#elastic IP addresses AWS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Quote
AWSのpublic IPv4課金の件、EC2だけではなく全サービスで、ALBも課金されるのIP数コントロールできないし、さすがにこれはひどいと思うんだ。 > In-use Public IPv4 address charges: $0.005 / IP / hour x 730 hours x 2 ALB Elastic IPs = $7.30/month
城陽人さんはTwitterを使っています
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introducing Gen 2 AWS Outpost Racks with Improved Speed

Outpost Racks
Amazon's latest edge computing innovation, second-generation Outpost racks, are now available. This new version supports the latest x86-powered Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances and features faster networking instances for ultra-low latency and high throughput applications and simpler network scalability and deployment. These enhancements boost on-premises workloads including telecom 5G Core and financial services core trading platforms.
For on-premises workloads. The second-generation at outpost racks process data locally and has low latency for multiplayer online gaming servers, consumer transaction data, medical records, industrial and manufacturing control systems, telecom BSS, edge inference of diverse applications, and machine learning (ML) models. Customers may now choose from the latest processor generation and Outposts rack configurations with faster processing, more memory, and more network bandwidth.
The latest EC2 instances
In AWS racks are compute-optimized C7i, general-purpose M7i, and memory-optimized R7i x86 instances. Older Outpost Rack C5, M5, and R5 instances had 40% less performance and double vCPU, RAM, and Internet bandwidth. Larger databases, real-time analytics, memory-intensive apps, on-premises workloads, CPU-based edge inference with complicated machine learning models. benefit tremendously from 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs. Newer EC2 instances, including GPU-enabled ones, will be supported.
Easy network scalability and configuration
Amazon has overhauled networking for its latest Outposts generation, making it easier and more scalable. This update centres on its new Outposts network rack, which centralises compute and storage traffic.
The new design has three key benefits. First, you may now grow compute capacity separately from networking infrastructure as workloads rise, increasing flexibility and lowering costs. Second, it started with network resiliency to keep your systems running smoothly. Network racks handle device failures automatically. Third, connecting to on-premises and AWS Regions is simple. You may configure IP addresses, VLANs, and BGP using a revamped console interface or simple APIs.
Amazon EC2 instances with faster networking
Enhanced Amazon EC2 instances with faster networking are being launched on Outpost racks. These instances are designed for mission-critical on-premises throughput, computation, and latency. A supplemental physical network with network accelerator cards attached to top-of-rack (TOR) switches is added to the Outpost logical network for best performance.
Bmn-sf2e instances, designed for ultra-low latency and predictable performance, are the first. The new instances use Intel's latest Sapphire Rapids processors (4th Gen Xeon Scalable) and 8GB of RAM per CPU core to sustain 3.9 GHz across all cores. Bmn-sf2e instances feature AMD Solarflare X2522 network cards that link to top-of-rack switches.
These examples provide deterministic networking for financial services customers, notably capital market companies, employing equal cable lengths, native Layer 2 (L2) multicast, and precision time protocol. Customers may simply connect to their trading infrastructure to meet fair trading and equitable access regulations.
The second instance type, Bmn-cx2, has low latency and high throughput. This example's NVIDIA ConnectX-7 400G NICs are physically coupled to fast top-of-rack switches, giving 800 Gbps bare metal network bandwidth at near line rate. This instance supports hardware PTP and native Layer 2 (L2) multicast, making it ideal for high-throughput workloads including risk analytics, real-time market data dissemination, and telecom 5G core network applications.
Overall, the next Outpost racks generation improves performance, scalability, and resilience for on-premises applications, particularly mission-critical workloads with rigorous throughput and latency constraints. AWS Management Console lets you pick and buy. The new instances preserve regional deployment consistency by supporting the same APIs, AWS Management Console, automation, governance policies, and security controls on-premises and in the cloud. improving IT and developer productivity.
Know something
Second-generation Outpost racks may be parented to six AWS regions: Asia Pacific (Singapore), US West (Oregon), US East (N. Virginia, and Ohio), and EU West (London, France).Support for more nations, territories, and AWS regions is coming. At launch, second-generation Outpost racks support several AWS services from first-generation racks. Support for more AWS services and EC2 instance types is coming.
#AmazonElasticComputeCloud#machinelearning#C7iinstances#AmazonEC2#EC2instance#AWSRegions#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
AWS Solutions Architect - Associate (SAA-C03) Latest Exam Questions 2025?
As you prepare for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) exam, effective time management is essential for success. Clearcatnet provides highly effective and up-to-date study materials tailored to help you master key concepts and exam objectives with ease. Our comprehensive resources include real-world scenarios, practice questions, and expert insights to enhance your understanding of AWS architecture. With our structured approach, you can confidently aim for a score above 98% on your first attempt. Invest in your success with Clearcatnet and take the next step in your AWS certification journey!
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) Exam Guide
Understand the Exam Structure
To excel in the AWS SAA-C03 exam, it is essential to understand its domains and weightings:
Design Secure Architectures – 30%
Design Resilient Architectures – 26%
Design High-Performing Architectures – 24%
Design Cost-Optimized Architectures – 20%
Exam Format
Exam Code: SAA-C03
Type: Proctored (Online or Test Center)
Duration: 130 minutes
Total Questions: 65
Passing Score: 70% (700/1000)
Languages Available: English, Japanese, Simplified Chinese, Korean, German, French, Spanish, Portuguese (Brazil), Arabic (Saudi Arabia), Russian, Traditional Chinese, Italian, Indonesian
Study Resources & Renewal
Free Learning Path: Available upon request after Premium Access (Contact Clearcatnet for the link)
Certification Level: Associate
Renewal Requirement: Every 12 months
Prepare strategically with Clearcatnet’s expert-curated materials and maximize your chances of passing on your first attempt!
What measures should be implemented to enable the EC2 instances to obtain the necessary patches?
A) Configure a NAT gateway in a public subnet.
B) Create a custom route table with a route to the NAT gateway for internet traffic and associate it with the private subnets.
C) Assign Elastic IP addresses to the EC2 instances.
D) Create a custom route table with a route to the internet gateway for internet traffic and associate it with the private subnets.
E) Configure a NAT instance in a private subnet.
