#cd4
Text
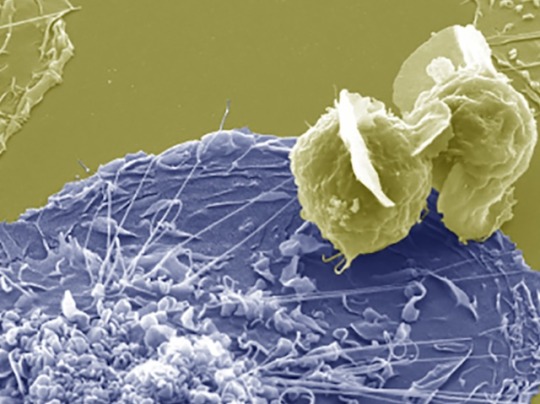
Infection by Fusion
Fusing HIV-infected CD4 T cells with macrophages – cells of the immune system that are a reservoir for HIV in tissue – infects them effectively, providing insight into the mechanisms of persistent infection
Read the published research paper here
Image from work by Rémi Mascarau and colleagues
Institut de Pharmacologie et Biologie Structurale (IPBS), Université de Toulouse, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Université Toulouse III - Paul Sabatier (UPS), Toulouse, France
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Journal of Cell Biology, March 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#hiv#immune system#macrophages#t cells#cd4#electron microscopy#scanning electron microscopy#viral infections
7 notes
·
View notes
Text






RTX 3080 Graphics Card
#3d art#3d artwork#3d model#3d modeling#3d render#animation#artwork#b3d#blender#3drender#cd4#cinema4d#cinematography#nvidia#rtx#art#3d#digital artist#artists on tumblr#gaming#pc
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reviewing questions:
Succinylcholine is a depolarizing paralytic agent that is degraded by the enzyme pseudocholinesterase. Pseudocholinesterase is synthesized in the liver. Metabolites include succinyl and choline, which are then excreted in the urine. In renal failure patients, hyperkalemia is a common occurrence, and succinylcholine results in an increase in serum potassium levels in normal subjects by 0.5 to 2 mEq/L. Given this fact, succinylcholine should not be used in a pt with elevated potassium level, as it puts her at high risk for arrhythmias.
Other adverse effects of succinylcholine toxicity include malignant hyperthermia, muscle pains, acute rhabdomyolysis with hyperkalemia, transient ocular hypertension, constipation, and changes in cardiac rhythm, including bradycardia and cardiac arrest. In patients with neuromuscular disease or burns, a single injection of succinylcholine can lead to massive release of potassium from skeletal muscles, potentially resulting in cardiac arrest. Conditions having susceptibility to succinylcholine-induced hyperkalemia are burns, closed-head injury, acidosis, Guillain–Barré syndrome, cerebral stroke, drowning, severe intra-abdominal sepsis, massive trauma, myopathy, and tetanus. In addition, the additive/synergistic effects of succinylcholine and an opioid, sedative, or anesthetic agent can lead to succinylcholine toxicity. In rare cases, acute rhabdomyolysis with hyperkalemia followed by ventricular dysrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and death have been reported in apparently healthy children and adolescents.
Bottom Line: In renal failure patients, hyperkalemia is a common occurence, and succinylcholine results in an increase in serum potassium levels in normal subjects by 0.5 to 2 mEq/L. Given this fact, succinylcholine should not be used in patients with preexisting hyperkalemia.
AIDS = CD4 count less than 200/mcL. There is a long list of AIDS-defining conditions that would qualify as AIDS even with a CD4 count above 200/mcL, but this list is beyond the scope of COMLEX Level 3, aside from a few commonly tested conditions.
The most current guidelines recommend against administering prophylactic therapy for Mycobacterium avium complex if antiretroviral therapy has been initiated. One should start prophylactic therapy with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole to protect against Pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in a pt with CD4 count of 45.
According to the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology guidelines, there are 2 options after ASCUS results: a repeat Pap smear in 1 year or human papillomavirus (HPV) testing. In the 25- to 29-year-old age group, the preferred option is HPV testing. If the HPV test is positive, then the patient should undergo colposcopy. If the HPV is negative, then the patient should have repeat cotesting with cervical cytology and HPV testing in 3 years. If the option was chosen to repeat the Pap in 1 year and the repeat Pap is normal, then the patient can resume normal testing. If the repeat Pap is abnormal (ASCUS or any other worse pathology), then the patient should undergo colposcopy.
If the patient was in the 21- to 24-year-old age group, then the guidelines give the same 2 options of repeat testing in 1 year or HPV testing. However, in this age group, the repeat testing in 1 year is the preferred method.
After age 30, routine screening involves cotesting (Pap and HPV test every 5 years) or Pap alone every 3 years. The same guidelines apply as for the 25- to 29-year-old age group for ASCUS pathology.
Bottom Line: A cytology report of atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance should be followed up with a human papillomavirus screen or repeat Pap smear in 1 year. If the screen is positive or the cytology at 1 year is abnormal, the patient should get a colposcopy.
High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) is considered a premalignant lesion. Management per the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) is an immediate loop electrosurgical excisional procedure (LEEP) or a colposcopy. If a colposcopy is chosen, further treatment depends on the grade of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. For grade 1 dysplasia found on the colposcopy, the options are to co-test at 12 and 24 months or perform a LEEP. If either of the co-tests shows the HSIL again, then the LEEP should be performed. If the initial colposcopy shows grade 2 or 3 dysplasia, then excision or ablation of the transformation zone is recommended.
Bottom Line: HSIL is considered a premalignant lesion, and thus an excisional procedure is indicated. The provider may go directly to a LEEP procedure or may first perform a colposcopy.
In order to respond to various pathogens, the CDC has grouped many different agents that could be used as biological terrorism into categories. This allows early detection and therefore appropriate response if there is concern for biological terrorism. The grouping of pathogens primarily depends on their capacity to cause harm and ease of dissemination. The organisms/toxins of concern are categorized as:
Category A - organisms that can be grown easily in large quantities, easily disseminated, and have a high mortality rate.
Category B - agents that are modestly easy to spread, cause less morbidity and mortality than Category A, but often require special diagnostic or surveillance techniques.
Category C - agents that could be engineered for mass dissemination and cause significant potential morbidity and/or mortality.
Category A Agents include Variola major (smallpox), Bacillus anthracis (anthrax), Yersinia pestis (plague), Clostridium botulinum toxin (botulism), Francisella tularensis (tularemia), Filoviruses (Ebola, Marburg), and Arenaviruses (Lassa, Junin, and related viruses).
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
CD4
I started my letrozole yesterday, ordered my trigger shot, scheduled my ultrasound for next Thursday, and planning for the IUI between next Saturday - Monday depending on how the follicles look! Let’s GO!
#infertility#ttccommunity#pcos#ttc with pcos#ttcjourney#iui treatment#iui procedure#IUI#cd4#letrozole
0 notes
Text
Book Appointment With HIV Specialist in Delhi
What is the HIV
HIV, or Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is a virus that attacks the immune system of the human body. It specifically targets CD4 cells, which are a type of white blood cell crucial to the immune system's function. HIV weakens the immune system over time, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and diseases.

