#Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Translation in eDiscovery#Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)#Data Translation in eDiscovery#Legal Data Translation#Neural Machine Translation (NMT)#eDiscovery Data Translations#Machine Translation in eDiscovery
0 notes
Text
A little bit about generative AI in translation
Every single time I see talks about generative AI and how bad it is for people, I can't stop myself but think about how awful it also is for translations.
Sure, generative AI has a huge impact on the environment and on how people think (and how it leads them to think) when using it. But this wall of text isn't about it. It's is about the impact it has on non-english speakers, or non-english natives, in their life.
As you might all know by now, generative AI isn't new, its uses in professionnal fields either (think about the system your dentist uses in order to detect your cavities, that's also generative AI). Not just that, but almost everyone has a use out of Statistical Machine Translation like Google Translate or DeepL, and those use a generative AI.
Statistical machine translation (SMT) works by basically being given a bilingual dictionnary, which leads it to taking each word, translating them, and replacing them based on statistics and other language elements. But while a narrow database can be good at the beginning, it still needs more data in order to be able to translate better. This means needing people using it in order to build it (yes, like for LLMs, it means that the more you use it the more it gains data). This, in essence, is a big problem, as languages do not work the same. The statistical system helps a little with the word order due to grammatical rules, but it still means that translation from a slightly gendered language (like English) to a gendered language (like French) will have a load of problems.
The upgrade from SMT is the neural machine translation (NMT) and instead of taking each words separately, it bases itself on different sentences in both the original and target language whose translations has been "approved". While this leads to better translations, it still needs data to continue improving, which is still what happens in different MT when you tell them the translation is wrong and propose another (logically better) one. But, this external data isn't necessarily good data, which leads to an internal fight between quantity and quality.
So, while NMTs are better than SMTs, they are still flawed, and if you want a proper and thoughtful translation, you'll still need a professionnal.
(I suggest you go read the first 4 pages of Pym's How automation through neural machine translation might change the skill sets of translators* in order to better understand what I am trying to explain here, but also to see how similar it is to LLMs and thus how stupid those AIs really are in term of language and their grammar.)
Now that you know all that, I can get a little bit deeper into my problem with NMT and especially its uses through LLMs.
As you might well know if you have ever learned another language (or tried to), translations are highly contextual, especially in heavily gendered languages like French. This means that if you do not have enough data/context, you'll have a hard time translating a piece properly.
Not just that, but there is roughly 7 100 languages in the world, meaning that you will inevitably need a translator at one point, and this is where MT come in play. MTs allows "common" people to be able to roughly understand things in another language than theirs, 24/7, for free. The better the MT, the better the translation and better the understanding of the original piece (which can be crucial at time).
However, big businesses (I'm thinking about Duolingo, Etsy and Patreon, to name a few I noticed problems with) do not really care about a good translation. This leads to them not only firing part of their non-english speaking staff, translation staff, but also to just... fully change the already existing good translations.
While the majority of english-speaking natives will not notice it (and not care), us non-english-speaking natives end up noticing the major problem everywhere. Not just that, but frankly for some of them, I'm not even sure they're using a NMT system as it looks more like a simple SMT system...
From the list above, let's dive into it a little bit and see some of the consequences.
Duolingo
As you might know on Tumblr (not really on other social medias, apparently), Duolingo fired a huge part of their translation staff to replace them with AI. Not only that, but the remaining staff was moved from translation and proof-reading duty to solely proof-reading (which is basically the pessimistic vision of Wei in his Challenges and Coping Strategies of Translation Technology in an Era of Artificial Intelligence (2018), also cited in Pym 2019).
Their proof-reading task was also to verify that the NMT was "acceptable", which obviously means that even if the translations sounded like someone with a B2 level, it should still be allowed to pass because it was "good enough". Which is... an interesting decision for the number one "let's learn a new language" app, as it will lead people to learn a new language badly (especially since Duolingo's quality already suffered several time through the removal of the grammatical explanation and the change from the tree format to a road format). And hell, even my mother, learning German, has noticed that some translations were garbage, which means that they effectively changed their staffs from every languages, since she learns it through French.
The use of generative AI in the case of Duolingo means that people not only have access to a now subpart quality tool, but also that they will learn a new language badly.
Etsy and Patreon
I'm putting those two together simply because the issue I have with them is virtually the same.
Let's take a look at Patreon's main page, since the disaster starts here.


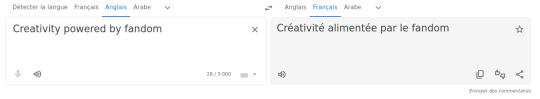
If you know French, you already have noticed a HUGE problem with this translation (and how clear it is that they are not using a translator for it, professionnal or not is irrelevant here).
"Creativity powered by fandom" is translated here into "Créativité alimenté par Fandom" and it tells us exactly where the different words come from.
First of, this heavily looks like an SMT and not an NMT since the words do not seem connected to each other.
Créativité, while not ending with an e, is feminine, which means that the adjective alimenté, relative to créativité, should be alimentée instead. Par is good. Fandom has two problem. First of, the capital F shows us that the LLM crawling led it to register the most used version of the word in french, which comes for the website Fandom (since this fucker is everywhere). Which leads to the second problem: as a word, it should be given a definite article, but there isn't any.
Second of, if you only take the French version, Patreon is apparently claiming that "Creativity is powered by Fandom™" and hum... bold assumption, but also factually untrue and there also might be some legal problems here?
Another thing that is killing me is the Pricing tab in the footer.


Priser, as a verb fitting the context of "price" or "deciding on a price for something", is an old term I've actually never seen in recent writing and more or less means estimer (to estimate, to assess), which, as you can see, cannot be a translation for pricing (Tarifs would be a better translation).
Which shows that not only did the LLM just grabbed some random translation but also just... took the French root and went with it.
Not just that, but this is a problem I noticed MONTHS AGO, notably from the Press (Presse) translation to Presser (to press).
And Etsy is no better.


While the word custom as a noun can be synonymous to tradition, it can also be an adjective as in customized.
Etsy is slightly better since they translated press properly, but still, a rather horrendous thing to see when you are supposed to spend money on this website.
Both those businesses decided to apparently put their entire websites through an LLM and just... let it do its thing without checking after it, which essentially meant deleting the previously proper translation and replacing it with a subpar one.
And frankly, I cannot trust those websites with my money. If, despite all their money, they can't be bothered to have one person look at the basic tagging system and translate it properly, nor look at the main page information and have it make sense? Why should I give their mine.
Ok, and?
Well, I think that's pretty fucking bad.
The fact that you cannot really translate things properly is a long and complicated debate (for example, writing an alt for an image can be considered a type of translation), but there is the need, especially on a legal and political level, to translate a piece as accurately as possible in order to be sure that the person who will read or hear your piece understands exactly what you are trying to say.
