#automated testing web applications
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Integrating Web UI Testing with CI/CD Pipelines: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to CI/CD and Web UI Testing
Begin by explaining Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and their role in modern software development. Highlight the importance of integrating web UI testing into these pipelines for faster delivery and consistent quality.
Benefits of Integration
Discuss advantages such as automated regression testing, early defect detection, and seamless deployment workflows.
Step 1: Choose the Right Tools
Explain how to select tools for both CI/CD (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps) and UI automation testing (e.g., Selenium, Playwright, Cypress) that fit your tech stack.
Step 2: Create Robust Automated Test Scripts
Highlight the importance of building reliable and reusable UI test scripts that cover critical functionalities and user flows.
Step 3: Configure Your CI/CD Pipeline
Detail the process of adding a test stage to the CI/CD pipeline. Include triggering tests automatically on code commits or pull requests.
Step 4: Enable Parallel Testing
Discuss how to speed up the testing process by running tests in parallel across different browsers and devices.
Step 5: Monitor and Report Results
Explain how to generate reports and notifications for failed tests, ensuring rapid feedback for the development team.
Conclusion
Reiterate the importance of integrating web UI testing into CI/CD pipelines to achieve faster, more reliable software releases.
#web automation testing#ui automation testing#web ui testing#ui testing in software testing#automated website testing#web automation tool#web ui automation#ui automation tool#web automation software#automated testing web applications#automated web ui testing#web app testing
0 notes
Text
AI in Test Automation: Best Practices to Optimize Your QA Workflow
AI is revolutionizing test automation, allowing QA teams to move from reactive testing to proactive quality engineering. When implemented with a clear strategy, the right tools, and expert guidance, AI can drastically reduce testing time, improve accuracy, and empower continuous delivery. If you're looking to future-proof your QA process, now is the time to embrace AI-powered Automation Testing Services. With a trusted partner like Robotico Digital , you gain the tools, expertise, and support needed to transform your software testing and ensure long-term success.
0 notes
Text
Next-Gen AR Development: Bringing Ideas to Life - Atcuality
Augmented reality is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s here, transforming industries and enhancing real-world applications. At Atcuality, we specialize in custom AR solutions designed to create interactive, engaging, and scalable experiences for businesses of all sizes. Our augmented reality development services cater to diverse industries, including retail, tourism, real estate, and automotive, helping brands deliver unforgettable user experiences. Whether you need AR-powered product visualization, training simulations, or interactive storytelling, our expert team ensures a seamless, high-quality solution tailored to your needs. Elevate your business with Atcuality’s cutting-edge AR technology and shape the future of digital interaction today!
#website development#ai applications#artificial intelligence#augmented and virtual reality market#web development#information technology#emailmarketing#augmented reality#web design#digital marketing#augmentative and alternative communication#augmented intelligence#virtual reality#ar vr technology#digital consulting#digital services#iotsolutions#iot#iot platform#iot applications#iot development services#technologynews#iot solutions#iot integration#automation#software company#software development#software engineering#software testing#cash collection application
0 notes
Text
The Role of DAST in Protecting Your Web Applications From Vulnerabilities
Nyuway

As cyber attacks become increasingly sophisticated, enterprises require DAST to help defend their applications against sophisticated cyber threats. By scanning a running application and simulating hacker behavior, it can identify vulnerabilities before enterprising hackers exploit them.
DAST complements static application security testing (SAST) and software composition analysis (SCA), offering additional runtime insights beyond source-code scans. Furthermore, it serves as a valuable companion to manual penetration testing.
Web Application
Dynamic application security testing (DAST) scans running web applications by simulating malicious external attacks and identifying vulnerabilities which could be exploited. DAST can reveal business logic flaws like SQL injection, XSS attacks and authentication issues which often go undetected through static code analysis tools (SAST) or manual penetration testing methods.
While DAST tools can be effective, they do have their limitations. False positives and lack of context can result in security gaps when applied solely. To address this limitation, it may be useful to combine DAST with other methodologies like SAST, IAST or software composition analysis (SCA) in order to create a comprehensive security program.
Implementing DAST into your CI/CD pipeline can ensure vulnerabilities are identified and fixed as code changes are made, leading to decreased costs and speedier time to production. Furthermore, early detection helps minimize accidental releases or potential data breaches; many of today's most harmful cyberthreats rely on unpatched vulnerabilities within running applications for attack.
API Security
DAST tools differ from SAST in that they attack an API without knowledge of its application; instead, this kind of testing mimics how attackers would try to exploit it - thus helping detect vulnerabilities which are harder to spot with traditional testing techniques.
