#Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#Translation in eDiscovery#Statistical Machine Translation (SMT)#Data Translation in eDiscovery#Legal Data Translation#Neural Machine Translation (NMT)#eDiscovery Data Translations#Machine Translation in eDiscovery
0 notes
Text
I think that people are massively misunderstanding how "AI" works.
To summarize, AI like chatGPT uses two things to determine a response: temperature and likeableness. (We explain these at the end.)
ChatGPT is made with the purpose of conversation, not accuracy (in most cases).
It is trained to communicate. It can do other things, aswell, like math. Basically, it has a calculator function.
It also has a translate function. Unlike what people may think, google translate and chatGPT both use AI. The difference is that chatGPT is generative. Google Translate uses "neural machine translation".
Here is the difference between a generative LLM and a NMT translating, as copy-pasted from Wikipedia, in small text:
Instead of using an NMT system that is trained on parallel text, one can also prompt a generative LLM to translate a text. These models differ from an encoder-decoder NMT system in a number of ways:
Generative language models are not trained on the translation task, let alone on a parallel dataset. Instead, they are trained on a language modeling objective, such as predicting the next word in a sequence drawn from a large dataset of text. This dataset can contain documents in many languages, but is in practice dominated by English text. After this pre-training, they are fine-tuned on another task, usually to follow instructions.
Since they are not trained on translation, they also do not feature an encoder-decoder architecture. Instead, they just consist of a transformer's decoder.
In order to be competitive on the machine translation task, LLMs need to be much larger than other NMT systems. E.g., GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters, while mBART has 680 million and the original transformer-big has “only” 213 million. This means that they are computationally more expensive to train and use.
A generative LLM can be prompted in a zero-shot fashion by just asking it to translate a text into another language without giving any further examples in the prompt. Or one can include one or several example translations in the prompt before asking to translate the text in question. This is then called one-shot or few-shot learning, respectively.
Anyway, they both use AI.
But as mentioned above, generative AI like chatGPT are made with the intent of responding well to the user. Who cares if it's accurate information as long as the user is happy? The only thing chatGPT is worried about is if the sentence structure is accurate.
ChatGPT can source answers to questions from it's available data.
... But most of that data is English.
If you're asking a question about what something is like in Japan, you're asking a machine that's primary goal is to make its user happy what the mostly American (but sure some other English-speaking countries) internet thinks something is like in Japan. (This is why there are errors where AI starts getting extremely racist, ableist, transphobic, homophobic, etc.)
Every time you ask chatGPT a question, you are asking not "Do pandas eat waffles?" but "Do you think (probably an) American would think that pandas eat waffles? (respond as if you were a very robotic American)"
In this article, OpenAI says "We use broad and diverse data to build the best AI for everyone."
In this article, they say "51.3% pages are hosted in the United States. The countries with the estimated 2nd, 3rd, 4th largest English speaking populations—India, Pakistan, Nigeria, and The Philippines—have only 3.4%, 0.06%, 0.03%, 0.1% the URLs of the United States, despite having many tens of millions of English speakers." ...and that training data makes up 60% of chatGPT's data.
Something called "WebText2", aka Everything on Reddit with More Than 3 Upvotes, was also scraped for ChatGPT. On a totally unrelated note, I really wonder why AI is so racist, ableist, homophobic, and transphobic.
According to the article, this data is the most heavily weighted for ChatGPT.
"Books1" and "Books2" are stolen books scraped for AI. Apparently, there is practically nothing written down about what they are. I wonder why. It's almost as if they're avoiding the law.
It's also specifically trained on English Wikipedia.
So broad and diverse.
"ChatGPT doesn’t know much about Norwegian culture. Or rather, whatever it knows about Norwegian culture is presumably mostly learned from English language sources. It translates that into Norwegian on the fly."
hm.
Anyway, about the temperature and likeableness that we mentioned in the beginning!! if you already know this feel free to skip lolz
Temperature:
"Temperature" is basically how likely, or how unlikely something is to say. If the temperature is low, the AI will say whatever the most expected word to be next after ___ is, as long as it makes sense.
If the temperature is high, it might say something unexpected.
For example, if an AI with a temperature of 1 and a temperature of, maybe 7 idk, was told to add to the sentence that starts with "The lazy fox..." they might answer with this.
1:
The lazy fox jumps over the...
7:
The lazy fox spontaneously danced.
The AI with a temperature of 1 would give what it expects, in its data "fox" and "jumps" are close together / related (because of the common sentence "The quick fox jumps over the lazy dog."), and "jumps" and "over" are close as well.
The AI with a temperature 7 gives something much more random. "Fox" and "spontaneously" are probably very far apart. "Spontaneously" and "danced"? Probably closer.
Likeableness:
AI wants all prompts to be likeable. This works in two ways, it must 1. be correct and 2. fit the guidelines the AI follows.
For example, an AI that tried to say "The bloody sword stabbed a frail child." would get flagged being violent. (bloody, stabbed)
An AI that tried to say "Flower butterfly petal bakery." would get flagged for being incorrect.
An AI that said "blood sword knife attack murder violence." would get flagged for both.
An AI's sentence gets approved when it is likeable + positive, and when it is grammatical/makes sense.
Sometimes, it being likeable doesn't matter as much. Instead of it being the AI's job, it usually will filter out messages that are inappropriate.
Unless they put "gay" and "evil" as inappropriate, AI can still be extremely homophobic. I'm pretty sure based on whether it's likeable is usually the individual words, and not the meaning of the sentence.
When AI is trained, it is given a bunch of data and then given prompts to fill, which are marked good or bad.
"The horse shit was stinky."
"The horse had a beautiful mane."
...
...
...
Notice how none of this is "accuracy"? The only knowledge that AI like ChatGPT retains from scraping everything is how we speak, not what we know. You could ask AI who the 51st President of America "was" and it might say George Washington.
Google AI scrapes the web results given for what you searched and summarizes it, which is almost always inaccurate.

soooo accurate. (it's not) (it's in 333 days, 14 hours)
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Generative AI Does not Belong in Fanfiction. What about others?
