#Parallel Desktop Error
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Ah, yes, I know which posts you're talking about (regarding the Hinata <--> Mito parallels / reincarnation)! There's this post by you, and then this post originally by @chennyyeo which you reblogged.
~*~
You think there's gonna be parallels between Hinata/Mito though? So far, there haven't been any leaks about Mito being in the manga. Plus, while the manga definitely shows MinaKushi, it's still mainly about Minato, so IDK how much of Mito we would see, especially since, while she was the previous Jinchuriki of the Nine-Tails before Kushina, she's not actually Kushina's grandmother (yes they are fellow clansmen, but their exact relation to each other is unknown... kinda like how Karin's exact relation to Naruto and Kushina, if any, is unknown).
{PS — I was going to reblog the post of the original Ask I sent, but I literally cannot reblog it. I tried on both the desktop and mobile Tumblr apps, and I get an Error Message when I try to reblog, so I had to send another Ask. Hmph. Dumb random Tumblr glitches. 😤}
Oh yeah Mito is in there a lot








3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Accelerate Your Manual Testing with Multi-Device Testing

In today’s digital landscape, delivering seamless, bug-free experiences across a wide range of devices is not just an advantage—it’s a necessity. As businesses expand their digital footprints, ensuring application functionality across devices, screen sizes, and operating systems has become a critical aspect of software quality assurance. Manual testing remains a vital part of this process, especially when validating user interfaces, workflows, and real-world usability. However, manual testing on multiple devices can quickly become overwhelming, slow, and error-prone. This is where multi-device testing, enhanced by platforms like GenQE.ai, steps in to accelerate the process and increase accuracy without sacrificing quality.
The Need for Speed in Manual Testing
Traditional manual testing involves running test cases one-by-one on individual devices. This approach becomes inefficient when teams need to test across a variety of platforms including smartphones, tablets, desktops, and different browser types. As applications grow more complex and user expectations continue to rise, manual testers are expected to do more in less time.
Key challenges with traditional manual testing include:
Device Fragmentation: With so many device models and screen sizes in use, covering all bases can be daunting.
Time Constraints: Manually testing across multiple devices can be highly time-consuming.
Human Error: Repetitive testing tasks often lead to inconsistencies and missed bugs.
Scaling Issues: As testing needs grow, manual teams struggle to keep up with limited resources.
To overcome these challenges, organizations must rethink their approach to manual testing. Multi-device testing is one such approach that can significantly streamline manual testing efforts.
What is Multi-Device Testing?
Multi-device testing refers to the practice of validating an application’s performance, layout, and usability across different device types and configurations. It ensures the application behaves consistently across:
Various screen resolutions
Operating systems (iOS, Android, Windows, macOS)
Browsers (Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Edge)
Device orientations (portrait, landscape)
While multi-device testing is commonly associated with automated testing, it is equally critical in manual testing scenarios. Manual testers can simulate real-world interactions, observe design responsiveness, and evaluate user experiences from a human-centric perspective. But to do this effectively and efficiently, they need an infrastructure that supports fast, parallel testing on real devices.
That’s where GenQE.ai comes in.
GenQE.ai: The Future of Scalable Manual Testing
GenQE.ai is a modern, AI-powered quality engineering platform designed to enhance and accelerate manual testing processes. By integrating advanced testing workflows with real-device access and intelligent insights, GenQE.ai empowers QA teams to test smarter—not harder.
Here’s how GenQE.ai revolutionizes manual testing with multi-device capabilities:
1. Centralized Access to Real Devices
Manual testers often need to physically handle multiple devices or rely on disparate systems to perform cross-device testing. GenQE.ai eliminates this chaos by offering a unified environment where testers can remotely access and interact with real devices. Whether testing on Android tablets, iPhones, or desktop browsers, testers can conduct manual sessions from a single interface—no switching between devices, no logistical hurdles.
This not only saves time but significantly improves the tester's ability to reproduce and report bugs with consistency.
2. Parallel Device Sessions
With GenQE.ai, manual testers are no longer constrained to testing on one device at a time. The platform supports parallel testing sessions, allowing teams to run the same test case simultaneously across multiple devices. For example, a tester can verify UI rendering on an iPhone 13 and a Samsung Galaxy S22 in parallel, identifying layout issues instantly without repeating the entire process.
This parallelism is a game-changer for efficiency, especially in regression testing and release cycles where time is limited.
3. Intelligent Bug Logging
Capturing bugs during manual testing can be tedious. Testers often need to take screenshots, record video evidence, and note down steps manually. GenQE.ai simplifies this process by integrating intelligent bug logging features directly into the testing interface. With a single click, testers can capture annotated screenshots, add notes, and log bugs directly into issue trackers.
This seamless integration enhances collaboration between testers and developers, ensuring faster bug resolution and more streamlined workflows.
4. Real-Time Collaboration
In distributed teams, manual testing often suffers from a lack of coordination. GenQE.ai supports real-time collaboration by allowing multiple testers or stakeholders to observe or participate in live sessions. QA leads can monitor the progress of manual tests, provide feedback instantly, or guide junior testers through complex scenarios—all from within the platform.
This improves accountability and speeds up test execution through effective team synergy.
5. Consistent Test Environments
Device-specific issues are often difficult to reproduce due to inconsistencies in the testing environment. GenQE.ai addresses this by offering standardized, pre-configured test environments that mimic real-world conditions accurately. Whether it's a specific OS version or browser configuration, testers can launch consistent environments every time—ensuring reproducibility and reliable bug tracking.
6. AI-Augmented Test Insights
Even in manual testing, AI can provide valuable assistance. GenQE.ai offers AI-powered insights based on test session data, helping testers spot anomalies, performance bottlenecks, and inconsistent behaviors that may go unnoticed. The platform continuously learns from past test sessions to provide smarter suggestions and prioritize areas that need attention.
This hybrid approach combines the intuition of manual testers with the speed and intelligence of automation.
Benefits of Multi-Device Testing with GenQE.ai
Implementing multi-device manual testing through GenQE.ai delivers measurable benefits across your QA lifecycle:
Faster Test Cycles: Reduce test execution time by over 50% through parallel device sessions and centralized access.
Improved Coverage: Test across more devices and configurations without additional hardware investment.
Higher Accuracy: Eliminate human error with structured workflows, intelligent logging, and consistent environments.
Better Collaboration: Enable seamless communication between testers, developers, and product owners through integrated tools.
Increased ROI: Optimize your QA resources and reduce the cost of quality by avoiding redundant work and post-release bugs.
Real-World Use Case: Agile Teams Releasing Weekly Builds
Consider an agile product team that pushes weekly builds to production. Manual testing remains a critical gatekeeper, especially for UI validation and exploratory testing. Without an effective multi-device strategy, the team would need days to validate every feature across major devices.
With GenQE.ai, the team sets up test environments for each device in minutes, runs test cases in parallel, and logs bugs with evidence directly into their workflow. They conduct full regression checks in hours instead of days, ensuring every release meets their quality standards without causing bottlenecks.
Conclusion: The Smart Way to Scale Manual Testing
Manual testing is not going away anytime soon. Its value in validating real user experiences, catching visual discrepancies, and exploring edge cases remains unparalleled. But to keep up with today’s fast-paced development cycles and high device diversity, manual testing must evolve.
Multi-device testing is the next step in this evolution, and platforms like GenQE.ai are leading the charge. By enabling fast, efficient, and intelligent manual testing across devices, GenQE.ai empowers QA teams to deliver quality at speed—without burning out their resources. Whether you’re a solo tester, a growing startup, or an enterprise-level QA team, embracing multi-device testing through GenQE.ai will not only accelerate your testing process but also elevate the overall quality of your software.
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Software Quality: The Ultimate No Code Test Automation Guide

Embracing Simplicity in Software Testing
No Code Test Automation transforms the way teams approach software testing. Traditional testing demands high-level coding skills and complex scripting. Many companies experience delays and higher costs because of the coding barriers. No code solutions bring speed and accessibility into the spotlight. Businesses achieve higher test coverage, fewer errors, and faster releases. ideyaLabs leads the charge in enabling teams to harness the power of automation without needing to write a single line of code.
What Defines No Code Test Automation?
No Code Test Automation offers intuitive interfaces. Testers create, execute, and manage test cases using drag-and-drop features or visual workflows. Any team member easily automates repetitive and complex scenarios. It eliminates dependency on technical resources. ideyaLabs equips clients with user-friendly tools that integrate seamlessly with existing development cycles.
The Benefits of Shifting to No Code Test Automation
Teams unlock significant advantages. Accessibility stands as the core benefit. Non-technical team members design, implement, and maintain test cases. Automation covers a wide range of applications including web, desktop, and mobile platforms. Productivity receives an immediate boost. QA cycles shorten. Releases roll out faster.
Error rates drop. Human involvement in test scripting decreases. Automated workflows perform consistent, repeatable actions every time. ideyaLabs’ approach ensures faster feedback loops and efficient bug detections.
Maintenance becomes hassle-free. Visual representations clarify test flows. Updates to test cases require simple changes, not code rewrites. Process optimization becomes achievable for all business sizes.
No Code Testing in the Modern SDLC
The landscape of application development changes rapidly. Agile methodologies and DevOps practices demand shorter release cycles and deeper collaboration. No Code Test Automation fits perfectly into these modern frameworks. Testing runs parallel with development. Teams validate features with each update.
ideyaLabs crafts integration-friendly no code solutions. Automation fits directly into CI/CD pipelines. Test results remain visible across teams. Bottlenecks decrease. Collaboration increases. Software reaches production with minimal delays.
ideyaLabs Approach: Intuitive, Scalable, Effective
ideyaLabs designs its No Code Test Automation platform for business users. The onboarding process takes minutes. User interfaces remain simple yet powerful. Test creation does not require any coding expertise.
Users assemble test cases using visual elements. Assertions, test data, and flows remain transparent and visual. Reports and dashboards empower decision-making. ideyaLabs ensures scalability from small startups to enterprise-level projects.
Common Use Cases for No Code Test Automation
Web application testing tops the list. Teams validate user journeys from login to complex transactions. Mobile testing also benefits. Devices, browsers, and operating systems receive comprehensive coverage. Desktop applications see greater reliability through automated scenarios.
Regression testing sees dramatic improvements. ideyaLabs enables teams to rerun suites with minor effort. Updates to the application never compromise the quality due to real-time automated checks.
Data-driven tests become manageable through structured inputs. Testing with varied data points increases confidence in application performance. ideyaLabs brings ease to data handling through built-in modules.
Building a Custom Test Suite with ideyaLabs
Test creation starts with a simple sign-in on the ideyaLabs platform. Users select modules relevant to their application. Drag-and-drop interfaces guide them through scenario building. Test cases align with business requirements. Teams assign custom parameters. Schedulers automate test execution during or after business hours.
Test failures trigger notifications. Teams investigate dashboards to identify issues. ideyaLabs provides actionable reports for every stakeholder. Stakeholders track trends and monitor overall software quality.
Integrating No Code Test Automation into Existing Workflows
No Code Test Automation does not disrupt established processes. ideyaLabs platforms adapt to various project management tools. Trackers, Jenkins, and collaboration apps link seamlessly. QA teams automate without leaving familiar environments.
Automation extends beyond single projects. Enterprises scale tests across multiple teams or products. Centralized management becomes straightforward. ideyaLabs platforms work with legacy systems and new applications alike.
The Future Outlook of No Code Test Automation
Technology continues to evolve. The reliance on traditional code-heavy test frameworks declines. ideyaLabs anticipates widespread adoption of No Code Test Automation across industries. As artificial intelligence and machine learning integrate deeper, automated test case creation and self-healing tests will become the standard.
Testing becomes part of the creative process. Developers and business analysts embrace automation as a natural extension of their workflows. Speed, consistency, and quality define software releases.
Overcoming Testing Challenges with ideyaLabs
Organizations face hurdles like limited technical resources, proficiency gaps, and evolving applications. ideyaLabs empowers teams to solve these challenges through adaptable, no code frameworks. Training times shrink. Test coverage expands. User adoption rates skyrocket due to intuitive designs.
Teams focus on product innovation instead of debugging test scripts. ideyaLabs enables this shift through commitment to simplicity, scalability, and support.
Getting Started with No Code Test Automation Today
Explore the ideyaLabs platform. Sign up for a demo. Bring your team together. Identify current QA pain points. ideyaLabs provides guidance on migration and integration. Start with core processes and expand automation coverage gradually.
Unlock the true potential of software testing. Experience rapid, reliable, and repeatable results with No Code Test Automation.
0 notes
Text
Top Automation Testing Frameworks for Efficient Software Development

