#What Is My Ipv4 Address
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Pull The Trigger
your favourite freak's writing agaain! you ever wanted to read a story about a homophobic gamer boy getting doxxed and raped? well here u go! ^-^ part two coming soon
cw: noncon, forced gay, slurs, shit like that
sandstone brick, towering ahead. trapped in a corner, waiting, ak-47 comfortable in hand. listening, watching, pixel-perfect gaze. the soft pitter patter of booted footsteps approaching on sand. spin, shoot before you see. three shots of triple-round burst to centre mass. dead.
multiple pings hit the wall ahead of him, pelted at while his back was turned. losing health rapidly. he flicks and sends his barrel spinning 180 in the opposite direction, blind trading fire.
he screams into his bulky turtle beach headphones as the body in front of him ragdolls, screen blurring with bloody low health warnings. “YEAAAH FAGGOT, YOU LIKE THAT?”
he’s swiftly popped into the win screen, all chat and winner microphones switched on to offer a chance to flaunt or whine.
[ALL] TriggerFinger: get GUD fags i’ll wipe u in the next one 2 lmao
[ALL] XxxGr1mR3eaperxxX: dude you suck u just got lucky
[ALL] TriggerFinger: i bet u kno a lot about sucking huh?
[ALL] TriggerFinger: just like your MOM
trigger clicks on to queue for the next game, a satisfied gleam plastering his face as everyone else is gone to the aether.
in the top left of his screen as loading screens trawl pops a message from an unfamiliar user. not on his friends list, rather it looks like they’re in the ‘recently played with’ section. probably just another noob coming to rage.
[PRIVATE] Anonymous-Specter: that was pretty rude, you know.
‘ThAt WaS pReTtY rUde-’ what a beta.
[PRIVATE] TriggerFinger: why shld i care? get a life faggot. lmao
[PRIVATE] Anonymous-Specter: you really shouldn’t talk to people like that.
this guy’s clearly got some form of retardation keeping him from getting the hint. but trigger’s got better shit to do. the loading screen for this game always takes so long. he grabs a pack of shrimp tempura cup ramen off the nearby shelf and fills it with day-old water from his water bottle, shoving it in the microwave for a couple minutes. he numbly trawls through social media feeds, doomscrolling the beautiful faces on instagram before that gets boring, then the stale porn on twitter, then the ragebait on 4chan. nothing satisfying his appetite except this one clip of some guy eating shit on his first try skateboarding, which too is ethereal in the drips of serotonin it gives.
ding!
he grabs his soppy steaming meal and brings it back over to his computer, stirring it with a stray fork before moving back into the screen. the first thing he sees is another message from the same person as before. he rolls his eye and opens the notification.
[PRIVATE] Anonymous-Specter: this you? 78.222.0.13
[PRIVATE] TriggerFinger: TF??
he thinks he’s so cool. trigger quickly tabs over to chrome, typing into the address bar ‘whats my ip ad-’ before it autofills. he clicks in, praying for the release of the little ball of stress slowing spreading in his chest. only to have it implode. IPv4… 78.222.0.13
ok. well, he’s probably just trying to scare you. theres not much you can do with a few numbers. he remembers the streamers he’s watched being ddos’ed and how freaked out they’d always get. he can’t find that humour in the angered horror on their faces now, though.
[PRIVATE] TriggerFinger: thats not my fuckin IP asshole. ur not funny
[PRIVATE] Anonymous-Specter: i think it’s pretty funny.
[PRIVATE] Anonymous-Specter: see you soon :)
trigger looks around his surroundings. nothing around, just the same open bland studio basement. mattress on the floor, check. couch, check. tv, check. tiny window that shows literally nothing but a foot of grass? check. its hard for him to hide the scowl of hatred at this empty rotting enclosure. shit, did you lock the door? he runs up and flicks it locked like how a child runs up the stairs when they’re scared a monsters behind them. not because of this ‘specter’ though. just normal precaution. he wouldn’t let another man take up space in his mind like that.
trigger sits. unable to pull his focus enough to start another game, or to divest himself entirely. stuck in a limbotic resting space. he grabs the monster can sitting on his desk - one of many - and pours it down his throat with anxious franticity. after staring at the screen for long enough, with nothing else he can see to do, he types.
[PRIVATE] TriggerFinger: What r u talking about? fuckin weirdo
10 minutes pass.
[PRIVATE] TriggerFinger: hello?
nothing at all. empty threats and childish games. who puts in that much effort just to cause a little scare? freak, probably a faggot too.
he sighs and switches over to spotify, plugging his favourite XXXtentacion album into his grindy bluetooth speaker and grabbing a pre-roll from his weed drawer. a rusted old lighter folds between his fingers. flick, flick. hot choking mist fills his mouth and then suffuses his screen as he blows it back into the stale air. he lies idly spinning in his gaming chair, puffing until its gone and until the words leave his head. empty.
but not for long, apparently.
a resoundingly loud knocking thuds at his door. earthquaking enough to shake him out of his seatlock. but the tremors remain, rocking through his veins. he gingerly lowers his eye to the peephole. a short man looks up from a foot away, holding some sort of black bag. this is it trigger, time to man up. he paces back with soft steps, pulling a steak knife from the block and holding it behind his back. no more games, this is real life. no more being harassed by that bitch landlord, no more bad looks when mom and dad visit. when the police find him beaten and you on top you won’t have to feel bad anymore.
he opens the door.
“Hello. uber for trig?”
he doesn’t remember ordering any food, was he really that faded?
“it’s… trigger. but that’s me, yeah.”
the man passes trigger an unlabelled brown bag from the bigger unlabelled black bag. something liquid seeps out of the corner.
“have a great night, sir!”
trigger tosses the bag onto the table already scattered with trash. throwing the knife onto the counter along with it. being paranoid is the sign of a weak mind, you need energy. he thinks about the shrooms his bro gave him a couple weeks back, saved for a special occasion in a box under his bed. the devil and angel on his shoulders scream.
he examines the food. taco bell crunchwrap and spilled soda, amazing. he begins to clean it up right as a CLFBKGBNJ clanging from the kitchenette behind his back rings out. he turns to see a tall, muscley imposing man already towering over him from there. backing up slowly, like hes a blind animal that’ll pounce at any moment.
“hey there.”
“hi???” his words spit out with a spiteful acidity, tantrumic.
“you must be trigger.” his monotone face twists upwards into a cruel mockery of a smile. he examines trigger up and down, who shivers at being ogled like meat.
he hears his dad in his head. puff up your chest, faggot. you can’t let people walk over you like a little bitch all the time. he straightens his back, stops retreating. his voice mimics a tough deepness.
“you need to g-get the fuck out of my house.”
specter tilts his head with curiosity. trigger can feel the aftershocks of monster and adrenaline crumpling his heart as he looks into the intruders eyes. a dark jade gazes back, blank. empty. like null space inside his skull, giving off only the aesthetic of a watching being. beyond the entrancing holes, partially hidden behind curtains of frayed brown locks, a jagged scar cuts through his face, curved and serrated with the impression of its assailant.
“it’s not really your house though, is it?”
trigger stares back dumbly. specter lifts up a chiseled arm and knocks on the roof, indicating where the landlord resides. “it’s theirs, really.” he takes a step forward.
“what’s your fucking problem man?”
another step back. guarding facade broken as quickly as it was put up. you’re weak. pathetic. he can smell it on you, just like they all can.
“here to give you an attitude adjustment.” he says it so monotone, like reading a script. as if you should know what that means. specter gives a wide scan of the interior. sizing up your crime scene? this won’t be going the way you think it will, buddy. “this is a pretty shit place you got here”
“not any more shit than the goon cave you probably got, bitch”
the molded smile on specter’s face drops in a second. in 3 sudden steps forward he closes most of the gap between them, the air between the two grows cold. trigger has no choice but to back up more to keep the feeling of safety. the distance between handler and beast, but there’s no leash here. and there’s no medic to save him.
“listen.. s-specter? right?” he looks into those dead eyes with a quiver hes kept hidden for so long. “i'm sorry i insulted you or- or whatever i didn’t mean it okay? that’s just online shit, this isn’t real.”
specter takes another wordless step, and trigger hits the wall. this isn’t real.
“why so quiet all of a sudden?” his hand reaches out and cups triggers chin, his face too frozen with animalistic chemicals to react. forcing trigger’s weak inebriated gaze to meet his, dead yet malevolent. “are you scared of me?”
trigger spits in his face. “you- couldn’t. scare me.”
untrimmed nails dig sharply into the base of his skull. “i will.”
“my dads the chief of police. you don’t wanna do this.” he tries to put on monotone the best he can, head as swirly with emotions as it is.
specter chortles. “no he’s not”
the music emanating from trigger’s desk scratches hard as it changes into a fast-paced track. specter’s eyes and ears twitch in its direction like a bat.
“this is what you listen to?” his smile almost looks genuine this time. he gestures at the ground below them. “stay here.”
he turns and moves to walk past trigger, when he jumps into action, leaping at the man with a guttural yell. “AA-”
immediately cut off by searing blunt force ripping through his gut, sending him crumpling to the floor with the force of extraneous gravity. so you’re a warlock, subclassed into gravitational magic, is that it? he gets up onto his hands and knees, a trail of saliva connecting his lips to the dirty linoleum floors. he chokes on each breath he tries to take in. the pain is unlike anything his soft and unexplored body has experienced before.
specter walks away to the booming speaker, pulling out a black rectangle from the pocket of the black jeans sticking to his legs.. the speakers switch to a new track, unfamiliar to his ears. some kind of aggressive rapping, underscored by a metallic sharp noise groove. he tries to listen for words, analyzing the rhythm and slotting it with memories of other songs to try and figure out what it is. but before he can comprehend the first words to come out, a rigid boot crashes into the side of his ribs.
dazed on the ground, heaving for the little pieces of air that’ll fit through his trachea, cartoons birds twirling over his head as he stares up into the ceiling.
a sharp sound cuts through his stupor. “you’re funny” says specter, “i really thought you’d have more fight in you.”
