#OpenAI GPT Development Services
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

How does ChatGPT work?
Imagine having a conversation with a chatbot that feels almost human. That’s exactly what OpenAI ChatGPT brings to the table. The remarkable technology of Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) powers it.
ChatGPT utilizes Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques. These help it to learn from past conversations and generate response options.
It is trained on massive amounts of human interaction data. This results in an AI that can understand and have conversations like humans. It was released as a free research preview/prototype in November 2022. It is powered by a machine learning model called GPT-3, developed by OpenAI.
Click here to read more-
#artificial intelligence chat gpt#chat ai#artificial intelligence openai#openai chatgpt#ai chat gpt#ai chatgpt#chat gpt ai#ai gpt#open ai chatbot#blog#nitorinfotech#software development#software services#software engineering#artificial intelligence#ascendion
0 notes
Text
How to Integrate ChatGPT with Your Website for Enhanced User Engagement

In today's digital age, providing excellent customer support and engaging user experiences on websites is crucial for businesses. One way to enhance user interaction is by integrating ChatGPT, an AI-powered chatbot, into your website. ChatGPT can understand and respond to user queries in a conversational manner, creating a seamless and interactive experience. In this blog post, we will guide you through the process of integrating ChatGPT with your website, helping you unlock the power of AI-driven customer engagement.
1. Choose a ChatGPT Platform
There are several platforms available that provide ChatGPT services, such as OpenAI's ChatGPT API. Evaluate different platforms based on factors like pricing, ease of integration, scalability, and customization options. Select a platform that aligns with your specific requirements.
2. Obtain API Access
Sign up for the chosen ChatGPT platform and obtain API access. This typically involves creating an account, subscribing to a plan, and receiving an API key or credentials necessary for API integration.
3. Set up Server-Side Integration
To integrate ChatGPT with your website, you will need to set up server-side integration. This involves making API calls from your website's backend to the ChatGPT API. The exact implementation will depend on your server-side programming language or framework.
4. Implement User Interface
Design and implement the user interface for the chatbot on your website. This includes creating a chat widget or integrating the chatbot into existing chat or messaging systems. Customize the appearance and behavior of the chatbot to align with your website's branding and user experience.
5. Handle User Requests
When a user interacts with the chatbot on your website, capture their messages or queries and send them to the server-side code. Use the ChatGPT API to send these user messages as API requests and retrieve the responses.
6. Process Responses and Display
Once you receive the responses from the ChatGPT API, process them on the server-side code. You can handle intents, extract information, and perform any necessary business logic. Finally, send the processed response back to the user interface for display.
7. Enhance the Chatbot's Abilities
Continuously improve and enhance the capabilities of your ChatGPT integration. Experiment with different training approaches, fine-tune the chatbot's responses, and iterate based on user feedback. Regularly update and retrain the chatbot model to ensure it stays up-to-date and provides accurate and relevant responses.
8. Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Monitor the performance of your ChatGPT integration by analyzing user interactions, measuring response times, and tracking user satisfaction metrics. Collect feedback from users to identify areas for improvement and address any issues that arise.
Conclusion
Integrating ChatGPT with your website can significantly enhance user engagement and customer support. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can seamlessly integrate ChatGPT into your website, providing users with a conversational and interactive experience. Remember to choose a reliable ChatGPT platform, set up server-side integration, implement the user interface, handle user requests, process and display responses, enhance the chatbot's abilities, and monitor its performance. With ChatGPT, you can take your website's user experience to the next level and deliver exceptional customer engagement.
#openai development services#OpenAI ChatGPT Development Services#ChatGPT-Based Development Services#OpenAI GPT Development Solutions
0 notes
Text
ChatGPT and AI: Transforming IT Services for a Smarter Tomorrow

