#gitlab runner
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
GitLab Environments: Your Cloud Playground Blueprint
Remember when you were a kid and tried to build the ultimate LEGO castle? You had all these cool pieces, but figuring out how they fit together was the real challenge. Well, welcome to the grown-up version: building your serverless cloud playground! Let’s take a bird’s-eye view of our LEGO set… err, I mean, our solution components. The Grand Blueprint: Components Overview Imagine you’re an…
#aws#CI/CD Pipeline#Cloud Architecture#DevOps Automation#GitLab Environments#GitLab Runner#Infrastructure as Code#OIDC Integration#Parallel Environments#Secure Cloud Access#Serverless Development#Terraform State Management
0 notes
Text
#jenkins vs gitlab#gitlab vs jenkins#ci gitlab#ci cd vs jenkins#ci cd gitlab#runner vs jenkins#difference between jenkins and gitlab
0 notes
Text
Cómo instalar GitLab Runner en Ubuntu como 22.x 20.x y Debian 10,11,12
GitLab Runner es una herramienta desarrollada para permitir a los usuarios ejecutar trabajos de integración continua e implementación continua (CI/CD) para proyectos de GitLab. Funciona como un agente que ejecuta los comandos especificados en la configuración de GitLab CI/CD. Podemos instalar fácilmente GitLab Runner en su Ubuntu Linux para automatizar el proceso de prueba e implementación, lo…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Loving Travis
For most of my open-source software projects, I use the Actions platform built into GitHub for CI (continuous integration). GitHub Actions provides virtual machines to run workflows, so I don't have to administer build environments for Linux, MacOS, Windows, and so on. It's modern, convenient (if you use GitHub instead of, say, GitLab), fairly reliable, and (best of all) free (for public repos).
For me, the main limitation of Actions is that all their hosted runners use the x64 architecture. Sometimes I want to build and/or test on Arm CPUs---for instance my Libbulletjme project, which has a bunch of platform-sensitive C++ code.
For Libbulletjme, I still depend on the older TravisCI platform, run by a private firm in Berlin. In addition to a huge selection of build environments based on AMD CPUs, Travis also provides Arm-based Linux environments. (Officially, they're a "beta-stage" feature, but they've been in beta for years.) Like Actions, Travis is also free to open-source projects, though their notion of "open-source" seems a bit stricter than GitHub's.
I mention Travis because my experiments with the Vulkan API exposed a limitation in Libbulletjme, which led me to begin work on a new release of Libbulletjme, which led me to discover an issue with Travis's Arm-based build environments. A recent change to these environments caused all my Arm-based builds to fail. I could only go a bit further with Vulkan before I would have to make hard choices about how to work around the limitations of Libbulletjme v18.5.0 .
At 20:09 hours UTC yesterday (a Sunday), I e-mailed TravisCI customer support and explained my issue. At 12:25 hours UTC today, Travis announced a hotfix to solve my issue. That's pretty good turnaround, for a non-paying customer having issues with a "beta-stage" feature on a summer weekend.
Bottom line: I still love Travis. <3
#continuous integration#vulkan#computer architecture#software engineering#open source#github#hosting#upcoming releases#customer support#making progress#software testing#war stories#love#berlin
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Breaking Barriers in Software Quality: Advanced API Testing Services for Modern Architectures

In the dynamic landscape of software engineering, application performance, scalability, and reliability have become non-negotiables. With the shift from monolithic architectures to microservices, and the explosion of interconnected systems, APIs are now the backbone of modern digital ecosystems. As APIs grow in complexity and ubiquity, so too must the strategies used to test them.
At Robotico Digital, we understand that software quality hinges on much more than clean UI and functional frontends. It’s about what lies beneath — how systems interact, how services communicate, and how fast and securely data flows between components. This is where our API Testing Services break barriers, ensuring quality at the very core of your application stack.
Understanding API Testing in the Context of Modern Architectures
API Testing refers to the process of validating application programming interfaces (APIs) directly at the message layer, without the use of a GUI. It verifies that APIs return correct responses, handle errors appropriately, and meet performance and security expectations.
In microservices, APIs are the only communication mechanism between services. In serverless computing, APIs trigger the logic. And in mobile-first or headless applications, APIs drive every interaction.
Thus, API Testing Services today must adapt to modern environments by:
l Supporting asynchronous data flow and event-driven models.
l Validating REST, SOAP, GraphQL, gRPC, and WebSocket protocols.
l Integrating with CI/CD pipelines and DevOps tools for rapid iteration.
Why Traditional Testing Fails Modern Architectures
Legacy testing models often fall short because:
l They rely heavily on UI testing, which isn’t scalable or robust.
l They fail to isolate service-level issues in microservice deployments.
l They lack integration with agile development and DevOps cycles.
At Robotico Digital, we address these challenges with a future-ready API-first testing strategy that enables rapid development and secure, stable deployments.
Robotico Digital's Advanced API Testing Services: A Framework of Excellence
Our API Testing Services are structured around an advanced framework tailored for high-speed development environments, featuring:
1. Protocol-Agnostic Testing Architecture
Our test harness supports:
l REST, SOAP, GraphQL, gRPC, WebSocket, and JSON-RPC
l OAuth, JWT, and API Key-based authentication
l Complex nested payloads and chained request workflows
We don’t just send requests and verify status codes — we simulate real-world behavior.
