#electronic navigation software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Embracing Digital Transformation: Unlocking the Benefits of ECDIS Charts Discover the advantages of ECDIS charts, digital nautical publications, and electronic record books. Embrace digital transformation at AMNautical for efficient navigation.
#electronic navigation software#digital navigation charts#digital charts#nautical charts#electronic navigation charts
0 notes
Text
Vehicle Recall: Ford Expedition, Maverick & F-Series; Lincoln Navigator:
#2022 Ford Maverick Pickup Trucks#25V132000#crash hazard#Electronics#Ford#Ford Expedition Sport Utility Vehicles ("SUVs")#Ford F-150 Pickup Trucks#Ford F-250 Pickup Trucks#Ford F-350 Pickup Trucks#Ford F-450 Pickup Trucks#Ford F-550 Pickup Trucks#Ford Maverick Pickup Trucks#Ford Motor Company#fuel leak hazard#injury hazard#Integrated Trailer Brake Control Module Software#Laceration hazard#Lincoln Navigator Sport Utility Vehicles ("SUVs")#NHTSA#NHTSA Campaign Number: 25V132000#Recalls Direct RIN: 19535-2025#software error#Software miscoding and/or malfunction#US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration ("NHTSA")
0 notes
Text
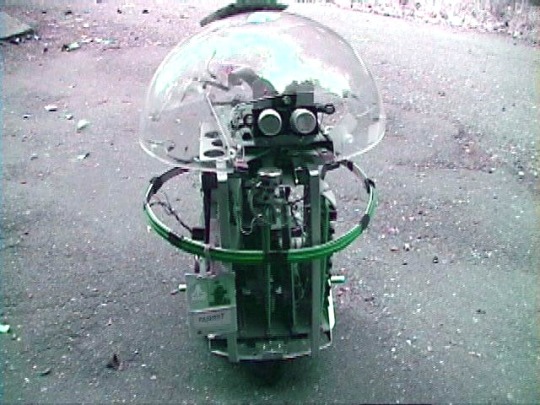
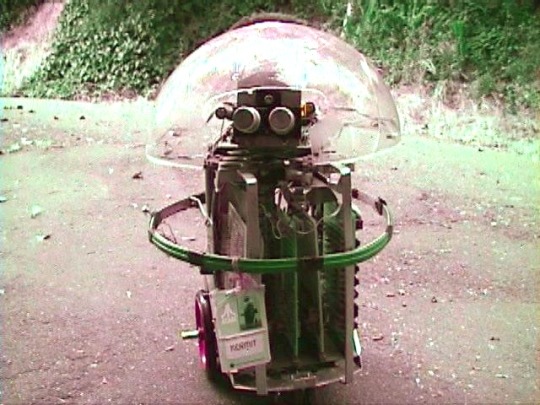
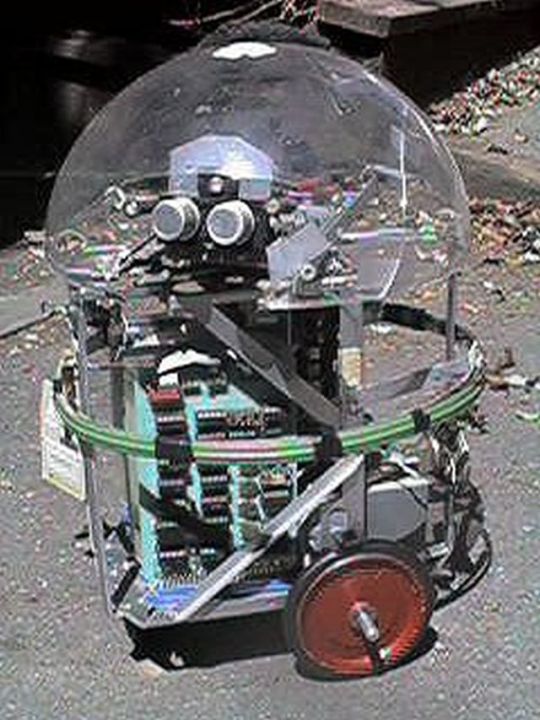
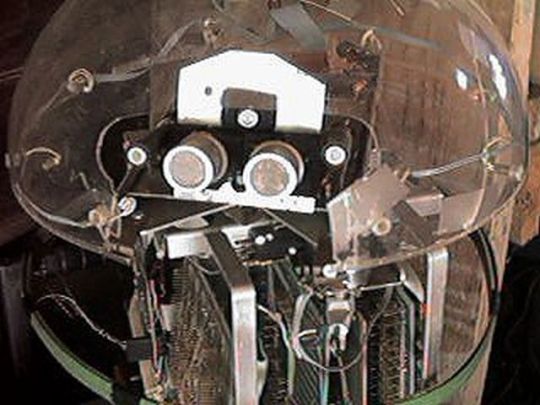




Kermit (1978), by Ron Milner and Larry Nicolson, Cyan Engineering, Atari's secret think tank in Grass Valley, CA.
"The robot was a pet project for Nolan Bushnell, then still the head of Atari and a very creative guy. Its purpose in life was as Nolan put it to "bring me a beer!" Navigation for robots was a sketchy thing at that time with lots of pioneering work at MIT but no consumer cost ideas. Nolan brought us the incredibly original idea to navigate a robot (which mostly meant knowing where it was) by means of scanning bar codes attached here and there to the baseboards in the rooms the robot was to service. Why it wasn't patented I don't know.
I had lots of fun building the R2D2 style robot about 20" tall. I liked to put mechanical and electronic things together and we had a great shop at Cyan. Its brain was one of the 6502 based single board computers-I think it was a KIM but not sure. Locomotion was two DC gear motor driven wheels and an instrumented caster-about the same rig as a modern Roomba. A rotatable turret covered with a plexiglass dome carried microphones, an IR sensor to detect people, and ultrasonic ranging sensors I built on a separate PC board. A speaker so Kermit could beep gleefully, of course.
A ring of contact-detecting burglar alarm sensing tape (green in the pictures) around Kermit's middle told the software he had hit something and should back off. The ultrasonics provided range to obstacles and to some extent direction as the turret was rotated, so we could go around things.
My pride and joy was the barcode remote scanner which was mounted on the bottom of the robot so its rotating head would be level with the barcodes on the baseboards. It had a vertical telescope tube with a beam splitter between the IR Led and the photodiode sensor and a lens to focus 2-20' away. It aimed down at a front surface mirror at 45 degree to scan horizontally. The mirror was mounted on a motor driven turret so it spun around continuously with a sensor once around to resolve the continuous angular position of the beam horizontally of course with respect to Kermit's rotational position. Unfortunately, this part of the robot did not survive the closing of our group. The barcodes I made for the prototype to detect were about 4" tall made of 3/4" reflective 3m tape on black poster board.
My programming partner on the project was Larry Nicholson, a really bright guy. He made the barcode reading work to detect not only the barcodes, but where they were angularly with respect to the robot and also their subtended angle or apparent size (all from timing of the rotation of the scanner) which was a measure of distance combined with angle from the barcode. We worked out some pretty clever math to resolve that information from two or three of the barcodes into a position and orientation of Kermit in the room. We had rented an empty room upstairs on the third floor of the Litton building to try all this out and work out the navigation. Larry and I got the basic navigation and obstacle avoidance working so Kermit could go from one place to a designated other place in the room and avoid wastebaskets placed randomly. We demonstrated it to Nolan and he was impressed.
Shortly thereafter Warner Communication who had bought Atari from Nolan kicked him out and the Kermit project was cancelled."
– Kermit The Robot Notes by Ron Milner.
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
So this is part 2 of this post, if yall wanna give it a read for context.
In this post, I’ll be talking about how Color’s physical disability of having only one eye would influence how he interacts with his special interests in photography and travel.