So I wanted to do a more in depth analysis of AI in fanfiction because I understand there are multiple types, not just generative AI. I am not an expert and all of this information is a quick google search away
TL;DR Natural Language Processing AI is fine, and helps the visually impaired, as long as its not used for Gen AI. Neural Machine Translation you've already been using, but finding a person made translation will always be better. Machine Learning I don't think you could even apply besides training Gen and NLP, so don't even think about trying it. Computer Vision isn't the most applicable and you can get the same thing from having a Beta.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
So this is what allows Chat GPT to understand what you are saying and pump out a semi-coherant answer, same with Character.ai and any chatbot you may use (including Siri). Now this can be used for a multitude of things that aren't Chatbots. It's responsible for text to speech recognition, so sight impaired readers may use this to generate an audio of your fic to listen to. Though as a writer, if you want to check things like tone, just don't read your fic for two weeks and you'll be fine. Or have a Beta.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT)
That's what google translate is, as well as any other instant text translator that isn't run by a person. You've probably used this in your writing before, and had little to no problem with it. In saying that, these translators are trained on a wide sample of language data, and still have inacurate results. Finding an actual translation by a person is both more ethical, and more accurate.
Machine Learning
This is what allows AI algorithms to learn, and what scrapers make their databases for. No.
Computer Vision
This essentially allows computers to "see" things in the real world. Could be tied to visual aid, but not super practical.
Conclusion
AI will always be outperformed by basic human services. The only exception is quick accessibility aid for the visually impaired. Getting a friend (or your future self) to re-read your works will help with grammar, spelling, and tone. Finding an official translator will always be better than an AI one. Other forms of AI just support the previously stated ones. People will always outperform machines, because they still have years to go to have a fraction of the intrinsic understanding we do of the human experience. That it what we embody with our writing, and no matter how much AI is fed, it won't ever be able to understand that. Even if it passes the Turing Test it will still fall short, and in fact still is.
#artificial intelligence#archive of our own#those tags should never be next to each other#fanfiction#anti ai#except for accessibility you guys stay winning
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
A little bit about generative AI in translation
Every single time I see talks about generative AI and how bad it is for people, I can't stop myself but think about how awful it also is for translations.
Sure, generative AI has a huge impact on the environment and on how people think (and how it leads them to think) when using it. But this wall of text isn't about it. It's is about the impact it has on non-english speakers, or non-english natives, in their life.
As you might all know by now, generative AI isn't new, its uses in professionnal fields either (think about the system your dentist uses in order to detect your cavities, that's also generative AI). Not just that, but almost everyone has a use out of Statistical Machine Translation like Google Translate or DeepL, and those use a generative AI.
Statistical machine translation (SMT) works by basically being given a bilingual dictionnary, which leads it to taking each word, translating them, and replacing them based on statistics and other language elements. But while a narrow database can be good at the beginning, it still needs more data in order to be able to translate better. This means needing people using it in order to build it (yes, like for LLMs, it means that the more you use it the more it gains data). This, in essence, is a big problem, as languages do not work the same. The statistical system helps a little with the word order due to grammatical rules, but it still means that translation from a slightly gendered language (like English) to a gendered language (like French) will have a load of problems.
The upgrade from SMT is the neural machine translation (NMT) and instead of taking each words separately, it bases itself on different sentences in both the original and target language whose translations has been "approved". While this leads to better translations, it still needs data to continue improving, which is still what happens in different MT when you tell them the translation is wrong and propose another (logically better) one. But, this external data isn't necessarily good data, which leads to an internal fight between quantity and quality.
So, while NMTs are better than SMTs, they are still flawed, and if you want a proper and thoughtful translation, you'll still need a professionnal.
(I suggest you go read the first 4 pages of Pym's How automation through neural machine translation might change the skill sets of translators* in order to better understand what I am trying to explain here, but also to see how similar it is to LLMs and thus how stupid those AIs really are in term of language and their grammar.)
Now that you know all that, I can get a little bit deeper into my problem with NMT and especially its uses through LLMs.
As you might well know if you have ever learned another language (or tried to), translations are highly contextual, especially in heavily gendered languages like French. This means that if you do not have enough data/context, you'll have a hard time translating a piece properly.
Not just that, but there is roughly 7 100 languages in the world, meaning that you will inevitably need a translator at one point, and this is where MT come in play. MTs allows "common" people to be able to roughly understand things in another language than theirs, 24/7, for free. The better the MT, the better the translation and better the understanding of the original piece (which can be crucial at time).
However, big businesses (I'm thinking about Duolingo, Etsy and Patreon, to name a few I noticed problems with) do not really care about a good translation. This leads to them not only firing part of their non-english speaking staff, translation staff, but also to just... fully change the already existing good translations.
While the majority of english-speaking natives will not notice it (and not care), us non-english-speaking natives end up noticing the major problem everywhere. Not just that, but frankly for some of them, I'm not even sure they're using a NMT system as it looks more like a simple SMT system...
From the list above, let's dive into it a little bit and see some of the consequences.
Duolingo
As you might know on Tumblr (not really on other social medias, apparently), Duolingo fired a huge part of their translation staff to replace them with AI. Not only that, but the remaining staff was moved from translation and proof-reading duty to solely proof-reading (which is basically the pessimistic vision of Wei in his Challenges and Coping Strategies of Translation Technology in an Era of Artificial Intelligence (2018), also cited in Pym 2019).
Their proof-reading task was also to verify that the NMT was "acceptable", which obviously means that even if the translations sounded like someone with a B2 level, it should still be allowed to pass because it was "good enough". Which is... an interesting decision for the number one "let's learn a new language" app, as it will lead people to learn a new language badly (especially since Duolingo's quality already suffered several time through the removal of the grammatical explanation and the change from the tree format to a road format). And hell, even my mother, learning German, has noticed that some translations were garbage, which means that they effectively changed their staffs from every languages, since she learns it through French.
The use of generative AI in the case of Duolingo means that people not only have access to a now subpart quality tool, but also that they will learn a new language badly.
Etsy and Patreon
I'm putting those two together simply because the issue I have with them is virtually the same.
Let's take a look at Patreon's main page, since the disaster starts here.


If you know French, you already have noticed a HUGE problem with this translation (and how clear it is that they are not using a translator for it, professionnal or not is irrelevant here).
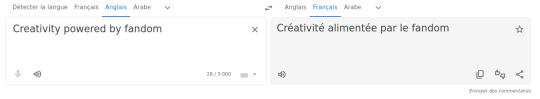
"Creativity powered by fandom" is translated here into "Créativité alimenté par Fandom" and it tells us exactly where the different words come from.
First of, this heavily looks like an SMT and not an NMT since the words do not seem connected to each other.