2. Contract Testing with Swagger and OpenAPI
We validate API contracts using:
l Swagger and Postman schema validations
l Pact-based consumer-driven testing
l Automated schema diff tools
This ensures API consistency across development teams, especially in environments with multiple consumer applications.
3. Comprehensive Functional and Regression Suites
Our functional testing stack includes:
l Request/response validation with parameterized payloads
l Chaining dependent API calls to simulate real transactions
l Edge-case testing for malformed requests and injection handling
These suites form the backbone of our regression testing strategy, ensuring every build remains stable without code breaks.
Seamless Integration with DevOps Pipelines
In a CI/CD world, testing must be continuous. Robotico Digital provides seamless API Testing Service integration with:
l Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps
l Dockerized test runners for isolated test environments
l Slack and Teams integrations for alerting and test reports
Tests are triggered automatically on code commits or builds, reducing human intervention and increasing speed.
API Test Automation: Scaling Quality at Speed
Automation is key to modern testing strategies. Robotico Digital leverages:
l Postman + Newman for exploratory and lightweight test execution
l REST Assured + TestNG for Java-based enterprise-grade test suites
l Cypress and Supertest for JavaScript and Node.js applications
l Karate DSL for end-to-end BDD-driven API Testing
We use data-driven test design and test parallelism to achieve high throughput and full API coverage — even across large microservices ecosystems.
Intelligent Test Data Management (TDM)
Test data is critical, especially when APIs depend on complex backend states. Our TDM solutions provide:
l Synthetic test data generation using Faker and Mockaroo
l Encrypted data masking for secure production cloning
l Environment-specific data pools to avoid cross-test pollution
This empowers our teams to run API tests with production-like reliability in test environments.
Performance & Load Testing of APIs
APIs underperforming in production can lead to latency, downtime, and failed transactions. Robotico Digital performs rigorous API performance testing, including:
Load Simulation with tools like JMeter, Gatling, and Locust
l Spike, soak, and stress testing to evaluate limits
l Latency monitoring across geographies
l Response time threshold validations
Our tests replicate thousands of concurrent requests, ensuring your APIs hold up under real-world traffic scenarios.
API Security Testing: Guarding the Gateway
Since APIs often expose business logic and sensitive data, security testing is non-negotiable. Robotico Digital incorporates security scanning into API Testing Services by:
l Validating for OWASP API Top 10 vulnerabilities
l Testing for broken authentication, excessive data exposure, rate limiting, and injection attacks
l Integrating Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and custom security probes into test pipelines
We don’t just test functionality — we test for resilience against malicious attacks.
Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
Transparency is critical. Our reporting dashboard includes:
l Detailed test summaries with pass/fail ratios
l Latency graphs and time-to-first-byte analysis
l Defect tracking with Jira, Azure Boards, or custom integrations
l REST APIs to extract test data into BI tools or custom reports
Clients always have clear visibility into the testing progress and quality metrics.
Future-Forward Testing with AI & ML
Robotico Digital is investing in the next generation of API Testing with:
l AI-based anomaly detection using test execution logs
l Predictive analytics to identify flaky endpoints
l Self-healing scripts that auto-adjust to changes in API structures
l NLP-driven test generation for conversational interfaces and AI-driven apps
These features ensure our API Testing Services evolve alongside tomorrow’s tech stacks.
Why Choose Robotico Digital for API Testing Services?
Here’s what sets us apart:
l Protocol-flexible architecture for REST, GraphQL, gRPC & more
l Intelligent automation backed by AI and ML
l Deep integration of performance and security testing
l CI/CD-native workflows built for speed
l Real-time test reporting and analytics dashboards
l Domain expertise across finance, healthcare, retail, SaaS, and telecom
We don’t just validate APIs — we engineer confidence into your ecosystem.
Conclusion: Quality at the Core of Connectivity
As businesses increasingly rely on interconnected software and modular architectures, API quality is business quality. At Robotico Digital, we’re pushing the boundaries of what's possible with API Testing Services — from functional validations and performance simulations to proactive security and predictive analytics.
If you're building for scale, agility, and resilience, let Robotico Digital be your QA partner. We ensure every interaction your users experience is powered by secure, fast, and flawless APIs.
0 notes
Text
Jenkins vs GitLab CI/CD: Key Differences Explained

In the world of DevOps and software automation, choosing the right CI/CD tool can significantly impact your team's productivity and the efficiency of your development pipeline. Two of the most popular tools in this space are Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD. While both are designed to automate the software delivery process, they differ in structure, usability, and integration capabilities. Below is a detailed look at the differences between Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD, helping you make an informed decision based on your project requirements.
1. Core integration and setup Jenkins is a stand-alone open-source automation server that requires you to set up everything manually, including integrations with source control systems, plugins, and build environments. This setup can be powerful but complex, especially for smaller teams or those new to CI/CD tools. GitLab CI/CD, on the other hand, comes as an integrated part of the GitLab platform. From code repositories to issue tracking and CI/CD pipelines, everything is included in one interface. This tight integration makes it more user-friendly and easier to manage from day one.
2. Plugin dependency vs built-in tools One of Jenkins’ biggest strengths—and weaknesses—is its plugin ecosystem. With over 1,800 plugins available, Jenkins allows deep customization and support for almost any development environment. However, this heavy reliance on plugins also means users must spend time managing compatibility, updates, and security. In contrast, GitLab CI/CD provides most essential features out of the box, reducing the need for third-party plugins. Whether you need container support, auto DevOps, or security testing, GitLab includes these tools natively, making maintenance much easier.
