#chambered nautilus
Note
Hi i'm back and i would like a chambered nautilus. pretty little fellas

Daily Cephalopod #174
#nautilus#chambered nautilus#squid mail くコ:彡#daily cephalopod#GOOBERS!!!#cephalopod#marine life#ocean creatures#ocean critters#marine biology#zoology#animals#biology#cephalopods#marine animals
492 notes
·
View notes
Text

#pucker up baby#marine biology#marine biology shitpost#marine life#wizardshitposts#nautiluses#chambered nautilus#cephalopods
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you asked me as a kid what my favorite animal was, there's a good chance I'd respond "chambered nautilus", though I probably would mispronounce it. I don't know if it's still my favorite but it's definitely up there in the pantheon of weird critters. For this Wet Beast Wednesday, I'll discuss my childhood favorite.
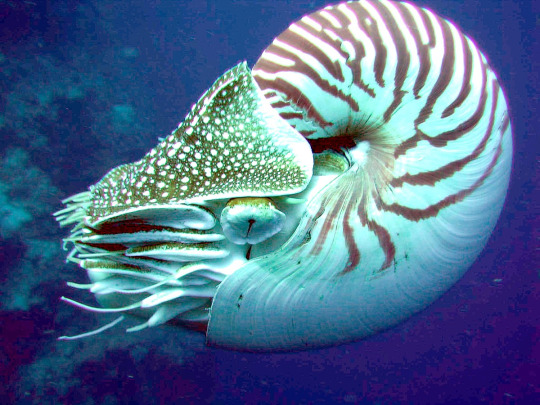

(image: a nautilus)
The nautilus is a cephalopod that lives in a curved shell and looks similar to (but is not closely related to) the extinct ammonites. There are 6 living species in two genera, but 90% of the time when someone is discussing nautiluses they are referring to the most well-known species: Nautilus pompilius or the chambered nautilus. Nautiloids are ancient, going back to at least the late triassic with their more primitive ancestors going back as far as the ordovician period, a time when only invertebrates and primitive plants occupied the land and true fish had not yet appeared. Because of their ancient history, nautiluses are sometimes considered living fossils. I have ranted before on how misleading the term "living fossil" is so I'll spare you that for now. Nautiloids are considered a sister group to the celoids, which contains all the squid, octopus, cuttlefish, and everything else we thinks of as cephalopods. Nautiluses should not be confused with paper nautiluses. Also called argonauts, paper nautiluses are a group of octopi that make an egg case which looks like a shell.

(image: a nautilus)
The most noticeable feature of a nautilus is its shell. The shell is smooth and finely curving, naturally growing in the shape of a logarithmic spiral (though not, as is commonly stated, a golden ratio spiral). The shell has a stripy outer layer and an inner layer coated with nacre. Internally, the shell is divided into camarae (chambers) separated from each other by walls called septa. Each septum has a small hole in it through which a strand of tissue called the siphuncle passes. Most of the nautilus's body is in the foremost and largest chamber. The shell grows new septa as the animal grows, with the nautilus's body moving to a new chamber as it becomes too large for previous ones. Juveniles are typically born with 4 septa, with adults having as many as 30. In addition to providing protection from predators, the shell is also key for regulating buoyancy. The septa can contain pressurized gas or water and the siphuncle regulates their contents by either adding or removing water to increase or decrease buoyancy. Because of its pressurized contents, the shell can only withstand pressure at depths up to 800 M (2,400 ft) before imploding. Oddly enough, nautiluses can be safely brought up from deep waters where most animals would be killed by the pressure changes. To move, the nautilus pulls water into the first chamber of the shell using its hyponome (siphon) and shoots it back out. The chambered nautilus is the largest species, with a maximum shell diameter of 25 cm (10 in), though most get no larger than 20 cm (8 in).
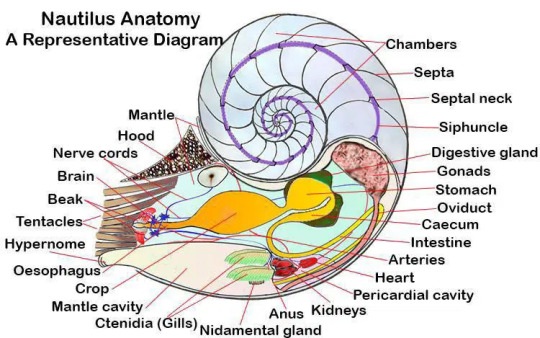
(image: a diagram of nautilus anatomy. source)
Where celoid cephalopods have tentacles, nautiluses instead have numerous cirri. Unlike tentacles, cirri are less muscular, are not elastic, and have no suckers. They are used to grab objects using their ridged surfaces and can hold in so hard that trying to take an object away from a nautilus can rip off its cirri, which will remain firmly attached. In addition, the nautilus has modified cirri that serve as olfactory receptors and a pair that serve to open and close the shell when the nautilus needs to retract into it or emerge. Nestled within the cirri is the beak, which is used to consume the nautilus's primary prey of invertebrates, though they have also been seen scavenging fish. Their eyes are less developed than most cephalopods, lacking a lens and consisting of a small pinhole that only allows the nautilus to see simple imagery. Their brains are differently structured than most cephalopods and studies have found them to have considerably shorter long-term memories.
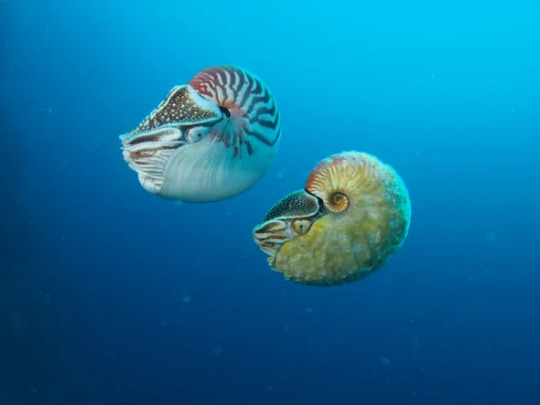

