#linux containers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Running 26 Linux distributions as containers. How much RAM do you think it will consume? The answer might surprise you, my friends. Just 1.2Gi RAM used on the freshly rebooted machine. Of course, this is a test lab running Ubuntu fully patched 22.04 LTS. But you get the gist. This stuff is born for enterprise workload. Here is how to set up a lab using shell script for fun and profit

-> Shell script to set up an LXD / Incus (Linux Containers) lab for testing purpose
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you're a linux[1] user who deploys multiple devices, I implore you: learn the command `scp`. It will change your life
It lets you copy files over an ssh pipe; if there's an ssh server on that host, you can essentially directly address a known file on that filesystem and say pwease gimme. And it's roughly the same syntax as `cp`, just with a `[user]@[host]:` before *either source or destination*[2].
And the real kicker is that neither source nor destination need be local:
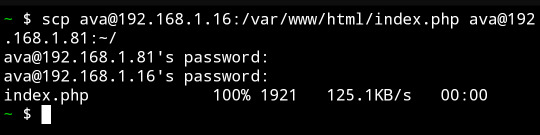
I copied a file from my web server to an icecast source client host by passing it through my phone.
Unreasonably handy tool to have on your toolbelt.
Footnotes under the cut.
[1] Okay, fine, you got me! It's not solely a linux util. SCP is part of the openssh suite, which means that it's available on virtually every OS under the sun... Including being included by default on Windows 10 1709 and later versions of Windows. It's already on your mac, your BSD system, and almost certainly your phone, too. SSH servers and *nix go together like picnics and baskets, though, so I wouldn't exactly pull the *average* windows user aside to recc' `scp`.
[2] What's most interesting to me is that the `[user]@[host]` is used for the SSH client to know where it's authenticating and how, but the actual filesystem location's format is not processed by the SSH client; it's the *server's* format, not the client, that matters for parsing the file location. In some cases this can lead to a mismatch on filenames that you're receiving vs requesting, but the -T flag disables that checking, and then use `[email protected]:D:\\Documents\\testdata.bin` (drive letter indicated and backslashes escaped) to refer to it
#openssh#scp#linux#i am sorry to secure contain protect fans who are uninterested in this being in your tags but. hash collisons happen
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
I asked my Linux nerd boyfriend what Linux distros he would recommend to the average TS2 user looking to move, and he recommended Fedora. Fedora is an easy install that has a desktop environment (Gnome) that takes a bit to get used to, but you can uninstall that for KDE Plasma for a streamlined Windows-esque experience.
Arch is not recommended at all unless you know what you're doing. Fullstop. It's for hardcore users.
He also does not recommend Ubuntu despite it's ease of use. It is radically different compared to Windows and other distros. Installing programs on Ubuntu is difficult because it sorts files in a different way than what installers expect so you need to do a ton of tweaking and troubleshooting.
#spell.txt#linux#this post is not made for experienced linux users btw i dont want this to breach containment#sims 2
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ansible Collections: Extending Ansible’s Capabilities
Ansible is a powerful automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. One of the key features that enhances its flexibility and extensibility is the concept of Ansible Collections. In this blog post, we'll explore what Ansible Collections are, how to create and use them, and look at some popular collections and their use cases.
Introduction to Ansible Collections
Ansible Collections are a way to package and distribute Ansible content. This content can include playbooks, roles, modules, plugins, and more. Collections allow users to organize their Ansible content and share it more easily, making it simpler to maintain and reuse.
Key Features of Ansible Collections:
Modularity: Collections break down Ansible content into modular components that can be independently developed, tested, and maintained.
Distribution: Collections can be distributed via Ansible Galaxy or private repositories, enabling easy sharing within teams or the wider Ansible community.