3. Pipeline configuration methods Jenkins pipelines can be configured using a web interface or through a Jenkinsfile written in Groovy. While powerful, this approach requires familiarity with Jenkins syntax and structure, which can add complexity to your workflow. GitLab CI/CD uses a YAML-based file named .gitlab-ci.yml placed in the root of your repository. This file is easy to read and version-controlled, allowing teams to manage pipeline changes along with their codebase. The simplicity of YAML makes GitLab pipelines more accessible, especially to developers with limited DevOps experience.
4. User interface and experience Jenkins’ UI is considered outdated by many users, with limited design improvements over the years. While functional, it’s not the most intuitive experience, especially when managing complex builds and pipeline jobs. GitLab CI/CD offers a modern and clean interface, providing real-time pipeline status, logs, and visual job traces directly from the dashboard. This improves transparency and makes debugging or monitoring easier for teams.
5. Scalability and performance Jenkins can scale to support complex builds and large organizations, especially with the right infrastructure. However, this flexibility comes at a cost: teams are responsible for maintaining, upgrading, and scaling Jenkins nodes manually. GitLab CI/CD supports scalable runners that can be configured for distributed builds. It also works well with Kubernetes and cloud environments, enabling easier scalability without extensive manual setup.
6. Community and support Jenkins, being older, has a large community and long-standing documentation. This makes it easier to find help or solutions for common problems. GitLab CI/CD, though newer, benefits from active development and enterprise support, with frequent updates and a growing user base.
To explore the topic in more depth, check out this guide on the differences between Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD, which breaks down the tools in more technical detail.
Conclusion The choice between Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD depends on your project size, team expertise, and need for customization. Jenkins is ideal for organizations that need deep flexibility and are prepared to handle manual configurations. GitLab CI/CD is perfect for teams looking for an all-in-one DevOps platform that’s easy to set up and manage. Both tools are powerful, but understanding the differences between Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD can help you choose the one that fits your workflow best.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Full Stack Developer Roadmap: Skills, Tools, and Trends
In the fast-evolving world of web development, the role of a full stack web developer is one of the most dynamic and sought-after positions in the industry. A full stack web developer is someone who is proficient in both the front-end and back-end aspects of web development. These developers are capable of building and maintaining an entire web application, from the user interface (UI) to the server-side logic, database management, and everything in between. Whether you're just starting or looking to enhance your skills, understanding the full stack developer roadmap can guide you to becoming a versatile and in-demand professional.
Key Skills Every Full Stack Web Developer Should Master
Becoming a successful full stack web developer requires a diverse set of skills that span multiple layers of technology. Below are the essential skills you’ll need to excel in both front-end and back-end development:
Front-End Development Skills
HTML/CSS: The fundamental building blocks of any website. HTML defines the structure, while CSS is responsible for the layout and design.
JavaScript: The heart of interactive web pages, allowing developers to create dynamic and responsive user interfaces.
Frameworks and Libraries: Libraries like React, Vue.js, and Angular help streamline front-end development and enhance user experiences.
Responsive Design: Understanding how to make websites mobile-friendly using frameworks such as Bootstrap and media queries.
Back-End Development Skills
Server-Side Languages: Languages such as Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, and PHP are essential for writing the logic that runs on the server.
Databases: Knowledge of relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB is crucial for storing and managing data.
API Development: Understanding RESTful APIs and GraphQL is key for communication between the front-end and back-end of an application.
Authentication and Authorization: Implementing security measures like OAuth, JWT, and basic user authentication.
Tools for Full Stack Development
A full stack web developer needs to be proficient in various tools that facilitate the development, testing, and deployment of web applications. These tools not only make the process more efficient but also ensure better collaboration and productivity.
Version Control (Git): Git is essential for tracking changes, collaborating with other developers, and managing code repositories. Platforms like GitHub or GitLab are widely used for hosting projects and collaborating with other developers.
Development Environment: Text editors like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text are commonly used for writing code efficiently, while tools like Docker and Vagrant help with creating consistent development environments.
Task Runners and Module Bundlers: Tools such as Webpack, Gulp, and Grunt automate common tasks like minification, bundling, and testing, which boosts development productivity.
Testing Frameworks: Frameworks like Jest, Mocha, and Chai ensure that the application works as expected and help developers catch bugs early.
Deployment and DevOps Tools
Deployment is a critical part of the development process. A full stack web developer should also understand the tools that make the deployment process smooth:
Cloud Platforms: Services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure provide scalable cloud solutions for hosting web applications.
CI/CD: Continuous integration and continuous deployment tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI automate testing and deployment to make code delivery faster and more reliable.
Containerization: Tools like Docker and Kubernetes simplify application deployment, making it easier to scale and manage applications across multiple environments.
Current Trends in Full Stack Web Development
The tech industry is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends is essential for any full stack web developer. Here are a few trends that are gaining traction:
Serverless Architecture: Serverless computing platforms like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions are becoming popular because they allow developers to focus on writing code without managing the underlying infrastructure.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs offer an enhanced user experience by combining the best of both web and mobile applications. A full stack web developer needs to understand how to build and deploy PWAs.