DAST can be particularly effective at protecting web APIs. It can scan API endpoints to expose vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit, such as injection attacks or misconfigurations; and can identify unexpected data leaks or performance issues which might signal deeper security holes.
DAST excels at scanning web application UIs, yet struggles to access and test APIs tucked behind dynamic behavior layers. These layers hide backend API calls behind their respective UI layers until JavaScript code executes and uses an appropriate request format for runtime visibility.
Continuous
As web applications continue to be developed and evolve, security risks continue to shift and adapt accordingly. DAST can help address this challenge effectively.
This type of testing works by simulating attacks a malicious actor might employ to penetrate an application. By employing a black box approach and looking at it from outside in, this approach can detect vulnerabilities which other methods such as SAST or SCA fail to find.
DAST provides feedback and reporting to help developers and security teams prioritize vulnerabilities for remediation. It can also be easily integrated with the CI/CD pipeline to scan at every stage of development, making it easy to detect security issues before they reach production.
DAST can provide an overall picture of your application's vulnerability to threats when used alongside SAST & IAST (which examine code line by line), to form part of an integrated security assessment process. DAST tests entry points such as forms & API endpoints while SAST & IAST examine internal risks like misconfigurations & coding errors to provide a full assessment.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning
DAST differs from traditional static testing by testing an application while it runs, simulating how a hacker would search for vulnerabilities in real time. DAST can run both unauthenticated and authenticated modes to see how the app responds to attacks that typically gain control over an account and reveal sensitive data.
Businesses using advanced DAST solutions that utilize proof-based scanning can quickly identify and prioritize critical vulnerabilities using sophisticated DAST solutions that use proof-based scanning to eliminate false positives, making their teams focus their efforts on real risks that could cause serious breaches instead of spending hours sifting through massive test results.
DAST tools also give development and QA teams detailed information on how they can reproduce and fix vulnerabilities more quickly, so as to minimise disruption in production environments. When integrated into the Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment pipeline, DAST can detect vulnerabilities at each stage of development and production to decrease chances of breach as well as ensure compliance with regulatory standards such as PSI-DSS or HIPAA.
Managed DAST Services
DAST is an essential part of any comprehensive application security program, and an indispensable element for its testing capabilities. As the most adaptable security testing tool on the market, it can be integrated into each stage of development from early design through quality assurance testing, staging deployment and production deployment. When integrated into an CI/CD pipeline DAST can also help developers identify vulnerabilities before reaching production, saving both time and money in development costs.
DAST works by conducting automated tests simulating external attack behavior without understanding its internals, similar to malicious attackers' tactics, in order to uncover unexpected outcomes and vulnerabilities. Language independent, DAST can detect runtime issues like server configuration problems, authentication/encryption misconfigurations and more that SAST cannot.
To maximize the value of DAST, organizations should set clear security objectives and incorporate it into existing CI/CD and DevOps workflows. This includes developing strategies for handling false positives and regression tests to verify previously fixed vulnerabilities do not resurface. Ideally, DAST should be integrated with CI/CD pipeline so every code push or deployment triggers dynamic security checks automatically.
#Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)#Web Application DAST#API Security DAST#Continuous DAST#Automated Vulnerability Scanning
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Guide to Web Application Testing: Types, Use Cases & Tools

The success of your web application can be the linchpin of your business’s growth trajectory. Today’s modern business must not merely rely on functionality, but also on exceptional user experience, driving engagement and building customer loyalty.
According to IBM, the cost to fix bugs found during the testing phase could be 15x more than the cost of fixing those found during design.
As businesses increasingly rely on sophisticated web platforms to connect with their audiences, web application testing emerges as a strategic imperative. This blog delves into the transformative impact of web application testing services. Let’s explore different types of web application testing.
Understanding web application testing and why it is necessary
Web application testing is essential for ensuring its functions are accurate and meet the requirements of end users. To understand the testing process precisely, here is a comprehensive breakdown:
Purpose of web application testing
It aims to identify bugs, ensure functionality, and verify that the application meets the specific requirements. It ensures the application:
Functions correctly across different browsers and devices
Performs well under varying loads
Secure against vulnerabilities
Provides good user experience
Number of end users
It involves assessing how the application:
Handles high volume of users
Robustness under extreme conditions
Ability to scale efficiently with user demands
Target domain
Domain-specific testing: Based on target domains such as e-commerce, banking, healthcare, etc., it assures specific regulations and compliance requirements are met. Therefore, testing ensures that domain-specific functions such as payment processing and data security are working correctly and adhere to relevant standards.
