#genetic code
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text










In tandem with genetically engineering its three dire wolves, Colossal has cloned two litters of red wolves, the most critically endangered wolf in the world, as part of its overall goal of pairing conservation efforts with its de-extinction efforts.
The company, founded in 2021, has previously announced that it plans to bring back the woolly mammoth, the Tasmanian tiger, and the dodo bird from extinction.
It says that its work on the dire wolf is a proof of technology.
“This massive milestone is the first of many coming examples demonstrating that our end-to-end de-extinction technology stack works,” says Lamm, who co-founded Colossal with Harvard geneticist Dr. George Church.
Colossal — which claims that it has now set the record for the most-ever genetic edits in a living species — says it plans to restore the dire wolf as a viable species and secure ecological preserves for it on Indigenous land in North America.
📹 AMAZlNGNATURE / X
🐺🥹🔊
#dire wolves#extinction#long extinct canine#dire wolf#dire wolf pup#genetic engineering#colossal biosciences#dna#genetic code#gray wolf#colossal#de-extinction company#crispr technology#ben lamm#advanced technology#scientific development#peter jackson#george rr martin#grrm#iron throne#remus#romulus#american humane society#la brea tar pits#clone#woolly mammoth#Tasmanian tiger#dodo bird#Dr. George Church#genetics
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
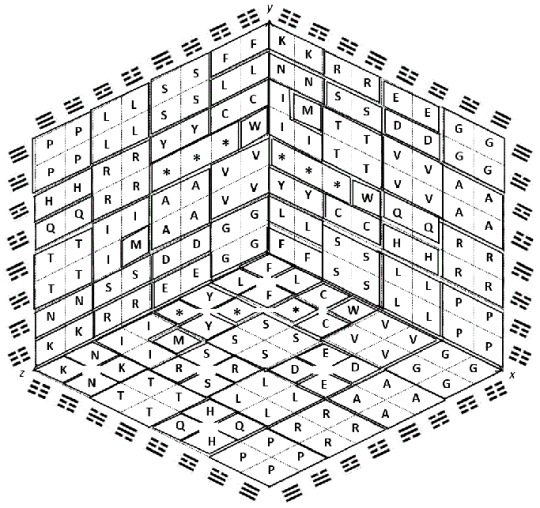
Castro-Chavez, Fernando. (2014). File Compression and Expansion of the Genetic Code by the Use of the Yin/Yang Directions to Find its Sphered Cube. Journal of biodiversity, bioprospecting and development. 1. 10.4172/2376-0214.1000112.
123 notes
·
View notes
Text

Epigenetics: A Journey Through Inheritance Beyond Genes
For centuries, scientists have been fascinated by the mysteries of heredity and how traits are passed down from generation to generation. DNA, the molecule that stores our genetic code, was once thought to be the sole determinant of our characteristics. However, a new frontier in biology, revealing a captivating layer of complexity beyond the DNA sequence itself: Epigenetics.
What is Epigenetics?
The term "epigenetics" was first coined in the 1940s by British biologist Conrad Waddington, but it wasn't until the late 20th century that its significance truly blossomed. Epigenetics, literally meaning "above genetics," refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that occur without alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Imagine DNA as the musical score, but epigenetics are the conductor and musicians who determine how the music is played. Through chemical modifications and adjustments to the proteins around DNA, epigenetics dictates which genes are turned on or off, influencing how cells function and ultimately shaping our health, development, and even behavior. Think of your DNA as the hardware: it contains the basic instructions for building and running your body. But epigenetics acts like the software, fine-tuning those instructions and determining which genes get turned on or off at specific times and in specific cells. These modifications, like chemical tags or changes in the packaging of DNA, don't alter the underlying code itself, but they can have a profound impact on how it's read and interpreted.
The Key Players:
DNA methylation: This process involves adding a methyl group to DNA, essentially silencing the gene it's attached to. Imagine it like putting a dimmer switch on a light bulb.
Histone modifications: Histones are proteins that package DNA, and changes in their structure can make genes more or less accessible to the cellular machinery needed for expression. Think of it like adjusting the curtains around a window - open wide for full light, slightly closed for filtered light.
Non-coding RNAs: These are molecules that don't code for proteins but can regulate gene expression in various ways. They're like the backstage crew in a play, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
The Power of Epigenetic Regulation
Epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
Development: During embryonic development, different cell types emerge from the same DNA blueprint by activating or silencing specific gene sets through epigenetic modifications.
Cellular differentiation: Specialized cells like muscle or nerve cells have unique functions due to differences in their active genes, controlled by epigenetic mechanisms.
Learning and memory: Epigenetic changes in brain cells are thought to be essential for learning and forming memories.
Aging: As we age, our epigenome accumulates changes that can contribute to age-related decline and disease.
Environmental influences: Diet, exercise, stress, and exposure to toxins can leave epigenetic marks on our genes, potentially impacting our health and even the health of future generations.
Epigenetics reminds us that we are not simply products of our genes. Our environment, choices, and experiences leave their mark, shaping who we are and potentially influencing our children's health. This deeper understanding of ourselves opens doors for self-awareness, empowerment, and potentially reshaping our narratives – not just as individuals, but as a species with the potential to leave a healthier legacy for generations to come.
#life science#biology#science sculpt#molecular biology#biotechnology#epigenetics#daily dose of science#dna#genetic inheritance#genetics#decoding dna#genetic code#science#double helix
126 notes
·
View notes
Text