Whether you are a seasoned developer or a newcomer, the need for tools that allow software developers to make their software high quality delivered quickly is a necessity. Automation Testing has proven to be a game changer, allowing the developers and QA teams to maintain the quality of the software, shorten time-to-market, and optimize repetitive testing processes. However, the main factor behind successful Automation Testing is selecting the appropriate test automation framework.
In this blog, we will discuss some of the most popular Test Automation frameworks, their features that make them unique and how they enhance QA process that helps in efficient Software Development. GhostQA can certainly help you in delivering seamless and efficient Automation Testing strategies if you're looking for a professional approach in implementing the ideal framework.
What is a Test Automation Framework?
A Test Automation framework means a collection of guidelines, tools, and practices that are used to automate the testing process in a simple and standardized way. This application serves as a guiding framework for scripting automation in a homogenous way which can be easily maintainable and scalable.
By adopting the right framework, the team can leverage the benefits of Automation Testing, such as increased speed, better coverage, and below human error.
Why Choosing the Right Framework Matters
The Test Automation framework is the single most important decision that will affect the effectiveness and reliability of testing efforts. Here’s why choosing the appropriate framework is important:
Ensure all technology stacks are compatible with your tech.
Makes test scripts easier to write and maintain.
Improves team collaboration and productivity.
Increases scalability for future project needs.
Decreases the overall test cost, without compromising on quality.
Top Automation Testing Frameworks
Let us look at some of the most used and efficient Automation Testing frameworks:
1. Selenium
Overview: Selenium is an open-source framework most commonly used to perform testing on web applications. It works with various browsers, platforms, and programming languages.
Features:
Functional on multiple browsers and multiple platforms.
Strong community support and regular iterations.
Best For: Web application functional and regression testing.
2. Appium
Overview: Appium is a widely used open-source framework for testing mobile applications. It is compatible with Android, iOS, and Windows apps.
Features:
Works with native, hybrid and mobile web apps.
It works with the same APIs across multiple platforms.
Enables scripts to be reused on multiple platforms.
Best For: The testing of apps for mobile devices.
3. TestNG
Overview: TestNG is a framework for the Java programming language inspired from JUnit. This supports a variety of different test setups and annotations.
Features:
Enables parallel execution to speed things up.
Various flexible options for test configuration
Provides extensive reporting that you can tailor to your specifications.
Best For: Integration, functional and unit testing.
4. Cypress
Overview: Cypress is an end-to-end testing framework for modern web applications.
Features:
Test execution with on-the-fly reloading.
Waits for commands and DOM updates implicitly.
Debugging tools for developers built into the platform.
Best For: UI Testing and end-to-end testing for web-based applications.
5. JUnit
Overview: JUnit is another popular framework for Java applications mainly focused on unit testing.
Features:
Makes test-driven development (TDD) easier.
Rich support for assertions and annotations.
Best for small and focused tests.
Best For: When writing unit tests for Java-based applications.
6. Katalon Studio
Overview: Katalon Studio is an end-to-end testing solution providing web, API, mobile, and desktop testing capabilities.
Features:
Built-in templates and intuitive interface
Favors manual as well as through automation testing.
Best For: Teams looking for a user-friendly, all-in-one solution.
7. Robot Framework
Overview: Robot Framework is a generic open-source test automation framework that uses a keyword-driven approach.
Features:
Easily readable test cases.
You can extend with libraries and tools.
Great for the less technical members of your team.
Best For: Acceptance test and RPA (Robotic process automation).
How Automation Testing Benefits Software Development
There are several advantages of adopting Automation Testing frameworks:
Faster Testing Cycles: Automated tests run faster than manual tests leading to a decreased testing time.
Improved Accuracy: Reduced human error leads to more accurate results
Reusability of Tests: The frameworks help in reusing the test scripts on different projects.
Increased Test Coverage: It allows the testing of huge datasets and numerous scenarios.
Cost Efficiency: Despite the initial investment, it saves a lot of time and resources in the long run.
Challenges in Automation Testing
Although Automation Testing comes with lots of advantages, there are also some challenges:
High Initial Costs: Setting up a framework will require time and resources.
Complex Tool Integration: Deciding to use the right tools and ensuring compatibility can be a struggle.
Skill Gaps: Team members might require training in order to effectively use advanced frameworks.
Maintenance Effort: Whenever the application changes, it is imperative to update the test scripts.
GhostQA: Your Trusted Partner for Automation Testing
GhostQA focuses on helping businesses with effective Automation Testing solutions. So, if you want help regarding selecting a Test Automation framework, or want us to implement solid strategies, GhostQA is your choice.
Why Choose GhostQA?
Deep knowledge of frameworks (Selenium, Appium, Cypress, etc.).
Custom solutions designed around your specific project requirements.
Proven approaches for overcoming automation dilemmas.
Professional service to guarantee that your testing workflow is smooth and trustworthy.
Best Practices for Using Automation Frameworks
Select the Right Framework: Make sure it suits your project requirements and team experience.
Plan Test Cases Strategically: Prioritize high-value and repeated tasks to be automated.
Incorporate Regular Maintenance: Refresh the scripts based on modifications in the application and the environment.
Use a Hybrid Approach: Integrate both manual and automated testing for coverage
Leverage Reporting Tools: Take advantage of detailed reports to monitor progress and find opportunities for growth.
Conclusion
It is obligatory to select the right Automation Testing framework for the best software development. Testing frameworks such as Selenium, Appium, and Katalon Studio have a variety of features that help fast-track testing tasks and improve product quality.
Joining forces with GhostQA gives you a road of expertise and solutions right for you making sure your Test Automation steps are easy and prosperous.
Start using the appropriate Automation Testing framework now to reduce your development cycles, enhance test accuracy, and build superior software. Get in touch with GhostQA to see how we can revolutionize your testing methodologies.
#quality assurance#automated testing#test automation#software testing#performance testing#automation testing#functional testing#regression testing#load testing
0 notes
Text
In the dynamic world of data science, staying updated with the latest tools and applications is crucial. These tools not only enhance productivity but also streamline complex workflows, allowing data scientists to focus on deriving insights and making informed decisions. Here’s a comprehensive guide to some of the best tools and apps that every data scientist should have in their arsenal. 1. Jupyter Notebook Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents containing live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It supports over 40 programming languages, including Python, R, and Julia. Jupyter is particularly useful for data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, and machine learning. Key Features: Interactive output that supports various visualizations. Integration with big data tools like Apache Spark. Extensibility through plugins and extensions. 2. Anaconda Anaconda is a distribution of Python and R for scientific computing and data science. It simplifies package management and deployment, making it easier to manage libraries and dependencies. Anaconda includes popular data science packages and tools, such as Jupyter, pandas, and scikit-learn. Key Features: Conda package manager for seamless installation and management of packages. Anaconda Navigator, a graphical interface to manage environments and launch applications. Built-in Jupyter and RStudio for comprehensive data analysis and visualization. 3. TensorFlow TensorFlow is an open-source machine learning library developed by Google. It is widely used for building and training neural networks, with a focus on deep learning. TensorFlow offers flexible deployment options and extensive support for various platforms, including desktops, mobile devices, and servers. Key Features: High-level APIs such as Keras for easy model building. TensorFlow Serving for deploying machine learning models in production environments. TensorBoard for visualizing the training process and metrics. 4. Tableau Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that helps data scientists and analysts to see and understand their data. It allows users to create a wide range of visualizations to interactively explore and analyze data. Tableau supports various data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and cloud services. Key Features: Drag-and-drop interface for creating interactive dashboards. Real-time collaboration and sharing capabilities. Extensive library of visualization types and customization options. 5. PyCharm PyCharm is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Python, developed by JetBrains. It provides a robust environment for coding, debugging, and testing Python applications. PyCharm is particularly useful for data scientists working with Python-based data analysis and machine learning projects. Key Features: Intelligent code editor with code completion and error highlighting. Integrated tools for debugging, testing, and version control. Support for Jupyter Notebook integration. 6. Apache Spark Apache Spark is an open-source distributed computing system that provides an interface for programming entire clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance. Spark is known for its speed and efficiency in processing large-scale data, making it a popular choice for big data analytics. Key Features: In-memory computing capabilities for faster data processing. Support for SQL queries, streaming data, and machine learning. Integration with Hadoop and other big data tools. 7. GitHub GitHub is a web-based platform used for version control and collaborative software development. It is essential for data scientists to manage their codebase, collaborate with team members, and track changes efficiently. GitHub also provides hosting for software development and a collaborative environment through its Git repositories.
Key Features: Branching and merging for parallel development. Issue tracking and project management tools. Integration with CI/CD pipelines for automated testing and deployment. 8. RStudio RStudio is an IDE for R, a programming language widely used for statistical computing and graphics. RStudio provides a user-friendly interface to work with R and supports a wide range of statistical and graphical techniques. Key Features: Code editor with syntax highlighting and code completion. Integrated tools for plotting, history, and workspace management. Support for R Markdown for creating dynamic reports. 9. Docker Docker is a platform for developing, shipping, and running applications in containers. Containers allow data scientists to package their applications and dependencies into a single, portable unit that can run consistently across different computing environments. Key Features: Isolation of applications and dependencies. Scalability and flexibility in deploying applications. Support for Docker Compose to manage multi-container applications. 10. KNIME KNIME (Konstanz Information Miner) is an open-source data analytics, reporting, and integration platform. It is designed to provide a comprehensive solution for data preprocessing, analysis, and visualization through a modular, workflow-based approach. Key Features: Drag-and-drop interface for creating data workflows. Integration with various data sources and machine learning libraries. Community extensions for additional functionalities. Conclusion Equipping yourself with the right tools and apps can significantly enhance your productivity and efficiency as a data scientist. From data cleaning and visualization to machine learning and deployment, these tools cover a wide spectrum of data science needs. Staying updated with these essential tools will not only streamline your workflow but also help you stay ahead in the ever-evolving field of data science.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Testing Automation Tools for Shopify App Developers in 2024

