#Teradata to BigQuery
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market in the United States entering an era of unstoppable scalability
Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 17.51 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 77.65 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.07% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is experiencing robust expansion as enterprises prioritize scalability, real-time access, and cost-efficiency in data management. Organizations across industries are shifting from traditional databases to cloud-native environments to streamline operations and enhance agility, creating substantial growth opportunities for vendors in the USA and beyond.
U.S. Market Sees High Demand for Scalable, Secure Cloud Database Solutions
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market continues to evolve with increasing demand for managed services, driven by the proliferation of data-intensive applications, remote work trends, and the need for zero-downtime infrastructures. As digital transformation accelerates, businesses are choosing DBaaS platforms for seamless deployment, integrated security, and faster time to market.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6586
Market Keyplayers:
Google LLC (Cloud SQL, BigQuery)
Nutanix (Era, Nutanix Database Service)
Oracle Corporation (Autonomous Database, Exadata Cloud Service)
IBM Corporation (Db2 on Cloud, Cloudant)
SAP SE (HANA Cloud, Data Intelligence)
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (RDS, Aurora)
Alibaba Cloud (ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB)
MongoDB, Inc. (Atlas, Enterprise Advanced)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB)
Teradata (VantageCloud, ClearScape Analytics)
Ninox (Cloud Database, App Builder)
DataStax (Astra DB, Enterprise)
EnterpriseDB Corporation (Postgres Cloud Database, BigAnimal)
Rackspace Technology, Inc. (Managed Database Services, Cloud Databases for MySQL)
DigitalOcean, Inc. (Managed Databases, App Platform)
IDEMIA (IDway Cloud Services, Digital Identity Platform)
NEC Corporation (Cloud IaaS, the WISE Data Platform)
Thales Group (CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager, Data Protection on Demand)
Market Analysis
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is being shaped by rising enterprise adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, growing volumes of unstructured data, and the rising need for flexible storage models. The shift toward as-a-service platforms enables organizations to offload infrastructure management while maintaining high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Key players in the U.S. are focusing on vertical-specific offerings and tighter integrations with AI/ML tools to remain competitive. In parallel, European markets are adopting DBaaS solutions with a strong emphasis on data residency, GDPR compliance, and open-source compatibility.
Market Trends
Growing adoption of NoSQL and multi-model databases for unstructured data
Integration with AI and analytics platforms for enhanced decision-making
Surge in demand for Kubernetes-native databases and serverless DBaaS
Heightened focus on security, encryption, and data governance
Open-source DBaaS gaining traction for cost control and flexibility
Vendor competition intensifying with new pricing and performance models
Rise in usage across fintech, healthcare, and e-commerce verticals
Market Scope
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market offers broad utility across organizations seeking flexibility, resilience, and performance in data infrastructure. From real-time applications to large-scale analytics, the scope of adoption is wide and growing.
Simplified provisioning and automated scaling
Cross-region replication and backup
High-availability architecture with minimal downtime
Customizable storage and compute configurations
Built-in compliance with regional data laws
Suitable for startups to large enterprises
Forecast Outlook
The market is poised for strong and sustained growth as enterprises increasingly value agility, automation, and intelligent data management. Continued investment in cloud-native applications and data-intensive use cases like AI, IoT, and real-time analytics will drive broader DBaaS adoption. Both U.S. and European markets are expected to lead in innovation, with enhanced support for multicloud deployments and industry-specific use cases pushing the market forward.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/cloud-database-and-dbaas-market-6586
Conclusion
The future of enterprise data lies in the cloud, and the Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is at the heart of this transformation. As organizations demand faster, smarter, and more secure ways to manage data, DBaaS is becoming a strategic enabler of digital success. With the convergence of scalability, automation, and compliance, the market promises exciting opportunities for providers and unmatched value for businesses navigating a data-driven world.
Related reports:
U.S.A leads the surge in advanced IoT Integration Market innovations across industries
U.S.A drives secure online authentication across the Certificate Authority Market
U.S.A drives innovation with rapid adoption of graph database technologies
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Mail us: [email protected]
#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market Growth#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market Scope
0 notes
Text
IoT Analytics Market Analysis: Size, Share, Scope, Forecast Trends & Industry Report 2032
The IoT Analytics Market was valued at USD 26.90 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 180.36 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 23.60% from 2024-2032.
The Internet of Things (IoT) Analytics Market is witnessing exponential growth as organizations worldwide increasingly rely on connected devices and real-time data to drive decision-making. As the number of IoT-enabled devices surges across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, retail, automotive, and smart cities, the demand for analytics solutions capable of processing massive data streams is at an all-time high. These analytics not only help in gaining actionable insights but also support predictive maintenance, enhance customer experiences, and optimize operational efficiencies.
IoT Analytics Market Size, Share, Scope, Analysis, Forecast, Growth, and Industry Report 2032 suggests that advancements in cloud computing, edge analytics, and AI integration are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in IoT ecosystems. The ability to process and analyze data at the edge, rather than waiting for it to travel to centralized data centers, is allowing businesses to act in near real-time. This acceleration in data-driven intelligence is expected to reshape entire industries by improving responsiveness and reducing operational lags.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/5493
Market Keyplayers:
Accenture (myConcerto, Accenture Intelligent Platform Services)
Aeris (Aeris IoT Platform, Aeris Mobility Suite)
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS IoT Core, AWS IoT Analytics)
Cisco Systems, Inc. (Cisco IoT Control Center, Cisco Kinetic)
Dell Inc. (Dell Edge Gateway, Dell Technologies IoT Solutions)
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP (HPE IoT Platform, HPE Aruba Networks)
Google (Google Cloud IoT, Google Cloud BigQuery)
OpenText Web (OpenText IoT Platform, OpenText AI & IoT)
Microsoft (Azure IoT Suite, Microsoft Power BI)
Oracle (Oracle IoT Cloud, Oracle Analytics Cloud)
PTC (ThingWorx, Vuforia)
Salesforce, Inc. (Salesforce IoT Cloud, Salesforce Einstein Analytics)
SAP SE (SAP Leonardo IoT, SAP HANA Cloud)
SAS Institute Inc. (SAS IoT Analytics, SAS Visual Analytics)
Software AG (Cumulocity IoT, webMethods)
Teradata (Teradata Vantage, Teradata IntelliCloud)
IBM (IBM Watson IoT, IBM Maximo)
Siemens (MindSphere, Siemens IoT 2040 Gateway)
Intel (Intel IoT Platform, Intel Analytics Zoo)
Honeywell (Honeywell IoT Platform, Honeywell Forge)
Bosch (Bosch IoT Suite, Bosch Connected Industry)
Trends Shaping the IoT Analytics Market
The evolution of the IoT analytics market is marked by key trends that highlight the sector’s transition from basic connectivity to intelligent automation and predictive capabilities. One of the most significant trends is the growing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into analytics platforms. These technologies enable smarter data interpretation, anomaly detection, and more accurate forecasting across various IoT environments.
Another major trend is the shift toward edge analytics, where data processing is performed closer to the source. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making it ideal for industries where time-sensitive data is critical—such as healthcare (real-time patient monitoring) and industrial automation (machine health monitoring). Additionally, multi-cloud and hybrid infrastructure adoption is growing as companies seek flexibility, scalability, and resilience in how they handle vast IoT data streams.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/5493
Market Segmentation:
By Type
Descriptive Analytics
Diagnostic Analytics
Predictive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics
By Component
Solution
Services
By Organization Size
Small & Medium Enterprises
Large Enterprises
By Deployment
On-Premises
Cloud
By Application
Energy Management
Predictive Maintenance
Asset Management
Inventory Management
Remote Monitoring
Others
By End Use
Manufacturing
Energy & Utilities
Retail & E-commerce
Healthcare & Life Sciences
Transportation & Logistics
IT & Telecom
Market Analysis
The IoT analytics market is expected to grow significantly, driven by the proliferation of connected devices and the need for real-time data insights. According to recent forecasts, the market is projected to reach multibillion-dollar valuations by 2032, growing at a robust CAGR. Key factors contributing to this growth include the increasing use of smart sensors, 5G deployment, and a shift toward Industry 4.0 practices across manufacturing and logistics sectors.
Enterprises are rapidly adopting IoT analytics to streamline operations, reduce costs, and create new revenue streams. In sectors such as smart agriculture, analytics platforms help monitor crop health and optimize water usage. In retail, real-time customer behavior data is used to enhance shopping experiences and inventory management. Governments and municipalities are also leveraging IoT analytics for smart city applications like traffic management and energy efficiency.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the IoT analytics market holds vast potential as the digital transformation of industries accelerates. Innovations such as digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets that use real-time data—will become more prevalent, enabling deeper analytics and simulation-driven decision-making. The combination of 5G, IoT, and AI will unlock new use cases in autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and industrial robotics, where instantaneous insights are essential.