Créativité, while not ending with an e, is feminine, which means that the adjective alimenté, relative to créativité, should be alimentée instead. Par is good. Fandom has two problem. First of, the capital F shows us that the LLM crawling led it to register the most used version of the word in french, which comes for the website Fandom (since this fucker is everywhere). Which leads to the second problem: as a word, it should be given a definite article, but there isn't any.
Second of, if you only take the French version, Patreon is apparently claiming that "Creativity is powered by Fandom™" and hum... bold assumption, but also factually untrue and there also might be some legal problems here?
Another thing that is killing me is the Pricing tab in the footer.


Priser, as a verb fitting the context of "price" or "deciding on a price for something", is an old term I've actually never seen in recent writing and more or less means estimer (to estimate, to assess), which, as you can see, cannot be a translation for pricing (Tarifs would be a better translation).
Which shows that not only did the LLM just grabbed some random translation but also just... took the French root and went with it.
Not just that, but this is a problem I noticed MONTHS AGO, notably from the Press (Presse) translation to Presser (to press).
And Etsy is no better.


While the word custom as a noun can be synonymous to tradition, it can also be an adjective as in customized.
Etsy is slightly better since they translated press properly, but still, a rather horrendous thing to see when you are supposed to spend money on this website.
Both those businesses decided to apparently put their entire websites through an LLM and just... let it do its thing without checking after it, which essentially meant deleting the previously proper translation and replacing it with a subpar one.
And frankly, I cannot trust those websites with my money. If, despite all their money, they can't be bothered to have one person look at the basic tagging system and translate it properly, nor look at the main page information and have it make sense? Why should I give their mine.
Ok, and?
Well, I think that's pretty fucking bad.
The fact that you cannot really translate things properly is a long and complicated debate (for example, writing an alt for an image can be considered a type of translation), but there is the need, especially on a legal and political level, to translate a piece as accurately as possible in order to be sure that the person who will read or hear your piece understands exactly what you are trying to say.
An example would the issue with Asus (?), that Gamers Nexus talked about and participated in. One of the issues with the warranty system explained wasn't clear and it was misleading, which caused a lot of issues with customers who felt like they were lied to.
They weren't lied to, they were mislead, and this was a result of a choice of words and how they were put. This is one of the reason why, for example, legal documents are worded so weirdly (and why you often need an attorney or else to help you understand them).
And this is roughly what is happening here with businesses using LLMs to translate their websites and other documents.
The translations are bad and people won't understand them properly, but when they'll want to take legal actions, they'll be told that actually, the original document, in its original language, is the only real documents they can use to attack them. And as stated, those documents won't have the same elements in it as the translated one.
Not just that, but in the case of websites such as Patreon and Esty, who work with monetary transactions, it becomes a huge problem.
Not only are we, non-english people, given subpar quality products (I don't which word would be better for that, sorry), we have absolutely no way to know if we even will be helped in case there is a problem.
That has been a problem before, mind you, Tumblr is a great example for it since even if the interface is in French, support is only in English and is given an MT. But with LLMs also handling the translations, and considering the quality of said translations, we have no way to get proper help, if any help is given at all (I'm looking at you, Meta, with your WhatsApp "support").
But here's the kicker. Why are the translations that bad?
Remember the Patreon example? Here it is in Google Translate.
And welp, here it is in DeepL, which is usually better at translating than GTL.

While DeepL does propose the bad translation from Patreon as alternatives, they're both still giving us a good translation.
So if NMTs can translate that well, why are translations on other websites are so bad? Not just that but they clearly just translate word by word, which is what SMTs were that bad at translating (and why your English/German/etc. teacher forbade you to use Google Translate).
How did we reverted back to 2010s level of translation?
The only answer I can possibly give is that LLMs are doing the translations, and apparently LLMs aren't as good at translating as they are at "speaking" and still use a basic statistical system to do so.
I frankly do not have a conclusion to that post, I mostly wanted to complain because such garbage level of translation on major websites is just horrendous. Not just that but I've also never seen anyone complain about it and welp, I guess now I've seen one (myself).
Do what you want with all those information.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Cloud Translation AI Improvements Support 189 Languages

189 languages are now covered by the latest Cloud Translation AI improvements.
Your next major client doesn’t understand you. 40% of shoppers globally will never consider buying from a non-native website. Since 51.6% of internet users speak a language other than English, you may be losing half your consumers.
Businesses had to make an impossible decision up until this point when it came to handling translation use cases. They have to decide between the following options:
Human interpreters: Excellent, but costly and slow
Simple machine translation is quick but lacks subtleties.
DIY fixes: Unreliable and dangerous
The problem with translation, however, is that you need all three, and conventional translation techniques are unable to keep up. Using the appropriate context and tone to connect with people is more important than simply translating words.
For this reason, developed Translation AI in Vertex AI at Google Cloud. Its can’t wait to highlight the most recent developments and how they can benefit your company.
Translation AI: Unmatched translation quality, but in your way
There are two options available in Google Cloud‘s Translation AI:
A necessary set of tools for translation capability is the Translation API Basic. Google Cloud sophisticated Neural Machine Translation (NMT) model allows you to translate text and identify languages immediately. For chat interactions, short-form content, and situations where consistency and speed are essential, Translation AI Basic is ideal.
Advanced Translation API: Utilize bespoke glossaries to ensure terminology consistency, process full documents, and perform batch translations. For lengthy content, you can utilize Gemini-powered Translation model; for shorter content, you can use Adaptive Translation to capture the distinct tone and voice of your business. By using a glossary, improving its industry-leading translation algorithms, or modifying translation forecasts in real time, you can even personalize translations.
What’s new in Translation AI
Increased accuracy and reach
With 189-language support, which now includes Cantonese, Fijian, and Balinese, you can now reach audiences around the world while still achieving lightning-fast performance, making it ideal for call centers and user content.
Smarter adaptive translation
You can use as little as five samples to change the tone and style of your translations, or as many as 30,000 for maximum accuracy.
Choosing a model according to your use case
Depending on how sophisticated your translation use case is, you can select from a variety of methods when using Cloud Translation Advanced. For instance, you can select Adaptive Translation for real-time modification or use NMT model for translating generic text.
Quality without sacrificing
Although reports and leaderboards provide information about the general performance of the model, they don’t show how well a model meets your particular requirements. With the help of the gen AI assessment service, you can choose your own evaluation standards and get a clear picture of how well AI models and applications fit your use case. Examples of popular tools for assessing translation quality include Google MetricX and the popular COMET, which are currently accessible on the Vertex gen AI review service and have a significant correlation with human evaluation. Choose the translation strategy that best suits your demands by comparing models and prototyping solutions.