As well as how his PTSD, autism, chronic fatigue, and separation anxiety from Killer could also affect things.
With one eye, Color might have reduced depth perception, which could make it challenging to gauge distances accurately. He might rely more on autofocus features, practice to enhance his spatial awareness, or use techniques like focus stacking for precise shots.
He might prefer using cameras with electronic viewfinders (EVF) or live view screens rather than optical viewfinders, which could be more challenging to use with one eye. Adjusting camera settings and composing shots via a larger display would be easier.
He might develop unique framing and composition techniques, leveraging his perspective creatively. Color could take extra time to ensure his shots are well-composed, possibly using grid overlays or other aids to help with alignment.
Customizing camera gear to suit his needs, such as using tripods, stabilizers, or remote controls, to help steady the camera and compose shots more comfortably.
He might spend additional time in post-processing to correct any minor misalignments or issues that arise from the reduced depth perception during the shooting process.
For travel, navigating unfamiliar places might require more caution, especially in crowded or complex environments. He might use mobility aids, rely on GPS and mapping apps, or travel with companions to ensure safety.
Color could engage in meticulous planning to minimize unexpected challenges, such as researching accessible routes, accommodations, and transportation options.
Color might use his experiences and perspective to connect with others, sharing how his disability influences his travel and photography, fostering understanding and empathy.
Developing strategies to cope with the physical demands of travel, such as pacing himself, taking regular breaks, and prioritizing destinations or activities that are less physically demanding.
His unique perspective could inspire him to create compelling stories or advocacy pieces about accessibility in travel and photography, raising awareness and inspiring others with disabilities.
Embracing his distinct view of the world, his photography could offer unique perspectives that stand out, turning his perceived limitation into an artistic advantage.
He might become involved in communities focused on accessible travel and photography, sharing tips, experiences, and inspiring others with similar challenges.
Autism and chronic fatigue would likely significantly impact Color’s ability to engage with his special interests in photography and travel.
In photography, chronic fatigue would necessitate careful energy management. Color might plan shorter, more focused photography sessions and prioritize rest to avoid burnout.
Streamlining his workflow, from setting up equipment to post-processing, to conserve energy. This could include using presets in editing software or organizing his gear for easy access.
He could chose photography locations that are easily accessible and require minimal physical exertion. He might also prefer locations close to home or base to reduce travel time and energy expenditure.
He would likely use ightweight equipment to reduce physical strain, possibly investing in high-quality but compact cameras and lenses. He might also use monopods or lightweight tripods for additional support.
Autism can come with sensory sensitivities. Color might choose quieter, less crowded locations for photography and use noise-canceling headphones or other tools to manage sensory overload.
With travel, he’d have to pace himself. Planning travel with built-in downtime to rest and recharge. He might avoid overly ambitious itineraries and allow for flexible scheduling to accommodate his energy levels.
He’d probably chose ccommodations that are comfortable, quiet, and accessible, ensuring he has a safe space to retreat to when needed.
He’d prefer modes of transportation that offer comfort and minimal stress, such as direct flights, train travel, or driving. He might also opt for private or semi-private tours to control the pace and environment.
Keeping up with healthcare needs, including regular check-ups, medication management, and any necessary accommodations. He might also carry a travel health kit tailored to his specific needs.
He’d combine photography with travel in a way that maximizes enjoyment and minimizes strain. For example, he might focus on travel photography during the golden hours (early morning and late afternoon) when conditions are optimal, and the rest of the day can be used for rest.
Creating content that reflects his experiences with autism and chronic fatigue, such as blogs, vlogs, or social media posts. This can help raise awareness and provide valuable insights to others with similar challenges.
Engaging with communities of autistic travelers and photographers to share experiences, tips, and support. This can provide a sense of camaraderie and practical advice tailored to his needs.
Establishing routines that provide predictability and reduce stress. This might include having a consistent photography and travel routine, preparing for trips well in advance, and creating checklists.
Practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques to manage stress and sensory overload. This can help maintain focus and calm, particularly in challenging environments.
Utilizing assistive technologies, such as apps for energy tracking, sensory-friendly gear, or digital tools that aid in planning and organization.
Color’s PTSD from solitary confinement and isolation in the Void, combined with his separation anxiety towards Killer, can create a complex situation that both challenges and shapes his engagement in traveling and photography.
Color’s need to stay on the move due to PTSD makes traveling appealing, as it provides a sense of freedom and escape from confinement. However, this constant movement could also become exhausting and anxiety-inducing if it lacks purpose or stability.
His separation anxiety towards Killer might lead him to seek Killer’s company while traveling. Traveling with Killer could provide a sense of security and reduce his anxiety, but it also means his travel plans would need to align with Killer’s availability and willingness to join him.
Color might need to carefully plan his travels to ensure he has safe and familiar places to stay, reducing the unpredictability that could trigger his PTSD. Having a structured itinerary could help him feel more in control and less anxious.
Traveling to new and unfamiliar places might sometimes trigger memories of his isolation, especially if he encounters situations that remind him of the Void. He would need to find a balance between exploring new places and ensuring his mental well-being.
Photography could serve as a therapeutic outlet, allowing Color to process and express his emotions through capturing images. It might help him make sense of his experiences and provide a way to externalize his trauma.
Color might be drawn to photographing subjects that reflect his internal state or provide a sense of solace. He could focus on themes like freedom, movement, and connection, finding meaning and healing in his work.
Having Killer around while engaging in photography could provide comfort and reduce his anxiety. Killer might even become a frequent subject in Color’s photos, symbolizing their bond and mutual support.
Color might need to develop strategies to manage his anxiety while photographing, such as taking breaks, grounding exercises, or having a trusted companion like Killer present. This would help him stay focused and engaged in his special interest.
The mutual separation anxiety between Color and Killer could strengthen their bond, as they rely on each other for emotional support. This bond could provide Color with the stability he needs to engage in his interests.
Color would need to balance his need for movement and exploration with Killer’s needs and limitations. They might develop a mutual understanding and compromise, ensuring both their well-being while pursuing their interests.
Color might prefer traveling to places where he can easily find comfort and familiarity, such as visiting friends or known locations. This reduces the stress of the unknown and helps him stay grounded.
Establishing routines or rituals while traveling and photographing can provide a sense of stability. For example, always starting the day with a specific activity or having regular check-ins with Killer can help Color manage his anxiety.
They might have frequent phone calls if Killer ever can’t join Color on his travels, at particular times of the day.
I can see Color sticking to this routine at the exact time and getting anxious and worried if Killer doesn’t call or pick up, which is likely to happen at some point simply because he has memory issues and sticking to routine is hard for him. But Color, at least for a bit, is likely to assume the worse.
Color might also keep a photograph of him and all his friends close by on his person. (I also like to think that Delta made his camera, he keeps some of Beta’s drawings with him, and also he’s memorized the recipe for Epic’s chocolate cookies.)
If he and Killer have already had their wedding by this point, he’d likely keep his ring close and near. Perhaps kissing it before bed, and fidgeting with it becomes a new comforting stim.
Over time, engaging in his special interests despite his PTSD and anxiety can help Color build resilience. Each successful trip or photography session can boost his confidence and reinforce his ability to cope with challenges.
Color might find deeper meaning in his travels and photography by using them as tools for healing and connection. Documenting his journey and sharing it with others can create a sense of purpose and community.
#utmv headcanons#color spectrum duo#colorkiller#color sans#colour sans#color!sans#killer sans#utmv#sans au#sans aus#killer!sans#killertale#othertale#othertale sans#other sans#undertale#autistic headcanon#utmv hc#undertale au#undertale aus#undertale multiverse#epic sanses#bad sanses#bad sans gang#< for reach#killercolor#undertale something new#epic!sans#delta!sans#cross!sans
39 notes
·
View notes
Note
How do you make UI recolors? I wanted to make my own but I don't know how to get started.