The market is also expected to see increased regulatory focus and data governance, particularly in sectors handling sensitive information. Ensuring data privacy and security while maintaining analytics performance will be a key priority. As a result, vendors are investing in secure-by-design platforms and enhancing their compliance features to align with global data protection standards.
Moreover, the democratization of analytics tools—making advanced analytics accessible to non-technical users—is expected to grow. This shift will empower frontline workers and decision-makers with real-time dashboards and actionable insights, reducing reliance on centralized data science teams. Open-source platforms and API-driven ecosystems will also support faster integration and interoperability across various IoT frameworks.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/iot-analytics-market-5493
Conclusion
The IoT analytics market is positioned as a cornerstone of the digital future, with its role expanding from simple monitoring to predictive and prescriptive intelligence. As the volume, variety, and velocity of IoT data continue to increase, so does the need for scalable, secure, and intelligent analytics platforms. Companies that leverage these capabilities will gain a significant competitive edge, transforming how they operate, interact with customers, and drive innovation.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Data Lakes and Data Warehouses

Introduction
Businesses generate vast amounts of data from various sources.
Understanding Data Lakes and Data Warehouses is crucial for effective data management.
This blog explores differences, use cases, and when to choose each approach.
1. What is a Data Lake?
A data lake is a centralized repository that stores structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Stores raw data without predefined schema.
Supports big data processing and real-time analytics.
1.1 Key Features of Data Lakes
Scalability: Can store vast amounts of data.
Flexibility: Supports multiple data types (JSON, CSV, images, videos).
Cost-effective: Uses low-cost storage solutions.
Supports Advanced Analytics: Enables machine learning and AI applications.
1.2 Technologies Used in Data Lakes
Cloud-based solutions: AWS S3, Azure Data Lake Storage, Google Cloud Storage.
Processing engines: Apache Spark, Hadoop, Databricks.
Query engines: Presto, Trino, Amazon Athena.
1.3 Data Lake Use Cases
✅ Machine Learning & AI: Data scientists can process raw data for model training. ✅ IoT & Sensor Data Processing: Real-time storage and analysis of IoT device data. ✅ Log Analytics: Storing and analyzing logs from applications and systems.
2. What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a structured repository optimized for querying and reporting.
Uses schema-on-write (structured data stored in predefined schemas).
Designed for business intelligence (BI) and analytics.
2.1 Key Features of Data Warehouses
Optimized for Queries: Structured format ensures faster analysis.
Supports Business Intelligence: Designed for dashboards and reporting.
ETL Process: Data is transformed before loading.
High Performance: Uses indexing and partitioning for fast queries.
2.2 Technologies Used in Data Warehouses
Cloud-based solutions: Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse.
Traditional databases: Teradata, Oracle Exadata.
ETL Tools: Apache Nifi, AWS Glue, Talend.
2.3 Data Warehouse Use Cases
✅ Enterprise Reporting: Analyzing sales, finance, and marketing data. ✅ Fraud Detection: Banks use structured data to detect anomalies. ✅ Customer Segmentation: Retailers analyze customer behavior for personalized marketing.
3. Key Differences Between Data Lakes and Data Warehouses
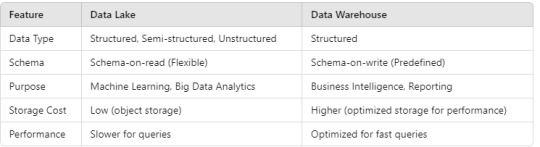
4. Choosing Between a Data Lake and Data Warehouse
Use a Data Lake When:
You have raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data.
You need machine learning, IoT, or big data analytics.
You want low-cost, scalable storage.
Use a Data Warehouse When:
You need fast queries and structured data.
Your focus is on business intelligence (BI) and reporting.
You require data governance and compliance.
5. The Modern Approach: Data Lakehouse
Combines benefits of Data Lakes and Data Warehouses.
Provides structured querying with flexible storage.
Popular solutions: Databricks Lakehouse, Snowflake, Apache Iceberg.
Conclusion
Data Lakes are best for raw data and big data analytics.
Data Warehouses are ideal for structured data and business reporting.
Hybrid solutions (Lakehouses) are emerging to bridge the gap.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/data-science-course-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
BigQuery service UDFs facilitate data manipulations globally

What is user defined function?
You can use a SQL statement or JavaScript code to create a function with a user-defined function (UDF). A UDF receives input in the form of columns, processes the data, and outputs the outcome as a value.
UDFs can be defined as temporary or persistent. Temporary UDFs are limited to the duration of a single query, but persistent UDFs can be utilized in repeated queries.
BigQuery user defined functions
BigQuery users, celebrate! Google Cloud is happy to announce that BigQuery User Defined Functions (UDFs) from the well-liked bigquery-utils repo may now be found in all BigQuery regions thanks to community contributions. With this expansion, you may use these strong capabilities to expedite your data transformations regardless of where your data warehouse workloads are being executed.
A feature of SQL that BigQuery supports, user-defined functions (UDFs) allow a user to design a function using JavaScript or another SQL expression. These functions take input columns as input, execute the actions, and return a value representing the outcome of the activities.
Migration and Community Functions
Community-contributed functions that carry out various BigQuery tasks can be found in the community subdirectory. The subfolders teradata, redshift, and oracle in the migration folder provide community-contributed functions that mimic the functionality of proprietary functions in other data warehouses. You can achieve feature parity when migrating data from another data warehouse to BigQuery with the aid of these functions.
Making Use of the UDFs
Every UDF in this repository can be found on publicly accessible datasets via the bqutil project. The shared UDFs in the US multi-region can then be accessed by queries using bqutil.<dataset>.<function>(). The public deployment of UDFs from this repository extends to all other regions that BigQuery facilitates. To utilise a UDF outside of the US multi-region, you can refer to it using a dataset that has a regional suffix: bqutil.<dataset>_<region>.<function>().
Putting the UDFs to Use
This repository’s UDFs are all kept up to date in SQLX format. By using this format, the Dataform CLI tool may be used to test and deploy the UDFs.
When installing the UDFs, the Dataform CLI is a helpful tool because it:
Permits the UDFs to be tested unit
Detects dependencies between UDFs automatically and then builds them in the proper sequence.
Installs the UDFs across several environments (dev, test, prod) with ease.
What are UDFs, and why is it important to know?
You can write custom functions in BigQuery called UDFs to perform particular tasks. Adapted to your own requirements, they function similarly to built-in SQL functions. You must parse complicated strings. Do you need to conduct computations that conventional SQL does not provide easily? UDFs are the solution. In the past, the bqutil project’s community-contributed UDFs were accessible to the general public but were restricted to the US multi-region. This required additional steps in their workflows for users from outside of the US who had to manually deploy UDFs to their own regional dataset within their own project. Google is removing this restriction today by making community-contributed BigQuery UDFs publicly available.
Why is this growth significant to clients?
Worldwide reach: Regardless of where your BigQuery data is stored, you may now use the extensive library of user-developed UDFs. This really democratises the use of sophisticated data transformation methods. Community cooperation: This growth demonstrates the effectiveness of open-source cooperation. It illustrates the collaborative efforts between Google Cloud and the broader community to create BigQuery the most user-friendly and adaptable data warehousing solution available.
User Defined Functions in SQL
In SQL, user-defined functions (UDFs) are basically custom functions you write to carry out particular operations inside your database. They take inputs (parameters), process them, and return an output result or group of values in a manner akin to functions in programming languages.
Below is a summary of the main features of UDFs in SQL:
UDFs Types:
The most popular kind of functions are scalar ones, which return a single value (such as a calculated value or formatted text).
Functions with table values: These, like a database table, return the entire collection of results.
Advantages of UDFs
Code reusability: Creating a UDF allows you to call it again in your SQL queries, which helps to organise your code and cut down on repetition.
Modular programming: UDFs improve code readability and maintainability by breaking down complicated logic into smaller, more manageable functions.
Encapsulation: UDFs improve data security by encapsulating certain functions and concealing internal implementation details.
Performance optimisation: Pre-calculating intricate tasks or lowering network traffic are two ways that UDFs can sometimes enhance performance.
Considerations for UDFs:
Database compatibility: The syntax of UDF may differ slightly across various database management systems (DBMS), such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Server.
Security: If UDFs are not used appropriately, there may be security problems. When granting permissions, exercise caution and refrain from utilising them for delicate tasks.
Performance: While some processes can be optimised with UDFs, too complex functions may have a negative effect on performance. Carefully consider the trade-offs.
