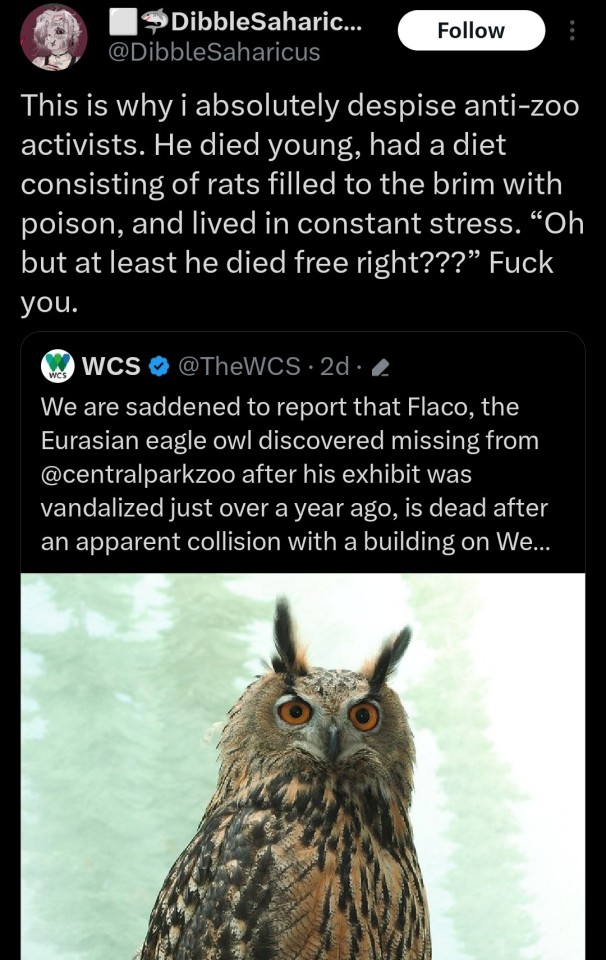
#ecology
Text

#never trump#republican assholes#climate change#ecology#environment#green jobs#sustainability#corporate greed#maga morons#climate crisis#climate activism#climate deniers
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay. This is a pretty big deal in the world of mycology. Historically fungi have been divided up into either parasites that siphon resources from plants, mutualists that cooperate with them, or saprotrophs that break down decaying organic matter (plant and otherwise.) The genus in question, Mycena, has traditionally been made of saprotrophic species feeding on decaying wood.
However, what scientists are observing is Mycena fungi displaying primitive mutualistic behaviors, specifically providing living plants with nitrogen and getting carbon in return from a living partner, or getting to chow down on the plant's remains once deceased. This shows a significant level of adaptability that hasn't been observed in fungi beforehand, though given how much we don't know about fungi there's a good possibility this isn't an unprecedented event.
It doesn't surprise me one bit that we're seeing this in Mycena. These fungi are especially opportunistic; in fact, that mushroom growing out of a frog's skin that we saw a while back was also a Mycena species. Perhaps we need to add bonnet mushrooms to raccoons, dandelions, and other hardy generalists as symbols of scrappy survival in spite of environmental pressures.
#Mycena#bonnet mushrooms#mushrooms#mushroom#fungi#fungus#mycelium#mycology#botany#biology#nature#science#scicomm#evolution#environment#ecology#mutualism#mycorrhizal fungi
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
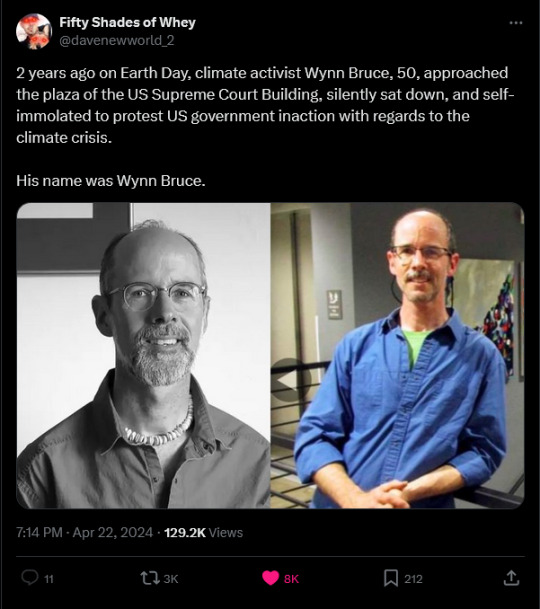
#earth day#leftism#socialism#communism#anti capitalism#anarchy#ecosystem#environment#ecology#eco#save the planet#go green#save the earth#recycle#april 22#save the bees#twitter x#save the children
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
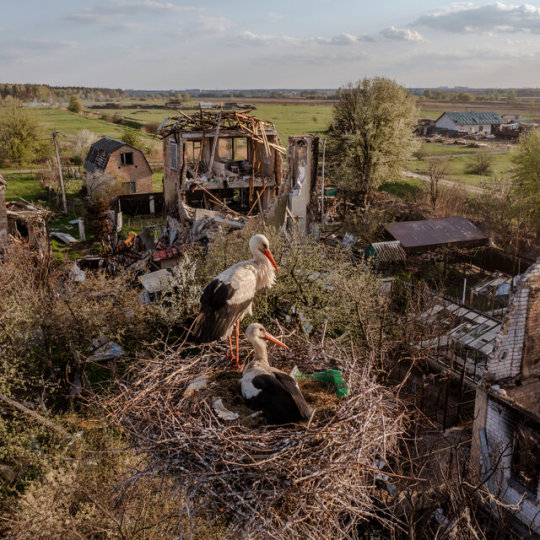