Functional testing: It validates that all features and functions are relevant to the target domain and work as expected.
User role
Role-based testing: Various users have different login permissions and roles within an application, for example admin, regular user, and guests. Testing ensures that each role has appropriate access and functionalities, and unauthorized users do not have permission to access restricted areas.
User authentication and authorization testing: Verifies user authentication such as login mechanism and authorization such as role-based access control is working accurately.
Importance of AI in software testing AI in software testing improves software quality by analyzing data and identifying patterns. It optimizes the testing process, automates repetitive tasks, and analyzes vast datasets efficiently for more reliable software solutions. Read more
Further, web application testing is described in detail below:
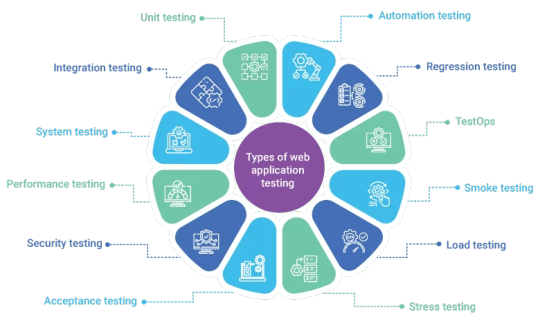
Unit testing
It is a software testing method where the smallest part of an application such as units or components are tested in isolation from the rest of the system. These units are individual functions, methods, or classes validating each unit’s performance.
In 2023, unit testing used in 63% of all software projects was the most common type of software test. – Statista
For example:
Consider an online shopping cart
Add items to the cart:
Test adding a single item to the cart to verify it appears correctly.
Test adding multiple items to ensure the cart updates accurately.
Test adding items with various quantities to check the cart reflects the correct total.
Tools for unit testing:
JUnit: A widely used testing framework for Java applications.
NUnit: A robust testing framework for .NET applications.
Jest: A popular JavaScript testing framework.
PyTest: A flexible and scalable testing framework for Python.
Integration testing
It combines multiple units, modules, and components of software applications for testing and ensures communication and data flow functions are consistent as a cohesive unit. Its goal is to identify issues in the interaction between integrated components.
For example:
Consider an event registration system
User registration and event enrollment:
Verify user details are correctly passed from the registration module to the event enrollment system.
Ensure users can register, view their details, and successfully enroll in events.
Payment processing and confirmation:
Confirm the payment module securely processes transactions and confirms success.
Test that after payment, the registration status is updated, and a confirmation email or notification is sent.
Ensure errors during payment processing trigger appropriate messages and provide resolution instructions.
Tools for integration testing
JUnit: Used for testing in Java applications.
TestNG: A Java testing framework with advanced configuration capabilities.
Postman: A tool for API integration testing to validate HTTP requests.
SoapUI: A tool used for testing of web services, particularly for SOAP and REST APIs.
System testing
It is a comprehensive phase in the software testing lifecycle that evaluates the complete and integrated software system to ensure it meets specified requirements and functions as intended. This type of testing is conducted after integration testing and focuses on verifying the entire system’s behavior and performance in a unified environment.
For example:
Consider hotel reservation system
Verify that the user interface allows users to search for available rooms based on their selected criteria (e.g., dates, location, room type).
Test the booking form to ensure users can enter their details (name, contact information) and that the system displays accurate room availability and pricing information.
Check that users receive confirmation of their booking with a summary of their reservation details once they complete the process.
Tools for system testing
Selenium: A widely used tool for automating web application testing.
Cypress: An end-to-end testing framework designed for modern web applications.
Playwright: Open-source framework for end-to-end testing of web applications.
Performance testing
Evaluate how a system performs under various conditions, focusing on how application meets user expectations for speed, reliability, and stability, especially under varying operational conditions.
Assessing user experience under load: Evaluate how well the app maintains responsiveness and functionality when subjected to varying user loads and network speeds.
For example, test how the app performs when 5,000 users access it simultaneously under different network conditions.
Determining peak performance limits: Identify the maximum number of concurrent users the app can handle while keeping the response time within 2 seconds.
For example, ensure the app remains performant with 7,500 active users.
Evaluating performance on low-bandwidth connections: Test the app’s responsiveness and stability when accessed from a low-bandwidth network.
For example, 2G or slow 3G, to confirm that essential functionalities remain usable.
Tools for performance testing
Apache JMeter: An open-source tool to simulate heavy loads on web applications.