An example would the issue with Asus (?), that Gamers Nexus talked about and participated in. One of the issues with the warranty system explained wasn't clear and it was misleading, which caused a lot of issues with customers who felt like they were lied to.
They weren't lied to, they were mislead, and this was a result of a choice of words and how they were put. This is one of the reason why, for example, legal documents are worded so weirdly (and why you often need an attorney or else to help you understand them).
And this is roughly what is happening here with businesses using LLMs to translate their websites and other documents.
The translations are bad and people won't understand them properly, but when they'll want to take legal actions, they'll be told that actually, the original document, in its original language, is the only real documents they can use to attack them. And as stated, those documents won't have the same elements in it as the translated one.
Not just that, but in the case of websites such as Patreon and Esty, who work with monetary transactions, it becomes a huge problem.
Not only are we, non-english people, given subpar quality products (I don't which word would be better for that, sorry), we have absolutely no way to know if we even will be helped in case there is a problem.
That has been a problem before, mind you, Tumblr is a great example for it since even if the interface is in French, support is only in English and is given an MT. But with LLMs also handling the translations, and considering the quality of said translations, we have no way to get proper help, if any help is given at all (I'm looking at you, Meta, with your WhatsApp "support").
But here's the kicker. Why are the translations that bad?
Remember the Patreon example? Here it is in Google Translate.
And welp, here it is in DeepL, which is usually better at translating than GTL.

While DeepL does propose the bad translation from Patreon as alternatives, they're both still giving us a good translation.
So if NMTs can translate that well, why are translations on other websites are so bad? Not just that but they clearly just translate word by word, which is what SMTs were that bad at translating (and why your English/German/etc. teacher forbade you to use Google Translate).
How did we reverted back to 2010s level of translation?
The only answer I can possibly give is that LLMs are doing the translations, and apparently LLMs aren't as good at translating as they are at "speaking" and still use a basic statistical system to do so.
I frankly do not have a conclusion to that post, I mostly wanted to complain because such garbage level of translation on major websites is just horrendous. Not just that but I've also never seen anyone complain about it and welp, I guess now I've seen one (myself).
Do what you want with all those information.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Evolution of Language Translation Services
Language is the bridge that connects people, cultures, and ideas. However, throughout history, the barrier of language has also stood as a challenge to communication and understanding. Translation services have evolved significantly from their humble beginnings, transitioning from simple manual methods to cutting-edge AI-driven solutions that can translate not just words, but context, tone, and intent. Let’s take a journey through time to explore the evolution of language translation services.
Early Beginnings: Manual Translation and the Role of Human Translators
The earliest translation services date back to ancient civilizations. The Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans all used scribes to translate religious texts, diplomatic messages, and trade agreements. The Bible, one of the most translated texts in the world, was first translated from Hebrew and Greek into Latin by St. Jerome in the 4th century.
During the Middle Ages, the translation process remained labor-intensive and was mainly performed by scholars. A small group of educated people, usually monks or clerks, would painstakingly translate documents by hand. In these early days, translation was a highly specialized skill, with only a few individuals having the expertise to navigate multiple languages.
Translation was limited not just by the skills of the translators, but by the technology of the time. Written translations, often slow and costly, could only be produced at a rate that kept them out of reach for the masses. Additionally, the lack of widespread literacy meant that translation services were typically reserved for the privileged few.
The Printing Press and the Rise of Commercial Translation
With the invention of the printing press in the 15th century, the production of written materials became more efficient, leading to the broader dissemination of translated works. This was particularly important for religious texts, which became more accessible to a larger audience as the Bible and other texts were translated into vernacular languages.
During the 18th and 19th centuries, globalization and increased international trade created a demand for more commercial translation services. As nations began to interact more frequently, translation became necessary for diplomacy, business, and scientific exchange. The 19th century saw the rise of professional translators, with many institutions, such as universities and businesses, establishing translation departments.
The Birth of Machine Translation: A Revolutionary Leap
While human translation remained the gold standard, the mid-20th century marked a significant turning point in language translation with the birth of machine translation (MT). The first notable attempt at automating translation occurred in the 1950s when researchers in the U.S. and the Soviet Union developed early forms of computer-assisted translation.
The most famous early example of machine translation was the 1954 Georgetown-IBM experiment. This experiment showcased the potential of computers to translate Russian sentences into English, although the translations were often inaccurate and simplistic. The technology was in its infancy, and researchers soon realized that translating meaning and context was far more complex than simply converting words from one language to another.
In the following decades, machine translation continued to evolve but faced significant limitations due to the lack of linguistic understanding and context-awareness in early computer algorithms. Despite these hurdles, MT showed promise for specific tasks, such as translating technical documents, where the language was more formulaic and less nuanced.
The Rise of Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)
In the 1990s, a breakthrough came with the development of Statistical Machine Translation (SMT). Unlike earlier methods, which were rule-based and reliant on manually crafted dictionaries and grammar rules, SMT used vast amounts of bilingual text data to "learn" translation patterns. By analyzing millions of sentence pairs, SMT could generate translations based on statistical probability, resulting in more accurate and natural translations.
The advent of SMT sparked a revolution in the field of translation services, as it allowed for scalable translations that could be applied to a wide range of languages and industries. The increasing availability of large databases, such as the European Parliament’s corpus and the United Nations’ multilingual documents, provided invaluable resources for training these models.
Popular translation services like Google Translate began to emerge in the early 2000s, offering free, online access to machine translations powered by SMT. While still imperfect, these services made translation accessible to anyone with an internet connection, breaking down language barriers in ways that were never before possible.
Neural Machine Translation: The AI Revolution
The most recent and transformative shift in the evolution of translation services came with the rise of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) in the 2010s. Powered by deep learning and artificial intelligence, NMT models are trained to understand entire sentences, not just individual words. This breakthrough enables translations that are contextually more accurate, preserving nuances, idiomatic expressions, and tone.
NMT systems work by mimicking how humans learn languages—processing information through neural networks that are capable of understanding complex patterns and relationships between words. These systems are constantly refined through large-scale datasets, leading to continuous improvements in translation quality. The ability of NMT to offer more fluent and human-like translations has made it the dominant technology in the field today.
One of the standout features of NMT is its adaptability. Unlike older machine translation systems, which struggled with context and meaning, NMT can now translate text with greater fluency. For example, it can distinguish between different meanings of a word depending on its context, offering translations that are far more nuanced.
The Future of Language Translation Services
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, so too will the field of language translation. While NMT is already impressive, future innovations will further refine the accuracy and adaptability of translation systems. Some areas of improvement include:
Real-time Translation: Devices like smart glasses and earbuds are beginning to offer real-time translations, which could revolutionize how people communicate across languages during conversations or while traveling.