All things considered, UDFs are an effective tool for increasing SQL’s functionality and enhancing the quality of database code. Making UDFs can improve the efficiency of your database and streamline your queries if you work with sophisticated logic or recurring operations.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
As a Developer or Database/Systems Administrator, there is always a need to use GUI tools that simplify management of database systems. One of such tools is DBeaver. DBeaver is free to use universal and multi-platform database administration tool created for anyone working with databases. As a developer, SQL programmer or analyst you’ll enjoy what this tool has to offer. DBeaver is based on Eclipse platform. The open source edition of DBeaver support any database system that has JDBC driver. Some of the databases supported are: MySQL/MariaDB PostgreSQL Oracle Google BigQuery SQL Server Sybase/SAP ASE SQLite, Firebird HSQLDB Derby Teradata Vertica Netezza Informix Among many other databases For use with non-JDBC data sources such as WMI, MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, then consider using DBeaver Enterprise Edition DBeaver is an amazing workbench tool for building SQL queries, editing, and transferring data, viewing trees of objects, completing database administration tasks, monitoring database connection sessions, and a lot more. Use the steps covered in this article to install and use DBeaver on Debian 11 / Debian 10 Linux system. Step 1: Install Java runtime We can use OpenJDK open source edition of Java JRE. The package is available on OS default repositories: sudo apt update sudo apt -y install default-jdk Check installed version of Java to confirm it works. $ java -version openjdk version "11.0.14" 2022-01-18 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.14+9-post-Debian-1deb11u1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.14+9-post-Debian-1deb11u1, mixed mode, sharing) Step 2: Add DBeaver CE repository and install DBeaver development team provides a managed repository with latest builds of the software. We can add the repository by running the following commands: echo "deb https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver-ce /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/dbeaver.list Another requirement is the importation of repo GPG keys. Add them using the commands: sudo apt install curl gpg gnupg2 software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl -fsSL https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/dbeaver.gpg After adding the repository, update the your package sources: $ sudo apt update Hit:1 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security InRelease Hit:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease Hit:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates InRelease Hit:4 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-backports InRelease Get:5 https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver-ce InRelease [2086 B] Get:6 https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver-ce Packages [461 B] Fetched 2547 B in 1s (4223 B/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done All packages are up to date. Step 3: Install DBeaver CE on Debian 11 / Debian 10 We’ve confirmed the repository added is working. Let’s proceed to install DBeaver CE on Debian 11 / Debian 10. sudo apt install dbeaver-ce The process of installation should be few seconds/minutes if you’ve good internet connectivity. Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: dbeaver-ce 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 109 MB of archives. After this operation, 140 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver-ce dbeaver-ce 21.3.4 [109 MB] Fetched 109 MB in 8s (13.4 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package dbeaver-ce. (Reading database ... 38539 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../dbeaver-ce_21.3.4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking dbeaver-ce (21.3.4) ... Setting up dbeaver-ce (21.3.4) ... Processing triggers for mailcap (3.69) ... Checking version of DBeaver installed on Debian Linux system. $ apt policy dbeaver-ce dbeaver-ce: Installed: 21.3.4
Candidate: 21.3.4 Version table: *** 21.3.4 500 500 https://dbeaver.io/debs/dbeaver-ce Packages 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status Step 4: Connecting Database Server to DBeaver Hooray!, DBeaver has been installed on Debian 11 / Debian 10 Linux system. The pending task is connecting database server to be administered using DBeaver. This can be any supported database system. In this example we’ll use MariaDB which can be installed on the same server hosting DBeaver solution. sudo apt install mariadb-server Start and enable mariadb service sudo systemctl enable mariadb sudo systemctl start mariadb Status of Database service: $ systemctl status mariadb ● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.5.12 database server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-02-12 14:32:29 UTC; 5 days ago Docs: man:mariadbd(8) https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/ Main PID: 585 (mariadbd) Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..." Tasks: 8 (limit: 2336) Memory: 100.0M CPU: 59.487s CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service └─585 /usr/sbin/mariadbd Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 mariadbd[585]: 2022-02-12 14:32:29 0 [Note] /usr/sbin/mariadbd: ready for connections. Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 mariadbd[585]: Version: '10.5.12-MariaDB-0+deb11u1' socket: '/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' port: 3306 Debian 11 Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 systemd[1]: Started MariaDB 10.5.12 database server. Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[613]: Upgrading MySQL tables if necessary. Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 mariadbd[585]: 2022-02-12 14:32:29 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 220212 14:32:29 Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[617]: Looking for 'mysql' as: /usr/bin/mysql Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[617]: Looking for 'mysqlcheck' as: /usr/bin/mysqlcheck Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[617]: This installation of MariaDB is already upgraded to 10.5.12-MariaDB, use --force if you still need to run mysql_upgrade Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[626]: Checking for insecure root accounts. Feb 12 14:32:29 debian-bullseye-01 /etc/mysql/debian-start[630]: Triggering myisam-recover for all MyISAM tables and aria-recover for all Aria tables Secure database server by setting root password and performing other hardening tasks $ sudo mariadb-secure-installation Enter current password for root (enter for none): Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] n Change the root password? [Y/n] y New password: Enter Password Re-enter new password: Re-Enter Password Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y DBeaver can be launched from terminal $ dbeaver $ dbeaver-ce Or from the Applications Launcher for your Desktop Environment. 1. Create a new database connection – Specify database type. 2. Provide database access details – Server, database user 3. Click “Test Connection” to verify the connection. When asked to download mariadb connection driver, please agree by clicking Download button. If connection is successful you should get to database details windows. You can now manage your database, tables, triggers, Procedures, Views, Events e.t.c using DBeaver. That’s all we had to share on the installation and usage of DBeaver CE on Debian 11 / Debian 10 Linux system. We hope this guide was of help to you. If there are any issues experienced on your end share them in the comments section.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Snowflake taps Python to take on Teradata, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift
Snowflake taps Python to take on Teradata, Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift
Cloud-based data warehouse company Snowflake on Tuesday at its annual Snowflake Summit introduced a new set of tools and integrations to take on rival firms such as Teradata, and services such as Google BigQuery, and Amazon Redshift. The new capabilities, which include data access tools and support for Python on the company’s Snowpark application development system, are aimed at data scientists,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Migrate Teradata to BigQuery with the best migration strategy and plan. Get simplified and quick teradata migration to GCP BigQuery with Datametica. Call us today!
0 notes
Text
Big Data: Neues Validierungstool prüft bei Cross-Plattform-Migration von Daten
Googles Data Validation Tool ist Open Source und kompatibel mit BigQuery, Cloud SQL, MySQL, Oracle, Teradata sowie weiteren Datenbanken und Dateisystemen. Read more www.heise.de/news/…-... www.digital-dynasty.net/de/blogs/team-blogs/…

http://www.digital-dynasty.net/de/blogs/team-blogs/32726-big-data-neues-validierungstool-prüft-bei-cross-plattform-migration-von-daten.html
0 notes
Text
With the growing demand for cloud-native solutions, Teradata to BigQuery migration is becoming a popular choice for organizations seeking scalable and cost-efficient data platforms. BigQuery’s serverless architecture and real-time analytics capabilities make it an ideal solution for modern data analytics needs.
By migrating from traditional on-premises systems like Teradata or Netezza, businesses can reduce infrastructure costs, scale automatically with data growth, and leverage BigQuery's advanced querying features for faster insights. Unlike legacy systems that require significant investments in physical hardware, BigQuery operates on a flexible pay-per-use pricing model, offering significant cost savings and operational efficiency.
The migration process from Teradata to BigQuery involves careful planning, data transformation, and ensuring compatibility with BigQuery’s cloud architecture. For businesses transitioning from Netezza to BigQuery migration, similar steps apply, ensuring a smooth transition to a more agile, cloud-based solution.
Overall, BigQuery’s integration with Google Cloud services, its scalability, and cost-effectiveness make it a powerful tool for businesses looking to modernize their data infrastructure. Moving to BigQuery enables real-time analytics and enhances decision-making, helping companies stay competitive in a data-driven world.
#TeradataToBigQuery#CloudMigration#BigQuery#DataAnalytics#DataMigration#CloudDataSolutions#NetezzaToBigQuery#RealTimeAnalytics#DataInfrastructure#GoogleCloud#BigData#DataTransformation
0 notes
Text
U.S. Cloud DBaaS Market Set for Explosive Growth Amid Digital Transformation Through 2032
Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 17.51 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 77.65 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.07% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is witnessing accelerated growth as organizations prioritize scalability, flexibility, and real-time data access. With the surge in digital transformation, U.S.-based enterprises across industries—from fintech to healthcare—are shifting from traditional databases to cloud-native solutions that offer seamless performance and cost efficiency.