How to make your own UI recolours for The Sims 3
note:
this guide is for the Windows PC, Steam Version of The Sims 3, because that is what i have
dino_rex's thread:
this thread is what got me started
you can download the starter packs on the attached files of this post
i don't use this starter pack anymore because it's limited and didn't include what i wanted to change
i would recommend that you use the other options below...
start small first:
i wrote a similar post on creating custom loading screens here, so this post will be VERY similar to that!
please start with that tutorial first to get familiarized with the whole editing process, then move on...
now, to do it yourself:
first, navigate to where your TS3 game is installed:
Steam -- Program Files (x86)\Steam\steamapps\common\The Sims 3\
DVD 34 bit-- Program Files\Electronic Arts\The Sims 3\
DVD 64 bit-- Program Files (x86)\Electronic Arts\The Sims 3\
Origin 34 bit -- Program Files\Origin Games\The Sims 3\
Origin 64 bit-- Program Files (x86)\Origin Games\The Sims 3\
// idk the path for non-Windows installations //
NOT THIS -- Documents\Electronic Arts\The Sims 3
navigate to:
\GameData\Shared\Packages\
and the packages you are looking for are:
FullBuild0.package
DeltaBuild0.package
for BOTH packages, do this:
Open in S3PE
Resource
Select all
Export
To file...
Choose a folder to export to (An example: have a primary YourProjectName folder, with 2 folders within it: Originals and Edited. Within Originals is 2 folders: FullBuild and DeltaBuild)
Export the files to the appropriate folder
now that you've exported the Originals, time to make your edits:
Navigate to YourProjectName folder
COPY the original file that you want to edit (from the Originals folder)
Place it in the Edited folder
Edit these files with your preferred image editor
Open S3PE and have your File Explorer up
Select the images you've edited in your File Explorer (Ctrl+A to select all)
Drag to S3PE
Popup window: Import
Wait until it's complete
Hit X to close S3PE
Save? Yes.
Choose a name for your package
Save
Copy this package to your Mods folder
Start your game. Changes should appear.
Repeat until you are satisfied with your changes
my version
my 3 UI recolour projects (Sakura, Wisteria, Celeste) are based on this starter template repository on GitHub. don't use this template because it is stylized / customized for MY OWN three projects, and may NOT be what you want. however, you can copy the folder structure and look up what files to change for your own project (as inspiration).
i highly recommend that you use GitHub to BACKUP and TRACK your changes (or another version control software)
happy editing!
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey! I’m gonna be a physics major next year, and I was wondering if the Mac and iPad combo have worked well for you, or if there’s something else you recommend tech wise?
short answer: yes.
but, im gonna use this has an opportunity to yap about my current study set up. this goes without saying, but what worked for me may not work for you, and my set up evolved over the years as i found what was best for me.
i use an iPad for lecture notes and homework. i think its the most organized you can get them to be without straight up LaTeXing the shit out of them (and i know people who do exactly that, more power to them)
i just write faster than i type, and an ipad allows me to copy paste equations and add photos and stuff which is helpful for diagrams. i use goodnotes 5, and i will sing its praises till the end of time.
i think it pays to develop a clear style for your homework and lecture notes, bc your work will be easier to navigate. here's an example of my lecture notes and my homework.

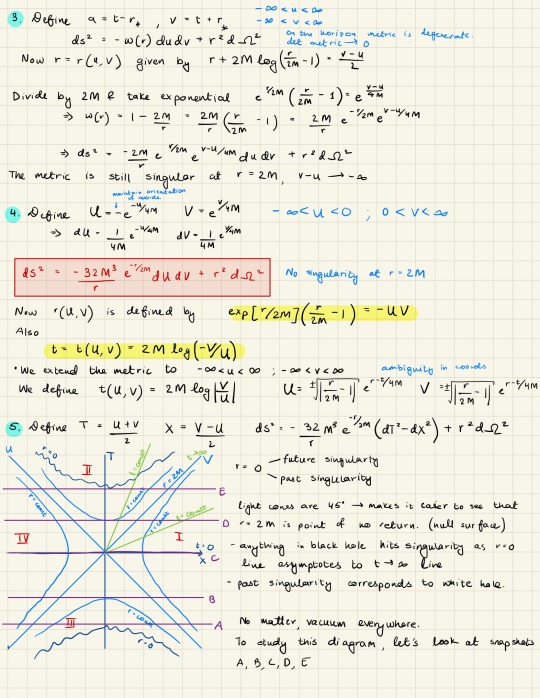
[hehe general relativity moment]
HOWEVER, you will mostly be having paper exams as a physics student so i recommend you don't get too reliant on your iPad. i tend to do all my studying in notebooks, or loose sheets that i can refer to. practice problems are always on paper.

[stat mech studying i did last week]
i started using legal pads for this from the end of junior year bc they're so convenient! im also incentivized by the stock our dept keeps in the mail room.
i have to do a lot of calculations for research and i prefer to do them on paper or a blackboard if it's something im reasoning out. idk it's so much easier to be stupid on paper than on goodnotes. ofc my research log is kept digitally, but i keep a binder with all my old calculations (both correct, and incorrect) along with my main reference papers.
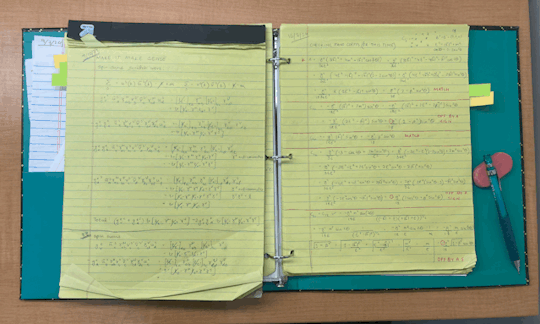
[i was flipping through this just now and realised how much bs is in it.]
LaTeX is a good skill to have which i didn't realise until too late. if you have to write any paper that's remotely scientific, LaTeX is the way to go. none of that google docs bs.
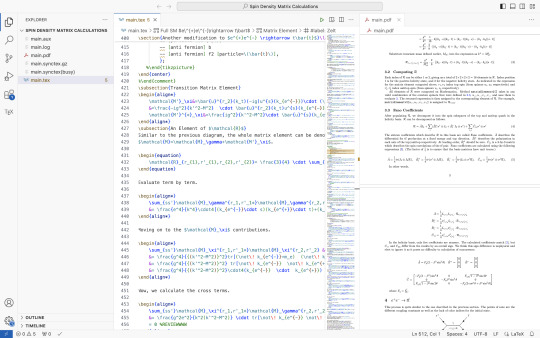
i use both vscode and Overleaf for editing. i mainly just LaTeX my finalized research calculations into one big doc. it's much easier to show my advisor. also it looks cool.
i got a monitor when my laptop screen broke sophomore spring (something inside me broke as well that semester it was so fun). and if you have the option, i would totally recommend getting one. it's useful having a second/bigger screen.

i use mine for a bunch of things: coding, reading textbooks, genshin impact, Netflix, grading.
on the topic of textbooks, i use digital bc im cheap. but i do buy secondhand physical copies that i rarely reference, but keep around bc it doesn't hurt to start your hypothetical professor office bookshelf early. i only buy the ones i actually respect, like Peskin's Intro to QFT. but the digital copies are usually much handier. i keep an extensive digital collection of books and papers i might never need.