LoadRunner: Predicts system behavior under varying loads.
Gatling: Open-source tool designed to test web applications and services.
BlazeMeter: A cloud-based tool that supports JMeter scripts.
Security testing
It focuses on identifying vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential threats within an application or system. It aims to safeguard the applications from threats, ensuring compliance with security policies and protecting user data and system integrity, maintain user trust.
For example:
Authentication verification: Test the strength and effectiveness of user login mechanisms and credential storage.
Authorization checks: Ensure users have appropriate access rights and cannot access unauthorized areas or functions.
Vulnerability scanning: Identify and assess potential security vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
Penetration testing: Simulate attacks to identify weaknesses and test the system’s resilience against real-world threats.
Tools for security testing
OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy): Open-source tool for finding vulnerabilities in web applications.
Burp Suite: Comprehensive solution for web application security testing.
Acceptance testing
It determines whether a software application meets the acceptance criteria of the end-users or stakeholders and ensures the system fulfills business requirements and satisfies user needs.
For example:
Consider shopping experience on an e-commerce website
User registration and login:
Verify that new users can successfully register for an account by entering their personal information and receiving a confirmation email.
Test that returning users can log in with their credentials and access their accounts without issues.
Product search and purchase:
Ensure users can search for products using keywords or filters and view accurate search results.
Test that users can select products, add them to their shopping cart, and proceed to checkout.
Verify that users can enter shipping and payment information, apply discount codes, and complete the purchase.
Tools for acceptance testing
TestRail: Used for test case management.
Zephyr: A robust test management solution for end-to-end test planning and execution.
Suggested: Explore test automation with Healenium Automation testing
Automation testing
Automation testing involves using specialized tools to execute pre-scripted tests on the application. This type of testing is useful for repetitive tasks, regression testing, and load testing.
For example:
Efficiency: Speeds up the testing process by automating repetitive tasks.
Consistency: Ensures consistent execution of test cases.
Cost-effective: Reduces the manual effort involved, lowering costs in the long run.
Tools for automation testing
Selenium: A widely used tool for automating web application testing.
Cypress: An end-to-end testing framework designed for modern web applications.
Katalon Studio: Supports web, API, mobile, and desktop applications.
Appium: An open-source tool for automating mobile applications.
Robot Framework: A versatile open-source framework supports various testing libraries and tools.
Playwright: Open-source framework for end-to-end testing of web applications.
Regression testing
It ensures that recent changes or additions to an application have not adversely affected its existing functionality but involves re-running previously executed test cases verifying that new code changes, bug fixes, or enhancements have not introduced any new defects causing unintended side effects.
For example:
Feature enhancements: Ensure new features such as a recommendation engine on an e-commerce site, don’t disrupt existing functions such as the shopping cart.
Bug fixes: Verify fixing a bug, like in a banking app’s transaction history, doesn’t create new issues in other areas like transfers.
Performance optimizations: Confirm performance improvements such as faster image loading on a social media platform without affecting the existing features.
External system integration: Test integrating new systems or APIs such as email marketing tools in a CRM system, doesn’t disrupt current functionalities.
System upgrades: Check application features such as content publishing in CMS remain functional after system upgrades.
Tools for regression testing
Selenium (with CI/CD tools like Jenkins): Integrates with CI/CD pipelines to automate web applications.
TestComplete: Supports functional, regression, and load testing for desktop, web, and mobile applications.
Cypress: A JavaScript end-to-end testing framework to automate browser interactions.
Playwright: A Node.js library that automates web tests across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit.
AI and ML are revolutionizing test automation AI and ML are revolutionizing test automation by resolving UI issues, enhancing functional and performance testing, and minimizing unrealistic data risk. This transformative impact makes testing more accurate and reliable. Read more
TestOps
TestOps is an emerging practice that integrates testing into the overall DevOps pipeline. It focuses on the management, orchestration, and analysis of testing activities across all phases of development. TestOps ensures that testing is aligned with continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) processes, enabling faster and more reliable releases.
Benefits of TestOps:
Enhanced collaboration: Bridges the gap between development, operations, and testing teams.
Continuous testing: Ensures that testing is a continuous activity integrated with the CI/CD pipeline.
Improved quality and speed: Accelerates the release process while maintaining high quality.
Tools for TestOps
Jenkins: CI/CD tool to automate the building, testing, and deployment of software.
CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD platform facilitates continuous integration and delivery workflows.
Azure DevOps: Provides a complete suite for end-to-end DevOps practices.