Versioning: Collections support versioning, allowing users to specify and depend on specific versions of a collection. How to Create and Use Collections in Your Projects
Creating and using Ansible Collections involves a few key steps. Here’s a guide to get you started:
1. Setting Up Your Collection
To create a new collection, you can use the ansible-galaxy command-line tool:
ansible-galaxy collection init my_namespace.my_collection
This command sets up a basic directory structure for your collection:
my_namespace/
└── my_collection/
├── docs/
├── plugins/
│ ├── modules/
│ ├── inventory/
│ └── ...
├── roles/
├── playbooks/
├── README.md
└── galaxy.yml
2. Adding Content to Your Collection
Populate your collection with the necessary content. For example, you can add roles, modules, and plugins under the respective directories. Update the galaxy.yml file with metadata about your collection.
3. Building and Publishing Your Collection
Once your collection is ready, you can build it using the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection build
This command creates a tarball of your collection, which you can then publish to Ansible Galaxy or a private repository:
ansible-galaxy collection publish my_namespace-my_collection-1.0.0.tar.gz
4. Using Collections in Your Projects
To use a collection in your Ansible project, specify it in your requirements.yml file:
collections:
- name: my_namespace.my_collection
version: 1.0.0
Then, install the collection using:
ansible-galaxy collection install -r requirements.yml
You can now use the content from the collection in your playbooks:--- - name: Example Playbook hosts: localhost tasks: - name: Use a module from the collection my_namespace.my_collection.my_module: param: value
Popular Collections and Their Use Cases
Here are some popular Ansible Collections and how they can be used:
1. community.general
Description: A collection of modules, plugins, and roles that are not tied to any specific provider or technology.
Use Cases: General-purpose tasks like file manipulation, network configuration, and user management.
2. amazon.aws
Description: Provides modules and plugins for managing AWS resources.
Use Cases: Automating AWS infrastructure, such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and RDS databases.
3. ansible.posix
Description: A collection of modules for managing POSIX systems.
Use Cases: Tasks specific to Unix-like systems, such as managing users, groups, and file systems.
4. cisco.ios
Description: Contains modules and plugins for automating Cisco IOS devices.
Use Cases: Network automation for Cisco routers and switches, including configuration management and backup.
5. kubernetes.core
Description: Provides modules for managing Kubernetes resources.
Use Cases: Deploying and managing Kubernetes applications, services, and configurations.
Conclusion
Ansible Collections significantly enhance the modularity, distribution, and reusability of Ansible content. By understanding how to create and use collections, you can streamline your automation workflows and share your work with others more effectively. Explore popular collections to leverage existing solutions and extend Ansible’s capabilities in your projects.
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#information technology#linux#containerorchestration#container#kubernetes#containersecurity#docker#dockerswarm#aws
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Google please I can see the fucking
Desktop icon
ENABLE IT NOW NOW NOW NOW NOW
#davepaste#having a full linux Desktop on my phone would fix me#(ive already ran linux on my phone; and on this particular phone i ran the arm version of windows 11 just to make it suffer some)#this is built in though. admittedly in a container. but that's fine#my phone is a foldable too. so like. it'll actually be somewhat comfortable to use#i wonder if I'll be able to install mobile DEs like phosh or mobile gnome#if thats available yet? gnome is ugly but i think their design philosophy will work very well for mobile devices
1 note
·
View note
Text
DogCat - Exploiting LFI and Docker Privilege Escalation -TryHackMe Walkthrough
In this walkthrough, we’ll explore the Dogcat room on TryHackMe, a box that features a Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability and Docker privilege escalation. LFI allows us to read sensitive files from the system and eventually gain access to the server.There are a total of 4 flags in this machine which we need to find. Let’s Dive in! Step 1: Scanning the Target Start by scanning the target…
#Backup Script Exploit#Bash Reverse Shell#Crontab Exploit#Cybersecurity in Docker#Docker Container Security#Docker Exploit Tutorial#docker privilege escalation#Docker Security#Docker Vulnerabilities#Linux Privilege Escalation#Netcat Listener Setup#Reverse Shell Exploit#Shell Injection Attack#Tar Archive Exploit#Volume Mount Vulnerability
1 note
·
View note
Text
accidently joined tumblr outside my "homework" qube
was not pretty
0 notes
Text
Experience Endless Space with CosmoPirates Card Battler