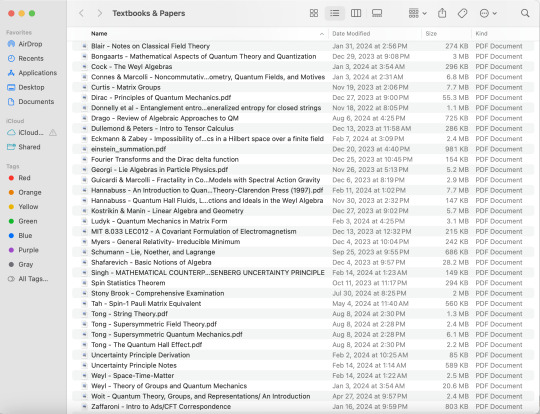
don't be like me keep your digital library more organized!
and yeah circling back to electronics! i use a Macbook Pro rn which has served me well. i guess things are different if you need to run solidworks or other specialized software, but you can always use the lab computers, so that was never a problem. i have an apple ecosystem bc im a slut for capitalism.. i mean i was already halfway there and now im just really used to it, so i like all my devices being friends with each other. my tip is always get more RAM than you thought you needed, and double the storage. but maybe that's bc im mean to my laptop and love hoarding files.
i also keep all my previous notes and printouts so may be i have an academic hoarding problem in general.
in the end, a mix of old school and new age technology bs works best for me!
thank you for your question! i hope this helps :)
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
I feel like every post on this site offering advice about how to navigate consumer electronics, providing links to online resources or downloads for software should come with a big flashing banner at the top stating that all information below will be obsolete in 6 months
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
NitroTracker
Made by 0xtob (NitrousTracker fork maintained by asiekierka and others) Downloads: - NitrousTracker, an improved fork with DSi Support - Original version - GameBrew Page

Music trackers, anyone? No? Have this anyway.
Personally, I would consider Nintendo DS systems a good way to make music. The console had lots of both official ways to compose tracks (like Rhythm Core Alpha 2, Rytmik series and - my favorite - Korg M01) and unofficial, the highlight being NitroTracker.
It's based on a FastTracker II interface and works with XM tracker module format for music and WAV format for samples. The tracker files are lightweight and can be easily played on other platforms - most modern music players support them quite well.
All the music creation is done by switching between two screens - one is used for managing the song, including instrument samples and music patterns, and the other one is where you put notes to play. This makes the interface, while a bit cluttered, quite easy to navigate.
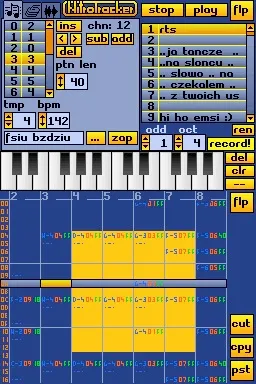
This is how the old one looked. Surprisingly not much different.
This DS homebrew is pretty ancient - it was made back in at least 2008! Around 2020, asiekierka started improving the homebrew with support for DSi mode (meaning more memory for samples and better performance), loop points in samples and other quality-of-life changes. There's also ability to set note effects in development.
I'd say this app is the most powerful when it comes to making music on your Nintendo DS, mainly because you can provide your own samples and even use XM modules made in other trackers.
Just for you all, I've collected some of the NitroTracker songs in a playlist. Most of them belong to Jungle, Drum & Bass or some other electronic genre, and there's a few that I made myself as well! (You'll know when you start hearing something bad in the playlist /j)
Feel free to experiment with this software and even share your tracks in the asks or replies or anywhere on Tumblr!
-- Red
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leveraging XML Data Interface for IPTV EPG
This blog explores the significance of optimizing the XML Data Interface and XMLTV schedule EPG for IPTV. It emphasizes the importance of EPG in IPTV, preparation steps, installation, configuration, file updates, customization, error handling, and advanced tips.
The focus is on enhancing user experience, content delivery, and securing IPTV setups. The comprehensive guide aims to empower IPTV providers and tech enthusiasts to leverage the full potential of XMLTV and EPG technologies.
1. Overview of the Context:
The context focuses on the significance of optimizing the XML Data Interface and leveraging the latest XMLTV schedule EPG (Electronic Program Guide) for IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) providers. L&E Solutions emphasizes the importance of enhancing user experience and content delivery by effectively managing and distributing EPG information.
This guide delves into detailed steps on installing and configuring XMLTV to work with IPTV, automating XMLTV file updates, customizing EPG data, resolving common errors, and deploying advanced tips and tricks to maximize the utility of the system.
2. Key Themes and Details:
The Importance of EPG in IPTV: The EPG plays a vital role in enhancing viewer experience by providing a comprehensive overview of available content and facilitating easy navigation through channels and programs. It allows users to plan their viewing by showing detailed schedules of upcoming shows, episode descriptions, and broadcasting times.
Preparation: Gathering Necessary Resources: The article highlights the importance of gathering required software and hardware, such as XMLTV software, EPG management tools, reliable computer, internet connection, and additional utilities to ensure smooth setup and operation of XMLTV for IPTV.
Installing XMLTV: Detailed step-by-step instructions are provided for installing XMLTV on different operating systems, including Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux (Debian-based systems), ensuring efficient management and utilization of TV listings for IPTV setups.
Configuring XMLTV to Work with IPTV: The article emphasizes the correct configuration of M3U links and EPG URLs to seamlessly integrate XMLTV with IPTV systems, providing accurate and timely broadcasting information.
3. Customization and Automation:
Automating XMLTV File Updates: The importance of automating XMLTV file updates for maintaining an updated EPG is highlighted, with detailed instructions on using cron jobs and scheduled tasks.
Customizing Your EPG Data: The article explores advanced XMLTV configuration options and leveraging third-party services for enhanced EPG data to improve the viewer's experience.
Handling and Resolving Errors: Common issues related to XMLTV and IPTV systems are discussed, along with their solutions, and methods for debugging XMLTV output are outlined.
Advanced Tips and Tricks: The article provides advanced tips and tricks for optimizing EPG performance and securing IPTV setups, such as leveraging caching mechanisms, utilizing efficient data parsing tools, and securing authentication methods.
The conclusion emphasizes the pivotal enhancement of IPTV services through the synergy between the XML Data Interface and XMLTV Guide EPG, offering a robust framework for delivering engaging and easily accessible content. It also encourages continual enrichment of knowledge and utilization of innovative tools to stay at the forefront of IPTV technology.
3. Language and Structure:
The article is written in English and follows a structured approach, providing detailed explanations, step-by-step instructions, and actionable insights to guide IPTV providers, developers, and tech enthusiasts in leveraging the full potential of XMLTV and EPG technologies.
The conclusion emphasizes the pivotal role of the XML Data Interface and XMLTV Guide EPG in enhancing IPTV services to find more information and innovative tools. It serves as a call to action for IPTV providers, developers, and enthusiasts to explore the sophisticated capabilities of XMLTV and EPG technologies for delivering unparalleled content viewing experiences.
youtube
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shortly before noon on Aug. 19, 2023, a Russian cruise missile sliced past the golden onion domes and squat apartment blocks of the Chernihiv skyline in northern Ukraine. The Iskander-K missile slammed into its target: the city’s drama theater, which was hosting a meeting of drone manufacturers at the time of the attack. More than 140 people were injured and seven killed. The youngest, 6-year-old Sofia Golynska, had been playing in a nearby park.
Fragments of the missile recovered by the Ukrainian armed forces and analyzed by Ukrainian researchers found numerous components made by U.S. manufacturers in the missile’s onboard navigation system, which enabled it to reach its target with devastating precision. In December, Ukraine’s state anti-corruption agency released an online database of the thousands of foreign-made components recovered from Russian weapons so far.
Russia’s struggle to produce the advanced semiconductors, electrical components, and machine tools needed to fuel its defense industrial base predates the current war and has left it reliant on imports even amid its estrangement from the West. So when Moscow launched its full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, major manufacturing countries from North America, Europe, and East Asia swiftly imposed export controls on a broad swath of items deemed critical for the Russian arms industry.