Introduction
Shopify app development is a competitive landscape where automation plays a crucial role in maintaining quality. In this blog, we analyze the top five automation tools that every Shopify developer should consider for testing apps efficiently in 2024.
Why Choose Automation for Shopify App Testing?
Faster Test Cycles: Save time with repetitive tasks like regression testing.
Improved Accuracy: Eliminate human errors common in manual testing.
Better Resource Allocation: Allow QA teams to focus on critical testing areas.
1. Selenium
Overview: A widely-used open-source tool for web application testing.
Features:
Supports multiple browsers and programming languages.
Ideal for UI testing of Shopify apps.
How to Use for Shopify:
Automate workflows like product addition, cart updates, and checkout.
Use plugins like Selenium Grid for parallel testing.
2. Cypress
Overview: A JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework.
Features:
Real-time testing with a built-in debugger.
Faster execution compared to Selenium.
How to Use for Shopify:
Perform frontend and API testing simultaneously.
Test responsive designs for mobile and desktop.
3. Postman
Overview: Popular for API testing and monitoring.
Features:
Comprehensive API validation with automated test scripts.
Supports CI/CD pipelines.
How to Use for Shopify:
Test Shopify's REST and GraphQL APIs for data retrieval.
Automate recurring API tests to catch inconsistencies early.
4. Appium
Overview: Ideal for mobile app testing, including Shopify apps built with mobile compatibility.
Features:
Supports iOS and Android platforms.
Open-source with a robust community.
How to Use for Shopify:
Test mobile-friendly features of your app.
Validate performance across devices and operating systems.
5. TestCafe
Overview: Modern framework for end-to-end testing with minimal setup.
Features:
No browser plugins required.
Supports ES6+ JavaScript syntax.
How to Use for Shopify:
Run quick UI tests for multiple browsers.
Test form submissions, navigation, and app speed.
Conclusion
Adopting the right automation tools can dramatically enhance your app's quality and reduce time-to-market. For comprehensive app testing solutions, turn to OyeCommerz Services, your trusted Shopify partner.
0 notes
Text
New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain
New Post has been published on https://sunalei.org/news/new-open-source-tool-helps-to-detangle-the-brain/
New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain
In late 2023, the first drug with potential to slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease was approved by the U.S. Federal Drug Administration. Alzheimer’s is one of many debilitating neurological disorders that together affect one-eighth of the world’s population, and while the new drug is a step in the right direction, there is still a long journey ahead to fully understanding it, and other such diseases.
“Reconstructing the intricacies of how the human brain functions on a cellular level is one of the biggest challenges in neuroscience,” says Lars Gjesteby, a technical staff member and algorithm developer from the MIT Lincoln Laboratory’s Human Health and Performance Systems Group. “High-resolution, networked brain atlases can help improve our understanding of disorders by pinpointing differences between healthy and diseased brains. However, progress has been hindered by insufficient tools to visualize and process very large brain imaging datasets.”
A networked brain atlas is in essence a detailed map of the brain that can help link structural information with neural function. To build such atlases, brain imaging data need to be processed and annotated. For example, each axon, or thin fiber connecting neurons, needs to be traced, measured, and labeled with information. Current methods of processing brain imaging data, such as desktop-based software or manual-oriented tools, are not yet designed to handle human brain-scale datasets. As such, researchers often spend a lot of time slogging through an ocean of raw data.
Gjesteby is leading a project to build the Neuron Tracing and Active Learning Environment (NeuroTrALE), a software pipeline that brings machine learning, supercomputing, as well as ease of use and access to this brain mapping challenge. NeuroTrALE automates much of the data processing and displays the output in an interactive interface that allows researchers to edit and manipulate the data to mark, filter, and search for specific patterns.
Untangling a ball of yarn
One of NeuroTrALE’s defining features is the machine-learning technique it employs, called active learning. NeuroTrALE’s algorithms are trained to automatically label incoming data based on existing brain imaging data, but unfamiliar data can present potential for errors. Active learning allows users to manually correct errors, teaching the algorithm to improve the next time it encounters similar data. This mix of automation and manual labeling ensures accurate data processing with a much smaller burden on the user.
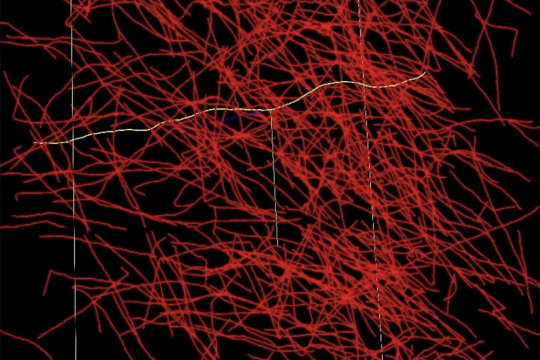
“Imagine taking an X-ray of a ball of yarn. You’d see all these crisscrossed, overlapping lines,” says Michael Snyder, from the laboratory’s Homeland Decision Support Systems Group. “When two lines cross, does it mean one of the pieces of yarn is making a 90-degree bend, or is one going straight up and the other is going straight over? With NeuroTrALE’s active learning, users can trace these strands of yarn one or two times and train the algorithm to follow them correctly moving forward. Without NeuroTrALE, the user would have to trace the ball of yarn, or in this case the axons of the human brain, every single time.” Snyder is a software developer on the NeuroTrALE team along with staff member David Chavez.
Because NeuroTrALE takes the bulk of the labeling burden off of the user, it allows researchers to process more data more quickly. Further, the axon tracing algorithms harness parallel computing to distribute computations across multiple GPUs at once, leading to even faster, scalable processing. Using NeuroTrALE, the team demonstrated a 90 percent decrease in computing time needed to process 32 gigabytes of data over conventional AI methods.
The team also showed that a substantial increase in the volume of data does not translate to an equivalent increase in processing time. For example, in a recent study they demonstrated that a 10,000 percent increase in dataset size resulted in only a 9 percent and a 22 percent increase in total data processing time, using two different types of central processing units.
“With the estimated 86 billion neurons making 100 trillion connections in the human brain, manually labeling all the axons in a single brain would take lifetimes,” adds Benjamin Roop, one of the project’s algorithm developers. “This tool has the potential to automate the creation of connectomes for not just one individual, but many. That opens the door for studying brain disease at the population level.”
The open-source road to discovery
The NeuroTrALE project was formed as an internally funded collaboration between Lincoln Laboratory and Professor Kwanghun Chung’s laboratory on MIT campus. The Lincoln Lab team needed to build a way for the Chung Lab researchers to analyze and extract useful information from their large amount of brain imaging data flowing into the MIT SuperCloud — a supercomputer run by Lincoln Laboratory to support MIT research. Lincoln Lab’s expertise in high-performance computing, image processing, and artificial intelligence made it exceptionally suited to tackling this challenge.
In 2020, the team uploaded NeuroTrALE to the SuperCloud and by 2022 the Chung Lab was producing results. In one study, published in Science, they used NeuroTrALE to quantify prefrontal cortex cell density in relation to Alzheimer’s disease, where brains affected with the disease had a lower cell density in certain regions than those without. The same team also located where in the brain harmful neurofibers tend to get tangled in Alzheimer’s-affected brain tissue.
Work on NeuroTrALE has continued with Lincoln Laboratory funding and funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to build up NeuroTrALE’s capabilities. Currently, its user interface tools are being integrated with Google’s Neuroglancer program — an open-source, web-based viewer application for neuroscience data. NeuroTrALE adds the ability for users to visualize and edit their annotated data dynamically, and for multiple users to work with the same data at the same time. Users can also create and edit a number of shapes such as polygons, points, and lines to facilitate annotation tasks, as well as customize color display for each annotation to distinguish neurons in dense regions.
“NeuroTrALE provides a platform-agnostic, end-to-end solution that can be easily and rapidly deployed on standalone, virtual, cloud, and high performance computing environments via containers.” says Adam Michaleas, a high performance computing engineer from the laboratory’s Artificial Intelligence Technology Group. “Furthermore, it significantly improves the end user experience by providing capabilities for real-time collaboration within the neuroscience community via data visualization and simultaneous content review.”
To align with NIH’s mission of sharing research products, the team’s goal is to make NeuroTrALE a fully open-source tool for anyone to use. And this type of tool, says Gjesteby, is what’s needed to reach the end goal of mapping the entirety of the human brain for research, and eventually drug development. “It’s a grassroots effort by the community where data and algorithms are meant to be shared and accessed by all.”
The codebases for the axon tracing, data management, and interactive user interface of NeuroTrALE are publicly available via open-source licenses. Please contact Lars Gjesteby for more information on using NeuroTrALE.
0 notes
Text
New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/new-open-source-tool-helps-to-detangle-the-brain/
New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain

In late 2023, the first drug with potential to slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease was approved by the U.S. Federal Drug Administration. Alzheimer’s is one of many debilitating neurological disorders that together affect one-eighth of the world’s population, and while the new drug is a step in the right direction, there is still a long journey ahead to fully understanding it, and other such diseases.
“Reconstructing the intricacies of how the human brain functions on a cellular level is one of the biggest challenges in neuroscience,” says Lars Gjesteby, a technical staff member and algorithm developer from the MIT Lincoln Laboratory’s Human Health and Performance Systems Group. “High-resolution, networked brain atlases can help improve our understanding of disorders by pinpointing differences between healthy and diseased brains. However, progress has been hindered by insufficient tools to visualize and process very large brain imaging datasets.”
A networked brain atlas is in essence a detailed map of the brain that can help link structural information with neural function. To build such atlases, brain imaging data need to be processed and annotated. For example, each axon, or thin fiber connecting neurons, needs to be traced, measured, and labeled with information. Current methods of processing brain imaging data, such as desktop-based software or manual-oriented tools, are not yet designed to handle human brain-scale datasets. As such, researchers often spend a lot of time slogging through an ocean of raw data.
Gjesteby is leading a project to build the Neuron Tracing and Active Learning Environment (NeuroTrALE), a software pipeline that brings machine learning, supercomputing, as well as ease of use and access to this brain mapping challenge. NeuroTrALE automates much of the data processing and displays the output in an interactive interface that allows researchers to edit and manipulate the data to mark, filter, and search for specific patterns.
Untangling a ball of yarn
One of NeuroTrALE’s defining features is the machine-learning technique it employs, called active learning. NeuroTrALE’s algorithms are trained to automatically label incoming data based on existing brain imaging data, but unfamiliar data can present potential for errors. Active learning allows users to manually correct errors, teaching the algorithm to improve the next time it encounters similar data. This mix of automation and manual labeling ensures accurate data processing with a much smaller burden on the user.
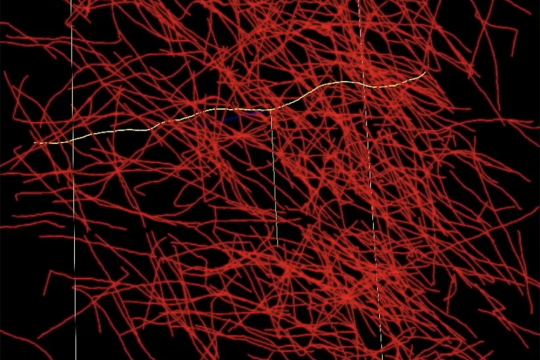
“Imagine taking an X-ray of a ball of yarn. You’d see all these crisscrossed, overlapping lines,” says Michael Snyder, from the laboratory’s Homeland Decision Support Systems Group. “When two lines cross, does it mean one of the pieces of yarn is making a 90-degree bend, or is one going straight up and the other is going straight over? With NeuroTrALE’s active learning, users can trace these strands of yarn one or two times and train the algorithm to follow them correctly moving forward. Without NeuroTrALE, the user would have to trace the ball of yarn, or in this case the axons of the human brain, every single time.” Snyder is a software developer on the NeuroTrALE team along with staff member David Chavez.
Because NeuroTrALE takes the bulk of the labeling burden off of the user, it allows researchers to process more data more quickly. Further, the axon tracing algorithms harness parallel computing to distribute computations across multiple GPUs at once, leading to even faster, scalable processing. Using NeuroTrALE, the team demonstrated a 90 percent decrease in computing time needed to process 32 gigabytes of data over conventional AI methods.
The team also showed that a substantial increase in the volume of data does not translate to an equivalent increase in processing time. For example, in a recent study they demonstrated that a 10,000 percent increase in dataset size resulted in only a 9 percent and a 22 percent increase in total data processing time, using two different types of central processing units.
“With the estimated 86 billion neurons making 100 trillion connections in the human brain, manually labeling all the axons in a single brain would take lifetimes,” adds Benjamin Roop, one of the project’s algorithm developers. “This tool has the potential to automate the creation of connectomes for not just one individual, but many. That opens the door for studying brain disease at the population level.”
The open-source road to discovery
The NeuroTrALE project was formed as an internally funded collaboration between Lincoln Laboratory and Professor Kwanghun Chung’s laboratory on MIT campus. The Lincoln Lab team needed to build a way for the Chung Lab researchers to analyze and extract useful information from their large amount of brain imaging data flowing into the MIT SuperCloud — a supercomputer run by Lincoln Laboratory to support MIT research. Lincoln Lab’s expertise in high-performance computing, image processing, and artificial intelligence made it exceptionally suited to tackling this challenge.
In 2020, the team uploaded NeuroTrALE to the SuperCloud and by 2022 the Chung Lab was producing results. In one study, published in Science, they used NeuroTrALE to quantify prefrontal cortex cell density in relation to Alzheimer’s disease, where brains affected with the disease had a lower cell density in certain regions than those without. The same team also located where in the brain harmful neurofibers tend to get tangled in Alzheimer’s-affected brain tissue.
Work on NeuroTrALE has continued with Lincoln Laboratory funding and funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to build up NeuroTrALE’s capabilities. Currently, its user interface tools are being integrated with Google’s Neuroglancer program — an open-source, web-based viewer application for neuroscience data. NeuroTrALE adds the ability for users to visualize and edit their annotated data dynamically, and for multiple users to work with the same data at the same time. Users can also create and edit a number of shapes such as polygons, points, and lines to facilitate annotation tasks, as well as customize color display for each annotation to distinguish neurons in dense regions.
“NeuroTrALE provides a platform-agnostic, end-to-end solution that can be easily and rapidly deployed on standalone, virtual, cloud, and high performance computing environments via containers.” says Adam Michaleas, a high performance computing engineer from the laboratory’s Artificial Intelligence Technology Group. “Furthermore, it significantly improves the end user experience by providing capabilities for real-time collaboration within the neuroscience community via data visualization and simultaneous content review.”
To align with NIH’s mission of sharing research products, the team’s goal is to make NeuroTrALE a fully open-source tool for anyone to use. And this type of tool, says Gjesteby, is what’s needed to reach the end goal of mapping the entirety of the human brain for research, and eventually drug development. “It’s a grassroots effort by the community where data and algorithms are meant to be shared and accessed by all.”
The codebases for the axon tracing, data management, and interactive user interface of NeuroTrALE are publicly available via open-source licenses. Please contact Lars Gjesteby for more information on using NeuroTrALE.
#000#2022#2023#Administration#ai#algorithm#Algorithms#Alzheimer's#Alzheimer's disease#artificial#Artificial Intelligence#automation#billion#Brain#brain imaging#brains#cell#challenge#Cloud#Collaboration#Color#Community#computing#Containers#content#data#Data Management#data processing#Data Visualization#datasets
0 notes
Text
This Week in Rust 559
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on X (formerly Twitter) or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Want TWIR in your inbox? Subscribe here.
Updates from Rust Community
Newsletters
thisweekinbevy - 0.14.1, tracking change detection, and more rendering examples
Project/Tooling Updates
Tauri 2.0 Release Candidate
CGlue 0.3 Future and Beyond
ratatui - v0.28.0
Pigg 0.3.3 the GUI for RPi GPIO interaction released, with Remote GPIO feature!
Announcing SeaORM 1.0
Danube - Queuing and Pub/Sub message patterns
Observations/Thoughts
Trying and mostly failing to optimize frustum culling in a WebGL + TS + Rust engine
Panic! At The Async Runtime Shutdown
Debugging a rustc segfault on illumos
Tracing my way with tracing-rs
[Series] The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Building a Distributed Filesystem in Rust.
Best Rust books for 2024
Phantom Menace: memory leak that wasn't there
Developing a cryptographically secure bootloader for RISC-V in Rust
Extending the #[diagnostic] tool attribute namespace
Rust Walkthroughs
Tracing Tokio Resources
[Series] Mastering Dependency Injection in Rust: Crafting a Custom Container
Research
The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Building a Distributed Filesystem in Rust.
Miscellaneous
Rustic: Enhanced Org Babel integration
Efficient Logging - Speeding up production code by logging more efficiently
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is WhenFS, a FUSE filesystem that misuses your google calendar as storage. And yes, your schedule will look as packed as mine once you store one or two files in there.
Despite yet another week fully devoid of suggestions nor votes, llogiq is reasonably pleased with his choice.
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Calls for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
RFCs
No calls for testing were issued this week.
Rust
No calls for testing were issued this week.
Rustup
No calls for testing were issued this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
rencfs - Abstract file access layer
rencfs - Add RustCrypto as a feature
rencfs - File and fs API
rencfs - io API
rfs - Coordinator node API)
rfs - Data node API
rfs - File upload and changes
rfs - Communication between Coordinator and Data nodes
syncoxiders - Two-way sync
syncoxiders - Sync chunks in parallel
syncoxiders - Integrate SurrealDB to store metadata
syncoxiders - Migrate scripts tests to integration tests
rencfs-desktop - Implement daemon
Proposal: Deprecate Tokio's LocalSet
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here or through a PR to TWiR or by reaching out on X (Formerly twitter) or Mastodon!
CFP - Events
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
No Calls for papers or presentations were submitted this week.
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the website through a PR to TWiR or by reaching out on X (formerly Twitter) or Mastodon!
Updates from the Rust Project
381 pull requests were merged in the last week
fix vita build of std and forbid unsafe in unsafe in the os/vita module
derive(SmartPointer): require pointee to be maybe sized
add #[must_use] to some into_raw* functions
add REDUNDANT_IMPORTS lint for new redundant import detection
add f16 and f128 math functions
allow overwriting the output of rustc --version
allow setting link-shared and static-libstdcpp with CI LLVM
android: remove libstd hacks for unsupported Android APIs
assert that all attributes are actually checked via CheckAttrVisitor and aren't accidentally usable on completely unrelated HIR nodes
better handle suggestions for the already present code and fix some suggestions
built-in derive: remove BYTE_SLICE_IN_PACKED_STRUCT_WITH_DERIVE hack and lint
cleanup sys module to match house style
create COFF archives for non-LLVM backends
custom MIR: add support for tail calls
delegation: second attempt to improve perf
delegation: support generics for delegation from free functions
detect non-lifetime binder params shadowing item params
do not fire unhandled attribute assertion on multi-segment AttributeType::Normal attributes with builtin attribute as first segment
don't re-elaborate already elaborated caller bounds in method probe
elaborate unknowable goals
emit an error if #[optimize] is applied to an incompatible item
enforce supertrait outlives obligations hold when confirming impl
fix removed box_syntax diagnostic if source isn't available
fix the invalid argument type
ignore use declaration reformatting in .git-blame-ignore-revs
implement UncheckedIterator directly for RepeatN
improve error message when global_asm! uses asm! operands
interpret: on a signed deref check, mention the right pointer in the error
make /// doc comments compatible with naked functions
mark Parser::eat/check methods as #[must_use]
match LLVM ABI in extern "C" functions for f128 on Windows
match lowering: Hide Candidate from outside the lowering algorithm
more unsafe attr verification
normalize when equating dyn tails in MIR borrowck
on short error format, append primary span label to message
peel off explicit (or implicit) deref before suggesting clone on move error in borrowck, remove some hacks
properly mark loop as diverging if it has no breaks
remove crate_level_only from ELIDED_LIFETIMES_IN_PATHS
revert recent changes to dead code analysis
set branch protection function attributes
simplify match based on the cast result of IntToInt
structured suggestion for extern crate foo when foo isn't resolved in import
temporarily switch ambiguous_negative_literals lint to allow
the output in stderr expects panic-unwind
turn invalid_type_param_default into a FutureReleaseErrorReportInDeps
tweak type inference for const operands in inline asm
use object in run-make/symbols-visibility
use a separate pattern type for rustc_pattern_analysis diagnostics
miri: add a flag to do recursive validity checking
miri: add miri_start support
miri: use Scalar consistently in foreign item emulation
linker: pass fewer search directories to the linker
use Vec in instantiate_binder_with_fresh_vars
change output normalization logic to be linear against size of output
check divergence value first before doing span operations in warn_if_unreachable
accelerate GVN a little
stabilize Wasm relaxed SIMD
stabilize unsafe extern blocks (RFC 3484)
enable std::io::copy specialisation for std::pipe::{PipeReader, PipeWriter}
rewrite binary search implementation
implement cursors for BTreeSet
implement the once_wait feature
configure which platforms have f16 and f128 enabled by default
hashbrown: implement Default for iterators
regex: rust nightly removed the lifetime from Pattern
cargo-miri: better error when we seem to run inside bootstrap but something is wrong
cargo: build-std: remove hack on creating virtual std workspace
cargo: config: Adjust MSRV resolve config field name / values
cargo: publish: Don't strip non-dev features
cargo: also build manpage for cargo.md
rustdoc-json: discard non-local inherent impls for primitives
rustdoc: cleanup CacheBuilder code for building search index
rustdoc: fix handling of Self type in search index and refactor its representation
rustdoc: make the hover trail for doc anchors a bit bigger
rustdoc: Make the buttons remain when code example is clicked
rustdoc: simplify body usage
rustfmt: add repo cloning to check-diff crate
rustfmt: check exit status of git commands spawned by build script
rustfmt: impl rewrite_result for Pat, TuplePatField
clippy: check exit status of subcommands spawned by rustc_tools_util