CosmoPirates deck building, card battling game launches on Linux and Windows PC. All the fun is brought to you by the talented team at BlackMoon Design. Available now on Steam with 100% Positive reviews. CosmoPirates is taking card battling and deck building to the final frontier with a mix of strategy and cartoonish comedy in endless, colorful space. Imagine exploring the galaxy, picking your battles, building up your crew, and crafting the perfect deck to challenge the mighty Overlord. That's also your mission, and it’s an epic one, on Linux. Every time you play, you get a brand-new galaxy to explore, due to launch into the game's procedurally generated universe. This means each run is full of fresh bounty, danger, quirky characters, and loads of high adventure. You get to choose your path, taking on challenges and quests in the order that suits your strategy. Whether you play it safe or go all out deck building in CosmoPirates, your crew is counting on you to lead them to victory! In this title, gadgets, weapons, gambits, and strategies are all at your fingertips. Each card you collect can turn the tide of battle. Find them during your travels, buy them from traders, win them in combat – whatever it takes to build your ultimate deck. You’ll also need to master combos and synergies to stay ahead. Will you lick a battery for extra power or read comic books to gain action points? The choice is yours.
CosmoPirates deck building Trailer
youtube
Your destiny in CosmoPirates deck building is to rise through the ranks and take down the dreaded pirate overlord. This villain has been ruling with an iron fist, and it's up to you to end their reign of terror. Once you defeat the overlord, you take their place, which wraps up your run. But here's the twist: the next time you play, you'll face off against your previous character, complete with all the power and abilities they acquired. CosmoPirates was created by two passionate developers who are dedicated to making the deck building game as fun and engaging as possible. They want to hear from you! Your feedback, ideas, and any issues you encounter are crucial in helping them make the game even better. So, jump into the action, share your thoughts on Discord, and help shape the future of the title. Whether you’re a seasoned card battler or new to the deck building genre, CosmoPirates offers an exciting and fresh experience. So gear up, rally your crew, and dive into the vibrant chaos of space adventures. Priced at $9.59 USD / £7.99 / 9,43€ with the 20% launch discount on Steam. Along with support for Linux and Windows PC.
#cosmopirates#deck building#card battler#linux#gaming news#blackmoon design#ubuntu#windows#pc#container electron#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Some People Using ZuluCrypt?
File:VeraCrypt screenshot.png I had more dreams, but I did not record them. Now, all that I can remember is barely part of my last dream. This dream involved ZuluCrypt and / or one or more other encryption programs / software / applications / apps like VeraCrypt et cetera. In this dream, some groups of people & individuals were on computers using the operating system, Linux, probably the…
View On WordPress
#Computer#Container#Container File#Container Format#Dismount#Encryption#Favorite#Linux#Mount#opensource#Program#Software#Ubuntu#VeraCrypt#ZuluCrypt
0 notes
Text
I have been using Btrfs for several months, and it has been stable enough for me. It is a file system that can be used as a storage driver for Linux containers like LXD, Incus, or Docker. If you want to install Btrfs support on Debian Linux and format & mount a disk drive, see my tutorial
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Open-Source DevOps Monitoring Tools in 2024
Best Open-Source DevOps Monitoring Tools in 2024 @vexpert #vmwarecommunities #devops #monitoring #opensource #freedevopstools #freemonitoringtools #infrastructureascode #iac #virtualization #docker #containers #vhtforums #virtualizationhowto
DevOps has become crucial in modern development practices as infrastructure-as-code, cloud services, and CI/CD is a huge part of modernized infrastructure. Along with provisioning resources, DevOps monitoring is an extremely important part of the overall picture of infrastructure. This blog post looks at the best open-source monitoring tools in DevOps for continuous monitoring tools, many of…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Unleashing Efficiency: Containerization with Docker
Introduction: In the fast-paced world of modern IT, agility and efficiency reign supreme. Enter Docker - a revolutionary tool that has transformed the way applications are developed, deployed, and managed. Containerization with Docker has become a cornerstone of contemporary software development, offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and portability. In this blog, we'll explore the fundamentals of Docker containerization, its benefits, and practical insights into leveraging Docker for streamlining your development workflow.