PHWACK. the sound of some elastic material slapping against skin, a black glove clinging to specter’s boney hand.
trigger’s shocked by the feeling of cold on his bare stomach, face twisting with rage but the rest of the body betrays him with frozen fear. specter begins to slowly lift triggers shirt, feeling up his concave flesh with rubber digits.
specter flinches back as a red handprint manifests on his cheek. i wasnt even thinking i didnt mean to i just-
a vice grip takes hold of his windpipe, holding it hostage. the hand begins to rise upwards, holding him against a wall that wasnt there two seconds ago, and then he has to fight with his noodlish body to stand up before it rips his throat right out. “you’re so weak. how did you make it so long, bullying people like that?” his other hand then puts itself to use. the cold rises up triggers body slow and nerve-wracking. he tries not to feel it and to just keep his eyes on him. the tangible, hurtable, beast.
his mind lags from his body, not realizing he’s on the ground before he already is. terrifyingly strong knees spreading his legs apart ever so slightly, invading hand-shaped ghosts pinning him into the dirty floor face-first. months of uncaring habitation coming back to bite him in the ass all at once. his eyes jump from little pieces of dust and crumbs, filling his vision more than their existence is intended for. brought low with the trash. maybe you should’ve listened to mom.
a bottle squirts loudly out of his sight. he tries to spin his head around but he’s just met with increased pressure on his neck, pinning him down like meat on a butcher’s table. fuck this. thrashing out with all the strength in his limbs- it forces specter to change up his positioning, but even then you can’t make a single scratch, slapping at this very real intruder like a whiney little girl.
“stop it.” he says it like he’s talking to a petulant child, dry and tired.
“fuck you! get off me!”
a rubbery object shoves itself down his throat as he opens his mouth to yell more obscenities. fingers ripping open his jaw, dispelling his pleas into inhuman garbling.
“reht rre throo!”
he looks around, there has to be something he can do. everything is dark blobs because of his eyes wetting from the fingers assault of his uvula. heavy whispers assault the back of his neck, venom in his blurred ears. “i could take out a tooth. how about that?”
he shakes his head, as much as he can crushed between these manly hands.
water trickles down from the corners of his eyes. fuck, don’t let him see you crying, that’s the ultimate defeat. man card revoked. the only benefit of this positioning is that only the tile can see your face’s treason.
the hand abruptly leaves and moves back to the rest of his body. not preferable, but at least now his eyes will stop coating themselves in water. there has to be something on this floor somewhere if he can look.
blood coats his vision. bloody floor, bloody nose, face shoved into a pool of it. he can feel his nose contort under the hard material, head bouncing off it with a loud crack.
‘look’, you shouldve known better. thousands of hours of experience watching torture scenes in COD, and you think he’s gonna give you a break? you’re not the shooter like you thought you were, you’re just the dead russian snitch.
slender hands dip under the waistband of his sweatpants, threatening with slow dragging downwards. fuck, he is a fag. so much screaming in his head, be a man be strong fight back faggot stop being a fucking BETA. but the weak trembling in every inch of his nervous system won’t let go. the part that knows what you are. weak little soyboy. shit, was it the burger king? he looks at the softness of his tiny arms splayed out in front of him, thinking back to all those impossible whoppers he had during that first (and last) year of college. sure there were the conspiracies but- he had to lose some weight and it was right next to his dorm and surely a little bit of hormonal meat couldn’t hurt anyone. well, apparently not. he shudders at the thought of all those tiny little girl particles running around in his bloodstream.
coldcoldcoldcoldcold fuck. something cold and wet drips down his ass, sending rippling twitches through his body. something small pokes and prods, forcing the wet inside, already he feels speared through, he has to purposefully hold his face together to not burst into open sobbing.
“shhh sh sh. it’s okay. you’ll take it.”
it pulls out, a hot emptiness filling all feeling. another squirt, and more wetness shoved so deep he cant handle in the choking cries. “please. please don’t. i don’t- i’m not-” cut off by the finger pulling out again, leaving his hole gaped. “Fuck stop im not gay pleasepleasepleasepl”
a sweaty palm wraps over his mouth.
something warm and hard and fleshy begins to rub circles around his hole. pressing up so close his breath hitches in fear it might go in and then pulling back and then repeating.
“be a good boy and stay quiet, trig.”
pushing pushing pushing pushing pushing pushing
“HEEEEELPP WAIT PLEASE SOMEONE HELP ME PLEASE HELP NONONONONONONO STOPP#&$*%9
&$#%^#^%)#!($#$^%
##&% %%#(% %$$*$#&
*#$&$THELP
* * *
specters hard chest presses up close and warm against trigger’s back. hot, heavy breathing forces its way into his ear. they stay there for a moment, frozen in time. a breaking point cut, getting a cinematic view of his own ruination. what a shitty fucking movie this is.
“mmhng-” specter pulls back, breaking the trance, almost making trigger wish he would’ve just stayed inside. he grunts at the feeling of trembling boyflesh seizing on his cock, shaking with each inch moved in either direction, clenching for dear life. he grips a handful of trigger’s hair and pulls it back, forcing his limp and drooling expression into specter’s vision.
“so, what was it?” the burning rod of pressure starts to move faster, thrusting with detached force, muscular hips bouncing off trigger’s ass. “dad beat you?” another assault forward, enunciating each bit of words with the slapping of their flesh. “mom molest you?” it hurts sososososososososo bad but he cant feel anything other than the pain nothing but searing waves of some long-forbidden feeling. “or- fuck- you just get bullied too much in those squishy formative years?”
boiling hot rain streams down his face, terror burning his eyes blind. choking sobs spit out little bits of snot and saliva pooling with his tears below him in a sad filth soup.
“oh c’mon-” specter reaches in closer, thoughtlessly pushing his cock into a switch that turns triggers legs to jelly. a waterfall of tears overlaid with shameful noises, the kind he’d before only ever heard through the speakers of a computer. each one abrading his will even more. he was supposed to be on the other side, not this. anything but this.
“please stop”
“it’s too late.” his hand brushes triggers cheek, mimicking a comforting motion with uncomfortable skin, “you can never take back what’s already happened… and what’s about to.”
#queue#puppy writing#rbs encouraged i want attention ><#triggers also the new boy name i go by btw but only real ones who look at this shit get to know that
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
stranger things s4e6 the dive
the way i get *so* distracted when a computer comes on screen. computer-brain was already piqued when she's talking about ip addresses (both arpanet moved to tcp/ip and ipv4 started in 83, ok) and using it to determine the location (squint), and plain calling it the internet. was anyone saying internet yet in 1986? i don't know. data mining. geolocation software! (squint aggressively)
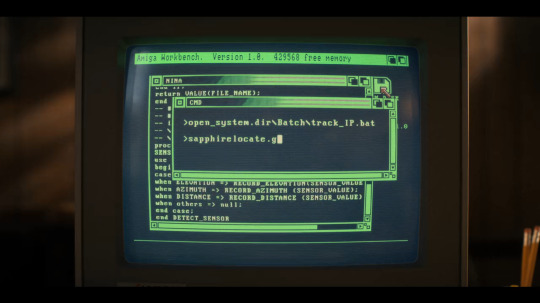
then i see this view and i was like, surely the ~1985 amiga was not using a cmd window and .bat files. that's msdos! but i don't know actually. so now i'm reading the amigados wikipedia page, have watched several people slowly boot 1.x versions of amiga workbench and someone who did briefly open a shell
oh my god this old amiga training video!


anyway confirmed it used forward slashes not back haha
then i'm like well. i wonder what programming language is back behind us here in that nina window. reading the comparison of programming languages syntax wikipedia page for semicolon terminated langs. ada???
so then i scroll back a bit earlier in the ep to see what else ended up on the screen and hello stdio.h in the comments lol
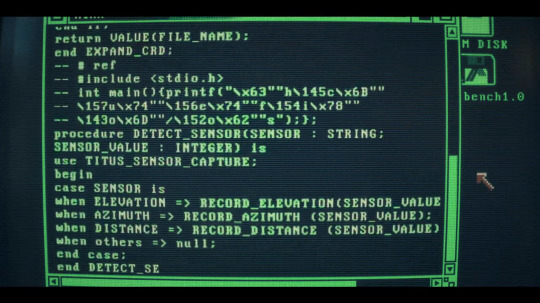
and then i try to go determine when stdio.h became a thing and oh my god STOP (unix version 7 1979???)
i do appreciate their effort. mostly.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
The public IP address displayed below, also known as 'my IP,' is visible to the outside world. Depending on your connection type, you may have an IPv4, an IPv6 or both. If you are behind a router, the IP shown is your router’s public IP, while your device receives a private IP from a DHCP server. To answer 'What Is My IP,' this tool reveals your network’s external identity. https://proxyv6.net/what-is-my-ip/
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, Klint! Welcome to the Internet. I have two questions for you, if that's alright?
1. Do you have any silly nicknames? I've seen your brother go by ziekkyboy.
2. I am DYING to know everything about how you hooked yourself up to the Internet from the afterlife. Can you please give me an explanation with as much technical details as possible? 🙏 I want every juicy little bit!
Miss Sara Nerdnag-
I am Lord Klint van Zieks, Crown Prosecutor of London in service to Her Royal Majesty the Queen. I expect you to know the correct form of address. There is no need to speak of what form of address the little... winged creature, or whatever it is, seems to think is acceptable.
As for the technology, now that I am more than happy to elaborate upon! London - and most of the British Empire - primarily has its communication facilitated fastest by telegraphy, specifically needle telegraphy. I trust you're already familiar with how it works. Tumblr itself is being managed out of one of the telegraphy companies, although I'm quite impressed that they were able to get connectivity in and out of Japan. I understand that they are using submarine cables, copper and electricity wrapped in rubber and latex.
The new Ministers of Foreign Affairs, it seems, have been busy. From what I understand, while telegraphy has been mostly handled by the various postal services, internet - and by extension, Tumblr - is a different matter altogether. The postal service is simple: you enclose who you are, your address, your message, the intended recipient, and their address into an envelope or telegram, and it makes its way to whom it is decided.
The internet, however, is much more complicated. Not only is there far more information that needs to be gathered and transmitted, it must be distributed in a much more widespread manner. What time you sent the message, what time the message is seen, to whom you wish it to be seen by, what your message is, your account information, and all sorts of other information.