U.S. Cloud Database & DBaaS Market Sees Robust Growth Amid Surge in Enterprise Cloud Adoption
U.S. Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 4.80 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 21.00 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.82% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market continues to evolve with strong momentum in the USA, driven by increasing demand for managed services, reduced infrastructure costs, and the rise of multi-cloud environments. As data volumes expand and applications require high availability, cloud database platforms are emerging as strategic assets for modern enterprises.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6586
Market Keyplayers:
Google LLC (Cloud SQL, BigQuery)
Nutanix (Era, Nutanix Database Service)
Oracle Corporation (Autonomous Database, Exadata Cloud Service)
IBM Corporation (Db2 on Cloud, Cloudant)
SAP SE (HANA Cloud, Data Intelligence)
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (RDS, Aurora)
Alibaba Cloud (ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB)
MongoDB, Inc. (Atlas, Enterprise Advanced)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB)
Teradata (VantageCloud, ClearScape Analytics)
Ninox (Cloud Database, App Builder)
DataStax (Astra DB, Enterprise)
EnterpriseDB Corporation (Postgres Cloud Database, BigAnimal)
Rackspace Technology, Inc. (Managed Database Services, Cloud Databases for MySQL)
DigitalOcean, Inc. (Managed Databases, App Platform)
IDEMIA (IDway Cloud Services, Digital Identity Platform)
NEC Corporation (Cloud IaaS, the WISE Data Platform)
Thales Group (CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager, Data Protection on Demand)
Market Analysis
The Cloud Database and DBaaS (Database-as-a-Service) Market is being fueled by a growing need for on-demand data processing and real-time analytics. Organizations are seeking solutions that provide minimal maintenance, automatic scaling, and built-in security. U.S. companies, in particular, are leading adoption due to strong cloud infrastructure, high data dependency, and an agile tech landscape.
Public cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market, while niche players continue to innovate in areas such as serverless databases and AI-optimized storage. The integration of DBaaS with data lakes, containerized environments, and AI/ML pipelines is redefining the future of enterprise database management.
Market Trends
Increased adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid database architectures
Growth in AI-integrated database services for predictive analytics
Surge in serverless DBaaS models for agile development
Expansion of NoSQL and NewSQL databases to support unstructured data
Data sovereignty and compliance shaping platform features
Automated backup, disaster recovery, and failover features gaining popularity
Growing reliance on DBaaS for mobile and IoT application support
Market Scope
The market scope extends beyond traditional data storage, positioning cloud databases and DBaaS as critical enablers of digital agility. Businesses are embracing these solutions not just for infrastructure efficiency, but for innovation acceleration.
Scalable and elastic infrastructure for dynamic workloads
Fully managed services reducing operational complexity
Integration-ready with modern DevOps and CI/CD pipelines
Real-time analytics and data visualization capabilities
Seamless migration support from legacy systems
Security-first design with end-to-end encryption
Forecast Outlook
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is expected to grow substantially as U.S. businesses increasingly seek cloud-native ecosystems that deliver both performance and adaptability. With a sharp focus on automation, real-time access, and AI-readiness, the market is transforming into a core element of enterprise IT strategy. Providers that offer interoperability, data resilience, and compliance alignment will stand out as leaders in this rapidly advancing space.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/cloud-database-and-dbaas-market-6586
Conclusion
The future of data is cloud-powered, and the Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is at the forefront of this transformation. As American enterprises accelerate their digital journeys, the demand for intelligent, secure, and scalable database services continues to rise.
Related Reports:
Analyze U.S. market demand for advanced cloud security solutions
Explore trends shaping the Cloud Data Security Market in the U.S
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
Big Data and Analytics in GCC Market: Size, Share, Scope, Analysis, Forecast, Growth and Industry Report 2032 – Retail and E-commerce Trends
Big Data and Analytics are transforming the operational frameworks of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) across the globe. As businesses increasingly recognize the pivotal role of data in driving strategic initiatives, Global Capability Centers are evolving into centers of excellence for data-driven decision-making. According to research 76% of Global Capability Centers identified data as a critical area for future growth,
Big Data and Analytics in GCC Market is experiencing rapid growth due to the region’s digital transformation initiatives. Governments and enterprises are leveraging data to drive innovation, optimize services, and improve decision-making. As a result, demand for data-driven strategies is surging across sectors.
Big Data and Analytics in GCC Market continues to evolve with the rising adoption of AI, cloud computing, and IoT technologies. From smart cities to healthcare and finance, businesses in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) are embracing analytics to remain competitive, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/4716
Market Keyplayers:
IBM Corporation (IBM Watson, IBM Cloud Pak for Data)
Microsoft Corporation (Microsoft Azure, Power BI)
Oracle Corporation (Oracle Analytics Cloud, Oracle Big Data Service)
SAP SE (SAP HANA, SAP BusinessObjects)
SAS Institute Inc. (SAS Viya, SAS Data Management)
Google LLC (Google Cloud Platform, BigQuery)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) (Amazon Redshift, Amazon EMR)
Tableau Software (Tableau Desktop, Tableau Online)
Teradata Corporation (Teradata Vantage, Teradata Cloud)
Cloudera, Inc. (Cloudera Data Platform, Cloudera Machine Learning)
Snowflake Inc. (Snowflake Cloud Data Platform)
MicroStrategy Incorporated (MicroStrategy Analytics)
Qlik Technologies (Qlik Sense, QlikView)
Palantir Technologies (Palantir Foundry, Palantir Gotham)
TIBCO Software Inc. (TIBCO Spotfire, TIBCO Data Science)
Domo, Inc. (Domo Business Cloud)
Sisense Inc. (Sisense for Cloud Data Teams, Sisense Fusion)
Alteryx, Inc. (Alteryx Designer, Alteryx Connect)
Zoho Corporation (Zoho Analytics, Zoho DataPrep)
ThoughtSpot Inc. (ThoughtSpot Search & AI-Driven Analytics)
Trends Shaping the Market
Government-Led Digital Initiatives: National visions such as Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and the UAE’s Smart Government strategy are fueling the adoption of big data solutions across public and private sectors.
Growth in Smart City Projects: Cities like Riyadh, Dubai, and Doha are integrating big data analytics into infrastructure development, transportation, and citizen services to enhance urban living.
Increased Investment in Cloud and AI: Cloud-based analytics platforms and AI-powered tools are gaining traction, enabling scalable and real-time insights.
Sector-Wide Adoption: Industries including oil & gas, healthcare, finance, and retail are increasingly utilizing analytics for predictive insights, risk management, and personalization.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/4716
Market Segmentation:
By Type
Shared Service Centers
Innovation Centers
Delivery Centers
By Industry Vertical
Banking and Financial Services
Healthcare
Retail
Manufacturing
Telecommunications
By Functionality
Descriptive Analytics
Predictive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics
Real-time Analytics
By Technology Type
Data Management
Analytics Tools
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
By End-User
Large Enterprises
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Market Analysis
Accelerated Digital Transformation: Organizations across the GCC are shifting to digital-first operations, creating vast amounts of data that require robust analytics solutions.
Public and Private Sector Collaboration: Joint efforts between governments and tech firms are fostering innovation, resulting in smart platforms for public services, energy, and education.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Businesses are leveraging data to improve ROI, streamline operations, and personalize offerings—especially in e-commerce, banking, and telecommunications.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Awareness: With the increase in data generation, there’s a growing emphasis on securing data through advanced governance and compliance frameworks.
Future Prospects
The Big Data and Analytics in GCC Market is expected to witness exponential growth over the next five years. With increasing internet penetration, 5G rollout, and continued focus on digital infrastructure, data-driven technologies will become even more central to economic and social development in the region.
Talent Development and Upskilling: Governments are investing in training programs and digital literacy to prepare a workforce capable of managing and interpreting big data.
Emerging Startups and Innovation Hubs: The GCC is witnessing a rise in homegrown analytics startups and incubators that are driving localized solutions tailored to regional needs.
AI Integration: The convergence of AI with big data will unlock new insights and automate complex tasks in sectors such as logistics, healthcare diagnostics, and financial modeling.
Regulatory Frameworks: Future success will depend on the creation of robust regulatory policies ensuring data privacy, cross-border data flows, and ethical AI usage.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/big-data-and-analytics-in-gcc-market-4716
Conclusion
The Big Data and Analytics in GCC Market stands at the forefront of digital transformation. With strong government backing, sector-wide adoption, and a growing tech ecosystem, the region is well-positioned to become a data-driven powerhouse. As the market matures, the focus will shift from data collection to intelligent utilization—empowering smarter decisions, better services, and sustainable growth across the GCC.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Photo

When migrating a data warehouse to BigQuery, one of the most critical tasks is mapping existing user www.mcafee.com/activate product key permissions to equivalent Google cloud management and access quality permissions and roles www.mcafee/activate. This is especially mcafee.com/activate product key true for migrating from large enterprise data warehouses like Teradata to Big query. The existing Teradata databases commonly contain www.mcafee.com/activate multiple user-defined roles that combine access permissions and capture common data access www.mcafee.com/activate download patterns. Mapping those Teradata roles to predefined or custom BigQuery IAM roles requires a deeper understanding of your organization's common data access patterns.
0 notes
Link
Select a ranking Special reports Ranking Complete Ranking DB-Engines RankingThe DB-Engines Ranking ranks database management systems according to their popularity. The ranking is updated monthly. Read more about the method of calculating the scores. 350 systems in ranking, February 2020RankDBMSDatabase ModelScoreFeb 2020Jan 2020Feb 2019Feb 2020Jan 2020Feb 20191.1.1.Oracle Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS, RDF store1344.75-1.93+80.732.2.2.MySQL Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store1267.65-7.00+100.363.3.3.Microsoft SQL Server Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS1093.75-4.80+53.694.4.4.PostgreSQL Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store506.94-0.25+33.385.5.5.MongoDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableDocument, Multi-model Document store, Search engine433.33+6.37+38.246.6.6.IBM Db2 Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, RDF store165.55-3.15-13.877.7. 8.Elasticsearch Detailed vendor-provided information availableSearch engine, Multi-model Search engine, Document store152.16+0.72+6.918.8. 7.Redis Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value, Multi-model Key-value store, Document store, Graph DBMS, Search engine, Time Series DBMS151.42+2.67+1.979.9.9.Microsoft AccessRelational128.06-0.52-15.9610.10.10.SQLite Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational123.36+1.22-2.8111.11.11.Cassandra Detailed vendor-provided information availableWide column120.36-0.31-3.0212.12. 13.SplunkSearch engine88.77+0.10+5.9613.13. 12.MariaDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS87.34-0.11+3.9114.14. 15.Hive Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational83.53-0.71+11.2515.15. 14.Teradata Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS, Time Series DBMS76.81-1.48+0.8416.16. 21.Amazon DynamoDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Key-value store62.14+0.12+7.1917.17. 16.SolrSearch engine56.16-0.41-4.8118. 19. 19.SAP HANA Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS54.97+0.28-1.5819. 18. 18.FileMakerRelational54.88-0.23-2.9120. 21. 17.HBaseWide column52.95-0.39-7.3321. 20. 20.SAP Adaptive ServerRelational52.73-1.86-3.0222.22.22.Neo4j Detailed vendor-provided information availableGraph51.21-0.45+3.3523.23.23.Couchbase Detailed vendor-provided information availableDocument, Multi-model Document store, Key-value store32.16+0.12-3.4224.24. 27.Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Graph DBMS, Key-value store, Wide column store31.95+0.44+7.0925.25.25.Microsoft Azure SQL DatabaseRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Graph DBMS31.41+3.20+4.2826.26. 33.Google BigQuery Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational27.56+0.81+8.8127. 28. 24.MemcachedKey-value25.30+0.20-4.1428. 27. 26.InformixRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Time Series DBMS24.89-0.25-1.4729.29. 28.Vertica Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store22.63-0.02-0.1730.30. 32.FirebirdRelational21.82-0.73+2.4731. 32. 35.InfluxDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series21.57+0.44+5.8132. 31. 29.Amazon Redshift Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational20.97-0.62-0.0233.33. 31.NetezzaRelational18.75-0.87-1.0334.34. 30.CouchDBDocument18.13-0.24-1.8735.35. 34.Spark SQLRelational16.95-0.19+0.3836.36. 37.ImpalaRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store15.71-0.32+0.9137.37. 40.dBASERelational14.20-0.58+2.3138. 39. 41.Firebase Realtime DatabaseDocument12.35+0.07+1.9239. 38. 36.MarkLogic Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Native XML DBMS, RDF store, Search engine12.25-0.11-2.7440.40. 38.GreenplumRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store11.93-0.21-0.9141.41. 39.Oracle EssbaseRelational10.64+0.07-1.3442.42. 44.Microsoft Azure SQL Data WarehouseRelational9.58+0.14+1.1243.43. 76.PrestoRelational9.53+0.39+6.0544. 46. 46.Realm Detailed vendor-provided information availableDocument8.85+0.62+1.9745. 44. 42.Datastax Enterprise Detailed vendor-provided information availableWide column, Multi-model Wide column store, Document store, Graph DBMS8.48-0.18-0.6746. 45. 43.Hazelcast Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value, Multi-model Key-value store, Document store8.28-0.08-0.6147.47. 53.Amazon AuroraRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store8.18+0.01+2.2948. 53. 45.SphinxSearch engine7.26+0.74-0.3149. 48.etcdKey-value7.24-0.0650. 49.50.H2Relational7.13+0.07+0.7151. 50. 48.Aerospike Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value6.88+0.06+0.2652. 51. 47.EhcacheKey-value6.68-0.01-0.1253. 52. 49.InterbaseRelational6.55-0.08+0.0154.54. 55.Microsoft Azure SearchSearch engine6.31-0.17+0.7755. 57. 72.Google Cloud FirestoreDocument6.21+0.55+2.4556. 55. 54.IngresRelational5.92-0.43+0.1657. 56. 59.SAP SQL AnywhereRelational5.75-0.03+0.5258. 59. 51.Riak KVKey-value5.47+0.07-0.6259. 58. 57.Kdb+ Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series, Multi-model Time Series DBMS, Relational DBMS5.38-0.11-0.0260.60. 58.DerbyRelational5.22-0.10-0.1061. 62. 63.SAP IQRelational5.01-0.14+0.5862. 64. 56.IgniteMulti-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS5.00-0.01-0.4263.63. 52.OrientDBMulti-model Document store, Graph DBMS, Key-value store4.94-0.17-1.1164. 67. 65.Google Cloud DatastoreDocument4.89+0.08+0.5865.65. 61.Microsoft Azure Table StorageWide column4.86-0.15+0.0866. 61. 64.ArangoDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Graph DBMS, Key-value store, Search engine4.85-0.35+0.5067. 66. 60.HyperSQLRelational4.85-0.11-0.2768. 69. 74.AlgoliaSearch engine4.69+0.07+0.9869. 68. 71.AdabasMultivalue4.53-0.13+0.7370.70. 73.MemSQLRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store4.49-0.03+0.7571.71. 67.JackrabbitContent4.36-0.14+0.3872. 73. 75.MaxDBRelational4.15+0.13+0.4473. 72. 93.PrometheusTime Series4.01-0.06+1.5174. 79. 80.Oracle NoSQL Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value, Multi-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS3.91+0.30+0.8775. 78. 100.ClickHouseRelational3.89+0.19+1.6076. 75. 107.CockroachDBRelational3.85+0.07+1.7777. 74. 66.AccumuloWide column3.83-0.09-0.2878. 81. 68.RavenDBDocument, Multi-model Document store, Graph DBMS3.82+0.37-0.1179. 76. 69.OpenEdgeRelational3.80+0.03-0.0980. 82. 70.CloudantDocument3.74+0.29-0.0981. 77. 62.RethinkDBDocument3.63-0.13-0.9082. 80. 78.InterSystems CachéMulti-model Key-value store, Object oriented DBMS, Relational DBMS, Document store3.43-0.10+0.1583.83. 82.GraphiteTime Series3.34-0.01+0.3984.84. 77.UniData,UniVerseMultivalue3.300.00-0.0785.85. 87.SAP Advantage Database ServerRelational3.13+0.01+0.4186.86. 91.Amazon CloudSearchSearch engine3.08+0.03+0.5687. 90. 81.Oracle Berkeley DBMulti-model Key-value store, Native XML DBMS2.98+0.14-0.0188.88. 84.PouchDBDocument2.96-0.01+0.0389. 87. 108.EXASOLRelational2.89-0.14+0.8390. 91. 79.Google Search ApplianceSearch engine2.77-0.03-0.2891. 96. 83.Virtuoso Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Graph DBMS, Native XML DBMS, Relational DBMS, RDF store, Search engine, Document store2.77+0.12-0.1792. 89. 86.LevelDBKey-value2.77-0.10+0.0393. 95. 96.4DRelational2.72+0.03+0.3394. 93. 85.Apache DrillMulti-model Document store, Relational DBMS2.69-0.05-0.1495. 92. 88.RRDtoolTime Series2.68-0.09-0.0296. 97. 98.RocksDBKey-value2.67+0.06+0.3497. 104.Microsoft Azure Data ExplorerRelational2.66+0.3398. 94. 92.InfinispanKey-value2.64-0.05+0.1499. 