👉 Correct Answers: A and B
Explanation:To enable private EC2 instances to access the internet without being directly exposed:For Get More Latest Questions and Answers and PDF so Visit:www.clearcatnet.com
#AWS#AWSCertified#AWSCertification#AWSCloud#AWSCommunity#SAAC03#AWSExam#AWSSolutionsArchitect#AWSSAA#AWSAssociate#CloudComputing#CloudCareer#ITCertification#TechLearning#CloudEngineer#StudyTips#ExamPrep#CareerGrowth#LearnAWS#AWSJobs
0 notes
Text
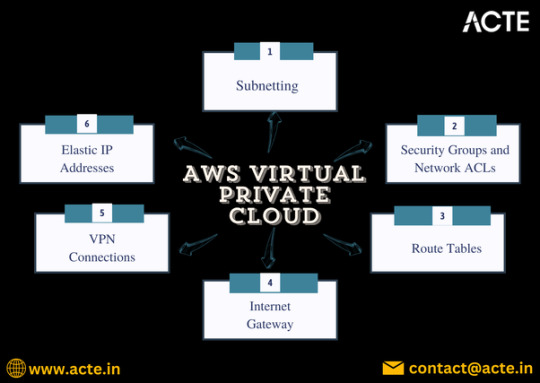
Demystifying AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
In the ever-evolving world of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as a leader, offering a wide array of services to meet diverse business needs. Among these services, the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is one of the most crucial components for organizations seeking to enhance their security and control over their cloud resources. This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to AWS VPC, exploring its features, benefits, and best practices.
If you want to advance your career at the AWS Course in Pune, you need to take a systematic approach and join up for a course that best suits your interests and will greatly expand your learning path.

What is AWS VPC?
AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows users to create a private, isolated section of the AWS cloud where they can launch and manage AWS resources. VPC enables businesses to control their virtual networking environment, including IP address ranges, subnets, routing, and security settings.
Key Features of AWS VPC
Custom IP Address Range:
When creating a VPC, you can define your own IP address range using Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation. This flexibility allows you to tailor your network architecture to your specific needs.
2. Subnets:
VPCs can be divided into subnets, which are smaller segments within the VPC. You can create public subnets (accessible from the internet) and private subnets (not directly accessible from the internet) to optimize resource security.
3. Security Groups and Network ACLs:
Security groups act as virtual firewalls for your instances, controlling inbound and outbound traffic. Network Access Control Lists (ACLs) provide an additional layer of security at the subnet level, enabling more granular traffic management.
4. Route Tables:
Route tables are used to determine where network traffic is directed. You can create custom routing rules to control the flow of traffic between your VPC, subnets, and the internet.
5. Internet Gateway and NAT Gateway:
An Internet Gateway allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet. A NAT Gateway enables instances in a private subnet to initiate outbound traffic while preventing unsolicited inbound traffic.
6. VPN Connections and AWS Direct Connect:
VPC supports VPN connections, allowing secure communication between your on-premises network and your VPC. AWS Direct Connect provides a dedicated network connection, improving performance and reliability.
7. Elastic IP Addresses:
Elastic IPs are static IP addresses that can be associated with your instances, ensuring consistent public IP addresses even when instances are stopped and restarted.
To master the intricacies of AWS and unlock its full potential, individuals can benefit from enrolling in the AWS Online Training.
Benefits of Using AWS VPC
Enhanced Security:
By isolating your resources within a VPC, you gain greater control over your network security. You can implement security measures tailored to your specific needs, enhancing data protection and compliance.
Flexibility:
AWS VPC provides the flexibility to design your network architecture according to your requirements. You can easily adjust your IP address ranges, subnets, and security settings.
Scalability:
VPCs are designed to scale seamlessly. You can add or remove resources as needed, ensuring your infrastructure can adapt to changing workloads without performance degradation.
Cost Efficiency:
With AWS's pay-as-you-go pricing model, you only pay for the resources you use. This makes VPC an economically viable option for organizations of all sizes.
Integration with Other AWS Services:
VPC integrates seamlessly with various AWS services, including Amazon EC2, RDS, and Lambda, allowing you to build comprehensive cloud solutions that meet your business needs.
Conclusion
AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a vital service for businesses looking to secure and manage their cloud resources effectively. With its extensive features and benefits, VPC empowers organizations to create a customized and controlled network environment.
By understanding how to leverage VPC and adhering to best practices, businesses can maximize their cloud investment and ensure a robust, secure infrastructure. Whether you're new to AWS or looking to enhance your existing setup, mastering AWS VPC is crucial for success in the cloud.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Amazon EC2: Launching Your First Virtual Machine

Introduction:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is one of AWS’s most powerful and popular services, providing scalable virtual servers in the cloud. Whether you’re hosting a website, running an application, or performing data analysis, EC2 gives you the flexibility and control to meet your needs. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the basics of EC2 and guide you in launching your first virtual machine.
What is Amazon EC2?
Introduce EC2 and its core features:
Elasticity: Scale up or down based on demand.
Customization: Choose the operating system, storage, and network configuration.
Pay-as-you-go Pricing: Only pay for what you use, whether it’s minutes or hours.
Global Availability: Deploy instances in multiple regions and availability zones for redundancy.
Briefly mention common use cases:
Hosting web applications
Running batch processing jobs
Development and testing environments
Key Concepts to Understand
Instances: Virtual servers in EC2.
AMI (Amazon Machine Image): Pre-configured templates for your instance.
Instance Types: Defines the hardware (CPU, memory, storage) of the instance. Examples: t2.micro (basic), m5.large (medium workload).
Regions and Availability Zones: Geographic locations for deploying your instances.
Key Pairs: Used for secure SSH access to instances.
Elastic IPs: Static IP addresses that can be associated with your instance.
Section 3: Prerequisites
An AWS account (refer to your earlier blog on setting up an AWS account).
Basic understanding of cloud computing and SSH (optional).
Section 4: Step-by-Step Guide to Launch Your First EC2 Instance
1. Open the EC2 Console:
Log in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to the EC2 Dashboard.
2. Choose a Region:
Select a region near your target audience for lower latency.
3. Launch an Instance:
Click on Launch Instance.
Name your instance (e.g., “MyFirstEC2Instance”).
4. Choose an AMI:
Select a pre-configured Amazon Machine Image (e.g., Amazon Linux 2023 or Ubuntu).
For beginners, stick with the Free Tier Eligible options.
5. Choose an Instance Type:
Select t2.micro (Free Tier eligible, suitable for light workloads).
6. Configure Instance Details:
Use the default settings for networking and storage.
Optional: Configure IAM roles or enable termination protection.
7. Add Storage:
Review and adjust storage size if needed (default is 8 GB).
8. Add Tags:
Add tags to organize and identify your instance (e.g., “Environment: Test”).
9. Configure Security Group:
Define inbound rules for accessing the instance:
Allow SSH (port 22) from your IP address.
Allow HTTP (port 80) if hosting a web application.
10. Review and Launch:
Confirm your settings and click Launch.
Select an existing key pair or create a new one for secure access.
Download the key pair file (.pem) and store it securely.
Section 5: Accessing Your EC2 Instance
Connect via SSH:Open a terminal and use the following command:
bash
ssh -i /path/to/key.pem ec2-user@<Public_IP>
Replace /path/to/key.pem with the path to your downloaded key file and <Public_IP> with the instance's public IP address.
Test Your Instance:
Run basic commands like uname -a or df -h to check system information.
Cleaning Up
To avoid unexpected charges, stop or terminate your instance when you’re done:
Navigate to the EC2 Dashboard.
Select your instance.
Choose Instance State > Terminate Instance.
