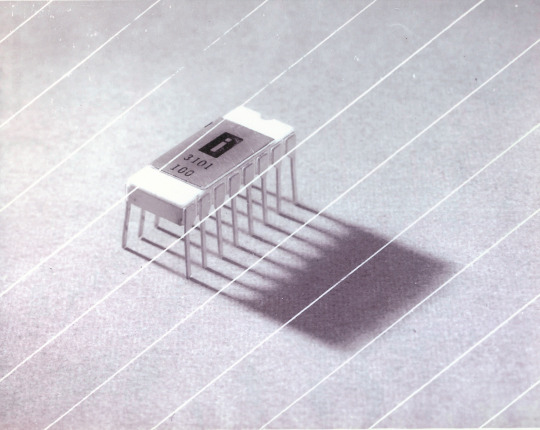

This one is cool because it's cute. Look at that. This thing was completely hand-designed by engineers drawing the shapes of transistor gates on sheets of overhead transparency and exposing pieces of crudely spun silicon to light in a """"cleanroom"""" that would cause most modern fab equipment to swoon like a delicate Victorian lady. Semiconductor manufacturing was maturing at this point but a fab still had more in common with a darkroom for film development than with the mega expensive building sized machines we use today.
As that link above notes, these things were really rough and tumble, and designs were being updated on the scale of weeks as Intel learned, well, how to make chips at an industrial scale. They weren't the first company to do this, in the 60's you could run a chip fab out of a sufficiently well sealed garage, but they were busy building the background that would lead to the next sixty years.
Lisp Chips
This is a family of utterly bullshit prototype processors that failed to be born in the whirlwind days of AI research in the 70's and 80's.
Lisps, a very old but exceedingly clever family of functional programming languages, were the language of choice for AI research at the time. Lisp compilers and interpreters had all sorts of tricks for compiling Lisp down to instructions, and also the hardware was frequently being built by the AI researchers themselves with explicit aims to run Lisp better.
The illogical conclusion of this was attempts to implement Lisp right in silicon, no translation layer.

Yeah, that is Sussman himself on this paper.
These never left labs, there have since been dozens of abortive attempts to make Lisp Chips happen because the idea is so extremely attractive to a certain kind of programmer, the most recent big one being a pile of weird designd aimed to run OpenGenera. I bet you there are no less than four members of r/lisp who have bought an Icestick FPGA in the past year with the explicit goal of writing their own Lisp Chip. It will fail, because this is a terrible idea, but damn if it isn't cool.
There were many more chips that bridged this gap, stuff designed by or for Symbolics (like the Ivory series of chips or the 3600) to go into their Lisp machines that exploited the up and coming fields of microcode optimization to improve Lisp performance, but sadly there are no known working true Lisp Chips in the wild.
Zilog Z80
Perhaps the most important chip that ever just kinda hung out. The Z80 was almost, almost the basis of The Future. The Z80 is bizzare. It is a software compatible clone of the Intel 8080, which is to say that it has the same instructions implemented in a completely different way.
This is, a strange choice, but it was the right one somehow because through the 80's and 90's practically every single piece of technology made in Japan contained at least one, maybe two Z80's even if there was no readily apparent reason why it should have one (or two). I will defer to Cathode Ray Dude here: What follows is a joke, but only barely

The Z80 is the basis of the MSX, the IBM PC of Japan, which was produced through a system of hardware and software licensing to third party manufacturers by Microsoft of Japan which was exactly as confusing as it sounds. The result is that the Z80, originally intended for embedded applications, ended up forming the basis of an entire alternate branch of the PC family tree.
It is important to note that the Z80 is boring. It is a normal-ass chip but it just so happens that it ended up being the focal point of like a dozen different industries all looking for a cheap, easy to program chip they could shove into Appliances.
Effectively everything that happened to the Intel 8080 happened to the Z80 and then some. Black market clones, reverse engineered Soviet compatibles, licensed second party manufacturers, hundreds of semi-compatible bastard half-sisters made by anyone with a fab, used in everything from toys to industrial machinery, still persisting to this day as an embedded processor that is probably powering something near you quietly and without much fuss. If you have one of those old TI-86 calculators, that's a Z80. Oh also a horrible hybrid Z80/8080 from Sharp powered the original Game Boy.
I was going to try and find a picture of a Z80 by just searching for it and look at this mess! There's so many of these things.

I mean the C/PM computers. The ZX Spectrum, I almost forgot that one! I can keep making this list go! So many bits of the Tech Explosion of the 80's and 90's are powered by the Z80. I was not joking when I said that you sometimes found more than one Z80 in a single computer because you might use one Z80 to run the computer and another Z80 to run a specialty peripheral like a video toaster or music synthesizer. Everyone imaginable has had their hand on the Z80 ball at some point in time or another. Z80 based devices probably launched several dozen hardware companies that persist to this day and I have no idea which ones because there were so goddamn many.
The Z80 eventually got super efficient due to process shrinks so it turns up in weird laptops and handhelds! Zilog and the Z80 persist to this day like some kind of crocodile beast, you can go to RS components and buy a brand new piece of Z80 silicon clocked at 20MHz. There's probably a couple in a car somewhere near you.
Pentium (P6 microarchitecture)
Yeah I am going to bring up the Hackers chip. The Pentium P6 series is currently remembered for being the chip that Acidburn geeks out over in Hackers (1995) instead of making out with her boyfriend, but it is actually noteworthy IMO for being one of the first mainstream chips to start pulling serious tricks on the system running it.