Russia quickly became the world’s most sanctioned country: Some 16,000 people and companies were subject to a patchwork of international sanctions and export control orders imposed by a coalition of 39 countries. Export restrictions were painted with such a broad brush that sunglasses, contact lenses, and false teeth were also swept up in the prohibitions. Even items manufactured overseas by foreign companies are prohibited from being sold to Russia if they are made with U.S. tools or software, under a regulation known as the foreign direct product rule.
But as the war reaches its two-year anniversary, export controls have failed to stem the flow of advanced electronics and machinery making their way into Russia as new and convoluted supply chains have been forged through third countries such as Kazakhstan, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates, which are not party to the export control efforts. An investigation by Nikkei Asia found a tenfold increase in the export of semiconductors from China and Hong Kong to Russia in the immediate aftermath of the war—the majority of them from U.S. manufacturers.
“Life finds a way,” said a senior U.S. intelligence official, quoting the movie Jurassic Park. The official spoke on background to discuss Russia’s evasion of export controls.
Some of the weapons and components analyzed by investigators were likely stockpiled before the war. But widely available Russian trade data reveals a brisk business in imports. More than $1 billion worth of advanced semiconductors from U.S. and European manufacturers made their way into the country last year, according to classified Russian customs service data obtained by Bloomberg. A recent report by the Kyiv School of Economics found that imports of components considered critical for the battlefield had dipped by just 10 percent during the first 10 months of 2023, compared with prewar levels.
This has created a Kafkaesque scenario, the report notes, in which the Ukrainian army is doing battle with Western weapons against a Russian arsenal that also runs on Western components.
It is an obvious problem, well documented by numerous think tank and media reports, but one without an easy solution. Tracking illicit trade in items such as semiconductors is an exponentially greater challenge than monitoring shipments of conventional weapons. Around 1 trillion chips are produced every year. Found in credit cards, toasters, tanks, missile systems, and much, much more, they power the global economy as well as the Russian military. Cutting Russia out of the global supply chain for semiconductors is easier said than done.
“Both Russia and China, and basically all militaries, are using a large number of consumer electronic components in their systems,” said Chris Miller, the author of Chip War: The Fight for the World’s Most Critical Technology. “All of the world’s militaries rely on the same supply chain, which is the supply chain that primarily services consumer electronics.”
Export controls were once neatly tailored to keep specific items, such as nuclear technology, out of the hands of rogue states and terrorist groups. But as Washington vies for technological supremacy with Beijing while also seeking to contain Russia and Iran, it has increasingly used these trade restrictions to advance broader U.S. strategic objectives. For instance, the Biden administration has placed wide-ranging prohibitions on the export of advanced chips to China.
“At no point in history have export controls been more central to our collective security than right now,” Matthew Axelrod, the assistant secretary for export enforcement at the U.S. Commerce Department, said in a speech last September. U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan has described export controls as “a new strategic asset in the U.S. and allied toolkit.”
Russia’s ability to defy these restrictions doesn’t just have implications for the war in Ukraine. It also raises significant questions about the challenge ahead vis-à-vis China.
“The technological question becomes a key part of this story and whether or not we can restrict it from our adversaries,” said James Byrne, the director of open-source intelligence and analysis at the Royal United Services Institute, a British think tank.
In the Russian city of Izhevsk, home to the factory that manufactures Kalashnikov rifles, shopping malls are being converted into drone factories amid a surge in defense spending that has helped the country’s economy weather its Western estrangement. Arms manufacturers have been urged to work around the clock to feed the Russian war machine, while defense is set to account for one-third of the state budget this year.
“We have developed a concept to convert shopping centers—which, before the start of the SMO [special military operation], sold mainly the products of Western brands—to factories for assembly lines of types of domestic drones,” Alexander Zakharov, the chief designer of the Zala Aero drone company, said at a closed event in August 2022, according to the Russian business newspaper Vedomosti. “Special military operation” is what the Russian government calls its war on Ukraine. Zala Aero is a subsidiary of the Kalashnikov Concern that, along with Zakharov, was sanctioned by the United States last November.
Defense companies have bought at least three shopping malls in Izhevsk to be repurposed for the manufacture of drones, according to local media, including Lancet attack drones, which the British defense ministry described as one of the most effective new weapons that Russia introduced to the battlefield last year. Lancets, which cost about $35,000 to produce, wreaked havoc during Ukraine’s offensive last year and have been captured on video striking valuable Ukrainian tanks and parked MiG fighter jets.
Like a lot of Russia’s weapons systems, Lancets are filled with Western components. An analysis of images of the drones published in December by the Washington-based Institute for Science and International Security found that they contained several parts from U.S., Swiss, and Czech manufacturers, including image processing and analytical components that play a pivotal role in enabling the drones to reach their targets on the battlefield.
“The recurring appearance of these Western products in Russian drone systems shows a keen dependence on them for key capabilities in the drone systems,” the report notes. Lancets are not the only drones found to contain Western components. Almost all of the electronic components in the Iranian Shahed-136 drones, which Russia is now manufacturing with Iranian help to use in Ukraine, are of Western origin, a separate analysis published in November concluded.
Early in the war, the Royal United Services Institute analyzed 27 Russian military systems, including cruise missiles, electronic warfare complexes, and communications systems, and found that they contained at least 450 foreign-made components, revealing Russia’s dependence on imports.
One of the principal ways that Russia has evaded Western export controls has been through transshipment via third countries such as Turkey, the UAE, and neighboring states once part of the Soviet Union. Bloomberg reported last November that amid mounting Western pressure, the UAE had agreed to restrict the export of sensitive goods to Russia and that Turkey was considering a similar move. Kazakh officials announced a ban on the export of certain battlefield goods to Russia in October.
Suspected transshipment is often revealed by striking changes in trade patterns before and after the invasion. The Maldives, an island chain in the Indian Ocean that has no domestic semiconductor industry, shipped almost $54 million worth of U.S.-made semiconductors to Russia in the year after the invasion of Ukraine, Nikkei Asia reported last July.
Semiconductor supply chains often span several countries, with chips designed in one country and manufactured in another before being sold to a series of downstream distributors around the world. That makes it difficult for companies to know the ultimate end user of their products. This may seem odd—until you realize that this is the case for many everyday products that are sold around the world. “When Coca-Cola sells Coca-Cola, it doesn’t know where every bottle goes, and they don’t have systems to track where every bottle goes,” said Kevin Wolf, a former assistant secretary for export administration at the U.S. Commerce Department.
While a coalition of 39 countries, including the world’s major manufacturers of advanced electronics, imposed export restrictions on Russia, much of the rest of the world continues to trade freely with Moscow. Components manufactured in coalition countries will often begin their journey to Moscow’s weapons factories through a series of entirely legal transactions before ending up with a final distributor that takes them across the border into Russia. “It starts off as licit trade and ends up as illicit trade,” said a second senior U.S. intelligence official, who spoke on condition of anonymity.
The further items move down the supply chain, the less insight governments and companies have into their ultimate destination, although sudden changes in behavior of importers can offer a red flag. In his speech last September, Axelrod, the assistant secretary, used the example of a beauty salon that suddenly starts to import electronic components.
But the Grand Canyon of loopholes is China, which has stood by Moscow since the invasion. In the first days of the war, U.S. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo warned that Washington could shut down Chinese companies that ignored semiconductor export controls placed on Russia. Last October, 42 Chinese companies were added to export control lists—severely undercutting their ability to do business with U.S. companies—for supplying Russian defense manufacturers with U.S. chips.
But as the Biden administration carefully calibrates its China policy in a bid to keep a lid on escalating tensions, it has held off from taking Beijing to task. “I think the biggest issue is that we—the West—have been unwilling to put pressure on China that would get China to start enforcing some of these rules itself,” said Miller, the author of Chip Wars.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) said: “Due to the restrictions imposed by the United States and key allies and partners, Russia has been left with no choice but to spend more, lower its ambitions for high-tech weaponry, build alliances with other international pariah states, and develop nefarious trade networks to covertly obtain the technologies it needs.