Tips for Beginners
Start with Free Tier Instances:
2.Use t2.micro to explore without incurring costs.
Monitor Instance Usage:
Use the AWS Cost Explorer or Billing Dashboard to track your usage.
Secure Your Instance:
Regularly update your instance and avoid exposing sensitive ports unnecessarily.
Conclusion
Launching an EC2 instance is an essential skill for anyone exploring cloud computing. Amazon EC2 provides the flexibility to run a variety of workloads, and with this guide, you’re now ready to start your journey. In future blogs, we’ll dive deeper into optimizing EC2 instances and exploring advanced features like Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing.
0 notes
Text
EC2 Auto Recovery: Ensuring High Availability In AWS

Understanding EC2 Auto Recovery: Ensuring High Availability for Your AWS Instances
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a wide range of services to ensure the high availability and resilience of your applications. One such feature is EC2 Auto Recovery, a valuable tool that helps you maintain the health and uptime of your EC2 instances by automatically recovering instances that become impaired due to underlying hardware issues. This blog will guide you through the essentials of EC2 Auto Recovery, including its benefits, how it works, and how to set it up.
1. What is EC2 Auto Recovery?
EC2 Auto Recovery is a feature that automatically recovers your Amazon EC2 instances when they become impaired due to hardware issues or certain software issues. When an instance is marked as impaired, the recovery process stops and starts the instance, moving it to healthy hardware. This process minimizes downtime and ensures that your applications remain available and reliable.
2. Benefits of EC2 Auto Recovery
Increased Availability: Auto Recovery helps maintain the availability of your applications by quickly recovering impaired instances.
Reduced Manual Intervention: By automating the recovery process, it reduces the need for manual intervention and the associated operational overhead.
Cost-Effective: Auto Recovery is a cost-effective solution as it leverages the existing infrastructure without requiring additional investment in high availability setups.
3. How EC2 Auto Recovery Works
When an EC2 instance becomes impaired, AWS CloudWatch monitors its status through health checks. If an issue is detected, such as an underlying hardware failure or a software issue that causes the instance to fail the system status checks, the Auto Recovery feature kicks in. It performs the following actions:
Stops the Impaired Instance: The impaired instance is stopped to detach it from the unhealthy hardware.
Starts the Instance on Healthy Hardware: The instance is then started on new, healthy hardware. This process involves retaining the instance ID, private IP address, Elastic IP addresses, and all attached Amazon EBS volumes.
4. Setting Up EC2 Auto Recovery
Setting up EC2 Auto Recovery involves configuring a CloudWatch alarm that monitors the status of your EC2 instance and triggers the recovery process when necessary. Here are the steps to set it up:
Step 1: Create a CloudWatch Alarm
Open the Amazon CloudWatch console.
In the navigation pane, click on Alarms, and then click Create Alarm.
Select Create a new alarm.
Choose the EC2 namespace and select the StatusCheckFailed_System metric.
Select the instance you want to monitor and click Next.
Step 2: Configure the Alarm
Set the Threshold type to Static.
Define the Threshold value to trigger the alarm when the system status check fails.
Configure the Actions to Recover this instance.
Provide a name and description for the alarm and click Create Alarm.
5. Best Practices for Using EC2 Auto Recovery
Tagging Instances: Use tags to organize and identify instances that have Auto Recovery enabled, making it easier to manage and monitor them.
Monitoring Alarms: Regularly monitor CloudWatch alarms to ensure they are functioning correctly and triggering the recovery process when needed.
Testing Recovery: Periodically test the Auto Recovery process to ensure it works as expected and to familiarize your team with the process.
Using IAM Roles: Ensure that appropriate IAM roles and policies are in place to allow CloudWatch to perform recovery actions on your instances.
Conclusion
EC2 Auto Recovery is a powerful feature that enhances the availability and reliability of your applications running on Amazon EC2 instances. By automating the recovery process for impaired instances, it helps reduce downtime and operational complexity. Setting up Auto Recovery is straightforward and involves configuring CloudWatch alarms to monitor the health of your instances. By following best practices and regularly monitoring your alarms, you can ensure that your applications remain resilient and available even in the face of hardware or software issues.
By leveraging EC2 Auto Recovery, you can focus more on developing and optimizing your applications, knowing that AWS is helping to maintain their availability and reliability.
0 notes
Text
What is Elastic Public IP?
Today we are going to discuss “Elastic Public IP”, a term that is often encountered in the cloud computing and networking space. So what exactly does Elastic Public IP mean? How is it different from a regular public IP? We'll answer them all today!

What is Elastic Public IP?
Elastic IP Address (EIP) is a public IP address that can be dynamically assigned, bound and unbound, and is usually used for virtual machines or other cloud resources in cloud service platforms (e.g., AliCloud, AWS, Tencent Cloud, etc.). Its “elasticity” is reflected in the fact that users can freely bind the IP address to different cloud servers (instances), and can unbind or reassign it at any time when needed.
Simply put, an elastic public IP is a public IP address that can be managed flexibly, so that users can bind it to different resources according to their needs, without having to change to a new IP every time.
Functions of Resilient Public IP
Ensure public network access Elastic Public IP enables resources in the cloud (such as virtual machines, databases, etc.) to be accessed over the Internet. An instance bound to an Elastic Public IP is equivalent to having its own “house number” and can be accessed by the outside world through this IP address.
IP address persistence Unlike ordinary dynamic public IPs, resilient public IPs are persistent. Even if the user stops or restarts the instance, the IP address will not change unless it is manually unbound. Therefore, it is suitable for scenarios where the same IP address needs to be used for a long time, such as building websites and servers.
Cross-Instance Binding The “elasticity” of the elastic public IP allows users to freely switch between different instances according to their needs. For example, when one instance has problems, you can quickly bind the Elastic IP to another healthy instance.
Convenient for Disaster Recovery Elastic public IP is very useful in disaster recovery. If one instance fails, you can immediately bind the same Elastic Public IP to another backup instance.
Elastic public IP provides a flexible public network access solution that not only ensures business continuity, but also allows you to flexibly cope with the adjustment of cloud resources.711Proxy can provide you with high-quality IP proxy services to help you navigate through complex network environments!
0 notes
Text
AWS ALB Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
Optimize your cloud spending with our detailed breakdown of AWS ALB pricing. Discover what AWS ALB is, how its pricing structure works, and explore various use cases to make the most of this service.
What Is AWS ALB? The Application Load Balancer (ALB) is a key component of AWS's Elastic Load Balancing suite, designed to manage modern web traffic efficiently. It distributes incoming user traffic across multiple servers in the cloud, ensuring your applications remain responsive and available, even as they scale.
How Does AWS ALB Work? Operating at the application layer (HTTP/HTTPS), AWS ALB intelligently directs traffic based on request content, such as URL paths or HTTP headers. This makes it ideal for complex architectures, including microservices and containers, as it can manage multiple ports and route traffic to IP addresses beyond AWS EC2.
