#drug absorption and metabolism
Text
Understanding Anti-Obesity Medications: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring the Mechanism of Anti-obesity medications: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the mechanism of anti-obesity medications can seem like a daunting task, but it doesn’t have to be. Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to digest, no pun intended.
If you want more information about diet, please visit my website! Here
Understanding Anti-Obesity Medications: A Comprehensive…
#anti-obesity medications#appetite suppressants#Bupropion-Naltrexone#effective weight loss#fat absorption inhibitors#healthcare consultation#Liraglutide#medical weight loss#medication side effects#metabolic rate increase#obesity management#Obesity Treatment#obesity-related health conditions#Orlistat#Phentermine-Topiramate#semaglutide#weight loss benefits#weight loss drugs#weight loss solutions#Weight Management
0 notes
Text
Winning The Battle Against Obesity: The Role Of Obesity Drugs
Greetings, health-conscious readers! Today, we're delving into a topic that impacts millions worldwide – the ongoing fight against obesity. This topic is close to our hearts because, after all, who doesn't aspire to live a healthy life? In this article, we'll explore the dynamic and ever-evolving world of obesity drugs. We'll discuss the challenges, breakthroughs, and all you need to know about these vital tools in the fight against excess weight.
Know more
#obesity drugs#weight management#obesity epidemic#obesity treatment#weight loss medications#appetite suppressants#fat absorption inhibitors#metabolic boosters#hormone regulators#obesity solutions#personalized medicine#obesity research
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of Thyroid medicines From Early Treatments to Modern Solutions
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating the body’s metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid malfunctions—whether through overactivity (hyperthyroidism) or underactivity (hypothyroidism)—the entire body can feel its effects. Over the years, thyroid conditions have become more widely recognized, leading to the evolution of effective medications that help manage these disorders. The development of thyroid medicines has come a long way, transitioning from early rudimentary treatments to modern pharmaceutical innovations that offer patients a higher quality of life.

In this blog, we will explore the history and evolution of thyroid drugs, highlighting how thyroid medicines manufacturers in India and thyroid medicines exporters play a critical role in this process. Additionally, we will discuss the increasing global demand for thyroid drugs, especially in regions like the Philippines, where thyroid medicines suppliers are crucial in ensuring access to life-saving medications.
The Early Days of Thyroid Treatments
Before modern thyroid drugs were developed, ancient civilizations used various natural remedies to manage symptoms of thyroid disorders. Historical texts from Egypt, Greece, and China mention goiter, a visible swelling of the thyroid gland, which was often linked to iodine deficiency. In these ancient times, treatments were rudimentary and primarily focused on addressing visible symptoms like goiter.
In the 19th century, scientific advancements began to shape the course of medical treatments. One of the first breakthroughs in thyroid treatment came in 1891 when George Murray successfully treated hypothyroidism with thyroid extract derived from sheep. This was the first instance of hormone replacement therapy and marked the beginning of the pharmaceutical management of thyroid disorders.
The Discovery of Iodine and Its Role in Thyroid Health
In the early 20th century, scientists discovered the importance of iodine in thyroid health. Iodine is a key component in the production of thyroid hormones—T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). It was found that iodine deficiency was one of the main causes of goiter and hypothyroidism. This discovery led to the development of iodized salt as a preventive measure against iodine deficiency, significantly reducing the incidence of goiter worldwide.
However, while iodized salt helped prevent thyroid disorders caused by iodine deficiency, it did not address all thyroid conditions. This led to the continued development of thyroid hormone replacement medicines for those with other forms of thyroid dysfunction.
The Emergence of Synthetic Thyroid medicines
In the mid-20th century, researchers made significant strides in developing synthetic thyroid hormones. The introduction of synthetic levothyroxine (T4) in the 1950s revolutionized the treatment of hypothyroidism. Levothyroxine, which is identical to the naturally occurring hormone produced by the thyroid gland, replaced the crude thyroid extracts used in earlier treatments. Its standardized dosage and predictable absorption made it the gold standard for treating hypothyroidism.
Levothyroxine remains one of the most prescribed thyroid drugs globally, helping millions of patients manage their condition effectively. Today, it is produced by leading thyroid medicines manufacturers in India and other countries, ensuring consistent quality and supply to meet global demand.
In addition to levothyroxine, synthetic T3 drugs, such as liothyronine, were developed to treat hypothyroidism. While T3 medicines are less commonly prescribed than T4 medicines, they offer an alternative for patients who do not respond well to T4 therapy.
The Modern Approach to Thyroid Treatment
With the advancement of medical research and technology, the approach to thyroid treatment has become more sophisticated. The focus is now on personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual’s specific thyroid hormone levels, symptoms, and overall health.
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy remains the cornerstone of treatment for hypothyroidism, but doctors now have a better understanding of the nuances in dosing and management. For example, some patients benefit from a combination of T4 and T3 therapies, while others may require adjustments based on factors like age, weight, and the presence of other medical conditions.
The rise of thyroid medicines manufacturers in India has been instrumental in meeting the growing demand for thyroid medications. Indian manufacturers are known for producing high-quality, cost-effective thyroid drugs, making these treatments accessible to patients worldwide. In particular, Indian pharmaceutical companies have made significant contributions as thyroid medicines exporters, ensuring that countries with limited pharmaceutical production capabilities have access to life-saving medications.
Global Demand for Thyroid Drugs
Thyroid disorders are common worldwide, affecting millions of people. Hypothyroidism, in particular, is a widespread condition that requires ongoing treatment with thyroid hormone replacement drugs. As awareness of thyroid health increases, so does the demand for effective medications.
India has emerged as a key player in the global pharmaceutical market, with many thyroid drugs manufacturers in India producing a wide range of thyroid medications. These manufacturers are able to meet both domestic and international demand by adhering to strict quality control measures and complying with global regulatory standards.
Indian companies are also recognized as leading thyroid drugs exporters, supplying medications to countries across Asia, Africa, Europe, and North America. For example, in the Philippines, thyroid disorders are a significant public health issue. Thyroid medicines suppliers in the Philippines rely on Indian manufacturers to provide a consistent supply of high-quality thyroid medications to meet the needs of their population.
The Role of Thyroid Drugs Suppliers in the Philippines
In countries like the Philippines, access to reliable thyroid medications is crucial for managing the high prevalence of thyroid disorders. The Philippines faces unique challenges in terms of healthcare access, particularly in rural areas where medical resources may be limited. As a result, thyroid medicines suppliers in the Philippines play an essential role in ensuring that patients have access to the medications they need.
By partnering with Indian thyroid drugs exporters, suppliers in the Philippines can provide patients with affordable and effective thyroid treatments. This collaboration helps address the healthcare needs of a growing population and ensures that patients receive timely and consistent care.
The Future of Thyroid Drugs
As research into thyroid disorders continues to evolve, so too does the development of new and improved thyroid drugs. Scientists are exploring new ways to optimize hormone replacement therapy, including the development of long-acting thyroid drugs that could reduce the need for daily dosing. Additionally, advancements in biotechnology may lead to the creation of more personalized treatments based on genetic and molecular profiling.
Another area of focus is improving the delivery of thyroid drugs. While oral tablets are the standard form of treatment today, researchers are investigating alternative delivery methods, such as transdermal patches and injectable formulations, which may offer more convenient options for patients.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to innovate, thyroid medicines manufacturers in India are expected to remain at the forefront of these developments, producing the next generation of thyroid treatments. With a strong presence as both manufacturers and exporters, Indian companies will continue to play a critical role in meeting the global demand for thyroid drugs.
Conclusion
The evolution of thyroid medicines from early treatments to modern solutions is a testament to the advancements in medical science and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Today, patients with thyroid disorders have access to safe, effective, and affordable treatments that allow them to lead healthy, normal lives.
India’s pharmaceutical industry, particularly thyroid medicines manufacturers and thyroid medicines exporters, has played a key role in ensuring that thyroid medications are available to patients worldwide. In regions like the Philippines, thyroid medicines suppliers are essential in meeting the needs of those affected by thyroid disorders, helping them access the treatments they require.
As we look to the future, continued innovation and collaboration within the pharmaceutical industry will further enhance the quality and accessibility of thyroid medicines, ensuring that patients everywhere receive the best possible care.
#Thyroid drugs supplier in Philippines#Thyroid drugs exporter#Thyroid drugs manufacturer in India#India#Philippines#TSH#T3#T4#thyroid stimulating hormome#hypothyroidism#hyperthyroidism#thyroid condition#free T3#free T4#thiamine#medicines#medications
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

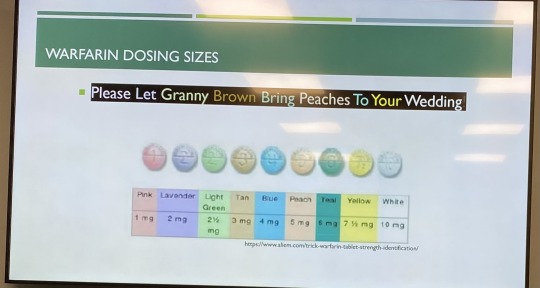


Anticoagulation Lecture 6/21/23
Factor Xa inhibitors = rivaroxaban, apixaban (Eliquis)
Direct thrombin inhibitor = dabigatran
Vitamin K inhibitor = warfarin
Apixaban has the lowest bleeding risk compared to the other Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs); avoid in pts with BMI greater than or equal to 40 or weight more than 120 kg. Avoid dual inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp.
VTE/PE tx = 10mg bid x7 days, then 5 mg bid
AFib = 5 mg bid (reduce to 2.5 mg bid if Cr greater than or equal to 1.5 or weight less than 60 kg or age greater than 80
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) = once daily dosing compared to Eliquis
VTE/PE: 15 mg bid x21 days; then 20 mg qd
AFib: 20 mg qd with food to increase absorption
PAD/CAD: 2.5 mg bid (+antiplatelets if at increased risk)
Avoid with CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers and P-gp
Edoxaban (Savaysa) – not used in pts with CrCl greater than 95
VTE/PE = parenteral anticoagulation for 5-10 days, then PO
VTE/PE/AFib = 60 mg qd
Does not have reversal agent like other DOACs do (which are reversed with Kcentra or andexanet)
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
AFib: 150 mg bid; consider 110 mg bid if bleeding risk
VTE/PE: 5 days IV, then 150 mg bid
VTE ppx after THA/TKA: initial 110 mg once, then 220 mg qd x10-35 days
5-10 day bridge required for PE/VTE
Caution in pts greater than 75 years due to increased bleeding risk
Has own reversal agent (praxbind; idarucizumab)
C/I in pts with prosthetic heart valve
Store in original bottle and discard if unused after 4 months
Eliquis and Xarelto can be crushed and given via feeding tubes.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Dosing is pt specific. Goal INR is 2-3. (2.5-3.5 if mechanical mitral valve).
Slow onset; slow time to steady state means dose taken today may not be reflected in INR for several days (2-4 days).
So many drug-drug interactions!
Metabolized by CYP pathways
Vitamin K antagonist
Dosing: recommend taking at night because INR is taken during the day, makes it easier to adjust dose.
Warfarin’s therapeutic steady state is based on half-lives of clotting factors. At least 5 days of consecutive warfarin needed for pt to be fully anticoagulated (this is why you use heparin until they get to this point).
Usually start with 5 mg qd. If bleeding risk, start with 2.5 mg qd. For obese pts or otherwise healthy/young can start with 7.5 mg qd. You go to maintenance protocol on 7th day.
Pts on VTE/PE tx are not anticoagulated the first 5 days, so use heparin IV or LMWH outpt. Once anticoagulated x24 hours, d/c heparin.
Start with 5 mg warfarin for first 3 days, then follow up with warfarin clinic on day 4. Typically, pt goes for weekly INRs. Then when at goal INR for 2 weeks, can spread out how often they f/u on their INR levels. Eventually they can go q6-8 weeks to check INR level.
VTE/PE – always bridge
AFib – risk assess to see whether heparin bridging is needed (assess bleeding risk [HASBLED]; CHA2DS2VASc for thrombotic risk).
Every 10 years, the dosing needed will decrease by 10%, so as pts age, the dose of warfarin needed will decrease.
DOACs = no INR monitoring, no dietary interactions, lower rates of bleeding, limited availability of reversal agent; contraindicated in pts with mechanical heart valves
AFib – AC (anticoagulate) indefinitely
1st VTE or PE that is provoked – AC for 3 months
1st episode of VTE/PE in setting of cancer – 3 months of AC (LMWH is better than DOAC or warfarin--new research shows DOAC may actually be more effective, so can use DOAC now; LMWH not preferred)
1st episode of VTE/PE unprovoked (no idea what caused it) – AC more than or equal to 3 months
2nd VTE – AC indefinitely
Heparin reversal – protamine (max dose is 50 mg), to reverse enoxaparin, give 1 mg protamine for each 1 mg of Lovenox
Warfarin reversal – vit K; 4 factor prothrombin compex (KCentra); FFP (if KCentra not available); KCentra is for life-threatening bleeding or if pt needs surgery for life-threatening condition
Apixaban/Rivaroxaban reversal – Kcentra (life threatening bleed or need emergency surgery; has thrombotic risk); FFP (Fresh Frozen Plasma); Andexanet Alfa. KCentra can cause clotting in 5% of pts; don’t give if you don’t need to.
Dabigatran reversal – idarucizumab (Praxbind); dosed as 5 g IV given 2.5 mg no more than 15 minutes apart)
Heparin lasts 2 hours
LMWH is preferred in pts who are pregnant (avoid warfarin). ESRD on dialysis – warfarin or Eliquis (avoid Xarelto). Obese pts – DOACs or warfarin. Cancer – use LMWH; recent study shows Eliquis is equal to or superior to LMWH in cancer pts who need anticoagulation.
Pregnancy = lovenox better, doesn’t cross placenta; UFH (unfractionated heparin) is an alternative in pts with poor renal function.
Stop heparin gtt and give Eliquis now or give 2 hours after stopping heparin gtt. Give loading dose Eliquis even if the pt was on heparin gtt.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is it safe to eat grapes while taking calcium channel blockers?
Calcium channel blockers are medications used to treat high blood pressure and other cardiovascular diseases. While these medications are effective in lowering blood pressure, there is concern about how foods may interact with them. In particular, grapes are a popular and nutritious fruit, rich in antioxidants and other health-promoting compounds. In this article, we will review the current scientific evidence about the interaction between calcium channel blockers and grapes and whether it is safe to consume grapes while taking these medications.
Mechanism of action of calcium channel blockers:
Calcium channel blockers are a class of drugs that act by inhibiting the flow of calcium through muscle cells. Calcium is important in muscle contraction, and by reducing its flow, calcium channel blockers help reduce blood pressure and improve cardiac function.
Interaction between calcium channel blockers and grapes:
Some studies have suggested that certain compounds in grapes, such as polyphenols, may affect drug absorption and metabolism. In particular, it has been found that polyphenols may inhibit the absorption of some drugs, including calcium channel blockers. In addition, some studies have suggested that ingesting large amounts of grapes may reduce the effectiveness of calcium channel blockers in lowering blood pressure and preventing coronary heart disease.
However, it is important to note that most of these studies have been conducted in animals or in vitro tests. Therefore, the evidence in humans is limited and more studies are needed to better understand the interaction between calcium channel blockers and grapes.
Is it safe to eat grapes while taking calcium channel blockers?
In general, moderate consumption of grapes should not be a problem for people taking calcium channel blockers. In fact, grapes are a healthy source of nutrients and antioxidants, which may have cardiovascular health benefits.
However, if you are taking calcium channel blockers, caution should be exercised when consuming large amounts of grapes or grape juice. It is always advisable to consult with your physician before making significant dietary or lifestyle changes, especially if you are taking medications to treat high blood pressure or other cardiovascular diseases.
Conclusion: Although evidence on the interaction between calcium channel blockers and grapes is limited, caution is advised when consuming large amounts of grapes while taking these medications. Patients taking calcium channel blockers should consult their physician before making significant changes to their diet to avoid potential complications in their treatment. In general, moderate consumption of grapes should be safe and beneficial for cardiovascular health.


7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the World of Weight Loss Supplements: Separating Fact from Fiction
In today's health-conscious society, the quest for an ideal body often leads many individuals to explore various avenues for weight loss. Among these options, weight loss supplements have gained popularity, promising quick and effortless results. However, before diving into the world of supplements, it's crucial to distinguish between evidence-based solutions and marketing hype.
Weight loss supplements are products designed to aid in reducing body weight through mechanisms such as appetite suppression, increased metabolism, or fat absorption inhibition. While some supplements have shown potential in limited studies, their effectiveness and safety vary widely.
One of the most well-known weight loss supplements is green tea extract, often praised for its thermogenic properties. Green tea contains compounds like catechins, which are believed to boost metabolism. Although research suggests that green tea extract may contribute to modest weight loss when combined with a healthy diet and exercise, it's important to note that the effects are generally small and may not lead to significant changes on their own.
Another frequently mentioned supplement is Garcinia cambogia, which contains hydroxycitric acid (HCA) and is claimed to suppress appetite and block fat production. However, the evidence supporting Garcinia cambogia's weight loss benefits is inconsistent, and more rigorous research is needed to validate these claims.
It's crucial to approach weight loss supplements with caution, as they are not regulated as strictly as pharmaceutical drugs. The lack of oversight can lead to variations in product quality, potency, and safety. Some supplements may even contain hidden ingredients that could have adverse effects on health.
Before incorporating any weight loss supplement into your regimen, consult a healthcare professional. They can help assess your individual needs and provide guidance on the most appropriate approach to achieving your weight loss goals. Remember that no supplement can replace a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
Moreover, keep in mind that sustainable weight loss is a gradual process that involves making long-term lifestyle changes. Relying solely on supplements may lead to disappointment and potential health risks. Instead, focus on creating a well-rounded routine that includes a nutrient-rich diet, regular exercise, proper sleep, and stress management.
In conclusion, the world of weight loss supplements is a complex landscape where scientific evidence often clashes with marketing claims. While some supplements may offer marginal benefits when used in conjunction with a healthy lifestyle, they should never be viewed as magic solutions. Prioritize informed decision-making and consult a healthcare professional before adding any supplement to your routine. Remember, the key to successful and sustainable weight loss lies in holistic approaches that prioritize overall health and wellness.
#weight loss#health & fitness#nutrition#bodybuilding#exercise#fitblr#fitspo#running#yoga#crossfit#gym#workout#weight lose#i wanna lose weight
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Effectiveness and Safety of Weight Loss Medications: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's world, where obesity has become a global epidemic, weight loss medications have gained significant attention as a potential solution. These medications, when used in conjunction with a healthy lifestyle, can assist individuals in achieving their weight loss goals. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the effectiveness and safety of weight loss medications. As we delve into the topic, we will also shed light on Mounjaro weight loss, a reputable website that offers weight loss medications.

Understanding Weight Loss Medications
1.1 Defining weight loss medications
Weight loss medications, also known as anti-obesity drugs, are prescription or over-the-counter medications designed to aid in weight reduction. These medications can be categorized into different types based on their mechanisms of action, such as appetite suppressants, fat absorption inhibitors, and metabolic enhancers.
1.2 Common types of weight loss medications
Some common weight loss medications include phentermine, orlistat, liraglutide, and bupropion/naltrexone. Each medication works differently to help individuals lose weight, whether by reducing appetite, blocking the absorption of dietary fat, or influencing metabolism.
1.3 How weight loss medications work in the body
Weight loss medications target various aspects of the body's physiology to promote weight loss. They may act on the brain to suppress appetite, affect the digestive system to inhibit fat absorption, or impact metabolism to enhance calorie burning.
The Effectiveness of Weight Loss Medications
2.1 Clinical Studies and Evidence
Numerous clinical studies have evaluated the effectiveness of weight loss medications. These studies often compare the outcomes of individuals using medications versus those following a placebo or non-medication intervention. The results show that weight loss medications can lead to greater weight loss compared to lifestyle changes alone.
2.2 Average weight loss with medication
The average weight loss achieved with weight loss medications varies depending on the specific medication and individual factors. However, studies have shown that individuals using weight loss medications, in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity, can expect to lose 5% to 10% of their initial body weight over a period of several months.
2.3 Factors influencing effectiveness
2.3.1 Individual response
The effectiveness of weight loss medications can vary among individuals. Factors such as genetics, metabolism, underlying medical conditions, adherence to medication, and lifestyle changes can influence the degree of weight loss achieved.
2.3.2 Adherence to medication and lifestyle changes
The success of weight loss medications is closely tied to an individual's adherence to the prescribed regimen. Consistently taking the medication as directed, following a balanced and calorie-controlled diet, and engaging in regular physical activity are essential for optimizing the effectiveness of these medications.
Safety Considerations of Weight Loss Medications
3.1 Regulatory Bodies and their role
Before weight loss medications are approved for public use, they undergo rigorous evaluation by regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). These agencies assess the safety and efficacy of the medications based on data from preclinical and clinical trials.
3.2 Common side effects of weight loss medications
Weight loss medications may cause side effects, which can vary depending on the specific medication. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, and insomnia. These side effects are generally mild and diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
3.3 Potential risks and precautions
3.3.1 Interactions with other medications
It is crucial to consider potential interactions between weight loss medications and other medications an individual may be taking. Some weight loss medications may interact with certain antidepressants, antidiabetic drugs, or other medications, leading to adverse effects or reduced efficacy.
3.3.2 Allergies and contraindications
Individuals with known allergies to specific weight loss medications should avoid using them. Additionally, weight loss medications may be contraindicated for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as uncontrolled hypertension, heart disease, or a history of substance abuse.
3.3.3 Long-term safety concerns
Since weight loss medications are relatively new, their long-term safety is still being studied. It is important to discuss any concerns or potential risks with a healthcare professional before initiating a weight loss medication regimen.
Mounjaro Weight Loss: A Reliable Source for Weight Loss Medications
4.1 Introduction to Mounjaro weight loss
Mounjaro weight loss is a reputable website that offers a range of weight loss medications. They provide a convenient and reliable platform for individuals seeking medically approved weight loss options.
4.2 Safety Standards and quality control
Mounjaro weight loss adheres to strict safety standards and ensures that all medications available on its platform are approved by regulatory authorities. They source their medications from trusted manufacturers and regularly monitor product quality.
4.3 Available weight loss medications and their effectiveness
Mounjaro weight loss offers a variety of weight loss medications, each with its unique mechanism of action. The website provides detailed information about the medications they offer, including their effectiveness, potential side effects, and usage instructions.
4.4 Customer Testimonials and Reviews
Mounjaro weight loss features customer testimonials and reviews, allowing individuals to gain insights from others who have used their services. These testimonials can provide valuable information about the effectiveness and customer satisfaction associated with the weight loss medications offered by Mounjaro.
Lifestyle Changes and Weight Loss Medications
5.1 Importance of lifestyle modifications
While weight loss medications can be effective, they should be used as part of a comprehensive weight management approach that includes lifestyle modifications. Adopting healthy eating habits, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are crucial for long-term weight management.
5.2 Synergy between weight loss medications and lifestyle changes
Weight loss medications can complement lifestyle changes by providing additional support for appetite control and metabolic regulation. When used in combination with a healthy lifestyle, these medications can enhance weight loss outcomes.
5.3 Incorporating Diet and Exercise for optimal results
To maximize the benefits of weight loss medications, individuals should follow a well-balanced, calorie-controlled diet and engage in regular physical activity. A healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and support in developing a suitable diet and exercise plan.
Choosing the Right Weight Loss Medication
6.1 Consultation with healthcare professionals
Before initiating any weight loss medication, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess individual needs, consider medical history, and provide guidance on choosing the most appropriate medication based on effectiveness, safety, and potential interactions.
6.2 Assessing individual needs and Goals
Weight loss medications should be tailored to individual needs and goals. Factors such as weight, overall health, medical conditions, and lifestyle should be taken into account when determining the most suitable medication.
6.3 Considering the medical history and potential contraindications
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or kidney problems, may require specific considerations when selecting a weight loss medication. A thorough assessment of medical history is essential to identify potential contraindications and ensure the chosen medication is safe to use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, weight loss medications can be valuable tools in the journey toward achieving a healthy weight. They can provide an additional boost when combined with lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise. However, it is essential to recognize that weight loss medications are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and careful consideration should be given to safety, effectiveness, and individual circumstances. Mounjaro weight loss stands as a trusted website offering a range of weight loss medications, but it is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any medication regimen. By understanding the effectiveness and safety of weight loss medications, individuals can make informed decisions to support their weight loss goals and improve their overall well-being.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
side effects of losing weight too fast

Lose 10 kg in 10 days!
You can eat as much as you want and still lose weight!
Size down in 1 day!
If you believe the advertising, you can lose weight quickly.
Trending diets and nutritional supplements for weight loss promise slim bodies in no time. Most consumers spend $33 billion annually on weight loss products.
Do any of these products really cause rapid weight loss? Is it safe to ingest? And what are the dangers of losing weight too quickly? Here's a look at some quick weight loss claims and the available evidence.
What is Fast Weight Loss?
Many sellers promise "quick weight loss," so it's hard to categorize them all.Most quick weight loss methods fall into the following categories.
Tablets and Dietary Supplements
Dozens of diet supplements promise to accelerate weight loss. In general, they claim to inhibit nutrient absorption, increase metabolism, or burn fat.
Very Low Calorie Diet (VLCD)
One of the most proven methods for rapid weight loss is the Physician-Supervised Very Low Calorie Diet (VLCD). Most of the information we know about rapid weight loss comes from studies of people following these diets.
worms, gadgets, magic
There seems to be no end to the questionable ideas being promoted in the name of rapid weight loss. Most of them promise to replace diet and exercise.
Does Fast Weight Loss Work?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements. However, treat it like food rather than medicine. The FDA also does not review claims made by over-the-counter weight loss products. Unlike pharmaceutical manufacturers, dietary supplement manufacturers do not have to prove the safety or efficacy of their products before marketing them. This means that dietary supplements do not have to be approved by the FDA before being placed on the market.
Other than very low calorie diets and weight loss surgery, no other product, pill, or diet has been proven to result in rapid weight loss. It is not intended for serious weight loss and may have side effects.In a fast weight loss program, it is not pills or some kind of food that burns fat, but the drastic reduction in calories associated with exercise.
What are the dangers of rapid weight loss?
Rapid weight loss causes physical stress on the body. Possible serious risks include:
Gallstones occur in 12-25% of people who lose a lot of weight in a few months.
Dehydration can be prevented by drinking plenty of water.
malnutrition. It is usually caused by not eating enough protein for several weeks.
An electrolyte imbalance that is rarely life threatening.
Other side effects of rapid weight loss are:
headache
hypersensitivity and irritability
Malaise
dizzy
constipation
Irregular menstruation
hair loss
muscle breakdown
The risk of rapid weight loss increases with the length of the diet. A diet without protein is very dangerous.
Is rapid weight loss always a bad idea?
Crash diets can have adverse effects, but so can obesity. Therefore, a very low calorie diet (VLCD) is recommended for those who are overweight (Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30) and who do not have specific goals such as exercise. A good choice for those who need to lose weight quickly because of such as weight loss surgery. Consider weight.
VLCD is a medically controlled diet that lasts for several weeks. Diets are nutritionally balanced but expensive - people end up spending thousands of dollars. VLCD reliably reduces weight by 15% to 25% in 12 weeks. This is for those who have completed the program.
25% to half of people fail to complete the program. If you stop dieting, your weight will return to where it was before, but this will happen quickly. Some experts say it's better to use sustainable approaches to weight loss than conventional diets.
Of course, most people who want to lose weight quickly usually do so on their own.Often the goal is to achieve a short-term goal. B. Reach your dress size or look good on the beach. Starving is definitely not a good idea. However, if you are medically fit, there is no harm in doing short-term, severe calorie restriction. You should tell your doctor what you are doing and make sure you are getting protein in your diet (70-100 grams per day). Take a multivitamin and eat foods high in potassium (tomatoes, oranges, bananas).
Also remember that crash diets rarely help you maintain a healthy weight. Most people will put the weight back on quickly.
Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
All About: Cannabis
History
- Cannabis probably originated in China. Medical and religious use can be traced to ancient China, India, Egypt and the Middle East.
- At the beginning of the 19th century, Napoleon’s soldiers brought cannabis to France from Egypt in the form of hashish.
- It became very popular with French writers and artists, who established Le Club des Hachichins (The Hashish-Eaters’ Club) in Paris.
Members included Theophile Gautier, Charles Baudelaire, Victor Hugo, Honore de Balzac, and Alexandre Dumas
- Hemp was grown in colonial America, but marijuana smoking probably came to the US with Mexican & Caribbean immigrants in the early 1900s.
- Cannabis (hemp) plant:
High THC content ---> Marijuana, recreational use
Low THC content (less than 0.3%) = industrial hemp
- In 1937, the Marijuana Tax Act instituted a national registration and taxation system aimed at discouraging all use of cannabis. It was overturned in 1969.
- Largely destroyed the hemp industry {note: this benefited paper manufacturers and thus indirectly benefited logging companies}
- United States Department of Agriculture lifted the tax on hemp cultivation during WWII
Legal Status
- In 1970, marijuana and THC became Schedule I illegal drugs.

2014 Farm Bill: permits cultivation of industrial hemp for research purposes
2018 Farm Bill: made industrial hemp legal, allowed CBD oil production
Preparation
- Marijuana is produced from flowering hemp (Cannabis sativa).
- Marijuana is a mixture of dried and crumbled leaves, small stems, and flowering tops.

- Hemp seeds have been used for oil and bird food.
- It can be consumed orally, as in cookies or brownies, but is usually smoked in rolled cigarettes known as “joints,” various kinds of pipes, or in hollowed-out cigars called “blunts.”
- Hashish is a cannabis derivative that can be smoked or eaten.
- It can refer to a relatively pure resin preparation with very high cannabinoid content, or a solvent extract of leaves or resin.

- Hash oil is an alcohol extract. A drop is placed on a tobacco or marijuana cigarette.
Ingredients
- Hemp contains 70 unique compounds known as cannabinoids, plus more than 400 other identified compounds.
- The psychoactive compound /_\9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) accounts for the use of cannabis as a drug. {note: that’s supposed to be a triangle; sorry}
- Marijuana potency (in terms of THC content) varies widely, depending on the genetic strain of the plant and growing conditions.
- Potency can be increased by preventing pollination and seed production by the female plants. This marijuana is called sinsemilla (”without seeds”).
- THC was identified as the major active ingredient in 1964.

- Burning marijuana causes the THC to vaporize and enter the smoker’s lungs in small particles.
- Effective dose and latency to onset of effects are influenced by the amount and potency of the plant used, and patterns of smoking (e.g. duration of held breath).
Administration & Absorption
Smoking
- Smoking marijuana is the quickest way to absorb THC, with blood levels peaking between 9-10 minutes into a smoke session.
- THC is easily absorbed by the lungs, and blood plasma levels rise quickly.
Edibles
- Thought to yield peak THC blood levels within 1-5 hours post-ingestion
- Poor absorption results in low and variable plasma levels, probably due to degradation in the stomach, first-pass metabolism.
Elimination
- Blood THC levels decline rapidly after smoking marijuana, but complete elimination from the body is much slower because of persistence in fat tissues.
- Half-life varies from a few hours to 3-4 days
- The gradual movement of THC metabolites back out of fat stores means that urine screening tests can detect them more than 2 weeks after a single incident of marijuana use.
Acute Behavioral Effects
- Effects of cannabinoid use vary depending on dose, frequency of use, characteristics of the user, and the setting in which use occurs.
- Subjective & behavioral effects of marijuana use can be separated into four stages: the “buzz,” the “high,” the stage of being “stoned,” and the “come-down.”
The “high” is associated with feelings of euphoria & exhilaration, and a sense of disinhibition.
Relaxation is the most commonly reported effect of being “stoned.”
- Smoking marijuana can sometimes produce transient psychotic symptoms such as depersonalization, derealization, agitation, and paranoia.
- Expectation also plays a role in what effects the drug will produce, as shown by placebo studies.
- Marijuana negatively affects cognitive functions.
Decreased performance for a variety of verbal, spatial, time estimation, and reaction time tasks has been noted.
Cannabinoids appear to interfere with all aspects of memory processing.
- Marijuana can affect psychomotor functioning under demanding task conditions, such as driving.
- Use of cannabis with or without alcohol is a risk factor in automobile accidents.
Acute Physiological Effects
- increased blood flow to the skin and flushing
- increased heart rate
- increased hunger
Chronic Behavioral Effects
- In young people amount of cannabis use is inversely related to educational performance.
- Some research supports the hypothesis that heavy cannabis use leads to persistent cognitive defects, impairing school performance.
- Alternatively, poor school performance and rejection of mainstream values (such as educational achievement) may increase cannabis use.
- Chronic cannabis use can also result in aimlessness, decreased motivation, lack of planning, and decreased productivity (amotivational syndrome).
{note: Amotivational syndrome can also be caused by SSRIs, and since there is a high rate of comorbidity between depression + anxiety, and between cannabis use + depression and/or anxiety, it can be difficult to determine whether SSRIs or cannabis are causing amotivational syndrome in patients who use both substances.}
- Heavy cannabis use over a long period may lead to impaired executive functioning for at least 2-3 weeks following cessation of use.
- Some data suggest that heavy, long-time users may continue to show impairment in decision-making, planning, and concept formation. It may negatively affect the prefrontal cortex.
- Imaging studies suggest that chronic marijuana use is associated with several kinds of abnormalities in the brain.
- Several studies have found a significant relationship between early heavy marijuana smoking and increased risk for later development of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
Mechanisms of Action
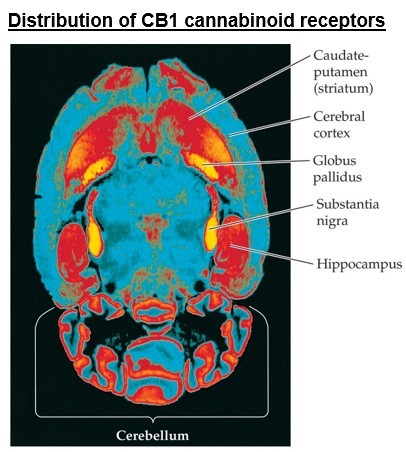
- A cannabinoid receptor in the CNS was identified in 1988.
- Receptors occur in many brain areas.
- Localization of cannabinoid receptors in these areas is consistent with the behavioral effects of these compounds on locomotor activity, coordination, and memory.
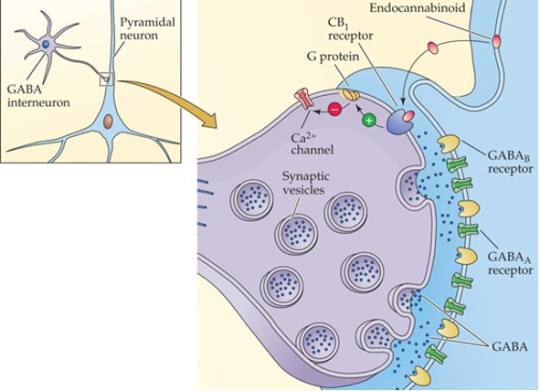
- Endogenous neurotransmitter-like substances that act on the receptors = endocannabinoids.
- Two main endocannabinoids have been found: anandamide and 2-AG.

- They are retrograde messengers; they carry information in the opposite direction from normal (i.e. postsynaptic to presynaptic).
- THC similar to endocannabinoids binds to cannabinoid receptors located presynaptically on the nerve terminal. They are metabotropic: they work via G-proteins to inhibit presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels, and open K+ channels.
- As a result, cannabinoids decrease neurotransmitter release from the terminal.
Reinforcement
- In one study, regular marijuana users could discriminate THC-containing marijuana cigarettes from placebos with no THC, and all subjects preferred the marijuana with THC when given a choice.
- Animal studies have also demonstrated reinforcing properties.
Lever pressing by squirrel monkeys for THC stopped when placebos were used.

- Mechanisms for reinforcement:
Activation of the mesolimbic dopamine system: VTA --> NAcc
Interactions between the cannabinoid and opioid systems may play a role in cannabinoid reward and reinforcement; opioid agonists enhance cannabinoid self-administration, and opioid antagonists have the opposite effect.
Tolerance & Dependence
- Animals exposed to THC or other CB1 agonists develop tolerance to the behavioral and physiological effects of these compounds.
- It appears to involve a combination of desensitization and down-regulation of CB1 receptors.
Adverse Health Effects
- There are no reports of death from overdose.
- Smoking marijuana can damage lungs: smoke contains tar, other carcinogens, carbon monoxide, etc.
- Possible adverse cardiac effects?
- Immune system suppression
- THC may affect reproductive functions:
In AFAB people, it can affect ovulation.
In AMAB people, regular smoking has been shown to decrease testosterone levels and sperm counts.
Animal research has demonstrated pregnancy failure, delayed embryonic development, and even fetal death with THC administration.
Smoking marijuana during pregnancy results in cognitive deficits, poor school achievement, and increased risk for tobacco and/or marijuana use later in life.
DSM-5: Cannabis Use Disorder
- Marijuana use typically begins in adolescence and peaks during young adulthood.
- If an individual has not yet tried marijuana by their mid-twenties, they are unlikely to begin at a later age.

- Cannabis use varies based on demographics.
- Research shows college students and young adults most commonly use cannabis...
To socially conform (~40%)
To experiment (~30%)
For enjoyment (~20%)
To manage stress or relax (~10%)
- Risk of dependence is related to drug use patterns. People who progress to daily use have a 10-20% probability of becoming dependent.
- Dependence manifests as a difficulty in stopping one’s use, a craving for marijuana, and (in heavy users) unpleasant withdrawal symptoms:
irritability
increased anxiety
depressed mood
sleep disturbances
heightened aggression
decreased appetite
- These are similar to the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal.
Treatment
- Most cannabis users do not seek treatment.
- Treatment in outpatient programs involves cognitive-behavioral therapy, relapse prevention training, and/or motivational enhancement therapy, but patients are very vulnerable to relapse.
- Some research on medications to relieve withdrawal symptoms has been done.
Therapeutic Uses of Cannabinoids
- AKA “medical marijuana”
- Many states now permit legal use, but clinical studies of its efficacy have produced mixed results.
- Smoked marijuana has the highest potential for adverse health effects and abuse; most researchers favor development of cannabinoid-based drugs instead.
- Information from the National Institute of Health
- The FDA has not approved the cannabis plant for any medical use. However, the FDA has approved several drugs that contain individual cannabinoids:
Epidiolex, which contains a purified form of CBD derived from cannabis, was approved for the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome or Dravet syndrome, two rare and severe forms of epilepsy.
Marinol and Syndros, which contain dronabinol (synthetic THC) to treat nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy. Dronabinol is also used to treat loss of appetite and weight loss in people with HIV/AIDS.
- Endocannabinoids enhance the incentive motivational properties of food and food-mediated reward.
- CB1 receptor antagonists reduce food consumption in animals and human subjects.
- In animal studies, marijuana was shown to relieve anxiety and depression.
- There’s some evidence that marijuana might reduce addiction and/or overdoses caused by other drugs.
- Pain perception: transgenic mice that lack CB1 and CB2 receptors demonstrate hyperalgesia (increased pain sensitivity).
- Clinical evidence for cannabinoids as analgesics has not been convincing.
- Nabiximols (Sativex) is a cannabis extract.
was approved in the UK in 2010 to treat pain and spasticity in multiple sclerosis patients (not yet approved in the US)
- A number of years ago, Jamaican researchers prepared eye drops from cannabis extracts (trade name Canasol) for the purpose of reducing ocular pressure in glaucoma patients.
However, the research is inconclusive and Canasol was never licensed by the FDA for legal marketing in the United States.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Does Metformin, a glucose-lowering drug, hurt the kidneys?
Metformin is a biguanide compound that reduces blood sugar mainly by reducing hepatic glucose output, improving insulin resistance, and reducing glucose absorption in the small intestine. It is currently one of the world's most widely used oral hypoglycemic drugs. Drug safety evaluation studies have found that Metformin has a good safety profile, no carcinogenic or mutagenic effects, and no evidence that Metformin can increase the risk of lactic acidosis. Medicilon has a professional team and experience in preclinical drug safety evaluation services, providing high-quality data and a fast turnaround time to support all drug safety evaluation studies.
Many patients are concerned about the effects of long-term metformin use on the kidneys. The drug does not directly damage the kidneys but can lead to drug accumulation when taken by patients with existing kidney damage. Both the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes (2017 edition) and the Expert Consensus on the Clinical Application of Metformin (2016 edition) suggest that Metformin is the drug of choice for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the absence of contraindications and intolerance, and should always be retained in the glucose-lowering regimen.
1, Benefits of Metformin.
Metformin can reduce hyperglycemia with no hypoglycemic effect on those with regular blood sugar; the drug has the following benefits in addition to hypoglycemia.
(1), Metformin has the effect of reducing body weight.
(2) Metformin has apparent cardioprotective effects and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in newly diagnosed and established type 2, diabetes patients.
(3) Metformin can improve lipid synthesis, metabolism, and lipid profile.
(4) Metformin significantly improved liver serological enzyme profile and metabolic abnormalities in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver.
2, Adverse reactions and countermeasures
The main adverse reactions of Metformin are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, gastric distension, and other gastrointestinal responses, which mainly occur in the early stage of treatment (the majority happen in the first ten weeks). Most patients can gradually tolerate them, or their symptoms disappear as the duration of treatment increases. Start taking small doses, gradually increase the amount, adjust the quantity at the right time, take with meals, and choose enteric preparations and other methods, which can reduce gastrointestinal reactions.
Three 、Does Metformin hurt the liver and kidney?
Metformin has no hepatic and renal toxicity; Metformin is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract for blood circulation, almost does not combine with plasma albumin, does not go through liver metabolism, does not compete with liver P450 enzymes, and does not degrade in the body, but acts directly on the liver and muscle, reducing hepatic glucose isomerism and increasing muscle glucose enzymes. Therefore, Metformin is not hepatotoxic.
Metformin is mainly excreted from the urine in its original form by the kidneys and is cleared rapidly, with approximately 90% clearance in 12-24h. The renal clearance of Metformin is about 3.5 times higher than that of creatinine, and renal tubular excretion is the main route of metformin clearance. Therefore, Metformin itself is not harmful to the kidney.
However, caution should be exercised when using Metformin in people with impaired liver and kidney function. Metformin should be avoided when serum transaminases exceed three times the upper limit of normal, and patients with renal insufficiency need to adjust the dose by estimating the level of glomerular filtration rate. Clinicians or pharmacists can assess the above.
4, long-term use of Metformin, the need for appropriate supplementation of vitamin B12
Studies have shown that: the incidence of vitamin B12 deficiency in glucose patients using Metformin is 5.8%, while the incidence of vitamin B12 deficiency in glucose patients not using Metformin and people without diabetes is 2.4% and 3.3%, respectively. Therefore, long-term metformin users should monitor vitamin B12 concentration regularly and increase the intake of vitamin B12-rich foods appropriately (vitamin B12 is mainly contained in animal proteins, such as meat, animal liver, fish, shellfish, eggs, etc.) to prevent and correct vitamin B12 deficiency. If this condition occurs, vitamin B12 should be supplemented in an appropriate amount under the guidance of professional doctors.
Five 、Stop taking Metformin 48 hours before and after doing a CT examination
Diabetic patients should stop taking Metformin 48 hours before and after doing enhanced CT because it is necessary to play contrast agent before doing CT. The contrast agent belongs to macromolecular substances excreted through the kidneys. If you retake Metformin, it will increase the burden on the kidney and cause contrast nephropathy.
6, the icing on the cake: combined with other glucose-lowering drugs
There are several different drugs when taking glucose-lowering drugs, often more than Metformin. This is because the combination of glucose-lowering medications mutually increases the hypoglycemic effect, improves insulin resistance, or reduces adverse reactions.
All diabetic patients should choose the appropriate hypoglycemic drugs according to their different conditions and pay attention to the indications and contraindications of each type of drug. At the same time, it is essential to emphasize that diet therapy and diet control are the cure for diabetic patients and must be adhered to for life. Diet therapy should not be relaxed or abandoned because of oral hypoglycemic drugs or increased dosages of hypoglycemic medications.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Anti-Obesity Medications: What You Need to Know
Exploring the Efficacy of Anti-Obesity Medications: A Comprehensive Guide
Anti-Obesity Medications: Understanding Their Role in Weight Loss
Introduction
Obesity is a significant global health concern that can lead to chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. For many, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are the first steps in managing obesity. However, some…
#anti-obesity medications#appetite suppressants#diet and exercise#effective weight loss#fat absorption inhibitors#healthcare guidance#Lorcaserin#metabolic enhancers#obesity#Obesity Treatment#obesity-related health risks#Orlistat#over-the-counter weight-loss pills#Phentermine#prescription weight-loss drugs#Weight Loss#weight loss journey#weight loss strategies#Weight Management#weight-loss medication side effects
0 notes
Text
What is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a psychoactive substance that activates the feel-good neurons in the brain to produce a ‘high.’ It is classified as a cannabinoid as it’s the primary component of cannabis that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system to influence the user's memory, thinking, pleasure, coordination, and time perception.
While THC is detectable in different bodily fluids, knowing how it works and its influences on the body is imperative.
How does THC work?
THC is contained in industrial hemp (also Indian hemp or Cannabis sativa), marijuana, and hashish, although in relatively different amounts. All these are a variety of cannabis grown for various purposes.
Cannabis grown for hemp has smaller amounts of THC than that grown for the production of hashish or marijuana. Once ingested, THC binds to the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB!) receptors in the brain to produce a feeling of euphoria.
Effects of THC include:
Relaxation.
Paranoia
Altered perceptions of space and time.
Dry mouth
Red eyes.
Increased appetite.
Sometimes, anxiety and hallucinations.
THC is consumed in cannabis-infused edibles, such as baked goods, candies, and drinks. It is also contained in products such as essential oils, tinctures, topicals, and flowers.
Another well-known cousin to THC is the cannabidiol (CBD) compound found in cannabis, and the difference between the two is that CBD is not psychoactive. It, therefore, does not give a ‘high.’
Uses of CBD
CBD is the compound exploited in cannabis for its therapeutic effects, including:
Controlling seizures.
Reducing pain and inflammation.
Reducing anxiety and depression.
Improving sleep quality.
Preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
Unlike THC, CBD does not bind to the CB1 receptors once ingested. The effects of both compounds may vary widely depending on the mode of consumption, dose taken, and individual tolerance.
When consumed together, they produce a synergistic effect.
How long does THC stay in the body?
Several factors affect how long THC lingers in the body. They are:
Frequency – individuals who abuse cannabis more frequently will have higher levels of THC in their bloodstream, meaning it would take longer to eliminate it.
Dosage – how much you take influences the time it takes to eliminate THC and its metabolites from the bloodstream entirely.
Mode of consumption – smoked or vaporised THC in cannabis is quickly absorbed through the lungs and into the bloodstream. There will be rapid absorption of THC, distributing rapidly throughout the body.
When ingested, THC is first taken to the digestive system, where it’s broken down into metabolites, which then enter the bloodstream and are distributed into various organs.
This means there will be higher concentrations of THC in the blood when smoked than when ingested.
Metabolism rate – the faster THC is broken down into metabolites in the body, the faster it is eliminated from your system.
Body fat percentage – cannabis users with higher body fat percentages have higher levels of THC. This is because THC is stored in body fat, which takes longer to eliminate.
Hydration – keeping your body well hydrated will help flush THC metabolites from your system.
THC detection window
Various cannabis drug tests have varying detection windows. While the above-mentioned factors affect the detection window, the type of drug test conduction plays a key role.
Urine test
This is the most common testing method. THC is detectable in urine for more than 30 days after last use for a chronic user. For a light user consuming daily, traces of THC in urine can be seen between 10-15 days after last use.
One-time users risk detection up to 3 days since last use.
Blood test
Blood tests detect cannabis use within the last 2-12 hours of consumption. But, for heavy users, THC metabolites remain in the bloodstream for about 30 days after last consumption.
Saliva test
This test has a shorter detection window, usually within 72 hours from the last use.
Like the alcohol blow roadside testing, cannabis saliva tests can also be conducted by the roadside using an oral fluid.
Hair test
Hair follicle tests detect drug use patterns for up to 90 days.
Now that we understand the working mechanisms of THC and detection methods in the body let’s learn about the risks of THC transmission during sex, breastfeeding and how to reduce exposure.
Can THC be transferred through bodily fluids?
Although there may be substantial traceable amounts of THC metabolites in blood, urine, and saliva, it can only be transmitted through semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk.
Studies have revealed that THC is detectable in vaginal fluids, semen, and breast milk and can potentially be transferred from one person to another through these bodily fluids.
While there’s scientific evidence supporting the transmission of THC through bodily fluids, proof of the extent of transmission remains insufficient.
THC binds to fat cells in the body, increasing its chances of being stored for weeks, even months, after ingestion. This THC is released from the fat cells into the bloodstream and transported into bodily secretions during metabolism.
THC transmission through semen
During unprotected sexual activity, semen containing traces of THC comes into contact with the mucous membranes in the genitals, anus, or mouth. The membranes then absorb THC molecules and transport them to the bloodstream of the recipient.
However, due to the low concentration of THC in semen, it is unlikely that the traces transmitted are enough to cause psychoactive effects in the recipient.
A 2022 study shows that quantifiable traces of THC metabolites are detected in the semen of chronic users of inhaled cannabis.
THC transmission through vaginal fluids
Limited research is available on the presence of THC in vaginal fluids. However, studies show higher chances of detecting the compound in the vaginal fluids of women who had used cannabis in the past 24 hours of the test.
Similarly, it is somewhat unclear whether the amount transmitted is high enough to cause psychoactive effects in the sexual partner.
Risk factors for transmission of THC during sexual intercourse
Unprotected sexual intercourse.
The frequency and dosage of cannabis ingested by the sexual partners.
Consistency of bodily fluids exchanged during sex since last use of cannabis.
Some studies suggest using lubricants increases the absorption of THC through the mucus membranes of the vaginal lining.
Presence of cuts, sores, or abrasions on the mucous membranes that increase the risk of THC absorption.
How to minimise the risk of THC transmission during sex
Using condoms or other barrier methods that hinder fluid exchange during sex and, ultimately, prevent THC transmission.
Open communication between sexual partners on cannabis use.
Avoid sexual activity when open wounds, sores, or abrasions of the mucous membranes are present.
Staying well hydrated before and after using cannabis.
THC transmission through breast milk
THC can be passed from a nursing mother to an infant through breastfeeding. As a fat-soluble chemical compound, THC has a high affinity to breast milk, which consists of 3-5% fat content. This fact is attributable to the longevity of THC in breast milk.
Chronic consumption of THC products can accumulate in breast milk in higher concentrations. Although it’s hard to determine how much of the intake is transferrable to a mother’s breast milk, studies suggest that lactating mothers who highly use cannabis transfer it to their infants in the ratio of 8:1
For regular or one-time cannabis-using lactating moms, their infants only consume 0.8% of the mother’s dosage.
How long does THC persist in breast milk?
How long THC metabolites stay in breast milk depends on multiple factors, similar to how long it stays in the body.
However, it is crucial to note that women’s bodies have more extensive reservoir storage for THC compared to men due to their high body fat percentage; about 25-30% of a woman’s body is made of fat.
This means that it would take longer for THC to thoroughly wash out of the system, thereby increasing its absorption into breast milk. Studies conducted in the test for THC metabolites reveal that the compound has a detection window of between 6 days to 6 weeks in breast milk.
Additionally, the mean half-life of THC in breast milk has been estimated to be 17 days. Nevertheless, for chronic lactating users, it is possible to detect THC metabolites in breast milk longer than 6 weeks after last use.
Effects of THC in breast milk
Although THC concentration in breast milk may not be high enough to cause observable ‘highs’ in the infant, the following can be a result:
Irregular sleep patterns.
Developmental delays.
Feeding difficulties.
Impaired cognitive function.
Hyperactivity.
Tremors
Irritability.
Lactating mothers should shun cannabis use to avoid predisposing their babies to the side effects above. In addition, the mother should avoid breastfeeding when high and substitute breast milk with available formulas.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), lactating mothers should avoid breastfeeding for at least 2 hours after using. This should be followed by a pump and dump for the first stream of milk after cannabis ingestion.
Since cannabis has both therapeutic and psychoactive effects, its consumption by lactating mothers should be done under a doctor’s advisory and implement the following to reduce THC metabolites in breast milk:
Use cannabis in minimal doses.
Stay well hydrated.
Exercise regularly.
Never smoke or vaporize cannabis.
THC transmission through the placenta
Although little is known about the maternal-fetal transfer of THC, it is possible to pass THC metabolites to the fetus through the placenta.
As a lipophilic molecule, THC passes from the fat cells of the placenta into the fetal bloodstream. This is the only possible means through which THC is transmitted through the bloodstream.
THC exposure to a developing fetus has the following effects:
It increases the risk of premature birth.
Impairs fetal growth, hence reduced birth weight.
Increases the risk of stillbirth.
Impairs fetal brain and nervous system development, which may lead to cognitive impairment, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and autism in the newborn.
Besides these neurodevelopment disorders in the fetus, an infant born of a cannabis-using mother may exhibit neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS).
These are a group of symptoms that occur in newborns exposed to certain drugs while in the womb. They include tremors, irritability, seizures, and feeding difficulties.
Pregnant women concerned about the risk of THC transmission to their unborn should see a doctor to help them understand the risks and benefits of cannabis and get support and guidance from qualified personnel.
0 notes
Text
Organ-on-Chip Devices: Revolutionizing Biomedical Research and Drug Development
Organ-on-chip devices are gaining attention as a breakthrough in biomedical research and drug development. These innovative microfluidic systems simulate the physiological environment of human organs, offering a more accurate and ethical alternative to traditional animal testing. In this blog, we’ll explore what organ-on-chip devices are, their benefits, and their transformative impact on healthcare and drug discovery.

Download PDF Brochure
What are Organ-on-Chip Devices?
Organ-on-chip (OoC) devices are micro-engineered systems designed to replicate the structural and functional characteristics of human organs. These small chips contain hollow channels lined with living human cells, allowing scientists to mimic the flow of blood, air, or other biological fluids. By incorporating various types of cells and tissue cultures, OoCs can simulate organ-level responses to diseases, drugs, or environmental stimuli.
How Do They Work?
Organ-on-chip devices are built using microfluidic technology, which manipulates tiny amounts of fluids within microscale channels. The devices often incorporate multiple cell types to mimic the complex interactions within an organ. For example, a lung-on-chip mimics breathing movements, while a heart-on-chip replicates the rhythmic beating of heart tissue. Sensors within the chip provide real-time data on cellular responses, such as changes in tissue behavior, oxygen levels, and drug absorption.
Benefits of Organ-on-Chip Devices
Enhanced Precision: Traditional in vitro models, such as petri dishes, lack the complexity and dynamic environment of human organs. Organ-on-chip devices offer a more accurate model by replicating organ-specific structures and functions, leading to better predictive results for drug efficacy and safety.
Reduction in Animal Testing: Ethical concerns surrounding animal testing have driven the need for alternative models. Organ-on-chip devices reduce the reliance on animal models, providing a more humane and scientifically advanced method of testing.
Personalized Medicine: OoCs can be customized using patient-derived cells, enabling researchers to simulate individual responses to treatments. This paves the way for personalized medicine, where therapies can be tailored to a patient’s specific biology, improving treatment outcomes.
Cost and Time Efficiency: Drug discovery is an expensive and time-consuming process. Organ-on-chip devices accelerate research by providing faster, more accurate testing, potentially reducing the time and cost associated with bringing new drugs to market.
Request Sample Pages
Applications in Drug Development
Organ-on-chip devices are making significant strides in pharmaceutical research and development. By providing a more realistic model of human organs, they help pharmaceutical companies screen potential drugs more efficiently. Researchers can study the effects of drugs on different organs, assess toxicology, and monitor potential side effects before clinical trials. This leads to fewer drug failures and better safety profiles.
For example, liver-on-chip models are used to study drug metabolism and toxicity, while gut-on-chip devices can simulate the effects of drugs on gastrointestinal function. This technology holds promise in identifying potential issues early in the drug development pipeline, saving both time and resources.
Future of Organ-on-Chip Devices
The future of organ-on-chip technology is exciting, with the potential for multi-organ chips to simulate entire biological systems. As advancements continue, researchers may eventually create “human-on-chip” platforms, integrating multiple organ chips to mimic the interactions between different organs. This would revolutionize personalized medicine and clinical trials by providing an individualized, comprehensive view of how a treatment might affect a patient’s entire body.
Conclusion
Organ-on-chip devices represent a paradigm shift in biomedical research and drug development. By offering more accurate, ethical, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional methods, these devices are poised to transform how we understand diseases, develop new treatments, and personalize healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, organ-on-chip systems will likely play an essential role in advancing modern medicine and improving patient outcomes.
Content Source:
https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2024/03/12/2844519/0/en/Organ-on-Chip-Market-is-Expected-to-Reach-631-073-thousand-MarketsandMarkets.html
0 notes
Text
Choosing the Right Gastrointestinal Tract Drug – Factors to Consider
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a complex system responsible for digestion and absorption of nutrients. Given its critical function, disorders affecting the GI tract can significantly impact overall health and quality of life. Selecting the right medication to treat these conditions is essential for effective management and recovery. Centurion HealthCare, a leading gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier in India, offers a range of high-quality medications designed to address various GI disorders. In this article, we will explore the factors to consider when choosing the right gastrointestinal tract drug, and why Centurion HealthCare stands out in the best pharmaceutical industry in India.

Understanding Gastrointestinal Tract Disorders
GI tract disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting different parts of the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. Common GI disorders include:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Hepatitis
Pancreatitis
Each condition requires specific treatment strategies and medications to manage symptoms, promote healing, and prevent complications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gastrointestinal Tract Drug
Choosing the right drug for treating GI disorders involves multiple factors, including the specific condition, the patient’s medical history, and potential side effects. Here are key considerations:
1. Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is the first step in selecting the appropriate medication. Physicians use various diagnostic tools such as endoscopy, colonoscopy, imaging studies, and laboratory tests to identify the specific GI disorder. Understanding the underlying cause and severity of the condition is crucial for effective treatment.
2. Mechanism of Action
Different gastrointestinal tract drugs work through various mechanisms to achieve therapeutic effects. Understanding how a drug works helps in selecting the most suitable option. Common mechanisms include:
Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid, providing quick relief from heartburn and indigestion.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Reduce the production of stomach acid, effective in treating GERD and peptic ulcers.
H2 Receptor Antagonists: Decrease acid production by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach lining.
Prokinetics: Enhance gut motility, useful in conditions like gastroparesis.
Antispasmodics: Relieve intestinal cramps and spasms, often used in IBS treatment.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Reduce inflammation in the GI tract, essential for managing IBD.
3. Efficacy and Safety
The efficacy and safety profile of a drug are critical factors in the decision-making process. Clinical trials and real-world studies provide valuable information on a drug’s effectiveness and potential side effects. Physicians must weigh the benefits against the risks to ensure the chosen medication offers the best possible outcome for the patient.
4. Patient-Specific Factors
Each patient is unique, and various individual factors can influence drug selection. These include:
Age: Certain drugs may be more suitable for children, adults, or the elderly.
Medical History: Pre-existing conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, can affect drug metabolism and tolerance.
Allergies: Patients with known drug allergies must avoid medications that could trigger adverse reactions.
Concurrent Medications: Drug interactions can impact efficacy and safety, requiring careful consideration of all medications the patient is currently taking.
5. Route of Administration
The route of administration can affect the drug’s efficacy and patient compliance. Common routes for GI drugs include:
Oral: Tablets, capsules, and liquids are convenient for most patients.
Intravenous: Used in severe cases or when oral administration is not feasible.
Topical: Suppositories and enemas are used for localized treatment in the lower GI tract.
6. Cost and Availability
Cost can be a significant factor, especially for long-term treatments. Generic versions of drugs often offer the same efficacy as brand-name medications at a lower cost. Availability of the drug in the local market is also crucial to ensure uninterrupted treatment.
Centurion HealthCare: Leading the Way in GI Tract Drug Supply
Centurion HealthCare has established itself as a premier gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier in India, renowned for its commitment to quality, innovation, and patient care. Here’s why Centurion HealthCare is a trusted name in the best pharmaceutical industry in India:
1. Comprehensive Product Range
Centurion HealthCare offers a wide range of gastrointestinal tract drugs, catering to various GI disorders. Their product portfolio includes antacids, PPIs, H2 receptor antagonists, prokinetics, antispasmodics, and anti-inflammatory medications, ensuring comprehensive treatment options for healthcare providers.
2. Quality Assurance
Quality is at the heart of Centurion HealthCare’s operations. The company adheres to stringent quality control measures, from raw material sourcing to final product testing, ensuring that every medication meets international standards for safety and efficacy.
3. Research and Development
Centurion HealthCare invests heavily in research and development to stay at the forefront of pharmaceutical innovation. Their R&D team continuously works on developing new formulations and improving existing products to address emerging healthcare needs.
4. Patient-Centric Approach
Understanding that each patient is unique, Centurion HealthCare adopts a patient-centric approach in drug development and supply. Their medications are designed to provide maximum therapeutic benefit with minimal side effects, enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
5. Global Reach
As a leading gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier, Centurion HealthCare has a robust distribution network that ensures their products are available not only across India but also in international markets. Their commitment to excellence has earned them a reputation as a reliable partner for healthcare providers worldwide.
6. Affordability
Centurion HealthCare is dedicated to making high-quality medications accessible to all. Their cost-effective solutions, including generic versions of popular GI drugs, help reduce the financial burden on patients while maintaining high standards of care.
Conclusion
Choosing the right gastrointestinal tract drug involves careful consideration of various factors, including accurate diagnosis, mechanism of action, efficacy, safety, patient-specific factors, route of administration, and cost. Centurion HealthCare, as a leading gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier in India, excels in providing high-quality, effective medications that cater to the diverse needs of patients with GI disorders.
With a commitment to quality, innovation, and patient-centric care, Centurion HealthCare stands out in the best pharmaceutical industry in India. Their comprehensive product range, stringent quality assurance, advanced R&D, global reach, and affordability make them a trusted partner for healthcare providers seeking reliable solutions for GI tract disorders.
By choosing Centurion HealthCare, you can be confident in the quality and efficacy of the medications you are prescribing or consuming, ensuring the best possible outcomes for gastrointestinal health.
#Best Indian pharma industry 2024#Best pharmaceutical industry in India#Gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier#Gastrointestinal tract drugs supplier in India
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are multiple risk factors for the development of osteoporosis. These include but are not limited to advanced age, cigarette smoking, chronic glucocorticoid therapy, low body weight, previous fractures, history of rheumatoid arthritis, and excessive alcohol intake.
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are associated with adverse effects on bone health. The AEDs most commonly associated with altered bone metabolism are those that induce the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Specifically, the AED phenytoin has a direct inhibitory effect on intestinal calcium absorption and can stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption.
A score of less than -2.5 on DEXA scanning would indicate osteoporosis, a score of -1.0 to -2.5 would indicate osteopenia, and a score greater than -1.0 indicates normal bone density. Additionally, a fragility fracture (fracture from minor trauma such as a fall from a standing height or less) is diagnostic of osteoporosis without any further workup.
Bottom Line: The risk factors for osteoporosis include advanced age, cigarette smoking, chronic glucocorticoid therapy, physical inactivity, poor intake of calcium and vitamin D, body weight less than 127 lb, previous fractures, anticonvulsant use, hyperthyroidism, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and excessive alcohol intake.
The characteristic need for the child to use his hands to push himself to an upright position when arising from the floor is the Gower sign. It results from weakness in the proximal lower extremity muscles. Physical examination reveals pseudohypertrophy of the calf, lumbar lordosis, a waddling gait, shortening of the Achilles tendons, hypotonia, and hyporeflexia or areflexia. Patients usually use wheelchairs by age 12 or 13. Additional complications include delayed growth, dilated cardiomyopathy, increased fractures, progressive scoliosis with impaired pulmonary function, cognitive impairment, and eventual respiratory insufficiency.
Bottom Line: Elevated laboratory markers in the setting of Duchenne muscular dystrophy include serum creatine kinase, aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine transaminase.
COMBANK Insight: DMD is a progressive, myopathic disorder inherited in an X-linked, recessive fashion and caused by a defective gene on the X chromosome responsible for dystrophin production. Dystrophin normally serves to stabilize and prevent the breakdown of muscle fibers. Loss of dystrophin thus leads to muscle fiber degeneration, resulting in muscle weakness.
Wilson Disease, also known as hepatolenticular degeneration, is an autosomal recessive defect involving an ATPase, Cu2+ -transporting, β-polypeptide. In this disease state, copper is deposited in tissues of the brain, liver, kidneys, and Descemet membrane of the cornea (known as Kayser-Fleischer rings, which are seen in the exhibit). Parkinsonian-like tremor and dementia may be evident when the nervous system is affected. Renal tubular damage occurs in the kidneys and cirrhosis can develop in the liver. Diagnosis can be made with the observation of decreased serum ceruloplasmin. Treatment includes penicillamine, which creates a soluble complex with the metal that can be excreted through the urine.
Bottom Line: A Kayser-Fleischer ring is a golden brown ring observed in the Descemet layer of the cornea as a result of copper deposition and is seen in Wilson disease. Labs reveal low serum ceruloplasmin and treatment with penicillamine can stop the progression of this degenerative disease state.
The types of cancers that metastasize to the bone most commonly are lung, breast, thyroid, renal, and prostate. Multiple myeloma and lymphoma can both form lytic lesions from their origins within the marrow.
A SPEP and UPEP are sensitive for multiple myeloma and should be obtained along with a measurement of the patient's total protein and globulin levels.
Bottom Line: The initial workup of a new lytic lesion generally involves a CT chest/abdomen/pelvis, SPEP/UPEP, bone scan, basic labs, and mammogram or PSA
#osteoporosis#Duchenne muscular dystrophy#muscular dystrophy#Wilsons disease#multiple myeloma#cancer
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shriram Pharmacy College: Premier Pharmacy College Option In India

Shriram Pharmacy College, situated in Bankner, is renowned as one of India’s premier pharmacy academies. Known for its rigorous academic programs and state-of-the-art facilities, the college offers a comprehensive education that covers all essential aspects of pharmaceutical sciences. This blog post delves into the core components of the curriculum, providing insights into the unique opportunities available at Shriram Pharmacy College.
### Study Effects Of Various Drugs
Understanding the effects of different drugs is crucial for effective pharmaceutical practice. At Shriram Pharmacy College, students delve deeply into the pharmacodynamics of various medications. They study how drugs interact with biological systems to produce therapeutic effects and potential side effects. This includes examining drug efficacy, safety profiles, and therapeutic ranges. By learning about the diverse effects of medications, students are better equipped to make informed decisions about drug use and patient care.
### Explore Drug Mechanisms Deeply
A thorough exploration of drug mechanisms is a cornerstone of pharmaceutical education. Shriram Pharmacy College emphasizes the importance of understanding how drugs work at a molecular level. Students learn about the biochemical interactions between drugs and their targets, including enzymes and receptors. This deep dive into drug mechanisms helps students grasp how medications exert their effects and provides a foundation for developing new therapeutic agents and improving existing ones.
### Understand Pharmacological Actions Comprehensively
Pharmacological actions refer to the physiological and biochemical changes that drugs induce in the body. At Shriram Pharmacy College, students receive a comprehensive education on pharmacological actions, covering topics such as drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. This holistic understanding is essential for predicting drug behavior, assessing therapeutic outcomes, and identifying potential adverse effects. The college’s curriculum ensures that students have a solid grasp of these concepts, which are vital for effective pharmaceutical practice.
### Analyze Drug Interactions Thoroughly
Drug interactions can significantly impact the efficacy and safety of medications. Shriram Pharmacy College places a strong emphasis on teaching students how to analyze and manage drug interactions. Students learn about different types of interactions, including pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions, and their potential effects on drug therapy. This knowledge is crucial for preventing adverse drug reactions and optimizing treatment regimens. The college’s program equips students with the skills to identify and address potential interactions in clinical settings.
### Research Drug Metabolism Processes Intricately
Drug metabolism is a critical aspect of pharmacology that influences drug efficacy and safety. At Shriram Pharmacy College, students engage in detailed research on drug metabolism processes. They study how drugs are metabolized in the body, including the roles of liver enzymes and other metabolic pathways. This research is essential for understanding how drugs are processed, how they interact with other substances, and how individual variations in metabolism can affect therapeutic outcomes.
### Learn About Pharmacokinetics And Dynamics
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are fundamental concepts in pharmacy education. Shriram Pharmacy College offers in-depth instruction on these topics, focusing on how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (pharmacokinetics) and how they affect the body (pharmacodynamics). Understanding these principles helps students predict drug behavior, optimize dosing regimens, and enhance therapeutic effectiveness. The college’s curriculum integrates theoretical knowledge with practical applications, ensuring students can apply these concepts in real-world scenarios.
### Focus On Drug Efficacy Studies
Drug efficacy studies are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of medications. Shriram Pharmacy College emphasizes the importance of conducting rigorous studies to assess how well drugs perform in treating specific conditions. Students learn how to design and conduct clinical trials, analyze data, and interpret results to determine a drug’s efficacy. This focus on evidence-based practice ensures that graduates are skilled in evaluating and improving therapeutic interventions.
### Apply Pharmacological Knowledge Practically
Practical application of pharmacological knowledge is essential for translating theoretical understanding into effective practice. At Shriram Pharmacy College, students have numerous opportunities to apply their knowledge through laboratory work, clinical placements, and research projects. This hands-on experience helps students develop practical skills in drug formulation, patient counseling, and therapeutic decision-making. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, the college prepares students for successful careers in the pharmaceutical industry.
/media/392aa7856f0d16e57541dda509fefd21
### FAQs
**1. What makes Shriram Pharmacy College the top choice for pharmacy education in India?**
Shriram Pharmacy College is renowned for its comprehensive curriculum, state-of-the-art facilities, and focus on practical experience. The college offers in-depth studies on drug mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, and drug interactions, ensuring that students are well-prepared for careers in the pharmaceutical industry.
**2. How does Shriram Pharmacy College support students in understanding drug mechanisms?**
The college provides a detailed curriculum that covers drug mechanisms at a molecular level. Students engage in lectures, laboratory work, and research projects to explore how drugs interact with biological systems, which enhances their understanding of drug action and development.
**3. What opportunities are available for hands-on experience at Shriram Pharmacy College?**
Students at Shriram Pharmacy College benefit from extensive hands-on experience through laboratory sessions, clinical placements, and research projects. These practical opportunities allow students to apply their theoretical knowledge, develop skills in drug formulation, and gain real-world insights into the pharmaceutical field.
**4. How does Shriram Pharmacy College address drug interactions in its curriculum?**
The college emphasizes the importance of analyzing and managing drug interactions through specialized coursework and practical training. Students learn about various types of interactions and their potential effects, preparing them to optimize drug therapy and prevent adverse reactions.
**5. What role does research play in the education provided by Shriram Pharmacy College?**
Research is a fundamental component of the education at Shriram Pharmacy College. Students engage in research projects related to drug metabolism, efficacy studies, and pharmacokinetics, allowing them to contribute to advancements in the field and gain valuable experience in scientific inquiry.
### Conclusion
Shriram Pharmacy College in Bankner stands out as India’s leading pharmacy academy, offering a top-notch education that prepares students for the dynamic pharmaceutical industry. With a focus on drug effects, mechanisms, and interactions, coupled with hands-on experience and research opportunities, the college equips students with the knowledge and skills needed for successful careers. By emphasizing practical application and continuous learning, Shriram Pharmacy College ensures its graduates are well-prepared to contribute to advancements in healthcare. For more updates and insights, please like, share, and subscribe to our YouTube channel.
### Stay Connected with Shriram Pharmacy College!
For the latest updates, educational content, and insights into the dynamic field of pharmacy, don’t miss out on the Shriram Pharmacy College YouTube channel. By liking, sharing, and subscribing, you’ll gain access to expert lectures, student testimonials, campus events, and much more. Stay informed about advancements in pharmaceutical sciences and become a part of our vibrant community. Your support helps us grow and continue providing valuable resources to students and professionals alike. Join us today and never miss an update!
#pharmacy#pharmacist#public health#hospital#online pharmacy#shriram nursing college#youtube#medicine#shriram medical college#shriram pharmacy college
0 notes