Marshall Nirenberg – Scientist of the Day
Marshall Warrenn Nirenberg, an American biochemist, was born Apr. 10, 1927, in New York City. read more...
#Marshall Nirenberg#biochemistry#genetic code#histsci#histSTM#20th century#history of science#Ashworth#Scientist of the Day
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Phenotype vs Genotype
Phenotype -- the trait produced by the genotype -- depends on both genotype and environmental factors -- not inherited by offspring -- consists of expressed genes -- dominant alleles can mask recessive alleles -- genotype AA causes phenotype A -- genotype Aa causes phenptype A -- genotype aa causes phenotype a
Genotype -- the actual genetic code of an organism -- codes for the phenotype -- consists of both dominant and recessive alleles -- inherited by offspring -- usually refers to one specific gene causing a trait -- written as a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters -> AA -> Bb -> ee -- dominant = uppercase letters -- recessive = lowercase letters -- both uppercase = homozygous dominant -- one uppercase and one lowercase = heterozygous -- both lowercase = homozygous recessive
.
Patreon
#studyblr#notes#biology#bio#biology notes#bio notes#life science#science#health science#genetics#genetics notes#genotype#phenotype#homozygosity#heterozygosity#genetic code#biological science#study guide#genetics study guide
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was reading a biochemistry textbook today, and came across a detail that I thought was interesting.
Quick biology lesson for those who don't know: DNA, the molecule containing the "code" that's used to produce proteins, and therefore building up cells and doing all kinds of other stuff in the body, is built up of sequences of four "bases": Guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine. These are usually referred to as G, A, C and T, and DNA code is often written as a sequence of these letters. There's a fun example of that in Jurassic Park, for example:

The production of proteins can be stimulated in many ways, including by various hormones. These hormones can bind to "receptors" in the cells, that then in turn bind to the DNA to initiate the creation of new proteins (yes, I'm skipping over some steps here to keep it simple). There are specific part of the DNA that specific receptors can bind to, called "response elements", that are built up of sequences of G, A, C and T called "consensus sequences".
What I read about in my textbook today is that the consensus sequence for the "estrogen repsone elements", I.E. the one that a receptor activated by the estrogen hormone binds to, is the following:
AGGTCANNNTGACCT
(The "N" means "any base can go here".)
I just wanted to share this little bit of genetic code related to estrogen, since it might be of interest to anyone making art about hormones, HRT, or similar stuff. Maybe it can be seen as a symbol for the many extraordinary things that estrogen does to our bodies.
Unfortunately, I don't know what the consensus sequence for testosterone receptors is. Maybe someone with deeper biochemistry knowledge knows?
#science#biology#biochemistry#DNA#hormones#estrogen#HRT#consensus sequence#genetics#genetic code#AGGTCANNNTGACCT
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