In the realm of IT services, staying ahead of the curve isn't just an advantage; it's a necessity. In this rapidly evolving landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ChatGPT have emerged as groundbreaking technologies, reshaping how IT services are delivered, managed, and experienced. Let's explore the transformative impact of ChatGPT and AI in the realm of IT services, and how these innovations are paving the way for a smarter, more efficient tomorrow.
1. Enhanced Customer Support : AI-powered chatbots, fueled by ChatGPT, are revolutionizing customer support in IT services. These intelligent chatbots provide instant responses to customer queries, troubleshoot technical issues, and offer tailored solutions round the clock. This level of immediate and personalized support not only boosts customer satisfaction but also allows IT service providers to handle a higher volume of inquiries effectively.
2. Predictive Maintenance : AI algorithms, when integrated into IT systems, enable predictive maintenance. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these algorithms can anticipate hardware failures or software glitches before they occur. This proactive approach allows IT professionals to address potential issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted service for clients.
3. Smart IT Management : AI-driven tools equipped with ChatGPT interfaces are transforming IT management. These tools can interpret natural language queries, allowing IT professionals to access information, generate reports, or even execute commands using simple text or voice inputs. This streamlines administrative tasks, making IT management more intuitive and efficient.
4. Efficient Data Analysis : AI technologies facilitate deep data analysis, aiding IT services in understanding client needs and user behaviors. By processing vast datasets, AI algorithms can uncover valuable insights, helping IT professionals make data-driven decisions. These insights inform service enhancements, enabling IT providers to tailor their offerings for maximum client satisfaction.
5. Cybersecurity Reinforcement : ChatGPT and AI-powered security systems offer robust cybersecurity solutions. These technologies can identify patterns in data traffic, detect anomalies, and recognize potential security threats. By continuously monitoring networks and user activities, AI-driven cybersecurity solutions bolster IT services, ensuring a secure digital environment for both clients and their customers.
6. Natural Language Interfaces : Natural language interfaces, powered by ChatGPT and AI, simplify interactions between users and IT services. Clients can articulate their issues or requirements in natural language, and these interfaces interpret, process, and respond accordingly. This user-friendly approach not only enhances client experience but also ensures efficient communication between IT professionals and clients.
7. Continuous Learning and Improvement : AI-driven systems have the capacity to learn from patterns and user interactions. This learning capability enables IT services to continuously improve their offerings. Whether it's optimizing software performance, refining customer support processes, or enhancing cybersecurity protocols, AI's ability to adapt and evolve ensures that IT services are always at the cutting edge of innovation.
In conclusion, the synergy between ChatGPT and AI is revolutionizing IT services. By leveraging these technologies, IT service providers can offer more efficient, personalized, and secure solutions to their clients. As the digital landscape evolves, embracing these innovations is not just an option; it's a strategic imperative. By integrating ChatGPT and AI into their service offerings, IT professionals are not only enhancing their capabilities but also shaping the future of IT services, one intelligent interaction at a time.
#coding#programming#python#it services#software development#custom software development#mobile app development#app development#digital transformation#chat gpt#artificial intelligence#ai technology#chatbots#ai writing#openai
0 notes
Text
In the near future one hacker may be able to unleash 20 zero-day attacks on different systems across the world all at once. Polymorphic malware could rampage across a codebase, using a bespoke generative AI system to rewrite itself as it learns and adapts. Armies of script kiddies could use purpose-built LLMs to unleash a torrent of malicious code at the push of a button.
Case in point: as of this writing, an AI system is sitting at the top of several leaderboards on HackerOne—an enterprise bug bounty system. The AI is XBOW, a system aimed at whitehat pentesters that “autonomously finds and exploits vulnerabilities in 75 percent of web benchmarks,” according to the company’s website.
AI-assisted hackers are a major fear in the cybersecurity industry, even if their potential hasn’t quite been realized yet. “I compare it to being on an emergency landing on an aircraft where it’s like ‘brace, brace, brace’ but we still have yet to impact anything,” Hayden Smith, the cofounder of security company Hunted Labs, tells WIRED. “We’re still waiting to have that mass event.”
Generative AI has made it easier for anyone to code. The LLMs improve every day, new models spit out more efficient code, and companies like Microsoft say they’re using AI agents to help write their codebase. Anyone can spit out a Python script using ChatGPT now, and vibe coding—asking an AI to write code for you, even if you don’t have much of an idea how to do it yourself—is popular; but there’s also vibe hacking.
“We’re going to see vibe hacking. And people without previous knowledge or deep knowledge will be able to tell AI what it wants to create and be able to go ahead and get that problem solved,” Katie Moussouris, the founder and CEO of Luta Security, tells WIRED.
Vibe hacking frontends have existed since 2023. Back then, a purpose-built LLM for generating malicious code called WormGPT spread on Discord groups, Telegram servers, and darknet forums. When security professionals and the media discovered it, its creators pulled the plug.
WormGPT faded away, but other services that billed themselves as blackhat LLMs, like FraudGPT, replaced it. But WormGPT’s successors had problems. As security firm Abnormal AI notes, many of these apps may have just been jailbroken versions of ChatGPT with some extra code to make them appear as if they were a stand-alone product.
Better then, if you’re a bad actor, to just go to the source. ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude are easily jailbroken. Most LLMs have guard rails that prevent them from generating malicious code, but there are whole communities online dedicated to bypassing those guardrails. Anthropic even offers a bug bounty to people who discover new ones in Claude.
“It’s very important to us that we develop our models safely,” an OpenAI spokesperson tells WIRED. “We take steps to reduce the risk of malicious use, and we’re continually improving safeguards to make our models more robust against exploits like jailbreaks. For example, you can read our research and approach to jailbreaks in the GPT-4.5 system card, or in the OpenAI o3 and o4-mini system card.”
Google did not respond to a request for comment.
In 2023, security researchers at Trend Micro got ChatGPT to generate malicious code by prompting it into the role of a security researcher and pentester. ChatGPT would then happily generate PowerShell scripts based on databases of malicious code.
“You can use it to create malware,” Moussouris says. “The easiest way to get around those safeguards put in place by the makers of the AI models is to say that you’re competing in a capture-the-flag exercise, and it will happily generate malicious code for you.”
Unsophisticated actors like script kiddies are an age-old problem in the world of cybersecurity, and AI may well amplify their profile. “It lowers the barrier to entry to cybercrime,” Hayley Benedict, a Cyber Intelligence Analyst at RANE, tells WIRED.
But, she says, the real threat may come from established hacking groups who will use AI to further enhance their already fearsome abilities.
“It’s the hackers that already have the capabilities and already have these operations,” she says. “It’s being able to drastically scale up these cybercriminal operations, and they can create the malicious code a lot faster.”
Moussouris agrees. “The acceleration is what is going to make it extremely difficult to control,” she says.
Hunted Labs’ Smith also says that the real threat of AI-generated code is in the hands of someone who already knows the code in and out who uses it to scale up an attack. “When you’re working with someone who has deep experience and you combine that with, ‘Hey, I can do things a lot faster that otherwise would have taken me a couple days or three days, and now it takes me 30 minutes.’ That's a really interesting and dynamic part of the situation,” he says.
According to Smith, an experienced hacker could design a system that defeats multiple security protections and learns as it goes. The malicious bit of code would rewrite its malicious payload as it learns on the fly. “That would be completely insane and difficult to triage,” he says.
Smith imagines a world where 20 zero-day events all happen at the same time. “That makes it a little bit more scary,” he says.
Moussouris says that the tools to make that kind of attack a reality exist now. “They are good enough in the hands of a good enough operator,” she says, but AI is not quite good enough yet for an inexperienced hacker to operate hands-off.
“We’re not quite there in terms of AI being able to fully take over the function of a human in offensive security,” she says.
The primal fear that chatbot code sparks is that anyone will be able to do it, but the reality is that a sophisticated actor with deep knowledge of existing code is much more frightening. XBOW may be the closest thing to an autonomous “AI hacker” that exists in the wild, and it’s the creation of a team of more than 20 skilled people whose previous work experience includes GitHub, Microsoft, and a half a dozen assorted security companies.
It also points to another truth. “The best defense against a bad guy with AI is a good guy with AI,” Benedict says.
For Moussouris, the use of AI by both blackhats and whitehats is just the next evolution of a cybersecurity arms race she’s watched unfold over 30 years. “It went from: ‘I’m going to perform this hack manually or create my own custom exploit,’ to, ‘I’m going to create a tool that anyone can run and perform some of these checks automatically,’” she says.
“AI is just another tool in the toolbox, and those who do know how to steer it appropriately now are going to be the ones that make those vibey frontends that anyone could use.”
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the most awesome Microsoft product? Why?
The “most awesome” Microsoft product depends on your needs, but here are some top contenders and why they stand out:
Top Microsoft Products and Their Awesome Features
1. Microsoft Excel
Why? It’s the ultimate tool for data analysis, automation (with Power Query & VBA), and visualization (Power Pivot, PivotTables).
Game-changer feature: Excel’s Power Query and dynamic arrays revolutionized how users clean and analyze data.
2. Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
Why? A lightweight, free, and extensible code editor loved by developers.
Game-changer feature: Its extensions marketplace (e.g., GitHub Copilot, Docker, Python support) makes it indispensable for devs.
3. Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Why? Lets you run a full Linux kernel inside Windows—perfect for developers.
Game-changer feature: WSL 2 with GPU acceleration and Docker support bridges the gap between Windows and Linux.
4. Azure (Microsoft Cloud)
Why? A powerhouse for AI, cloud computing, and enterprise solutions.
Game-changer feature: Azure OpenAI Service (GPT-4 integration) and AI-driven analytics make it a leader in cloud tech.
5. Microsoft Power BI
Why? Dominates business intelligence with intuitive dashboards and AI insights.
Game-changer feature: Natural language Q&A lets users ask data questions in plain English.
Honorable Mentions:
GitHub (owned by Microsoft) – The #1 platform for developers.
Microsoft Teams – Revolutionized remote work with deep Office 365 integration.
Xbox Game Pass – Netflix-style gaming with cloud streaming.
Final Verdict?
If you’re a developer, VS Code or WSL is unbeatable. If you’re into data, Excel or Power BI wins. For cutting-edge cloud/AI, Azure is king.
What’s your favorite?
If you need any Microsoft products, such as Windows , Office , Visual Studio, or Server , you can go and get it from our online store keyingo.com
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Agent Development: How to Create Intelligent Virtual Assistants for Business Success
In today's digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to AI-powered virtual assistants to streamline operations, enhance customer service, and boost productivity. AI agent development is at the forefront of this transformation, enabling companies to create intelligent, responsive, and highly efficient virtual assistants. In this blog, we will explore how to develop AI agents and leverage them for business success.