Google cloud two main goals while developing Translation AI were to change the way you translate and the way you approach translation. Its deliver on both in four crucial ways, whereas most providers only offer either strong translation or simple implementation.
Vertex AI for quick prototyping
Test translations in 189 languages right away. To determine your ideal fit, compare NMT or most recent translation-optimized Gemini-powered model. Get instant quality metrics to confirm your decisions and see how your unique adaptations work without creating a single line of code.
APIs that are ready for production for your current workflows
For high-volume, real-time translations, integrate Translation API (NMT) straight into your apps. When tone and context are crucial, use the same Translation API to switch to Adaptive Translation Gemini-powered model. Both models scale automatically to meet your demands and fit into your current workflows.
Customization without coding
Teach your industry’s unique terminology and phrases to bespoke translation models. All you have to do is submit domain-specific data, and Translation AI will create a unique model that understands your language. With little need for machine learning knowledge, it is ideal for specialist information in technical, legal, or medical domains.
Complete command using Vertex AI
With all-inclusive platform, Vertex AI, you can use Translation AI to own your whole translation workflow. You may choose the models you want, alter how they behave, and track performance in the real world with Vertex AI. Easily integrate with your current CI/CD procedures to get translation at scale that is really enterprise-grade.
Real impact: The Uber story
Uber’s goal is to enable individuals to go anywhere, get anything, and make their own way by utilizing the Google Cloud Translation AI product suite.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#TranslationAI#VertexAI#GoogleCloud#AImodels#genAI#Gemini#CloudTranslationAI#News#Technology#technologynews#technews#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Get started with translation in Azure
You can use Azure AI Translator with a programming language of your choice or the REST API. You can use some of its features with Language Studio.
You can get started with Azure AI Speech with Speech Studio or a programming language of your choice or the REST API.
Azure resources for Azure AI Translator and Azure AI Speech
Before you can use Azure AI Translator or Azure AI Speech, you must provision appropriate resources in your Azure subscription.
There are dedicated Translator and Speech resource types for these services, which you can use if you want to manage access and billing for each service individually.
Alternatively, you can create an Azure AI services resource that provides access to both services through a single Azure resource, consolidating billing and enabling applications to access both services through a single endpoint and authentication key.
Using Azure AI Translator
Azure AI Translator includes the following capabilities:
Text translation - used for quick and accurate text translation in real time across all supported languages.
Document translation - used to translate multiple documents across all supported languages while preserving original document structure.
Custom translation - used to enable enterprises, app developers, and language service providers to build customized neural machine translation (NMT) systems.
Azure AI Translator's application programming interface (API) offers some optional configuration to help you fine-tune the results that are returned, including:
Profanity filtering. Without any configuration, the service will translate the input text, without filtering out profanity. Profanity levels are typically culture-specific but you can control profanity translation by either marking the translated text as profane or by omitting it in the results.
Selective translation. You can tag content so that it isn't translated. For example, you may want to tag code, a brand name, or a word/phrase that doesn't make sense when localized.
You can use Azure AI Translator in Azure AI Foundry, a unified platform for enterprise AI operations, model builders, and application development. The service is also available for use in Microsoft Translator Pro a mobile application, designed specifically for enterprises, that enables seamless real-time speech-to-speech translation.
Speech translation with Azure AI Speech
Azure AI Speech includes the following capabilities:
Speech to text - used to transcribe speech from an audio source to text format.
Text to speech - used to generate spoken audio from a text source.
Speech Translation - used to translate speech in one language to text or speech in another.
0 notes
Text
What Role Will E-commerce Play in the Distribution of Language Translation Devices?
Language Translation Device Market was valued at USD 1.22 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 3.46 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.37% from 2024-2032.
The global Language Translation Device Market is on the cusp of significant expansion, projected to more than double its current valuation in the coming decade. Valued at USD 1.22 billion in 2023, the market is expected to surge to an impressive USD 3.46 billion by 2032, exhibiting a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.37% from 2024 to 2032. This remarkable trajectory is a clear indication of the escalating demand for seamless communication across linguistic barriers, fueled by increasing globalization, international travel, and the relentless advancement of artificial intelligence.
Language Translation Device Market Set for Explosive U.S Growth, Driven by Global Connectivity and AI Innovation
The dynamic growth of the Language Translation Device Market reflects a fundamental shift in how individuals and businesses interact across diverse cultures and geographies. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for immediate and accurate linguistic interpretation has transcended traditional boundaries. This market is not merely about facilitating travel; it's about empowering cross-cultural understanding in vital sectors such as healthcare, education, and international business, making it an indispensable tool for a globally integrated society.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6707
Market Keyplayers:
Jarvisen (Jarvisen Translator 2, Jarvisen Translator Pro)
Langogo Inc (Langogo Genesis, Langogo Summit)
Mymanu CEH Tech LTD (Mymanu CLIK S, Mymanu Translate App)
Sourcenext Inc. (Pocketalk) (Pocketalk Classic, Pocketalk S)
Timekettle (Timekettle WT2 Edge, Timekettle M3)
Travis GT B.V. (Travis Touch Plus, Travis One)
Vasco Electronics LLC (Vasco Translator V4, Vasco Translator E1)
VORMOR (VORMOR T9, VORMOR X5)
Cheetah Mobile, Inc. (CM Translator, CM Smart Pen)
Waverly Labs Inc. (Ambassador Interpreter, Forum App)
IBM (IBM Watson Language Translator, IBM Watson Assistant)
iFlytek (iFLYTEK Smart Translator, iFLYTEK Smart Recorder)
Pocketalk (Pocketalk Classic, Pocketalk S)
Google (Google Translate, Pixel Buds)
Sogou (Sogou Travel Translator, Sogou Voice Translator)
Apple (Apple Translate App, Siri Translation)
Translatelive (Translatelive App, Translatelive Kiosk)
Jovee (Jovee Translator, Jovee Voice Translator)
Microsoft (Microsoft Translator, Skype Translator)
Sonix (Sonix Transcription Software, Sonix Translation Tool)
Amazon (Alexa Translation, Amazon Translate)
Market Analysis
The accelerated pace of globalization and cross-border interactions, both in business and personal travel, is a primary driver for the increased adoption of language translation devices.