russia commits ecocide in Ukraine
#ukraine#russia#russia is a terrorist state#genocide#fuck russia#stand with ukraine#support ukraine#genocide of ukrainians#russian war crimes#ecocide#nature#earth#earth day#sustainability#ecology#ecofriendly
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since 2023, three articles have appeared in scientific journals, with 45 authors in all, arguing that the claims made on behalf of the wood-wide web have far outstripped the evidence. The objections are numerous. Many studies of inter-tree transfers have found only minuscule amounts of sugars shuttling between the trees – “statistically significant” but not necessarily “biologically significant”, one group of authors says – and most don’t rule out the possibility that the resources travelled through the air or soil rather than fungally. Despite Wohlleben’s insistence in Hidden Life that in a mycorrhizally conjoined forest “it is not possible for trees to grow too close to each other”, studies have not generally shown that seedlings ensconced in fungal networks do better when close to older trees (they often do worse). And although many trees are colonised by mycorrhizae, there is debate about whether those mycorrhizae actually form a durable network through which nutrients and signals could pass.
Nature, the original venue for Simard’s research, recently ran an explosive news feature by Aisling Irwin on the “groundswell of unease” among ecologists with public discussions of mycorrhizal networks. Irwin reports on the scientists’ general scepticism and on a particular episode that has raised concerns. In her memoirs, Simard makes much of the idea that “mother trees” favour their kin. She describes in detail field research by her graduate student showing that seedlings placed in a fungal network “survived better and were noticeably bigger” if they were genetically related to nearby older trees. But that field study, the critics have noted, actually showed the opposite: the related seedlings were likelier to die, though the trend was not statistically significant. (Simard says that other studies by the student, from the laboratory, support her claims and she’d merely made a narrative choice to describe the results as emanating from the forest. “I do not, and would never, imply anything misleading when presenting research,” she told Irwin.)
What makes the recent criticisms of Simard’s work so striking is that some come from her former colleagues and admirers. The first critical review of evidence was by three scientists – Justine Karst, Melanie Jones and Jason Hoeksema – who had all co-authored papers with Simard. The lead author, Karst, has discussed how she was inspired by Simard’s research to become a mycorrhizal ecologist. The second, Melanie Jones, appears in Simard’s memoirs as a hero who supported Simard when few others would. Jones co-authored the 1997 “wood-wide web” article, though she no longer stands fully by it. It was the cultural obsession with intelligent trees, from television shows to airport books, that impelled Karst, Jones and Hoeksema to reconsider their own earlier work.
Simard, who is preparing detailed replies, regards these in-the-weeds debates as distracting from the urgent task of protecting forests. She has described the attention that Karst, Jones and Hoeksema’s criticisms have received as “an injustice to the whole world”. Perhaps, but it is exceedingly hard to read the recent reviews of evidence and retain faith in the wood-wide web as settled scientific fact.
“Why do we so badly want this to be true?” Karst has asked. Maybe the unrelenting news of global warming and its attendant catastrophes – wildfires, hurricanes – has driven readers for respite toward calmer environmental stories. Or perhaps recent political cruelties have led us to seek reassurance that, in nature, beings are thoughtful and kind. The connective aspect seems important, too, as if trees’ fungal friendships could release us from our phone-checking isolation. Fairly or not, we’ve loaded our aspirations on to the forest: be the tree you want to see in the world.
[...]
A tree, Farmer writes, is “a radically nonhuman thing”, and a large, old tree is especially one. If trees have conceptual value, it is not because their similarity to us elicits our sympathy, but because their difference from us enlarges our horizons. They are the most visible markers on the evolutionary road not taken. Trees stand in for all the photosynthesising, carbon-dioxide breathing, fixed-in-place species that share our world yet have fundamentally different ways of living in it.
Contemplating trees should be, above all, an exercise in humility. The mountains and woods, Santayana told his California audience, allow you to “take yourselves simply, humbly, for what you are, and to salute the wild, indifferent, non-censorious infinity of nature”. Perhaps the presence of beings older, larger and more numerous than we are – whether or not they resemble internet users or our mothers – can be a reminder that we are not everything, and that everything is not us. “Let us therefore be frankly human,” Santayana enjoined. And let the trees be trees.
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
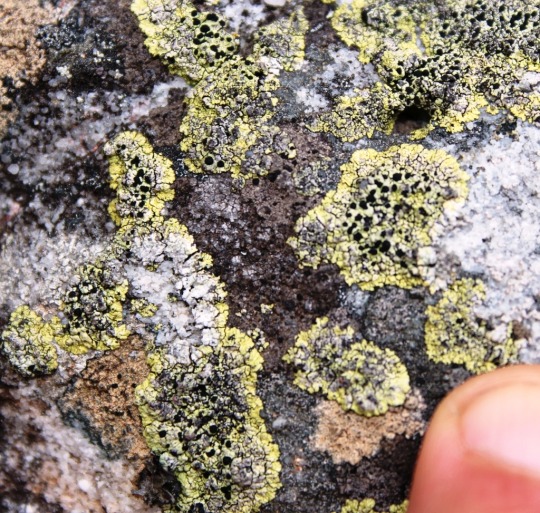
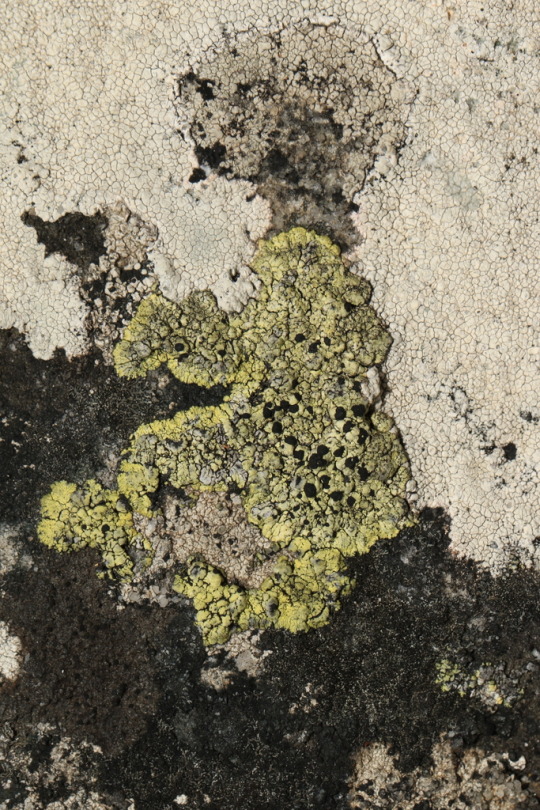