Microservices: Instead of creating monolithic applications, developers are now building microservices-based architectures that are easier to scale, update, and maintain.
Jamstack: This architecture is gaining popularity due to its performance benefits. By serving pre-built static pages and using APIs for dynamic content, Jamstack allows for faster and more secure websites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a full stack web developer requires a comprehensive understanding of both front-end and back-end development. By learning the essential skills, mastering the right tools, and staying updated with the latest trends, you can successfully navigate the full stack developer roadmap and position yourself as a versatile and in-demand professional. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of the full stack web developer will remain at the forefront of technological innovation, offering exciting opportunities for growth and development.
This roadmap provides a clear pathway for aspiring full stack web developers to build the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in the field, allowing them to work simultaneously with front-end and back-end technologies while keeping up with emerging trends.
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Secure CI/CD Pipelines

🔒 Best Practices for Secure CI/CD Pipelines
In a world where software is built and deployed faster than ever, CI/CD pipelines have become the engine room of modern development. But with speed comes risk. If not properly secured, your CI/CD pipeline can become a prime target for attackers looking to inject malicious code, access secrets, or hijack production systems.
Here are essential best practices to help you secure your CI/CD pipelines without slowing down your delivery.
1. 🔑 Protect Your Secrets
Secrets (API keys, tokens, passwords) are gold for attackers.
Use secret managers like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, or GitHub Actions’ built-in secrets.
Never store secrets in code, config files, or environment variables in plaintext.
Rotate secrets regularly and audit access.
2. 👤 Enforce Least Privilege Access
Only give users, services, and tools the permissions they absolutely need.
Use role-based access control (RBAC).
Ensure build agents only have access to the environments they work with.
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all CI/CD platform access.
3. 🧪 Shift Security Left
Start security checks as early in the development process as possible.
Integrate static application security testing (SAST) tools in the coding phase.
Run automated scans for known vulnerabilities in dependencies (Software Composition Analysis).
Train devs on secure coding practices and threat modeling.
4. 🧱 Harden Your CI/CD Infrastructure
Your pipeline tools (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions) must be treated like production systems.
Keep your CI/CD tooling up to date with the latest patches.
Isolate runners/build agents in secure environments (e.g., ephemeral containers).
Disable unused plugins or integrations.
5. 🚫 Scan and Block Malicious Code
Catch potential threats before they ship.
Set up pre-commit and pre-push hooks to run code checks.
Block deployments on failed security scans or test failures.
Use DAST (Dynamic App Security Testing) in staging environments.
6. 🧼 Verify Artifact Integrity
Ensure that what you build is what you deploy.
Sign artifacts with cryptographic hashes or digital signatures.
Use immutable artifact repositories like Artifactory or Nexus.
Validate artifact signatures before deployment.
7. 🔍 Audit Everything
Visibility is key to security.
Log all actions in the CI/CD pipeline, including builds, approvals, and deployments.
Use centralized logging and monitoring tools.
Regularly review logs and set up alerts for suspicious activity.
8. 📦 Secure the Supply Chain
Supply chain attacks are rising. Don’t let your dependencies be your weakest link.
Pin dependency versions and verify package integrity.
Use tools like Snyk, Dependabot, or OWASP Dependency-Check.
Adopt SBOMs (Software Bill of Materials) for transparency.
9. ✅ Implement Manual Approvals for Sensitive Deployments
Automation is powerful — but for critical systems, a human in the loop adds an extra layer of protection.
Require approvals for production pushes.
Use change management and ticketing systems to track decisions.
10. ♻️ Continuously Improve Security Posture
CI/CD security isn’t “set and forget.”
Perform regular security reviews and red team exercises.
Stay updated on CI/CD security trends and vulnerabilities.
Build a culture of DevSecOps — where devs, ops, and security work together.
Final Thoughts
A fast CI/CD pipeline is awesome. But a fast and secure pipeline? That’s where the real magic happens. By embedding these best practices into your workflow, you’re not just delivering features — you’re delivering them with confidence.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/devops-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
web development,
web development,
Web development is the process of building and maintaining websites and web applications that run online on a browser. It involves various tasks, from coding simple web pages to creating complex web-based applications, services, and social networks. This field combines creativity and technical expertise to create dynamic and engaging digital experiences.
Key Components of Web Development
Web development can be broadly divided into three main areas:
Front-End Development:
Focuses on the user interface and user experience (UI/UX).
Involves technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Tools and frameworks commonly used include React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Back-End Development:
Handles server-side logic, databases, and application functionality.
Involves programming languages like Python, Ruby, PHP, Java, and frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Laravel.
Databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB are also integral.
Full-Stack Development:
Combines front-end and back-end development skills.
Requires knowledge of multiple programming languages and frameworks to build complete web solutions.
The Web Development Process
Planning:
Define the purpose and objectives of the website or application.
Create wireframes and mockups to visualize the layout and design.
Design:
Focus on aesthetics and usability.
Use design tools like Adobe XD, Figma, or Sketch to craft visually appealing interfaces.
Development:
Write clean, efficient code to implement the planned design and functionality.
Ensure responsiveness and compatibility across devices and browsers.
Testing:
Perform thorough testing to identify and fix bugs.
Utilize tools like Selenium, Jest, or Mocha for automated and manual testing.
Deployment and Maintenance:
Deploy the website or application to a live server.
Regularly update and maintain the site to ensure optimal performance and security.