This information, once enclosed in such a way that it is not intercepted and modified, must make its way back to the host network - in this case Tumblr - and redistributed to all others on the network, in a timely fashion. What, then, if your location changes? A message for Lady Mikotoba should reach her if she is in Japan or in England. It instead does not locate to her physical address, but to the virtual location of her Tumblr account.
Even so, it must be more complicated than that! It is not a matter of delivering messages in a timely fashion: any message I would send would not reach the recipient as soon as possible, but instead reaches them when they open Tumblr and ask to see what has been posted and sent to them in their absence.
Tumblr then must take all the information they have received, find out what of that information must be given to the user in question, and return it without anything being modified. How, then, can it be sure that it is you speaking to me, and not someone only claiming to be you? At a post office, they might get to know your face, and the faces of those you allow to speak in your stead.
It is my understanding that currently, we are using a protocol known as IPv4, to connect. So long as I am using the same IP address and the same account credentials, it can be trusted that I am myself. My own IP address, when I query my network credentials, is 192.168.10.5. I should not share my account credentials, obviously, but that IP address is the equivalent of my physical home address, only telling you as much as where I live.
So when my query for information reaches Tumblr, they know to send me the posts and messages and questions meant for me.
But I suppose that wasn't quite what you were asking. You asked how I might myself gain access to the internet, and to Tumblr, even though I am a ghost and have been deceased for a decade.
It was actually through the genius of several people, a very odd creature I had to explain to Balmung is off-limits to hunting, and the determination of the dead to speak to the living. While here in the West, the existence of the dead being in our own way sapient and sentient is a hotly debated topic, our good friends in the Far East have already settled this matter.
In fact, it was Detective Asogi who brought to me this information: he told tale once of a clan known as the Ayasato, shrine maidens turned spirit mediums and channelers, able to speak to the dead and bridge the gap of the veil. So, from there, it must be reasoned that should someone who is dead and someone who is alive wish greatly to speak with each other, it should be no more complicated than trying to speak to someone through a thick wall, with only a minuscule hole that transmits light but not sound.
If one side can reach a cable and push it through, they must indeed trust that the other side will reach back and pull it through. They must then trust that the other side will do their part, and they will both work to connect an agreed-upon device to both ends, and only pray that it might work.
The one who pens under the name of John Wilson should take most of the credit: all that was needed was someone soon to die, who understood enough of the device and its installation to recreate it on the other side of the veil, and connect it properly. If both sides configured the device correctly, it would be able to transmit and receive information, exactly like a needle telegraph from across the sea.
A person soon to die was easily found, if admittedly because of circumstances and factors I would rather wish not be the case. A man who escaped justice, already condemned to die at the hands of the Reaper, agreed that should he die, he would do what he could to recreate the device - a router, so named because it routes messages - on this side of the veil.
Fortunately for that particular man, we the dead are perfectly capable of taking notes on blueprints, and by the time the Reaper had his little joke, most of the router was already complete. What we needed, the reason why we couldn't fully configure our end alone, was a means of actually passing through the veil, transmitting messages from one router to another.
The man died holding the cable, and when he appeared to us in the clothes he died in, he was still holding it. We connected it, we configured the agreed-upon IPv4 address through static routing-information-protocol, we pinged the router we knew had been constructed in the daylight, and we watched it return our pings.
From there, it took us some time to expand upon our network. We could speak to one router through a static, established connection: it knew our IP address, and we knew its. We needed connectivity farther out, we needed a means of ensuring our messages did not break down in transit, we needed more power to keep our router functional.
We weren't truly able to communicate through more than Morse code, at first. On, off, on, off. And even that would get jumbled! There were delays that we couldn't predict, so parts of our messages would come through at incorrect times, making anagrams. We needed a method of securing our information in the correct order.
We found it through IPv4's packet structure, which also had to compensate for submarine cables, and through using RIP round-robin routing. So every time I go to query tumblr, it sends one packet out, waits for an acknowledgement, and then sends out the next. This has gone well to reduce failed connectivity, and that took us several months of troubleshooting.
Fortunately, our correspondent on the other side of the veil wasn't losing faith in us, even when it was hours between signals of activity. It was obvious we were communicating back, just having issues with consistency. Once we were able to get that far, we had to properly encrypt our messages, so that they wouldn't be altered in transit. Even if they were damaged, it would be possible to reverse-engineer them into a message that made sense.
Admittedly, we would have been here much sooner if encryption was not an issue, given that we could not exactly voice any concerns or discuss the final plans, but eventually we settled on AES 128, which was a nightmare to set up but did work out eventually.
Once we got that far, catastrophe struck, and our cables started to break. In a stroke of genius, our living correspondent hooked us up to a telephone signal, which transmitted our signals into audio instead of simple electric pulses, known as dialup technology. Then, it was only a matter of agreeing on a code, and creating a device that would translate what it heard into symbols.
This solved our issue of incomprehensible anagrams permanently: voices and audio came through consistently enough that it would stop colliding with other bits of information in the network passageways and cables.
Once that was solved, just a couple days ago, we were finally up in proper communication, and set to testing everything we could, and now here I am, with a Tumblr of my very own, and I can finally say hello to everyone!
Yours in delighted correspondence,
Prosecutor van Zieks
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) Networking
As the world moves towards IPv6 to accommodate the ever-growing number of devices, one key protocol makes sure everything runs smoothly: IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). This protocol is crucial for devices to find each other, configure their IP addresses, and ensure proper communication over an IPv6 network. In simpler terms, it’s like a “digital handshake,” allowing devices to talk and exchange important information seamlessly.
In this guide, we’ll break down the workings of NDP in a way that’s easy to understand, even for those new to networking. Whether you’re a network engineer, a student learning about IPv6, or simply someone curious about how your devices connect, this article will provide you with all the essential insights you need to master the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol and improve your understanding of IPv6 networks.
What Is IPv6 Neighbor Discovery?
Imagine you’ve just moved to a new neighborhood. You don’t know anyone yet and have no clue where the grocery store is or how to reach the nearest bus stop. Naturally, you’d walk around, introduce yourself, ask for directions, and gradually get familiar with your surroundings.
Choose platforms that align with your audience and goals. For more information on choosing the right platforms, check out this guide from Networkerden
Well, computers do something similar on an IPv6 network.
The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) helps devices
In simpler words, it’s the way devices on IPv6 networks say, “Hi, who are you?” and “Are we connected properly?”
In IPv4, we had something called ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). However, in IPv6, NDP is the new standard.
Key Features of NDP
Here’s what NDP does under the hood:
Each of these steps ensures devices can talk to each other smoothly and securely.
NDP Message Types
Let’s say you're new to a college campus. Here's how you might interact and how NDP mimics those interactions.
1. Router Solicitation (RS)
"Hey, is there any router out there?"
A new device (host) sends this message to discover local routers.
2. Router Advertisement (RA)
"Yes! I'm your router. Here are the network details."
Routers reply with necessary information like prefix, MTU, and default gateway.
3. Neighbor Solicitation (NS)
"Hey, I need your MAC address. Can you share it?"
Used to resolve the link-layer address of a neighbor or to check if a neighbor is reachable.
4. Neighbor Advertisement (NA)
"Here I am! Here's my MAC address."
Devices respond to NS messages, confirming they are active.
5. Redirect
"Hey, I’m not the best route. Use that other router instead."
Routers use this to guide hosts to better next-hop addresses.
Step-by-Step: How Devices Use NDP
Here’s a step-by-step example of what happens when your device connects to an IPv6 network:
What About Security?
NDP, by default, is a bit too trusting. That’s where SEND (Secure Neighbor Discovery) comes in, like installing a security camera on your network block.
SEND protects against:
It's not widely used everywhere yet, but it's available for high-security environments.
NDP vs. ARP: What's the Difference?
NDP is smarter, safer, and more flexible than ARP.
Why Should You Care?
Whether you’re a student, IT professional, or a curious tech enthusiast, knowing about IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol helps you understand how devices "talk" on modern networks.
And if you're setting up IPv6-enabled products, routers, or even enterprise networks, this knowledge is crucial. When your network behaves strangely, it's often due to misconfigured NDP settings.
Planning to buy an IPv6 router or firewall? Now you know exactly what features to look for. make sure it supports proper NDP handling and even SEND if needed.
Check out this list of top IPv6-capable routers for reliable options.
A Quick Anecdote: When NDP Saved the Day
Last year, an IT admin named Ravi was migrating a mid-size company's internal systems to IPv6. Everything seemed perfect — until random devices lost connectivity. After hours of debugging, it turned out that the Router Advertisement messages weren’t reaching all subnets.
A simple configuration of RA intervals and proper NDP multicast support fixed everything. The lesson? Never underestimate the power of protocol details!
FAQs About IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
1. What is IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)?
NDP is a system that helps devices find each other on an IPv6 network, get their IP addresses, and make sure they can communicate properly. It’s like devices introducing themselves and checking if they are on the same network.
2. How Does Neighbor Discovery Work?
NDP sends messages between devices. First, a device looks for routers. Then, it gets information from them. Devices also ask each other for MAC addresses to communicate. NDP also checks if two devices have the same IP address to avoid conflicts.
3. What Are the Benefits of NDP in IPv6?
c
Yes! NDP can be secured with Secure Neighbor Discovery (SEND), which uses encryption to prevent hackers from sending fake messages or intercepting communication.
Final Thoughts: Make Friends with NDP
Over to You
Have you ever faced an NDP issue or gotten stuck while setting up IPv6? Share your experience below — let’s learn from each other. Or feel free to connect with us for a deeper dive!
#tech#technology#ipv6#IPv6 protocol overview#IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)#IPv6 global unicast addresses
1 note
·
View note
Text
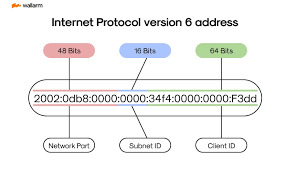
(2024-10-20 image ©wallarm) What is my IP? When connected to the 4G network the page returns an IPv4 address and states, for me at least, IPv6 Not Detected. If I do the same when connected to my home WiFi I get a different IPv4 address; but still no IPv6 address.