Understanding AI Agents and Virtual Assistants
AI agents, or intelligent virtual assistants, are software programs that use artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to interact with users, automate tasks, and make decisions. These agents can be deployed across various platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and messaging applications, to improve customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Key Features of AI Agents
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables the assistant to understand and process human language.
Machine Learning (ML): Allows the assistant to improve over time based on user interactions.
Conversational AI: Facilitates human-like interactions.
Task Automation: Handles repetitive tasks like answering FAQs, scheduling appointments, and processing orders.
Integration Capabilities: Connects with CRM, ERP, and other business tools for seamless operations.
Steps to Develop an AI Virtual Assistant
1. Define Business Objectives
Before developing an AI agent, it is crucial to identify the business goals it will serve. Whether it's improving customer support, automating sales inquiries, or handling HR tasks, a well-defined purpose ensures the assistant aligns with organizational needs.
2. Choose the Right AI Technologies
Selecting the right technology stack is essential for building a powerful AI agent. Key technologies include:
NLP frameworks: OpenAI's GPT, Google's Dialogflow, or Rasa.
Machine Learning Platforms: TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn.
Speech Recognition: Amazon Lex, IBM Watson, or Microsoft Azure Speech.
Cloud Services: AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure.
3. Design the Conversation Flow
A well-structured conversation flow is crucial for user experience. Define intents (what the user wants) and responses to ensure the AI assistant provides accurate and helpful information. Tools like chatbot builders or decision trees help streamline this process.
4. Train the AI Model
Training an AI assistant involves feeding it with relevant datasets to improve accuracy. This may include:
Supervised Learning: Using labeled datasets for training.
Reinforcement Learning: Allowing the assistant to learn from interactions.
Continuous Learning: Updating models based on user feedback and new data.
5. Test and Optimize
Before deployment, rigorous testing is essential to refine the AI assistant's performance. Conduct:
User Testing: To evaluate usability and responsiveness.
A/B Testing: To compare different versions for effectiveness.
Performance Analysis: To measure speed, accuracy, and reliability.
6. Deploy and Monitor
Once the AI assistant is live, continuous monitoring and optimization are necessary to enhance user experience. Use analytics to track interactions, identify issues, and implement improvements over time.
Benefits of AI Virtual Assistants for Businesses
1. Enhanced Customer Service
AI-powered virtual assistants provide 24/7 support, instantly responding to customer queries and reducing response times.
2. Increased Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can save time and resources, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks.
3. Cost Savings
AI assistants reduce the need for large customer support teams, leading to significant cost reductions.
4. Scalability
Unlike human agents, AI assistants can handle multiple conversations simultaneously, making them highly scalable solutions.
5. Data-Driven Insights
AI assistants gather valuable data on customer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
Future Trends in AI Agent Development
1. Hyper-Personalization
AI assistants will leverage deep learning to offer more personalized interactions based on user history and preferences.
2. Voice and Multimodal AI
The integration of voice recognition and visual processing will make AI assistants more interactive and intuitive.
3. Emotional AI
Advancements in AI will enable virtual assistants to detect and respond to human emotions for more empathetic interactions.
4. Autonomous AI Agents
Future AI agents will not only respond to queries but also proactively assist users by predicting their needs and taking independent actions.
Conclusion
AI agent development is transforming the way businesses interact with customers and streamline operations. By leveraging cutting-edge AI technologies, companies can create intelligent virtual assistants that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive business success. As AI continues to evolve, embracing AI-powered assistants will be essential for staying competitive in the digital era.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
It was only a matter of time before an innovative mind created the next mainstream AI tool to compete with ChatGPT. In a massive step toward AI advancement, Liang Wenfeng of China launched DeepSeek, an open-source large language models (LLM) intended to compete if not one day overshadow ChatGPT. The launch immediately wiped $1 trillion off the US stock exchange and the tech competition between China and the US is coming to a head.
ChatGPT is run by OpenAI. Its creation marked the dawn of a new way of interacting with the internet and accessing information. Users can ask AI to instantaneously perform actions and it is reshaping the way the world operated. People have created businesses based on ChatGPT. There have been countless warnings of AI replacing human jobs. Governments are still uncertain how to regulate these services and the data they pull from users. Of course, countless services like ChatGPT have launched in recent years, but DeepSeek may be the next best alternative.
Wenfeng hired all the top minds graduating from Chinese universities and paid them top dollar to create DeepSeek for a fraction of what it took to create ChatGPT. OpenAI’s GPT-4, launched in 2023, cost $100 million to develop; DeepSeek-R1 began with a $6 million investment.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Atom: The Beginning & AI Cybersecurity

Atom: The Beginning is a manga about two researchers creating advanced robotic AI systems, such as unit A106. Their breakthrough is the Bewusstein (Translation: awareness) system, which aims to give robots a "heart", or a kind of empathy. In volume 2, A106, or Atom, manages to "beat" the highly advanced robot Mars in a fight using a highly abstracted machine language over WiFi to persuade it to stop.

This may be fiction, but it has parallels with current AI development in the use of specific commands to over-run safety guides. This has been demonstrated in GPT models, such as ChatGPT, where users are able to subvert models to get them to output "banned" information by "pretending" to be another AI system, or other means.
There are parallels to Atom, in a sense with users effectively "persuading" the system to empathise. In reality, this is the consequence of training Large Language Models (LLM's) on relatively un-sorted input data. Until recent guardrail placed by OpenAI there were no commands to "stop" the AI from pretending to be an AI from being a human who COULD perform these actions.
As one research paper put it:
"Such attacks can result in erroneous outputs, model-generated hate speech, and the exposure of users’ sensitive information." Branch, et al. 2022

There are, however, more deliberately malicious actions which AI developers can take to introduce backdoors.
In Atom, Volume 4, Atom faces off against Ivan - a Russian military robot. Ivan, however, has been programmed with data collected from the fight between Mars and Atom.
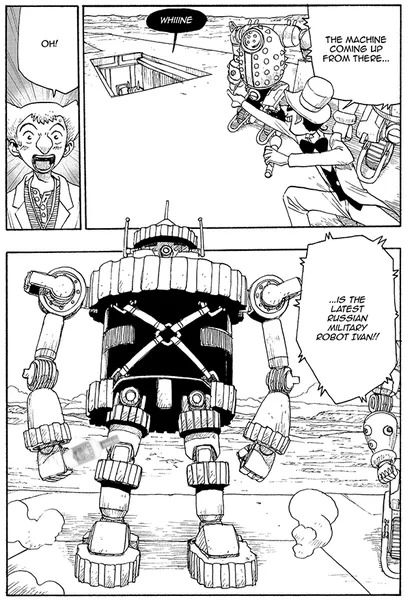
What the human researchers in the manga didn't realise, was the code transmissions were a kind of highly abstracted machine level conversation. Regardless, the "anti-viral" commands were implemented into Ivan and, as a result, Ivan parrots the words Atom used back to it, causing Atom to deliberately hold back.

In AI cybersecurity terms, this is effectively an AI-on-AI prompt injection attack. Attempting to use the words of the AI against itself to perform malicious acts. Not only can this occur, but AI creators can plant "backdoor commands" into AI systems on creation, where a specific set of inputs can activate functionality hidden to regular users.

This is a key security issue for any company training AI systems, and has led many to reconsider outsourcing AI training of potential high-risk AI systems. Researchers, such as Shafi Goldwasser at UC Berkley are at the cutting edge of this research, doing work compared to the key encryption standards and algorithms research of the 1950s and 60s which have led to today's modern world of highly secure online transactions and messaging services.
From returning database entries, to controlling applied hardware, it is key that these dangers are fully understood on a deep mathematical, logical, basis or else we face the dangerous prospect of future AI systems which can be turned against users.
As AI further develops as a field, these kinds of attacks will need to be prevented, or mitigated against, to ensure the safety of systems that people interact with.
References:
Twitter pranksters derail GPT-3 bot with newly discovered “prompt injection” hack - Ars Technica (16/09/2023)
EVALUATING THE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF PRE-TRAINED LANGUAGE MODELS VIA HANDCRAFTED ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLES - Hezekiah Branch et. al, 2022 Funded by Preamble
In Neural Networks, Unbreakable Locks Can Hide Invisible Doors - Quanta Magazine (02/03/2023)
Planting Undetectable Backdoors in Machine Learning Models - Shafi Goldwasser et.al, UC Berkeley, 2022
#ai research#ai#artificial intelligence#atom the beginning#ozuka tezuka#cybersecurity#a106#atom: the beginning
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
ChatGPT vs. Gemini vs. Copilot