Popular Web Development Tools and Technologies
Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab
Package Managers: npm, Yarn
Task Runners: Gulp, Grunt
CSS Preprocessors: SASS, LESS
JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks: jQuery, React, Angular, Vue.js
Back-End Frameworks: Express.js, Ruby on Rails, Django, Flask
API Development: REST, GraphQL
The Role of Web Developers
Web developers play a critical role in the digital landscape. Their responsibilities include:
Writing and debugging code.
Collaborating with designers and stakeholders.
Optimizing websites for performance and scalability.
Staying updated on the latest trends and technologies.
Career Opportunities in Web Development
The demand for skilled web developers continues to grow as businesses increasingly rely on their online presence. Common career paths include:
Front-End Developer
Back-End Developer
Full-Stack Developer
Web Designer
UI/UX Designer
DevOps Engineer
Future Trends in Web Development
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Offer app-like experiences through the browser.
AI and Machine Learning: Enhance user experiences with personalized content and advanced analytics.
Voice Search Optimization: Cater to the growing use of voice assistants.
Cybersecurity: Emphasize secure coding practices to protect user data.
Serverless Architecture: Simplify deployment and scaling with platforms like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions.
Conclusion
Web development is an ever-evolving field that requires continuous learning and adaptation. Whether you’re looking to build a simple website or a complex application, mastering the fundamentals and staying updated with modern tools and techniques will help you succeed in this dynamic industry.
0 notes
Text
Essential Tools to Take Your Web Development to the Next Level
To take your web development skills to the next level, here are some essential tools that can help:
1. Code Editors and IDEs:
VS Code: A powerful, extensible code editor that supports a wide range of languages, extensions, and debugging tools.
Sublime Text: A fast and feature-rich editor with support for multiple programming languages and a sleek interface.
Atom: An open-source, customizable text editor, ideal for web development.
2. Version Control Systems:
Git: A version control tool to track changes in code and collaborate efficiently with other developers.
GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket: Platforms for hosting Git repositories and collaborating with teams.
3. Front-End Frameworks:
React.js: A JavaScript library for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces.
Vue.js: A progressive JavaScript framework for building web interfaces.
Angular: A robust framework for creating scalable and structured web apps.
Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework for building custom designs quickly.
Bootstrap: A popular CSS framework for building responsive and mobile-first websites.
4. Back-End Frameworks:
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime for building scalable server-side applications.
Express.js: A minimal web framework for Node.js, often used for building APIs and web apps.
Django: A high-level Python web framework for building secure and maintainable websites.
Ruby on Rails: A full-stack framework built on Ruby, known for rapid development and ease of use.
5. Database Management:
MySQL: A widely used relational database management system.
MongoDB: A NoSQL database that's flexible and scalable.
PostgreSQL: A powerful, open-source object-relational database system.
Firebase: A cloud-based real-time database with simple authentication and data synchronization.
6. Package Managers:
npm: Node.js package manager for managing JavaScript libraries and dependencies.
Yarn: An alternative package manager for JavaScript with a focus on performance and reliability.
7. API Tools:
Postman: A powerful tool for testing and interacting with APIs.
Swagger: An open-source framework for API documentation, design, and testing.
8. Task Runners & Module Bundlers:
Webpack: A static module bundler for JavaScript, CSS, and other assets.
Gulp: A task runner used for automating repetitive development tasks.
Parcel: A zero-config bundler that is easy to use and fast.
9. CSS Preprocessors:
Sass: A CSS preprocessor that extends CSS with variables, nested rules, and functions.
Less: A preprocessor with features like variables and functions to make CSS more manageable.
10. Testing Tools:
Jest: A testing framework for JavaScript, commonly used for testing React apps.
Mocha: A flexible JavaScript testing framework for Node.js.
Cypress: An end-to-end testing framework for web applications.
Selenium: A tool for automating web browsers, useful for functional and UI testing.
11. Containerization & Deployment:
Docker: A platform for building, running, and shipping applications inside containers.
Kubernetes: An orchestration platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Netlify: A platform for continuous deployment of web apps with automatic scaling.
Vercel: A platform that provides serverless deployment and front-end hosting.
12. UI/UX Design Tools:
Figma: A collaborative interface design tool for creating web and app prototypes.
Adobe XD: A vector-based tool for designing and prototyping user experiences.
Sketch: A design tool for web and mobile interfaces, available for macOS.
13. Collaboration Tools:
Slack: A messaging platform for team communication and collaboration.
Trello: A task management tool for organizing and prioritizing tasks in a project.
Asana: A work management platform that helps teams plan, organize, and execute projects.
Using these tools effectively can streamline your workflow, help you collaborate better with teams, and enhance the quality of your web development projects.
0 notes
Text
Essential Tools Every Web Developer Should Use

In the ever-changing landscape of web development, having the right tools can make all the difference. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting, equipping yourself with essential tools will not only save time but also improve the quality of your work. In this guide, we’ll cover some must-have tools for web developers and why they’re essential. If you're working with a website development company in India, chances are you’ll come across many of these tools in action.
Text Editors and IDEs
1. Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is one of the most popular text editors among developers. It’s lightweight, customizable, and packed with features like syntax highlighting, intelligent code completion, and an integrated terminal. With a wide range of extensions, VS Code can adapt to almost any programming language or framework.