“We are deeply concerned regarding [Chinese] support for Russia’s defense industrial base. BIS has acted to add over 100 [China]-based entities to the Entity List for supporting Russia’s military industrial base and related activities.”
Export controls have typically focused on keeping specific U.S.-made goods out of the hands of adversaries, while economic and financial sanctions have served broader foreign-policy objectives of isolating rogue states and cauterizing the financing of terrorist groups and drug cartels. The use of sanctions as a national security tool grew in wake of the 9/11 attacks; in the intervening decades, companies, government agencies, and financial institutions have built up a wealth of experience in sanctions compliance. By contrast, the use of export controls for strategic ends is relatively novel, and compliance expertise is still in its infancy.
“It used to be that people like me could keep export controls and sanctions in one person’s head. The level of complexity for each area of law is so intense. I don’t know anyone who is truly an export control and sanctions expert,” Wolf said.
Export controls, experts say, are at best speed bumps designed to make it harder for Russia’s defense industrial base to procure Western components. They create “extra friction and pressure on the Russian economy,” said Daniel Fried, who as the State Department coordinator for sanctions policy helped craft U.S. sanctions on Russia after its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Russia is now paying 80 percent more to import semiconductors than it did before the war, according to forthcoming research by Miller, and the components it is able to acquire are often of dubious quality.
But although it may be more cumbersome and expensive, it’s a cost that Moscow has been willing to bear in its war on Ukraine.
Western components—and lots of them—will continue to be found in the weapons Russia uses on Ukraine’s battlefields for the duration of the war. “This problem is as old as export controls are,” said Jasper Helder, an expert on export controls and sanctions with the law firm Akin Gump. But there are ways to further plug the gaps.
Steeper penalties could incentivize U.S. companies to take a more proactive role in ensuring their products don’t wind up in the hands of the Russian military, said Elina Ribakova, a nonresident senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics. “At the moment, they’re not truly motivated,” she said.
Companies that run afoul of sanctions and the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, a U.S. federal law that prohibits the payment of bribes, have been fined billions of dollars. Settlements of export control violations are often an order of magnitude smaller, according to recently published research.
In a speech last month, Axelrod said the United States would begin issuing steeper penalties for export control violations. “Build one case against one of the companies extremely well, put out a multibillion-dollar fine negotiation, and watch everybody else fall in line,” Ribakova said.
And then there’s the question of resources. BIS has an annual budget of just $200 million. “That’s like the cost of a few fighter jets. Come on,” said Raimondo, speaking at the Reagan National Defense Forum last December.
The agency’s core budget for export control has, adjusted for inflation, remained flat since 2010, while its workload has surged. Between 2014 and 2022, the volume of U.S. exports subject to licensing scrutiny increased by 126 percent, according to an agency spokesperson. A 2022 study of export control enforcement by the Center for Strategic and International Studies recommended a budget increase of $45 million annually, describing it as “one of the best opportunities available anywhere in U.S. national security.”
When it comes to enforcement, the bureau has about 150 officers across the country who work with law enforcement and conduct outreach to companies. The Commerce Department has also established a task force with the Justice Department to keep advanced technologies out of the hands of Russia, China, and Iran. “The U.S. has the most robust export enforcement on the planet,” Wolf said.
But compared with other law enforcement and national security agencies, the bureau’s budgets have not kept pace with its expanding mission. The Department of Homeland Security has more investigators in the city of Tampa, Florida, than BIS does across the entire country, Axelrod noted in his January speech.
On the other side, you have Russia, which is extremely motivated to acquire the critical technologies it needs to continue to prosecute its war. The Kremlin has tasked its intelligence agencies with finding ways around sanctions and export controls, U.S. Treasury Undersecretary Brian Nelson said in a speech last year. “We are not talking about a profit-seeking firm looking for efficiencies,” the second senior U.S. intelligence official said. “There will be supply if there is sufficient demand.”
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why do some car manufacturers make it extremely difficult to change a headlight bulb, sometimes requiring a trip to the dealership?
Why Some Car Manufacturers Make Headlight Bulb Replacement Difficult Replacing headlight bulbs in modern vehicles can feel like navigating an engineering maze, often requiring specialized tools or dealership intervention. This complexity stems from design priorities, regulatory compliance, and advanced technology integration. Below are the key reasons and their implications:
Advanced Lighting Systems
Modern vehicles increasingly use adaptive headlights (e.g., auto-leveling, cornering beams) and integrated LED arrays or laser modules instead of traditional bulbs. These systems are tightly controlled by onboard computers and sensors. For example: Adaptive Headlights: Adjust brightness and direction based on steering input or road conditions. Even minor misalignment can disrupt the entire system, requiring recalibration with proprietary software.
Integrated LED/Laser Modules: Often soldered into sealed assemblies rather than using replaceable bulbs. Replacing them may necessitate swapping the entire headlight unit.
Engineering and Aesthetic Trade-offs
Manufacturers prioritize sleek, aerodynamic designs and compact packaging, which often result in tightly packed engine bays and headlight housings: Space Constraints: Headlights may be fused with grilles, fenders, or bumper components. Accessing the bulb might require removing the wheel well liner, battery, or air filter housing.
Proprietary Fasteners: Custom clips or screws demand specialized tools, discouraging DIY repairs.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Strict homologation rules (e.g., SAE, ECE) mandate precise beam patterns, brightness, and alignment. To ensure compliance: Tamper-Proof Designs: Manufacturers discourage aftermarket modifications by sealing systems or using non-standard components. Non-OEM parts risk failing inspections or causing glare hazards.
Self-Leveling Requirements: Adaptive headlights must maintain proper alignment with the road, which can only be reset via dealership diagnostics.
Profit and Service Model
Dealerships and certified repair shops benefit from locked-in servicing: Software Dependencies: Adaptive systems require proprietary diagnostic tools (e.g., OEM scanners) to reset error codes or recalibrate sensors.
Warranty Control: Manufacturers may void warranties if non-certified technicians attempt repairs, steering owners to dealerships.
Safety and Durability Considerations
Sealed Assemblies: Protect sensitive electronics from moisture and dust, ensuring longevity and UV resistance.
Electrical Complexity: Modern bulbs (e.g., HID, LED) require precise voltage regulation. Incorrect handling can damage the vehicle’s electrical system or reduce bulb lifespan.
Key Takeaways Factor Impact on DIY Replacement Advanced Tech Requires calibration tools and software Regulatory Compliance Tamper-resistant designs Aesthetic Design Tight packaging limits access Service Incentives Encourages dealership dependency
Advice for Owners: Consult Manuals: Some models allow bulb access via hidden panels.
Invest in Professional Help: For adaptive or laser systems, dealerships ensure compliance and safety.
Avoid Aftermarket Modifications: Non-homologated parts risk fines or accidents.
While frustrating, these design choices reflect a balance between innovation, safety, and market dynamics. For complex systems, dealerships remain the safest (if pricier) option.

#led lights#car lights#led car light#youtube#led auto light#led headlights#led light#led headlight bulbs#ledlighting#young artist#headlight bulbs#headlight bulb#car culture#cars#classic cars#race cars#cartoon#car#suv#porsche#truck#carlos sainz#supercar#automobile#car light#headlight restoration#headlamps#headlamp#headlight#aftermarket new lamp
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Electronic Navigation: Exploring IHO Standard S-100 an
In the ever-evolving world of maritime navigation, technological advancements have played a pivotal role in enhancing safety and efficiency at sea. Electronic Chart Display and Information Systems (ECDIS) have become indispensable tools for modern-day seafarers. These systems rely on standardized electronic navigation charts (ENCs) to provide accurate and up-to-date navigational information.