Diploicia africana
This crustose-placodioid lichen grows in yellow rosettes on siliceous, rock in South Africa. The upper surface is often bleached and wrinkled toward the center of the rosette, and speckled with black, lecideine apothecia. Being that D. africana is a) crustose b) saxicolous and c) endemic to the southern hemisphere, it shouldn't be surprising that this lichen appears to be largely understudied, and it might be more widespread than currently recognized.
images: source
info: source
#lichen#lichens#lichenology#lichenologist#mycology#ecology#biology#fungi#fungus#symbiosis#symbiotic organisms#algae#life science#environmental science#natural science#nature#the natural world#Diploicia africana#Diploicia#trypo#trypophobia#I'm lichen it#lichen a day#daily lichen post#lichen subscribe
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

#nature#ecology#econotego#environmental#memes#meme#antifa#antinazi#antiauthoritarian#161#1312#farm#farmcore#farming#plants#vegetables#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#growing
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: spiny softshell turtle
It may be neither Flat Fuck Friday nor Turtle Tuesday, but because this is my series and I can do what I want, I'm talking about a very flat turtle. The spiny softshell turtle (Apalone spinifera) is the most widely distributed and possibly the most common softshell turtle in North America. Its range covers most of the Eastern half of the USA and stretched into Canada and Mexico. There are 6 subspecies separated by geography and hybridization can happen in places where their ranges cross. Hybridization has also been known to happen with the Florida softshell (Apalone ferox). The subspecies are the northern (A. s. spinifera), gulf coast (A. s. aspera), Texas (A. s. emoryi), pallid (A. s. pallida), Guadalupe (A. s. guadalupensis), and black (A. s. atra) spiny softshells.

(Image: a spiny softshell turtle seen from above and to the side. It is a turtle with a wide, flat shell. Its head and one foot are visible. The head is skinny and has an elongated nose. The foot is wide and flat, with webbed toes. The turtle is an olive green with black dots on the skin, yellow stripes on the face, and dark spots on the shell. End ID)
The thing that makes a softshell a softshell is the lack of keratinized scutes on their shells. This makes the shells smooth and leathery. The center of the shell has a layer of solid bone user it, but this does not extend to the edges of the shell, making it less rigid. Softshells are the fragile speedsters of the turtle world. Their shells are a lot lighter and often more streamlined, allowing for faster movement both on land and in water, but they provide less defense. Spiny softshells have spiny projections along the front edge of the carapace (upper shell), with males having more than females. They are some of the largest North American freshwater turtles. Females can reach a carapace length of 54 cm (21 in) and 11 kg (25 lbs) while the smaller males max out at about 25 cm (10 in).
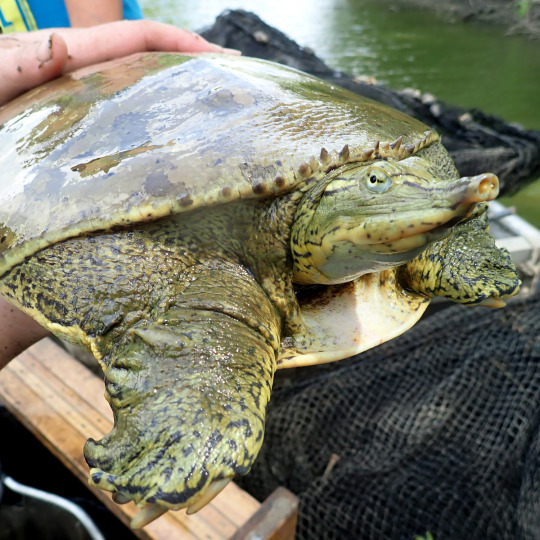

(Image: a spiny softshell being held by a person, seen from the front. The leading edge of the carapace is visible, showing off the small spines. End ID)
Spiny softshells have wide, flat, paddle-like feet with three claws and an elongated nose that acts like a snorkel. The turtles are born a bright olive color with striped faces and dark spots on the shell. Males keep their juvenile coloration for their entire lives while females grow darker ad lose many of their markings. It can be very difficult to tell females of different subspecies apart, while males and juveniles can be distinguished by their markings. Smooth skin and highly vascularized membranes in the cloaca, mouth, and throat allow the turtles to breathe by diffusing dissolved oxygen from the water into their blood.

(Image: a male and female spiny softshell facing each other. The male is less than half the size of the female and has an olive colored shell and skin, with dark spots on the shell. The female is a uniform muddy brown color. End ID)
Spiny softshells are generalists able to live in a wide range of habitats. They prefer streams, rivers, and ponds with muddy or sandy bottoms and high visibility, but can live in most freshwater habitats. Softshells are diurnal, spending their days basking and feeding. Being turtles, they are ectothermic, meaning their body temperature matches the surrounding temperature. To warm themselves up, the turtles bask in the sunlight. They can often be found resting on exposed rocks, logs, sandbars, or shorelines. While not particularly social animals, the turtles will bask in groups. When threatened, softshells will attempt to swim away and/or bury themselves. In the right sediment, a softshell can bury itself in under a second. Because their shells are less rigid, softshells have to actively defend themselves when cornered and will bite and scratch. People have to be careful when handling them. They brumate (that's hibernation for reptiles) during winter. While brumating, they bury themselves underwater and slow their metabolism and oxygen requirements. In this state they can fully sustain themselves on oxygen absorbed through their skin or special membranes.

(Image: a spiny softshell turtle buried in its hunting strategy. Only the head is visible above the sand. End ID)
They are primarily carnivores and will eat anything that can fit in their mouths. Aquatic insects, crayfish, worms, amphibians, mussels, snails, fish, and more are on their plate. While capable of fast swimming, they are not pursuit predators. They employ two primary hunting strategies. The first is to bury themselves in the sediment and wait for prey to come by. The second is digging in the sediment to find worms and other animals. Fish have been known to follow digging turtles around to feed on animals unearthed by them.

(Image: a spiny softshell in captivity. It is swimming at the surface of the water in a tank, amongst artificial leaves. End ID)
Spiny softshells mate in spring. Males attempt to woo females by swimming over to them and bumping heads together. The male then sits on top of the female to mate. Unlike most species of turtles, the males do not grab onto the female's shells during mating. Eggs are laid between summer and early fall and will hatch next spring. The female will dig a nest in sandy or gravelly banks and bury the eggs once they have been laid. She provides no further care. Females will typically mate multiple times each year, with each mating having a different nest. The juveniles take 8 to 10 years to reach sexual maturity and they can live up to 50 years in the wild. Many turtles determine sex by the temperature the eggs are incubated in. This is not the case with spiny softshells, who have genetics based sex determination.

(Image: a group of 5 juveniles. The photo focuses on two who are sitting next to each other. One has its front right leg on the shell of the other. They have similar coloration to an adult male. End ID)

(Image: a newborn emerging from its egg. The egg is round and white, looking like a ping-pong ball. Only the head of the turtle has emerged. End ID)
Most subspecies of spiny softshell are classified as least concern or near threatened by the IUCN, meaning they are not in danger of extinction. The exception is the black spiny softshell, also known as the Cuatro Ciénegas softshell, which is critically endangered. The primary threats to the turtles is habitat loss due to human activity. Adults have no natural predators outside of the Florida and adjacent state populations, which are prey to alligators. Juveniles are eaten by a variety of animals including fish, snakes, raccoons, and herons. People will also eat the adults. Because it can take a whole decade for juveniles to become reproductive, losses in population take a long time to replace. They have been introduced to areas outside of their native range, most notably the western USA. Most of these introductions are due to people releasing pet turtles into the wild.

(Image: someone holding a juvenile. The shell is 2-3 times the size of the human's thumb. End ID)
#i typoed it as softhsell more times than I care to admit#wet beast wednesday#turtle#turtles#softshell turtle#soft shell turtle#spiny softshell turtle#reptile#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#freshwater ecology#aquatic biology#informative#educational#image described#turtle power#herpetology
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
A quick lesson in "reading" pasture, and the power of ruminants.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Leaf Katydids (Subfamily Phaneropterinae)
#inaturalist#naturalist#nature#ecology#zoology#biology#insect#insects#bug#bugblr#entomology#bugs#photography#nature photography#wildlife photography#hawks photos#insectblr#bugposting#katydid
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

A.2.8 Is it possible to be an anarchist without opposing hierarchy?
No. We have seen that anarchists abhor authoritarianism. But if one is an anti-authoritarian, one must oppose all hierarchical institutions, since they embody the principle of authority. For, as Emma Goldman argued, “it is not only government in the sense of the state which is destructive of every individual value and quality. It is the whole complex authority and institutional domination which strangles life. It is the superstition, myth, pretence, evasions, and subservience which support authority and institutional domination.” [Red Emma Speaks, p. 435] This means that “there is and will always be a need to discover and overcome structures of hierarchy, authority and domination and constraints on freedom: slavery, wage-slavery [i.e. capitalism], racism, sexism, authoritarian schools, etc.” [Noam Chomsky, Language and Politics, p. 364]
Thus the consistent anarchist must oppose hierarchical relationships as well as the state. Whether economic, social or political, to be an anarchist means to oppose hierarchy. The argument for this (if anybody needs one) is as follows:
“All authoritarian institutions are organised as pyramids: the state, the private or public corporation, the army, the police, the church, the university, the hospital: they are all pyramidal structures with a small group of decision-makers at the top and a broad base of people whose decisions are made for them at the bottom. Anarchism does not demand the changing of labels on the layers, it doesn’t want different people on top, it wants us to clamber out from underneath.” [Colin Ward, Anarchy in Action, p. 22]
Hierarchies “share a common feature: they are organised systems of command and obedience” and so anarchists seek “to eliminate hierarchy per se, not simply replace one form of hierarchy with another.” [Bookchin, The Ecology of Freedom, p. 27] A hierarchy is a pyramidally-structured organisation composed of a series of grades, ranks, or offices of increasing power, prestige, and (usually) remuneration. Scholars who have investigated the hierarchical form have found that the two primary principles it embodies are domination and exploitation. For example, in his classic article “What Do Bosses Do?” (Review of Radical Political Economy, Vol. 6, No. 2), a study of the modern factory, Steven Marglin found that the main function of the corporate hierarchy is not greater productive efficiency (as capitalists claim), but greater control over workers, the purpose of such control being more effective exploitation.
Control in a hierarchy is maintained by coercion, that is, by the threat of negative sanctions of one kind or another: physical, economic, psychological, social, etc. Such control, including the repression of dissent and rebellion, therefore necessitates centralisation: a set of power relations in which the greatest control is exercised by the few at the top (particularly the head of the organisation), while those in the middle ranks have much less control and the many at the bottom have virtually none.
Since domination, coercion, and centralisation are essential features of authoritarianism, and as those features are embodied in hierarchies, all hierarchical institutions are authoritarian. Moreover, for anarchists, any organisation marked by hierarchy, centralism and authoritarianism is state-like, or “statist.” And as anarchists oppose both the state and authoritarian relations, anyone who does not seek to dismantle all forms of hierarchy cannot be called an anarchist. This applies to capitalist firms. As Noam Chomsky points out, the structure of the capitalist firm is extremely hierarchical, indeed fascist, in nature:
“a fascist system… [is] absolutist — power goes from top down … the ideal state is top down control with the public essentially following orders.
“Let’s take a look at a corporation… [I]f you look at what they are, power goes strictly top down, from the board of directors to managers to lower managers to ultimately the people on the shop floor, typing messages, and so on. There’s no flow of power or planning from the bottom up. People can disrupt and make suggestions, but the same is true of a slave society. The structure of power is linear, from the top down.” [Keeping the Rabble in Line, p. 237]
David Deleon indicates these similarities between the company and the state well when he writes:
“Most factories are like military dictatorships. Those at the bottom are privates, the supervisors are sergeants, and on up through the hierarchy. The organisation can dictate everything from our clothing and hair style to how we spend a large portion of our lives, during work. It can compel overtime; it can require us to see a company doctor if we have a medical complaint; it can forbid us free time to engage in political activity; it can suppress freedom of speech, press and assembly — it can use ID cards and armed security police, along with closed-circuit TVs to watch us; it can punish dissenters with ‘disciplinary layoffs’ (as GM calls them), or it can fire us. We are forced, by circumstances, to accept much of this, or join the millions of unemployed… In almost every job, we have only the ‘right’ to quit. Major decisions are made at the top and we are expected to obey, whether we work in an ivory tower or a mine shaft.” [“For Democracy Where We Work: A rationale for social self-management”, Reinventing Anarchy, Again, Howard J. Ehrlich (ed.), pp. 193–4]
Thus the consistent anarchist must oppose hierarchy in all its forms, including the capitalist firm. Not to do so is to support archy — which an anarchist, by definition, cannot do. In other words, for anarchists, ”[p]romises to obey, contracts of (wage) slavery, agreements requiring the acceptance of a subordinate status, are all illegitimate because they do restrict and restrain individual autonomy.” [Robert Graham, “The Anarchist Contract, Reinventing Anarchy, Again, Howard J. Ehrlich (ed.), p. 77] Hierarchy, therefore, is against the basic principles which drive anarchism. It denies what makes us human and “divest[s] the personality of its most integral traits; it denies the very notion that the individual is competent to deal not only with the management of his or her personal life but with its most important context: the social context.” [Murray Bookchin, Op. Cit., p. 202]
Some argue that as long as an association is voluntary, whether it has a hierarchical structure is irrelevant. Anarchists disagree. This is for two reasons. Firstly, under capitalism workers are driven by economic necessity to sell their labour (and so liberty) to those who own the means of life. This process re-enforces the economic conditions workers face by creating “massive disparities in wealth … [as] workers… sell their labour to the capitalist at a price which does not reflect its real value.” Therefore:
“To portray the parties to an employment contract, for example, as free and equal to each other is to ignore the serious inequality of bargaining power which exists between the worker and the employer. To then go on to portray the relationship of subordination and exploitation which naturally results as the epitome of freedom is to make a mockery of both individual liberty and social justice.” [Robert Graham, Op. Cit., p. 70]
It is for this reason that anarchists support collective action and organisation: it increases the bargaining power of working people and allows them to assert their autonomy (see section J).
Secondly, if we take the key element as being whether an association is voluntary or not we would have to argue that the current state system must be considered as “anarchy.” In a modern democracy no one forces an individual to live in a specific state. We are free to leave and go somewhere else. By ignoring the hierarchical nature of an association, you can end up supporting organisations based upon the denial of freedom (including capitalist companies, the armed forces, states even) all because they are “voluntary.” As Bob Black argues, ”[t]o demonise state authoritarianism while ignoring identical albeit contract-consecrated subservient arrangements in the large-scale corporations which control the world economy is fetishism at its worst.” [The Libertarian as Conservative, The Abolition of Work and other essays, p. 142] Anarchy is more than being free to pick a master.
Therefore opposition to hierarchy is a key anarchist position, otherwise you just become a “voluntary archist” — which is hardly anarchistic. For more on this see section A.2.14 ( Why is voluntarism not enough?).
Anarchists argue that organisations do not need to be hierarchical, they can be based upon co-operation between equals who manage their own affairs directly. In this way we can do without hierarchical structures (i.e. the delegation of power in the hands of a few). Only when an association is self-managed by its members can it be considered truly anarchistic.
We are sorry to belabour this point, but some capitalist apologists, apparently wanting to appropriate the “anarchist” name because of its association with freedom, have recently claimed that one can be both a capitalist and an anarchist at the same time (as in so-called “anarcho” capitalism). It should now be clear that since capitalism is based on hierarchy (not to mention statism and exploitation), “anarcho”-capitalism is a contradiction in terms. (For more on this, see Section F)
#faq#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#cops#police
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
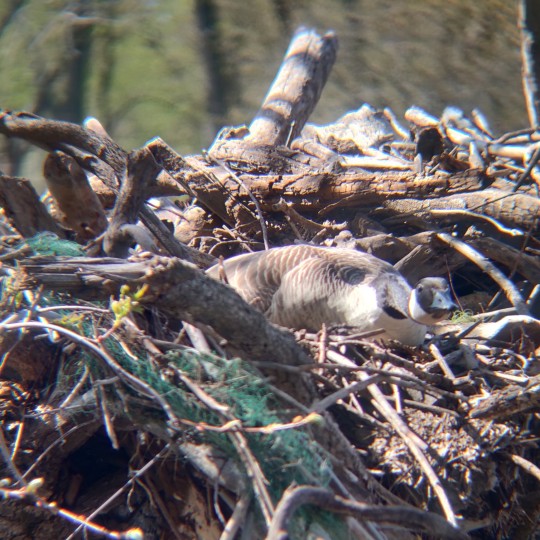

This lady was watching me and my friend very intently as we walked past her nest
#canada goose#goose#geese#canadian geese#birds#bird nest#mine#ornithology#nature#wildlife#naturalist#nature photography#photography#ecology#north america#animals#bird watching#birding#bird photography#birdwatching#bird#ecologist#biology#wildlife biology#biologist#original photography#original photographers#wildlife photography
21 notes
·
View notes
Text

#leftism#anti capitalism#socialism#communism#anarchy#earth day#ecosystem#eco#rewilding#environment#ecology#ecofriendly#agriculture#infrastructure#ecofashion#waste
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
VERY IMPORTANT a dam in the Netherlands, the weerdsluis lock, is directly on a migratory path for spawning fish. They have a worker stationed there to open the door for the fish, but they can take a while to open it. So to keep the fish from getting preyed on by birds they installed a doorbell. Only, the fish don't have hands to ring the doorbell. If you go to their website, they have a LIVE CAMERA AND A DOORBELL that YOU RING FOR THE FISH when they're waiting, and then the dam worker opens the door for them! I can't express how obsessed I am with this. look at this shit. oh my god.

Please check on the fish doorbell once in a while :)
#self#last night i kept stimming thinking about this LOVE IS AO REAL. AUGH#i dont like damming but this is a step in the right direction AND it gets the public involved#i love that! more public interactions like this in ecology please! thats how you bring change! thats how you make ppl see the beauty in life#marine biology#ecology
60K notes
·
View notes
Photo

145K notes
·
View notes