The P6 microarchitecture comes out swinging with like four or five tricks to get around the numerous problems with x86 and deploys them all at once. It has superscalar pipelining, it has a RISC microcode, it has branch prediction, it has a bunch of zany mathematical optimizations, none of these are new per se but this is the first time you're really seeing them all at once on a chip that was going into PC's.
Without these improvements it's possible Intel would have been beaten out by one of its competitors, maybe Power or SPARC or whatever you call the thing that runs on the Motorola 68k. Hell even MIPS could have beaten the ageing cancerous mistake that was x86. But by discovering the power of lying to the computer, Intel managed to speed up x86 by implementing it in a sensible instruction set in the background, allowing them to do all the same clever pipelining and optimization that was happening with RISC without having to give up their stranglehold on the desktop market. Without the P5 we live in a very, very different world from a computer hardware perspective.
From this falls many of the bizzare microcode execution bugs that plague modern computers, because when you're doing your optimization on the fly in chip with a second, smaller unix hidden inside your processor eventually you're not going to be cryptographically secure.
RISC is very clearly better for, most things. You can find papers stating this as far back as the 70's, when they start doing pipelining for the first time and are like "you know pipelining is a lot easier if you have a few small instructions instead of ten thousand massive ones.
x86 only persists to this day because Intel cemented their lead and they happened to use x86. True RISC cuts out the middleman of hyperoptimizing microcode on the chip, but if you can't do that because you've girlbossed too close to the sun as Intel had in the late 80's you have to do something.
The Future
This gets us to like the year 2000. I have more chips I find interesting or cool, although from here it's mostly microcontrollers in part because from here it gets pretty monotonous because Intel basically wins for a while. I might pick that up later. Also if this post gets any longer it'll be annoying to scroll past. Here is a sample from a post I have in my drafts since May:
I have some notes on the weirdo PowerPC stuff that shows up here it's mostly interesting because of where it goes, not what it is. A lot of it ends up in games consoles. Some of it goes into mainframes. There is some of it in space. Really got around, PowerPC did.
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
hwough. okay. not sick anymore. no more funerals, no more weddings, no more birthdays, nothing on the calendar until like november. there is nothing standing in the way of my goals except me. let's make a big ol' list of Shit I Could Do Today, and then pare it down:
finish the Tonnera art and post a TFJ recap
call the plumber about replacing this toilet
sketch some character designs for Candi and Dart
implement growths and leveling up in-game in MW
move a bunch of training videos to this LMS site for work
talk to Patrick about full-time employment
catch up on WK reviews
do that SB voice request that's in my inbox
prototype a glossary menu in Ren'Py
exercise
do some planning for the Dark Site Aspen raid
also various media to finish consuming:
the sekimeiya
cockatiel x chameleon
death of the king
quiet and antagonism
time to orbit unknown
failure to launch
today, let's...
do the LMS work thing
finish drawing tonnera
call the plumber
do the SB thing
exercise
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Integrating Skill Assessments into Your Existing HR Systems

Introduction
As organizations strive to build a skilled and efficient workforce, integrating skill assessments into existing HR systems has become a crucial strategy. By embedding skill evaluations within HR workflows, companies can enhance hiring accuracy, streamline employee development, and make data-driven workforce decisions. This blog explores the benefits, challenges, and best practices of integrating skill assessments into HR systems, with insights on how platforms like Gappeo can facilitate the process.
Why Integrate Skill Assessments into HR Systems?
Integrating skill assessments within HR platforms offers numerous advantages, including:
Improved Hiring Accuracy: Objective skill evaluations help recruiters identify the most suitable candidates, reducing reliance on resumes alone.
Efficient Onboarding: Pre-assessed skills enable HR teams to tailor onboarding programs, ensuring new hires receive targeted training.
Employee Development & Training: Ongoing skill assessments allow HR teams to track employee growth and implement personalized training programs.
Workforce Planning: Insights from assessments help HR leaders identify skill gaps and plan for future workforce needs.
Key Considerations for Integration
Before incorporating skill assessments into your HR system, consider the following:
Compatibility: Ensure the assessment platform integrates seamlessly with your existing HR software (e.g., ATS, LMS, or HRIS).
Customization: Choose a system that allows tailored assessments aligned with job roles and industry needs.
Scalability: The platform should support growing workforce demands and adapt to evolving skill requirements.
User Experience: Both recruiters and candidates should find the system easy to navigate and engage with.
How Gappeo Simplifies Skill Assessment Integration
Gappeo, a leading talent and skill assessment platform, offers seamless integration with various HR systems. Key features include:
Pre-Built API Integrations: Easily connect with popular HR platforms.
Customizable Assessment Modules: Design skill tests specific to job roles.
Audio and Video Assessments: Enhance evaluation accuracy by analyzing verbal and non-verbal cues.
Comprehensive Reporting: Generate insights to support hiring and workforce development decisions.
Steps to Successfully Integrate Skill Assessments
Evaluate Your HR System: Assess your current HR software capabilities and identify integration points.
Select the Right Assessment Platform: Choose a solution like Gappeo that aligns with your HR objectives.
Customize Assessments: Develop skill tests that reflect the competencies required for different roles.
Pilot Test the Integration: Run a small-scale implementation to ensure seamless functionality.
Train HR Teams: Educate HR personnel on using the integrated system effectively.
Monitor and Optimize: Continuously track performance metrics and refine assessment processes.
Conclusion
Integrating skill assessments into HR systems is a game-changer for talent management, enabling data-backed hiring, employee development, and strategic workforce planning. With solutions like Gappeo, organizations can streamline skill evaluations while ensuring a seamless experience for both HR professionals and candidates.
Ready to enhance your HR processes? Discover how Gappeo can help you integrate skill assessments effortlessly!
#assessment#hiring#recruitment#saas development company#saas platform#hr#hrsystems#hrprocesses#evaluation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech4Biz Solutions’ Showcase: Driving Future-Ready Business with Cutting-Edge Innovations