0 notes
Text

F-22 Retirement in 2030 Unlikely as USAF Looks to Spend $7.8 Billion on It Before Then
March 27, 2024 | By John A. Tirpak
The Air Force seems to be rethinking its plan to start retiring the F-22 around 2030, as its spending plans for the air dominance fighter go well beyond that date, according to the service’s fiscal 2025 budget request.
The Air Force’s planned F-22 budget through fiscal year 2029 includes $4.7 billion for procurement and $3.1 for research, development, test, and evaluation, for a total of $7.8 billion. While the RDT&E line closes out in FY29, procurement beyond that date—labeled “to completion” in budget documents—comes to $1.2 billion.
Senior Air Force leaders have described the F-22 program now through 2030 as a “bridge” to the Next-Generation Air Dominance Fighter and its family of systems, and several have said that the technologies being developed for the F-22 in its waning service years will be directly applicable to NGAD.
The budget assumes the F-22 fleet will be reduced by 32 aircraft, to about 153 airplanes, but the documents say only 142 will receive the full lineup of improvements.
The 32 jets the Air Force wants to divest are of the Block 20 configuration, and Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall has said it would cost upwards of $50 million each to bring them up to Block 30, the most up-to-date standard. The Air Force prefers to spend that money making the younger models more capable against the anticipated threat; mainly the air-to-air challenge posed by China’s fifth-generation fighters and advanced air-to-air missiles.
The Air Force has also said that a congressional mandate to upgrade the older F-22s—which have been used only as training jets—couldn’t be accomplished until it was almost time to retire them. They would also need all the new capabilities the F-22 is receiving, to preserve fleet standardization, at even greater cost.
Pentagon officials agreed that, despite the urgency of the threat, it would be foolish to upgrade the F-22s at such expense and retire them a few months later. One said that the timing of the F-22’s retirement “hasn’t been decided … and it depends on progress with NGAD” and other factors.
Budget justification documents for the F-22 say that the procurement activities over the next five years will upgrade “the air vehicle, engine, Operational Flight Program (OFP), and training systems to improve F-22 weapons, communications, navigation, pilot-vehicle interface, and electronic warfare suite.”
Updates called out in the documents show the Air Force is giving the F-22 stealthy, range-extending drop tanks, infrared sensors, identification, friend-or-foe improvements, better Link 16 connectivity, software upgrades, and electronic warfare and navigation enhancements, as well as new weapons and hardware changes to make it more reliable and available.
The long-range tanks and infrared systems were revealed in artwork released by Air Combat Command in mid-2022, without explanation at the time. Test aircraft sporting the new underwing tanks and IR sensors have since been photographed near western test ranges, but the Air Force has declined to discuss them.

Among the new capabilities being prepared for the F-22 Raptor are the still-classified AIM-260 Joint Advanced Tactical Missile, evoked here in an image released in 2022 by Gen. Mark Kelly, head of Air Combat Command. Developed by Lockheed Martin, JATM is an air-to-air weapon designed to attack targets beyond visual range. It is needed to counter China’s next-generation PL-15 weapon. USAF illustration
The budget documents say the critical design review for the stealthy tanks took place in early 2023 and that technology demonstrations have been underway since. “Required Assets Available” with the tanks, which usually translates to initial operational capability, is set for the second quarter of fiscal 2026.
The infrared detection system (IRDS), which is likely to be the two slender, chiseled pods on the outer wing of the F-22 in the artwork, will enter full-up flight test in the first quarter of fiscal 2026. Production is to begin in early 2028, with deliveries the following year.
A sensor enhancement package for the F-22 includes IRST and possibly radar and other detection systems. Together, they will “improve the F-22’s sensing and tracking and ensures Air Superiority by preserving the first-look, first-shot and first-kill capabilities of the 142 Block 30/35 F-22 aircraft,” according to the justifications.
“The first 71 Sensor Enhancements Group A kits were purchased under F-22’s Rapid Fielding Middle Tier Acquisition (MTA) program authority,” the Air Force said. The new sensors are slated for flight demonstration in FY24. A follow-on production decision is scheduled to follow closely. Developmental Test and Evaluation is scheduled for the third quarter of FY25, and in the last quarter of FY26, Operational Test and Evaluation will begin.
The low-drag tank and pylons “are advanced technological designs” which will “minimally increase drag” while permitting longer range, even at supersonic speed, for the F-22.
“The pylons are equipped with smart rack pneumatic technology to accurately control ejection performance and maintain minimum drag without stores,” the documents said.
The program calls for 286 each of the tanks and pylons—enough to fully equip 143 jets, at two for each jet. They have to work at a speed of at least Mach 1.2. Wind tunnel and ground tests were completed in fiscal 2023, and flight testing is targeted to begin in the second quarter of fiscal 2024, shortly after which a critical design review is scheduled. The initial lots will be bought later in FY24. Developmental and operational testing is set to conclude in mid-fiscal 2026, with required assets available soon after.
The F-22 will also get a new Controlled Reception Pattern Antenna to help it navigate in a “GPS-degraded environment,” and achieve resilient position, navigation and timing. Retrofits will be made on 142 F-22s, of which 27 will be operated by the Air National Guard. There will be a production readiness review in June of this year, and flight testing starts in early 2025.
A series of reliability, availability, and maintainability program (RAMP) initiatives meant to make the F-22 more ready when needed are also in the funding plan. Candidates were selected for their ability to rapidly reduce maintenance workload or increased durability of the F-22’s stealth features. There is “high variability in the number of projects and kit quantities,” the Air Force said in its budget justification books.
“The RAMP program includes funding for retrofit installation labor and modifications which address corrosion, reduce maintenance hours, increase safety and provide urgent response requirements identified by the user to the F-22 fleet,” the Air Force said. These projects are also addressing safety-of-flight issues and to ease “technology insertion.” One such program replaces old fiber-optic cabling; another for a “Low Observable Mighty Tough Boot … leads to an estimated three percent increase in aircraft reliability.”
What was originally an ad-hoc Link 16 connectivity program now gives the F-22 a transmit/receive capability with Link 16 rehosted to a system that also plugs it into the Multi-functional Information Distribution Service/Joint Tactical Radio System (MIDS/JTRS), with an open architecture to speed insertion of new capabilities.
Much of the F-22 RDT&E request is for software to integrate and exploit all the new sensors and equipment the fleet will receive. The Air Force is attempting to “leverage commercially-based agile software and hardware best practices and tools” to speed the introduction of new capabilities. It’s also funding Software Integration Labs for most of the specific systems.
Other RDT&E efforts include cryptographic upgrades, technology demonstrations, “threat modeling support,” engine enhancements cybersecurity and open mission system (OMS) integration. Software is to be delivered “using a scheduled cadence for capabilities as they mature.”
The RDT&E program also includes “Project Geyser,” described as an “advanced capability” that will be assessed for “fielding configuration options.” No details were given about this project, but there will be “continued flight demonstrations and … test fleet modification into planned production configuration” in fiscal 2025.
@AirandSpaceForces.com via X
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
luring someone to my abode under the guise of "epic training". they think its like a really amazing kink thing but when they get there i reveal i am an epic superuser and i am now going to teach them how to navigate electronic medical record software
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigate the New Rules of ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2
The digital shift in Saudi Arabia’s tax landscape is picking up speed. At the center of it all is ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2—a mandatory evolution for VAT-registered businesses that brings more structure, security, and real-time integration to how invoices are issued and reported.
If you’ve already adjusted to Phase 1, you’re halfway there. But Phase 2 introduces new technical and operational changes that require deeper preparation. The good news? With the right understanding, this shift can actually help streamline your business and improve your reporting accuracy.
Let’s walk through everything you need to know—clearly, simply, and without the technical overwhelm.
What Is ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2?
To recap, ZATCA stands for the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority in Saudi Arabia. It oversees tax compliance in the Kingdom and is driving the movement toward electronic invoicing through a phased approach.