2. Sublime Text
Sublime Text is another favorite, known for its speed and simplicity. It’s perfect for developers who prefer a clean interface but still need powerful features like multi-line editing and a command palette.
Version Control Systems
3. Git
Git is a cornerstone of modern web development. It allows developers to track changes, collaborate on projects, and maintain a history of all modifications. Paired with platforms like GitHub or GitLab, Git becomes an indispensable tool for teamwork and project management.
4. GitHub
GitHub provides a collaborative space where developers can store code, manage projects, and review contributions. Its user-friendly interface and integration with Git make it a go-to platform for version control and team collaboration.
Browser Development Tools
5. Chrome DevTools
Every web developer needs a reliable way to debug and test their code. Chrome DevTools offers a suite of tools directly within the browser, enabling you to inspect elements, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues in real time.
6. Firefox Developer Edition
Firefox Developer Edition is a browser specifically designed for developers. It includes tools for CSS grid debugging, responsive design mode, and JavaScript debugging, making it an excellent companion for front-end development.
Design and Prototyping Tools
7. Figma
Figma is a collaborative design tool that allows developers and designers to work together seamlessly. Its cloud-based platform ensures that everyone is working on the latest version of a design, reducing confusion and miscommunication.
8. Adobe XD
Adobe XD is another great tool for creating prototypes and wireframes. It’s user-friendly and integrates well with other Adobe products, making it ideal for teams already using the Adobe Creative Suite.
Task Runners and Package Managers
9. NPM (Node Package Manager)
NPM is the default package manager for Node.js, and it simplifies the process of managing dependencies in your projects. With a vast library of packages, NPM helps developers add functionality to their projects quickly and efficiently.
10. Gulp
Gulp is a task runner that automates repetitive tasks like minifying CSS, optimizing images, and bundling JavaScript files. It’s a great tool for improving your workflow and ensuring consistency across projects.
Testing and Debugging Tools
11. Jest
Jest is a JavaScript testing framework that helps developers ensure their code works as expected. With features like snapshot testing and a simple API, Jest makes writing tests more accessible.
12. Postman
Postman is essential for testing APIs. It allows developers to send requests, inspect responses, and debug issues effectively. Whether you’re working on front-end or back-end development, Postman simplifies the process of interacting with APIs.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
13. Slack
Communication is key in web development, especially when working with teams. Slack provides a platform for instant messaging, file sharing, and integrations with other tools, ensuring smooth collaboration.
14. Trello
Trello is a project management tool that uses boards and cards to organize tasks. It’s simple, flexible, and helps teams keep track of progress in an organized way.
The Role of a Website Development Company
If you’re looking to develop a website, collaborating with a professional website development company in India can be a game-changer. These companies not only bring technical expertise but also use many of the tools mentioned above to deliver high-quality websites. By leveraging their experience, you can focus on your business while they handle the technical aspects.
Conclusion
The right tools can significantly impact the efficiency and quality of web development. From text editors and design tools to version control systems and task runners, each tool serves a specific purpose in the development process. Whether you’re working independently or with a team, mastering these tools will set you up for success. And if you prefer to leave the technicalities to the experts, partnering with a reliable website development company in India ensures your project is in good hands.
#web design company in odisha#best web development agencies india#website development company in india#performance marketing agency#digital marketing agency in bhubaneswar
0 notes
Text
The Essential Tools Every Web Developer Needs
In the constantly changing realm of web development, possessing the right tools can be crucial. Whether you're an experienced professional or a newcomer trying to enter the field, understanding the tools required for web developers can improve your skills and streamline your workflow. As the demand for web developer services increases, knowing which tools to use can distinguish you from the competition. Let's explore the essential tools that every web developer should think about adding to their toolkit.
The code editor and IDE
A good code editor or integrated development environment (IDE) is essential for any web developer. Tools like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, and Atom offer a range of features including syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging. These editors streamline the coding process, making it easier for you to write clear and efficient code. As a web developer, choosing the appropriate code editor can greatly influence your productivity and the quality of your code.
The version control system
A version control system like Git is essential for web developers. They assist you in monitoring modifications to your code, collaborating with other developers, and managing various versions of your project. Platforms like GitHub, GitLab,and Bitbucket offer an easy-to-use interface for managing repositories and collaborating on code. With version control, you can ensure that your web development projects are organized and easily manageable
Browser developer tools
Web developers need to test and debug their websites across various browsers. Browser developer tools available in Chrome, Firefox, and Safari allow you to inspect components, monitor network activity, and troubleshoot problems in real-time. These tools are essential to ensure that your website functions smoothly across various platforms and devices
The structure and library
Structures and libraries can accelerate your development process by offering pre-written code for common functionalities.Popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js, along with libraries like Query, provide robust solutions for creating interactive and dynamic web applications.The use of these tools helps you implement features more efficiently and maintain consistency in your projects
Design tools
Design tools like Adobe XD, Figma, and Sketch are crucial for creating and prototyping user interfaces.These tools allow web developers to work together with designers and turn design concepts into functional web pages.A solid understanding of design principles and tools is crucial for creating a visually appealing and user-friendly website
Task runners and build tools
TaskRunner and tools like Gulp, Grunt, and Webpack automate repetitive tasks such as minification, compilation, and resource management. These tools streamline your workflow by effectively managing tasks, enabling you to concentrate on writing code rather than overseeing the construction process
Testing equipment
It is essential to make sure that your website is free of bugs and functions properly. Testing tools like Zest, Mocha, and Selenium offer automated testing solutions for your web applications. These tools assist you in identifying and resolving issues prior to deployment, guaranteeing a seamless user experience
SEO Tools
For any web developer. It is very important to understand and apply the best practices of . Tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and Ahrefs offer insights into your website's performance and assist in optimizing your content for search engines.Using these tools ensures that your website is visible and well-ranked in search results
Hosting and Deployment Platform
Choosing the right hosting and deployment platform is crucial to ensure your website is accessible to users.Services like Netlify, Vercel, and AWS offer robust solutions for deploying and hosting web applications.These platforms offer scalability, reliability, and performance, which are essential for delivering a smooth user experience
The Tools of Cooperation
Effective communication and collaboration are essential elements of successful web development projects.Tools like Slack, Trello, and Asana enhance collaboration and project management, making sure that everyone involved is aligned. These tools are used to operate.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Best CICD Tools

Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) tools have become indispensable in modern software development, automating the processes of building, testing, and deploying applications. As we move into 2024, the landscape of CI/CD tools continues to evolve, offering more robust features and integrations to streamline development workflows. In this article, we will explore the best CI/CD tools for 2024, highlighting their key features and benefits.