In a world where technology is reshaping industries at an unprecedented pace, businesses must adapt to stay competitive. Tech4Biz Solutions has emerged as a trailblazer in providing future-ready business solutions that empower organizations to thrive in the digital age. With a comprehensive portfolio of offerings showcased on its platform, Tech4Biz Solutions is helping businesses unlock new possibilities and drive long-term growth.
1. Embracing Innovation for Business Growth
Innovation is no longer optional—it’s essential for business success. Companies need to adopt cutting-edge technologies to enhance their processes, improve customer experiences, and respond to evolving market demands. Tech4Biz Solutions understands the transformative power of technology and has developed a range of solutions that cater to the unique needs of different industries.
The company’s Showcase platform is a testament to its commitment to innovation, offering businesses a window into the latest advancements and success stories that demonstrate the impact of its solutions.
2. Key Offerings from Tech4Biz Solutions
Tech4Biz Solutions’ Showcase features a diverse range of services designed to accelerate business transformation. Here’s a closer look at some of its standout offerings:
Digital Twins for Operational Optimization: By creating virtual models of physical assets and processes, businesses can gain real-time insights and make data-driven decisions to improve operational efficiency.
Custom AI Models for Cybersecurity: With cyber threats growing more sophisticated, Tech4Biz provides AI-driven models that proactively detect and mitigate security risks.
Cloud Infrastructure Deployment: Tech4Biz helps businesses transition to the cloud with scalable, reliable infrastructure that supports agility and growth.
Learning Management Systems (LMS): From training to professional development, Tech4Biz’s LMS solutions make it easy for companies to upskill employees and stay competitive in today’s knowledge-driven economy.
These offerings are designed to deliver tangible results, helping businesses enhance productivity, reduce risks, and create new growth opportunities.
3. Real-World Impact: Case Studies from the Showcase
One of the most compelling features of the Tech4Biz Solutions Showcase is its portfolio of case studies. These success stories illustrate how businesses across industries have leveraged Tech4Biz’s solutions to achieve remarkable outcomes.
Manufacturing Excellence: A manufacturing company used Tech4Biz’s digital twin technology to reduce downtime and improve production efficiency by 20%.
Retail Transformation: A retailer partnered with Tech4Biz to deploy cloud infrastructure, resulting in a 25% increase in online sales and improved customer engagement.
Cybersecurity Strengthening: A financial services firm adopted Tech4Biz’s AI-powered cybersecurity solutions, which helped prevent data breaches and ensured compliance with industry regulations.
These examples highlight the real-world benefits of adopting cutting-edge innovations from Tech4Biz Solutions.
4. A Customer-Centric Approach to Innovation
At the heart of Tech4Biz Solutions’ success is its commitment to a customer-centric approach. The company tailors its solutions to meet the specific needs of each client, ensuring maximum impact and long-term success.
Here’s how Tech4Biz ensures its solutions are effective:
Customized Solutions: Every business is different, and Tech4Biz takes the time to understand each client’s unique challenges and goals before developing a tailored solution.
Seamless Integration: Tech4Biz ensures its solutions integrate smoothly with existing systems, minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency.
Expert Consultation: Clients benefit from access to experienced professionals who provide strategic guidance and support throughout the implementation process.
Continuous Support: Tech4Biz offers ongoing support and training to help clients get the most out of their technology investments.
This comprehensive approach ensures businesses can fully leverage the potential of Tech4Biz’s innovations.
5. Preparing Businesses for the Future
Tech4Biz Solutions is committed to staying ahead of emerging trends and technologies, ensuring its clients are always prepared for what’s next. The company’s forward-thinking approach includes:
Advanced Automation: Developing new automation tools to streamline workflows and free up human resources for higher-value tasks.
Predictive Analytics: Leveraging data to provide businesses with actionable insights and better decision-making capabilities.
Sustainability Solutions: Focusing on eco-friendly innovations that help businesses reduce their environmental impact while maintaining profitability.
These initiatives position Tech4Biz Solutions as a leader in driving future-ready business transformation.
6. Unlocking Potential with Tech4Biz Solutions
Tech4Biz Solutions’ Showcase is more than just a platform—it’s a roadmap for businesses looking to navigate the complexities of the digital era. By exploring the Showcase, businesses can discover the latest innovations and see firsthand how Tech4Biz’s solutions can help them achieve their transformation goals.
Whether it’s optimizing operations, enhancing cybersecurity, or transitioning to the cloud, Tech4Biz Solutions has the expertise and resources to empower businesses at every stage of their journey.
Conclusion
Tech4Biz Solutions is at the forefront of delivering cutting-edge innovations that drive business transformation. With a robust portfolio of services and a customer-centric approach, the company is helping businesses unlock new opportunities and stay competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Explore the Tech4Biz Solutions Showcase today to discover how your business can become future-ready with the latest technological advancements. Together, we can shape the future of business transformation.
For more details, reachout us: https://showcase.tech4bizsolutions.com/.
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you think ozpin and qrow could some how be friends again/ qrow trust ozpin again
Hello there anon-chan! Thank you for the inbox!
In all honesty m’fam, this was a subject matter I was hoping the series would’ve covered after V6. After that season, I was hoping that part of Qrow’s development moving forward would’ve had him reconsidering his entire relationship with Ozpin; touching base on things such as how they first met and really giving the audience a further deep dive in their history together. This would then ultimately leed up to Qrow realizing that he was wrong for how he treated Oz after the reveal, learning to forgive him again and the two would essentially reboot their friendship with deeper feelings of trust and understanding.
Judging from the events of V6, a lot of Qrow’s feelings about himself were synonymous with his ties with Oz. There was no doubt that Oz was someone Qrow revered and thought of highly.

It’s as he told him back during that season. No one else in his life---not his clan, not even his own sister---ever believed in him due to his misfortune semblance. According to Qrow, he was cursed. But it was Oz who made him gain some confidence in his own self worth by making him believe in the good he could accomplish even with the type of semblance he had.
Words alone are not enough to surmise my disappointment in the fact that right after the writers teased the history and meaningful dynamic that Qrow and Oz shared together, they just dropped it after V6. Instead of making Qrow focus on his bond with Oz, they instead awkwardly did everything they could to have Qrow not discuss Oz.
Instead they had Qrow pining over his relationship with Clover for two seasons. Clover---a character he barely knew and just happened to develop a small kindred comradery for like a couple of months versus Ozpin who he has known FOR YEARS. Probably since he was even a student at Beacon and had remained loyal to well into middle age. Like seriously?
Don't get me wrong, I liked Clover as a character. However I honestly hated how he was the focus

Qrow wasn’t even allowed to focus on his friendship with Winter since even their rivalry dating back to the events of V3 was pushed aside in favour of Clover who only first appeared in V7.

Don’t get me wrong. I actually thought Clover was a decent character. However I really didn’t like how he suddenly became a person of massive importance to Qrow when the two barely knew each other.
If Clover shared the same past with Qrow or the two were actually good friends/rivals who knew each other dating way back to their academy days then I can get behind why Qrow cared that much about him after his death.

But no. There were other characters that Qrow shared deeper bonds than Clover, like Oz, and yet, all Qrow focused on between V7 to V8 was this one dude. I will never understand why the Writers chose this route to go for Qrow. It just felt so off and misplaced; at least to me.
Shout-out to my fellow Snowbird shippers since we too were robbed of any potential further development between Qrow and Winter since that it seems their dynamic was replaced in favour of one brewing with Robyn Hill.