Key Use Cases for AWS ALB AWS ALB is versatile and can enhance the performance and reliability of various applications, including:
Containerized Applications: Direct traffic to specific containers managed by Amazon ECS or EKS. High-Traffic Websites: Manage large volumes of user traffic seamlessly, avoiding server overload. Fault-Tolerant Applications: Automatically reroute traffic from failed instances to healthy ones. Real-Time Applications: Support applications that require immediate interactions, such as gaming and financial services. Dynamic Content Routing: Direct users to different backend services based on request content. Understanding AWS ALB Pricing AWS ALB pricing comprises several components, allowing users to pay only for what they use:
Load Balancer Capacity Units (LCUs): Charges are based on the highest resource usage during the hour, which includes:
New connections Active connections Processed bytes Rule evaluations For example, pricing in the US East (Ohio) region is $0.0082 per LCU-hour.
Data Processing Charges: You’ll incur costs for data processed through ALB, typically $0.008 per GB.
Hourly Charges: Each ALB incurs a base hourly charge, around $0.0225 per hour.
Additional Features: Costs may increase with features like SSL termination or advanced routing options.
Elastic IP Addresses: Assigning Elastic IPs also incurs standard charges.
Pricing Example Consider an ALB processing 100 GB of data over a month. Here’s a rough estimate of costs:
Data Charges: 100 GB x $0.008 = $0.80 Hourly Charges: 24 hours x 30 days x $0.0225 = $16.20 Total Estimated Cost: Approximately $17.00 per month.
Reducing AWS ALB Costs To optimize your spending on AWS ALB, consider the following strategies:
Utilize AWS Cost Management Tools: Tools like AWS Cost Explorer can help track and analyze your ALB costs. Automate Elasticity: Implement AWS Auto Scaling to adjust capacity based on actual demand. Choose the Right ALB Type: Ensure you're using the most cost-effective ALB for your needs. Consolidate Load Balancers: Reduce the number of underutilized ALBs to lower hourly charges. Cost Management with cloudnito Managing AWS costs can be complex, but tools like cloudnito can provide valuable insights:
Real-Time Cost Monitoring: Keep track of your AWS costs as they occur, helping identify unexpected charges. Cost Analytics: Dive deep into spending patterns and pinpoint areas for cost reduction. Cost Optimization Recommendations: Receive actionable insights to optimize resource usage and configuration. Frequently Asked Questions about AWS ALB Pricing
How is AWS ALB priced?
AWS ALB pricing is based on hourly rates and LCUs consumed, which factor in new connections, active connections, processed bytes, and rule evaluations.
What can unexpectedly increase my costs?
Traffic surges, misconfigured routing rules, or underutilized ALBs can lead to increased costs.
Are there free-tier options?
Yes, AWS offers a Free Tier, which includes 750 hours of shared usage and 15 LCUs for AWS ALB. Conclusion Understanding AWS ALB pricing is crucial for effective cloud cost management. By leveraging the insights provided in this guide and utilizing tools like cloudnito, you can optimize your AWS spending and maintain efficient application performance.
Ready to optimize your AWS costs? Schedule a demo with cloudnito today!
cloudnito
1 note
·
View note
Text
Skills Required For Learning AWS: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has become a ruling force in the cloud computing industry, offering various services from computing power to machine learning. Certain skills are essential to master for individuals looking to dive into AWS, whether for career advancement or personal growth. Here's a detailed guide to the necessary skills to learn and utilize AWS effectively.
Basic Understanding Of Cloud Computing:
Before diving into AWS specifics, it's crucial to have a foundational understanding of cloud computing. Embark on a transformative journey into cloud computing with AWS Training in Chennai at Infycle Technologies. As a leading provider of AWS training, we offer comprehensive courses designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in cloud computing. It includes knowing:
Cloud Concepts: Understanding the basic principles of cloud computing, including its benefits (scalability, elasticity, cost-efficiency) and deployment models (public, private, hybrid).
Service Models: Familiarity with the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service.
Familiarity With AWS Core Services:
AWS offers a plethora of services, but starting with the core services provides a strong foundation:
Compute EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for scalable computing capacity.
Storage: S3 (Simple Storage Service) for object storage and EBS (Elastic Block Store) for block storage.
Databases: RDS (Relational Database Service) and DynamoDB for NoSQL databases.
Networking: VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) for isolated network environments.
Basic Networking Knowledge:
Understanding networking basics is essential for effectively using AWS services:
IP Addressing: Knowledge of IP addresses, subnets, and CIDR notation.
DNS: Understanding how the Domain Name System (DNS) works, particularly with Route 53.
Load Balancing And CDN: Familiarity with concepts like load balancing (ELB) and content delivery networks (CloudFront).
Proficiency In Scripting And Programming:
Some level of scripting or programming knowledge is beneficial, particularly for automating tasks and managing AWS resources:
Python or Node.js: These are commonly used languages for AWS Lambda (serverless computing).
Shell Scripting: Useful for managing and automating AWS instances.
JSON/YAML: Understanding these formats is crucial for working with AWS CloudFormation and configuration files.
Understanding Of Security Practices:
Security is a most important concern in the cloud, and AWS provides various tools and best practices to secure resources:
IAM (Identity and Access Management): Managing users, roles, and permissions.
Encryption: Knowledge of data encryption at rest and in transit.
Security Groups And NACLs: Configuring firewall rules to control traffic to AWS resources.
Familiarity With Monitoring And Management Tools:
Monitoring and managing AWS resources requires knowledge of several AWS tools:
CloudWatch: This is for monitoring and logging AWS resources.
CloudTrail: This is for auditing and tracking API calls.
Trusted Advisor: For insights and recommendations on AWS best practices.
DevOps And Automation Skills:
AWS and DevOps go hand in hand, with numerous services designed to facilitate continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD):
AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild: These are used to automate build and deployment processes.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Using AWS CloudFormation or Terraform to manage infrastructure through code.
Configuration Management: Familiarity with tools like Ansible, Chef, or Puppet to maintain consistency across environments.
Hands-On Experience:
Theory alone isn't enough. Unlock your potential and shape a rewarding career in the dynamic world of software development with Infycle Technologies, recognized as the Best Software Training Institute in Chennai. Practical, hands-on experience is crucial:
AWS Free Tier: Utilize the free tier to experiment with AWS services without incurring costs.
Labs And Projects: Engage in labs and build projects to solve real-world problems using AWS.
Certifications: Consider pursuing AWS certifications (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect) to validate your skills and knowledge.
Continuous Learning And Adaptation:
The tech landscape, particularly cloud computing, is ever-evolving. Continuous learning is essential:
AWS Documentation and Whitepapers: Regularly read AWS documentation and whitepapers to stay updated on best practices and new services.
AWS Read Webinars: Participate in AWS events and webinars to get knowledge from experts and community members.
Community Engagement: Engage with AWS communities, forums, and users to give knowledge and learn from others.