Back in the early 1980's when IPv4 addresses were devised it was thought that th system of 4 blocks of numbers 0 to 255 would be enough for all computing devices. But this is not the case any more. The router at home has an IPv4 address, and all the computing devices have a local address, an address relative to the router address. If you wish to connect to an IP camera or a web site on your home network then you will use a port on the router, and set up the routing from the port to the device on your router manually. You need access to the router to do this.
Why am I saying all this on a mobile phone technology blog? Well the way my 4G phone connects to Vodafone is similar the way a home router works. A number of Vodafone have the same IPv4 address and Vodafone routes the data to the correct phone. This does mean I cannot run a camera or web server on the Vodafone network unless I persuade then to give me a unique static IPv4 address.
IPv6 came along a decade later when IPv4 addresses were running out. It is a testimate to our ingenuity to state the IPv4 still works in 2024. With 128bits IPv6 addresses can uniquely identify any device with a chip in it now and decades to come. Anyone who has smart devices at home could have say 60 devices connected to their home router, which would need 60 IPv6 addresses which is easy to obtain and so each device can have a unique IP number. Despite IPv6 being over 30 years old we still have not switched over. But if we did then mobile phone technology would be in a better place to have more and more devices connected to the network and addressable from anywhere, with no restrictions. This would open up mobile networks as a more direct competitor to land bases systems, allowing more applications.
1 note
·
View note
Text
ITNW1337 MODULE 1 TO 3 GANGBO'S PORTFOLIO
Bio
30 years old, originally from the Benin Republic. Currently stationed at Fort Hood, Texas, serving as a combat engineer in the US Army. Immigrated to the US in 2016 to improve English and pursue personal development. Now pursuing an associate degree in Information Technology (IT), aiming for a successful transition from military to civilian life. Enthusiastic about online education and eager to connect with fellow students.
INTRODUCTION
The Internet is a vast network of interconnected computers that enables users to communicate, access, and share information. It serves as a platform for various online activities, such as research, communication, and entertainment. My ITNW 1337 class, covering modules 1 to 3, explores a wide range of topics, starting with the methods and tools required to connect to the Internet, including various types of connections like broadband and mobile, as well as network setup.
The course introduces web browsers—software applications that facilitate Internet navigation—discussing features like tabs, bookmarks, and history. It also focuses on effective searching techniques using search engines, providing tips for refining search queries to quickly find relevant information.
Additionally, the modules cover the basics of email, including how to create an account, send and receive messages, and manage attachments. There's an exploration of cloud storage solutions that allow users to store and access files online, along with productivity tools that enhance collaboration and efficiency.
The course discusses different methods for transferring files, such as email attachments, cloud services, and FTP (File Transfer Protocol). It examines various online platforms for sharing information and engaging with communities, highlighting their functionalities and purposes.
Furthermore, the modules introduce technologies that enable quick access to information through mobile devices, discussing their applications in marketing and communication. Finally, the course module 3 summarizes eight essential skills or tools necessary for effectively navigating the digital landscape, emphasizing their importance in everyday online interactions.
Overall, these modules aim to equip users with the essential skills needed to navigate the Internet successfully and utilize its vast resources for both personal and professional growth.
Module 1
Key Concepts
What is the Internet?
The Internet is the largest global network of interconnected computers, known as a "network of networks," enabling communication and data transfer between billions of devices.
Originating from ARPANET, it transitioned from a government project to a public network by 1995.
How the Internet Works
The Internet relies on physical infrastructure like fiber optics, cable, and telephone lines.
Devices communicate using an addressing system based on the Internet Protocol (IP), with IPv4 being the original structure, now transitioning to IPv6 to accommodate more devices.
Domain Name Servers (DNS) translate human-friendly URLs into IP addresses, simplifying web navigation.
Accessing the Internet
Access requires a device and an Internet connection, typically through ISPs. Major connection types include Fiber Optic, Cable, DSL, Fixed Wireless, Satellite, and Cellular.
Web Browser Basics
Web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari) are applications used to access the World Wide Web. They retrieve web pages based on URLs.
Internet Search Tools
Search engines help users find information online by indexing web pages using algorithms (e.g., PageRank) to determine relevance.
Effective searching requires understanding how to use search engines, including query operators and advanced search techniques.
Documents and Links
Links or documents that support my learning.
youtube
youtube
youtube
content.ctcd.edu/courses/itnw1337oer/m21/docs/cheat_sheet_search.pdf
www.bing.com/ck/a?!&&p=54eebb917e039ffee2bdc5f50a891bd748bcdd37c467dfda4f890a8fc71c52c5JmltdHM9MTcyNjk2MzIwMCZpbnNpZD01MjEx&ptn=3&ver=2&hsh=4&fclid=2f1955d3-0e7c-615d-1d19-41000f2b6077&psq=Visual+representation+of+IPv4+vs.+IPv6&u=a1aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cueW91dHViZS5jb20vd2F0Y2g_dj12bzVnbEs5Y3pJRQ&ntb=1
Overall understanding the fundamental concepts of the Internet, how it works, and the tools available for accessing and navigating it is crucial for both personal and professional growth. This knowledge empowers me to use the Internet more effectively, enabling efficient research, communication, and collaboration. I can apply these skills to improve my online learning experience and help others in navigating digital spaces, fostering a more connected and informed community. By mastering search techniques and browser functionalities, I’ll be better equipped to find reliable information
Module 2
This module explores essential communication and productivity tools that enhance both personal and professional life, such as email services, cloud storage, and file transfer protocols. These technologies enable instant communication, data storage, and easy file sharing across devices, improving efficiency in today’s digital world.
Key Concepts Learned
Email Services:
Definition: Email is an electronic communication tool allowing users to send and receive messages via the Internet.
Key Elements: Emails include a username and domain name separated by the “@” symbol. Hosted email addresses (e.g.gov, Edu, .mil) are organization-specific, while webmail services (e.g., Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook) are free and widely used for personal and business purposes.
Common Features: Address book, calendar, and instant messaging options are often included.
Cloud Storage and Productivity:
Definition: Cloud storage allows users to save data on remote servers (not their local computers) and access it from any device with an Internet connection.
Common Cloud Services: Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, and Apple iCloud.
Benefits: File sharing, collaboration, data backup, and the ability to work from anywhere.
Productivity Tools: Web-based applications like Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365 allow users to create and collaborate on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
Transfer of Information on the Internet:
Email Attachments: Files can be attached to emails for easy sharing.
Cloud Storage File Sharing: Users can upload files to cloud services and invite others to view or download them.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): A method for transferring large files over the Internet, often used by web developers. FTP requires an FTP client like FileZilla or WinSCP to manage file transfers.
Links to Resources
youtube
youtube
youtube
Reflection Section
This module helped me understand how communication technologies like email and cloud storage simplify both personal and professional tasks. I can now effectively use cloud storage services to backup and share files. Additionally, learning about FTP has broadened my understanding of how web developers manage large file transfers. In my future career, especially in IT, I see myself applying these skills to enhance collaboration and streamline workflows, particularly in remote work environments.
Module 3
This module covers the evolution of communication platforms and digital interactions through social media, blogs, wikis, and forums, along with innovations like QR codes, NFC technology, and emerging technologies. These tools revolutionize how we connect, share information, and engage with digital content, while advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT are shaping the future.
Key Concepts Learned and Definitions
Social Media Platforms:
Definition: Social media includes a wide variety of platforms that allow users to share content, connect, and collaborate. These platforms range from blogs and forums to content communities and wikis.
Examples:
Content Communities: YouTube, Pinterest
Blogs: WordPress, Blogger
Forums: Quora, StackExchange
Wikis: Wikipedia, WikiHow
Social Networks: Facebook, LinkedIn, X (formerly Twitter)
Podcasts: BuzzSprout, Spreaker
Usage:
Social media allows for different types of interaction:
Blogs: Author-centric platforms for sharing opinions and information with readers.
Wikis: Collaborative platforms where content is created and modified by multiple users.
Forums: Discussion-based platforms where users can share their thoughts on specific topics.
QR Codes, SnapTags, and NFC Technology:
QR Codes: Two-dimensional barcodes that can be scanned with mobile devices to access digital content or websites.
SnapTags: An advanced version of QR codes, offering additional features and interactivity without needing special apps or high-end phones.
NFC (Near Field Communication): A short-range wireless technology that allows devices to exchange information when they are in close proximity (less than 4 inches), widely used in contactless payments and data sharing.
The Essential Eight Technologies:
Internet of Things (IoT): A network of physical devices connected via the Internet, capable of collecting and sharing data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Machines simulating human intelligence to perform tasks like decision-making and problem-solving.
Blockchain: A decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers securely.
Augmented Reality (AR): Technology that overlays digital content onto the real world through devices like smartphones.
Virtual Reality (VR): A simulated experience using a headset that immerses users in a digital environment.
Advanced Robotics: Robots with enhanced capabilities used in fields like manufacturing, healthcare, and defense.
Quantum Computing: A new computing paradigm that leverages quantum mechanics to solve complex problems faster than classical computers.
Neuromorphic Computing: Computing systems designed to mimic the human brain's neural structure for improved AI processing.
Links to Resources
youtube
youtube
youtube
Reflection Section
This module introduced me to the various tools we use for digital communication and collaboration, such as social media platforms, QR codes, and NFC technology. I was particularly interested in learning how platforms like blogs and forums differ in terms of interactivity and content ownership. Additionally, exploring technologies like NFC, SnapTags, and the Essential Eight provided valuable insights into the future of digital communication, payments, and AI-driven innovations.
In my IT career, I can apply this knowledge by leveraging NFC for secure data exchange or contactless payments, and by staying informed about how emerging technologies like AI and blockchain will impact industries. Understanding these tools will help me adapt to new tech trends and possibly integrate these advancements into business solutions.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What are the methods of determining IP addresses?
IP address is an important identifier for our connection to the Internet. So, do you know how to determine the IP address of your device? Today we will explain several common methods of IP address determination to help you easily understand the network information of your device!