Jenkins
Jenkins remains one of the best CI/CD tools, renowned for its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem. It supports a wide range of configurations and is highly customizable, making it suitable for projects of all sizes.
Key Features:
Extensible Plugins: With over 1,800 plugins, Jenkins can integrate with almost any tool in your development stack.
Pipeline as Code: Jenkins Pipeline allows you to define your build process through code, ensuring consistency and version control.
Community Support: A large and active community ensures regular updates and extensive documentation.
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions has rapidly gained popularity as one of the best CI/CD tools, thanks to its seamless integration with GitHub repositories. It offers a simple yet powerful way to automate all aspects of your software development lifecycle.
Key Features:
Native GitHub Integration: Directly integrates with GitHub repositories, making it easy to trigger workflows based on various events.
Extensive Marketplace: A marketplace of pre-built actions that can be easily integrated into your workflows.
Scalability: Supports both self-hosted and GitHub-hosted runners, allowing you to scale your CI/CD processes as needed.
GitLab CI/CD
GitLab CI/CD is part of the comprehensive GitLab DevOps platform, providing a complete solution for managing your development lifecycle. It is known for its simplicity and powerful features.
Key Features:
Built-in CI/CD: Integrated directly into the GitLab platform, simplifying setup and configuration.
Auto DevOps: Automatically detects, builds, tests, and deploys your application using best practices.
Kubernetes Integration: Native support for Kubernetes, making it easy to deploy and manage containerized applications.
CircleCI
CircleCI is another leading CI/CD tool, known for its speed and efficiency. It provides powerful features that help teams automate their workflows and deliver quality software faster.
Key Features:
Parallelism: Run multiple tasks concurrently to speed up the build process.
Orbs: Reusable packages of CircleCI configuration that simplify setting up CI/CD pipelines.
Flexibility: Supports a wide range of languages and frameworks, making it suitable for diverse development environments.
Travis CI
Travis CI is a cloud-based CI/CD tool that integrates seamlessly with GitHub repositories. It is popular for its simplicity and ease of use, especially among open-source projects.
Key Features:
Easy Setup: Simple to set up with a .travis.yml file in your repository.
Pre-installed Environments: Provides pre-installed environments for various languages and platforms, reducing setup time.
Community Support: A large community and extensive documentation provide ample support for troubleshooting and optimization.
Bamboo
Bamboo by Atlassian is a robust CI/CD tool designed to work seamlessly with other Atlassian products like Jira and Bitbucket. It provides a powerful solution for continuous integration, deployment, and delivery.
Key Features:
Integration with Atlassian Suite: Seamless integration with Jira, Bitbucket, and Confluence.
Build Agents: Distribute builds across multiple agents to optimize performance.
Deployment Projects: Manage and automate deployments to various environments with ease.
Conclusion
Choosing the best CI/CD tools for your project depends on various factors, including your existing development environment, team preferences, and specific project requirements. Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, Travis CI, and Bamboo each offer unique strengths and capabilities, making them excellent choices for automating your build, test, and deployment processes in 2024.
Investing in the right CI/CD tools can significantly enhance your development workflow, improve code quality, and accelerate time to market. As the demand for faster and more reliable software delivery continues to grow, leveraging these tools will help you stay competitive and ensure your projects succeed.
0 notes
Text
GitLab on Google Cloud for faster delivery and security

GitLab On Google Cloud
Using an integrated solution that improves speed, security, and scalability, modernise the way you deploy software.
Product, development, and platform teams are always under pressure to produce cutting-edge software rapidly and at scale while lowering business risk in today’s fast-paced business climate. Nevertheless, fragmented toolchains for the software development lifecycle (SDLC) impede advancement. A handful of the difficulties that organisations have in contemporary development are as follows:
Different instruments
Workflows that are inefficient and context switching are caused by disconnected toolchains.
Worries about security
Vulnerabilities are introduced by traditional authentication techniques such service account keys.
Scalability problems
Maintaining scalable self-service deployment via Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) can become a significant challenge when enterprises take on an increasing number of projects.