Multimodal Translation: AI is moving toward the integration of visual and auditory inputs for translation, where not only text but also images, videos, and voice are translated in real time, enhancing accessibility and understanding.
Cultural Context: AI models are gradually improving their ability to take into account cultural nuances, ensuring that translations are not just linguistically accurate but also culturally appropriate.
AI-Powered Localization: As businesses and content creators expand globally, the need for tailored localization will grow. AI will play a key role in adapting translations to specific cultural contexts, improving user experience across markets.
Conclusion
Language translation services have come a long way, from hand-crafted manuscripts to the sophisticated AI-powered translation tools we use today. The evolution of these services has not only made communication easier but has also fostered greater global collaboration, understanding, and connection. As technology continues to advance, we can expect the gap between languages to narrow even further, bringing the world closer together. The future of translation services is bright, and we are only just beginning to scratch the surface of what’s possible.
0 notes
Text
Exploring Arabic Machine Translation
Arabic Machine Translation plays a key role in breaking language barriers between Arabic and other languages. As technology evolves, machine translation has become an essential tool for businesses, researchers, and everyday users who need quick and understandable translations. However, translating Arabic — a language known for its complexity and rich structure — presents unique challenges that require thoughtful solutions.
What is Arabic Machine Translation?
Arabic Machine Translation refers to the process of using computer algorithms to automatically translate text between Arabic and other languages. This can include translating Arabic to English, French, or even other dialects within the Arabic language itself. The goal is to create translations that are not only grammatically correct but also clear and meaningful.
Why Arabic Translation is Challenging
Arabic is a highly complex language with unique features that make it different from many other languages. For example, Arabic is written from right to left, has a rich root-based word system, and includes a variety of dialects alongside Modern Standard Arabic. Additionally, words often change form based on context, gender, and grammatical structure.
Machine translation systems must account for these complexities. A single Arabic word can carry multiple meanings depending on the sentence, which makes it hard for algorithms to select the correct translation without deeper contextual understanding.
Types of Arabic Machine Translation Systems
Rule-Based Systems – These systems rely on predefined linguistic rules and dictionaries to translate words and phrases. While they work well for simple sentences, they often struggle with more complex structures and idioms.
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) – This approach analyzes large volumes of bilingual text to find patterns and predict the most likely translations. Though effective, SMT can produce awkward or incorrect translations when context is unclear.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) – A more advanced method that uses artificial intelligence to learn from vast amounts of data. NMT systems consider entire sentences, improving fluency and accuracy. This approach is now widely used by major translation services like Google Translate and Microsoft Translator.
Common Issues in Arabic Machine Translation
Dialect Confusion – Arabic has many regional dialects, such as Egyptian, Levantine, and Gulf Arabic. Machine translation systems trained on Modern Standard Arabic may struggle to understand dialectal phrases or slang.
Ambiguity – Words with multiple meanings can confuse translation algorithms. For example, the word كتب (kataba) means wrote, but the same root can form كتاب (kitab), meaning book. Without context, the system might choose the wrong meaning.
Grammar and Sentence Structure – Arabic often places verbs before subjects, while English typically does the opposite. Translating directly without restructuring the sentence can lead to awkward phrasing.
Cultural Nuances – Some Arabic expressions don't have direct equivalents in other languages. A literal translation may sound odd or lose the intended meaning entirely.
Improving Arabic Machine Translation
To improve Arabic Machine Translation, developers continue refining translation models and expanding language databases. Training algorithms on more diverse datasets, including different dialects and specialized terminology, helps increase accuracy. Additionally, combining machine translation with human post-editing ensures better quality — especially for professional content like legal documents or medical instructions.
Final Thoughts
Arabic Machine Translation has made impressive progress, making communication across languages faster and more accessible. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and data collection are helping to create more accurate, natural, and culturally sensitive translations. As machine translation evolves, it will continue to play an important role in connecting Arabic speakers with the rest of the world.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of AI in Language Translation: How PDF AI Translate is Revolutionizing Communication
Description: Explore the transformative role of AI in language translation, with a focus on PDF AI Translate technology. Discover how this innovation is breaking down language barriers and enhancing global communication.
Introduction
In the digital age, the ability to communicate across languages is more important than ever. As businesses expand globally and individuals connect across borders, the demand for efficient and accurate translation tools has skyrocketed. Among the most significant advancements in this field is PDF AI Translate, a technology that leverages artificial intelligence to translate documents seamlessly. This article delves into the evolution of AI in language translation, the mechanics of PDF AI Translate, and its impact on various sectors.
The Evolution of AI in Language Translation
The journey of AI in language translation began with simple rule-based systems that relied on predefined grammatical rules and dictionaries. These early systems, while groundbreaking at the time, were limited in their ability to handle the nuances of human language. The advent of statistical machine translation (SMT) in the 1990s marked a significant leap forward. SMT systems used large corpora of bilingual text to predict the most likely translation, improving accuracy and fluency.
However, the real game-changer came with the introduction of neural machine translation (NMT) in the mid-2010s. NMT systems, powered by deep learning algorithms, revolutionized the field by enabling more context-aware and natural-sounding translations. Today, AI-driven translation tools like PDF AI Translate are pushing the boundaries even further, offering real-time, high-quality translations for a wide range of document types.
How PDF AI Translate Works
PDF AI Translate is a cutting-edge technology that combines the power of AI with the versatility of PDF documents. The process begins with the extraction of text from the PDF file, which is then fed into an AI-driven translation engine. This engine, often based on NMT, analyzes the text, considers the context, and generates a translation that is both accurate and fluent.
One of the key advantages of PDF AI Translate is its ability to preserve the original formatting of the document. This is particularly important for legal, medical, and technical documents, where the layout and structure are crucial. Additionally, PDF AI Translate can handle complex elements such as tables, images, and embedded fonts, ensuring that the translated document is as close to the original as possible.
Applications of PDF AI Translate
The applications of PDF AI Translate are vast and varied, spanning multiple industries. In the business world, companies use this technology to translate contracts, reports, and marketing materials, enabling them to operate seamlessly in international markets. Educational institutions leverage PDF AI Translate to make research papers and academic resources accessible to a global audience.
In the legal sector, accurate translation of documents is paramount. PDF AI Translate ensures that legal texts are translated with precision, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and legal disputes. Similarly, in the medical field, the technology is used to translate patient records, research studies, and pharmaceutical documentation, facilitating better healthcare outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, PDF AI Translate is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for bias in AI-driven translations. Since these systems learn from existing data, they may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the training material. Additionally, while PDF AI Translate excels at handling common languages, it may struggle with less widely spoken languages or dialects.