Method 1: Check the local IP address through the operating system
Different operating systems have built-in tools that can help you quickly view the internal IP address of your device.
Windows
1. Press Win + R and type cmd to open the command prompt.
2. In the command prompt, type ipconfig and press enter.
3. Look for the “IPv4 address” field, which shows your local IP address.
For macOS system
1. Click on the Apple icon in the upper left corner and select “System Preferences.
2. Select “Network”.
3.In the network connection status, you can see your local IP address.
Linux system
1. Open Terminal.
2. Type ifconfig or ip addr and press enter.
3. Look for the address after inet, which shows the local IP address.
Method 2: Check device IP address through router background
If you want to know the internal IP addresses of all the devices in your home, you can check them through the management background of your router:
1. Open your browser and enter the IP address of your router (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) in the address bar.
2. Enter the router's administrator username and password.
3. In the Device Manager or Connected Devices list, you can see the internal IP address of each connected device.
Method 3: Use network tools to view external IP address
Want to know your external IP address, i.e. the IP of the device on the Internet?Here are a few easy ways to do it:
· via search engine: directly search “my IP address” in Google or Baidu, and your external IP address will be displayed at the top of the search result page.
· Use IP query websites: e.g. visit whatismyip.com, ipinfo.io, etc. They will display your external IP address and some related information such as geographic location.
Method 4: View IP address through applications
In addition to the tools that come with your operating system, you can also use third-party applications to view and manage your device's IP address:
·Network Utility (comes with macOS): It can help you diagnose network problems and view the IP address.
·Fing (iOS and Android): can scan all devices in the network and display their IP addresses.
Method 5: Check device settings
For mobile devices such as cell phones and tablets, you can view the local IP address directly in the device's Wi-Fi settings:
·iOS devices: Open “Settings”, select “Wi-Fi”, click the currently connected Wi-Fi network, and the IP address of the device will be displayed on the page.
·Android device: Open “Settings”, go to “Network & Internet” or “Wi-Fi” settings, tap the currently connected network, and then check the IP address. network, and then check the IP address.
There are many ways to determine your IP address. IP addresses are an integral part of your network, and understanding and managing them can help optimize your experience. If you want to manage your IP address more flexibly and securely, try 711Proxy, which provides high quality proxy IP service to cope with all kinds of network needs easily!
0 notes
Text

buy ipv4 addresses
How to Get People's IP Address: Essential Tips and Tricks
Understanding how to get someone's IP address can be crucial for various technical needs. Here, we explore three effective methods for finding someone else's IP address.
3 Ways to Find Someone Else’s IP Address
1. IP Lookup IP lookup tools allow you to find an IP address by entering a website URL or domain name. These tools provide details about the IP address, including location and ISP.
2. Email Headers Email headers contain the IP address of the sender. To find it:
Open the email.
View the email headers.
Look for lines starting with "Received" to find the originating IP address.
3. Command Prompt
Run ipConfig
Open Command Prompt.
Type ipconfig and press Enter.
This displays your own IP address and other network details.
Run ping
Open Command Prompt.
Type ping [website/domain] and press Enter.
This shows the IP address of the website or domain.
Buying IPv4 Addresses: A Brief Guide
While finding an IP address is useful, understanding how to buy IPv4 addresses is equally important for network expansion. When you buy IPv4 addresses, ensure you're dealing with reputable brokers and follow proper procedures to avoid legal issues.
FAQs
Q1: Is it legal to find someone's IP address? A: Generally, finding an IP address is legal, but using it for malicious purposes is illegal.
Q2: Can I buy IPv4 addresses for my business? A: Yes, you can buy IPv4 addresses for your business. It's essential to work with a trusted broker.
Q3: What should I look for when buying IPv4 addresses? A: Ensure the addresses are clean, without any associated negative history, and that the transaction is transparent.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ask The Videoguys - Tech Advice and Top Tech Tips from the Videoguys - Videoguys
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/ask-the-videoguys-tech-advice-and-top-tech-tips-from-the-videoguys-videoguys/
Ask The Videoguys - Tech Advice and Top Tech Tips from the Videoguys - Videoguys


On this weeks Videoguys Live, James hosts Ask the Videoguys where he will give Technical Advice for your production as well as sharing our Top Videoguys Tech Tips. James will share tips on frame rates/bit rates for live streaming, differences between 3G, 6G, & 12G SDI, finding the IP address of NDI PTZ Cameras, setting up a REMI production, differences between RAID 0, 1, 5, & 6, on the go storage solutions, and more!
Watch the full video below:
youtube
What streaming resolutions/frame rates do different CDNs recommend? What bitrate should I use?
Platform
Resolution
Compression
Bit Rate
Facebook
1080 60p
H.264
4.5-9mbps
YouTube
4k 60p
H.265/H.264
10mbps/35mbps
1080 60p
H.265/H.264
4mbps/12mbps
LinkedIn
720 30p
H.264
3.5-6mbps
Tech Tip: use the highest common denominator for resolution and frame rates when streaming to multiple destinations if your encoder doesn’t allow different settings
What is the difference between 3G, 6G and 12G SDI? And why would I choose SDI over HDMI?
3G SDI – Up to 1080 60
6G SDI – Up to 4k 30
12G SDI – Up to 4k 60
SDI Pro SDI Con HDMI Pro HDMI Con Long Cable Run Can Cost More Inexpensive Short Cable Run BNC Locking Mechanism Need to know if it’s 3G, 6G, or 12G Common No Locking Mechanism 4K 60 through a standard cable
Tech Tip: Consider using AV over IP as it is the best of both worlds giving long cable runs, on a common cable with a locking mechanism!
How do I find the IP address of my NDI PTZ camera and change it to either DHCP or Static?
Download NDI Tools
Open NDI Analysis
Plug camera into network
Run the “NDIAnalysis.exe /find” command
Find the IP address of the desired camera
Plug in external Network Adaptor to computer
In Network settings on computer change Network adapter settings to be on the same range as the camera
Select “Change Network Adaptors”
Right click on USB Ethernet
Select “TCP/IPv4”
Change Ip address to be same range as range from NDI Analysis
Plug camera into network adaptor and turn on camera
Now you can access the cameras web gui to change camera settings to DHCP or a Fixed Ip of your choosing
Once DHCP or Static is selected, unplug the camera and plug into Network Switch
For complete Remi control, what products do you recommend starting with?
PTZOptics Hive Studio
BirdDog Cloud
Epiphan Connect
NDI Bridge
LiveU Studio
Now Is the Perfect time to get into Remote Productions with so many workflows!
What is the difference between Raid 0, Raid 1, Raid 5 and Raid 6?
RAID 0 (Striping): Data is stored evenly across the number of disks in the array. This process is called disk striping and involves splitting data into blocks and writing it simultaneously/sequentially on multiple disks. It provides improved performance but no redundancy
RAID 1 (Mirroring): Data is duplicated and stored on each drive. This process is called mirroring, and it ensures you won’t lose your files if a drive fails. It provides redundancy but no performance gain
RAID 5: Uses disk striping with parity. It sets aside “one drive’s worth” of disk space for parity data. RAID 5 requires fewer hard drives but can provide protection against a single drive failure
RAID 6: Similar to RAID 5 but introduces dual parity. It sets aside “two drives’ worth” of disk space for parity data. RAID 6 can provide protection against two simultaneous drive failures
What is the best storage system for storage on the go?
Definition: Portable rugged SSD drives are high-capacity, high-speed storage devices that are designed to withstand harsh conditions.
Use Cases: Ideal for outdoor use, travel, and situations where data might be exposed to rough handling or environmental hazards.
Advantages: They offer the speed of SSDs, combined with a design that is resistant to shock, dust, and water.
We can help you find the perfect drive for your on-the-go needs, whether it’s waterproof, dust proof, shock proof or all of the above
#4K#6G#Advice#amp#Analysis#Best Of#bridge#Cameras#change#Cloud#command#compression#computer#data#Design#devices#dhcp#Difference Between#dust#Environmental#Facebook#Full#Giving#gui#hazards#hdmi#Hive#how#it#LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
what's my ip address vpn
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
what's my ip address vpn
Dirección IP
Una dirección IP (Protocolo de Internet) es un identificador único asignado a cada dispositivo que se conecta a una red informática. Se compone de una serie de números que permiten la comunicación entre distintos dispositivos a través de Internet.
Existen dos tipos de direcciones IP: IPv4 e IPv6. IPv4 es el formato más común y está compuesto por cuatro números separados por puntos, mientras que IPv6 es una versión más avanzada que utiliza ocho grupos de números y letras. A medida que la cantidad de dispositivos conectados a Internet ha aumentado, la transición de IPv4 a IPv6 se ha vuelto cada vez más necesaria para garantizar la disponibilidad de direcciones IP únicas para todos los dispositivos.
Las direcciones IP pueden ser estáticas o dinámicas. Una dirección IP estática es aquella que se asigna manualmente y permanece constante, lo que la hace ideal para servidores y otros dispositivos que necesitan una dirección fija. Por otro lado, una dirección IP dinámica se asigna automáticamente por un servidor DHCP y puede cambiar periódicamente, lo que es común en dispositivos domésticos y de oficina.
Es importante proteger la privacidad de nuestra dirección IP, ya que puede revelar información sobre nuestra ubicación y actividad en línea. El uso de redes privadas virtuales (VPN) y software de protección de la privacidad puede ayudar a mantener segura nuestra dirección IP y nuestra información personal mientras navegamos por Internet.
VPN
Un VPN, o Red Privada Virtual, es una herramienta cada vez más popular en el mundo digital de hoy en día. Se utiliza para proteger la privacidad y la seguridad en línea al enmascarar la dirección IP del usuario y encriptar sus datos mientras navega por internet.
Una de las principales ventajas de utilizar un VPN es que permite acceder de forma segura a sitios web restringidos geográficamente, como servicios de streaming o redes sociales que podrían estar bloqueados en ciertas regiones. Además, al utilizar un VPN, se evita que los proveedores de servicios de internet (ISP) o los ciberdelincuentes accedan a la información personal y hábitos de navegación del usuario.
Otro beneficio clave de un VPN es la capacidad de mantener la privacidad al navegar por internet. Al encriptar la conexión, un VPN permite a los usuarios proteger su actividad en línea de posibles miradas indiscretas. Esto es especialmente importante en redes públicas, donde la seguridad de la información puede estar comprometida.
En resumen, un VPN es una herramienta fundamental para aquellos que valoran su privacidad y seguridad en línea. Con su capacidad para enmascarar la dirección IP, encriptar datos y acceder a contenido restringido, un VPN ofrece una solución integral para protegerse en el mundo digital actual. Si buscas mantener tu privacidad en línea y navegar de forma segura, considera utilizar un VPN para proteger tus datos y disfrutar de una experiencia en línea más libre y segura.
Identificación de IP
La identificación de IP es un proceso fundamental en el mundo digital actual. Una dirección IP es un identificador único asignado a cada dispositivo conectado a una red, ya sea en internet o en una red local. La identificación de IP es esencial para la comunicación entre diferentes dispositivos y para asegurar que la información se envíe y reciba de manera correcta.
Existen diferentes métodos para identificar una dirección IP. Uno de los más comunes es a través del Protocolo de Internet, que asigna direcciones IP de forma dinámica o estática a los dispositivos según sea necesario. También se pueden utilizar herramientas como el comando "ipconfig" en sistemas operativos Windows o el comando "ifconfig" en sistemas basados en Unix para identificar la dirección IP de un dispositivo.
La identificación de IP tiene importantes implicaciones en la seguridad cibernética. Las direcciones IP pueden ser utilizadas para rastrear la actividad en línea de un dispositivo y pueden ser usadas para identificar posibles amenazas o vulnerabilidades en una red. Es por eso que la identificación de IP es crucial para mantener la seguridad de la información en línea.
En resumen, la identificación de IP es un proceso clave en la comunicación digital y en la seguridad cibernética. Entender cómo funciona y cómo se utiliza esta dirección única es esencial para garantizar una comunicación segura y efectiva en el mundo digital actual.
Protección de datos
La protección de datos es un tema de suma importancia en la actualidad, especialmente en un mundo cada vez más digitalizado. Se refiere a todas las medidas y procedimientos necesarios para garantizar la seguridad y confidencialidad de la información personal de los individuos.
En muchos países, existen leyes y regulaciones estrictas que establecen cómo las organizaciones deben recolectar, almacenar y procesar los datos personales de las personas. El incumplimiento de estas normativas puede llevar a sanciones severas, multas económicas y daños a la reputación de una empresa.
Es fundamental que las empresas implementen medidas de seguridad adecuadas, como cifrado de datos, firewalls, políticas de privacidad claras y entrenamiento para empleados sobre la importancia de la protección de datos. Además, es crucial obtener el consentimiento explícito de los individuos antes de recopilar y utilizar su información personal.
La protección de datos no solo beneficia a los individuos al garantizar su privacidad, sino que también genera confianza en los clientes y mejora la reputación de una empresa. Las organizaciones que se toman en serio la seguridad de los datos demuestran su compromiso con la transparencia y el respeto hacia sus usuarios.
En resumen, la protección de datos es un aspecto fundamental en la era digital, y todas las empresas deberían priorizar la seguridad y confidencialidad de la información personal de las personas. Al hacerlo, no solo cumplen con la ley, sino que también construyen relaciones sólidas y duraderas con sus clientes.
Privacidad en línea
La privacidad en línea es un tema de suma importancia en la actualidad, ya que vivimos en un mundo cada vez más digitalizado donde compartimos una gran cantidad de información personal en internet. Es fundamental tomar medidas para proteger nuestra privacidad y seguridad en línea.
Una de las principales recomendaciones para salvaguardar nuestra privacidad en línea es ser conscientes de la información que compartimos en la red. Es importante revisar las configuraciones de privacidad en nuestras redes sociales y limitar la cantidad de información personal que compartimos públicamente. Además, es aconsejable utilizar contraseñas seguras y actualizarlas regularmente, así como evitar conectarse a redes Wi-Fi públicas no seguras.
Otra medida importante es utilizar herramientas de seguridad, como firewalls y programas antivirus, para proteger nuestros dispositivos de posibles amenazas en línea. Asimismo, es recomendable ser cautos al hacer clic en enlaces sospechosos o descargar archivos de fuentes desconocidas, ya que podrían contener malware.
En resumen, cuidar nuestra privacidad en línea es fundamental para proteger nuestra información personal y prevenir posibles riesgos en internet. Adoptar medidas de seguridad y ser conscientes de la información que compartimos son pasos clave para mantenernos seguros en el mundo digital en el que vivimos.
0 notes
Text
what is my ip address vpn
🔒🌍✨ Obtén 3 Meses GRATIS de VPN - Acceso a Internet Seguro y Privado en Todo el Mundo! Haz Clic Aquí ✨🌍🔒
what is my ip address vpn
Dirección IP
Una dirección IP, también conocida como Protocolo de Internet, es un identificador único asignado a cada dispositivo conectado a una red de computadoras que utiliza el protocolo de Internet para la comunicación. Las direcciones IP se utilizan para identificar y localizar dispositivos en una red, lo que permite la transmisión de información de un dispositivo a otro a través de Internet.
Existen dos tipos de direcciones IP: IPv4 e IPv6. IPv4 es el estándar original y consta de una serie de cuatro números separados por puntos, mientras que IPv6 es una versión más reciente que utiliza una serie de ocho grupos de números y letras separados por dos puntos. A medida que la cantidad de dispositivos conectados a Internet sigue aumentando, IPv6 se está implementando gradualmente para hacer frente a la limitada cantidad de direcciones IPv4 disponibles.
Las direcciones IP se dividen en direcciones públicas y direcciones privadas. Las direcciones IP públicas son aquellas utilizadas para identificar dispositivos en Internet, mientras que las direcciones IP privadas se utilizan para identificar dispositivos en una red local, como un hogar o una oficina.
Es importante proteger la dirección IP de un dispositivo para evitar posibles amenazas de seguridad, como el robo de identidad o el acceso no autorizado a la red. Utilizar una red privada virtual (VPN) o un cortafuegos puede ayudar a proteger la dirección IP y la información confidencial que se transmite a través de Internet.
VPN
Un VPN, o red privada virtual en español, es una herramienta cada vez más popular entre los usuarios de Internet. Pero, ¿qué es exactamente un VPN y por qué deberías considerar usarlo?
Un VPN es un servicio que te permite navegar de forma segura y anónima por Internet. Cuando te conectas a un VPN, tu conexión se encripta, lo que significa que tus datos estarán protegidos de posibles ciberataques o robos de información. Además, al ocultar tu dirección IP real, un VPN te permite mantener tu privacidad en línea y evitar la censura impuesta por gobiernos u otras entidades.
Pero las ventajas de un VPN no se limitan a la seguridad y la privacidad. También te permite acceder a contenido restringido geográficamente, como páginas web o servicios de streaming que no están disponibles en tu país. Esto es especialmente útil para aquellas personas que viajan con frecuencia o desean disfrutar de contenido exclusivo de otros lugares.
En resumen, un VPN es una herramienta versátil que te proporciona seguridad, anonimato y libertad en Internet. Si valoras tu privacidad y deseas navegar por la web de forma segura, considera utilizar un VPN para proteger tus datos y disfrutar de una experiencia en línea sin restricciones.
Identificación de ubicación
La identificación de ubicación es un proceso fundamental en el ámbito de la tecnología y la seguridad informática. Consiste en determinar la ubicación geográfica de un dispositivo, usuario o recurso en internet. Esta información es crucial para diversas aplicaciones, como la prestación de servicios basados en la ubicación, la seguridad de la información y la prevención de fraudes.
En el ámbito de la seguridad informática, la identificación de ubicación se utiliza para verificar la autenticidad de un usuario o un dispositivo. Por ejemplo, al acceder a una cuenta bancaria en línea, el sistema puede verificar la ubicación del usuario para detectar posibles intentos de fraude. De esta manera, se pueden tomar medidas para proteger la información y prevenir accesos no autorizados.
Además, la identificación de ubicación es fundamental en la prestación de servicios basados en la ubicación, como la navegación GPS, la búsqueda localizada y la publicidad dirigida. A través de la geolocalización, las empresas pueden ofrecer a los usuarios información relevante y personalizada de acuerdo a su ubicación física.
En resumen, la identificación de ubicación es un aspecto clave en la tecnología actual, que permite mejorar la seguridad, personalizar los servicios y facilitar la interacción con los dispositivos electrónicos. Es importante seguir desarrollando tecnologías y políticas que protejan la privacidad de los usuarios, al tiempo que aprovechan los beneficios de la geolocalización en el mundo digital.
Seguridad en línea
La seguridad en línea es un tema de vital importancia en la era digital en la que vivimos actualmente. Con el crecimiento exponencial de la tecnología y el uso generalizado de internet, es fundamental estar al tanto de las medidas de seguridad que debemos tomar para proteger nuestra información personal y nuestra privacidad en línea.
Uno de los aspectos clave de la seguridad en línea es la protección de nuestros datos personales. Es fundamental ser conscientes de la información que compartimos en la web y asegurarnos de que solo la compartimos en sitios seguros y de confianza. Utilizar contraseñas seguras y cambiarlas regularmente, así como activar la verificación en dos pasos, son prácticas recomendadas para proteger nuestras cuentas en línea.
Otro aspecto importante de la seguridad en línea es la protección contra malware y virus. Es fundamental contar con un buen software antivirus y mantenerlo actualizado para proteger nuestros dispositivos de posibles amenazas. Evitar hacer clic en enlaces sospechosos o descargar archivos de fuentes desconocidas también contribuye a mantenernos seguros en línea.
En resumen, la seguridad en línea es una responsabilidad que recae en cada uno de nosotros. Estar informados, tomar precauciones y ser conscientes de nuestra presencia en línea son pasos fundamentales para garantizar una experiencia segura y protegida en el mundo digital. ¡Protege tu información, protege tu privacidad, protege tu seguridad en línea!
Privacidad en internet
La privacidad en internet es un tema cada vez más importante en la actualidad. Con el crecimiento exponencial de la tecnología y la presencia digital en nuestras vidas, es crucial entender la importancia de proteger nuestros datos y nuestra información personal en línea.
Existen múltiples amenazas a nuestra privacidad en internet, desde el rastreo de nuestras actividades en línea por parte de empresas y anunciantes, hasta posibles hackeos de cuentas y robo de identidad. Es por eso que es fundamental tomar medidas para proteger nuestra privacidad y seguridad en línea.
Una de las formas de proteger nuestra privacidad en internet es utilizando contraseñas seguras y únicas para cada cuenta que tengamos. También es recomendable activar la autenticación de dos factores siempre que sea posible, para añadir una capa adicional de seguridad a nuestras cuentas.
Otra medida importante es ser consciente de qué información compartimos en línea y con quién la compartimos. Antes de proporcionar datos personales en un sitio web, es importante asegurarse de que es seguro y confiable.
Además, es recomendable utilizar herramientas como VPNs para navegar de forma más segura y anónima en internet, protegiendo nuestra privacidad de posibles rastreadores y hackers.
En resumen, proteger nuestra privacidad en internet es fundamental en esta era digital. Tomar medidas proactivas para proteger nuestros datos y nuestra información personal nos ayudará a navegar de forma más segura y tranquila en el vasto mundo en línea.
0 notes
Text
what is my ip address vpn
🔒🌍✨ Ganhe 3 Meses de VPN GRÁTIS - Acesso à Internet Seguro e Privado em Todo o Mundo! Clique Aqui ✨🌍🔒
what is my ip address vpn
Endereço IP
Um endereço IP (Internet Protocol) é um identificador único atribuído a cada dispositivo que se conecta a uma rede de computadores. Ele permite que os dispositivos se comuniquem entre si na internet, seguindo um conjunto de regras de protocolo de internet.
Existem dois tipos principais de endereços IP: IPv4 e IPv6. O IPv4 é o formato mais antigo e consiste em quatro conjuntos de números de 0 a 255, separados por pontos, por exemplo, 192.168.0.1. Já o IPv6 é o formato mais recente e tem uma estrutura alfanumérica mais complexa, para lidar com o esgotamento de endereços do IPv4.
Os endereços IP desempenham um papel fundamental na comunicação online, permitindo que os dispositivos sejam identificados e localizados na rede. Além disso, são essenciais para o funcionamento da internet, pois possibilitam a transmissão de dados entre os diferentes dispositivos conectados.
É importante ressaltar que os endereços IP podem ser estáticos ou dinâmicos. Os endereços IP estáticos são permanentes e são atribuídos manualmente, enquanto os dinâmicos são temporários e são atribuídos automaticamente por um servidor DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) toda vez que um dispositivo se conecta a uma rede.
Em resumo, o endereço IP é o que permite a conexão e a comunicação entre dispositivos na internet. Seja para acesso a sites, envio de e-mails ou qualquer outra atividade online, o endereço IP desempenha um papel fundamental no funcionamento da rede mundial de computadores.
VPN
Um serviço VPN, ou Rede Virtual Privada, é uma ferramenta cada vez mais popular que oferece aos usuários uma camada extra de segurança e privacidade ao navegar na internet. A principal função de um VPN é criar uma conexão segura entre o dispositivo do usuário e a internet, protegendo seus dados de possíveis ataques de hackers ou violações de privacidade.
Além da segurança, os serviços VPN também permitem que os usuários acessem conteúdos que podem estar restritos em determinadas regiões geográficas. Por exemplo, é possível assistir a filmes e séries de streaming que só são disponíveis em outros países, contornando assim as limitações geográficas.
Outra vantagem do uso de um VPN é a proteção da privacidade online. Com a crescente preocupação com a coleta de dados por empresas e governos, muitos usuários optam por utilizar um VPN para manter suas informações pessoais seguras e fora do alcance de terceiros.
É importante ressaltar que a escolha de um serviço VPN confiável e seguro é essencial para garantir uma experiência positiva e protegida na internet. É recomendável pesquisar e comparar as opções disponíveis no mercado antes de tomar uma decisão.
Em resumo, um serviço VPN pode oferecer segurança, privacidade e acesso a conteúdos restritos, tornando-se uma ferramenta essencial para usuários que buscam uma experiência mais protegida e livre na internet.
Identificação de localização
A identificação de localização é um processo fundamental nos dias de hoje, em meio à proliferação de dispositivos eletrônicos e à necessidade de serviços personalizados baseados na localização do usuário. Através dessa prática, é possível determinar a localização geográfica precisa de um indivíduo, dispositivo ou objeto, o que tem inúmeras aplicações tanto no campo pessoal quanto no empresarial.
No âmbito pessoal, a identificação de localização permite que os usuários acessem facilmente informações relevantes com base em sua proximidade com determinados locais, como restaurantes, lojas ou eventos. Além disso, essa tecnologia é essencial para serviços de navegação e transporte, ajudando as pessoas a se deslocarem com eficiência de um ponto a outro.
Já no setor empresarial, a identificação de localização desempenha um papel crucial em estratégias de marketing e publicidade direcionadas. Ao conhecer a localização dos consumidores, as empresas podem personalizar campanhas promocionais, ofertas e conteúdo com base nas preferências e comportamentos locais de cada público-alvo.
No entanto, é importante ressaltar que a identificação de localização levanta questões de privacidade e segurança, uma vez que envolve a coleta e o armazenamento de dados sensíveis sobre a movimentação das pessoas. Por essa razão, é fundamental que as empresas e os desenvolvedores de tecnologia adotem práticas responsáveis de proteção de dados e forneçam transparência aos usuários sobre o uso de suas informações de localização.
Em resumo, a identificação de localização é uma ferramenta poderosa que oferece inúmeras possibilidades de inovação e conveniência, desde serviços personalizados até estratégias de negócios avançadas. No entanto, seu uso responsável e ético é essencial para garantir a confiança dos usuários e o respeito à privacidade de cada indivíduo.
Proteção de dados
A proteção de dados é um tema de extrema importância nos dias de hoje, especialmente com a quantidade cada vez maior de informações pessoais que são compartilhadas online. A proteção de dados diz respeito às medidas tomadas para garantir que as informações pessoais dos indivíduos sejam utilizadas de forma segura e responsável.
No contexto empresarial, a proteção de dados se torna ainda mais relevante, uma vez que as organizações lidam com uma grande quantidade de informações sensíveis de clientes e colaboradores. É fundamental que as empresas adotem práticas e políticas de segurança adequadas para garantir a privacidade e a segurança desses dados.
A implementação do Regulamento Geral de Proteção de Dados (GDPR) na União Europeia foi um marco importante nesse sentido, estabelecendo diretrizes claras sobre como as empresas devem coletar, armazenar e utilizar dados pessoais. Além disso, o GDPR prevê penalidades severas para as organizações que não cumprirem as normas estabelecidas, o que reforça a importância da proteção de dados.
Ao proteger os dados de forma eficaz, as empresas não apenas cumprem com as obrigações legais, mas também constroem a confiança dos clientes e colaboradores. A transparência e a segurança no tratamento das informações pessoais são essenciais para manter relacionamentos saudáveis e duradouros com o público.
Em resumo, a proteção de dados é um pilar fundamental para a segurança e o sucesso das empresas na era digital. Investir em medidas de segurança e privacidade é essencial para garantir a confiança dos stakeholders e manter a integridade das operações comerciais.
Navegação anônima
A navegação anônima é uma ferramenta essencial para quem preza pela privacidade e segurança ao utilizar a internet. Também conhecida como modo privado, essa funcionalidade permite que os usuários naveguem na web sem que os dados de navegação sejam armazenados no histórico do navegador.
Ao ativar a navegação anônima, o navegador não salva cookies, dados de formulários e informações de navegação, proporcionando um maior nível de confidencialidade. Isso é especialmente útil para evitar que terceiros coletem informações pessoais, como preferências de pesquisa, histórico de navegação e dados de login.
Além disso, a navegação anônima pode ser útil em diversas situações, como ao pesquisar presentes de forma discreta, compartilhar um dispositivo com outras pessoas, ou ao acessar uma conta pessoal em um computador público. No entanto, é importante ressaltar que essa funcionalidade não garante total anonimato, pois a conexão ainda pode ser rastreada por meio do endereço de IP.
Para ativar a navegação anônima, basta acessar as configurações do navegador e selecionar a opção de modo privado. É uma forma simples e eficaz de proteger sua privacidade enquanto navega na internet. Portanto, caso deseje maior segurança e privacidade ao utilizar a web, considere utilizar a navegação anônima em seu navegador.
0 notes
Text
what is my ip vpn address
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
what is my ip vpn address
IP address definition
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two primary functions: identifying the host or network interface and providing the location of the device in the network.
In simpler terms, think of an IP address like a home address in the digital world. It helps data packets find their way to the right destination across the vast network of interconnected devices that make up the internet.
There are two main types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4, the older version, consists of a 32-bit number expressed in four sets of digits separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1). With the increasing number of devices connecting to the internet, IPv6 was introduced to accommodate the growing demand for IP addresses. IPv6 uses a 128-bit address format, allowing for an exponentially larger number of possible addresses compared to IPv4.
IP addresses can be static or dynamic. A static IP address remains constant and is manually assigned to a device, while a dynamic IP address is assigned automatically by a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server whenever a device connects to the network. Dynamic IP addresses are more commonly used by ISPs (Internet Service Providers) for residential connections, as they are more cost-effective and efficient in managing IP address allocation.
Overall, IP addresses play a crucial role in facilitating communication and data exchange between devices on the internet. Without them, devices would be unable to identify each other or transmit information across the vast digital landscape.
VPN definition
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a powerful tool that safeguards your online privacy and security by creating a secure and encrypted connection to the internet. By using a VPN, your web traffic is routed through a remote server operated by the VPN service provider. This means that your IP address is masked, making your online actions virtually untraceable.
One of the key benefits of using a VPN is the ability to browse the internet anonymously. This is particularly important when using public Wi-Fi networks, as these are often targeted by hackers who can intercept your data. With a VPN, all data passing between your device and the VPN server is encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains secure.