98. 106.Apache Jena - TDBRDF2.62+0.02+0.44100.100. 104.IMSNavigational2.59+0.16+0.38101. 107. 102.Snowflake Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational2.56+0.32+0.30102. 101. 105.CloudKitDocument2.53+0.16+0.34103. 99. 90.Percona Server for MySQLRelational2.52+0.07-0.05104. 103. 101.Amazon SimpleDBKey-value2.46+0.13+0.19105. 102. 95.EnterpriseDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store2.38+0.02-0.06106. 108. 99.Oracle CoherenceKey-value2.38+0.23+0.07107. 109. 89.TimesTen Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational2.31+0.19-0.39108. 106. 111.Google Cloud BigtableWide column2.27+0.02+0.58109. 110. 133.ScyllaDBWide column2.25+0.19+1.19110. 112. 103.OpenTSDBTime Series2.14+0.17-0.10111. 113. 110.Google Cloud SpannerRelational2.13+0.20+0.44112. 111. 94.DatomicRelational2.12+0.14-0.34113. 105. 97.OmniSci Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational2.08-0.22-0.27114. 118. 117.jBASEMultivalue1.99+0.19+0.43115. 121. 134.Amazon NeptuneMulti-model Graph DBMS, RDF store1.96+0.23+0.90116. 117. 119.MonetDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store1.95+0.14+0.50117. 116. 118.DruidMulti-model Relational DBMS, Time Series DBMS1.91+0.03+0.42118. 120. 113.IBM Db2 warehouseRelational1.90+0.13+0.25119. 115. 115.Versant Object DatabaseObject oriented1.89+0.00+0.24120. 119. 125.JanusGraphGraph1.88+0.11+0.65121. 114. 149.TimescaleDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series, Multi-model Time Series DBMS, Relational DBMS1.88-0.04+1.00122. 124.122.GeodeKey-value1.81+0.22+0.53123.123. 112.VoltDBRelational1.78+0.14+0.12124. 122. 109.GridGainMulti-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS1.77+0.10-0.24125. 126. 126.TiDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store1.73+0.16+0.50126. 127. 116.Red BrickRelational1.64+0.08+0.06127. 130. 166.D3Multivalue1.61+0.18+0.88128. 125. 120.TiberoRelational1.59+0.00+0.18129.129.129.ObjectStoreObject oriented1.57+0.14+0.37130. 128. 114.mSQLRelational1.46-0.02-0.19131. 134.131.SQLBaseRelational1.46+0.13+0.38132. 136. 123.BaseXNative XML1.43+0.19+0.16133. 132. 124.MnesiaDocument1.43+0.07+0.20134. 131. 121.Db4oObject oriented1.38-0.03+0.07135.135. 127.DatameerDocument1.34+0.06+0.12136. 133. 128.EmpressRelational1.29-0.05+0.06137. 139. 130.CubridRelational1.24+0.13+0.10138. 144. 154.TarantoolKey-value1.22+0.16+0.38139. 138. 132.MatisseObject oriented1.21+0.08+0.14140. 143. 138.Altibase Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational1.20+0.14+0.20141. 142. 147.HFSQLRelational1.16+0.10+0.27142. 145. 169.Dgraph Detailed vendor-provided information availableGraph1.16+0.11+0.45143. 137. 152.GraphDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Graph DBMS, RDF store1.14+0.00+0.28144. 140. 189.InterSystems IRIS Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Key-value store, Object oriented DBMS, Relational DBMS1.13+0.06+0.60145. 141. 170.LiteDBDocument1.08+0.01+0.38146. 152. 172.CitusRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store1.07+0.07+0.39147. 158. 153.NuoDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational1.06+0.12+0.21148. 159. 146.WiredTigerKey-value1.05+0.13+0.15149. 157. 155.NCache Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value1.05+0.11+0.24150. 149. 142.Model 204Multivalue1.03+0.02+0.09151. 147. 139.InfobrightRelational1.01-0.02+0.04152. 153. 137.Oracle RdbRelational1.01+0.02+0.01153. 155. 140.NonStop SQLRelational1.00+0.03+0.05154. 166. 214.FaunaDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Graph DBMS, Relational DBMS, Time Series DBMS0.98+0.18+0.62155. 146. 135.IDMSNavigational0.98-0.05-0.05156. 148. 136.GiraphGraph0.98-0.04-0.03157. 150. 143.DataEaseRelational0.98-0.04+0.06158. 163. 141.1010dataRelational0.96+0.10+0.01159. 156. 145.GT.MKey-value0.950.00+0.04160. 154. 151.SednaNative XML0.94-0.04+0.08161.161. 156.FoundationDBMulti-model Document store, Key-value store, Relational DBMS0.94+0.08+0.14162. 165. 171.Stardog Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Graph DBMS, RDF store0.91+0.10+0.22163. 160. 144.HAWQRelational0.90-0.01-0.01164. 169. 174.DBISAMRelational0.89+0.10+0.22165. 151. 173.TigerGraph Detailed vendor-provided information availableGraph0.87-0.13+0.19166. 182.Amazon DocumentDBDocument0.84+0.16167. 162. 148.AllegroGraph Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Document store, Graph DBMS, RDF store0.84-0.01-0.04168. 171. 225.YugabyteDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store, Wide column store0.83+0.06+0.52169. 168. 161.R:BASERelational0.82+0.03+0.06170. 164. 163.ZODBKey-value0.820.00+0.07171. 167. 150.XAPMulti-model Document store, Key-value store, Object oriented DBMS0.81+0.01-0.06172. 170. 180.GemStone/SObject oriented0.81+0.03+0.19173. 172. 159.KognitioRelational0.79+0.02+0.01174. 173. 160.Objectivity/DBObject oriented0.78+0.02+0.01175.175. 167.solidDBRelational0.730.00+0.00176. 174. 178.XapianSearch engine0.73-0.02+0.08177. 186. 157.Splice MachineRelational0.73+0.06-0.06178. 180. 165.Datacom/DBRelational0.72+0.02-0.01179.179. 177.WebSphere eXtreme ScaleKey-value0.71+0.00+0.05180. 178. 164.ScaleArcRelational0.710.00-0.03181. 176. 179.FrontBaseRelational0.71-0.01+0.08182. 177. 175.ClustrixRelational0.70-0.01+0.03183. 184. 176.eXist-dbNative XML0.70+0.02+0.03184. 183. 186.Event StoreEvent0.70+0.02+0.14185. 202. 206.PerstObject oriented0.70+0.14+0.29186. 181. 168.Actian VectorRelational0.690.00-0.03187. 193. 201.Northgate RealityMultivalue0.69+0.08+0.27188.188. 187.Tokyo CabinetKey-value0.68+0.04+0.11189. 187. 158.BigchainDBDocument0.67+0.00-0.12190. 191. 188.CrateDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Relational DBMS, Search engine, Document store0.67+0.04+0.13191. 199. 190.ObjectDBObject oriented0.65+0.08+0.11192. 189. 191.BlazegraphMulti-model Graph DBMS, RDF store0.640.00+0.11193. 185. 162.MapR-DBMulti-model Document store, Wide column store0.63-0.04-0.12194. 190. 184.OpenBaseRelational0.62-0.02+0.05195. 194. 198.SQL.JSRelational0.610.00+0.15196. 192. 181.SciDBMultivalue0.60-0.02-0.01197. 205. 182.Percona Server for MongoDBDocument0.60+0.080.00198.198. 193.KineticaRelational0.59+0.02+0.07199. 203. 185.VistaDBRelational0.58+0.03+0.02200. 197. 183.Graph EngineMulti-model Graph DBMS, Key-value store0.58+0.00+0.01201. 196. 192.NexusDBRelational0.57-0.02+0.04202. 195. 196.OpenInsightMultivalue0.57-0.04+0.07203. 201. 194.KairosDBTime Series0.56+0.01+0.04204. 206. 226.c-treeACE Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS0.51-0.01+0.21205. 210. 209.ObjectBoxObject oriented0.51+0.03+0.12206. 212. 211.BoltDBKey-value0.51+0.03+0.13207. 200.YellowbrickRelational0.50-0.06208. 222. 213.AlaSQLMulti-model Document store, Relational DBMS0.49+0.10+0.12209. 204. 231.GridDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series, Multi-model Time Series DBMS, Key-value store, Relational DBMS0.48-0.04+0.21210. 207.210.RedlandRDF0.48-0.04+0.10211. 213. 197.MapDBKey-value0.48+0.00-0.01212. 208. 237.Alibaba Cloud MaxComputeRelational0.47-0.02+0.22213. 211. 203.Postgres-XLRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Document store0.47-0.02+0.05214. 216. 199.Tokyo TyrantKey-value0.46+0.01+0.01215. 214. 207.SQream DB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational0.44-0.02+0.04216. 209. 218.JadeObject oriented0.44-0.04+0.10217. 215. 202.RasdamanMultivalue0.44-0.01+0.02218.218. 205.TrafodionRelational0.43+0.01+0.02219. 217. 204.eXtremeDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Relational DBMS, Time Series DBMS0.42-0.02+0.01220. 