(image: a chambered nautilus (upper left) next to a rare Allonautilus scrobiculatus. source)
Cephalopod reproduction is quite different than that of other cephalopods. While most cephalopods are short-lived and semelparous (reproducing only once), nautiluses can live over 20 years and reproduce multiple times (iteroparity). They do not reach sexual maturity until around 15 years old, with females laying eggs once per year. Eggs are attached to rocks and take 8 to 12 months to hatch. Males have a structure called the spadix composed of 4 fused cirri that they use to transfer sperm to females. Females lose their gonads after laying their eggs and will regenerate them for the next year's mating season. Interestingly, male nautiluses seem to vastly outnumber the females. EDIT: @bri-the-nautilus in the replies found an alternate explanation for the disparity in male and female numbers you should check out. TLDR; the females are asocial.

(image: nautiluses mating)
Nautiluses are found in the Indo-Pacific reagion of the ocean and can be found on the steep slopes of coral reefs. They prefer to inhabit waters several hundred meters down. It was once believed that they would rise to shallow waters at night to feed, lay eggs, and mate, but their vertical migration behavior has since been shown to be more complex than that. They have noon been fished by humans for their shells, which have become popular subjects in art and can be made into a number of decorative pieces. The nacre of the shell can be polished into osmeña pearl, which can be quite valuable. Demand for the shells combined with the late sexual maturity and low fecundity is threatening all the species. As of 2016, nautiluses have been added to the CITES Appendix II, making them protected by limiting international trade of their shells. Despite this, they are still threatened and require further protection

(image: a carved and painted nautilus shell from the Poldi Pezzoli Museum, Milan)
#wet beast wednesday#nautilus#chambered nautilus#cephalopod#marine biology#zoology#biology#ecology#animal facts
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
🐙Daily Cephalopod Fact:🐙
Chambered Nautilus: The nautilus is an octopus’ cousin. It has more than 90 tentacles — the most of any cephalopod — which it uses to feel and grope along the reefs for food. Unlike those of other cephalopods, a nautilus’s tentacles have grooves and ridges instead of suckers. The nautilus is the only cephalopod with an external shell. Much like zebras, nautiluses can be individually identified based on their striped shell patterns.
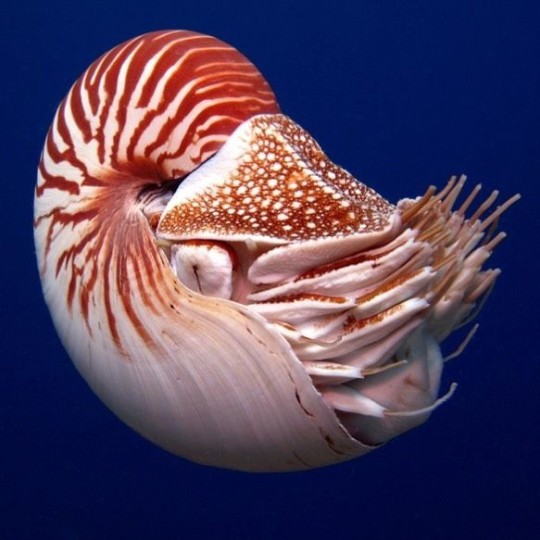