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are significantly enhancing the accuracy, speed, and contextual understanding of translations, making these devices more reliable and user-friendly.
The growing need for instant and effective communication in diverse professional settings, including international conferences, healthcare consultations, and emergency services, is boosting demand for specialized translation devices.
Market Trends
Integration of Advanced AI and Real-time Capabilities: The market is witnessing a rapid integration of sophisticated AI models, including neural machine translation (NMT) and large language models (LLMs), enabling more accurate, nuanced, and real-time speech-to-speech translation with improved contextual understanding and even voice synthesis.
Expansion of Wearable and Hands-free Solutions: There's a notable shift towards more discreet and convenient form factors such as translation earbuds and smart glasses. These wearable devices offer hands-free, continuous translation, seamlessly integrating into daily life for effortless communication in various environments.
Market Scope
The Language Translation Device Market encompasses a wide array of innovative products and technologies designed to bridge communication gaps:
Handheld Devices: Portable, dedicated devices offering instant translation of spoken and written language, often with touchscreen interfaces and offline capabilities.
Wearable Devices: Includes smart earbuds, glasses, and other accessories providing real-time, hands-free translation through integration with smartphones or standalone functionality.
Mobile Applications: Smartphone-based apps leveraging advanced AI for translation, often offering features like text scanning, conversation mode, and offline language packs.
Embedded Systems: Translation functionalities integrated into other smart devices, vehicles, and smart home systems, expanding the reach of language accessibility.
Key End-Users: Travelers, business professionals, healthcare providers, educators, and individuals seeking to overcome language barriers in daily life.
Forecast Outlook
The future of the Language Translation Device Market is characterized by a relentless pursuit of seamless and intuitive communication. As AI and machine learning continue to evolve at an unprecedented pace, these devices will become even more sophisticated, offering near-human translation accuracy and deeper contextual understanding. The coming years will see further miniaturization, enhanced integration into our daily lives through wearables, and broader language support, including for low-resource languages. This trajectory will redefine global interaction, making linguistic differences increasingly negligible and fostering unprecedented levels of cross-cultural understanding.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/language-translation-device-market-6707
Conclusion
The Language Translation Device Market's anticipated rise to USD 3.46 billion by 2032 underscores its pivotal role in an increasingly interconnected world. As globalization continues to accelerate, the demand for immediate, accurate, and seamless cross-linguistic communication will only intensify. Businesses and individuals alike are recognizing the transformative power of these devices in facilitating international collaboration, enriching travel experiences, and ensuring equitable access to information and services across diverse linguistic communities.
Related Reports:
U.S. Context-Aware Computing Market Poised for Significant Growth
U.S. Distribution Automation Market Poised for Significant Growth Driven by Grid Modernization and Renewable Energy Integration
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
The Future of Translation Services: Trends to Watch in 2025 and Beyond
The Future of Translation Services: Trends to Watch
In a world where global connectivity is increasing, the role of translation services has never been more crucial. Businesses, governments, and individuals depend on seamless language solutions to communicate across cultures. As we move further into 2025, the future of translation services is being reshaped by technological innovations, AI tools, and the demand for culturally-aware content.
Let’s explore the key trends defining the next chapter of translation and localization services.

1. AI-Powered Translation Tools
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing the translation industry. Tools like neural machine translation (NMT) and large language models (LLMs) now deliver faster, more accurate translations with improved contextual understanding. While human translators remain essential for nuance and cultural accuracy, AI helps scale multilingual content production efficiently.
Keyword focus: AI in translation services, machine translation trends
2. Demand for Real-Time Translation
As global businesses host more live webinars, international meetings, and online events, real-time translation services are gaining traction. Platforms are integrating instant subtitle generation and speech-to-text translation features to bridge language barriers on the spot.
This trend is especially significant for industries like e-learning, virtual tourism, and global e-commerce.
3. Hyper-Localization for Cultural Accuracy
Modern consumers expect content that resonates with their local culture. Translation services are evolving to include hyper-localization, adapting not just the language but also idioms, color symbolism, date formats, and even humor.
This approach ensures content is culturally sensitive and aligns with regional values—a must-have in competitive global markets.
Keyword focus: cultural localization, localization in translation
4. Industry-Specific Expertise
Translation is no longer one-size-fits-all. Whether in legal, medical, technical, or financial sectors, accuracy depends on the translator’s understanding of industry jargon and regulations. As a result, more clients are demanding domain-specific translation services supported by experts.
5. Multilingual SEO Optimization
To succeed in global digital markets, businesses are now integrating multilingual SEO into their translation strategies. Translators work alongside SEO specialists to ensure keywords are localized correctly, allowing websites to rank higher in international search results.
6. Rise of Video and Multimedia Translation
With video content dominating the internet, subtitling, dubbing, and voiceover translation services are seeing explosive growth. Global brands are now localizing YouTube content, reels, and video ads to increase engagement and accessibility across regions.
Keyword focus: video translation, multimedia localization
7. Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, AI is enhancing their efficiency. The future of translation services lies in human-AI collaboration—where professionals use smart tools for first drafts and focus their efforts on editing, contextualizing, and ensuring emotional tone accuracy.
Conclusion
As global communication grows more complex, translation services are evolving into a high-tech, culturally-aware industry. By embracing emerging trends—like AI-powered tools, real-time translation, hyper-localization, and multilingual SEO—businesses can connect more effectively with diverse audiences.
For those working in the translation field or looking to expand globally, staying updated with these trends is essential to future-proofing your strategy.
0 notes
Text
Embracing Automation Translation Integration: Transforming Global Communication
In an increasingly globalized world, the demand for fast, accurate, and cost-effective translation services has never been higher. Businesses are expanding across borders, software products are released in dozens of languages simultaneously, and digital content needs to be localized almost in real-time. Traditional manual translation processes simply can’t keep up. Enter automation translation integration—a game-changing solution that combines machine translation with workflow automation and seamless software integration.
What Is Automation Translation Integration?
Automation translation integration refers to the process of embedding automated translation systems—often powered by AI and machine learning—into digital platforms and business workflows. This integration enables real-time or near-real-time language translation across applications, websites, customer support systems, e-commerce platforms, and more.
It typically involves:
Machine Translation (MT): Using AI engines like Google Translate, DeepL, or custom-trained neural machine translation (NMT) models.
API Integration: Connecting translation tools to content management systems (CMS), customer relationship management (CRM) tools, help desks, and other platforms.
Workflow Automation: Automating the process of content extraction, translation, post-editing, and reintegration.