So, in a nutshell anon-chan, I do think Qrow can trust Oz again and rekindle their friendship. However, it’s up to the CRWBY Writers to implement that into the story canon. Thus far, they haven’t done a good job on having Qrow focus on his ties to Oz. But who knows? Perhaps we’ll get something in that epilogue series that was recently announced by RT. RWBY Beyond.
Hopefully that series will drop some crumbs on the aftermath of Qrow and Oz’s relationship, finally giving closure to of us who were wondering about it.
LMS (2024)
#squiggles answers: rwby#qrow branwen#professor ozpin#qrow and ozpin#qrow and clover#qrow and winter#qrow and robyn
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
you mention the apollo guidance computer in your bio.
do you have any nerdy fun facts about it?
Thanks for the ask!
It's difficult to convey everything the AGC was, concisely, but here's some highlists:
In terms of size and power, it's comparable to the Apple II, but predates it by 11 years. There are some obvious differences in the constraints placed on the two designs, but still, that's pretty ahead of it's time.
The bare-bones OS written for the AGC was one of the first to ever implement co-operative multi-tasking and process priority management. This would lead problems on Apollo 11, when an erroneously deployed landing radar overloaded the task scheduler on Eagle during the Lunar landing (the infamous 1201/1202 program alarms). Fortunately, it didn't end up affecting the mission, and the procedures were subsequently revised/better followed to avoid the situation ever reoccurring.
Relatedly, it was also designed to immediately re-boot, cull low-priority tasks, and resume operations following a crash -- a property essential to ensuring the spacecraft could be piloted safely and reliably in all circumstances. Many of the reliability-promoting techniques used by Apollo programmers (led by Margaret Hamilton, go women in STEM) went on to become foundational principles of software engineering.
Following the end of the Apollo, Skylab, and Apollo-Soyuz missions, a modified AGC would be re-purposed into the worlds first digital fly-by-wire system. (Earlier fly-by-wire used analogue computers, which are their own strange beasts.) This is, IMO, one of the easiest things to point to when anyone asks "What does NASA even do for us anyway?" Modern aircraft autopilots owe so, so much to the AGC -- and passengers owe so much to those modern autopilots. While there are some pretty well-known incidents involving fly-by-wire (lookin' at you, MCAS), it speaks to the incredible amount of safety such systems normally afford that said incidents are so rare. Pilot error killed so many people before computers hit the cockpit.
AGC programs were stored in a early form of read only memory, called "core rope memory", where bits were literally woven into an array of copper wire and magnets. As a Harvard-architecture machine (programs and variables stored and treated separately), it therefore could not be re-programmed in flight. This would be problem on Apollo 14, when an intermittent short in the LM's abort switch nearly cancelled the landing -- if it occurred during decent, the computer would immediately discard the descent engine and return to orbit. A second, consecutive failure (after Apollo 13) would have almost certainly ended in the cancellation of the program, and the loss of the invaluable findings of Apollo 15, 16, and 17. (These were the missions with the lunar roving vehicles, allowing treks far from the LM.) Fortunately, the MIT engineers who built the AGC found a solution -- convince the computer it had, in fact, already aborted, allowing the landing to occur as normal -- with a bit of manual babysitting from LMP Edgar Mitchell.
Finally, it wasn't actually the only computer used on Apollo! The two AGCs (one in the command module, the other in the Lunar Module, a redundancy that allowed Apollo 13 to power off the CM and survive their accident) were complemented by the Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (LVDC) designed by IBM and located in S-IVB (Saturn V's third stage, Saturn-I/IB's second stage), and the Abort Guidance System (AGS) located in the LM. The AGS was extremely simple, and intended to serve as a backup should the AGC have ever failed and been unable to return the LM to orbit-- something it was fortunately never needed for. The LVDC, on the other hand, was tasked with flying the Saturn rocket to Earth orbit, which it did every time. This was very important during Apollo 12, when their Saturn V was struck by lightning shortly after launch, completely scrambling the CM's electrical system and sending their gimbal stacks a-spinning. Unaffected by the strike, the LVDC flew true and put the crew into a nominal low Earth orbit -- where diagnostics began, the AGC was re-set, and the mission continued as normal.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Talentserve #Blendedlearning
Blended learning