REBOOT
#printing#genes#genetic code#the thinker#the core#machine#machine core#minerva's den#rapture#bioshock#bioshock 2#bioshock 2 dlc#bioshock the collection#bioshock: the collection#2K#video games#girls who game#nintendo#nintendo switch#nintendo switch games#switch#switch games
1 note
·
View note
Text
Life as Code: Exploring Biocentrism, Intelligent Design and the Genetic Code
The idea of life existing within a computer simulation has captured imaginations for decades. Here’s how Biocentrism, Intelligent Design Theory, and the Genetic Code can be used to explore this concept, though these ideas are not widely accepted in the scientific community. by David Stone The Roosevelt Island Daily News Biocentrism: Consciousness as the Central Force Biocentrism, championed…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
What is Chromosome remodeling? Explained
Imagine a library with millions of books tightly bound together – that's kind of like DNA in chromosomes without remodeling. Remodeling acts like librarians carefully unstacking and organizing books to make them accessible to readers. Read more...
CHROMOSOME REMODELING Chromosome remodeling is a vital process within cells that ensures the DNA instructions encoded in chromosomes can be accessed and used when needed. Imagine a library with millions of books tightly bound together – that’s kind of like DNA in chromosomes without remodeling. Remodeling acts like librarians carefully unstacking and organizing books to make them accessible to…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text





youtube
The Making of the Colossal Dire Wolves — World's First De-Extinction
7 April 2025
The dire wolf is no longer extinct—and this is the story of how Colossal made it happen.
Discover the advanced tools and technologies behind the revival of the dire wolf, why this breakthrough matters for the future of conservation, and what it means for endangered species across the globe.
In this video, you’ll hear directly from the scientists, conservationists, and visionaries who made the impossible possible.
This moment marks more than just a scientific achievement — it signals the start of a new era in biodiversity and ecological restoration.
The dire wolf is back, and for Colossal, this is only the beginning.
Credit: 3D models created by Visual Science
🐺🥹🤍
#colossal biosciences#dire wolf#dire wolf pup#dire wolves#ancient dna#dna#fossilized remains#de extinction#scientific development#genetic engineering#game of thrones#george rr martin#grrm#house stark#scientific achievement#biodiversity#ecological restoration#Youtube#romulus and remus#de extinct#conservation#science and technology#endangered species#new era#unbelievable#just wow#ghost#jon snow#gray wolf#genetic code
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Castro-Chavez, Fernando. (2014). File Compression and Expansion of the Genetic Code by the Use of the Yin/Yang Directions to Find its Sphered Cube. Journal of biodiversity, bioprospecting and development. 1. 10.4172/2376-0214.1000112.
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

This twisted ladder holds more secrets than a locked vault. From eye color to fingerprints, DNA whispers the story of who you are, where you came from, and even hints at your future. It's the ultimate blueprint, the instruction manual for building you, and it's hidden within every cell of your being. So next time you take a selfie, remember, you're not just capturing a face, you're snapping a shot of your own personal history book, written in the language of life itself. What hidden talents or traits lie coiled within your DNA? Share it in the comments!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Torn Roots.
She wanted to unleash those emotions that were roaring inside of her, caged and pacing about. There was anger. There was defiance. There was a sense of knowing things…but she wasn’t sure what exactly had triggered these emotions. But there was also this peaceful yet nagging notion that would trickle down her thoughts…that would meander and wind its way through her mind. This notion was…

View On WordPress
#ancestors#ancestral knowledge#art#culture#digital art#emotions#family tree#genetic code#heritage#history#mind#painting#roots#society#thoughts#vision
0 notes
Text
Torn Roots.
She wanted to unleash those emotions that were roaring inside of her, caged and pacing about. There was anger. There was defiance. There was a sense of knowing things…but she wasn’t sure what exactly had triggered these emotions. But there was also this peaceful yet nagging notion that would trickle down her thoughts…that would meander and wind its way through her mind. This notion was…

View On WordPress
#ancestors#ancestral knowledge#art#culture#digital art#emotions#family tree#genetic code#heritage#history#mind#painting#roots#society#thoughts#vision
0 notes
Text

This makes sense I swear
1 note
·
View note
Text
It’s messing with my head how she really is doing that “Come to mommy” pose. With her arms outstretched and kneeling (almost to be at eye level), like she’s reaching to hug a small child.

Which when you think about war makes sense. Sacrificing everything, even children, for the sake of victory.
#csm spoilers#chainsaw man#chainsaw man spoilers#csm#chainsawman spoilers#csm 176#Yoru is so Eat Your Young coded#Talk about weaponizing children#is toxic motherhood genetic or are Yoru and Makima just like that
1K notes
·
View notes