219. 228.Amazon TimestreamTime Series0.41+0.01+0.13221. 228. 219.4storeRDF0.40+0.03+0.06222. 232. 215.Project VoldemortKey-value0.40+0.05+0.04223. 220. 217.RDF4JRDF0.390.00+0.05224.224. 222.ScalarisKey-value0.39+0.01+0.07225. 226. 220.HibariKey-value0.39+0.01+0.06226. 223. 208.InfiniteGraphGraph0.39+0.00-0.01227. 225. 235.LokiJSDocument0.38+0.00+0.13228. 231. 245.SnappyDataRelational0.37+0.02+0.16229. 237. 224.Mimer SQLRelational0.37+0.07+0.06230. 227. 234.c-treeEDGE Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS0.370.00+0.11231. 221.RocksetDocument, Multi-model Document store, Relational DBMS, Search engine0.37-0.02232. 230. 221.Raima Database ManagerRelational0.37+0.00+0.04233. 229. 212.StarcounterObject oriented0.35-0.01-0.02234. 259. 227.Actian PSQLRelational0.35+0.15+0.04235. 233. 216.ModeShapeContent0.35+0.02+0.00236.236. 247.Alibaba Cloud Table StoreWide column0.32+0.02+0.12237. 234. 233.Alibaba Cloud HybridDBRelational0.32+0.01+0.06238. 248. 240.Kyoto CabinetKey-value0.31+0.06+0.06239. 240. 242.PipelineDBRelational0.31+0.01+0.07240. 252. 238.IBM Db2 Event StoreMulti-model Event Store, Time Series DBMS0.30+0.08+0.05241. 235. 223.TajoRelational0.30-0.01-0.01242. 239. 232.SearchBloxSearch engine0.30+0.01+0.03243. 245. 236.FlockDBGraph0.29+0.02+0.03244. 241. 230.OpenQMMultivalue0.28-0.01+0.00245. 246. 246.Riak TSTime Series0.28+0.02+0.07246. 244. 229.SequoiadbMulti-model Document store, Relational DBMS0.270.00-0.01247. 242. 241.LovefieldRelational0.27-0.01+0.03248. 251. 274.HeroicTime Series0.27+0.04+0.17249. 243. 278.GRAKN.AI Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Graph DBMS, Relational DBMS0.27-0.01+0.17250. 238. 263.ITTIARelational0.25-0.05+0.11251. 247. 248.AxibaseTime Series0.250.00+0.05252. 255.DolphinDBTime Series0.25+0.04253. 249. 239.Comdb2Relational0.23-0.02-0.01254.254. 265.Valentina ServerRelational0.23+0.02+0.10255. 262. 276.EJDBDocument0.21+0.03+0.11256.256. 270.XtremeDataRelational0.200.00+0.09257. 253. 293.LeanXcaleMulti-model Key-value store, Relational DBMS0.20-0.02+0.14258. 260. 254.HyperGraphDBGraph0.20+0.01+0.03259. 258. 250.ElevateDBRelational0.19-0.010.00260. 250.260.RedStoreRDF0.18-0.06+0.03261. 263.QuestDBTime Series, Multi-model Time Series DBMS, Relational DBMS0.180.00262. 257. 292.MulgaraRDF0.17-0.03+0.10263. 264. 253.TransLatticeRelational0.17+0.00-0.01264. 261. 284.Transbase Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational0.17-0.02+0.09265. 300. 251.Warp 10Time Series0.15+0.09-0.03266. 265. 252.EsgynDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableRelational0.15-0.01-0.03267. 299.Nebula Graph Detailed vendor-provided information availableGraph0.14+0.08268. 266. 257.CubicWebRDF0.14+0.00-0.02269. 268. 275.TinkerGraphGraph0.14+0.01+0.04270. 275.KeyDBKey-value0.13+0.02271. 289. 264.AnzoGraph Detailed vendor-provided information availableMulti-model Graph DBMS, RDF store0.13+0.05-0.01272. 270.GeoSpockRelational, Multi-model Relational DBMS, Time Series DBMS0.12-0.01273. 267. 258.AgensGraphMulti-model Graph DBMS, Relational DBMS0.12-0.01-0.04274. 269. 311.GraphBaseGraph0.12-0.01+0.07275. 271. 303.BrytlytRelational0.11-0.01+0.07276. 273. 268.SparkseeGraph0.11-0.01-0.01277. 272. 305.searchxmlMulti-model Native XML DBMS, Search engine0.11-0.01+0.06278. 284. 267.WakandaDBObject oriented0.10+0.02-0.02279. 278. 266.Quasardb Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series0.10+0.00-0.03280. 276. 294.BluefloodTime Series0.100.00+0.03281.281. 299.JethroDataRelational0.10+0.00+0.04282. 302. 306.Resin CacheKey-value0.09+0.03+0.05283. 279. 256.NEventStoreEvent0.09-0.01-0.08284. 283. 281.SenseiDBDocument0.09+0.00+0.00285. 277. 279.DensoDBDocument0.09-0.02-0.01286. 288. 255.STSdbKey-value0.09+0.01-0.09287. 334. 331.IndicaSearch engine0.08+0.08+0.08288. 285. 273.BadgerKey-value0.080.00-0.03289. 274. 290.StrabonRDF0.08-0.03+0.01290. 286. 319.Manticore SearchSearch engine0.080.00+0.05291.291. 271.RaptorDBDocument0.08+0.00-0.04292. 297. 259.Hawkular MetricsTime Series0.08+0.01-0.07293. 280. 325.HGraphDBGraph0.08-0.02+0.06294. 290. 282.BrightstarDBRDF0.08+0.00-0.01295. 282.M3DBTime Series0.08-0.01296. 293. 308.Kyoto TycoonKey-value0.070.00+0.03297. 318. 314.UpscaledbKey-value0.07+0.04+0.04298. 292. 269.VelocityDBMulti-model Graph DBMS, Object oriented DBMS0.070.00-0.05299. 314.WeaviateGraph, Multi-model Graph DBMS, Search engine0.07+0.03300. 296. 287.WhiteDBDocument0.070.00-0.01301. 315.VictoriaMetricsTime Series0.07+0.03302. 301. 283.DydraRDF0.060.00-0.02303. 295. 291.EllipticsKey-value0.06-0.01-0.01304. 294. 297.ToroDBDocument0.06-0.010.00305.305. 298.IRONdb Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series0.06+0.01+0.01306. 304. 316.InfinityDBKey-value0.06+0.00+0.03307. 287. 300.SwayDBKey-value0.06-0.02+0.01308. 303. 307.Machbase Detailed vendor-provided information availableTime Series0.06+0.00+0.02309. 308. 323.OrigoDBMulti-model Document store, Object oriented DBMS0.06+0.00+0.04309. 313. 321.SiriDBTime Series0.06+0.01+0.04311.311.HugeGraphGraph0.06+0.00312. 307. 277.NosDBDocument0.05+0.00-0.04313. 306. 285.MemgraphGraph0.050.00-0.02314. 309. 326.TerarkDBKey-value0.050.00+0.04315. 332. 331.Sadas EngineRelational0.05+0.04+0.05316. 312. 304.BigObjectRelational0.04-0.010.00317. 298.CovenantSQLRelational0.04-0.03318. 310. 301.SiaqodbObject oriented0.04-0.02-0.01319. 316. 302.DBSightSearch engine0.04+0.00-0.01320. 317. 296.SmallSQLRelational0.030.00-0.03321. 330. 315.HyperLevelDBKey-value0.03+0.020.00322. 327. 309.LedisDBKey-value0.02+0.01-0.02323. 320. 322.NewtsTime Series0.02-0.01+0.00324.324. 272.Versant FastObjectsObject oriented0.020.00-0.10325. 321. 320.FinchDBMulti-model Document store, Search engine0.02-0.01-0.01326. 323. 317.CortexDBMulti-model Document store, Key-value store0.02-0.01-0.01327. 325. 324.LinterRelational0.02-0.01+0.00328. 334. 331.SiteWhereTime Series0.01+0.01+0.01329. 326. 289.BangdbKey-value0.01-0.01-0.06330. 322. 312.ExorbyteSearch engine0.01-0.01-0.03331.331. 313.iBoxDBDocument0.01+0.00-0.03332. 328. 318.ScaleOut StateServerKey-value0.01-0.01-0.02333.333. 261.ActorDBRelational0.00+0.00-0.14334.334. 331.BergDBKey-value0.00±0.00±0.00334.334. 331.Cachelot.ioKey-value0.00±0.00±0.00334.334. 331.DaggerDBRelational0.00±0.00±0.00334. 329. 330.Edge IntelligenceRelational0.00-0.010.00334.334. 262.EloqueraObject oriented0.00±0.00-0.15334.334.FlureeDBGraph0.00±0.00334.334. 331.HeliumKey-value0.00±0.00±0.00334.334.HyprcubdTime Series0.00±0.00334.334. 329.JaguarDB Detailed vendor-provided information availableKey-value0.00±0.000.00334.334. 331.JasDBDocument0.00±0.00±0.00334.334. 331.JSqlDbMulti-model Document store, Object oriented DBMS0.00±0.00±0.00334.334. 331.K-DBRelational0.00±0.00±0.00334. 319. 327.SparkleDBRDF0.00-0.03-0.01334.334.TerminusDBGraph, Multi-model Graph DBMS, Document store, RDF store0.00±0.00334.334. 310.TomP2PKey-value0.00±0.00-0.04334.334. 331.YaacomoRelational0.00±0.00±0.00334.334. 331.YanzaTime Series0.00±0.00±0.00 Share this page
0 notes
Text
Apache Flume vs NiFi и еще 2 потоковые ETL-платформы Big Data и IoT/IIoT

Рассмотрев пакетные ETL-инструменты больших данных, сегодня мы поговорим про потоковые средства загрузки и маршрутизации информации из различных источников: Apache NiFi, Fluentd и StreamSets Data Collector. Читайте в нашей статье про их сходства, различия, достоинства и недостатки. Также мы собрали для вас реальные примеры их практического использования в Big Data системах и интернете вещей (Internet of Things, IoT), в т.ч. индустриальном (Industrial IoT, IIoT).