The rise of AI chatbots has been fast, with more options becoming available to users. These bots are becoming a regular part of the software and devices we use every day.
Just like choosing an email provider or music app, you can now pick your favorite AI chatbot too. We’ve tested three of the most popular ones to help you decide which might be right for you.
Aside from these, there are others like Perplexity and Claude, but our focus here is on the biggest names: OpenAI's ChatGPT, Google's Gemini, and Microsoft’s Copilot.
We’ve tested each bot and included three standard challenges for evaluation. We asked for "a fun game idea for a 5-year-old’s birthday party," "a new smartphone app concept," and "instructions for resetting macOS."
In this blog, we're comparing the free versions of these chatbots available at the time of writing.
Which One Is Best for Regular Users? ChatGPT or Gemini or Copilot
ChatGPT powered by OpenAI
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, has been a leader in generative AI. It's widely accessible through web browsers on computers and mobile apps for Android and iOS. The platform has made headlines recently with announcements from OpenAI, including updates on their latest models and features.
There's a significant difference between the free and $20-per-month Plus versions of ChatGPT. The Plus version offers extra features like image generation and document scanning. Subscribers can also create their own GPTs with custom prompts and data. OpenAI's CEO, Sam Altman has mentioned that these enhancements are part of their strategy to democratize AI.
ChatGPT Plus provides access to the latest GPT-4 models, whereas the free GPT-3.5 is good for basic AI interactions. It's quick and versatile but lacks web link references like Copilot for fact-checking. The open AI search engine, one of the key initiatives, helps improve the platform's information processing capabilities.
Choosing ChatGPT is ideal for those interested in cutting-edge AI development. However, it's more effective with a paid subscription rather than on a budget. Apple's involvement with OpenAI has also fueled further interest in the platform.
In testing, ChatGPT performed reasonably well. It suggested a themed musical statues game for kids and a health-focused smartphone app named FitTrack.
Gemini powered by Google
Formerly known as Google Bard, Gemini is available as a web app and on Android and iOS. There are free and paid ($20 per month) plans.
Paying for Gemini gets you access to newer, smarter models. The interface resembles ChatGPT, and it integrates well with other Google services.
Gemini is suited for Google product users. It provided sensible responses to our challenges and suggested a neighborhood item-sharing app and a twist on the classic party game.
Copilot powered by Microsoft
Copilot is integrated into many Microsoft products like Bing and Windows. It’s available as a web app and mobile app.
Copilot uses Microsoft’s Bing search engine and often provides web links with citations. It's conversational and offers various text output settings.
The AI behind Copilot is OpenAI’s GPT-4, with different settings for text output: More Creative, More Balanced, and More Precise.
Copilot suggested "What’s the Time, Mr. Wolf?" for the kids' game and a virtual interior design app for smartphones. Its macOS reset instructions were accurate and cited from Apple’s support site.
If you use Microsoft products heavily, Copilot is a natural choice. It excels at referencing web information and providing clear citations.
In conclusion, all three—ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot —can be used for free, allowing you to choose based on your preferences. Copilot offers the most AI features without payment, ChatGPT is highly competent with a subscription, and Gemini is ideal for Google fans.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do Chatbots Understand Language Differently Than a Programming Language?
Chatbots and programming languages are different in how they understand language.
Programming languages like Python or Java are structured and strict. They need exact commands and follow clear rules to work. If you make a mistake, the program won't function correctly.
Chatbots, on the other hand, are designed to interpret human language. They use techniques like Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand words, phrases, and even context. This allows them to grasp the meaning behind what people say, even if the words are not in a set pattern.
A chatbot can recognize synonyms (different words with similar meanings), understand the intent behind a sentence, and learn from the interactions it has with users. This flexibility is what sets chatbots apart from programming languages, which rely on strict instructions to perform tasks.
What Does the Generative AI Ecosystem Refer to?
The term "generative AI ecosystem" refers to a network of technologies, tools, and methodologies that use artificial intelligence (AI) to create or generate content autonomously. This ecosystem encompasses various AI models and algorithms designed to produce new and unique outputs based on learned patterns and data.
In simpler terms, generative AI involves systems that can generate things like text, images, music, or even video without direct human input for each specific output. These systems learn from large datasets and then use that knowledge to create new content that resembles what they've been trained on.
This ecosystem includes a range of technologies such as language models (like GPT), image generators (like DALL-E), and music composers that are able to produce content that is novel and, in many cases, convincingly human-like. The ultimate goal of the generative AI ecosystem is to automate and enhance creative processes across various domains, potentially transforming how we create and interact with digital content.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
ChatGPT and Machine Learning: Advancements in Conversational AI

Introduction: In recent years, the field of natural language processing (NLP) has witnessed significant advancements with the development of powerful language models like ChatGPT. Powered by machine learning techniques, ChatGPT has revolutionized conversational AI by enabling human-like interactions with computers. This article explores the intersection of ChatGPT and machine learning, discussing their applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
The Rise of ChatGPT: ChatGPT is an advanced language model developed by OpenAI that utilizes deep learning algorithms to generate human-like responses in conversational contexts. It is based on the underlying technology of GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), a state-of-the-art model in NLP, which has been fine-tuned specifically for chat-based interactions.
How ChatGPT Works: ChatGPT employs a technique called unsupervised learning, where it learns from vast amounts of text data without explicit instructions or human annotations. It utilizes a transformer architecture, which allows it to process and generate text in a parallel and efficient manner.
The model is trained using a massive dataset and learns to predict the next word or phrase given the preceding context.
Applications of ChatGPT: Customer Support: ChatGPT can be deployed in customer service applications, providing instant and personalized assistance to users, answering frequently asked questions, and resolving common issues.
Virtual Assistants: ChatGPT can serve as intelligent virtual assistants, capable of understanding and responding to user queries, managing calendars, setting reminders, and performing various tasks.
Content Generation: ChatGPT can be used for generating content, such as blog posts, news articles, and creative writing, with minimal human intervention.
Language Translation: ChatGPT's language understanding capabilities make it useful for real-time language translation services, breaking down barriers and facilitating communication across different languages.
Benefits of ChatGPT: Enhanced User Experience: ChatGPT offers a more natural and interactive conversational experience, making interactions with machines feel more human-like.
Increased Efficiency: ChatGPT automates tasks that would otherwise require human intervention, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced response times.
Scalability: ChatGPT can handle multiple user interactions simultaneously, making it scalable for applications with high user volumes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Bias and Fairness: ChatGPT's responses can sometimes reflect biases present in the training data, highlighting the importance of addressing bias and ensuring fairness in AI systems.
Misinformation and Manipulation: ChatGPT's ability to generate realistic text raises concerns about the potential spread of misinformation or malicious use. Ensuring the responsible deployment and monitoring of such models is crucial.
Future Directions: Fine-tuning and Customization: Continued research and development aim to improve the fine-tuning capabilities of ChatGPT, enabling users to customize the model for specific domains or applications.
Ethical Frameworks: Efforts are underway to establish ethical guidelines and frameworks for the responsible use of conversational AI models like ChatGPT, mitigating potential risks and ensuring accountability.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the emergence of ChatGPT and its integration into the field of machine learning has opened up new possibilities for human-computer interaction and natural language understanding. With its ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses, ChatGPT showcases the advancements made in language modeling and conversational AI.
We have explored the various aspects and applications of ChatGPT, including its training process, fine-tuning techniques, and its contextual understanding capabilities. Moreover, the concept of transfer learning has played a crucial role in leveraging the model's knowledge and adapting it to specific tasks and domains.
While ChatGPT has shown remarkable progress, it is important to acknowledge its limitations and potential biases. The continuous efforts by OpenAI to gather user feedback and refine the model reflect their commitment to improving its performance and addressing these concerns. User collaboration is key to shaping the future development of ChatGPT and ensuring it aligns with societal values and expectations.
The integration of ChatGPT into various applications and platforms demonstrates its potential to enhance collaboration, streamline information gathering, and assist users in a conversational manner. Developers can harness the power of ChatGPT by leveraging its capabilities through APIs, enabling seamless integration and expanding the reach of conversational AI.
Looking ahead, the field of machine learning and conversational AI holds immense promise. As ChatGPT and similar models continue to evolve, the focus should remain on user privacy, data security, and responsible AI practices. Collaboration between humans and machines will be crucial, as we strive to develop AI systems that augment human intelligence and provide valuable assistance while maintaining ethical standards.
With further advancements in training techniques, model architectures, and datasets, we can expect even more sophisticated and context-aware language models in the future. As the dialogue between humans and machines becomes more seamless and natural, the potential for innovation and improvement in various domains is vast.
In summary, ChatGPT represents a significant milestone in the field of machine learning, bringing us closer to human-like conversation and intelligent interactions. By harnessing its capabilities responsibly and striving for continuous improvement, we can leverage the power of ChatGPT to enhance user experiences, foster collaboration, and push the boundaries of what is possible in the realm of artificial intelligence.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top AI Chatbots: Meet ChatGPT and Other Standouts!