Conclusion:
Learning AWS is a multifaceted journey that requires combining technical knowledge, practical skills, and continuous learning. By Embedding the skills outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to leverage AWS's vast ecosystem, drive innovation, and advance your career in the cloud computing domain. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, these skills will provide a solid foundation for your AWS learning path.
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Implementing Network Load Balancers
Implementing requires careful planning and adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your application and network requirements to determine the appropriate load balancing strategy. Choose a load balancing algorithm that aligns with your traffic distribution needs, whether it's round-robin, least connections, or weighted round-robin.Next, deploy redundant load balancers for high availability and fault tolerance. Configure health checks to monitor backend server status and automatically remove or add servers based on their health. Additionally, optimize security by implementing SSL termination and enforcing access control policies. Regularly monitor and tune your load balancers to accommodate changing traffic patterns and scale as needed. Following these best practices will help maximize the effectiveness of your network load balancers and ensure seamless application delivery
Overview of Network Load Balancers
Explore the fundamental concepts of network load balancer (NLBs) in modern IT infrastructure. Learn how NLBs efficiently distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources to optimize performance and reliability.
Benefits of Network Load Balancers
Discover the key benefits of using network load balancers. Explore how NLBs improve application availability, scalability, and responsiveness by intelligently distributing traffic and managing server loads.
Network Load Balancer Deployment Strategies
Discuss different deployment strategies for network load balancers. Explore options such as hardware-based vs. software-based NLBs, on-premises vs. cloud-based deployments, and considerations for scalability and high availability.
Load Balancing Algorithms
Examine popular load balancing algorithms used in network load balancers. Discuss algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, and IP hash, and understand how they influence traffic distribution and server selection.
Security Considerations with Network Load Balancers
Address security considerations associated with network load balancers. Explore features such as SSL termination, DDoS protection, and access control mechanisms that enhance security posture when using NLBs.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Learn about monitoring tools and techniques for network load balancers. Explore performance optimization strategies, including health checks, metrics monitoring, and scaling policies to ensure efficient traffic management.
Integration with Cloud Services and Container Orchestration
Discuss the integration of network load balancers with cloud services and container orchestration platforms. Explore how NLBs interact with AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Kubernetes Ingress controllers, and service mesh technologies like Istio for managing microservices traffic.
Conclusion
Implementing requires adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance and reliability in your IT infrastructure. By following established guidelines for load balancer sizing, health monitoring, and configuration of routing policies, organizations can achieve high availability and scalability. It's essential to prioritize security measures such as SSL termination, encryption, and access control to protect against cyber threats. Regular monitoring and performance optimization are key to identifying and addressing potential issues proactively. Additionally, leveraging automation and orchestration tools can streamline load balancer deployment and management processes. By adopting these best practices, businesses can maximize the benefits of improving application delivery and user experience while maintaining robustness and resilience in their network architecture.
0 notes
Text
How AWS Cost Optimization Can Transform Your Cloud Strategy

Effective AWS cost optimization is crucial for managing cloud expenditures and maximizing the value of your cloud investments. This blog explores the concept of AWS cost optimization, why it's essential for businesses using Amazon Web Services, and provides actionable strategies to help you reduce costs while maintaining or enhancing cloud performance.
Understanding AWS Cost Optimization
AWS cost optimization refers to the process of adjusting your AWS setup to reduce costs without compromising on service quality or performance. The goal is to ensure you're only paying for the resources you need and use, while also taking advantage of pricing models and tools offered by AWS that can help decrease your spending.
Why AWS Cost Optimization Matters
For many businesses, cloud spending is a significant part of the IT budget. Without careful management, costs can spiral, especially as cloud environments grow in complexity. Optimizing these costs ensures operational efficiency and can free up resources to invest back into the business, driving growth and innovation.
Key Strategies for AWS Cost Optimization
Right-Sizing Resources:
Ensure that you are using the most efficient instance types and sizes for your workload. AWS offers a variety of instances that can be tailored to different needs, which means regular review and adjustment of your resources can lead to substantial savings.
Leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans:
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans are two cost-saving options provided by AWS that allow you to commit to usage in exchange for a lower rate. Analyzing your usage and making a calculated commitment can significantly cut your expenses.
Eliminating Wasted Resources:
Regularly review and terminate unused or idle resources. This includes unattached Elastic IP addresses, obsolete snapshots, and outdated data that incur costs.
Utilizing Auto Scaling:
Auto Scaling helps you match resource capacity with changes in demand without manual intervention. By automatically adjusting capacity, you ensure efficiency and avoid paying for unnecessary resources.
Optimizing Data Transfer Costs:
Data transfer costs can be a hidden drain on your budget. Optimize these costs by selecting the right types of data storage and transfer solutions and using AWS’s Content Delivery Network (CDN), Amazon CloudFront, to reduce costs associated with data delivery.
Using Cost Management Tools:
AWS provides powerful tools like AWS Cost Explorer to track and analyze your expenditures. These tools can help you understand your spending patterns and identify opportunities for cost reduction.
Incorporating Cost Optimization into Cloud Management
Integrating cost optimization into your overall cloud management strategy is essential for sustained efficiency. This involves not just implementing the strategies above but also fostering a culture of cost awareness and accountability throughout the organization.
Conclusion: The Benefits of AWS Cost Optimization
AWS cost optimization is not just about cutting costs—it’s about making smart decisions that align cloud expenditures with business needs, thus maximizing both operational efficiency and budget effectiveness. By embracing these optimization strategies, companies can enjoy a more cost-effective and resource-efficient cloud environment.
To learn more about implementing effective cost-saving measures and optimizing your AWS setup, visit our detailed guide on AWS cost optimization.
0 notes
Text
What Is Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPC? Benefits, Features

What is Amazon VPC?
AWS resources can be launched in a logically isolated virtual network that you specify using the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) service. You are in total control of your virtual networking environment, including choosing your own range of IP addresses, setting up subnets, and configuring network gateways and route tables. The majority of the resources in your VPC are compatible with both IPv4 and IPv6, which helps to provide safe and convenient access to resources and apps.
Customizing the network setup of your VPC is simple using Amazon VPC, one of AWS’s core services. For your web servers with internet connection, you can set up a subnet that is visible to the public. Additionally, it enables you to locate your backend systems like databases or application servers in a subnet that faces the private sector and is not connected to the internet. Several security layers, such as network access control lists and security groups, can be used with Amazon VPC to assist manage access to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances within each subnet.
Benefits of Amazon VPC
Increase security
Within your virtual network, secure and keep an eye on connections, filter traffic, and limit instance access.
Save time
Reduce the amount of time you spend configuring, maintaining, and verifying your virtual network.
Manage and control your environment
Create subnets, configure route tables, and select your own IP address range to personalize your virtual network.
How it works
You have complete control over your virtual networking environment with Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), including connectivity, security, and resource placement. Set up your VPC in the AWS service panel to get started. Add resources like Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) instances and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) after that. Lastly, specify how your VPCs interact with one another across AWS Regions, Availability Zones, and accounts.