Blended learning, the fusion of traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning elements, has emerged as a transformative approach in education. This pedagogical model combines the best of both worlds, offering students the flexibility of online learning while retaining the benefits of in-person interaction. With its emphasis on personalized learning experiences and adaptable delivery methods, blended learning has gained traction across educational institutions worldwide. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of blended learning, its components, benefits, challenges, implementation strategies, and future prospects.
Understanding Blended Learning Blended learning encompasses a spectrum of instructional methods that integrate traditional classroom teaching with digital tools and resources. At its core, it seeks to optimize learning outcomes by leveraging technology to complement and enhance face-to-face instruction. This hybrid approach allows students to engage with course materials, collaborate with peers, and receive feedback through both online platforms and in-person interactions with educators.
Components of Blended Learning Blended learning models vary in structure and implementation, but they typically consist of the following components:
Face-to-Face Instruction: Traditional classroom sessions where teachers deliver lectures, facilitate discussions, and conduct hands-on activities. Online Learning: Virtual learning environments hosted on learning management systems (LMS) or educational platforms, providing access to course materials, multimedia resources, interactive modules, and communication tools. Asynchronous Activities: Self-paced online assignments, readings, quizzes, and multimedia content that students can access and complete independently. Synchronous Activities: Real-time online sessions, such as webinars, video conferences, or virtual classrooms, where students interact with instructors and peers in a live setting. Assessment and Feedback: Continuous evaluation through online assessments, quizzes, discussion forums, and timely feedback from instructors to monitor student progress and comprehension. Benefits of Blended Learning Blended learning offers numerous advantages for both educators and learners:
Flexibility and Accessibility: Students can access course materials anytime, anywhere, allowing for personalized learning experiences that accommodate diverse schedules, learning styles, and abilities. Increased Engagement: The integration of multimedia resources, interactive activities, and online discussions promotes active learning, collaboration, and student participation. Enhanced Learning Outcomes: Blended learning caters to individual learning needs by offering personalized instruction, adaptive feedback, and opportunities for self-directed learning, leading to improved academic performance and knowledge retention. Cost-Efficiency: By leveraging digital resources and reducing the need for physical infrastructure, blended learning can lower educational costs associated with travel, accommodation, and classroom maintenance. Preparation for the Digital Age: By integrating technology into the learning process, blended learning equips students with essential digital literacy skills, critical thinking abilities, and adaptability to thrive in the digital workforce. Challenges of Blended Learning Despite its potential benefits, blended learning also presents several challenges that educators and institutions must address:
Technological Barriers: Unequal access to technology, limited internet connectivity, and technical difficulties can hinder students' ability to fully engage with online learning resources. Pedagogical Integration: Effective integration of digital tools and online activities into the curriculum requires careful planning, training, and ongoing support for educators to ensure alignment with learning objectives and instructional practices. Assessment Validity: Ensuring the validity and reliability of online assessments and evaluations poses challenges related to plagiarism, cheating, and the authenticity of student work in virtual environments. Time and Resource Constraints: Designing, implementing, and managing blended learning initiatives require substantial time, resources, and expertise in instructional design, technology integration, and curriculum development. Student Motivation and Engagement: Maintaining student motivation and engagement in online learning environments can be challenging, particularly for self-paced activities or asynchronous discussions that lack the immediacy of face-to-face interactions. Strategies for Implementing Blended Learning Successful implementation of blended learning requires careful planning, collaboration, and ongoing evaluation. Here are some key strategies:
Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough analysis of students' needs, learning preferences, and technological readiness to inform the design and delivery of blended learning experiences. Clear Learning Objectives: Establish clear learning objectives and outcomes aligned with curriculum standards, instructional goals, and assessment criteria to guide the development of blended learning activities. Technology Integration: Select appropriate digital tools, learning management systems, and online resources that support active learning, collaboration, and engagement while addressing accessibility and usability concerns. Pedagogical Training: Provide professional development opportunities, training workshops, and ongoing support for educators to enhance their digital literacy skills, instructional strategies, and ability to facilitate blended learning environments effectively. Feedback and Iteration: Solicit feedback from students, educators, and stakeholders through surveys, focus groups, and formative assessments to identify strengths, challenges, and areas for improvement in the blended learning experience. Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by revising, refining, and adapting blended learning initiatives based on evidence-based practices, student feedback, and emerging technologies. Future Trends and Prospects As technology continues to evolve and reshape the educational landscape, blended learning is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of learning. Several trends and developments are likely to influence the evolution of blended learning in the years to come:
Personalized Learning: Advances in adaptive learning technologies, artificial intelligence, and data analytics will enable personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs, preferences, and learning trajectories. Immersive Technologies: The integration of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) into blended learning environments will offer immersive, interactive experiences that enhance student engagement and comprehension. Global Collaboration: Blended learning will facilitate cross-cultural collaboration, global networking, and international exchanges, allowing students to connect with peers, experts, and resources from diverse cultural backgrounds and geographical locations. Hybrid Learning Models: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of hybrid learning models that combine in-person instruction with online elements, providing flexibility, resilience, and continuity in times of crisis or disruption. Lifelong Learning: Blended learning will support lifelong learning initiatives, professional development programs, and continuing education opportunities for learners of all ages, fostering a culture of lifelong learning and skill development in the digital age. Conclusion In conclusion, blended learning represents a dynamic, innovative approach to education that harnesses the power of technology to enhance teaching and learning outcomes. By integrating traditional pedagogical methods with digital tools and online resources, blended learning offers flexibility, accessibility, and personalized learning experiences that cater to the diverse needs of students in the 21st century. While challenges such as technological barriers, pedagogical integration, and assessment validity remain, strategic implementation strategies, ongoing professional development, and a commitment to continuous improvement can maximize the benefits of blended learning and prepare students for success in an ever-changing world. As we navigate the complexities of education in the digital age, blended learning stands as a beacon of innovation and opportunity, empowering learners to thrive in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rambly FYP post very stream-of-conciousness:
So, final year project update. Reframing the project as developing a selective beamforming scheme, based on prior works like OABF (on-off adaptive beamforming). There's some good literature that I need to chew through, so hopefully i can get my attention to stay on it long enough.
Current state is: I have a working adaptive beamformer, using particle swarm optimisation to change antenna element complex weights to form the far-field array factor that I want (treating elements as isotropic transmitters). It's convergence is a little funny, I need to verify that the particles are behaving in the way I want.
Next step is the introduction of the element selection (into groups of tiles). Elements with similar complex weights are grouped together. In a real antenna, these element groups are driven by the same RF chain (analogue phase shifers, feeding into individual RF amplifiers). This technique, while not producing optimal results, should (hopefully) produce adequate adaptive beamforming, with a reduced number of RF chains. The benefit of this is reduction of cost and complexity of the overall system.
Generally, I'm seeing some decent results and getting well into a good implementation. My next task is to define some figures of merit I can use to compare my technique to prior art (various LMS impls., MVDR, OABF, etc.) I've got some technical limitations, writing the simulator myself, so there's some interesting challenges here.
Antennas are cool and all but I still wanna do fusion instead. gaugh.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Learning: A Deep Dive into Education ERP Innovations
In today's fast-paced world, the landscape of education is constantly evolving. Technological advancements have revolutionized the way we learn, and one of the most significant innovations in the field of education is the advent of Education ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems. These sophisticated solutions are reshaping the future of learning by streamlining administrative processes, enhancing communication, and providing a more personalized educational experience.
What is Education ERP?
Education ERP refers to a comprehensive software solution tailored to meet the unique needs of educational institutions. It integrates various functions like admissions, student management, finance, human resources, and academic management into a single platform. This integration empowers schools and universities to efficiently manage their operations, resulting in enhanced productivity and a more immersive learning environment.
Streamlining Administrative Processes
One of the primary advantages of Education ERP innovations is the automation of administrative tasks. From student admissions to fee management and timetable scheduling, these systems simplify and expedite the often complex processes that educational institutions face. This streamlining not only saves time but also minimizes human errors, ensuring a smoother operation.
Enhancing Communication
Effective communication is at the core of any successful educational institution. Education ERP systems provide a centralized platform for communication between teachers, students, parents, and administrative staff. This seamless interaction fosters collaboration and understanding, leading to a more supportive and connected learning community.
Personalizing Education
Education ERP innovations enable the personalization of the learning experience. With data analytics and insights, educators can tailor their teaching methods to meet the unique needs of each student. This personal touch enhances engagement and ensures that no one falls through the cracks in the educational system.
Bursting the Bubble of Traditional Education
Traditional educational systems have long been criticized for their one-size-fits-all approach. Education ERP systems burst this bubble by introducing a new era of individualized learning. This innovation allows students to learn at their own pace, explore their interests, and receive the support they need to excel.
The Future of Learning Management
The shift towards online learning and remote education is further driving the need for Education ERP systems. These innovations are the backbone of modern Learning Management Systems (LMS), which are essential for delivering courses, managing assignments, and tracking progress. LMS powered by Education ERP technology are making education more accessible and flexible than ever before.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Education ERP systems are a goldmine of data that can be harnessed to make informed decisions. By analyzing student performance, resource allocation, and overall institution management, educational leaders can identify areas that need improvement and implement strategic changes to enhance the quality of education.
Conclusion
The future of learning is bright with the ongoing innovations in Education ERP systems. These solutions are transforming the way educational institutions operate, enhancing communication, personalizing education, and bursting the bubble of traditional learning. As we move forward, the education sector will continue to evolve, and Education ERP innovations will play a vital role in shaping this transformation.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Effective Ways to Improve the Enterprise Training Process
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, continuous learning and development have become essential for enterprises to stay competitive and adapt to changing market trends. A well-structured and effective training process is crucial for enhancing the skills and knowledge of employees, fostering a culture of growth, and achieving organizational success. In this article, we will explore some proven strategies to improve the enterprise training process, with a particular focus on the innovative solution Level Up 360° - Group Training Program provided by CCS Learning Academy.