Looking ahead, the future of PDF AI Translate is promising. Advances in AI and machine learning are expected to further enhance the accuracy and capabilities of translation tools. We can anticipate more sophisticated context-aware systems, improved handling of rare languages, and greater integration with other technologies such as voice recognition and augmented reality.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI in language translation has been nothing short of remarkable. From rudimentary rule-based systems to the sophisticated PDF AI Translate technology we have today, the journey has been marked by continuous innovation and improvement. As we move forward, PDF AI Translate will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in breaking down language barriers and fostering global communication. Whether in business, education, law, or healthcare, the impact of this technology is profound and far-reaching, heralding a new era of interconnectedness and understanding.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Modern Approach to English to Odia Translation

Translation from one language to another has become a significant concern in this world. Millions of Odia speakers exist everywhere on the globe, and they need information and communication in their mother tongue. Here is the role that English to Odia translation plays. The article below deals with modern approaches to this translation process, considering the movements as well as the challenges in it.
The Translation Revolution
Traditionally, translation was laborious, depending upon mere bilingualism and dictionary use. However, technology has dramatically altered the situation of translation in many ways. Modern translation bears no resemblance whatsoever to what it was done before. Today, it forms part of the translation landscape to incorporate machine translation systems that work on complex algorithms and giant data banks.
Contingent Modern Methods of Translating from English to Odia
Various contingent modern methods are followed for translating from English into Odia, with different merits and demerits associated with each method.
1. SMT or Statistical Machine Translation: This relies on statistical models learned from large parallel corpora, which, in this case, means texts in both Odia and English, to predict the most probable translation of an English text given. It is effective at translating routine phrases and sentences but becomes weaker with more complex grammatical structures and idiomatic expressions.
2. NMT or Neural Machine Translation: The newest approach with artificial neural networks, especially the deep learning model, is to learn about the complex relationships between languages. NMTs have proved to be excellent systems in improvement with fluently natural-sounding translations over SMTs. Contextual is better with sensitivity towards language nuances.
3. Hybrid Approaches: Hybrid approaches combine the best of SMT and NMT, using statistical models for specific tasks and neural networks for others. This may result in more efficient and accurate translation outcomes.
4. RBMT: Not so popular these days, RBMT systems rely on linguistic rules and grammar to translate from one language to another. Although they produce an extremely accurate translation in a specific domain, they still require extensive manual work to develop and maintain the rules.
MT has come a long way, but human translators still play an essential role in maintaining quality. Their linguistic and cultural backgrounds describe nuances and produce accurate translations that sound natural as if they were born from the native speaker's vocabulary. Besides, they furnish the necessary post-editing of MT output, error correction, and enhancement of the quality of translation.
Future of English to Odia Translation
The future of English to Odia translation seems bright with continuous research and development in MT and other related technologies. Improvements in deep learning, natural language processing, and data collection will take the MT systems forward toward high accuracy and fluency. Further, increased digital resources and online platforms have been helping translators and researchers collaborate and share knowledge.
New ways of translating English into Odia, especially NMT, have significantly increased efficiency and quality. However, bottom-line problems persist as humans dominate and command this sector. Combining the best from the technology bag and human skills handbags, we can ensure effective communication between the English-speaking or Odia-speaking populations for better interaction and cooperation among people moving around in this increasingly interdependent world.
#Odia Translation Solution#English to Odia Translation#Modern Translation Solutions#Language Translation India#Odia Language Solutions#Translation Technology#AI Powered Translation#Odia Global Connect#Breaking Language Barriers
0 notes
Text
Transformer Impact: Has Machine Translation Been Solved?
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/transformer-impact-has-machine-translation-been-solved/
Transformer Impact: Has Machine Translation Been Solved?
Google recently announced their release of 110 new languages on Google Translate as part of their 1000 languages initiative launched in 2022. In 2022, at the start they added 24 languages. With the latest 110 more, it’s now 243 languages. This quick expansion was possible thanks to the Zero-Shot Machine Translation, a technology where machine learning models learn to translate into another language without prior examples. But in the future we will see together if this advancement can be the ultimate solution to the challenge of machine translation, and in the meanwhile we can explore the ways it can happen. But first its story.
How Was it Before?
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)
This was the original method that Google Translate used. It relied on statistical models. They analyzed large parallel corpora, collections of aligned sentence translations, to determine the most likely translations. First the system translated text into English as a middle step before converting it into the target language, and it needed to cross-reference phrases with extensive datasets from United Nations and European Parliament transcripts. It’s different to traditional approaches that necessitated compiling exhaustive grammatical rules. And its statistical approach let it adapt and learn from data without relying on static linguistic frameworks that could quickly become completely unnecessary.
But there are some disadvantages to this approach, too. First Google Translate used phrase-based translation where the system broke down sentences into phrases and translated them individually. This was an improvement over word-for-word translation but still had limitations like awkward phrasing and context errors. It just didn’t fully understand the nuances as we do. Also, SMT heavily relies on having parallel corpora, and any relatively rare language would be hard to translate because it doesn’t have enough parallel data.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
In 2016, Google made the switch to Neural Machine Translation. It uses deep learning models to translate entire sentences as a whole and at once, giving more fluent and accurate translations. NMT operates similarly to having a sophisticated multilingual assistant within your computer. Using a sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) architecture NMT processes a sentence in one language to understand its meaning. Then – generates a corresponding sentence in another language. This method uses huge datasets for learning, in contrast to Statistical Machine Translation which relies on statistical models analyzing large parallel corpora to determine the most probable translations. Unlike SMT, which focused on phrase-based translation and needed a lot of manual effort to develop and maintain linguistic rules and dictionaries, NMT’s power to process entire sequences of words lets it capture the nuanced context of language more effectively. So it has improved translation quality across various language pairs, often getting to levels of fluency and accuracy comparable to human translators.
In fact, traditional NMT models used Recurrent Neural Networks – RNNs – as the core architecture, since they are designed to process sequential data by maintaining a hidden state that evolves as each new input (word or token) is processed. This hidden state serves as a sort of a memory that captures the context of the preceding inputs, letting the model learn dependencies over time. But, RNNs were computationally expensive and difficult to parallelize effectively, which was limiting how scalable they are.
Introduction of Transformers
In 2017, Google Research published the paper titled “Attention is All You Need,” introducing transformers to the world and marking a pivotal shift away from RNNs in neural network architecture.
Transformers rely only on the attention mechanism, – self-attention, which allows neural machine translation models to focus selectively on the most critical parts of input sequences. Unlike RNNs, which process words in a sequence within sentences, self-attention evaluates each token across the entire text, determining which others are crucial for understanding its context. This simultaneous computation of all words enables transformers to effectively capture both short and long-range dependencies without relying on recurrent connections or convolutional filters.
So by eliminating recurrence, transformers offer several key benefits:
Parallelizability: Attention mechanisms can compute in parallel across different segments of the sequence, which accelerates training on modern hardware such as GPUs.