#chambered nautilus#nautilus#octopus cousin#living fossil#respect the locals#cephalopod#daily cephalopod#daily cephalopod fact#cephalopod facts#facts about cephalopods#marine#marine animals#marine biology#marine life#ocean#ocean life#shark blog
100 notes
·
View notes
Text

its excellent shell and way of siphoning water to swim around have captivated me
#chambered nautilus#marine biology#there are many benefits to being a marine biologist#marine biology memes#sea creatures
705 notes
·
View notes
Text

my OC Tera at the Shellendorf Institute, enjoying some sun from the overhead skylights.
I saw an outfit on Pinterest that I liked so much I decided to draw her in it haha
#Heehee hoohoo I have a fancy new watermark now#I might makes some lighting changes but this is fine for now#my art#splatoon#splatoon oc#splatoon 3#nautilus#chambered nautilus#nautiloid#splatoon art#splatoon fandom#oc art#character design#creature design
99 notes
·
View notes
Photo
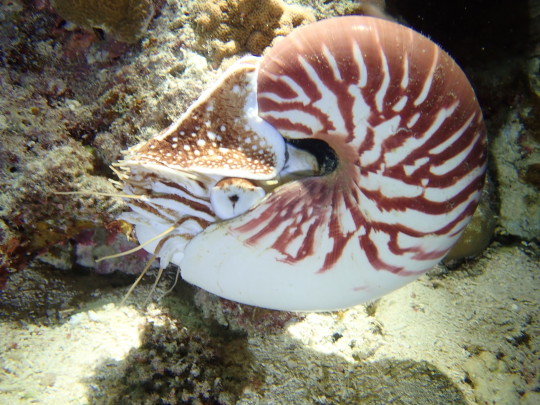

Chambered Nautilus (Nautilus pompilius)
Family: Nautilus Family (Nautilidae)
IUCN Conservation Status: Unassessed
The fossil record shows that hard external shells were common among early cephalopods, but today the six living species of nautilus are the last cephalopods to retain the external shells of their ancestors, limiting their agility and flexibility but providing them with a highly effective defence against predators (primarily octopuses and large fish) and granting them a high degree of control over their buoyancy: within the shell of a nautilus there are several chambers with a tube-like structure across which gas and water can be transferred, known as a siphuncle, running between them - by filling a chamber with gas the nautilus can increase its buoyancy, by filling a chamber with water it can decrease its buoyancy, and by balancing the number of gas-filled chambers and water-filled chambers it can maintain neutral buoyancy. The Chambered Nautilus is the largest living nautilus (with exceptionally large individuals having a shell diameter of up to 25cm/10 inches, although smaller sizes are more typical), and can be found in the Indian and western Pacific oceans where it typically inhabits shallow coastal waters and coral reefs. It swims by forcing water out of a flexible tube-like structure near its head called a siphon (which can be aimed to alter its direction of movement), and feeds largely on carrion and detritus which it locates using a pair of chemical-sensitive structures that protrude from above its eyes, known as rhinophores. Although they lack true tentacles, Chambered Nautiluses possess as many as 90 small limbs beneath their eyes (called cirri), which lack the strength and adhesive suction cups of the limbs of squids and octopuses but are capable of grasping carrion (as well as the occasional live animal, such as small crabs) and transporting it to the small, parrot-like beak hidden beneath them. When food is abundant Chambered Nautiluses often gorge themselves, storing excess food in a muscular pouch-like organ called a crop where it can be slowly released into the stomach when it is needed. Chambered Nautiluses reproduce by laying eggs (which are typically hidden in cracks in rocks or between lobes of coral, and hatch after about a year into small but fully-developed young instead of the larvae seen in most cephalopods), and while most cephalopods reach maturity, mate and die within just a few years nautiluses are relatively long-lived, reaching maturity at around 5 years old and potentially living for 15-20 years. The interior of a Chambered Nautilus’ shell is lined with a beautiful silvery substance known as nacre or mother-of-pearl which helps to protect the internal organs if the outer shell is damaged, and the demand for nacre (as well as full nautilus shells) for use in decorations and jewellery has led to a high rate of both legal and illegal hunting of this species, resulting in the Chambered Nautilus being classified as a CITES Appendix II species in 2016 (essentially meaning that they are not currently threatened with extinction, but are now legally protected so as to prevent them from being put at risk of extinction in the future.)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image Source: https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/123467-Nautilus-pompilius
#Chambered Nautilus#Nautilus#naurtiluses#nautiloids#cephalopods#zoology#biology#Teuthology#animal#animals#marine wildlife#marine biology#cephalopod#wildlife
444 notes
·
View notes
Text