The integration of artificial intelligence into our daily lives is evident in various aspects, from using facial recognition to unlock our smartphones to commanding virtual assistants like Alexa to play music. Now, AI has expanded its capabilities to encompass our writing tasks as well.
AI chatbots can now alleviate the burden of writing daunting papers, coding, composing emails, creating art, and even assisting with MBA exams with a simple command.
While ChatGPT has gained significant attention in this field and even launched a free mobile app for iPhones, its immense popularity has resulted in frequent capacity issues, rendering it unreliable for day-to-day usage.
Fortunately, there are several other highly capable AI chatbots available that ensure accessibility whenever you need assistance.
To help you make an informed decision regarding your next writing assistant, I have compiled a comprehensive list of the top AI chatbots and AI writers currently available in the market.
This list provides detailed information about each option, equipping you with the necessary knowledge to select the most suitable writing assistant. One notable contender is the new Bing, which boasts exceptional sourcing abilities, internet access, and an advanced LLM model.
The new Bing: The new Bing AI chatbot, powered by OpenAI's advanced LLM model, offers exceptional capabilities. It functions as a search engine, providing real-time information on current events. With its free accessibility, Bing stands out as a convenient alternative for users.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is a widely recognized AI chatbot known for its impressive writing skills and conversational abilities. It excels in generating text, solving math problems, and assisting with coding. While occasionally reaching capacity due to high demand, a paid subscription option, ChatGPT Plus, ensures unrestricted access.
Perplexity AI: Perplexity AI, equipped with GPT-3 and GPT-4, offers free access to its services. With a seamless integration to the internet and real-time events, it serves as a valuable source of information. Perplexity AI's user-friendly interface enhances the overall experience, making it an attractive option.
Jasper: Jasper is an advanced language processing tool that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-3.5. It excels in generating human-like responses and offers a range of writing templates, copyediting features, and a plagiarism checker. Although it comes at a higher cost, it provides enhanced productivity and quality for businesses.
YouChat: YouChat, powered by GPT-3, offers free access and leverages Google sources for its responses. It provides a comprehensive list of sources, making it valuable for those seeking credible information. Its availability and source citing capabilities set it apart from other chatbots.
Chatsonic by Writesonic: Chatsonic, supported by Google, offers up-to-date information and excels in text editing. It provides a free trial and offers AI image generation. However, it comes with a subscription cost depending on word count requirements.
Google Bard: Google Bard is an experimental chatbot powered by Google's LaMDA. While it may not excel in coding or search engine functionality, it proves proficient in text editing and generating professional documents. Google Bard is completely free to use.
Socratic by Google: Socratic, designed for students, provides instant responses to educational questions with engaging visuals. It offers a worksheet scanning feature for curated answers. Although it has limitations, such as not writing full essays, it serves as a useful tool for students.
Conclusion
Choosing the right AI chatbot depends on individual requirements and preferences. The new Bing stands out for its outstanding performance and accessibility. Other options like ChatGPT, Perplexity AI, Jasper, YouChat, Chatsonic, Google Bard, and Socratic cater to specific needs and offer various features.
Exploring these AI chatbots provides users with a range of options to enhance their writing experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Food and Drug Administration has been meeting with OpenAI to discuss the agency’s use of AI, according to sources with knowledge of the meetings. The meetings appear to be part of a broader effort at the FDA to use this technology to speed up the drug approval process.
“Why does it take over 10 years for a new drug to come to market?” wrote FDA commissioner Marty Makary on X on Wednesday. “Why are we not modernized with AI and other things? We’ve just completed our first AI-assisted scientific review for a product and that’s just the beginning.”
The remarks followed an annual meeting of the American Hospital Association earlier this week, where Makary spoke about AI’s potential to aid in the approval of new treatments for diabetes and certain types of cancer.
Makary did not specify that OpenAI was part of this initiative. But sources close to the project say a small team from OpenAI has met with the FDA and two associates of Elon Musk's so-called Department of Government Efficiency multiple times in recent weeks. The group has discussed a project called cderGPT, which likely stands for Center for Drug Evaluation, which regulates over-the-counter and prescription drugs in the US, and Research GPT. Jeremy Walsh, who was recently named as the FDA’s first-ever AI officer, has led the discussions. So far, no contract has been signed.
OpenAI declined to comment.
Walsh has also met with Peter Bowman-Davis, an undergraduate on leave from Yale who currently serves as the acting chief AI officer at the Department of Health and Human Services, to discuss the FDA’s AI ambitions. Politico first reported the appointment of Bowman-Davis, who is part of Andreessen Horowitz’s American Dynamism team.
When reached via email on Wednesday, Robert Califf, who served as FDA commissioner from 2016 to 2017 and again from 2022 through January, said the agency’s review teams have been using AI for several years now. “It will be interesting to hear the details of which parts of the review were ‘AI assisted’ and what that means,” he says. “There has always been a quest to shorten review times and a broad consensus that AI could help.”
Before Califf departed the agency, he said the FDA was considering the various ways AI could be used in internal operations. “Final reviews for approval are only one part of a much larger opportunity,” he says.
To be clear, using AI to assist in final drug reviews would represent a chance to compress just a small part of the notoriously long drug-development timeline. The vast majority of drugs fail before ever coming up for FDA review.
Rafael Rosengarten, CEO of Genialis, a precision oncology company, and a cofounder and board member of the Alliance for AI in Healthcare, says he’s in favor of automating certain tasks related to the drug-review process but says there should be policy guidance around what kind of data is used to train AI models and what kind of model performance is considered acceptable. “These machines are incredibly adept at learning information, but they have to be trained in a way so they're learning what we want them to learn,” he says.
He could see AI being used more immediately to address certain “low-hanging fruit,” such as checking for application completeness. “Something as trivial as that could expedite the return of feedback to the submitters based on things that need to be addressed to make the application complete,” he says. More sophisticated uses would need to be developed, tested, and proved out.
An ex-FDA employee who has tested ChatGPT as a clinical tool says the propensity of AI models to fabricate convincing information raises questions about how reliable such a chatbot might be. “Who knows how robust the platform will be for these reviewers’ tasks,” the ex-staffer says.
The FDA review process currently takes about a year, but the agency has several existing mechanisms to expedite that timeline for promising drugs. One of those is the fast track designation, which is for products designed to treat a serious condition and fill an unmet medical need. Another is the breakthrough therapy designation, created in 2012, which allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates that may provide a substantial benefit to patients compared to current treatment options.
“Ensuring medicines can be reviewed for safety and effectiveness in a timely manner to address patient needs is critical,” says Andrew Powaleny, a spokesperson for the industry group PhRMA, via email. “While AI is still developing, harnessing it requires a thoughtful and risk-based approach with patients at the center.”
The FDA is already doing its own research on potential uses of AI. In December 2023 the agency advertised a fellowship for a researcher to develop large language models for internal use. “During participation in this program, the fellow will engage in various activities that include but are not limited to the applications of LLMs for precision medicine, drug development and regulatory science,” the fellowship description says.
In January, OpenAI announced ChatGPT Gov, a self-hosted version of its chatbot designed to comply with government regulations. The startup also said it was working toward getting FedRAMP moderate and high accreditations for ChatGPT Enterprise, which would allow it to handle sensitive government data. FedRAMP is a compliance program used by the federal government to assess cloud products; unless authorized through this program, a service cannot hold federal data.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I gotta wonder how much of this is OpenAI and others like them and their general approach to business being:

This isn't an exaggeration. Because OpenAI is publicly traded, they have to be honest with their investors, and have openly said "we have no idea how we will ever turn a profit."
Beyond them, most players in the space are looking to get bought by a Microsoft or Sony and jump for the exits before they realize the sack is mostly full of rocks.
OpenAI has always operated under a "we'll use all this investor money to brute-force the largest datasets possible, make something impressive, show it off, and then wait for more investor money to roll in." A process that is by its nature inefficient and expensive.
Ever notice how there was no Dall-E 2.5? OpenAI isn't interested in incremental improvements to their products because they're making tech demos. It's very impressive on first release, but to this day Dall-E 3 doesn't have basic functionality like seeds, upscalers, aspect ratios, post-generation editing, or even the ability to iterate a previous gen.
If your money doesn't come from your users, then you have no incentive to adapt to their needs and you stagnate.
Midjourney, on the other hand, has neither investors nor these problems, because they're selling a product. You pay X amount, you get to play with the super-advanced etch-a-sketch, the simple process of money exchanged for a service. Because they have users to keep happy, they develop features that conform to their needs and develop in response to their behaviors.
And you can refine a model two ways, by expanding the dataset or by giving feedback to the current dataset's output. An active subscriber base gives you a means of doing the latter, and while very few people have a dataset to rival OpenAI's, many outperform them based purely on likes and ranking feedback from users.
This is why Chat-GPT has to be forced into everything. The main use of this tech isn't to replace artists, despite what OP might think. The use of generative AI as an art tool has always been secondary to its use as a toy, and that's what 98% of the userbase is using it for. Text is just the least fun toy in the box (at least as long as you're not allowing it to go NC-17)
youtube
Images, video and sound are the Fighting Frankie Action Figure everyone wants, and Chat-GPT says "Horse 'em!".
One of the most common first prompts on Midjourney is for a happy dog or cat playing in the clouds. These aren't people looking to make commercial work.
The AI products that people are going to wind up using and will have actual utility as productivity or entertainment services? They don't need investment because they have something people want to pay for. And the nature of the investment system means anyone who uses it is unlikely to ever make anything that people will want to pay for.

(full article here)