Use cases
Launch a simple website or blog
Enforce restrictions on inbound and outbound connections to strengthen the security posture of your web application.
Host multi-tier web applications
Establish network connectivity and limitations among your databases, application servers, and web servers.
Create hybrid connections
Create and oversee a VPC network that works with both your on-premises and AWS services.
Amazon virtual private cloud pricing
Why Amazon Virtual Private Cloud?
Although setting up and utilizing an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is free, you can pay for its extra features using usage-based fees. You may modify your Amazon VPC’s control, connectivity, monitoring, and security with the help of AWS’s tools and services. Please refer to the following for precise pricing rates for these components.
There are still usage fees associated with other Amazon Web Services products, like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), which include data transfer fees. Pricing is per VPN connection-hour if you use the optional hardware virtual private network (VPN) connection to link your VPC to your corporate data center. Data transported across VPN connections will be invoiced at standard AWS Data Transfer rates, and partial hours are billed as full hours.
Amazon VPC features
Logs of Flow
To get operational insight into your network dependencies and traffic patterns, identify irregularities and stop data leaks, and troubleshoot network connectivity and configuration issues, you can keep an eye on your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) flow logs that are sent to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) or Amazon CloudWatch. You can discover more about who started your TCP connections and the packet-level source and destination of traffic passing through intermediary layers by examining the expanded information in flow logs. To help you ful fill some compliance obligations, you can additionally archive your flow logs.
IP Address Manager (IPAM)
Planning, tracking, and monitoring IP addresses for your AWS workloads is made simpler with IPAM. IPAM eliminates the need for spreadsheet-based or in-house planning software by automating IP address assignments to your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPC. Additionally, it improves network observability by displaying IP utilization across several VPCs and accounts in a single operational view.
IP Addressing
Resources in your VPC can communicate with resources over the internet and with each other thanks to IP addresses. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing protocols are supported by Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). IPv4-only, dual-stack, and IPv6-only subnets can be created in a VPC, and Amazon EC2 instances can be started in these subnets. Additionally, Amazon offers you a variety of choices for giving your instances public IP addresses. You can use an IP address from the Amazon-provided IPv6 CIDRs, Elastic IPv4 addresses, or public IPv4 addresses. In addition, you have the choice to assign these instances your own IPv4 or IPv6 addresses within the Amazon VPC.
Ingress Routing
This functionality allows you to redirect all incoming and outgoing traffic to and from a virtual private gateway or internet gateway to the elastic network interface of a particular Amazon EC2 instance. Before any traffic reaches your business workloads, route it to a gateway or an Amazon EC2 instance in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Network Access Analyzer
You can confirm that your network on AWS complies with your network security and compliance requirements by using Network Access Analyzer. With the help of Network Access Analyzer, you may define your standards for network security and compliance and find unauthorized network access that doesn’t fit your needs. With the help of Network Access Analyzer, you can comprehend network access to your resources, find ways to strengthen your cloud security posture, and quickly show compliance.
Network Access Control List
An optional security feature for your VPC is a network access control list (network ACL), which functions as a firewall to regulate traffic entering and leaving one or more subnets. Network ACLs can be configured using rules that are comparable to those in your security groups.
Manager of Networks
To assist you in managing and keeping an eye on your network on AWS, Network Manager offers capabilities and tools. IP administration, network security and governance, connectivity management, and network monitoring and troubleshooting are all made simpler with Network Manager.
Analyzer of Reachability
You can examine and troubleshoot network reachability between two resources in your VPC using this static configuration analysis tool. When the source and destination resources are reachable, Reachability Analyzer generates hop-by-hop information about the virtual path between them; when they are not, it identifies the blocking factor.
Security Groups
Establish security groups to regulate incoming and outgoing traffic at the instance level, serving as a firewall for related Amazon EC2 instances. An instance can be linked to one or more security groups at the time of launch. The instance is automatically linked to the VPC’s default group if you don’t specify a group. In your VPC, each instance may be a member of a distinct group.
Mirroring of Traffic
With this capability, you can transfer network traffic to out-of-band security and monitoring appliances for deep packet inspection after copying it from an elastic network interface of Amazon EC2 instances. You may create security and compliance controls, troubleshoot problems, obtain operational insights, and identify network and security anomalies. You can directly view the network packets passing through your VPC with traffic mirroring.
Lattice
You can reliably connect, keep an eye on, and protect conversations between your apps with the aid of this service. Network traffic control, access, and monitoring policies can simplify and standardize compute service connections across instances, containers, and serverless apps.
Public Access Is Blocked by VPC
This feature ensures that resources in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) are not accidentally exposed to the public by offering a single declarative control that makes it simple to prevent direct Internet access VPCs via the Internet Gateway or Egress-only Gateway. You can choose to ban only ingress Internet connections or both egress and ingress Internet connections in the VPC.
Read more on Govidhtech.com
#AmazonEC2#AmazonVirtualPrivateCloud#VPC#AmazonVPC#IPaddresses#EC2instances#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
does aws console traffic go through a vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does aws console traffic go through a vpn
AWS Console VPN Integration
Title: Streamlining Network Security: AWS Console VPN Integration
In the realm of cloud computing, securing data transmission is paramount. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a robust solution through VPN (Virtual Private Network) integration within its console. This integration empowers businesses to establish secure connections between their on-premises networks and AWS resources, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
One of the primary benefits of AWS Console VPN Integration is its simplicity and ease of setup. By navigating the AWS Management Console, users can effortlessly configure VPN connections using the intuitive interface provided by AWS. This streamlined process eliminates the need for complex manual configurations, saving valuable time and resources.
Furthermore, AWS Console VPN Integration offers scalability to meet the evolving needs of businesses. Whether it's establishing connections between multiple office locations or facilitating secure access for remote employees, AWS VPN can accommodate diverse networking requirements. This scalability is particularly advantageous for businesses experiencing growth or fluctuations in network traffic.
Security is at the core of AWS Console VPN Integration. By leveraging industry-standard encryption protocols such as IPSec (Internet Protocol Security), VPN connections are fortified against unauthorized access and eavesdropping. Additionally, AWS provides robust authentication mechanisms, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure only authorized users can access VPN resources.
Moreover, AWS Console VPN Integration enhances network resilience and reliability. By leveraging AWS's global infrastructure, businesses can establish VPN connections with low latency and high availability. This ensures consistent performance and uptime, even in the face of network disruptions or traffic spikes.
In conclusion, AWS Console VPN Integration offers a comprehensive solution for securing network communication within the AWS environment. Its simplicity, scalability, security features, and reliability make it an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to fortify their cloud infrastructure against potential threats. By seamlessly integrating VPN capabilities into the AWS Management Console, businesses can uphold the highest standards of data protection and compliance.