There are two main types of HIV:
HIV-1: This is the most common and widespread type of HIV. It is responsible for the majority of HIV infections worldwide.
HIV-2: This type of HIV is less common and primarily found in West Africa. It tends to progress more slowly than HIV-1.
HIV is transmitted through contact with certain body fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, rectal fluids, and breast milk from a person who has HIV. The most common modes of transmission include unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles or syringes for drug use, and from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
HIV infection can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) if left untreated. AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection when the immune system is severely damaged, and the individual becomes vulnerable to a wide range of opportunistic infections and certain cancers.
While there is no cure for HIV, it can be effectively managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which helps control the virus's replication and slows down the progression of the disease. Early diagnosis and timely initiation of treatment are crucial for managing HIV and preventing its progression to AIDS. Additionally, practicing safe sex, using clean needles, and taking other preventive measures can help reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
What is the difference HIV and Aids?
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) are related but distinct terms that describe different stages of the same disease process:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus):
HIV is the virus that causes the infection.
When a person is infected with HIV, the virus enters their bloodstream and begins to attack and destroy CD4 cells (a type of white blood cell), weakening the immune system.
HIV infection can remain asymptomatic for many years, during which time the virus continues to replicate and damage the immune system.
People with HIV may experience flu-like symptoms shortly after infection, but these symptoms usually go away, and the person may feel healthy for a long time.
HIV can be controlled and managed with antiretroviral therapy (ART), which helps reduce the viral load in the body and maintain or restore immune function.
Many people with HIV who receive appropriate medical care and treatment can live long and healthy lives.
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome):
AIDS is the advanced and final stage of HIV infection.
It is characterized by a severely weakened immune system, with a significant decline in CD4 cell count.
Individuals with AIDS are at high risk of developing opportunistic infections (infections that typically do not affect people with healthy immune systems) and certain cancers.
AIDS is diagnosed when a person with HIV infection has a CD4 cell count below a certain threshold (usually less than 200 cells/mm³ of blood) or has specific AIDS-defining illnesses, regardless of CD4 count.
Without medical intervention and treatment, AIDS can be life-threatening.
In summary, HIV is the virus that initially infects a person, while AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection characterized by a severely compromised immune system and the occurrence of specific opportunistic infections or cancers. With proper medical care and early intervention, the progression of HIV to AIDS can often be delayed or prevented through the use of antiretroviral therapy (ART) and appropriate healthcare measures. It's important for individuals at risk of HIV infection to get tested, seek medical care, and adhere to treatment plans to manage the virus and prevent the development of AIDS.
youtube
Dr. Raina’s Safe Hands Clinic
Dr. Vinod Raina HIV Doctors in Kalkaji
Contact Us-9136363692 | 9871605858
Address: — Saket E-34, Ekta Apartments
near Malviya Nagar Metro Station Gate No-4
New Delhi-110017
1 note
·
View note
Text
Epigenetisches Medikament zur Behandlung von Blutkrebs, seltenen Sarkomen, kann das Wachstum von Blasenkrebs stoppen
Ein epigenetisches Medikament, das derzeit zur Behandlung von Blutkrebs und seltenen Sarkomen eingesetzt wird, kann das Wachstum von Blasenkrebs stoppen, indem es das Immunsystem aktiviert, berichtet eine neue Studie der Northwestern Medicine an Mäusen.
Es ist das erste Mal, dass ein Medikament zur Behandlung von hämatologischen Malignomen und seltenen Sarkomen zur Behandlung eines der häufigsten soliden Tumoren eingesetzt wird. Das Medikament Tazemetostat wurde ursp...
#Biochemie #Blase #Blasenkrebs #BLUT #CD4 #Epigenetik #Forschung #Gen #gene #Genetik #Immunreaktion #Immunsystem #Immuntherapie #Klinische_Studie #Krebs #Krebsbehandlung #Lymphom #Medizin #OKT #tumor #Urologie #Veteranenangelegenheiten
#Medical_Condition_News#Medical_Research_News#Medical_Science_News#News#Biochemie#Blase#Blasenkrebs#BLUT#CD4#Epigenetik#Forschung#Gen#gene#Genetik#Immunreaktion#Immunsystem#Immuntherapie#Klinische_Studie#Krebs#Krebsbehandlung#Lymphom#Medizin#OKT#tumor#Urologie#Veteranenangelegenheiten
0 notes
Text
Poche ma fondamentali: le TSCM di memoria in HIV/AIDS
Poche ma fondamentali: le TSCM di memoria in HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS, dopo quarant’anni dalla sua scoperta, continua ad essere un problema di salute pubblica globale. Sebbene la ricerca scientifica abbia prodotto delle classi di farmaci utilizzate in combinazione come terapia antiretrovirale (ART), ancora non è possibile eliminare completamente il virus se si viene contagiati.
(more…)