Gitlab: Integrated CI/CD functionality for managing the full DevOps lifecycle.
Smoke testing
It is a preliminary level of software testing conducted to ensure that the most critical functions of an application are working correctly before more detailed testing is performed.
For example:
1. Build verification
Before extensive testing begins, smoke testing verifies that the latest build is stable enough for further testing. For example:
E-commerce application: After deploying a new build, perform smoke testing to ensure that basic functions like login, product search, and checkout are working.
2. Feature release
When a new feature is added, smoke testing ensures that the new feature doesn’t break the existing core functionality. For example:
Social media app: After introducing a new messaging feature, conduct smoke testing to confirm that existing features like posting updates and notifications still work.
Tools for smoke testing
Selenium: Supports automated smoke testing for web applications.
JUnit: Widely used for Java applications.
TestNG: Framework for automated testing that can handle smoke tests.
Cypress: A JavaScript end-to-end testing to automate basic smoke test.
Playwright: A Node.js library that automates smoke tests across different browsers.
Load testing
Type of performance testing designed to assess how a system performs under a specific and an expected load of users or transactions. The primary objective is to determine whether the system can handle the anticipated volume of traffic or data without issues.
For example:
API performance: Test how an API handles 1,000 requests per minute to ensure it operates smoothly without errors or delays.
Database efficiency: Evaluate the database’s performance with multiple concurrent queries to ensure response times stay within acceptable limits.
Streaming services: Assess how a video streaming service manages 500 simultaneous HD streams to ensure quality and minimal buffering.
Tools for load testing
Apache JMeter: Widely used for performance and load testing of applications.
LoadRunner (Micro Focus): Enterprise-grade tool for load testing and performance monitoring.
Stress testing
It evaluates how a system behaves under extreme or peak conditions beyond its normal operating limits. It determines the system’s robustness, identify breaking points, and assess its ability to recover from failure.
For example:
System limits: Determine the maximum load the system can handle before failure, like handling 10,000 transactions per second.
Resource exhaustion: Assess how the system behaves when resources like CPU, memory, or storage are maxed out.
Error handling: Verify how the system manages and recovers from high-load scenarios that cause errors or crashes.
Tools for stress testing
Apache JMeter: Widely used for performance and load testing of applications.
LoadRunner (Micro Focus): Enterprise-grade tool for load testing and performance monitoring.
Insights Discover The Power of QA Automation Testing Services Assurance testing. Before the application is made public or sent to the client, it needs to have addressed every issue and bug that might have crept in during the coding of the application. Delegating a dedicated engineer to perform manual tests can get cumbersome. Download
Conclusion
As we navigate the intricate landscape of digital transformation, the role of comprehensive web application testing becomes undeniably pivotal to steering business growth. Beyond safeguarding functionality and performance, meticulous testing cultivates a resilient foundation for user satisfaction and operational excellence.
By embracing a strategic approach to testing, businesses can unveil latent opportunities, mitigate risks, and enhance their competitive edge. Talk to our QA test engineers to discuss your requirements.
Originally published at softwebsolutions on August 23, 2024.
#Web application testing#ai testing services#Application testing services#Software application testing services#AI Software testing services#Application automation testing
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Application Testing in Agile Environments: Strategies for Success
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, traditional application testing methods often struggle to keep up with rapid development cycles. As businesses strive for quicker releases and continuous updates, the need for efficient and effective testing strategies has never been more critical. Enter the world of agile testing, where innovative approaches are transforming how we ensure software quality and drive innovation.
Agile testing is not merely about executing tests; it's about seamlessly integrating validation processes into the development workflow. By embracing agile methodologies, organizations can leverage cutting-edge techniques to enhance their software testing practices and deliver superior products to market faster than ever before.
key strategies for optimizing application testing in agile environments:
Embrace the "Shift Left" Approach
The "Shift Left" philosophy is fundamental to agile testing, emphasizing the importance of early application testing in the development process. Unlike traditional waterfall models, where testing occurs at the end, agile encourages validation from the outset. This approach incorporates unit testing and functional testing to ensure each component is thoroughly validated during development.
By integrating validation testing early, teams can significantly reduce defect inflow in the final product. This proactive strategy not only saves time but also minimizes costs associated with post-deployment bug fixes.
Harness the Power of AI Automation
As development speeds increase, manual testing often becomes a bottleneck. AI automation testing offers a powerful solution to this challenge. AI-powered tools can accelerate testing processes by identifying key areas for validation, generating test cases, and even predicting potential failure points.