clippy: fix redundant_closure false positive with closures has return type contains 'static
clippy: fix redundant_slicing when the slice is behind a mutable reference
clippy: fix broken list for lints config
clippy: fix false positive for missing_backticks in footnote references
clippy: limit number of nonminimal_bool ops
clippy: lintcheck: force warn all lints
clippy: make restriction lints use span_lint_and_then (a → e)
clippy: make restriction lints use span_lint_and_then (q → w)
clippy: remove multispan_sugg[_with_applicability]
clippy: remove duplicated peel_middle_ty_refs
clippy: simplify lint deprecation
clippy: use a deterministic number of digits in rustc_tools_util commit hashes
clippy: use a single multipart suggestion for implicit_hasher
rust-analyzer: implement diagnostic for await outside of async
rust-analyzer: load sysroot library via cargo metadata
rust-analyzer: support inlay hint for more expr with label
rust-analyzer: apply IndexMut obligations for non-assigning mutable index usages
rust-analyzer: errors on method call inferences with elided lifetimes
rust-analyzer: insert a generic arg for impl Trait when lowering generic args
rust-analyzer: insert a tail Ok(()) for expr block instead of wrapping with Ok
rust-analyzer: panic in path transform with default type parameters
rust-analyzer: remove AbsPath requirement from linkedProjects
rust-analyzer: surpress type mismatches in calls with mismatched arg counts
rust-analyzer: improve crate manifests, adding missing [package.repository] and [package.description] fields
rust-analyzer: segregate syntax and semantic diagnostics
rust-analyzer: split out syntax-bridge into a separate crate
rust-analyzer: when josh-proxy screws up the roundtrip, say what the involved commits are
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
This week saw several large improvements caused mostly by the update to LLVM 19. There were some regressions in several pull requests, but most of them were immediately fixed in a follow-up PR.
Triage done by @kobzol. Revision range: 7e3a9718..8c7e0e16
Summary:
(instructions:u) mean range count Regressions ❌ (primary) 1.0% [0.2%, 3.8%] 91 Regressions ❌ (secondary) 1.9% [0.2%, 19.2%] 104 Improvements ✅ (primary) -4.4% [-15.8%, -0.3%] 120 Improvements ✅ (secondary) -3.3% [-10.4%, -0.2%] 70 All ❌✅ (primary) -2.1% [-15.8%, 3.8%] 211
6 Regressions, 3 Improvements, 5 Mixed; 4 of them in rollups 51 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
Merge RFC 3529: Add named path bases to cargo
Merge RFC 3668: Async closures
Promote aarch64-apple-darwin to Tier 1
RFC for project goals
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
No RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Tracking Issues & PRs
Rust
[disposition: merge] Stabilize raw_ref_op (RFC 2582)
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for Ready::into_inner()
[disposition: merge] Tracking issue for thread::Builder::spawn_unchecked
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for is_none_or
[disposition: merge] CloneToUninit impls
[disposition: close] Tracking issue for HashMap OccupiedEntry::{replace_key, replace_entry}
[disposition: close] Tracking issue for HashMap::raw_entry
[disposition: merge] Implement DoubleEnded and ExactSize for Take\<Repeat> and Take\<RepeatWith>
[disposition: merge] Implement owned ops for HashSet and BTreeSet
[disposition: merge] Tracking Issue for Option::get_or_insert_default
[disposition: merge] Unify run button display with "copy code" button and with mdbook buttons
[disposition: merge] Greatly speed up doctests by compiling compatible doctests in one file
Cargo
No Cargo Tracking Issues or PRs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Language Team
No Language Team Tracking Issues or PRs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Language Reference
[disposition: \] Reformat (and only reformat) the inline assembly chapter
Unsafe Code Guidelines
No Unsafe Code Guideline Tracking Issues or PRs entered Final Comment Period this week.
New and Updated RFCs
[new] crates.io: Remove dev-dependencies from the index
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-08-07 - 2024-09-04 🦀
Virtual
2024-08-07 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - with Social Distancing
2024-08-08 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-08-08 | Virtual (Nürnberg, DE) | Rust Nuremberg
Rust Nürnberg online
2024-08-08 | Virtual (Tel Aviv, IL) | Code Mavens
Rust Source Code Reading: The thousands crate (English)
2024-08-13 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday: Typestate Pattern in Rust
2024-08-15 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn Meetup
2024-08-20 | Virtual (Washington, DC, US) | Rust DC
Mid-month Rustful
2024-08-21 | Hybrid - Virtual and In-Person (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-08-22 | Virtual | Conf42: Online Tech Events
Conf42 Rustlang 2024
2024-08-22 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-08-22 | Virtual (Karlsruhe, DE) | Karlsruhe Functional Programmers Group
Stammtisch (gemeinsam mit der C++ UG KA): various topics, from C++ to Rust
2024-08-27 | Virtual | Ardan Labs
Fearless Concurrency with Rust
2024-08-27 | Virtual (Bordeaux, FR) | Rust Bordeaux
Live coding - A distance #1
2024-08-27 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Last Tuesday
2024-08-27 | Virtual (Tel Aviv, IL) | Code Mavens
Declarative macros in Rust (Virtual) - מקרוים בראסט
2024-08-28 | Virtual (Tel Aviv, IL) | Code Mavens
Command Line Tools: Implementing wc in Rust (English, Virtual)
2024-08-29 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust Hack and Learn | Mirror: Rust Hack n Learn Meetup
2024-09-03 | Virtual (Buffalo, NY, US) | Buffalo Rust Meetup
Buffalo Rust User Group
2024-09-04 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - with Social Distancing
Europe
2024-08-14 | Köln/Cologne, DE | Rust Cologne
This Month in Rust, August
2024-08-14 | Reading, UK | Reading Rust Workshop
Reading Rust Meetup
2024-08-20 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Hack Night
2024-08-21 | Nürnberg, DE | Rust Nuremberg
Walk'n'Talk around Wöhrder See (+ Burritos)
2024-08-22 | Manchester, UK | Rust Manchester
Rust Manchester Talks August
2024-08-26 | Mainz, DE | Fachschaft Mathematik+Informatik der JGU Mainz
Ferienkurs Rust
2024-08-29 | Berlin, DE | OpenTechSchool Berlin + Rust Berlin
Rust and Tell - Title
North America
2024-08-08 | Mountain View, CA, US | Mountain View Rust Meetup
Rust Meetup at Hacker Dojo
2024-08-08 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
August Meetup
2024-08-19 | Minneapolis, MN US | Minneapolis Rust Meetup
Minneapolis Rust Meetup: "State of Rust GPU Programming" & Happy Hour
2024-08-20 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC: Doing the Bare Minimum with Isograph (talk)
2024-08-20 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
2024-08-21 | Virtual and In-Person (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-08-28 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATC
Rust Lunch - Fareground
2024-08-29 | Nashville, TN, US | Music City Rust Developers
Music City Rust Developers : placeholder
Oceania
2024-08-22 | Auckland, NZ | Rust AKL
Rust AKL: Dot IX: Diagram Generator + Deep Learning from Scratch in Rust
2024-08-27 | Canberra, ACT, AU | Canberra Rust User Group (CRUG)
June Meetup
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
Want to have a crate with a million features? Host your own registry and revel in the combinatorial explosion of choices!
– Jake Goulding on rust-users
Thanks to Jonas Fassbender for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
0 notes
Text
Quantum Computers: Speed Demons or Misunderstood Marvels?
The world of computers is on the cusp of a revolution, with the enigmatic quantum computer taking center stage. But compared to our trusty laptops and desktops, are these machines truly faster? The answer, like the technology itself, is a fascinating exploration of potential and purpose.
Beyond Brute Force: A Different Kind of Speed
Regular computers, also known as classical computers, rely on bits, which can be either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, however, harness the bizarre world of quantum mechanics. Here, qubits hold the possibility of being both 0 and 1 simultaneously, a state called superposition. This lets them explore many solutions concurrently, offering a theoretical speed advantage for specific problems.
Imagine a maze. A classical computer would have to check each path one by one. A quantum computer, in theory, could explore all paths simultaneously, finding the exit much faster for certain mazes. This "quantum parallelism" is what grants quantum computers their potential edge in solving specific problems.
The Power of Untangling: Quantum Supremacy and Beyond
In 2019, Google's Sycamore chip achieved "quantum supremacy," solving a problem in minutes that would take a classical computer thousands of years. This breakthrough demonstrated the power of quantum computers for specific tasks. However, it's crucial to understand that quantum supremacy isn't about raw processing speed for everything.
Think of it this way. A quantum computer might be a master lockpick, adept at cracking specific codes. But for everyday tasks like web browsing or running spreadsheets, a classical computer remains efficient.
Why Build Quantum Computers Then? A World of Applications Awaits
While not universal speed demons, quantum computers hold immense promise for revolutionizing various fields:
Drug Discovery: Simulating complex molecules could lead to faster development of life-saving drugs and materials.
Materials Science: Quantum computers can design materials with never-before-seen properties, like superconductors that work at room temperature.
Financial Modeling: By factoring large numbers efficiently, they could unlock new possibilities in finance and risk management.
Cryptography: While some encryption methods might become vulnerable, quantum computers could also lead to the development of unbreakable codes.
Artificial Intelligence: Quantum machine learning algorithms could lead to significant advancements in AI, tackling problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and the Race for Quantum Advantage
Building and controlling quantum computers remains a monumental challenge. Qubits are fragile and prone to errors, requiring significant advancements in error correction. Additionally, developing efficient quantum algorithms for specific problems is an ongoing research area.
The race for "quantum advantage" – where a quantum computer demonstrably outperforms a classical one for a practical task – is well underway. Companies like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are heavily invested in this area, with the potential rewards being immense.
The Future is a Quantum Cocktail: Collaboration is Key
Quantum computers won't replace their classical counterparts; they'll work alongside them. The future lies in harnessing the strengths of both – classical computers for everyday tasks and quantum computers for tackling specific problems that would take classical machines an eternity.
Collaboration between quantum and classical computing experts will be crucial. As quantum computing matures, expect to see hybrid systems that leverage the best of both worlds.
In Conclusion: A New Era of Computing Dawns
Quantum computers are not simply faster versions of classical computers. They represent a fundamentally different approach to problem-solving, with the potential to revolutionize various fields. While challenges remain, the potential rewards are vast. The future of computing lies in a powerful collaboration between these two paradigms, ushering in a new era of discovery and innovation.
0 notes
Text
Understanding TestComplete: A Comprehensive Guide to Automated Testing
n today's fast-paced software development landscape, delivering high-quality applications swiftly is crucial. One of the essential elements in ensuring software reliability is robust testing. Automated testing tools like TestComplete online training have become indispensable for modern development teams striving for efficiency and accuracy in their testing processes.
What is TestComplete?
TestComplete, developed by SmartBear Software, is an all-encompassing automated testing tool designed to facilitate test creation, execution, and management across various platforms and applications. It supports testing for web, mobile, and desktop applications, offering a unified solution for diverse testing needs.
Key Features of TestComplete:
Cross-platform Testing: TestComplete supports testing on different platforms, including Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
User-Friendly Interface: Its intuitive and user-friendly interface enables both technical and non-technical users to create and manage tests efficiently.
Scripting Options: TestComplete offers flexibility by supporting multiple scripting languages such as JavaScript, Python, VBScript, and more, allowing testers to choose according to their proficiency and project requirements.
Object Recognition: It uses robust object recognition capabilities, allowing testers to interact with application elements easily, even as the application’s UI evolves.
Test Visualizer: The Test Visualizer feature provides a visual representation of test execution, making it easier to identify and analyze test results.
Integration with CI/CD: Seamless integration with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines streamlines the testing process and allows for automated test runs in development workflows.
How TestComplete Works:
TestComplete operates through a series of steps:
Test Creation: Users can create tests through recording, scripting, or using keyword-driven testing methodologies, enabling various approaches for creating test cases.
Test Execution: Tests can be run on multiple platforms and environments, with the ability to perform parallel test runs, saving time and resources.
Result Analysis: TestComplete generates comprehensive reports and logs, enabling testers to analyze results and identify issues efficiently.
Benefits of Using TestComplete:
Time and Cost Efficiency: Automated testing reduces the time required for regression testing and increases test coverage, ultimately reducing costs associated with manual testing efforts.
Enhanced Accuracy: Automated tests reduce human error, ensuring consistent and reliable test results.
Increased Test Coverage: TestComplete allows for broader test coverage across multiple platforms and devices, enhancing the overall quality of the application.
Improved Collaboration: Its user-friendly interface fosters collaboration between testers, developers, and other stakeholders, streamlining communication and feedback loops.
Conclusion:
TestComplete stands as a robust solution in the realm of automated testing, empowering development teams to achieve higher efficiency, reliability, and quality in their software products. With its versatile features and ease of use, TestComplete continues to be a go-to choice for organizations aiming to optimize their testing processes in today's dynamic software development landscape.
0 notes
Text
Getting Started With Microsoft Flow

Microsoft flow is a cloud-based workflow engine, Using Flow end users can create cross application workflows (no code workflows). Flow is a part of office 365 E3 suite. It is a successor of SharePoint designer workflows. Complex level Flows can be promoted to an Azure logic app.
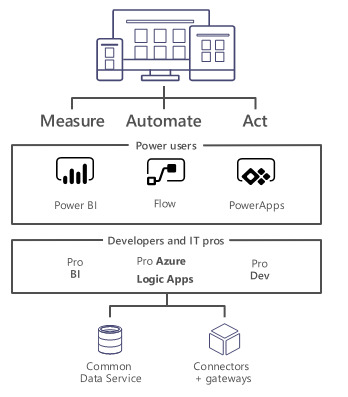
Microsoft Flows Vs SharePoint Designer Workflows

Anatomy of Microsoft Flow
Flow Designer
Connectors, Triggers & Actions
Variables & Data Flow
Expressions
Branching, Error Handling & Scopes
Flow Designer – Create a Flow from Browser or Mobile Application
Desktop Version
Go to https://flow.Microsoft.com
Sign-in with Office 365 Account
Start from existing template or import from disk or create from scratch (both in desktop & mobile browsers)
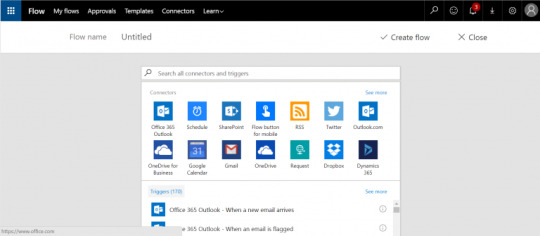
Mobile Version
Install flow mobile app, sign in
Create new flow (template or from scratch).
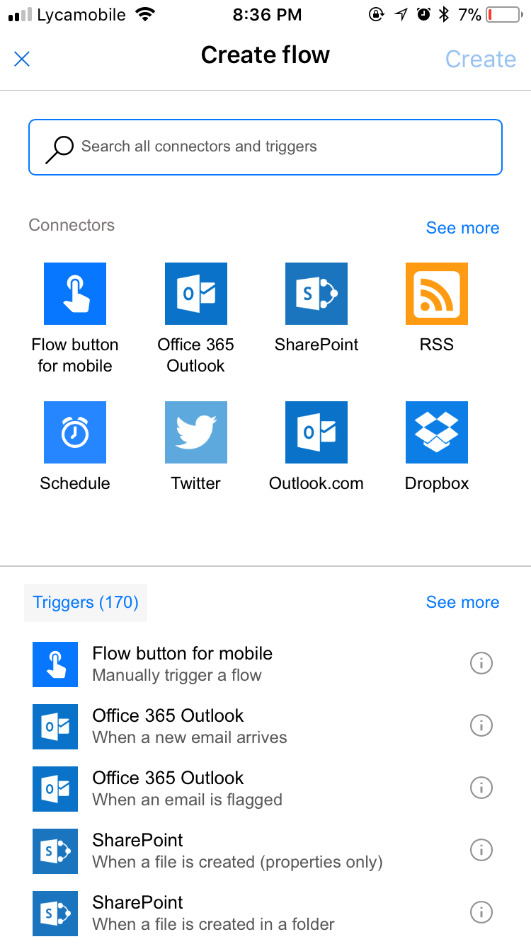
Connectors
Connectors Wrapper around an API that allows Flow to talk with other services.It exposes Triggers & Actions.
Standard Connectors – included as part of E3
Microsoft Connectors (SharePoint, Azure Blob storage, SQL Server.)
Non-Microsoft Connectors (Twitter, Slack.)
https://us.flow.microsoft.com/en-us/connectors/?filter=&category=standard
Premium Connectors – additional cost
Microsoft Connectors (HTTP with Azure AD.)
Other Connectors (Salesforce, MySQL.)
https://us.flow.microsoft.com/en-us/connectors/?filter=&category=premium
Custom Connectors – additional cost , development
ISV, System Integrators, End users can create custom connectors to integrate any system/application/service.
https://us.flow.microsoft.com/en-us/connectors/?filter=&category=custom
Triggers
Run based on user action or event
From other apps in office 365 – PowerApps, SharePoint, etc.
From SQL
From dedicated Flow button
Run on a schedule
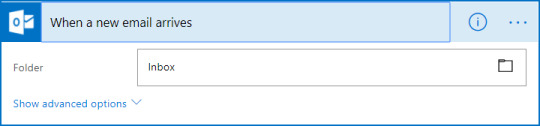
Flow also run based on time schedule, From every minute to 1 am on Days.
Run by HTTP GET/POST to URL generated by flow
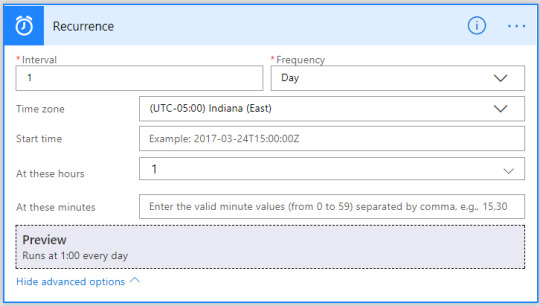
Call another Flow
Call from any application/service/HTTP calls
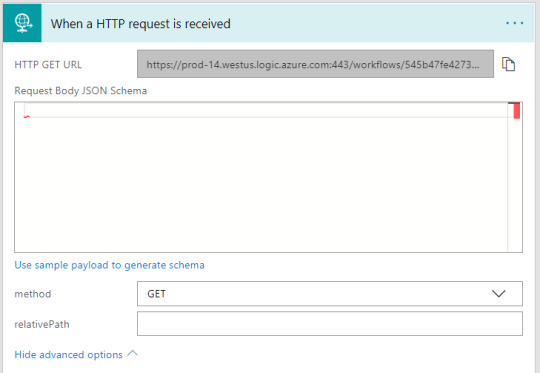
Scenarios & Types of Triggers
Triggers - Scenarios
Simple: Flows start with a Trigger.
Advanced: Flows can have more than 1 trigger (async actions)
Custom: Flows can have custom triggers
Types
Polling Trigger
Periodically checks the service
Checks count as executions
Push Triggers
Listen for data on an endpoint or wait for event.
Actions
Execute CRUD operations with workflow context
SharePoint: Create Item, Delete Item, Create File.
SQL: Insert Row, Update Row, Delete Row, Get Row.
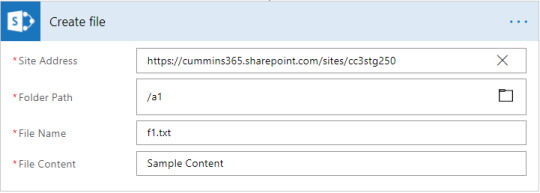
Transform Data
Inline – using expressions (e.g. string operations, math operations.)
Other services – Html to text.
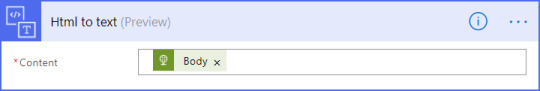
Send Notification
Send mobile notification, send email notification etc.
Call other Flow
Chain Flows to create complex Flows.
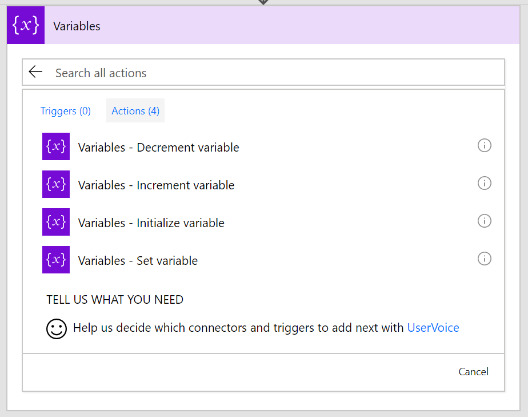
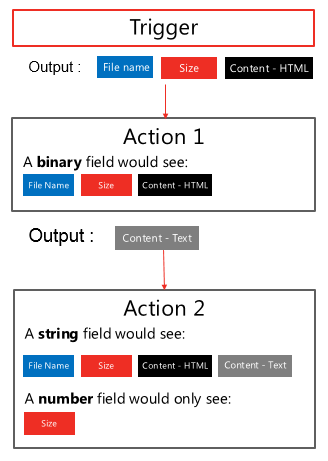
Variables
Use Variables connector*
Initialize & then set value
Supported value types (Boolean, String, Object, Array, Float).
Variables are NOT always necessary!
Why variables are not always necessary?
Data Flows from each step and is available for all later steps
‘Add Dynamic Content’ allows us to select outputs from previous steps
Certain outputs show up based on the types of the inputs and outputs.
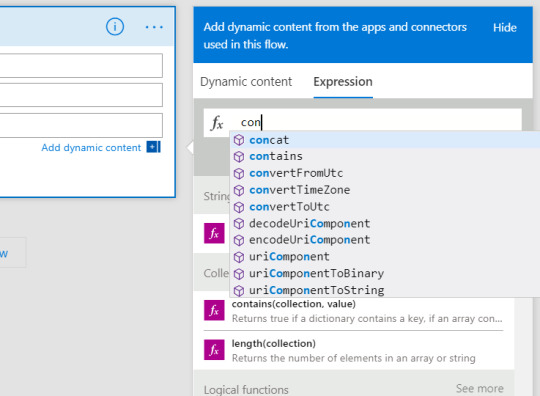
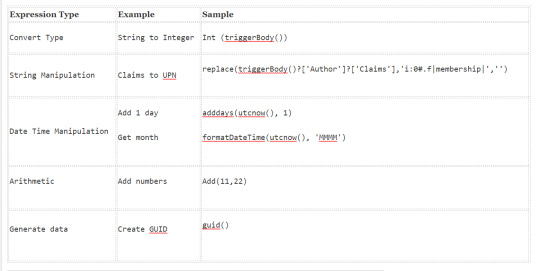
Expressions
Expressions can be used in most of the fields to transform data inline
IntelliSense available as you type

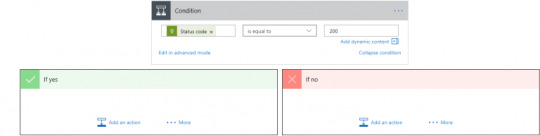
Branching
If-then-else
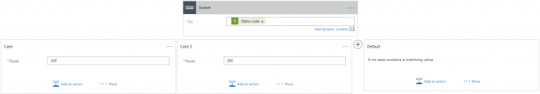
Switch
For-Each
By default, parallel
Parallel (20 exec)
Supports sequential
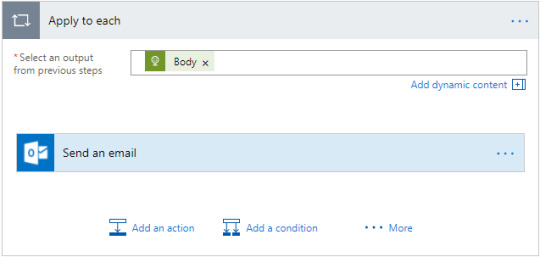
Do-Until
Emulate State machines
Help in approvals & more

Parallel branches
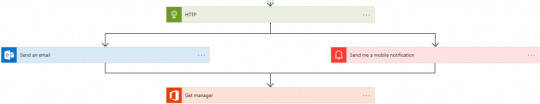
Error Handling
Actions can be set to run if previous action fails/times out.
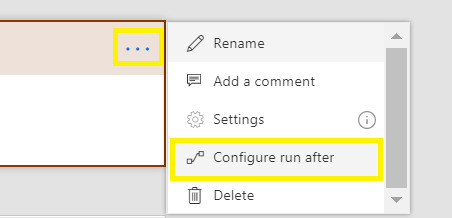
Scopes
Logically group actions
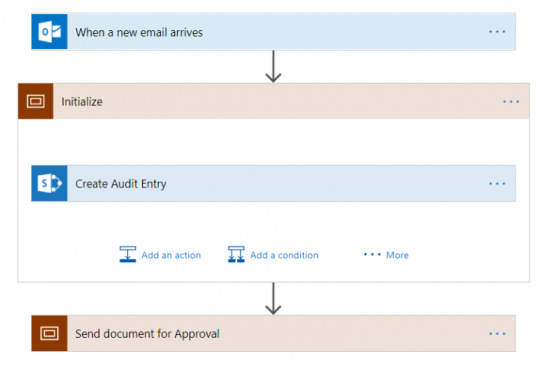
Allow advanced error handling for a group of actions
Scope boxes are in brown boxes.
0 notes
Text
"Tech Giants' Choice: The Appeal of Python's Advantages"
Python is a general-purpose dynamic programming language that provides high-level readability and is interpreted. As Python is a dynamic programming language, it has some helpful advantages, so now we will learn about the Advantages of Python.
I gained expertise in Python programming through my training at ACTE Technologies. This learning experience was thorough and valuable. ACTE Technologies offered a well-structured Python course that enabled me to understand the basics of the language and advance to more advanced concepts.

The Main Advantages of Python Applications:
Simple and Easy to Learn Python is incredibly easy to learn and read because its syntax is similar to English. It's a powerful language that's also free and open source. You don't need to be highly skilled to start learning Python. It's a high-level language, meaning you can write code that's more human-readable, and Python takes care of converting it to a language the computer understands. Python helps catch errors early by interpreting the code.
Portable and Extensible
Python's portability and extensibility are significant advantages. It can run on various platforms, including Windows, Linux, Macintosh, and even gaming consoles that support Python. Python's extensibility allows you to integrate components from other programming languages like Java and .NET. Additionally, you can invoke libraries written in languages like C and C++.
3. Object-Oriented Programming
Python's support for object-oriented programming (OOP) is a valuable feature. It allows for concepts like polymorphism and inheritance, which make code more flexible and reusable. In Python, you can create shareable classes, enabling the reuse of code and providing a protective layer by abstracting knowledge. This makes it easier to develop prototypes quickly and write efficient and organized code, making Python a popular choice for many software development projects.
4.Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves creating computer programs that can mimic human intelligence and perform smart tasks using algorithms and programs. Python plays a significant role in AI development. It has libraries like scikit-learn, which simplify complex calculations with concise code. Additionally, popular AI libraries such as Keras and TensorFlow are seamlessly integrated with Python, enhancing its machine learning capabilities.
5. Computer Graphics
Python is a versatile programming language that serves developers well in various domains. It finds extensive use in both small and large-scale projects for creating Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) and developing desktop applications. Additionally, Python offers a dedicated game development framework, empowering developers to create interactive games and applications efficiently. Whether for GUI-based software or gaming projects, Python provides robust solutions to meet diverse development needs.

6. Testing Framework:
Python is well-suited for startups and product development. It offers integrated testing frameworks, like Pytest and Selenium, making it easier to conduct automated testing, detect and fix bugs, and streamline workflows.
7.Big Data:
Python is capable of handling large datasets and supports parallel computing. Libraries like Pydoop, Pandas, and PySpark enable data processing, analysis, and manipulation, making Python a valuable tool in the field of big data.
8. Scripting and Automation:
Python serves as an excellent scripting language. You can write scripts to automate tasks, such as web scraping, content posting, or any repetitive processes, making it a versatile choice for automation.
9. Data Science:
Python has become the preferred language for data scientists due to libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and Seaborn. It excels in data analysis, visualization, and manipulation, helping researchers gain insights from vast datasets.
10.Popularity and High Salary:
Python's popularity has surged in recent years, and Python programmers often receive competitive salaries. Prominent tech companies like Google, YouTube, Instagram, Dropbox, and Facebook rely on Python for various purposes, contributing to its widespread use. Its ease of use and versatility make Python a top choice for both beginners and experienced programmers in various domains.
You can enroll in Python training at ACTE Technologies, where they offer comprehensive programs to help you become proficient in Python programming. These courses cover everything from the basics of Python to advanced topics like data science, machine learning, and web development. ACTE Technologies provides a structured and hands-on learning experience, allowing you to gain practical skills in Python for various purposes.
0 notes
Text
El Capitan Bootcamp Windows 10
For more information about using Windows on your Mac, open Boot Camp Assistant and click the Open Boot Camp Help button. If you're using an iMac (Retina 5K, 27-inch, Late 2014) or iMac (27-inch, Late 2013) or iMac (27-inch, Late 2012) with a 3TB hard drive and macOS Mojave or later, learn about an alert you might see during installation.
Install Windows 10 El Capitan Boot Camp
El Cap seems to have nuked my Bootcamp created Windows 10 partition and it won't let me install one outright. I get the 'This is GPT partition style' error, and I'm not sure how to fix it under El Capitan.
Aug 23, 2021 Windows 10, 64-bit Windows 7 SP1, 64-bit. OS X El Capitan (10.11) eDrawings 2017. Apple Mac ® based machines running Windows using Boot Camp are not supported.
A mid-2011 iMac or similar running OSX El Capitan; An 8GB or larger USB drive; An ISO containing Windows 10 (I used Windows 10 Enterprise) 50GB free disk space, 100GB recommended; Step 1: Disable El Capitan's System Integrity Protection. El Capitan ships with a new OS X feature: System Integrity Protection (SIP), also known as 'rootless' mode.
Aug 18, 2015 Aug 18, 2015. One serious bug should be considered when trying to do this. El Capitan boot camp assistant will fail to remove your Windows partition if you don't want that Windows installation. And you will likely end up with backing up your Mac OS X and format the whole disk to bring everything back to normal.

Is it possible to play Genshin Impact on Mac

Developed by miHoYo Limited, Genshin Impact is an open-world role-playing action released almost a month ago. From the beginning, a pair of twins is set to arrive on the land called Teyvat, a fictional place with lots of artifacts and mysteries yet to be unlocked. However, the impact of an unknown god keeps one of them trapped from leaving the place. This is where the adventure begins. Emerge yourself into a magic world full of epic bosses to beat through and reach a long-lost sibling of the main character. Perceive the power of all elements laid down in the world to defeat the most perilous and challenging monsters throughout the game. You can also unite with 3 more players to travel and explore the ubiquitous beauty of Teyvat together. Genshin Impact is a great anime-like video game accompanied by color-saturated graphics attained thanks to the Unity engine. Despite the game can be officially played across PS4, IOS, Android, and Windows for free, we will help extend this list to cover Mac users as well.
System Requirements
MinimalRecommendedOS: Windows 7 SP1 64-bit, Windows 8.1 64-bit or Windows 10 64-bitOS: Windows 7 SP1 64-bit, Windows 8.1 64-bit or Windows 10 64-bitProcessor: Intel Core i5 equivalent or higherProcessor: Intel Core i7 equivalent or higherRAM: 8 GBRAM: 16 GBVideo card: NVIDIA GeForce GT 1030 and higherVideo card: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 6 GB and higherDirectX: from 11 versionDirectX: from 11 versionDisc space: 30 GBDisc space: 30 GB
Play Genshin Impact on Mac with Parallels
Genshin Impact requires lots of PC resources, but if you have a powerful Mac computer (iMac, iMac Pro, or Mac Pro) Parallels Desktop can be a solution. This is software for Windows virtualization on Mac with the full support of DirectX and GPUs. It allows you to install Windows 10 on Mac with a couple of clicks and switch between MacOS and Windows instantly. You can run Windows just like on a regular PC, install Steam and enjoy the Genshin Impact game on Mac.
Play Genshin Impact on Mac with Vortex.gg or Nvidia Geforce Now
Vortex.gg or Nvidia Geforce Now don’t have Genshin Impact in their catalog yet, however, there are thousands of requests from users to add it. Since it is one of the most popular games, this can be brought to life soon.
If you have an old Mac or it cannot satisfy Genshin Impact game system requirements, there is an easy solution. Cloud gaming provides you sufficient cloud resources for a fixed fee. All you need is a small client program and a good internet connection starting from 15 Mbits/s. There are several great services, that provide such an opportunity, among the best are Vortex.gg and Nvidia Geforce Now. Both services may have Genshin Impact in their game catalog soon, and you can play on any Mac computer (starting from MacOS 10.10) and even Android!
Play Genshin Impact on Mac with BootCamp
This method is simple but time-consuming. If your Mac meets the system requirements above, this is probably the best way to play Genshin Impact for now. You need to set up a dual boot of Windows and Mac via BootCamp. BootCamp allows users to choose the system to work in on startup, however, you won’t be able to switch between systems like in Parallels. You will need to reboot your machine every time you switch from Mac to Windows and vice versa. Remember that Mac is just a computer, that uses common processors, RAM, disks, and other components. So you can install Windows on Mac by allocating disc space of a minimum of 64 Gb (to be able to run Windows and a couple of games). To set up Windows via BootCamp, please, do the following:
For OS X El Capitan 10.11 or later
Mention, that for MacOS versions prior to OS X El Capitan 10.11 you will need to create bootable Windows USB.
Download Windows ISO file
Open Boot Camp Assistant (Go to Applications >Utilities)
Define the Windows partition size choose downloaded Windows ISO file
Format Windows partition and go through all Windows installation steps
When Windows boots for the first time follow on-screen instructions to install Boot Camp and Windows support software (drivers)
One such finding relates to how El Capitan handles the installation of Windows through the Boot Camp Assistant. Apple's OS X El Capitan is finally here and Mac owners are installing the software in droves. Oct 05, 2015 Installing Windows 10 on OS X El Capitan is not very complicated, but there are a few pitfalls. This tutorial will show you how to successfully install Windows 10 on a MacBook Pro.
What you need to install Windows 10 on Mac
MacBook introduced in 2015 or later
MacBook Air introduced in 2012 or later
MacBook Pro introduced in 2012 or later
Mac mini introduced in 2012 or later
iMac introduced in 2012 or later1
iMac Pro (all models)
Mac Pro introduced in 2013 or later
The latest macOS updates, which can include updates to Boot Camp Assistant. You will use Boot Camp Assistant to install Windows 10.
64GB or more free storage space on your Mac startup disk:
Your Mac can have as little as 64GB of free storage space, but at least 128GB of free storage space provides the best experience. Automatic Windows updates require that much space or more.
If you have an iMac Pro or Mac Pro with 128GB of memory (RAM) or more, your startup disk needs at least as much free storage space as your Mac has memory.2
An external USB flash drive with a storage capacity of 16GB or more, unless you're using a Mac that doesn't need a flash drive to install Windows.

A 64-bit version of Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro on a disk image (ISO) or other installation media. If installing Windows on your Mac for the first time, this must be a full version of Windows, not an upgrade.
If your copy of Windows came on a USB flash drive, or you have a Windows product key and no installation disc, download a Windows 10 disk image from Microsoft.
If your copy of Windows came on a DVD, you might need to create a disk image of that DVD.
How to install Windows 10 on Mac
To install Windows, use Boot Camp Assistant, which is included with your Mac.
1. Use Boot Camp Assistant to create a Windows partition
Open Boot Camp Assistant, which is in the Utilities folder of your Applications folder. Then follow the onscreen instructions.
Boot Camp Windows In Mac Pro 3 1 El Capitan Update
If you're asked to insert a USB drive, plug your USB flash drive into your Mac. Boot Camp Assistant will use it to create a bootable USB drive for Windows installation.
When Boot Camp Assistant asks you to set the size of the Windows partition, remember the minimum storage-space requirements in the previous section. Set a partition size that meets your needs, because you can't change its size later.
2. Format the Windows (BOOTCAMP) partition
When Boot Camp Assistant finishes, your Mac restarts to the Windows installer. If the installer asks where to install Windows, select the BOOTCAMP partition and click Format. In most cases, the installer selects and formats the BOOTCAMP partition automatically.
3. Install Windows
Unplug any external devices that aren't necessary during installation. Then click Next and follow the onscreen instructions to begin installing Windows.
4. Use the Boot Camp installer in Windows
After Windows installation completes, your Mac starts up in Windows and opens a ”Welcome to the Boot Camp installer” window. Follow the onscreen instructions to install Boot Camp and Windows support software (drivers). You will be asked to restart when done.
If the Boot Camp installer never opens, open the Boot Camp installer manually and use it to complete Boot Camp installation.
If you have an external display connected to a Thunderbolt 3 port on your Mac, the display will be blank (black, gray, or blue) for up to 2 minutes during installation.
How to switch between Windows and macOS
Restart, then press and hold the Option (or Alt) ⌥ key during startup to switch between Windows and macOS.
Learn more
If you have one of these Mac models using OS X El Capitan 10.11 or later, you don't need a USB flash drive to install Windows:
MacBook introduced in 2015 or later
MacBook Air introduced in 2015 or later3
MacBook Pro introduced in 2015 or later3
iMac introduced in 2015 or later
iMac Pro (all models)
Mac Pro introduced in late 2013
To remove Windows from your Mac, use Boot Camp Assistant, not any other utility.
For more information about using Windows on your Mac, open Boot Camp Assistant and click the Open Boot Camp Help button.
1. If you're using an iMac (Retina 5K, 27-inch, Late 2014) or iMac (27-inch, Late 2013) or iMac (27-inch, Late 2012) with a 3TB hard drive and macOS Mojave or later, learn about an alert you might see during installation.
2. For example, if your Mac has 128GB of memory, its startup disk must have at least 128GB of storage space available for Windows. To see how much memory your Mac has, choose Apple menu > About This Mac. To see how much storage space is available, click the Storage tab in the same window.
3. These Mac models were offered with 128GB hard drives as an option. Apple recommends 256GB or larger hard drives so that you can create a Boot Camp partition of at least 128GB.
Boot Camp Windows In Mac Pro 3 1 El Capitan Free
Krausewich wrote:
I loaded Windows 7 onto my machine through bootcamp, then upgraded to Windows 10, then installed a bunch of software, then restarted into the Mac environment before loading the Bootcamp WindowsSupport files.
Your 2008 MP does not support W10. There are no Apple-certified drivers for W10 on your model as stated in Use Windows 10 on your Mac with Boot Camp - Apple Support . The only MP which supports W10 is the 2013 Cylinder.
If I set the startup disk to the Windows partition it restarts to a black screen with a blinking cursor, no doubt because the BIOS mediator was not installed.
The BIOS mediator is the EFI firmware on your MP. It does not need to be installed. It was already there when you were running W7.
Everything is there as it is supposed to be as I can see it through the MAC finder... just can't boot into it. AAARGH !!
Boot Camp Windows In Mac Pro 3 1 El Capitan De
I thought to boot up with the Windows 10 iso disk and reinstall the OS, but I am afraid I will overwrite everything I loaded or perhaps corrupt the dll's or registry entries.
We can try to resurrect the Windows installation. I presume you have a W7 backup somewhere before you started the W10 upgrade. Is this a single-disk MP? From OSX Terminal, please post the output of
Boot Camp Windows In Mac Pro 3 1 El Capitan Download
diskutil list
diskutil cs list
Install Windows 10 El Capitan Boot Camp
Oct 22, 2016 9:49 PM
1 note
·
View note
Text
JAVA 8 Basics
What is functional programming? FP is a paradigm that takes complex computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions (lambda expressions) which makes the code easier to understand, less complex, and reasonable to test. The original Java programming language is based on Von Neumann architecture. The biggest problem of using object-oriented or imperative programming is the mutability and complexity. Functional programming pacifies these problems and works more on expressions than statements. Its concepts are primarily based on immutability (the state cannot be changed) and pure function.
All new desktop and laptop computers are multicore computers. The problem is that a classic Java program uses just a single one of these cores, and the power of the others is wasted. Java 8 facilitates new programming styles to better exploit such computers.
Functions are first-class values.
Java 8 Features
The Streams API
A stream is a sequence of data items that are conceptually produced one at a time
Supports many parallel operations to process data.
It avoids the need for you to write code that uses 'synchronized', which is not only highly error prone but is also more expensive on multicore CPUs.
The addition of Streams in Java 8 can be seen as a direct cause of the two other additions to Java 8:
concise techniques to pass code to methods (method references, lambdas)
default methods in interfaces.
Techniques for passing code to methods
Java 8 adds functions as new forms of value. These facilitate the use of Streams, which Java 8 provides to exploit parallel programming on multicore processors.
File[] hiddenFiles = new File(".").listFiles(File::isHidden);
The function isHidden available, so you just pass it to thelistFiles method using the Java 8 method reference :: syntax (meaning “use this method as a value”);
Analogously to using an object reference when you pass an object around (created by new), in Java 8 when you write File::isHidden you create a method reference,
Lambdas
Passing methods as values is useful, but it’s a bit annoying having to write a definition for short methods such as isHeavyApple and isGreenApple when they’re used perhaps only once or twice. But Java 8 introduces a new notation (anonymous functions, or lambdas) that enables you to write just
filterApples(inventory, (Apple a) -> "green".equals(a.getColor()) );
or
filterApples(inventory, (Apple a) -> a.getWeight() > 150 );
Default methods in interfaces
An interface can now contain method signatures for which an implementing class doesn’t provide an implementation. The missing method bodies are given as part of the interface (hence default implementations).
References:-
https://www.journaldev.com/2389/java-8-features-with-examples
#JAVA 8#Default methods in interfaces#Lambdas#passing code to methods#anonymous functions#Streams#method references#Functions are first-class values
1 note
·
View note
Text
How To Fix Parallel Desktop Errors On Mac
How To Fix Parallel Desktop Errors On Mac
Since Parallel released Parallels Desktop 14.1.1-45xxx updates for Mac computers, many MacOS Mojave users had trouble with installing this update on their device. After clicking on the Parallels.dmg file, there is not any installation continuing after that. So, if your Mac is running MacOS Mojave and you are facing the same issue when installing Parallels Desktop application, then this post can…
View On WordPress
0 notes