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Más detalles en nuestro blog https://leucococitas.blogspot.com/ #CD4 (martes de cluster of differentiation) #hematologia #flowcytometry #CD4 (en Chile) https://www.instagram.com/p/Cf5SBKauSwj/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
Even asymptomatic maternal COVID-19 can potentially cause pregnancy complications
Even asymptomatic maternal COVID-19 can potentially cause pregnancy complications
A recent study published in the Cell Reports journal analyzed immune ecology at the placenta in mild or asymptomatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection during pregnancy.
Study: Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals immunological rewiring at the maternal-fetal interface following asymptomatic/mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. Image Credit: MIA Studio /…

View On WordPress
#Antigen#Asymptomatic#Blood#CD4#cell#Chemokine#Complications#Coronavirus#Coronavirus Disease COVID-19#COVID19#Cytokine#Cytometry#Flow Cytometry#Macrophage#Maternal#Monocyte#pandemic#Placenta#potentially#pregnancy#receptor#Respiratory#RNA#RNA Sequencing#SARS#SARS-CoV-2#Severe Acute Respiratory#Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome#syndrome
0 notes
Photo

この辺り . . . #instadaily #inspiration #3dart #cd4 #purple #textures #alonesometimes #3dcomunity (at 3D-Art) https://www.instagram.com/p/Ce3-YthuxMZ/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
Laser Scan Animation
#animation#artwork#graphic design#3d#3d art#blender#3d model#3d render#3d modeling#blender 3d#b3d#3d artwork#3drender#blender render#motion graphics#digital art#movement#cd4#cinema 4d#c4dart#art#original art#my art#ps5#gaming#playstation#playstation 5#gamer#videogame#houdini
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

ideal threesome dynamics
#this is the thought that made me start this blog#CD4 T cells#CD8 T cells#dendritic cells#article is laidlaw et al 2016
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
gorgeous gorgeous girls drive all the way to the lab just to find out they forgot their laptop at home (and it is essential for today's work)
#ughhdhdhd#like if i was just doing cd4 isolations it be fine but noooo i actualmy have to WRITE today
1 note
·
View note
Text
Due to having some social contact outside work and school settings, my schedule has fallen apart and I don't know how I'll do
#another test coming up#have went through 37 slides out of 102#i can remember TCR structure#and the number of CDR on each chain but idk what cdr meant. complementarity determining region? god knows#the structure of CD4 and CD8 is 😭😭😭 like bestieesss why must i suffer#but i recall CD4 and CD8 binding sites on MHC#forgot what CD stands for#i know the difference between coreceptor and costimulating receptor. if thats what theyre called#so now i have to learn BCR (i know already smth) and CDR of them and then there was something.#was it the gene regions? it probably was. idk. something that is analogous for both TCR and BCR#anyway. i know i make no sense but this was a good review session for me#i cant even make a meme out of this#oh wait i have to know immunological synapse. i made a meme abt that before#yeah thats in the other bigger part of the presentation i havent covered#i have a day lol.#oof#if you read my tags. do you have immunology flashcards? do you want to share? do you love me?
4 notes
·
View notes