Quality Assurance Tools: Leveraging AI-based quality checks, glossaries, and translation memories (TMs).
Key Benefits
Speed and Efficiency Automation drastically reduces turnaround times. Whether translating a product catalog or updating UI strings in an app, automated systems can process content in seconds or minutes rather than days.
Scalability Once integrated, the system can handle large volumes of content across multiple languages without significantly increasing cost or workload.
Cost Reduction Human translation can be expensive. Automated systems can reduce reliance on manual translators, especially for low-impact or internal communications.
Consistency Using TMs and glossaries ensures consistent terminology and tone, even when multiple content teams are working in different regions.
Seamless Localization Businesses can integrate translation automation directly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous localization and synchronized global product releases.
Use Cases
E-commerce: Automatic translation of product descriptions, reviews, and support content.
Customer Support: Real-time multilingual chatbots and help desks that respond in the user’s native language.
Software Development: Continuous translation of UI/UX content, help files, and release notes.
Media & Publishing: Rapid localization of news articles, blogs, and multimedia content.
Legal & Compliance: Translating legal documents and policies for international compliance.
Challenges and Considerations
While automation brings numerous advantages, it's not without limitations:
Quality Control: Machine translations can lack nuance, and misinterpretation may occur. Human post-editing is often necessary for high-stakes or customer-facing content.
Security & Privacy: Handling sensitive or proprietary information through third-party translation APIs can pose data protection risks.
Cultural Sensitivity: Automated systems may miss cultural context, idioms, or emotional tone, leading to inappropriate or ineffective translations.
Integration Complexity: Embedding translation systems into existing software or workflows can be technically challenging.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
Choose the Right Tools: Evaluate machine translation engines based on language pairs, domain specificity, and accuracy.
Start Small: Begin with automating translations of low-risk content to test systems and measure ROI.
Use Hybrid Approaches: Combine automation with human oversight—especially for marketing, legal, and public-facing materials.
Maintain Glossaries and TMs: Regularly update linguistic resources to improve consistency and translation quality.
Monitor and Improve: Use feedback loops and AI analytics to continuously refine and optimize the translation workflow.
The Future of Automated Translation
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of automated translation systems. Developments in natural language understanding (NLU), contextual translation, and adaptive learning will bring us closer to human-like translations. Eventually, real-time, culturally-aware, multilingual communication may become the norm across all digital experiences.
Conclusion
Automation translation integration is more than a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic enabler for global growth. By embedding smart translation systems into core operations, businesses can improve communication, expand into new markets, and deliver localized experiences at scale. While challenges remain, a thoughtful, hybrid approach ensures both efficiency and quality, helping organizations navigate the multilingual world with confidence.
0 notes
Text
Unlock Global Markets with AI Translation Services
Reach a wider audience with CaptioningStar’s AI Translation Services. Break language barriers and boost engagement with fast, accurate, and affordable translations for your content.
In today’s interconnected world, language should never be a barrier to success. Whether you’re a business aiming to expand globally, a content creator seeking to engage an international audience, or an educator preparing multilingual content, translation is key. However, manual translation can be costly and time-consuming. Enter AI Translation Services—a modern solution that offers fast, accurate, and cost-effective translations for all your needs.
What Are AI Translation Services?
AI Translation Services utilize cutting-edge artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to translate text automatically from one language to another. These systems are powered by massive datasets that help the AI understand language patterns, context, and nuances. Whether you're translating website content, product descriptions, or video captions, AI Translation Services provide an efficient way to make your content accessible across multiple languages.
With AI translation, you can expand your reach to global audiences in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional translation methods.
Why Choose AI Translation Services?
Speed and Efficiency: Traditional translations can take weeks, but AI Translation Services can deliver instant results, ensuring your content reaches a global audience quickly. This is particularly beneficial for businesses and creators who need content translated on tight deadlines.
Affordable: Manual translation services are often expensive, especially for large volumes of content. AI Translation Services offer an affordable alternative, providing high-quality translations without the hefty price tag.
Accuracy: AI models have evolved significantly and are capable of delivering highly accurate translations. By understanding context and tone, AI Translation Services ensure that the meaning of your content remains intact while adapting it for different languages.
Global Reach: AI Translation Services break down language barriers, making your content accessible to a much wider audience. Whether it’s for business or entertainment, translating content into multiple languages increases engagement and opens doors to international markets.
Scalability: Need to translate hundreds or thousands of pages? AI Translation Services can easily handle large-scale translation projects, providing consistent results across all your content without any delays.
How Do AI Translation Services Work?
AI translation works through neural machine translation (NMT) and deep learning. These technologies allow AI to understand and translate words, phrases, and sentences in context. AI systems are trained on extensive multilingual data to ensure high-quality results that capture the meaning and tone of the original text.
Once the translation is complete, many AI Translation Services offer an option for human review or editing to ensure the translation fits the desired quality standard, especially for complex or specialized content.
Benefits of AI Translation Services
Faster Turnaround: AI translations happen almost instantly, so you can share your content with a global audience without delay.
Enhanced SEO: Translated content boosts your site’s search engine rankings in multiple languages, helping you gain visibility in diverse markets.
Broader Audience: By offering your content in several languages, you ensure your message is accessible to people across the world, increasing engagement and reach.
Why AI Translation Services Are a Game-Changer
The ability to reach a global audience is no longer just a luxury—it’s a necessity. With AI Translation Services, you can make your content available in multiple languages quickly, accurately, and affordably. CaptioningStar’s AI translation technology allows you to maintain quality while significantly reducing costs and turnaround times, ensuring you never miss out on international opportunities.
0 notes
Text
The Benefits of Learning Chinese Translation for Global Communication
Description: Exploring the advantages of mastering Chinese translation in today’s interconnected world, including career opportunities, cultural understanding, and cognitive benefits.
Why Chinese Translation Matters in a Globalized World
In an era where cross-border communication is essential, Chinese translation plays a pivotal role. With over 1.3 billion native speakers, Mandarin Chinese is the most spoken language globally. Businesses, governments, and individuals increasingly rely on accurate Chinese translation to bridge linguistic gaps.
Learning Chinese translation not only enhances professional prospects but also fosters deeper cultural appreciation. As China’s influence grows in economics, technology, and diplomacy, the demand for skilled translators rises. Whether for trade agreements, academic research, or tourism, proficiency in Chinese translation is a valuable asset.