The Two Phases at a Glance:
Phase 1 (Generation Phase): Started in December 2021, requiring businesses to issue digital (structured XML) invoices using compliant systems.
Phase 2 (Integration Phase): Began in January 2023, and requires companies to integrate their invoicing systems directly with ZATCA for invoice clearance or reporting.
This second phase is a big leap toward real-time transparency and anti-fraud efforts, aligning with Vision 2030’s goal of building a smart, digital economy.
Why Does Phase 2 Matter?
ZATCA isn’t just ticking boxes—it’s building a national infrastructure where tax-related transactions are instant, auditable, and harder to manipulate. For businesses, this means more accountability but also potential benefits.
Benefits include:
Reduced manual work and paperwork
More accurate tax reporting
Easier audits and compliance checks
Stronger business credibility
Less risk of invoice rejection or disputes
Who Must Comply (and When)?
ZATCA isn’t pushing everyone into Phase 2 overnight. Instead, it’s rolling out compliance in waves, based on annual revenue.
Here's how it’s working:
Wave 1: Companies earning over SAR 3 billion (Started Jan 1, 2023)
Wave 2: Businesses making over SAR 500 million (Started July 1, 2023)
Future Waves: Will gradually include businesses with lower revenue thresholds
If you haven’t been notified yet, don’t relax too much. ZATCA gives companies a 6-month window to prepare after they're selected—so it’s best to be ready early.
What Does Compliance Look Like?
So, what exactly do you need to change in Phase 2? It's more than just creating digital invoices—now your system must be capable of live interaction with ZATCA’s platform, FATOORA.
Main Requirements:
System Integration: Your invoicing software must connect to ZATCA’s API.
XML Format: Invoices must follow a specific structured format.
Digital Signatures: Mandatory to prove invoice authenticity.
UUID and Cryptographic Stamps: Each invoice must have a unique identifier and be digitally stamped.
QR Codes: Required especially for B2C invoices.
Invoice Clearance or Reporting:
B2B invoices (Standard): Must be cleared in real time before being sent to the buyer.
B2C invoices (Simplified): Must be reported within 24 hours after being issued.
How to Prepare for ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2
Don’t wait for a formal notification to get started. The earlier you prepare, the smoother the transition will be.
1. Assess Your Current Invoicing System
Ask yourself:
Can my system issue XML invoices?
Is it capable of integrating with external APIs?
Does it support digital stamping and signing?
If not, it’s time to either upgrade your system or migrate to a ZATCA-certified solution.
2. Choose the Right E-Invoicing Partner
Many local and international providers now offer ZATCA-compliant invoicing tools. Look for:
Local support and Arabic language interface
Experience with previous Phase 2 implementations
Ongoing updates to stay compliant with future changes
3. Test in ZATCA’s Sandbox
Before going live, ZATCA provides a sandbox environment for testing your setup. Use this opportunity to:
Validate invoice formats
Test real-time API responses
Simulate your daily invoicing process
4. Train Your Staff
Ensure everyone involved understands what’s changing. This includes:
Accountants and finance officers
Sales and billing teams
IT and software teams
Create a simple internal workflow that covers:
Who issues the invoice
How it gets cleared or reported
What happens if it’s rejected
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Transitioning to ZATCA e-Invoicing Phase 2 isn’t difficult—but there are a few traps businesses often fall into:
Waiting too long: 6 months isn’t much time if system changes are required.
Relying on outdated software: Non-compliant systems can cause major delays.
Ignoring sandbox testing: It’s your safety net—use it.
Overcomplicating the process: Keep workflows simple and efficient.
What Happens If You Don’t Comply?
ZATCA has teeth. If you’re selected for Phase 2 and fail to comply by the deadline, you may face:
Financial penalties
Suspension of invoicing ability
Legal consequences
Reputation damage with clients and partners
This is not a soft suggestion—it’s a mandatory requirement with real implications.
The Upside of Compliance
Yes, it’s mandatory. Yes, it takes some effort. But it’s not all downside. Many businesses that have adopted Phase 2 early are already seeing internal benefits:
Faster approvals and reduced invoice disputes
Cleaner, more accurate records
Improved VAT recovery processes
Enhanced data visibility for forecasting and planning
The more digital your systems, the better equipped you are for long-term growth in Saudi Arabia's evolving business landscape.
Final Words: Don’t Just Comply—Adapt and Thrive
ZATCA e-invoicing phase 2 isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about future-proofing your business. The better your systems are today, the easier it will be to scale, compete, and thrive in a digital-first economy.
Start early. Get the right tools. Educate your team. And treat this not as a burden—but as a stepping stone toward smarter operations and greater compliance confidence.
Key Takeaways:
Phase 2 is live and being rolled out in waves—check if your business qualifies.
It requires full system integration with ZATCA via APIs.
Real-time clearance and structured XML formats are now essential.
Early preparation and testing are the best ways to avoid stress and penalties.
The right software partner can make all the difference.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
12 Advantages and Disadvantages of ECommerce | Imagency Media
The rapid growth of eCommerce has transformed the way businesses operate, bringing both remarkable advantages and notable challenges. Understanding these can help businesses leverage eCommerce to its fullest potential or address its drawbacks effectively. Let’s dive into 12 key advantages and disadvantages of eCommerce.

Advantages of eCommerce
Global Reach eCommerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach customers worldwide. This expansive reach helps businesses tap into new markets and grow their customer base beyond local limitations.

Lower Operational Costs Running an online store can be significantly cheaper than maintaining a physical storefront. Costs like rent, utilities, and staffing are greatly reduced, allowing businesses to reinvest savings into marketing and product development.
24/7 Availability Unlike traditional stores, eCommerce sites operate round the clock. This availability caters to customers in different time zones, providing a seamless shopping experience anytime, anywhere.
Personalization and Customer Experience eCommerce platforms can gather data on customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history, allowing businesses to offer personalized recommendations and improve the overall shopping experience.

Easy Scaling and Growth Scaling an online business is much simpler than expanding a brick-and-mortar store. Adding new products or services, targeting new demographics, and adjusting to market demands can be done quickly and efficiently.
Enhanced Marketing Opportunities Digital marketing strategies such as social media advertising, email marketing, and SEO are particularly effective for eCommerce. These channels allow businesses to target specific audiences and track results in real-time.
Disadvantages of eCommerce
Lack of Personal Touch Despite technological advances, online shopping often lacks the personal interaction found in physical stores. This absence of human touch can make it harder to build customer loyalty.
Security and Privacy Concerns With the rise in cybercrime, protecting customer data is a major concern for eCommerce businesses. Ensuring robust security measures is critical but can be costly and complex.

Dependence on Technology eCommerce heavily relies on technology, including websites, payment gateways, and software. Technical glitches, downtime, or slow-loading pages can lead to lost sales and damage to the brand’s reputation.
High Competition and Price Wars The ease of starting an online store has led to increased competition, making it difficult for smaller businesses to stand out. Price wars are common, often squeezing profit margins.
Shipping and Logistics Challenges While eCommerce allows businesses to reach a global audience, shipping products efficiently can be complex and costly. Issues like delayed deliveries, high shipping fees, and logistics mishaps can affect customer satisfaction.

Difficulty in Handling Returns and Refunds Returns are more prevalent in eCommerce, especially in fashion and electronics sectors. Handling returns and refunds can be costly and time-consuming, often eroding profit margins.
Conclusion
eCommerce offers vast opportunities for growth, flexibility, and global reach, but it also comes with challenges that businesses must address. By understanding these advantages and disadvantages, companies can better strategize and create a seamless, customer-friendly eCommerce experience.
Contact us
Imagency Media can help you navigate the eCommerce landscape, providing expert insights and tailored solutions to maximize your online success.
#digital services#digital marketing#social media marketing#business#marketing#google ads#ecommerce business#ecommerce
4 notes
·
View notes