1. Assess Training Needs:
The first step in enhancing the training process is to identify the organization's specific learning needs and objectives. Conduct a thorough assessment of the skills gap existing within the workforce and align the training programs accordingly. Gathering feedback from employees, managers, and stakeholders will help in understanding the areas where improvement is required.
Looking for free IT classes to gain knowledge, practical tips and get all your queries answered with certified instructors? Upgrade yourself and train your teams with CCSLA free classes.
2. Embrace Blended Learning:
Traditional classroom-based training may not always be the most effective method. Embracing blended learning approaches that combine online modules, workshops, webinars, and interactive sessions can create a more engaging and personalized learning experience. It allows employees to learn at their own pace, reinforcing knowledge retention and promoting self-directed learning.
3. Implement Microlearning:
Microlearning involves delivering content in short, bite-sized modules that focus on one concept at a time. This approach is highly effective in catering to the modern workforce's busy schedules and shorter attention spans. By breaking down complex topics into smaller chunks, microlearning enhances knowledge retention and improves the overall learning experience.
4. Gamification for Engagement:
Gamification is an innovative technique that leverages gaming elements, such as points, badges, and leaderboards, in non-gaming contexts like training. By incorporating gamification into the training process, employees are motivated to participate actively, compete with peers, and achieve learning milestones. This fosters a fun and engaging learning environment while ensuring effective knowledge transfer.
5. Provide Real-life Simulations:
Hands-on training through real-life simulations can significantly improve employees' practical skills and problem-solving abilities. Simulations allow learners to apply their knowledge in a risk-free environment, gaining confidence and expertise before implementing them in real-world scenarios. This approach is particularly valuable for technical and operational training.
6. Personalized Learning Paths:
Every employee has different learning preferences and varying skill levels. Offering personalized learning paths ensures that individuals receive training content tailored to their specific needs and interests. This approach enhances employee satisfaction and results in more effective skill development.
7. Adopt Level Up 360:
Level Up 360 is a cutting-edge enterprise solution offered by CCS Learning Academy and is an excellent addition to any organization's training process. This innovative platform is designed to streamline and enhance employee development by offering a wide range of features. Level Up 360 provides a comprehensive learning management system (LMS) that enables seamless content delivery, tracking, and reporting.
The platform offers interactive and engaging content, including videos, quizzes, and gamified assessments, ensuring that learning remains enjoyable and impactful. With Level Up 360, managers can easily track employees' progress, identify areas of improvement, and provide targeted support when needed.
Additionally, Level Up 360 allows for the integration of various training modalities, such as classroom training, virtual sessions, and e-learning, creating a flexible and blended learning experience.
Moreover, Level Up 360 comes with advanced analytics and reporting tools that provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the training programs. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make informed decisions, refine their training strategies, and achieve better learning outcomes.
In conclusion, enhancing the enterprise training process is vital for fostering employee growth, improving performance, and achieving organizational excellence. By embracing innovative solutions like Level Up 360 and combining various effective training strategies such as blended learning, microlearning, and gamification, enterprises can create a culture of continuous learning that drives success in today's dynamic business world. Remember that investing in employees' professional development is not just beneficial for the individuals but also contributes significantly to the overall success and competitiveness of the organization.
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
I actually have some info on Springy And The Galaxy Gears. So, I have a (now passed) relative who worked for the company I'm pretty sure developed SATGG before it was scrapped.
In his attic, he had a floppy disk which contains a more experimental version of the current discovered version of the game. This version is actually a fairly complete game. FMV cutscenes are implemented, but use low-quality screencaps of storyboards and sometimes distort heavily. Multiplayer modes (being a CO-OP version of the Story Mode and a weird split-screen/LAN-based Last Man Standing mode) are included, but LMS maps seem to be unfinished and offline enemy AI seems to be glitched.
He also had an Atari Jaguar cartridge for what I assume to be a port intended for side-by-side release with the PC version. The game is similar, but in a 2.5D style. Maps, albeit modified to make use of the 3D-ish rendering with various turns and effects, are carried over but with a decent amount lacking textures for the extra dimension of view. Most enemies are implemented, but quite a lot use their original sprites as placeholders (I may have to note that this build used a Doom-like method for most in-game things in rendering sprites with rotations for each object/character instead of using models). The multiplayer story mode is included, and a strange split-screen deathmatch mode is added in place of LMS using the same maps. While there are fully completed sprites for second, third and fourth characters, none of them seem to be implemented as a recolored Springy takes the place of every multiplayer player character.
Oooh, interesting! Could you send us some footage from the disk, if you'd be so kind? -Mod Liam
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Classroom Solution: Introduction, Benefits, Features
Explore the world of digital classroom solutions, including an introduction to the concept, its benefits, and essential features. Discover how digital classrooms can revolutionize education and enhance the learning experience for both students and teachers.
Benefits of Digital Classroom Software
Digital classroom software is a revolutionary tool that has transformed the way we approach education. It has numerous benefits that make learning more convenient, engaging, and cost-effective. While the article briefly mentions some of these benefits, there are other advantages worth considering.
Increased Student Engagement
Digital classroom software provides an interactive and engaging learning experience for students. The software includes various features such as videos, animations, and interactive quizzes that make learning fun and interesting. Students can also ask questions and collaborate with their peers, which promotes active participation and enhances their understanding of the material.
Digital classroom software enables teachers to personalize learning experiences for each student. The software can be programmed to adapt to the individual learning needs of each student and provide feedback on their progress. This ensures that students receive the appropriate level of instruction and support, which can improve learning outcomes.
Challenges of Implementing Digital Classroom Software
Digital classroom software provides students with access to a vast range of learning resources that may not be available in a traditional classroom setting. This includes online textbooks, multimedia content, and educational games. The software can also connect students with experts and educators from around the world, which expands their horizons and exposes them to different cultures and perspectives.
While digital classroom software has many benefits, implementing it can be a challenging task. Some of the main challenges include:
Teacher Training: Adequate Technological Infrastructure
Teachers may require training on how to use digital classroom software effectively. This includes understanding how to use the software features, creating engaging content, and managing classroom activities. Without proper training, teachers may struggle to integrate the software into their teaching practices, which can hinder student learning outcomes.
To use digital classroom software, schools require a reliable and fast internet connection, appropriate devices such as laptops or tablets, and appropriate software. If schools do not have the necessary infrastructure, implementing digital classroom software may not be feasible.
Students or Parents:
Some students or parents may resist the use of digital classroom software due to concerns about privacy, data security, or perceived disadvantages compared to traditional classroom settings. Educators must address these concerns and provide assurance that digital classroom software is safe, secure, and beneficial for student learning.
Types of Digital Classroom Software
Digital classroom software refers to a wide range of software applications that enable teachers to create, manage, and deliver digital content to students. Some popular types of digital classroom software include:
Learning Management Systems (LMS):
Learning management systems provide a platform for creating and delivering digital content such as lessons, assignments, and assessments. They also offer tools for communication and collaboration between teachers and students, such as discussion forums and messaging.
Virtual Learning Environments (VLE):
Virtual learning environments provide a digital space for students to learn and interact with their peers and teachers. They typically include features such as video conferencing, online chat, and digital whiteboards.
Best Practices for Using Digital Classroom Software
To effectively use digital classroom software, educators should consider the following best practices:
Before using digital classroom software, educators should set clear objectives for their lessons and identify which software features are most appropriate to achieve these objectives.
Educators should plan their lessons in advance and ensure that all necessary resources are available on the digital classroom software. This includes multimedia content, quizzes, and assignments.
Digital classroom software provides opportunities for students to actively participate in their learning. Educators should encourage student engagement by incorporating interactive elements such as quizzes, polls
In order for digital classroom software to be effective, it is important for teachers to understand how to use it properly. One of the key best practices is to ensure that the software is integrated into teaching practices in a way that enhances student learning. This means that teachers need to carefully consider which features of the software will be most useful for their particular classroom and curriculum.
For example, some teachers may find that recording lectures and making them available for students to review at their own pace is particularly helpful, while others may prefer to use the software for live videoconferencing or collaborative group work. Teachers can also use digital classroom software to track student progress, provide feedback on assignments, and communicate with parents and other educators.
Effectiveness of digital classroom software:
While digital classroom software has become increasingly popular in recent years, there is still relatively little research on its effectiveness in improving student outcomes. However, some studies have suggested that digital classroom software can have a positive impact on student engagement, motivation, and learning.
For example, a study by the National Center for Education Statistics found that students who used digital textbooks and online resources scored higher on standardized tests than those who used traditional print materials. Other studies have shown that digital classroom can help students develop critical thinking skills, enhance creativity, and improve collaboration and communication.
Ethical considerations of using digital classroom software:
While digital classroom software has the potential to revolutionize education, it is important to consider the ethical implications of its use. One of the main concerns is data privacy and security. Digital classroom software collects and stores large amounts of personal data about students, including their academic performance, behavior, and personal information.
There is a risk that this data could be misused or accessed by unauthorized individuals, leading to potential privacy breaches and other security concerns. Additionally, there is a risk that the use of digital classroom software could lead to increased surveillance of students, creating potential ethical concerns around privacy and consent.
Another ethical concern is the potential for bias in automated grading systems. Some digital classroom software uses algorithms to grade student assignments, which could lead to errors and inaccuracies if the algorithms are not properly designed or implemented. There is also a risk that these systems could perpetuate existing biases and inequalities in education, leading to unfair outcomes for certain students.
In conclusion, classroom has the potential to transform education by providing teachers and students with powerful tools for learning and collaboration. However, it is important to consider the benefits and challenges of using this technology, as well as the ethical implications of its use. By understanding these issues and using best practices for integration and optimization, teachers can harness the power of digital classroom software to create engaging and effective learning experiences for their students.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Classrooms:
Advantages
Increased student engagement
Personalized learning experiences
Access to a wider range of resources
Convenience and cost savings
Flexibility in scheduling and delivery
Enhanced collaboration and communication
Real-time feedback and assessment
Improved teacher-student communication
Disadvantages
Dependence on technology
Technical difficulties
Internet connectivity issues
Lack of face-to-face interaction
Potential for distractions
Resistance from students or parents to change
Need for teacher training and support
Potential for unethical or biased automated grading
Here, is the list of some ( FAQs ) Frequently Asked Questions About Digital Classrooms. Few examples are:
What are the benefits of digital classrooms?
Digital classrooms provide many benefits, such as increased accessibility to educational resources, greater student engagement, and personalized learning experiences.
What are the elements of a digital classroom?
The elements of a digital classroom can include hardware and software tools such as computers, tablets, projectors, digital whiteboards, learning management systems, and online collaboration tools.
What is digital classroom technology?
Digital classroom technology refers to the hardware and software tools used in a digital classroom to facilitate teaching and learning, such as computers, tablets, learning management systems, and online collaboration tools.
What is digital tools in classroom?
Digital tools in the classroom refer to software and hardware tools that are used to facilitate teaching and learning, such as digital whiteboards, educational apps, and online collaboration tools.
What is the importance of digital classroom to students?
Digital classrooms provide students with greater access to educational resources, increased engagement, and personalized learning experiences that can enhance their academic performance and better prepare them for future careers.
What is the difference between digital classroom and online classroom?
A digital classroom typically refers to a physical classroom that has been outfitted with digital tools and technology to facilitate teaching and learning, while an online classroom typically refers to a virtual classroom that is entirely online and does not have a physical classroom component.
What is the important role of a teacher in a digital classroom?
Teachers play a critical role in a digital classroom, as they must be able to effectively use digital tools and technology to deliver instructional content and support student learning. They must also be able to adapt to new technologies and teaching methods as they evolve.
What are the different types of digital learning?
The different types of digital learning can include blended learning, which combines traditional classroom learning with digital learning, online learning, which is entirely online and does not have a physical classroom component, and adaptive learning, which uses technology to personalize the learning experience based on the individual needs of each student.
How important is digital learning?
Digital learning is becoming increasingly important in today’s digital age, as it provides students with greater access to educational resources, personalized learning experiences, and career opportunities that require digital skills. It can also help to improve student engagement and academic performance.
#DigiClass #SmartClassSolution #SmartClassroom #DigitalClassroom #SmartClass #EducationTechnology #DigitalTeacher #Physics #CodeandPixels
#digital teacher#digital classroom#digi class#online learning application#elearning#digital learning#learning app#online learning app#online learning platform#online education#digital education#online classes#digital class software#digital class#digital class solution#education#education technology#digital classrooms#smart class#smart classes#smart classroom software
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Maximize Workplace Efficiency Using Microlearning | MaxLearn

In today's fast-paced business environment, companies must keep their workforce agile, efficient, and continuously updated. Traditional training methods often fall short — they’re time-consuming, hard to retain, and costly to implement at scale. That’s where microlearning steps in. Designed for modern learners, microlearning breaks down complex topics into bite-sized, highly focused content that can be consumed quickly and retained longer. By integrating the right Microlearning Platform, businesses can boost productivity while enhancing employee engagement and knowledge retention.
Why Microlearning Works
Microlearning is rooted in cognitive science and learning behavior. Rather than overwhelming employees with long, lecture-style sessions, microlearning delivers short, targeted lessons that are easier to absorb. This method also suits today's mobile, on-the-go workforce. Employees can engage with content during a commute, between meetings, or as a quick refresher during work hours — all without sacrificing productivity.
Microlearning Courses for the Modern Workforce
The success of microlearning depends largely on the quality and relevance of the content. Well-designed microlearning courses focus on specific skills or knowledge points, allowing employees to master one topic at a time. Whether it's compliance training, software tutorials, or customer service techniques, microlearning courses make it easier to update and scale training across an entire organization.
Choosing the Right Microlearning Platform
A high-performing microlearning platform is essential for managing, delivering, and tracking learning outcomes. Top microlearning platforms offer intuitive interfaces, seamless mobile access, and detailed analytics that give managers visibility into employee progress and engagement. The best platforms are designed to support rapid learning without interrupting workflow.
Microlearning Application in the Workplace
Integrating a Microlearning Application into daily operations makes training feel less like a chore and more like a natural part of work. Many companies embed microlearning tools into communication apps like Slack or Microsoft Teams, enabling learning in the flow of work. This kind of seamless integration supports just-in-time learning — a key driver of workplace efficiency.
Leveraging Microlearning Tools and Software
To maximize impact, businesses should leverage advanced microlearning tools and software that support multimedia content, quizzes, gamification, and real-time feedback. These features keep learners engaged and encourage higher completion rates. Additionally, microlearning software allows L&D teams to personalize content for different roles, teams, or learning styles, increasing relevance and effectiveness.
Create with Microlearning Authoring Tools
Creating compelling, digestible learning content requires powerful Microlearning Authoring Tools. These tools enable instructional designers and subject matter experts to develop and update content quickly, without needing technical expertise. Whether it’s video snippets, infographics, or interactive assessments, authoring tools simplify the development process and help keep learning current.
The Rise of AI in Microlearning
The future of microlearning is being shaped by artificial intelligence. An AI-powered authoring tool can automate content creation, recommend learning paths based on user behavior, and adapt content to individual needs. These features reduce the burden on L&D teams while delivering more personalized and effective learning experiences. Similarly, an AI-powered learning platform can analyze performance data to optimize training strategies and improve ROI.
Microlearning LMS: A Strategic Advantage
A microlearning LMS (Learning Management System) serves as the backbone for delivering and managing bite-sized training. Unlike traditional LMS platforms that focus on long-form courses, a microlearning LMS is built for speed, agility, and mobile-first learning. It helps track progress, assess performance, and ensure compliance — all while promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Microlearning is not just a trend — it's a strategic approach to learning that aligns perfectly with how today’s employees absorb information. By adopting the right Microlearning Tools, platforms, and AI-driven technology, organizations can deliver impactful training that fits into busy schedules and boosts workplace efficiency. As the business landscape continues to evolve, microlearning will remain a vital tool for upskilling and empowering employees at scale.
#Microlearning Platform#MicrolearningPlatform#Microlearning Courses#MicrolearningCourses#Microlearning Platforms#MicrolearningPlatforms#microlearning application#MicrolearningApplication#microlearningapplication#microlearning authoring tools#MicrolearningAuthoringTools#microlearningauthoringtools#microlearning tools#MicrolearningTools#microlearningtools#microlearning software#MicrolearningSoftware#microlearningsoftware#micro learning courses#MicrolearningLMS#microlearninglms#micro learning platform#AIPoweredAuthoringTool#AI Powered Authoring Tool#AIPoweredLearningPlatform#aipoweredlearningplatform#ai powered learning platform#microlearning lms#Microlearning Application#Microlearning Authoring Tools
0 notes