Understanding Docker Containerization: At its core, Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to package applications and their dependencies into lightweight, self-contained units known as containers. Unlike traditional virtualization, where each application runs on its own guest operating system, Docker containers share the host operating system's kernel, resulting in significant resource savings and improved performance.
Key Benefits of Docker Containerization:
Portability: Docker containers encapsulate the application code, runtime, libraries, and dependencies, making them portable across different environments, from development to production.
Isolation: Containers provide a high degree of isolation, ensuring that applications run independently of each other without interference, thus enhancing security and stability.
Scalability: Docker's architecture facilitates effortless scaling by allowing applications to be deployed and replicated across multiple containers, enabling seamless horizontal scaling as demand fluctuates.
Consistency: With Docker, developers can create standardized environments using Dockerfiles and Docker Compose, ensuring consistency between development, testing, and production environments.
Speed: Docker accelerates the development lifecycle by reducing the time spent on setting up development environments, debugging compatibility issues, and deploying applications.
Getting Started with Docker: To embark on your Docker journey, begin by installing Docker Desktop or Docker Engine on your development machine. Docker Desktop provides a user-friendly interface for managing containers, while Docker Engine offers a command-line interface for advanced users.
Once Docker is installed, you can start building and running containers using Docker's command-line interface (CLI). The basic workflow involves:
Writing a Dockerfile: A text file that contains instructions for building a Docker image, specifying the base image, dependencies, environment variables, and commands to run.
Building Docker Images: Use the docker build command to build a Docker image from the Dockerfile.
Running Containers: Utilize the docker run command to create and run containers based on the Docker images.
Managing Containers: Docker provides a range of commands for managing containers, including starting, stopping, restarting, and removing containers.
Best Practices for Docker Containerization: To maximize the benefits of Docker containerization, consider the following best practices:
Keep Containers Lightweight: Minimize the size of Docker images by removing unnecessary dependencies and optimizing Dockerfiles.
Use Multi-Stage Builds: Employ multi-stage builds to reduce the size of Docker images and improve build times.
Utilize Docker Compose: Docker Compose simplifies the management of multi-container applications by defining them in a single YAML file.
Implement Health Checks: Define health checks in Dockerfiles to ensure that containers are functioning correctly and automatically restart them if they fail.
Secure Containers: Follow security best practices, such as running containers with non-root users, limiting container privileges, and regularly updating base images to patch vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: Docker containerization has revolutionized the way applications are developed, deployed, and managed, offering unparalleled agility, efficiency, and scalability. By embracing Docker, developers can streamline their development workflow, accelerate the deployment process, and improve the consistency and reliability of their applications. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just getting started, Docker opens up a world of possibilities, empowering you to build and deploy applications with ease in today's fast-paced digital landscape.
For more details visit www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhat#linux#docker#aws#agile#agiledevelopment#container#redhatcourses#information technology#ContainerSecurity#ContainerDeployment#DockerSwarm#Kubernetes#ContainerOrchestration#DevOps
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Auslastung eines Containers unter Docker auslesen (CPU + RAM)
Zur Analyse und zur Überprüfung der Leistung unseres Docker-Servers kann es praktisch sein, die aktuelle CPU-Auslastung und den Arbeitsspeicher von einzelnen Containern auszulesen. Dafür bietet die beliebte Plattform für Containerisierung...[Weiterlesen]
0 notes
Text
Master containerization with #Docker training. Discover the tools that streamline the deployment, scaling, and management of applications. Become an indispensable part of the DevOps ecosystem. https://www.dclessons.com/docker-overview-installing-docker
#docker#containers#containerization#devops#kubernetes#cloudcomputing#linux#virtualization#softwaredevelopment#infrastructureascode#automation#orchestration
0 notes