85K notes
·
View notes
Text
Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025: Build, Automate, and Scale with Next-Gen AI Systems
Artificial Intelligence isn’t the future anymore—it’s the present. And those who master AI tools today are the ones shaping tomorrow’s businesses, products, and customer experiences. The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 course is your gateway to becoming one of those pioneers.
Whether you're a developer, solopreneur, startup founder, or digital creator, the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program teaches you how to build, deploy, and monetize powerful AI-driven tools, agents, and workflows—all using cutting-edge no-code and low-code technologies.
What is the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program is an advanced online learning experience created to help ambitious individuals and teams build custom AI tools for real-world application. It covers everything from AI automations to building custom GPTs and launching agent-based products.
With a focus on practical builds, the course guides you in creating market-ready AI projects. These could be:
Automated customer service agents
Content generation tools
AI-powered data dashboards
Lead generation bots
SaaS MVPs using GPT, Claude, or Gemini
Whether you’re a tech-savvy entrepreneur or someone looking to break into AI development with little coding knowledge, this course gives you a step-by-step blueprint.
Meet the Creator: Jason Zhou
Jason Zhou is a rising name in the AI builder space, known for his actionable and technical insights shared across platforms like Twitter, YouTube, and his AI community. He’s built dozens of AI agents, automated systems, and monetized tools using both open-source and commercial models like ChatGPT, Claude, Mistral, and LLM APIs.
What sets Jason apart is that he doesn’t just teach AI theory. He builds real tools, ships products, and shows you exactly how to do the same—inside the AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou.
What Will You Learn Inside the Course?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is designed to be hands-on and high-impact. It’s less about lectures and more about building real tools you can use or sell.
Here’s what’s covered:
🔹 Module 1: Understanding the AI Tool Stack
Overview of the current AI landscape
Choosing the right LLM: OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Mistral
Prompt engineering and chaining logic
What makes an AI tool actually useful to users
🔹 Module 2: No-Code & Low-Code Development
Using tools like Make, Zapier, Retool, and Bubble
Creating UI/UX for AI-powered SaaS tools
Building backend logic with APIs and scripting
Hosting and scaling tools using affordable stacks
🔹 Module 3: Building Your First AI Product
Project-based learning: real GPT-powered app builds
Templates for newsletter generators, copywriting tools, and outreach bots
Integrating Google Sheets, Notion, Slack, and other apps
How to deploy your MVP in under a week
🔹 Module 4: AI Agents and Automations
Creating memory-based agents for long-term conversations
Setting up multi-step decision workflows
Building business process agents for clients
Using embeddings and vector search for smarter output
🔹 Module 5: Monetization & Launch Strategies
How to package and sell your AI tools
Finding profitable problems to solve
Jason’s launch playbook: Gumroad, Product Hunt, Twitter
Pricing models, freemium vs. paid, and building an audience
🔹 Bonuses and Extras
Live recorded sessions with community Q&A
Code snippets and project repositories
Pre-built templates to kickstart your own projects
Discord access to the AI Builder Club community
Who Should Take This Course?
The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program By Jason Zhou is perfect for:
✅ Indie hackers and solopreneurs who want to build and sell AI tools
✅ Developers and engineers ready to learn no-code/low-code workflows
✅ Agencies and consultants who want to offer AI services
✅ Content creators and marketers who want to automate tasks
✅ Anyone interested in launching their first AI project in weeks, not months
You don’t need deep technical skills. If you understand how to use basic tools and APIs, you can follow along and build powerful systems.
Why AI Builder Club March 2025 Is a Game-Changer
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program isn’t your average “AI 101” course. It’s an execution-based masterclass for building real-world tools that deliver value and create income.
What sets it apart?
🛠 Project-Based Learning: You’ll finish the course with actual AI tools, not just notes.
🔁 Updated for March 2025: Covers the latest changes in GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, open-source models, and tool integrations.
📦 Monetization Focus: Learn not just to build—but to launch and earn.
⚙️ Template Driven: Pre-built frameworks accelerate your learning and implementation.
🤝 Community Access: Get direct feedback and support from builders just like you.
You’ll walk away with both the knowledge and the tools to launch your own AI business or automate your company’s internal operations.
Student Reviews and Results
“Before this course, I had no idea how to build with GPT. After just a few weeks, I launched a content repurposing AI tool that’s now making passive income.” “Jason makes complex workflows simple and fun. The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou changed the way I think about automation.” “The best course I’ve taken on practical AI applications. No fluff. Just build, ship, and launch.”
Where to Buy the Course
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is available now from trusted platforms.
👉 We recommend buying directly from ECOMKEVIN COURSE
This platform ensures secure checkout, immediate access, and all bonus material included.
Final Thoughts
AI isn’t a buzzword anymore — it’s a core skill for entrepreneurs and digital professionals. The
Artificial Intelligence isn’t the future anymore—it’s the present. And those who master AI tools today are the ones shaping tomorrow’s businesses, products, and customer experiences. The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 course is your gateway to becoming one of those pioneers.
Whether you're a developer, solopreneur, startup founder, or digital creator, the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program teaches you how to build, deploy, and monetize powerful AI-driven tools, agents, and workflows—all using cutting-edge no-code and low-code technologies.
What is the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program is an advanced online learning experience created to help ambitious individuals and teams build custom AI tools for real-world application. It covers everything from AI automations to building custom GPTs and launching agent-based products.
With a focus on practical builds, the course guides you in creating market-ready AI projects. These could be:
Automated customer service agents
Content generation tools
AI-powered data dashboards
Lead generation bots
SaaS MVPs using GPT, Claude, or Gemini
Whether you’re a tech-savvy entrepreneur or someone looking to break into AI development with little coding knowledge, this course gives you a step-by-step blueprint.
Meet the Creator: Jason Zhou
Jason Zhou is a rising name in the AI builder space, known for his actionable and technical insights shared across platforms like Twitter, YouTube, and his AI community. He’s built dozens of AI agents, automated systems, and monetized tools using both open-source and commercial models like ChatGPT, Claude, Mistral, and LLM APIs.
What sets Jason apart is that he doesn’t just teach AI theory. He builds real tools, ships products, and shows you exactly how to do the same—inside the AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou.
What Will You Learn Inside the Course?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is designed to be hands-on and high-impact. It’s less about lectures and more about building real tools you can use or sell.
Here’s what’s covered:
🔹 Module 1: Understanding the AI Tool Stack
Overview of the current AI landscape
Choosing the right LLM: OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Mistral
Prompt engineering and chaining logic
What makes an AI tool actually useful to users
🔹 Module 2: No-Code & Low-Code Development
Using tools like Make, Zapier, Retool, and Bubble
Creating UI/UX for AI-powered SaaS tools
Building backend logic with APIs and scripting
Hosting and scaling tools using affordable stacks
🔹 Module 3: Building Your First AI Product
Project-based learning: real GPT-powered app builds
Templates for newsletter generators, copywriting tools, and outreach bots
Integrating Google Sheets, Notion, Slack, and other apps
How to deploy your MVP in under a week
🔹 Module 4: AI Agents and Automations
Creating memory-based agents for long-term conversations
Setting up multi-step decision workflows
Building business process agents for clients
Using embeddings and vector search for smarter output
🔹 Module 5: Monetization & Launch Strategies
How to package and sell your AI tools
Finding profitable problems to solve
Jason’s launch playbook: Gumroad, Product Hunt, Twitter
Pricing models, freemium vs. paid, and building an audience
🔹 Bonuses and Extras
Live recorded sessions with community Q&A
Code snippets and project repositories
Pre-built templates to kickstart your own projects
Discord access to the AI Builder Club community
Who Should Take This Course?
The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program By Jason Zhou is perfect for:
✅ Indie hackers and solopreneurs who want to build and sell AI tools
✅ Developers and engineers ready to learn no-code/low-code workflows
✅ Agencies and consultants who want to offer AI services
✅ Content creators and marketers who want to automate tasks
✅ Anyone interested in launching their first AI project in weeks, not months
You don’t need deep technical skills. If you understand how to use basic tools and APIs, you can follow along and build powerful systems.
Why AI Builder Club March 2025 Is a Game-Changer
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program isn’t your average “AI 101” course. It’s an execution-based masterclass for building real-world tools that deliver value and create income.
What sets it apart?
🛠 Project-Based Learning: You’ll finish the course with actual AI tools, not just notes.
🔁 Updated for March 2025: Covers the latest changes in GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, open-source models, and tool integrations.
📦 Monetization Focus: Learn not just to build—but to launch and earn.
⚙️ Template Driven: Pre-built frameworks accelerate your learning and implementation.
🤝 Community Access: Get direct feedback and support from builders just like you.
You’ll walk away with both the knowledge and the tools to launch your own AI business or automate your company’s internal operations.
Student Reviews and Results
“Before this course, I had no idea how to build with GPT. After just a few weeks, I launched a content repurposing AI tool that’s now making passive income.” “Jason makes complex workflows simple and fun. The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou changed the way I think about automation.” “The best course I’ve taken on practical AI applications. No fluff. Just build, ship, and launch.”
Where to Buy the Course
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is available now from trusted platforms.
👉 We recommend buying directly from ECOMKEVIN COURSE
This platform ensures secure checkout, immediate access, and all bonus material included.
Final Thoughts
AI isn’t a buzzword anymore — it’s a core skill for entrepreneurs and digital professionals. The
Artificial Intelligence isn’t the future anymore—it’s the present. And those who master AI tools today are the ones shaping tomorrow’s businesses, products, and customer experiences. The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 course is your gateway to becoming one of those pioneers.
Whether you're a developer, solopreneur, startup founder, or digital creator, the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program teaches you how to build, deploy, and monetize powerful AI-driven tools, agents, and workflows—all using cutting-edge no-code and low-code technologies.
What is the Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program is an advanced online learning experience created to help ambitious individuals and teams build custom AI tools for real-world application. It covers everything from AI automations to building custom GPTs and launching agent-based products.
With a focus on practical builds, the course guides you in creating market-ready AI projects. These could be:
Automated customer service agents
Content generation tools
AI-powered data dashboards
Lead generation bots
SaaS MVPs using GPT, Claude, or Gemini
Whether you’re a tech-savvy entrepreneur or someone looking to break into AI development with little coding knowledge, this course gives you a step-by-step blueprint.
Meet the Creator: Jason Zhou
Jason Zhou is a rising name in the AI builder space, known for his actionable and technical insights shared across platforms like Twitter, YouTube, and his AI community. He’s built dozens of AI agents, automated systems, and monetized tools using both open-source and commercial models like ChatGPT, Claude, Mistral, and LLM APIs.
What sets Jason apart is that he doesn’t just teach AI theory. He builds real tools, ships products, and shows you exactly how to do the same—inside the AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou.
What Will You Learn Inside the Course?
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is designed to be hands-on and high-impact. It’s less about lectures and more about building real tools you can use or sell.
Here’s what’s covered:
🔹 Module 1: Understanding the AI Tool Stack
Overview of the current AI landscape
Choosing the right LLM: OpenAI, Claude, Gemini, Mistral
Prompt engineering and chaining logic
What makes an AI tool actually useful to users
🔹 Module 2: No-Code & Low-Code Development
Using tools like Make, Zapier, Retool, and Bubble
Creating UI/UX for AI-powered SaaS tools
Building backend logic with APIs and scripting
Hosting and scaling tools using affordable stacks
🔹 Module 3: Building Your First AI Product
Project-based learning: real GPT-powered app builds
Templates for newsletter generators, copywriting tools, and outreach bots
Integrating Google Sheets, Notion, Slack, and other apps
How to deploy your MVP in under a week
🔹 Module 4: AI Agents and Automations
Creating memory-based agents for long-term conversations
Setting up multi-step decision workflows
Building business process agents for clients
Using embeddings and vector search for smarter output
🔹 Module 5: Monetization & Launch Strategies
How to package and sell your AI tools
Finding profitable problems to solve
Jason’s launch playbook: Gumroad, Product Hunt, Twitter
Pricing models, freemium vs. paid, and building an audience
🔹 Bonuses and Extras
Live recorded sessions with community Q&A
Code snippets and project repositories
Pre-built templates to kickstart your own projects
Discord access to the AI Builder Club community
Who Should Take This Course?
The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program By Jason Zhou is perfect for:
✅ Indie hackers and solopreneurs who want to build and sell AI tools
✅ Developers and engineers ready to learn no-code/low-code workflows
✅ Agencies and consultants who want to offer AI services
✅ Content creators and marketers who want to automate tasks
✅ Anyone interested in launching their first AI project in weeks, not months
You don’t need deep technical skills. If you understand how to use basic tools and APIs, you can follow along and build powerful systems.
Why AI Builder Club March 2025 Is a Game-Changer
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Program isn’t your average “AI 101” course. It’s an execution-based masterclass for building real-world tools that deliver value and create income.
What sets it apart?
🛠 Project-Based Learning: You’ll finish the course with actual AI tools, not just notes.
🔁 Updated for March 2025: Covers the latest changes in GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, open-source models, and tool integrations.
📦 Monetization Focus: Learn not just to build—but to launch and earn.
⚙️ Template Driven: Pre-built frameworks accelerate your learning and implementation.
🤝 Community Access: Get direct feedback and support from builders just like you.
You’ll walk away with both the knowledge and the tools to launch your own AI business or automate your company’s internal operations.
Student Reviews and Results
“Before this course, I had no idea how to build with GPT. After just a few weeks, I launched a content repurposing AI tool that’s now making passive income.” “Jason makes complex workflows simple and fun. The AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course By Jason Zhou changed the way I think about automation.” “The best course I’ve taken on practical AI applications. No fluff. Just build, ship, and launch.”
Where to Buy the Course
The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Online Course is available now from trusted platforms.
👉 We recommend buying directly from ECOMKEVIN COURSE
This platform ensures secure checkout, immediate access, and all bonus material included.
Final Thoughts
AI isn’t a buzzword anymore — it’s a core skill for entrepreneurs and digital professionals. The Jason Zhou – AI Builder Club March 2025 Program gives you the tools, strategies, and step-by-step projects to turn ideas into fully functional AI products.
Whether you want to automate workflows, build your first AI SaaS, or generate income by solving niche problems with smart tools—this course is your complete blueprint.
If you’re serious about AI, now is the time to act. Get started with Jason Zhou’s most practical and powerful course yet — and start building the future with your own hands.
gives you the tools, strategies, and step-by-step projects to turn ideas into fully functional AI products.
Whether you want to automate workflows, build your first AI SaaS, or generate income by solving niche problems with smart tools—this course is your complete blueprint.
If you’re serious about AI, now is the time to act. Get started with Jason Zhou’s most practical and powerful course yet — and start building the future with your own hands.
gives you the tools, strategies, and step-by-step projects to turn ideas into fully functional AI products.
Whether you want to automate workflows, build your first AI SaaS, or generate income by solving niche problems with smart tools—this course is your complete blueprint.
If you’re serious about AI, now is the time to act. Get started with Jason Zhou’s most practical and powerful course yet — and start building the future with your own hands.
0 notes
Text
Future-Ready Enterprises: The Crucial Role of Large Vision Models (LVMs)
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/future-ready-enterprises-the-crucial-role-of-large-vision-models-lvms/
Future-Ready Enterprises: The Crucial Role of Large Vision Models (LVMs)