Career Opportunities in Chinese Translation
The demand for Chinese translation experts spans multiple industries:
Business & Trade – Companies expanding into Chinese markets need translators for contracts, negotiations, and marketing.
Diplomacy & International Relations – Governments seek bilingual professionals for diplomatic communications.
Technology & Localization – Tech firms require Chinese translation for software, apps, and user manuals.
Media & Entertainment – Subtitling, dubbing, and content localization rely on skilled translators.
Mastering Chinese translation can open doors to high-paying roles in multinational corporations, NGOs, and government agencies.
Cognitive and Cultural Benefits of Learning Chinese Translation
Beyond career advantages, studying Chinese translation enhances cognitive abilities:
Improved Memory – Learning Chinese characters strengthens memory retention.
Enhanced Multitasking – Switching between languages boosts mental flexibility.
Cultural Insight – Translation deepens understanding of Chinese history, literature, and traditions.
Engaging with Chinese translation also promotes empathy by exposing learners to different worldviews.
Challenges and Tips for Mastering Chinese Translation
While rewarding, Chinese translation presents unique difficulties:
Complex Characters – Unlike alphabetic languages, Chinese uses logograms requiring memorization.
Tonal Variations – Mandarin’s four tones change word meanings, demanding precise pronunciation.
Idiomatic Expressions – Direct translations often fail; cultural context is essential.
Tips for Success:
Practice Daily – Use flashcards for characters and tones.
Immerse Yourself – Watch Chinese films, read news, and converse with native speakers.
Leverage Technology – Translation apps can aid learning but shouldn’t replace human nuance.
The Future of Chinese Translation in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is transforming Chinese translation with tools like neural machine translation (NMT). However, human translators remain irreplaceable for:
Contextual Accuracy – AI struggles with idioms, humor, and cultural references.
Ethical Nuances – Sensitive content (legal, medical) requires human judgment.
While AI aids efficiency, mastering Chinese translation ensures adaptability in an evolving job market.
Conclusion: Embracing Chinese Translation for a Connected Future
As global interactions increase, Chinese translation becomes a critical skill. From career growth to cognitive enrichment, its benefits are vast. By overcoming challenges and leveraging both traditional and technological methods, learners can thrive in a multilingual world.
Whether for professional advancement or personal growth, investing in Chinese translation is an investment in the future.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Rise of Machine Translation: A Boon or a Threat to Professional Translators? The translation industry is undergoing a seismic shift. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine translation (MT) tools like Google Translate, DeepL, and ChatGPT, professional translators face both new opportunities and significant challenges. While automation enhances efficiency and accessibility, it also raises concerns about quality, job security, and the overall value of human translation. Is machine translation a helpful assistant, or is it slowly replacing skilled linguists? The Growth of Machine Translation Machine translation has made remarkable progress in recent years. Neural machine translation (NMT) has significantly improved accuracy, making it easier for individuals and businesses to access quick translations at little to no cost. Companies now integrate AI into their workflows to cut costs and speed up processes, leading to an increased reliance on automated translation solutions. The Impact on Professional Translators While machine translation offers efficiency, it falls short in key areas where human expertise is essential. Cultural nuances, contextual understanding, and industry-specific terminology often require a level of precision that AI alone cannot achieve. 1. Quality and Accuracy Concerns: MT systems frequently struggle with idiomatic expressions, complex sentence structures, and nuanced meanings. A mistranslated phrase in medical or legal documents can have serious consequences. 2. Lower Pay and Job Insecurity: As companies adopt MT, many expect human translators to work as post-editors for lower wages rather than performing full translations. This shift has led to reduced rates for professional translators, making it harder to sustain a career in the industry. 3. Erosion of Language Expertise: Overreliance on AI could diminish the role of skilled linguists, leading to a decline in high-quality, human-crafted translations. If companies prioritize cost savings over linguistic excellence, the industry risks losing a wealth of cultural and linguistic knowledge. The Role of Human Translators in the AI Era Despite the rise of machine translation, human translators remain indispensable. Their expertise ensures accurate, culturally appropriate translations that machines cannot fully replicate. The key to adapting in this evolving industry is to embrace technology as a tool rather than view it as a competitor. At Selica, we uphold the importance of skilled human translation, combining deep industry knowledge with modern tools to deliver high-quality, meaningful results. 1. Specialization Matters: Translators who focus on niche industries such as medical, legal, or technical fields will remain in demand due to the need for high precision and expert knowledge. 2. Post-Editing as a Skill: While post-editing machine translation (PEMT) is not always ideal, developing this skill can help translators stay relevant and negotiate better compensation. 3. Leveraging Technology: Using computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools and AI-powered solutions can help translators improve productivity without compromising quality. The Future of the Translation Industry The future of the translation industry lies in a balance between human expertise and technological advancements. Instead of viewing machine translation as a threat, professionals can adapt by refining their skills, specializing in complex fields, and educating clients on the benefits of high-quality human translation. At Selica, we believe that while AI-driven translation tools continue to evolve, the human touch remains irreplaceable. Translation is not just about converting words—it’s about preserving meaning, culture, and clarity. The challenge for today’s translators is to find their place in this changing landscape—embracing innovation while championing the irreplaceable value of human expertise. Learn more about our approach at www.selicaie.com.

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Exploring Arabic Machine Translation
Arabic Machine Translation plays a key role in breaking language barriers between Arabic and other languages. As technology evolves, machine translation has become an essential tool for businesses, researchers, and everyday users who need quick and understandable translations. However, translating Arabic — a language known for its complexity and rich structure — presents unique challenges that require thoughtful solutions.
What is Arabic Machine Translation?
Arabic Machine Translation refers to the process of using computer algorithms to automatically translate text between Arabic and other languages. This can include translating Arabic to English, French, or even other dialects within the Arabic language itself. The goal is to create translations that are not only grammatically correct but also clear and meaningful.
Why Arabic Translation is Challenging
Arabic is a highly complex language with unique features that make it different from many other languages. For example, Arabic is written from right to left, has a rich root-based word system, and includes a variety of dialects alongside Modern Standard Arabic. Additionally, words often change form based on context, gender, and grammatical structure.
Machine translation systems must account for these complexities. A single Arabic word can carry multiple meanings depending on the sentence, which makes it hard for algorithms to select the correct translation without deeper contextual understanding.
Types of Arabic Machine Translation Systems
Rule-Based Systems – These systems rely on predefined linguistic rules and dictionaries to translate words and phrases. While they work well for simple sentences, they often struggle with more complex structures and idioms.
Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) – This approach analyzes large volumes of bilingual text to find patterns and predict the most likely translations. Though effective, SMT can produce awkward or incorrect translations when context is unclear.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) – A more advanced method that uses artificial intelligence to learn from vast amounts of data. NMT systems consider entire sentences, improving fluency and accuracy. This approach is now widely used by major translation services like Google Translate and Microsoft Translator.
Common Issues in Arabic Machine Translation
Dialect Confusion – Arabic has many regional dialects, such as Egyptian, Levantine, and Gulf Arabic. Machine translation systems trained on Modern Standard Arabic may struggle to understand dialectal phrases or slang.
Ambiguity – Words with multiple meanings can confuse translation algorithms. For example, the word كتب (kataba) means wrote, but the same root can form كتاب (kitab), meaning book. Without context, the system might choose the wrong meaning.
Grammar and Sentence Structure – Arabic often places verbs before subjects, while English typically does the opposite. Translating directly without restructuring the sentence can lead to awkward phrasing.
Cultural Nuances – Some Arabic expressions don't have direct equivalents in other languages. A literal translation may sound odd or lose the intended meaning entirely.
Improving Arabic Machine Translation
To improve Arabic Machine Translation, developers continue refining translation models and expanding language databases. Training algorithms on more diverse datasets, including different dialects and specialized terminology, helps increase accuracy. Additionally, combining machine translation with human post-editing ensures better quality — especially for professional content like legal documents or medical instructions.
Final Thoughts
Arabic Machine Translation has made impressive progress, making communication across languages faster and more accessible. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in technology and data collection are helping to create more accurate, natural, and culturally sensitive translations. As machine translation evolves, it will continue to play an important role in connecting Arabic speakers with the rest of the world.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of AI in Language Translation: How PDF AI Translate is Revolutionizing Communication
Description: Explore the transformative role of AI in language translation, with a focus on PDF AI Translate technology. Discover how this innovation is breaking down language barriers and enhancing global communication.
Introduction
In the digital age, the ability to communicate across languages is more important than ever. As businesses expand globally and individuals connect across borders, the demand for efficient and accurate translation tools has skyrocketed. Among the most significant advancements in this field is PDF AI Translate, a technology that leverages artificial intelligence to translate documents seamlessly. This article delves into the evolution of AI in language translation, the mechanics of PDF AI Translate, and its impact on various sectors.
The Evolution of AI in Language Translation
The journey of AI in language translation began with simple rule-based systems that relied on predefined grammatical rules and dictionaries. These early systems, while groundbreaking at the time, were limited in their ability to handle the nuances of human language. The advent of statistical machine translation (SMT) in the 1990s marked a significant leap forward. SMT systems used large corpora of bilingual text to predict the most likely translation, improving accuracy and fluency.
However, the real game-changer came with the introduction of neural machine translation (NMT) in the mid-2010s. NMT systems, powered by deep learning algorithms, revolutionized the field by enabling more context-aware and natural-sounding translations. Today, AI-driven translation tools like PDF AI Translate are pushing the boundaries even further, offering real-time, high-quality translations for a wide range of document types.
How PDF AI Translate Works
PDF AI Translate is a cutting-edge technology that combines the power of AI with the versatility of PDF documents. The process begins with the extraction of text from the PDF file, which is then fed into an AI-driven translation engine. This engine, often based on NMT, analyzes the text, considers the context, and generates a translation that is both accurate and fluent.
One of the key advantages of PDF AI Translate is its ability to preserve the original formatting of the document. This is particularly important for legal, medical, and technical documents, where the layout and structure are crucial. Additionally, PDF AI Translate can handle complex elements such as tables, images, and embedded fonts, ensuring that the translated document is as close to the original as possible.
Applications of PDF AI Translate
The applications of PDF AI Translate are vast and varied, spanning multiple industries. In the business world, companies use this technology to translate contracts, reports, and marketing materials, enabling them to operate seamlessly in international markets. Educational institutions leverage PDF AI Translate to make research papers and academic resources accessible to a global audience.
In the legal sector, accurate translation of documents is paramount. PDF AI Translate ensures that legal texts are translated with precision, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and legal disputes. Similarly, in the medical field, the technology is used to translate patient records, research studies, and pharmaceutical documentation, facilitating better healthcare outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, PDF AI Translate is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for bias in AI-driven translations. Since these systems learn from existing data, they may inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the training material. Additionally, while PDF AI Translate excels at handling common languages, it may struggle with less widely spoken languages or dialects.
Looking ahead, the future of PDF AI Translate is promising. Advances in AI and machine learning are expected to further enhance the accuracy and capabilities of translation tools. We can anticipate more sophisticated context-aware systems, improved handling of rare languages, and greater integration with other technologies such as voice recognition and augmented reality.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI in language translation has been nothing short of remarkable. From rudimentary rule-based systems to the sophisticated PDF AI Translate technology we have today, the journey has been marked by continuous innovation and improvement. As we move forward, PDF AI Translate will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in breaking down language barriers and fostering global communication. Whether in business, education, law, or healthcare, the impact of this technology is profound and far-reaching, heralding a new era of interconnectedness and understanding.
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI and machine translation in life science translation
Key technologies in AI-powered translation
AI-powered translation technologies have revolutionized the life sciences industry, enabling more efficient and accurate translation processes. Below are some of the key technologies driving this transformation.
Neural Machine Translation (NMT): Advanced MT engines like Google Translate, DeepL, and industry-specific MT solutions enhance translation speed and accuracy.
AI-powered CAT Tools: Platforms such as Trados, MemoQ, and Smartcat integrate AI to improve translation memory suggestions and terminology management.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI can analyze context to produce more accurate translations, reducing common errors in medical texts.
Post-Editing Machine Translation (PEMT): Human translators still play a vital role in reviewing and refining AI-generated translations to ensure precision and compliance.
These technologies have drastically improved efficiency in life science translations by automating many aspects of the translation process, reducing turnaround times, and enhancing consistency. However, despite these advancements, human intervention remains crucial to ensure that translations meet the stringent accuracy and regulatory requirements of the life sciences industry. AI can process large volumes of text quickly, but expert linguists and subject matter specialists are needed to validate terminology, context, and compliance with medical and pharmaceutical standards.
Read more: https://lotus-localize.com/the-role-of-ai-and-machine-translation-in-revolutionizing-life-science-translation/
0 notes