Network Traffic Routing in AWS
Network traffic routing in AWS is a critical aspect of ensuring efficient communication between different resources within the cloud environment. By effectively managing the flow of data packets, organizations can achieve improved performance, scalability, and security for their applications and services running on the AWS platform.
AWS offers a range of tools and services that facilitate network traffic routing, including Amazon Route 53, Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), and AWS Direct Connect. These services enable users to control how incoming and outgoing traffic is directed within their virtual network, helping to optimize resource utilization and minimize latency.
Amazon Route 53 is a scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service that allows users to route end users to internet applications by translating domain names into IP addresses. By leveraging Route 53's routing policies, users can implement traffic-routing strategies such as latency-based routing, geolocation-based routing, and weighted round-robin routing to achieve high availability and fault tolerance for their applications.
Within a VPC, users can define custom routing tables to control the flow of traffic between different subnets and to external networks. By configuring route propagation and implementing route priorities, users can tailor their network architecture to meet specific performance and security requirements.
Elastic Load Balancing distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, to ensure optimal resource utilization and fault tolerance. Users can create load balancers with different routing algorithms, including round-robin, least connections, and IP hash, to efficiently manage traffic distribution based on specific application needs.
AWS Direct Connect provides a dedicated network connection between an organization's on-premises data center and the AWS cloud, enabling predictable network performance and reduced data transfer costs. By establishing private connectivity with AWS, users can bypass the public internet and route traffic directly to their VPCs, enhancing security and reliability for mission-critical workloads.
In conclusion, effective network traffic routing in AWS is essential for optimizing performance, scalability, and security across cloud environments. By leveraging AWS's comprehensive set of routing tools and services, organizations can design robust network architectures that meet their specific requirements and deliver seamless user experiences for their applications and services.
VPN Configuration for AWS Console
VPN Configuration for AWS Console
Setting up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) console is crucial for ensuring secure connectivity and protecting sensitive data. By configuring a VPN in the AWS console, you can establish encrypted communication channels between your on-premises infrastructure and your AWS resources, creating a private and secure network environment.
To begin the VPN configuration process in the AWS console, you first need to select the Virtual Private Gateway (VPG) and set up the necessary routing and security settings. The VPG serves as the entry and exit point for traffic flowing between your on-premises network and AWS. Next, you will need to configure the Customer Gateway (CGW), which represents your physical device or software application responsible for connecting to the AWS VPN endpoint.
Once the VPG and CGW are set up, you can create a VPN connection that establishes the secure tunnel between your on-premises network and AWS. This connection utilizes industry-standard encryption protocols to safeguard data in transit. You can then update the routing tables to direct traffic through the VPN tunnel for secure communication.
Additionally, it is essential to configure appropriate security groups and network access control lists (ACLs) to restrict and monitor traffic flow within the VPN environment. Regularly monitoring and auditing your VPN configuration in the AWS console is crucial to ensure compliance with security best practices and prevent any unauthorized access.
In conclusion, configuring a VPN in the AWS console enhances data security, promotes secure communication, and establishes a private network environment for your cloud resources. By following the necessary steps and best practices, you can establish a robust VPN infrastructure to protect your valuable data assets in the cloud.
Tunneling AWS Console Traffic
Tunneling AWS Console Traffic: Enhancing Security in Cloud Environments
Securing AWS console traffic is paramount for businesses relying on Amazon Web Services (AWS) for their infrastructure and services. One effective strategy to bolster security is through tunneling AWS console traffic. This method involves encapsulating console traffic within a secure tunnel, adding an extra layer of protection against potential threats.
One commonly used approach for tunneling AWS console traffic is leveraging Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology. By establishing a VPN connection between the client's network and AWS infrastructure, all console traffic is encrypted and transmitted securely over the internet. This helps prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping by malicious actors.
Another method for tunneling AWS console traffic is utilizing Secure Shell (SSH) tunneling. SSH tunneling creates a secure connection between the client's local machine and an SSH server deployed within the AWS environment. Console traffic is then routed through this encrypted tunnel, safeguarding it from interception or tampering.
Furthermore, AWS offers its own solution for tunneling console traffic through the AWS Client VPN service. This managed VPN service allows clients to securely connect to their AWS resources, including the AWS Management Console, from any location while ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
Implementing tunneling for AWS console traffic not only enhances security but also provides additional benefits such as improved network performance and flexibility in accessing AWS resources remotely. However, it's essential to configure and manage tunneling solutions properly to avoid potential misconfigurations or security vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, tunneling AWS console traffic is a proactive measure to bolster security in cloud environments. Whether through VPNs, SSH tunneling, or AWS Client VPN, organizations can safeguard their sensitive data and operations while leveraging the scalability and agility of AWS services. By prioritizing security measures like tunneling, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure a robust defense against evolving cyber threats in the cloud.
Secure Connectivity to AWS Console
When it comes to accessing the AWS Management Console, ensuring secure connectivity is crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. There are several best practices and methods that users can implement to enhance the security of their connection to the AWS console.
One of the fundamental steps to secure connectivity is the use of strong and unique passwords. Users should create complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters to make it harder for cyber attackers to crack them. Additionally, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of verification, such as a code from a mobile device, along with their password.
Furthermore, users should always access the AWS Management Console using a secure network connection. Utilizing a virtual private network (VPN) encrypts the data transmitted between the user's device and AWS servers, making it difficult for hackers to intercept and read sensitive information.
Regularly updating software and enabling encryption protocols are also vital to maintaining secure connectivity to the AWS console. Users should ensure that their browsers and operating systems are up to date to patch any security vulnerabilities. Enabling secure socket layer (SSL) and transport layer security (TLS) protocols encrypt data during transmission, strengthening the overall security of the connection.
Overall, by following these security best practices, users can establish and maintain a secure connection to the AWS Management Console, safeguarding their data and protecting their AWS resources from potential threats.
0 notes
Text
EC2 Auto Recovery: Ensuring High Availability In AWS
In the modern world of cloud computing, high availability is a critical requirement for many businesses. AWS offers a wide range of services that can help achieve high availability, including EC2 Auto Recovery. In this article, we will explore what it is, how it works, and why it is important for ensuring high availability in AWS.
What is EC2 Auto Recovery? EC2 Auto Recovery is a feature provided by AWS that automatically recovers an EC2 instance if it becomes impaired due to underlying hardware or software issues. It works by monitoring the health of the EC2 instances and automatically initiates the recovery process to restore the instance to a healthy state.
How does EC2 Auto Recovery work? It works by leveraging the capabilities of the underlying AWS infrastructure. It continuously monitors the EC2 instances and their associated system status checks. If it detects an issue with an instance, it automatically triggers the recovery process.
The recovery process involves stopping and starting the impaired instance using the latest available Amazon Machine Image (AMI). By using the latest AMI, the instance can be restored to a known good state, ensuring that any software or configuration issues causing the impairment are resolved.
In addition to using the latest AMI, it also restores any previously attached secondary EBS volumes as well as any instance-level metadata associated with the instance. This ensures that the recovered instance is as close to the original state as possible.