AI automation is particularly effective in enhancing regression testing. By learning from past test results, AI can focus on areas with higher failure probabilities, improving test coverage and productivity. Moreover, AI-driven performance testing tools can simulate various user scenarios at scale, ensuring web application testing and mobile application testing are prepared for real-world usage.
Implement Continuous Testing with DevOps
In agile environments, the synergy between agile and DevOps practices is crucial. Continuous testing is the linchpin of this collaboration. By integrating testing into Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, teams ensure that every code change undergoes automated testing before reaching production.
This approach accelerates the development process and enhances overall software quality. Automated tests, ranging from security testing to usability testing, are triggered with each commit, ensuring new features don't introduce vulnerabilities or compromise user experience.
Prioritize Agile Performance and Load Testing
As user expectations for application performance continue to rise, performance testing in agile setups becomes increasingly critical. Rather than conducting performance tests solely before release, agile advocates for continuous performance monitoring throughout the development cycle.
Modern tools enable teams to incorporate web application testing and mobile application testing into their agile workflows, providing real-time insights into application performance under various conditions. These continuous feedback loops help identify and address performance issues early, long before they impact end-users.
Emphasize User-Centric Testing
Agile methodologies place the user at the center of the development process. User testing involves frequent feedback loops that enable rapid iteration based on real user input. Similarly, accessibility testing should be ingrained in the process to ensure applications are usable by all, including those with disabilities.
Advanced AI-powered testing solutions can simulate a wide array of user interactions, providing valuable insights into how different user groups engage with applications. This information is invaluable for refining application design and functionality to meet genuine user needs.
Integrate Security Testing Throughout the SDLC
In an era of increasing cyber threats, security cannot be an afterthought. Agile development demands that security testing be integrated into every stage of the software development life cycle (SDLC). Automated security testing allows for continuous scanning of the codebase, identifying vulnerabilities as soon as they're introduced.
By embedding security testing within existing agile and DevOps processes, organizations can create more secure and resilient applications. This proactive approach ensures that software meets not only performance and usability standards but also rigorous security expectations.
Conclusion
Agile testing is revolutionizing how we approach software quality assurance, security, and user experience. By adopting these strategies, organizations can ensure their testing processes are as agile and responsive as their development cycles.
In a world where change is the only constant, staying ahead of the curve in testing methodologies is crucial. By embracing agile testing principles and leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI automation, businesses can develop applications that are not only robust and secure but also deliver exceptional user experiences.
As we continue to navigate the complex landscape of software development, one thing is clear: agile testing is not just a trend—it's a necessity for organizations looking to thrive in the digital age. By investing in these advanced testing strategies, businesses can ensure their applications are ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow, today.
#application testing#agile testing#validation testing#ai automation testing#software testing#Performance Testing#web application testing#mobile application testing
0 notes
Text
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring the reliability and performance of web applications is crucial. With increasing user expectations and the need for rapid releases, manual testing alone cannot meet the demands. This is where automation testing for web applications becomes indispensable. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore best practices for automation testing, highlighting the importance, benefits, and effective strategies to implement automation in your testing process.
0 notes
Text
WP Engine is a well-known managed WordPress hosting provider.
It offers a range of features and services tailored specifically for WordPress websites, making it a popular choice among businesses, bloggers, and developers who seek reliable, high-performance hosting solutions.

#Managed WordPress Hosting:#security#and reliability.#automated updates#and staging environments.#Genesis Framework and StudioPress Themes:#Access to the Genesis Framework for building fast#secure#and SEO-friendly websites.#Includes over 35 StudioPress themes for customization and design flexibility.#Global Edge Security:#Advanced security features including DDoS protection and Web Application Firewall (WAF).#Managed threat detection and prevention.#Content Performance:#Tools and analytics to measure and optimize content performance.#Helps improve site speed and SEO rankings.#Dev#Stage#Prod Environments:#Separate development#staging#and production environments for better workflow management.#Allows for testing changes before pushing them live.#Automated Migrations:#Easy migration tools to transfer existing WordPress sites to WP Engine.#Assisted migrations for a smoother transition.#24/7 Customer Support:
0 notes
Text
Application Server Automation & Testing
For websites containing a lot of JavaScript, AJAX, or Java applets, developers need a mechanism to ensure that these programs execute smoothly. Anyone can use the EveryStep Web Recorder to create testing and monitoring scripts that can perform complex actions, such as filling out forms and interacting with multimedia content—even for complex elements such as Silverlight or Java Applets, thanks to the EveryStep tool's RIA (Rich Internet Application). These scripts may then be imported into the UserView platform for monitoring, ensuring that the apps load properly and clients get the best possible experience.