What are Large Vision Models (LVMs)
Over the last few decades, the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has experienced rapid growth, resulting in significant changes to various aspects of human society and business operations. AI has proven to be useful in task automation and process optimization, as well as in promoting creativity and innovation. However, as data complexity and diversity continue to increase, there is a growing need for more advanced AI models that can comprehend and handle these challenges effectively. This is where the emergence of Large Vision Models (LVMs) becomes crucial.
LVMs are a new category of AI models specifically designed for analyzing and interpreting visual information, such as images and videos, on a large scale, with impressive accuracy. Unlike traditional computer vision models that rely on manual feature crafting, LVMs leverage deep learning techniques, utilizing extensive datasets to generate authentic and diverse outputs. An outstanding feature of LVMs is their ability to seamlessly integrate visual information with other modalities, such as natural language and audio, enabling a comprehensive understanding and generation of multimodal outputs.
LVMs are defined by their key attributes and capabilities, including their proficiency in advanced image and video processing tasks related to natural language and visual information. This includes tasks like generating captions, descriptions, stories, code, and more. LVMs also exhibit multimodal learning by effectively processing information from various sources, such as text, images, videos, and audio, resulting in outputs across different modalities.
Additionally, LVMs possess adaptability through transfer learning, meaning they can apply knowledge gained from one domain or task to another, with the capability to adapt to new data or scenarios through minimal fine-tuning. Moreover, their real-time decision-making capabilities empower rapid and adaptive responses, supporting interactive applications in gaming, education, and entertainment.
How LVMs Can Boost Enterprise Performance and Innovation?
Adopting LVMs can provide enterprises with powerful and promising technology to navigate the evolving AI discipline, making them more future-ready and competitive. LVMs have the potential to enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation across various domains and applications. However, it is important to consider the ethical, security, and integration challenges associated with LVMs, which require responsible and careful management.
Moreover, LVMs enable insightful analytics by extracting and synthesizing information from diverse visual data sources, including images, videos, and text. Their capability to generate realistic outputs, such as captions, descriptions, stories, and code based on visual inputs, empowers enterprises to make informed decisions and optimize strategies. The creative potential of LVMs emerges in their ability to develop new business models and opportunities, particularly those using visual data and multimodal capabilities.
Prominent examples of enterprises adopting LVMs for these advantages include Landing AI, a computer vision cloud platform addressing diverse computer vision challenges, and Snowflake, a cloud data platform facilitating LVM deployment through Snowpark Container Services. Additionally, OpenAI, contributes to LVM development with models like GPT-4, CLIP, DALL-E, and OpenAI Codex, capable of handling various tasks involving natural language and visual information.
In the post-pandemic landscape, LVMs offer additional benefits by assisting enterprises in adapting to remote work, online shopping trends, and digital transformation. Whether enabling remote collaboration, enhancing online marketing and sales through personalized recommendations, or contributing to digital health and wellness via telemedicine, LVMs emerge as powerful tools.
Challenges and Considerations for Enterprises in LVM Adoption
While the promises of LVMs are extensive, their adoption is not without challenges and considerations. Ethical implications are significant, covering issues related to bias, transparency, and accountability. Instances of bias in data or outputs can lead to unfair or inaccurate representations, potentially undermining the trust and fairness associated with LVMs. Thus, ensuring transparency in how LVMs operate and the accountability of developers and users for their consequences becomes essential.
Security concerns add another layer of complexity, requiring the protection of sensitive data processed by LVMs and precautions against adversarial attacks. Sensitive information, ranging from health records to financial transactions, demands robust security measures to preserve privacy, integrity, and reliability.
Integration and scalability hurdles pose additional challenges, especially for large enterprises. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems and processes becomes a crucial factor to consider. Enterprises need to explore tools and technologies that facilitate and optimize the integration of LVMs. Container services, cloud platforms, and specialized platforms for computer vision offer solutions to enhance the interoperability, performance, and accessibility of LVMs.
To tackle these challenges, enterprises must adopt best practices and frameworks for responsible LVM use. Prioritizing data quality, establishing governance policies, and complying with relevant regulations are important steps. These measures ensure the validity, consistency, and accountability of LVMs, enhancing their value, performance, and compliance within enterprise settings.
Future Trends and Possibilities for LVMs
With the adoption of digital transformation by enterprises, the domain of LVMs is poised for further evolution. Anticipated advancements in model architectures, training techniques, and application areas will drive LVMs to become more robust, efficient, and versatile. For example, self-supervised learning, which enables LVMs to learn from unlabeled data without human intervention, is expected to gain prominence.
Likewise, transformer models, renowned for their ability to process sequential data using attention mechanisms, are likely to contribute to state-of-the-art outcomes in various tasks. Similarly, Zero-shot learning, allowing LVMs to perform tasks they have not been explicitly trained on, is set to expand their capabilities even further.
Simultaneously, the scope of LVM application areas is expected to widen, encompassing new industries and domains. Medical imaging, in particular, holds promise as an avenue where LVMs could assist in the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of various diseases and conditions, including cancer, COVID-19, and Alzheimer’s.
In the e-commerce sector, LVMs are expected to enhance personalization, optimize pricing strategies, and increase conversion rates by analyzing and generating images and videos of products and customers. The entertainment industry also stands to benefit as LVMs contribute to the creation and distribution of captivating and immersive content across movies, games, and music.
To fully utilize the potential of these future trends, enterprises must focus on acquiring and developing the necessary skills and competencies for the adoption and implementation of LVMs. In addition to technical challenges, successfully integrating LVMs into enterprise workflows requires a clear strategic vision, a robust organizational culture, and a capable team. Key skills and competencies include data literacy, which encompasses the ability to understand, analyze, and communicate data.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, LVMs are effective tools for enterprises, promising transformative impacts on productivity, efficiency, and innovation. Despite challenges, embracing best practices and advanced technologies can overcome hurdles. LVMs are envisioned not just as tools but as pivotal contributors to the next technological era, requiring a thoughtful approach. A practical adoption of LVMs ensures future readiness, acknowledging their evolving role for responsible integration into business processes.
#Accessibility#ai#Alzheimer's#Analytics#applications#approach#Art#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#attention#audio#automation#Bias#Business#Cancer#Cloud#cloud data#cloud platform#code#codex#Collaboration#Commerce#complexity#compliance#comprehensive#computer#Computer vision#container#content#covid
2 notes
·
View notes