Why is EC2 Auto Recovery important? It is important for ensuring high availability in AWS for several reasons:
1. Automated recovery: EC2 Auto Recovery automates the recovery process, reducing the need for manual intervention in the event of an instance impairment. This helps in minimizing downtime and ensuring that the services running on the EC2 instance are quickly restored.
2. Proactive monitoring: EC2 Auto Recovery continuously monitors the health of the EC2 instances and their associated system status checks. This allows for early detection of any issues and enables proactive recovery before it becomes a major problem. This helps in maintaining the overall health and stability of the infrastructure.
3. Simplified management: Managing the recovery process of impaired instances manually can be complex and time-consuming. It simplifies the management by automating the entire process, saving time and effort for the administrators.
4. Enhanced availability: By automatically recovering impaired instances, EC2 Auto Recovery enhances the availability of EC2 instances and the services running on them. It helps in minimizing the impact of hardware and software failures on the overall system availability.
Enabling EC2 Auto Recovery Enabling EC2 Auto Recovery for an instance is a straightforward process. It can be done either through the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or AWS SDKs. The following steps outline the process through the AWS Management Console:
1. Open the EC2 console and select the target instance.
2. In the “Actions” drop-down menu, select “Recover this instance”.
3. In the recovery settings dialog, select the “Enable” checkbox for EC2 Auto Recovery.
4. Click on “Save” to enable EC2 for the instance.
Once EC2 Auto-Recovery is enabled for an instance, it starts monitoring the instance and automatically initiates the recovery process when necessary.
Limitations and Best Practices While EC2 Auto Recovery is a powerful feature, it is important to be aware of its limitations and follow best practices to ensure optimal usage. Some of the limitations and best practices include:
1. Instance types: Not all instance types are currently supported by EC2 Auto Recovery. It is important to check the AWS documentation for the list of supported instance types before enabling it.
2. Elastic IP addresses: If an instance has an associated Elastic IP address, it will be disassociated during the recovery process. To ensure seamless transition and avoid disruptions, it is recommended to use an Elastic Load Balancer and Route 53 DNS failover records.
3. Custom monitoring and recovery: EC2 Auto Recovery is primarily designed for system status checks. If you have custom monitoring in place, it is important to ensure that it is integrated with it.
4. Testing and validation: It is recommended to test and validate the recovery process regularly to ensure that it works as expected. This can be done by manually triggering a recovery or using the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) or SDKs.
Conclusion EC2 Auto Recovery is a powerful feature provided by AWS that helps ensure high availability by automatically recovering impaired it’s instances. By automating the recovery process, it reduces downtime, simplifies management, and enhances overall availability. It is important to be aware of the limitations and follow best practices to ensure it’s optimal usage. By leveraging this feature, businesses can effectively improve the reliability and resilience of their infrastructure in the cloud.
0 notes
Text
Essential Requirements for Starting Your AWS Journey
Before embarking on your journey to master Amazon Web Services (AWS), it's crucial to ensure you have a solid understanding of key foundational concepts from The Best AWS Course in Bangalore.

Cloud Computing Fundamentals:
Familiarize yourself with the core principles of cloud computing, including virtualization, scalability, elasticity, and the pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Networking Basics:
Develop a grasp of essential networking concepts like IP addressing, subnets, routing, and firewall configurations, as these form the backbone of virtual networks in AWS.
Operating System Proficiency:
Acquire proficiency in operating systems, particularly Linux, which is widely used in AWS environments. Command-line proficiency is also beneficial for efficient management.
If you want to learn more about AWS , I highly recommend the AWS online training because they offer certifications and job placement opportunities. You can find these services both online and offline.

Understanding Web Technologies:
Gain knowledge of web technologies such as HTTP/HTTPS protocols, DNS management, SSL certificates, and web server configurations, which are integral to AWS for web hosting and deployment.
Programming Skills (Optional but Recommended):
While not mandatory, having programming skills, especially in Python, can greatly facilitate interactions with AWS through automation and scripting for enhanced efficiency.
Foundational Security Principles:
Understand fundamental security principles like encryption techniques, access control mechanisms, and data protection strategies, as security is paramount in AWS and cloud computing.
Database Fundamentals:
Familiarize yourself with basic database concepts including relational databases, NoSQL databases, and data modeling, as AWS offers a wide range of database services.
Embrace Lifelong Learning:
Recognize that AWS is a dynamic ecosystem with continuously evolving services and features. Cultivate a mindset of continuous learning to stay abreast of the latest advancements in cloud computing and AWS.
By ensuring a solid grasp of these foundational areas, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of AWS and leverage its diverse array of services effectively. Remember to reinforce your learning through practical application and hands-on experimentation. Happy exploring on your AWS journey!
0 notes
Text
How to deploy an application and make it publicly available to the Internet on AWS
Your application must run on a server, which listens to traffic on an Internal port. Expose it to the Internet with a Reverse Proxy (something that catches traffic from outside through a certain port, say 443 or 80, and directs it to something listening inside your server, on a local port such as 3000).
Apache can be used as a reverse proxy, but there are myriad other ways to do it. NGINX is a very good one. Traefik also works as a reverse proxy if you're into golang.
Then, you would have to make sure that your server is not behind a firewall that blocks traffic on ports 80 or 443. In AWS the equivalent of this is to enable certain security groups on your VPC.
If you control your Network Gateway (router), you'd need to port forward traffic from the Internet, on ports 80/443/etc. onto your reverse proxy server.
At this point you should be able to access your content by sending HTTP requests to :80 or :443 from anywhere on the internet (WARNING: EC2 instances have internal and public (external) IP addresses. Do not confuse the EC2-specific internal address with your public address).
You don't control the "Network Gateway" so to say in AWS, so you may want to do the following: fall back onto their managed services to procure ingress.
Your mileage may vary but simply setting up an ELB is the recommended course of action in AWS. Yes, I know that AWS ELB is intended for scalability scenarios, but you can effectively set an ELB with just one sole entry.
You can create a Classic (L6) or Application (L7) Elastic Load Balancer, which will allow you to configure rules to port forward. You can also setup redundancy and high availability through this, but that's advanced territory. Which level you need, is usually up to you because balancing at different levels of the OSI level allows you to do certain tricks or not. For example, you can balance depending on the contents of the HTTP request headers if you use an L7 (Application) load balancer; L6 usually implies that the load balancing is performed at the router (DNS) level.
The LB will produce a generic "URL" that you will use to access your server.
Another AWS managed service, "API gateway" can also do this for you so you don't have to. You can create either a REST API or HTTP API on AWS API Gateway, which basically handles Ingress to your infrastructure with a few extra niceties baked in on top.
Finally, you probably want to configure things so you can access your application using a domain name of your choice. This is achieved through configuring the A and C records for your domain with an internet-wide DNS provider. AWS has this, with Route 53 --you can use a different DNS provider too, most domain name registrars provide this service too.
0 notes