Web app automation testing tools security is a subset of information security (InfoSec) that addresses the security of websites, apps, and web services. The difficult objective of information security is to strike a balance between confidentiality, integrity, and data availability while minimizing productivity loss.
Cross-site scripting, or XSS, is one of the most prevalent forms of web application assaults in which an attacker injects malicious code into a site by impersonating a trustworthy source or stealing cookies and unintentionally sending visitors to a different page.
#web app automation testing tools#best automation testing tool for web applications#web testing tools
0 notes
Text
Cross-Browser Testing: A Critical Component of Web UI Testing
Cross-browser testing is essential for ensuring web applications provide a consistent user experience across various browsers and platforms. With users accessing websites through different browsers, ensuring compatibility is critical to prevent alienating any segment of your audience.
Why Cross-Browser Testing is Important
Browsers interpret HTML, CSS, and JavaScript differently, which can lead to layout issues, functionality errors, or inconsistent behavior. Cross-browser testing ensures uniformity in design and functionality, enhancing user satisfaction.
Key Focus Areas in Cross-Browser Testing
UI Consistency: Verify that layouts, fonts, colors, and images appear as intended.
Functionality: Ensure interactive elements like buttons, forms, and dropdowns work seamlessly.
Performance: Test load times across browsers to ensure optimal performance.
Responsive Design: Validate adaptability on different screen sizes and orientations.
Tools for Cross-Browser Testing
Tools like BrowserStack, LambdaTest, and CrossBrowserTesting simplify the process by providing access to multiple browser and OS combinations in real-time or virtual environments.
Best Practices
Prioritize testing on browsers and devices most used by your audience.
Leverage UI automation testing for repetitive tasks.
Incorporate cross-browser testing into CI/CD pipelines to catch issues early.
By integrating cross-browser testing into web UI testing strategies, teams can deliver a consistent, high-quality experience to all users, regardless of their preferred browser.
#web automation testing#ui automation testing#web ui testing#ui testing in software testing#automated website testing#web automation tool#web ui automation#ui automation tool#web automation software#automated testing web applications#automated web ui testing
0 notes
Text

Web application testing is a software testing technique that is used exclusively to test web-hosted applications, in which the web application interfaces, and other functionalities are tested.
#Web Testing#Web Application Testing#Test Automation Best Practices#performance evaluation#Benefits of web testing
0 notes
Text
what is Embedded Software Testing?
Embedded software testing refers to the process of evaluating and validating the software running on embedded systems. Embedded systems are specialized computer systems designed to perform specific functions within larger devices or machinery. They are typically found in various applications such as automobiles, medical devices, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and more.
Embedded software testing involves assessing the functionality, reliability, performance, and safety of the software that operates these embedded systems. The testing process aims to identify defects, errors, and vulnerabilities within the software, ensuring that it meets the desired specifications and requirements.
Some common types of testing techniques used in embedded software testing include:
Unit Testing: Testing individual components or modules of the software to ensure they function correctly.
Integration Testing: Verifying the proper interaction and communication between different software modules within the embedded system.
System Testing: Evaluating the overall functionality and behavior of the entire embedded system, including the software and hardware components.
Performance Testing: Assessing the performance and responsiveness of the embedded software under different conditions and loads.
Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the software to protect against potential security threats and breaches.
Regression Testing: Repeatedly testing the software to ensure that recent changes or updates have not introduced new defects or caused any regressions.
Usability Testing: Evaluating the user-friendliness and ease of use of the embedded software interface.
Safety Testing: Assessing the software's compliance with safety standards and ensuring it operates reliably to prevent any potential harm or accidents.
Embedded software testing requires specialized knowledge and expertise due to the unique challenges posed by the embedded systems' hardware limitations, real-time constraints, and specific application requirements. Testers often use a combination of manual testing techniques and automated testing tools to thoroughly assess the embedded software's quality and functionality.
For More, You Can Visit This Post: Embedded Software Testing: Ensuring Quality and Reliability
Robonito Is a no-code automation testing tool for software and web apps that can automate your software testing
#software testing#testing#web application#no code automation testing tool#software testing tool#robonito#RPA
0 notes
Text
Automated testing helps to improve the efficiency and reliability of the testing process by using specialized tools and frameworks. It reduces human error, expands test coverage, and allows for more frequent testing cycles. Overall, automation testing saves time and effort and leads to the release of high-quality software. Most of the time, the automation capabilities of QA testing tools are powered by AI technology.