Moreover, a VPN allows you to access geo-restricted content by changing your virtual location. This means you can bypass censorship or access services that may be restricted in your current location. Whether you want to stream your favorite shows while traveling abroad or access websites not available in your country, a VPN can help you achieve that.
In addition to privacy and access benefits, VPNs are also utilized by businesses to provide remote employees with secure access to company resources. By encrypting connections and ensuring data integrity, VPNs enable remote workers to connect to corporate networks as if they were in the office, enhancing productivity while maintaining security measures.
Overall, a VPN is a versatile tool that offers a myriad of benefits, from safeguarding your online privacy to bypassing restrictions and enhancing security for remote work. Whether you're a casual internet user or a business professional, investing in a reliable VPN service is a wise decision to secure your online activities.
My IP address location
An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique set of numbers assigned to every device connected to a computer network. This address serves as the device's identity on the network and enables it to communicate with other devices. When it comes to knowing the location of an IP address, there are tools available that can provide this information.
One such tool is an IP geolocation service, which can determine the approximate physical location of an IP address. These services use a variety of data sources, such as GPS data, Wi-Fi access points, and databases of known IP addresses, to triangulate the location of a particular IP address.
By using an IP geolocation service, you can find out the country, region, city, and even the latitude and longitude coordinates associated with a specific IP address. This information can be useful for a variety of reasons, such as tracking the location of website visitors, verifying the origin of emails, or troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
It's important to note that while IP geolocation services can provide general location information, they may not always be 100% accurate. Factors such as dynamic IP addresses, proxy servers, and VPNs can affect the accuracy of the location data provided.
In conclusion, knowing the location of your IP address can be helpful for various purposes, and IP geolocation services offer a convenient way to access this information. Just keep in mind the limitations of these services and use the data accordingly.
Difference between IP address and VPN
An IP address and a VPN (Virtual Private Network) are both integral components of the online world, but they serve distinct purposes. To understand the difference between the two, it's essential to comprehend their individual functions and how they impact your online activities.
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It serves as an identifier for your device, allowing other devices and servers to locate and communicate with it on the internet. Your IP address can reveal your geographic location and internet service provider, potentially compromising your privacy and security online.
On the other hand, a VPN is a service that enhances your online security and privacy by creating a secure connection over the internet. When you connect to a VPN server, your internet traffic is encrypted, masking your IP address and making your online activities anonymous. This added layer of security is especially crucial when using public Wi-Fi networks or accessing geo-restricted content.
In summary, while an IP address is like the digital address of your device on the internet, a VPN acts as a protective tunnel that encrypts your data and hides your actual IP address. By using a VPN, you can safeguard your online privacy and security, whereas your IP address serves as the unique identifier for your device on the internet.
Secure browsing with VPN
In today's digitally driven world, protecting your online activity is of utmost importance. One effective way to ensure secure browsing is by using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates a secure connection between your device and the internet, encrypting your data and routing it through a remote server. This process shields your online activity from prying eyes, such as hackers, advertisers, or government agencies.
One key benefit of using a VPN for secure browsing is the anonymity it provides. By masking your IP address, a VPN prevents websites and online services from tracking your location and collecting data about your browsing habits. This enhances your online privacy and security, reducing the risk of identity theft or targeted advertising.
Moreover, a VPN enables users to access geo-restricted content by changing their virtual location. This is particularly useful for streaming services, social media platforms, or news websites that may be blocked in certain regions. By connecting to a server in a different country, users can bypass these restrictions and enjoy unrestricted access to the content they want.
When choosing a VPN provider for secure browsing, it is essential to consider factors such as encryption protocols, server locations, and logging policies. Opt for a reputable VPN service that prioritizes user privacy and offers strong security features to safeguard your online data.
By utilizing a VPN for secure browsing, you can surf the web with peace of mind, knowing that your online activity is shielded from potential threats and invasions of privacy. Stay safe and secure online by harnessing the power of a VPN for your browsing needs.
0 notes
Text
does my ip change when i use a vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does my ip change when i use a vpn
IP Address
An IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. This address serves two primary purposes: network interface identification and location addressing.
In simpler terms, think of an IP address as the digital equivalent of a home address. It enables devices to find and communicate with each other on a network. Every device that connects to the internet, whether it's a computer, smartphone, or smart home device, is assigned an IP address.
IP addresses come in two main versions: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses are composed of four sets of numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1), while IPv6 addresses are longer and use hexadecimal notation (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
One crucial aspect of IP addresses is their role in enabling communication between devices across the globe. When you visit a website, for example, your device sends a request to the website's server, and the server responds by sending the requested data back to your device using its IP address.
Additionally, IP addresses can be dynamic or static. Dynamic IP addresses are assigned by a DHCP server and can change over time, whereas static IP addresses remain constant and are typically manually configured.
While IP addresses are essential for facilitating internet communication, they also raise privacy concerns. Websites and online services can track users' activities using their IP addresses, leading to debates about online privacy and data protection.
In conclusion, IP addresses play a fundamental role in connecting devices to the internet and enabling communication between them. Understanding how they work is crucial for navigating the digital world effectively.
VPN Connection
Title: Unlocking the Power of VPN Connection: Ensuring Security and Privacy Online
In today's digitally interconnected world, safeguarding your online activities is paramount. Enter the Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection, a robust tool designed to enhance your security and privacy on the internet.
So, what exactly is a VPN connection? At its core, a VPN creates a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the internet. By routing your internet traffic through a remote server operated by the VPN service, your data becomes encrypted, making it virtually impossible for cybercriminals, ISPs, or government agencies to intercept or decipher.
One of the primary benefits of using a VPN connection is the assurance of anonymity. Your real IP address is concealed, and instead, you're assigned a temporary IP address associated with the VPN server location. This means your online activities are anonymized, protecting your identity and location from prying eyes.
Moreover, VPNs are instrumental in bypassing geo-restrictions. Whether you're traveling abroad or simply want access to region-locked content, a VPN can help you circumvent these barriers by masking your true location and granting you access to content from anywhere in the world.
Another crucial aspect of VPN connections is their role in securing sensitive data, especially when connected to public Wi-Fi networks. These networks are notorious hunting grounds for hackers, but with a VPN in place, your data remains encrypted, safeguarding it from potential breaches.
However, not all VPN services are created equal. When choosing a VPN provider, consider factors such as encryption protocols, server locations, speed, and logging policies to ensure you're getting the best protection for your needs.
In conclusion, VPN connections are indispensable tools for maintaining security and privacy in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape. By encrypting your internet traffic, anonymizing your online activities, and bypassing geo-restrictions, VPNs empower you to browse the web with confidence and peace of mind.
Dynamic IP
A dynamic IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a temporary address assigned to a device on a network. Unlike a static IP address, which remains constant and is typically used for hosting websites or servers, a dynamic IP address changes periodically. This dynamic assignment is usually managed by a server, router, or internet service provider, making it a convenient option for home users and small businesses.
One of the key advantages of a dynamic IP address is enhanced privacy and security. Since the address changes regularly, it becomes harder for malicious actors to track your online activity or target your device. Additionally, dynamic IP addresses are more cost-effective and easier to manage than static IP addresses, making them a popular choice for users with dynamic networking needs.
However, there are some drawbacks to using a dynamic IP address. One common issue is the potential for connectivity disruptions when the address changes, which can temporarily interrupt your internet service or remote access to your devices. Additionally, if you require constant access to a specific device, such as a network printer or security camera, a dynamic IP address may not be the most suitable option.
In conclusion, dynamic IP addresses offer flexibility, improved privacy, and cost savings for many users. By understanding the advantages and limitations of dynamic IP addressing, you can make an informed decision about whether it aligns with your specific networking requirements.
Network Security
Network security is a critical aspect of modern technology systems, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access, cyber-attacks, and malicious activities. It involves the implementation of various measures to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of network resources.
One of the primary components of network security is the implementation of firewalls, which act as barriers between internal networks and external threats. Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, helping to prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
In addition to firewalls, encryption plays a crucial role in network security by converting sensitive data into a secure code that can only be accessed by authorized users with the appropriate decryption key. This helps to protect the confidentiality of data as it travels across the network, making it more difficult for cybercriminals to intercept and exploit.
Another key aspect of network security is the implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems, which monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and potential security threats. These systems can help to identify and block malicious activities in real-time, reducing the risk of security incidents and data breaches.
Regular security audits, updates, and patch management are also essential for maintaining network security. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in network infrastructure and software, organizations can proactively reduce the risk of cyber-attacks and ensure a higher level of protection for their data and resources.
Overall, network security is a multidimensional approach that requires continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement to effectively mitigate security risks and protect against evolving cyber threats in today's digital landscape.
Internet Privacy
Title: Safeguarding Your Online Privacy: Tips for Protecting Your Digital Footprint
In an age where much of our personal and professional lives are conducted online, safeguarding our internet privacy has become paramount. Internet privacy refers to the level of privacy and security individuals have over their personal data and online activities. With the proliferation of social media, e-commerce platforms, and online services, maintaining control over our digital footprint is essential to protecting sensitive information and preventing potential breaches.
One of the first steps to enhancing internet privacy is to utilize strong, unique passwords for each online account. Password managers can assist in generating and storing complex passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to accounts. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring both a password and a secondary verification method, such as a text message or authentication app.
Furthermore, being mindful of the information shared on social media platforms is crucial. Oversharing personal details can inadvertently expose individuals to identity theft, phishing scams, and cyberbullying. Adjusting privacy settings to limit the audience for posts and refraining from posting sensitive information, such as birthdates and addresses, can mitigate these risks.
Investing in virtual private networks (VPNs) can also bolster internet privacy by encrypting internet traffic and masking IP addresses, making it challenging for third parties to track online activities. Similarly, using encrypted messaging apps for communication adds another layer of protection to sensitive conversations and shared media.
Lastly, regularly updating software and devices with the latest security patches and antivirus software can prevent vulnerabilities exploited by cybercriminals. Staying informed about emerging threats and practicing vigilant online habits are essential in safeguarding internet privacy and maintaining control over one's digital identity. By implementing these measures, individuals can navigate the digital landscape with greater peace of mind and confidence in their online privacy.
0 notes