Как используется Apache Flume для потоковых ETL-задач
Из систем потоковой загрузки данных среди проектов фонда Apache Software Foundation (ASF), кроме NiFi, на практике часто используется Apache Flume – распределенная и высоконадежная система для эффективного сбора, агрегации и сохранения больших объемов логов из множества различных источников в централизованное хранилище данных. Изначально созданный для потоковой обработки логов в конвейерах, Flume масштабируется горизонтально и управляется событиями. Этот ETL-инструмент характеризуется низкой временной задержкой (low latency), отказоустойчивостью и гибкими возможностями дополнения за счет мощного API-интерфейса и SDK (software development kit). Из недостатков Flume стоит отметить, что он, как и Apache NiFi, гарантирует доставку сообщений в семантиках «максимум один раз» (at most once) и «по крайней мере один раз» (at least once). Это позволяет быстро перемещать данные и удешевлять обеспечение отказоустойчивости за счет минимизации состояний, которые нужно хранить. Также Flume позволяет доставлять события «по крайней мере один раз», но это сказывается на пропускной способности системы и может привести к дублированию сообщений [1]. Тем не менее, на практике Apache Flume широко используется в качестве ETL-средства для Big Data. В частности, сингапурская ИТ-компания Capillary Technologies, которая предоставляет облачную платформу электронной коммерции и сопутствующие услуги для розничных продавцов и брендов Omnichannel Customer Engagement, применяет Flume для агрегации логов с 25 различных источников данных. Корпорация Mozilla использует Flume вместе с ElasticSearch в проекте BuildBot по созданию своего инструмента непрерывной интеграции при разработке программного обеспечения, который автоматизирует цикл компиляции или тестирования, необходимый для проверки изменений в коде проекта. Сейчас это средство используется в Mozilla, Chromium, WebKit и многих других проектах. Один из крупнейших травел-агрегаторов Индии, компания Goibibo также применяет Flume для передачи журналов из своих производственных систем в HDFS [2].
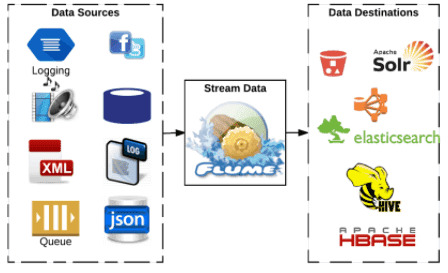
Apache Flume часто используется для ETL-задач и маршрутизации потоков Big Data
Другие решения для потокового ETL в Big Data
Среди платформ загрузки и маршрутизации данных, не являющихся проектами фонда ASF, наиболее часто для передачи информации между разными источниками и приемниками используются следующие: · Fluentd – открытый ��оллектор данных, предназначенный для объединения и систематизации масштабируемой инфраструктуры логов. Собранные с помощью Fluentd могут быть переданы для хранения и дальнейшей обработки в базы данных (MySQL, PostgreSQL, CouchBase, CouchDB, MongoDB, OpenTSDB, InfluxDB) распределенные файловые системы, включая HDFS, облачные сервисы (AWS, Google BigQuery), поисковые инструменты (Elasticsearch, Splunk, Loggly) [3]. · StreamSets Data Collector – наиболее похожая на Apache NiFi корпоративная инфраструктура непрерывного приема больших данных с открытым исходным кодом. Благодаря наличию пользовательского веб-GUI она позволяет разработчикам, инженерам, аналитикам и ученым по данным легко создавать ETL-конвейеры со сложными сценариями загрузки. StreamSets Data Collector интегрирован со множеством распределенных систем, от файловых хранилищ до реляционных СУБД, включая NoSQL и системы управления очередями сообщений: HDFS, HBase, Hive, Cassandra, MongoDB, Apache Solr, Elasticsearch, Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Netezza, Teradata и другие реляционные СУБД с поддержкой JDBC, Apache Kafka, JMS, Kinesis, Amazon S3 и т.д. [4]. В отличие от Apache NiFi, управляемого потоковыми файлами (FileFlow), StreamSets Data Collector управляется записями, что обусловливает дальнейшую разницу в эксплуатации этих систем. Подробнее про сходства и различия Apache NiFi и StreamSets Data Collector читайте в нашей новой статье. В практическом применении Fluentd часто используется как DevOps-инструмент и средство системного администрирования для сбора и анализа логов из множества распределенных приложений. Оно позволяет работать с контейнерами и системами управления контейнеризованными приложениями, в частности, Docker и Kubernetes. Это существенно облегчает процессы тестирования и развертывания в соответствии с методологией непрерывной интеграции и поставки программного обеспечения [5]. Из примеров практического использования StreamSets Data Collector отметим опыт американской компании OmniSci, которая разрабатывает программное обеспечение графических и центральных процессоров для визуализации больших данных. В частности, при создании реалистичных видеоигр по мотивам соревнований «Формула 1», с помощью StreamSets Data Collector был построен конвейер получения телеметрических данных о вождении автомобилей с периферийных IIoT-устройств, упаковка данных в UDP-пакет и непрерывная отправка информации в брокер сообщений Apache Kafka. Далее выполняется перевод двоичного потока в строки и конвертация в файл JSON, который дополняется временными метками и уникальным идентификатором сессии. Зат��м обогащенные данные снова записываются в кластер Kafka, откуда они расходятся по различным системам-приемникам: базам данных, BI-дэшбордам и т.д. Вся эта сложная схема маршрутизации телеметрических данных о движущемся автомобиле с целью их интерактивного отображения на визуальных панелях была построена в рамках StreamSets Data Collector [6].
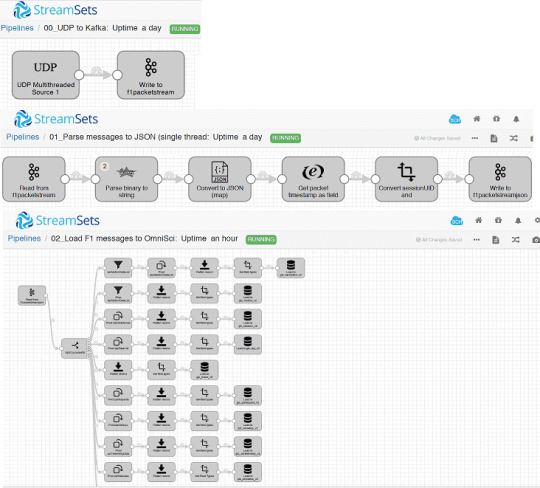
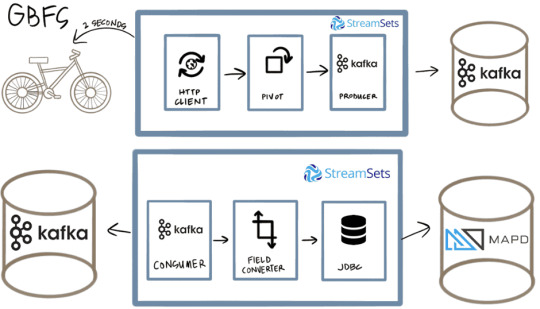
Конвейер передачи IIoT-данных в компании OmniSci на базе StreamSets Data Collector Аналогичным образом, в рамках IIoT-направления, разработчик распределенных решений One Click Retail использовала StreamSets Data Collector для чтения данных о локации и состоянии прокатных велосипедов Ford GoBike и отправки их в базу данных MapD через Kafka и JDBC-подключение [7].
ETL-конвейер на основе StreamSets Data Collector для IIoT в прокате велосипедов Больше примеров практического использования StreamSets Data Collector, его сходства и отличия от Apache NiFi читайте в нашей следующей статье. Освойте все тонкости установки, администрирования и эксплуатации потокового ETL в Big Data на нашем практическом курсе Кластер Apache NiFi в л��цензированном учебном центре обучения и повышения квалификации ИТ-специалистов (менеджеров, архитекторов, инженеров, администраторов, Data Scientist’ов и аналитиков Big Data) в Москве.

Смотреть расписание занятий

Зарегистрироваться на курс Источники 1. https://moluch.ru/archive/202/49512/ 2. https://www.dezyre.com/article/sqoop-vs-flume-battle-of-the-hadoop-etl-tools-/176 3. https://blog.selectel.ru/sbor-i-analiz-logov-s-fluentd/ 4. https://github.com/streamsets/datacollector 5. https://habr.com/ru/company/selectel/blog/250969/ 6. https://streamsets.com/blog/omnisci-f1-demo-real-time-data-ingestion-streamsets/ 7. https://streamsets.com/blog/real-time-bike-share-data-pipeline-streamsets-kafka-mapd/ Read the full article
0 notes