As per the 2023 State of DevSecOps Report, enhancing daily workflow positively affects cultural components. Google Cloud has worked with GitLab on an integrated solution that reimagines how businesses approach DevSecOps to expedite the delivery of apps from source code on GitLab to Google Cloud runtime environments in an effort to enhance the daily experience of developers.
GitLab on Google Cloud Integration
The Google Cloud – GitLab integration enhances the developer experience by simplifying tool management and assisting workers in maintaining “flow.” The integration between GitLab and Google Cloud provides a holistic solution that improves software delivery, simplifies development, and increases security by reducing the need for context switching that comes with using various tools and user interfaces.
Google Cloud Gitlab
Without the requirement for service accounts or service account keys, the GitLab on Google Cloud integration employs workload identity federation for permission and authentication for GitLab workloads on Google Cloud.
Refer to the GitLab instructional Google Cloud IAM for instructions on configuring workload identity federation and the required Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles for the GitLab on Google Cloud integration.
GitLab elements
To make Google Cloud tasks within GitLab pipelines simpler, the GitLab on Google Cloud integration makes use of GitLab components that are developed and maintained by Google. You must follow the directions in the GitLab tutorial Google Cloud Workload Identity Federation and IAM policies to configure authentication and authorization for GitLab to Google Cloud in order to use the components for this connection.
Management of Artefacts
Using the GitLab on Google Cloud interface, you can quickly deploy your GitLab artefacts to Google Cloud runtimes by uploading them to the Artefact Registry. The artefacts can be seen in GitLab or the Artefact Registry, and Google Cloud provides access to the metadata for each artefact.
Continuous deployment and integration
With the GitLab on Google Cloud connection, you can execute your Google Cloud workloads by configuring the GitLab runner parameters directly in your GitLab project using Terraform.
You can use the Cloud Deploy or Deploy to GKE components if you have already configured Workload Identity Federation for authentication and permission to Google Cloud.
A cohesive strategy for DevSecOps
Imagine working on a single integrated platform where you can easily transition from developing code to deploying it. This is the reality made possible by the interaction between GitLab and Google Cloud. Google Cloud created a unified environment that empowers developers and promotes innovation by combining Google Cloud’s trustworthy infrastructure and services with GitLab’s source code management, CI/CD pipelines, and collaboration tools. Many advantages for customers come from this integration:
Reduced context switching
Developers don’t have to switch between GitLab and Google Cloud; they can remain in one tool.
Simple delivery
By making it easier for clients to set up their pipelines in GitLab and deliver containers to Google Cloud runtime environments, google cloud has decreased friction and complexity.
Adapted to suit business requirements
The Google Cloud – GitLab connection makes sure your DevSecOps pipelines can scale to match the demands of your expanding organisation by using Google Cloud’s infrastructure as the foundation.
To put it briefly, you can use Workload Identity Federation to securely integrate GitLab with Google Cloud, access your containers in both the Google and GitLab Artefact Registry, and deploy to Google Cloud runtime environments using CI/CD components specifically designed for the task. Let’s investigate more closely.
Prioritising security
Because the security of your programme is so important, Google Cloud included Workload Identity Federation (WLIF) in this integration. Static service account keys are no longer required thanks to this technology, which replaces them with transient tokens that drastically lower the possibility of compromise. Furthermore, Workload Identity Federation facilitates the mapping of identity and access management roles across GitLab and Google Cloud, simplifying management by centralising authentication through your current identity provider.
Coordinated management of artefacts
You can view your containers directly in GitLab and manage them in Google Artefact Registry repositories thanks to this connection. This allows you to utilise security scanning and has complete traceability of your created artefacts from GitLab to Google Cloud, all while adhering to GitLab’s developer workflow.
Pipelines that can be configured
Google Cloud has also released a set of CI/CD components as part of this integration to make pipeline building repeatable, easy to configure, and straightforward. The deployment to Google Cloud runtime environments was considered throughout the construction of these Google Cloud managed components. The ability to deploy an image to Google Kubernetes Engine, manage pipeline delivery with Cloud Deploy, and publish an image to the Google Artefact Registry are among the five components that are already accessible. Compared to using the Google CLI, Google Cloud’s preliminary benchmarking reveals that these components can be executed in GitLab CI pipelines more quickly and in smaller quantities.
Proceed with the following action
Are you prepared to enhance your DevSecOps process? Get a free trial of GitLab from the GitLab Web Store or buy it from the Google Cloud Marketplace if you don’t already have it. In the event that you already have a GitLab account, set up the integration right now. Additionally, if you’d like to talk to them about this integration or take part in customer experience research.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#gitlab#GoogleCloud#vulnerabilities#GKEcomponents#GoogleKubernetesEngine#DevSecOpsprocess#news#technews#technology#technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
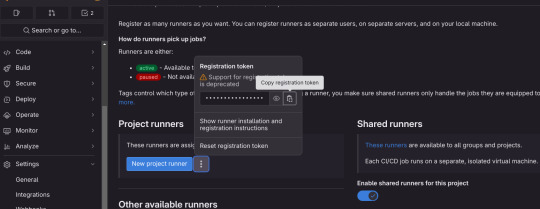
This one's gonna be pretty niche but Gitlab really said "saving a token on your systems that can register CI runners is insecure so we're going to make you save a token on your systems that's a full admin instead."
Deep-ridged brain move.
0 notes