deep sea creachur appreciation post!!!!
#all#image#spooky#meme#creature#here we go#fish#crustacean#cephalopod#nudibranch#giant isopod#black swallower#blue glaucus#nautilus#chambered nautilus#crab#yeti crab#shark#frilled shark#shrimp#mantis shrimp#peacock mantis shrimp#lanternfish#oarfish#squid#vampire squid#coelacanth
200 notes
·
View notes
Photo

A forget-me-nautilus!
Had this terrible play on words stuck in my brain for ages, and finally got around to drawing it! This one’s for you, Orph!
#nautilus#sea life#sea creature#ocean life#chambered nautilus#mollusc#flowers#forget me nots#doodles
262 notes
·
View notes
Text

Jan. 2023
188 notes
·
View notes
Text
:0
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
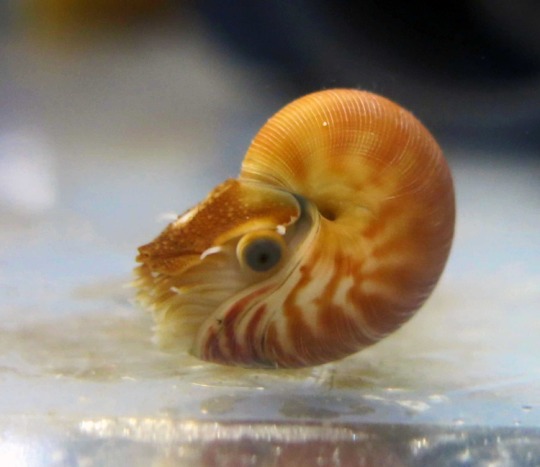

Daily Cephalopod #34
#nautilus#chambered nautilus#just a baby!#daily cephalopod#cephalopod#cephalopods#marine life#marine critters#marine creatures#marine animals#marine biology#ocean creatures#ocean critters#ocean animals#ocean life#sea animals#sea life#sea creatures#aquatic life#biology#zoology#animals
535 notes
·
View notes
Text


nautilus and bonus snuffkin
78 notes
·
View notes
Photo
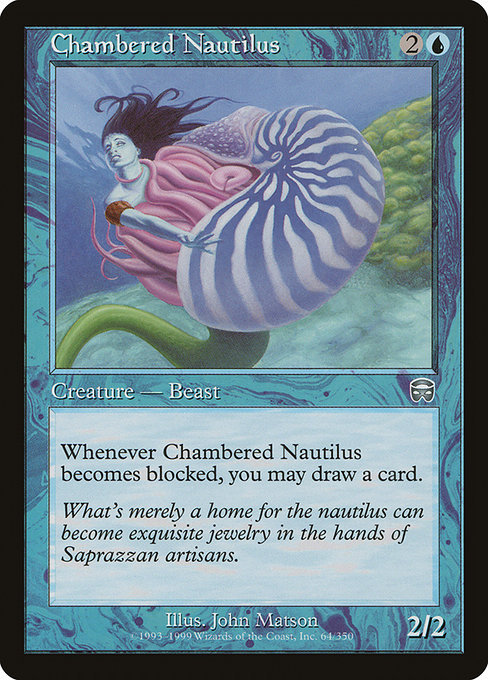

Chambered Nautilus
What's merely a home for the nautilus can become exquisite jewelry in the hands of Saprazzan artisans.
Artist: John Matson
TCG Player Link
Scryfall Link
EDHREC Link
#mtg#magic the gathering#tcg#$0.15#john matson#chambered nautilus#mercadian masques#creature#nautilus#beast
18 notes
·
View notes
Text


tattoo design commissions i've done for friends!
if you want to see more of my work, you can follow my tattoo ig here
#rlynchtattoos#ill be posting my flash sheets here too mostly just to show them off to my mutuals hehe#there's not a big market for ppl actually wanting to get tattooed by me here cause i have like 2 sacramento mutuals#anyways. look away#blackwork#woodcut#tattoos#handpoke#independent artist#nautilus#raven#chambered nautilus#artists on tumblr#queer artists#jewish artist#trans art#lgbt
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's review what was made this year!
January






#artadventcalendar#advent calendar#artoftheday#cuteness#animal art#sunbear#opossums#chambered nautilus#cross fox#doodle
58 notes
·
View notes