Training Efficiency: They also require significantly less training time compared to traditional RNN-based or CNN-based models, delivering better performance in tasks like machine translation.
Zero-Shot Machine Translation and PaLM 2
In 2022, Google released support for 24 new languages using Zero-Shot Machine Translation, marking a significant milestone in machine translation technology. They also announced the 1,000 Languages Initiative, aimed at supporting the world’s 1,000 most spoken languages. They have now rolled out 110 more languages. Zero-shot machine translation enables translation without parallel data between source and target languages, eliminating the need to create training data for each language pair — a process previously costly and time-consuming, and for some pair languages also impossible.
This advancement became possible because of the architecture and self-attention mechanisms of transformers. Thetransformer model’s capability to learn contextual relationships across languages, as a combo with its scalability to handle multiple languages simultaneously, enabled the development of more efficient and effective multilingual translation systems. However, zero-shot models generally show lower quality than those trained on parallel data.
Then, building on the progress of transformers, Google introduced PaLM 2 in 2023, which made the way for the release of 110 new languages in 2024. PaLM 2 significantly enhanced Translate’s ability to learn closely related languages such as Awadhi and Marwadi (related to Hindi) and French creoles like Seychellois and Mauritian Creole. The improvements in PaLM 2’s, such as compute-optimal scaling, enhanced datasets, and refined design—enabled more efficient language learning and supported Google’s ongoing efforts to make language support better and bigger and accommodate diverse linguistic nuances.
Can we claim that the challenge of machine translation has been fully tackled with transformers?
The evolution we are talking about took 18 years from Google’s adoption of SMT to the recent 110 additional languages using Zero-Shot Machine Translation. This represents a huge leap that can potentially reduce the need for extensive parallel corpus collection—a historically and very labor-extensive task the industry has pursued for over two decades. But, asserting that machine translation is completely addressed would be premature, considering both technical and ethical considerations.
Current models still struggle with context and coherence and make subtle mistakes that can change the meaning you intended for a text. These issues are very present in longer, more complex sentences where maintaining the logical flow and understanding nuances is needed for results. Also, cultural nuances and idiomatic expressions too often get lost or lose meaning, causing translations that may be grammatically correct but don’t have the intended impact or sound unnatural.
Data for Pre-training: PaLM 2 and similar models are pre trained on a diverse multilingual text corpus, surpassing its predecessor PaLM. This enhancement equips PaLM 2 to excel in multilingual tasks, underscoring the continued importance of traditional datasets for improving translation quality.
Domain-specific or Rare Languages: In specialized domains like legal, medical, or technical fields, parallel corpora ensures models encounter specific terminologies and language nuances. Advanced models may struggle with domain-specific jargon or evolving language trends, posing challenges for Zero-Shot Machine Translation. Also Low-Resource Languages are still poorly translated, because they do not have the data they need to train accurate models
Benchmarking: Parallel corpora remain essential for evaluating and benchmarking translation model performance, particularly challenging for languages lacking sufficient parallel corpus data.The automated metrics like BLEU, BLERT, and METEOR have limitations assessing nuance in translation quality apart from grammar. But then, we humans are hindered by our biases. Also, there are not too many qualified evaluators out there, and finding the perfect bilingual evaluator for each pair of languages to catch subtle errors.
Resource Intensity: The resource-intensive nature of training and deploying LLMs remains a barrier, limiting accessibility for some applications or organizations.
Cultural preservation. The ethical dimension is profound. As Isaac Caswell, a Google Translate Research Scientist, describes Zero-Shot Machine Translation: “You can think of it as a polyglot that knows lots of languages. But then additionally, it gets to see text in 1,000 more languages that isn’t translated. You can imagine if you’re some big polyglot, and then you just start reading novels in another language, you can start to piece together what it could mean based on your knowledge of language in general.” Yet, it’s crucial to consider the long-term impact on minor languages lacking parallel corpora, potentially affecting cultural preservation when reliance shifts away from the languages themselves.
#000#2022#2023#2024#Accessibility#applications#approach#architecture#attention#attention mechanism#barrier#benchmarking#Building#Capture#challenge#change#CNN#Collections#computation#computer#data#datasets#Deep Learning#deploying#Design#development#domains#efficiency#English#european parliament
0 notes
Text
May 30, 2024
QUESTION 151:
Are there industry experts that still prefer Statistical MT over Neural MT solutions?
Chat GPT's Response:
While Neural Machine Translation (NMT) has become the dominant paradigm in the field of machine translation due to its superior performance, there are still some experts and practitioners who advocate for the continued use of Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) in certain contexts. Here are a few reasons why some industry experts might prefer SMT over NMT:
Resource Constraints: NMT requires substantial computational resources and large amounts of parallel data for training. In scenarios where these resources are limited, SMT might be more feasible. SMT systems can often be trained with less data and computational power.
Domain-Specific Customization: SMT systems can sometimes be easier to adapt to specific domains or specialized vocabularies with less data. While NMT can also be customized, it typically requires more data and computational resources to achieve high-quality domain adaptation.
Interpretability and Debugging: SMT models, which are based on phrases and rules, can be more interpretable and easier to debug. For some users, the transparency of SMT makes it easier to understand and improve the system. NMT models, on the other hand, operate as black boxes, making it more challenging to understand why they produce certain outputs.
Error Types: The types of errors produced by SMT and NMT systems can differ, and in some cases, SMT errors might be more predictable and manageable. For example, SMT might make more grammatical errors, while NMT might produce fluent but semantically incorrect translations. Depending on the application, some users might prefer the error profile of SMT.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues: In certain regulated industries, the use of black-box models like NMT can raise concerns about accountability and compliance. SMT's more transparent nature can be preferable in these cases.
Despite these reasons, it's important to note that the trend in the industry heavily favors NMT due to its superior performance in most general use cases. Many of the world's leading translation services, including Google Translate and Microsoft Translator, have transitioned to NMT because of its ability to produce more fluent and accurate translations. However, the considerations above illustrate why SMT still holds value in certain niche applications and for specific user needs.
0 notes
Text
Decoding the Global Machine Translation Market
So, you stumbled upon this fascinating report on the Global Machine Translation (MT) Market, and you’re probably wondering, “How on earth can I make sense of all these numbers and acronyms without falling into a deep, AI-induced slumber?” Well, fear not! We’re here to break it down for you in a casual, no-nonsense chat that even your coffee break buddy can understand.

The Big Picture
The global MT market seems to be on a wild ride, growing from a cool USD 861 million in 2021 to a projected USD 2693.98 million by 2030. That’s like going from a cozy local diner to dining in a Michelin-starred restaurant, but for machines. The growth rate? A not-so-shabby 5.52%, making it a steady climber in the business world.
The Tech Talk
Let’s get nerdy for a moment and dive into the technology behind it. There are two big players here: Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) and Neural Machine Translation (NMT). SMT is like the wise grandparent, considering entire phrases and sentences for that perfect translation. Meanwhile, NMT is the cool, self-learning teenager adapting to diverse languages and industry jargon. Guess who’s stealing the spotlight? NMT, obviously!
Applications in the Real World
Now, where does this MT magic happen? Think of it like a multitalented friend — it’s everywhere! From automotive to healthcare, e-commerce to legal, and IT & telecommunications, MT is the go-to buddy for various applications. E-commerce, in particular, is the popular kid in the MT playground, with its need for multilingual support in product descriptions and user interfaces.
Regional Rollercoaster
Picture this: North America as the tech-savvy neighborhood, dominating the MT market due to its fancy technological infrastructure. On the other side of the globe, Asia-Pacific is the rising star, fueled by digital transformation and a hunger for effective language solutions. The machines are getting a global tour!
For More Information: https://www.skyquestt.com/report/machine-translation-market
Driving Forces and Roadblocks
What’s pushing this MT market forward? Advancements in NMT technology, real-time translations, and the global need for cross-border communication. But, of course, every success story has its challenges. Achieving high fluency, especially in specialized domains, and privacy concerns are the villains trying to slow things down.
Meet the Players
Now, let’s talk about the cool kids on the block. Google, Microsoft, Amazon, IBM — these are not just your everyday tech giants. They are the rockstars of the MT world, investing in cutting-edge technologies and dancing the dance of innovation. Startups? They’re the rising stars, introducing niche solutions and keeping the giants on their toes.
Recent Drama and Gossip
In the world of MT, there’s always drama and gossip. Intento and e2f joined forces for a comprehensive analysis of the MT and Generative AI market. Lionbridge, ever the visionary, predicts a new paradigm shift with Generative AI and Large Language Models. It’s like the MTV of the tech world!
Wrapping It Up
In a nutshell, the global MT market is not just about numbers and graphs; it’s a dynamic playground with tech giants, startups, drama, and growth trends. So, the next time someone talks about Machine Translation, you can casually join the conversation and say, “Oh, I know a thing or two about that. It’s like having a multilingual best friend for your business!”
About Us-
SkyQuest Technology Group is a Global Market Intelligence, Innovation Management & Commercialization organization that connects innovation to new markets, networks & collaborators for achieving Sustainable Development Goals.
Contact Us-
SkyQuest Technology Consulting Pvt. Ltd.
1 Apache Way,
Westford,
Massachusetts 01886
USA (+1) 617–230–0741
Email- [email protected]
Website: https://www.skyquestt.com
0 notes
Text
Decoding the Global Machine Translation Market
So, you stumbled upon this fascinating report on the Global Machine Translation (MT) Market, and you’re probably wondering, “How on earth can I make sense of all these numbers and acronyms without falling into a deep, AI-induced slumber?” Well, fear not! We’re here to break it down for you in a casual, no-nonsense chat that even your coffee break buddy can understand.

The Big Picture
The global MT market seems to be on a wild ride, growing from a cool USD 861 million in 2021 to a projected USD 2693.98 million by 2030. That’s like going from a cozy local diner to dining in a Michelin-starred restaurant, but for machines. The growth rate? A not-so-shabby 5.52%, making it a steady climber in the business world.
The Tech Talk
Let’s get nerdy for a moment and dive into the technology behind it. There are two big players here: Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) and Neural Machine Translation (NMT). SMT is like the wise grandparent, considering entire phrases and sentences for that perfect translation. Meanwhile, NMT is the cool, self-learning teenager adapting to diverse languages and industry jargon. Guess who’s stealing the spotlight? NMT, obviously!
Applications in the Real World
Now, where does this MT magic happen? Think of it like a multitalented friend — it’s everywhere! From automotive to healthcare, e-commerce to legal, and IT & telecommunications, MT is the go-to buddy for various applications. E-commerce, in particular, is the popular kid in the MT playground, with its need for multilingual support in product descriptions and user interfaces.
Regional Rollercoaster
Picture this: North America as the tech-savvy neighborhood, dominating the MT market due to its fancy technological infrastructure. On the other side of the globe, Asia-Pacific is the rising star, fueled by digital transformation and a hunger for effective language solutions. The machines are getting a global tour!
For More Information: https://www.skyquestt.com/report/machine-translation-market
Driving Forces and Roadblocks
What’s pushing this MT market forward? Advancements in NMT technology, real-time translations, and the global need for cross-border communication. But, of course, every success story has its challenges. Achieving high fluency, especially in specialized domains, and privacy concerns are the villains trying to slow things down.
Meet the Players
Now, let’s talk about the cool kids on the block. Google, Microsoft, Amazon, IBM — these are not just your everyday tech giants. They are the rockstars of the MT world, investing in cutting-edge technologies and dancing the dance of innovation. Startups? They’re the rising stars, introducing niche solutions and keeping the giants on their toes.
Recent Drama and Gossip
In the world of MT, there’s always drama and gossip. Intento and e2f joined forces for a comprehensive analysis of the MT and Generative AI market. Lionbridge, ever the visionary, predicts a new paradigm shift with Generative AI and Large Language Models. It’s like the MTV of the tech world!
Wrapping It Up
In a nutshell, the global MT market is not just about numbers and graphs; it’s a dynamic playground with tech giants, startups, drama, and growth trends. So, the next time someone talks about Machine Translation, you can casually join the conversation and say, “Oh, I know a thing or two about that. It’s like having a multilingual best friend for your business!”
About Us-
SkyQuest Technology Group is a Global Market Intelligence, Innovation Management & Commercialization organization that connects innovation to new markets, networks & collaborators for achieving Sustainable Development Goals.
Contact Us-
SkyQuest Technology Consulting Pvt. Ltd.
1 Apache Way,
Westford,
Massachusetts 01886
USA (+1) 617–230–0741
Email- [email protected]
Website: https://www.skyquestt.com
0 notes
Text
Machine Learning in Natural Language Processing: Enhancing Understanding and Communication
Machine Learning (ML) has emerged as a powerful tool in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), revolutionizing the way computers understand and communicate with human language. Through the application of ML algorithms, NLP systems have gained the ability to process, analyze, and generate text, leading to significant advancements in AI-driven language understanding. In this blog post, we will explore the role of Machine Learning in NLP and how it enhances the way we communicate and interact with AI systems.
Understanding Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP revolves around facilitating the interaction and communication between computers and human language. It involves tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, language translation, and chatbot interactions. Machine Learning plays a vital role in NLP by providing algorithms and models that can automatically learn patterns, structures, and meanings from text data.
Text Classification and Sentiment Analysis:
Machine Learning algorithms find extensive application in text classification tasks, automatically assigning predefined categories to text. Sentiment analysis, a specific form of text classification, involves determining the sentiment or emotional tone of a text. ML models, such as Support Vector Machines (SVM), Naive Bayes, and Neural Networks, learn from labelled data to classify text accurately.
Named Entity Recognition (NER):
NER is a crucial NLP task that involves identifying and classifying named entities in text, such as names, locations, organizations, and dates. Machine Learning techniques, including Conditional Random Fields (CRF) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), have significantly improved NER performance by learning contextual information and capturing dependencies between words.
Language Translation:
Machine Learning has revolutionized language translation by enabling the development of Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) and Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models. SMT models leverage statistical techniques to translate text, while NMT models, based on deep neural networks, provide more accurate and context-aware translations, capturing nuances and idiomatic expressions.
Question Answering and Chatbots:
Machine Learning enables AI systems to engage in interactive conversations and answer questions accurately. Question Answering (QA) models use ML algorithms to understand queries and provide relevant responses by extracting information from textual sources. Chatbots, powered by ML, can understand user intent, generate human-like responses, and simulate natural conversations.
Text Generation and Summarization:
Machine Learning algorithms have made significant contributions to text generation and summarization tasks. By learning patterns from vast amounts of text data, models like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Transformers can generate coherent and contextually relevant text, enhancing content generation and automatic summarization capabilities.
Speech Recognition and Natural Language Understanding:
ML plays a crucial role in speech recognition, converting spoken language into text. Deep Learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), have enabled significant advancements in automatic speech recognition, enabling voice-controlled systems and voice assistants.
Wrapping Up!!!
Machine Learning has transformed Natural Language Processing, empowering computers to understand and communicate with human language effectively. Through techniques like text classification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, language translation, question answering, and text generation, ML algorithms have enhanced the accuracy and capabilities of NLP systems. As ML continues to advance, it will further revolutionize the way we interact with AI-driven systems, enabling more natural and intuitive communication.
Celebal Technologies, an innovative IT company, was recently honored with the prestigious title of 'Microsoft AI Partner of the Year 2023,' acknowledging its leadership and expertise in the field of artificial intelligence. The company believes that Machine Learning (ML) has had a significant impact on the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). ML algorithms have revolutionized the way computers understand and process human language, enabling a wide range of applications.
For a more comprehensive understanding of the company's offerings, it is advisable to reach out to the AI experts at [email protected]. To gain additional information about their recent accomplishment, please refer to the article provided.
0 notes
Text
Brief about Human Translation and Machine Translation- MLTMS INC

Language translation services are professional services that provide translation of written or spoken content from one language to another. These services help individuals, businesses, and organizations overcome language barriers and communicate effectively across different linguistic and cultural contexts. Translation services are typically offered by professional translators or translation agencies that have expertise in multiple languages.
Translation services can cover various types of content, including documents, websites, software, marketing materials, legal contracts, medical records, and more. The process involves converting the text or speech in the source language into the equivalent text or speech in the target language while maintaining the intended meaning and tone.
Translation services can be categorized into two main types: human translation and machine translation.
Human Translation: Professional translators who are bilingual in the source and destination languages carry out human translation. They possess in-depth knowledge of the languages, cultural nuances, and subject matter expertise. Human translators ensure accurate and high-quality translations, taking into account context, idiomatic expressions, and local cultural factors.
Machine Translation: Machine translation relies on automated systems to translate text or speech from one language to another. Machine translation can be further divided into two categories:
a. Rule-based machine translation (RBMT): RBMT uses predefined rules and linguistic databases to translate text. It requires extensive linguistic knowledge and manual rule creation for each language pair.
b. Statistical machine translation (SMT): SMT uses statistical models and algorithms to generate translations based on patterns found in large bilingual corpora. It learns from existing translations to make predictions about how to translate new content.
Recently, neural machine translation (NMT) has emerged as a more advanced approach to machine translation. NMT utilizes deep learning techniques, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or transformer models, to improve translation quality by considering the entire sentence context.
It's worth noting that while machine translation has made significant advancements, it may still produce less accurate and fluent translations compared to human translation, especially for complex or specialized content.
Translation services can be accessed through various channels, including translation agencies, freelance translators, online platforms, and specialized software or applications. The choice of service depends on factors such as the required quality, turnaround time, language pair, domain expertise, and budget.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is Machine Translation?
Machine translation (MT) is the most important innovation in the field of technology. It is basically a task which is used to translate a text from one source language to another. It is referred my a short form of MT. The basic function of MT is performing simple substitution of words in one language to another. It is also used to translate an enormous amount of information, which normally includes millions of words that cannot be translated in a more traditional way. This is widely used by the translation companies to increase the productivity of their translators, it is cost-effective also and they provide post-editing services to their clients.
Machine Translation is not new as it has been existing for a fairly long time. IT surfaced around the 1970s and it surfaced through three ways.
Rule-based Machine Translations (RBMT): 1970s-1990s.
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT): 1990s - 2010s.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT): 2010s - to date.
There are a few types of MT, namely Generic MT, Customizable MT and Adoptive MT. In the generic types, there are platforms like Google Translate, Yandex, Bing and Naver. The advantage of these platforms are companies can provide ad-hoc solutions to millions across the world and also connect to their own systems in the form of APIs. In the Customizable MT, it can be used to train to improve the accuracy of the terminology. This is preferred over the Genric ones because of its almost 100% accuracy. The Adoptive MT is the more reformed in the sense of productivity of the translator. It is pipped to challenge the translation memory technology in the near future.
There are a few approaches which are being used in the Machine Translation. As the translation is based on the linguistic rules, the words will be translated in a linguistic way and mostly it will in the spoken language of the target language.
The types of approaches are Rule-based, Transfer-based Machine Translation, dictionary-based Machine Translation, Statistical based MT, Example-based MT, Hybrid and Neural based MT.
There are quite a few concerns surrounding over MT like many words will have multiple meanings and that’s why the need of a universal dictionary was mooted so that words having two meaning will be dealt with. Due to its problem over the accuracy, it is not being preferred as a teaching tool. The MT also goes through the evaluation process, and it is being calculated by pages by hour basis. They also go through automated tests. The automatic testing metric is called as BLEU ( Bilingual evaluation understudy) and it shows the translation matches with the human translation of the same text. There are other quality metrics such as METOUR, ROGUE, HYSTER and NIST.
MT is the most important feature to come out, but it has its own set of limitations as translations used on platforms like Google Translate are not confidential as the data can be retrieved by anyone. The other thing is the clients should be informed beforehand if MT is being used during the course of the project which has been given to the translation company.
0 notes
Text
Machine Translation Market Unidentified Segments – The Biggest Opportunity Of 2023
Latest business intelligence report released on Global Machine Translation Market, covers different industry elements and growth inclinations that helps in predicting market forecast. The report allows complete assessment of current and future scenario scaling top to bottom investigation about the market size, % share of key and emerging segment, major development, and technological advancements. Also, the statistical survey elaborates detailed commentary on changing market dynamics that includes market growth drivers, roadblocks and challenges, future opportunities, and influencing trends to better understand Machine Translation market outlook. List of Key Players Profiled in the study includes market overview, business strategies, financials, Development activities, Market Share and SWOT analysis are:
Applications Technology (AppTek) (United States)
Asia Online Pte Ltd. (Singapore)
Cloudwords Inc. (United States)
IBM Corporation (United States)
Lighthouse IP Group (United States)
Lingo24 Ltd. (United Kingdom)
Lingotek Inc. (United States)
Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. (United States)
Lucy Software and Services GmbH (Germany)
RWS Holdings (Moravia IT) (United Kingdom)
Pangeanic (Spain)
ProMT (Russia) Over the past few decades, due to increasing international trades across the globe, the need for language translators is needed. In addition to this, manual translators are time-consuming and not totally reliable. Thus, the introduction to machine translators has minimized the time consumed as well as increased the reliability of the machine translators. Machine translation (MT) is an automated translation process by which computer software is used to translate a text from one natural language (such as mostly used language like English) to another language (Italian, Spanish and many others). The increasing demand from numerous applications will further show lucrative growth over the forecasted period. Key Market Trends: Increasing Adoption of Artificially Intelligent Machine Translators
Introduction to Video Localization Leading to Increasing Regional Expansion Opportunities: Time Saving Operations has led to Improved Business Growth
Provides Comparatively Cheaper Solution for Software Solutions Market Growth Drivers: Upsurging Need for Timely and Accurate Translation of Large Amounts
Existence of Larger Developers and Increasing Government Initiatives Assisting Machine Translation Challenges: Hard to Design Automated Translator Based on Human Intelligence and Error Handling Capability The Global Machine Translation Market segments and Market Data Break Down by Type (Rule-Based Machine Translation (RBMT), Statistical Machine Translation (SMT), Example-Based Machine Translation (EBMT), Hybrid Machine Translation (HMT), Neural Machine Translation (MT)), Industry Verticals (IT & Telecommunication, Military & Defense, Legal, E-commerce, Healthcare, Others), Offering (Software, Services {Multi-Domain Machine Translation Services, Specialized Machine Translation Services})
Presented By
AMA Research & Media LLP
0 notes
Text
Machine Translation Market Detailed Strategies, Competitive Landscaping and Developments for next 5 years
Latest study released by AMA Research on Global Machine Translation Market research focuses on latest market trend, opportunities and various future aspects so you can get a variety of ways to maximize your profits. Machine Translation Market predicted until 2027*. Over the past few decades, due to increasing international trades across the globe, the need for language translators is needed. In addition to this, manual translators are time-consuming and not totally reliable. Thus, the introduction to machine translators has minimized the time consumed as well as increased the reliability of the machine translators. Machine translation (MT) is an automated translation process by which computer software is used to translate a text from one natural language (such as mostly used language like English) to another language (Italian, Spanish and many others). The increasing demand from numerous applications will further show lucrative growth over the forecasted period. Some of Key Players included in Machine Translation Market are
Applications Technology (AppTek) (United States)
Asia Online Pte Ltd. (Singapore)
Cloudwords Inc. (United States)
IBM Corporation (United States)
Lighthouse IP Group (United States)
Lingo24 Ltd. (United Kingdom)
Lingotek Inc. (United States)
Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. (United States)
Lucy Software and Services GmbH (Germany)
RWS Holdings (Moravia IT) (United Kingdom)
Pangeanic (Spain)
ProMT (Russia)
Market Trends: Increasing Adoption of Artificially Intelligent Machine Translators
Introduction to Video Localization Leading to Increasing Regional Expansion
Drivers: Upsurging Need for Timely and Accurate Translation of Large Amounts
Existence of Larger Developers and Increasing Government Initiatives Assisting Machine Translation
Challenges: Hard to Design Automated Translator Based on Human Intelligence and Error Handling Capability
Opportunities: Time Saving Operations has led to Improved Business Growth
Provides Comparatively Cheaper Solution for Software Solutions
The titled segments and Market Data are Break Downby Type (Rule-Based Machine Translation (RBMT), Statistical Machine Translation (SMT), Example-Based Machine Translation (EBMT), Hybrid Machine Translation (HMT), Neural Machine Translation (MT)), Industry Verticals (IT & Telecommunication, Military & Defense, Legal, E-commerce, Healthcare, Others), Offering (Software, Services {Multi-Domain Machine Translation Services, Specialized Machine Translation Services})
Presented By
AMA Research & Media LLP
0 notes
Text
Google translate bot text to speech

#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH HOW TO#
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH PORTABLE#
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH FOR ANDROID#
It is able to scan text or a picture using the device and have it translated instantly. In May 2014, Google acquired Word Lens to improve the quality of visual and voice translation. As of February 2010, it was integrated into browsers such as Chrome and was able to pronounce the translated text, automatically recognize words in a picture and spot unfamiliar text and languages.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH PORTABLE#
In January 2010, Google introduced an Android app and iOS version in February 2011 to serve as a portable personal interpreter. Despite this, Google initially did not hire experts to resolve this limitation due to the ever-evolving nature of language. Since SMT uses predictive algorithms to translate text, it had poor grammatical accuracy. The input text had to be translated into English first before being translated into the selected language. Originally, Google Translate was released as a statistical machine translation service. It translates multiple forms of texts and media such as words, phrases and webpages. Google Translate is a web-based free-to-user translation service developed by Google in April 2006. 4.2 Languages in development and beta version.It uses this broader context to help it figure out the most relevant translation, which it then rearranges and adjusts to be more like a human speaking with proper grammar". In November 2016, Google announced that Google Translate would switch to a neural machine translation engine – Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) – which translates "whole sentences at a time, rather than just piece by piece. Its accuracy, which has been criticized and ridiculed on several occasions, has been measured to vary greatly across languages.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH HOW TO#
During a translation, it looks for patterns in millions of documents to help decide which words to choose and how to arrange them in the target language. Rather than translating languages directly, it first translates text to English and then pivots to the target language in most of the language combinations it posits in its grid, with a few exceptions including Catalan-Spanish. Launched in April 2006 as a statistical machine translation service, it used United Nations and European Parliament documents and transcripts to gather linguistic data. As of September 2022, Google Translate supports 133 languages at various levels, and as of April 2016, claimed over 500 million total users, with more than 100 billion words translated daily, after the company stated in May 2013 that it served over 200 million people daily.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH FOR ANDROID#
It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, and an API that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. Google Translate is a multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google to translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. November 15, 2016 5 years ago ( ) (as neural machine translation) April 28, 2006 16 years ago ( ) (as statistical machine translation)

0 notes