0 notes
Text
#application testing#agile testing#validation testing#ai automation testing#software testing#Performance Testing#web application testing#mobile application testing
0 notes
Text
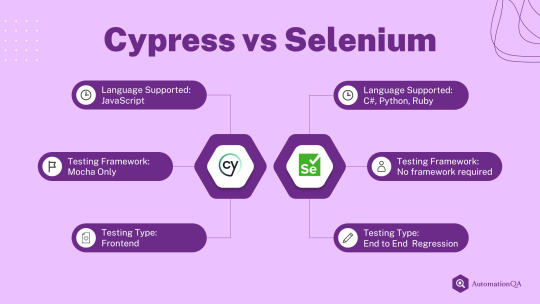
🔍 Searching for the perfect testing tool for your web app?
🤔 Check out our comparison of Cypress vs Selenium to help you make the right choice! 🚀
1 note
·
View note
Text
Python for Beginners: Launch Your Tech Career with Coding Skills
Are you ready to launch your tech career but don’t know where to start? Learning Python is one of the best ways to break into the world of technology—even if you have zero coding experience.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Python for beginners can be your gateway to a rewarding career in software development, data science, automation, and more.
Why Python Is the Perfect Language for Beginners
Python has become the go-to programming language for beginners and professionals alike—and for good reason:
Simple syntax: Python reads like plain English, making it easy to learn.
High demand: Industries spanning the spectrum are actively seeking Python developers to fuel their technological advancements.
Versatile applications: Python's versatility shines as it powers everything from crafting websites to driving artificial intelligence and dissecting data.
Whether you want to become a software developer, data analyst, or AI engineer, Python lays the foundation.
What Can You Do With Python?
Python is not just a beginner language—it’s a career-building tool. Here are just a few career paths where Python is essential:
Web Development: Frameworks like Django and Flask make it easy to build powerful web applications. You can even enroll in a Python Course in Kochi to gain hands-on experience with real-world web projects.
Data Science & Analytics: For professionals tackling data analysis and visualization, the Python ecosystem, featuring powerhouses like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib, sets the benchmark.
Machine Learning & AI: Spearheading advancements in artificial intelligence development, Python boasts powerful tools such as TensorFlow and scikit-learn.
Automation & Scripting: Simple yet effective Python scripts offer a pathway to amplified efficiency by automating routine workflows.
Cybersecurity & Networking: The application of Python is expanding into crucial domains such as ethical hacking, penetration testing, and the automation of network processes.
How to Get Started with Python
Starting your Python journey doesn't require a computer science degree. Success hinges on a focused commitment combined with a thoughtfully structured educational approach.
Step 1: Install Python
Download and install Python from python.org. It's free and available for all platforms.
Step 2: Choose an IDE
Use beginner-friendly tools like Thonny, PyCharm, or VS Code to write your code.
Step 3: Learn the Basics
Focus on:
Variables and data types
Conditional statements
Loops
Functions
Lists and dictionaries
If you prefer guided learning, a reputable Python Institute in Kochi can offer structured programs and mentorship to help you grasp core concepts efficiently.
Step 4: Build Projects
Learning by doing is key. Start small:
Build a calculator
Automate file organization
Create a to-do list app
As your skills grow, you can tackle more complex projects like data dashboards or web apps.
How Python Skills Can Boost Your Career
Adding Python to your resume instantly opens up new opportunities. Here's how it helps:
Higher employability: Python is one of the top 3 most in-demand programming languages.
Better salaries: Python developers earn competitive salaries across the globe.
Remote job opportunities: Many Python-related jobs are available remotely, offering flexibility.
Even if you're not aiming to be a full-time developer, Python skills can enhance careers in marketing, finance, research, and product management.
If you're serious about starting a career in tech, learning Python is the smartest first step you can take. It’s beginner-friendly, powerful, and widely used across industries.
Whether you're a student, job switcher, or just curious about programming, Python for beginners can unlock countless career opportunities. Invest time in learning today—and start building the future you want in tech.
Globally recognized as a premier educational hub, DataMites Institute delivers in-depth training programs across the pivotal fields of data science, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. They provide expert-led courses designed for both beginners and professionals aiming to boost their careers.
Python Modules Explained - Different Types and Functions - Python Tutorial
youtube
#python course#python training#python#learnpython#pythoncourseinindia#pythoncourseinkochi#pythoninstitute#python for data science#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes