#membrane repolarized
Text
page 183 - When I was younger and in boy scouts, badges were it. I worked my way through the badge section of the scout book, applying for the badges I already thought I qualified for and working steadily to achieve the ones that asked for something new. I started working on one for trapping and skinning animals, really thought about where I should run my trap line and what kinds of animals I might catch. I didn't know how to trap but thought I could figure it out, or that the scout leader would eventually get around to showing us some techniques.
I didn't understand that a trap line wasn't something like a clothesline that you set up in the woods. You didn't walk the string every few days plucking off whatever creature had been unlucky enough to have its leg caught or its neck snapped. I never understood the mechanics of it all. And after months of waiting I re-read the book and noticed that badge was only available to boys who lived in the north where trapping happened.
Anyway, I feel weird. This badge is for identifying four supernovae and having your discovery confirmed by a national astronomical body.
#biology#biologist#zoology#zoologist#membrane#membrane polarity reversed#membrane reconstitution#membrane repolarized#picture on oscilloscope#diagram illustrating relationship between nerve impulses and the oscilloscope record they produce#spike#boy scouts#merit badges#merit#badges#gotta catch em all#astronomy#stars#intergalactic#interstellar#solar#solar system#galaxies#planets#james webb space telescope
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
The crucial role of Ca and K in cardiac muscle and the amazing role of Ca/K pump play in our body 🫀
Calcium and potassium play crucial roles in cardiac muscle physiology. Calcium is involved in the initiation of muscle contraction. When an action potential travels down the cardiac muscle cell, it triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. These ions bind to troponin, allowing the myosin and actin filaments to interact and contract the muscle.
On the other hand, potassium is crucial for muscle relaxation. After contraction, potassium ions move out of the cell, leading to repolarization. This repolarization is essential for the cardiac muscle to relax and prepare for the next contraction. The balance between calcium-induced contraction and potassium-induced relaxation is vital for the rhythmic beating of the heart.
Ca/K pump
The calcium-potassium pump, also known as the Ca²⁺/K⁺ pump is a vital component of cellular function, particularly in maintaining ion balance. In cardiac muscle cells, this pump helps regulate the levels of calcium and potassium.
The pump works by actively transporting calcium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell against their respective concentration gradients. This process requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The calcium-potassium pump plays a crucial role in restoring the resting membrane potential after each cardiac muscle contraction, contributing to the overall electrical and mechanical activity of the heart.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did I understand how a membrane potential works, as well as what is a potential, as well as what is the physiological meaning of depolarization, repolarization and hyperpolarization of a cell, as well as what is a depolarization wave in the heart, as well as how it is evaluated by an ECG, as well as how ECG works, as well as how an electrode works, as well as how to read an ECG in D2, what means each freaking wave and why the hell do they look like this?
Sure. I did. It tooks me a whole afternoon.
Did I have a meltdown because of how hard to grasp those concepts are for me? Sure.
#lar rants#i didn't understand it for almost 5 years and i was driving me insane#but my bf took the time and energy to explain to me#and to help regulate myself after my meltdown#it tooks so long#it was so difficult#I'm so tired now aaaah#but it was worth it ig
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
About Action Potentials
Alright, listen up broskis. I’m explaining how brain cells (AKA neurons) activate, the technical terms being how they create an action potential.
We start at the resting potential of the membrane at around -70 millivolts, this number is just a comparison of the inside of the neuron to the outside. Other neurons give the membrane signals to become more positive or more negative. Making it more positive increases the likelihood of the neuron actually firing because the membrane has to reach -55 millivolts to activate, anything below this number and nothing will happen (the creatively named ‘All or Nothing’ Principle). From there it will fire up to +40 millivolts, called depolarization. It gets so positive because sodium ions, which are positive, enter the membrane and make it more positive.
As they say, what comes up must also come down, and so we enter repolarization, the nosedive back into the negative millivolts. This part of neural firing involves potassium ions, again positive, to leave the membrane and lower the charge of the membrane to make it more negative. The next part of this journey leads the neuron membrane to become even more negative than it was at the start of this fun process, and professionals call this the refractory period. This period just gives the neuron a bit of a break and makes sure it can’t fire for a small time after an action potential. Towards the end of this time, potassium ions stop leaving the membrane and the membrane voltage returns to the resting potential.
I can explain this using a more familiar process that people might be able to understand better: a laundromat. When you go to use a washer in a laundromat, it’s at a resting potential, that being having no clothes in it. Going to start it, it’ll only start when you pay all the money it requires, not some of the money. This represents that ‘All or Nothing’ Principle. Next the depolarization happens: it washes your clothes with detergent. The repolarization phase is the rinsing and wind down at the end of a cycle. Your clothes being in it and needing taken out is the refractory period because the washer can’t wash another load with the current load still in it. The washer enters its resting potential when you take your clothes out to move them to a dryer.
And that, my friends, is how action potential works. I hope you appreciated my real-life example because I had to work for it.
0 notes
Text
Hyperkalemia ecg findings

The PR and QRS intervals may lengthen.3įurther elevations in potassium levels can lead to sinoatrial and atrioventricular conduction blocks with resulting escape beats and rhythms. As a result, P-wave amplitude decreases and P waves flatten and may disappear altogether. Atrial tissue is more sensitive to this effect than ventricular tissue. In particular, the inverted lateral T waves associated with left ventricular hypertrophy may pseudonormalize.2 These T-wave changes result from acceleration of the terminal repolarization of the myocytes and are often most pronounced in the precordial leads.Īs potassium levels rise further, cardiac conduction between myocytes is suppressed. However, in most patients, the ECG shows largeamplitude T waves rather than the classic tented T waves.1 In addition, the direction of the T wave may change. The earliest ECG signs of hyperkalemia are “tented” T waves, which are classically described as tall, symmetrically narrow, and peaked (see Figure 2). Pseudohyperkalemia results when potassium is released from platelets in the setting of thrombocytosis. Spuriously elevated potassium levels can occur with hemolysis during phlebotomy. Methamphetamine use can cause renal failure. The causes of hyperkalemia include acute and chronic renal failure, diabetic ketoacidosis, mineralocorticoid deficiency, type IV renal tubular acidosis, medications (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics, lithium, NSAIDs, and beta-adrenergic antagonists), acute digoxin toxicity, rhabdomyolysis, burns, crush injuries, and severe dehydration-as well as any combination of the above. As a result, changes in serum potassium level can have dramatic effects on cardiac cell conduction and, consequently, on the ECG. Potassium, the predominant intracellular cation, plays an important role in maintenance of the potential across the cellular membrane, as well as in depolarization and repolarization of myocytes and neurons. Although this response to bicarbonate might also be associated with a toxicologic insult (such as can cause ventricular tachycardia), the finding of peaked T waves points strongly to an elevated serum potassium level. The patient’s ECG response to bicarbonate makes primary cardiac disease and ischemia less likely. The findings on these 2 ECGs suggest hyperkalemia, B. The second ECG (Figure 2), obtained after administration of bicarbonate, reveals slowing of the heart rate, narrowing of the QRS complex, and the presence of “tented,” or peaked, T waves, primarily in the precordial leads. The potential causes of ventricular tachycardia are numerous among them are primary cardiac disease ischemia and other primary noncardiac disorders, such as toxicologic insults and electrolyte abnormalities. The first ECG reveals a regular wide-complex tachycardia of unclear origin (Figure 1). The differential diagnosis for this finding includes supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy or bundle-branch block, pacemaker-mediated tachycardia, sodium channel blocker toxicity, hyperkalemia, preexcitation, and ventricular tachycardia. Which of the following diagnoses is best supported by the ECGs and clinical findings? Fifteen minutes later, a second ECG is obtained (B). After arterial blood gas measurement reveals significant metabolic acidosis (pH, 7.08 PO2, 217 mm Hg PCO2, 22 mm Hg), sodium bicarbonate is administered. Initial treatment includes oxygen, intravenous fluids, and lidocaine the patient’s condition does not change. Neurologic examination demonstrates mild diffuse symmetric weakness.Īn ECG is obtained (A). A 2/6 systolic murmur is audible. Abdomen is soft and nontender. Heart rate is 152 beats per minute and regular respiration rate, 24 breaths per minute blood pressure, 142/68 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry shows that oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. He has no history of cardiac disorders, and he denies chest pain, palpitations, and abdominal pain. A 34-year-old man presents to the emergency department with progressive, generalized weakness and shortness of breath that began 2 weeks earlier.

0 notes
Photo

Can you answer today’s question 🙋♀️?! Q: Which of the following are slow undulating changes in the resting membrane potential (RMP) of the gastrointestinal smooth muscles initiated by the interstitial cells of Cajal, and composed of gradual depolarization followed by gradual repolarization, and caused by cyclic activation and deactivation of Na/K pump? 🤔…#physiology #biology #neet #nurse #doctor https://www.instagram.com/p/CjepZZQuduc/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
PROPERTIES OF MUSCLES
Why are muscles so important? All the different types of muscles do have their functions but there are general properties of the muscles that we must know.
Conductibility- conduct action potential.
In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarisation then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize.
As an action potential (nerve impulse) travels down an axon there is a change in electric polarity across the membrane of the axon. In response to a signal from another neuron, sodium- (Na+) and potassium- (K+) gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. Na+ channels open at the beginning of the action potential, and Na+ moves into the axon, causing depolarization. Repolarization occurs when the K+ channels open and K+ moves out of the axon, creating a change in electric polarity between the outside of the cell and the inside. The impulse travels down the axon in one direction only, to the axon terminal where it signals other neurones.
Irritability- react when stimulated.
It’s stands for the ability of an organism or a specific tissue to react to the environment. In physiology it is the state of being abnormally responsive to slight stimuli, or unduly sensitive. myotatic irritability the ability of a muscle to contract in response to stretching.
Contractibility- muscle can shorten or produce tension.
Contractibility is the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten. For instance, in order to flex (decrease the angle of a joint) your elbow you need to contract (shorten) the biceps brachii and other elbow flexor muscles in the anterior arm. Notice that in order to extend your elbow, the posterior arm extensor muscles need to contract. Thus, muscles can only pull, never push.
Relaxation- Return to resting properties after contraction.
Distensibility(dilated)- ability to be stretched by an outer force (muscle is not injured unless stretched beyond its physiological limits)
Elasticity- elongation, return back to its original position.
Elasticity is the ability to recoil or bounce back to the muscle's original length after being stretched.

3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tremblay et al.: Figures and Boxes
Figure 1: Diversity, Classification, and Properties of Neocortical GABAergic INs
Neocortical GABAergic IN: GABA-releasing (likely inhibitory) interneuron (connecting between perception/motor output?) within the fetal brain
all of these express one of [PV parvalbumin (relation to general albumin carrier in the blood?), somatostatin (insulin/glucagon balance regulator), 5HT3a serotonin receptor] and can thus be categorized by those markers
further classification of different neocortical GABA-ergic INs can be obtained via morphology, targeting biases, other biomarkers, and electrophysiological/synaptic properties
tree classification: 1 of 3 markers » morphology » targeting bias » anatomy » biophysical properties of firing (firing patterns, spiking, refractory) » synaptic properties » addt'l markers
Figure 2: Laminar Distribution of IN Groups
L1, 2, 3, 4, 5a, 5b, and 6 are all layers in the neocortex
distribution of the three major GABA-ergic IN types as distinguished by PV, Sst, and 5HT3a marker expression (5HT3a separated into VIP and non-VIP expressing cells) varies with neocortical layer
significance: varying compositional make-up of L layers signifies likely variance in roles they play in fetal brain function + later development of cognition
Box 1: PV FS Basket Cells Are Specialized for Speed, Efficiency, and Temporal Precision
physical properties of PV FS cells suit them for rapid, precise firing
machinery for fast EPSPs: AMPA receptors w/ GluR1 subunits only, low membrane resistance, very active dendrites
machinery for brief and highly repetitive APs: sub-threshold Kv1 channels that allow for quick repolarization, "Na+ channels with slower inactivation and faster recovery"
these components are all concentrated at the appropriate areas of the neuron to reach high efficacy
Figure 3: Cell-Specific Connectivity and Subcellular Domains Targeted by IN Subtypes
Sst martinotti cells synapse near the soma of the L2/3 cell
nonVIP 5HT3aR NGFCs synapse near the branches of the L2/3 dendrite/axon
in L5/6 pyramidal cells, NGFC inputs are broken up by different layers (?)
Figure 4: Circuit Motifs Involving INs
different functions of interneurons in modulating synaptic signaling are dependent on placement of IN and source of excitatory input
feedforward inhibition: distal excitation » IN and pyramidal cell; IN then also inhibits pyramidal cell to modulate the effects of the distal excitation
feedback inhibition: PC excitation » IN inhibits the original PC source of excitation to gradually modulate its signal » IN also inhibits same-layer proximal PCs to unify regional signaling pattern
disinhibition: IN » IN » PC so that the end result is the reduction of inhibition on the pyramidal cell's excitatory activity
Figure 5: Thalamocortical FFI by PV Neurons Imposes Coincidence Detection
FFI via PV neurons allows for temporal summation window in certain spaces/moments of time
this is achieved by increasing inhibition at all other time periods; now "near-synchornous inputs are required for efficient summation of EPSPs and to drive AP firing on the PC"
[I think that] NGFCs weaken the PV inhibition of PCs, allowing for a wider window of temporal summation and lateral signaling recruitment of other PCs?
FFI prevents saturation via PV cell recruitment; NGFC signaling weakens this mechanism. Thus, depending on how much FFI is needed in certain regions, the NGFC vs. PV cell population concentration ratios will vary
Figure 6: FBI and Differential Effect of PV and Sst IN-Mediated Inhibition
difference between PV and Sst IN inhibition: PVs show decreased response to repeated external inputs due to anatomical and synaptic features from Box 1; Ssts show increased response due to "opposing" or somewhat "antithetical" physical properties to PVs
thus PVs function to synchronize activity laterally across two or more pyramidal cells, i.e., spatial summation; Ssts function to amplify all inputs to a single PC, i.e., temporal summation
PVs have high permeability (low resistance) which means that EPSPs generated diffuse and disperse easily, so highly repetitive inputs do not build up and the cell is unable to undergo temporal summation; on the other hand, insensitivity to temporal summation means that the cell can 'detect' synchronized spatial summation » it's not just a LACK of temporal summation, it's that a "large amount of input at one time" must be present, which means it's uniquely suited to spatial summation
Ssts have low permeability (high resistance) which means they can essentially STORE charge and thus undergo temporal summation with highly repetitive inputs from external sources
Figure 7: Vip IN-Mediated Disinhibition
Vip INs selectively inhibit Sst INs that are targeting a single pyramidal cell, so that when Vips fire, PCs are disinhibited
area-wide excitability is increased broadly as Vips are recruited; or, if a single Vip is activated, so too are just a few selected PCs disinhibited
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

page 183 - merit badge railway sign
#biology#biologist#zoology#zoologist#membrane#membrane polarity reversed#membrane reconstitution#membrane repolarized#picture on oscilloscope#diagram illustrating relationship between nerve impulses and the oscilloscope record they produce#spike#merit#merit badges#boy scouts#scouts#baden powell#beavers#cubs#nft#railway#train#signal#do not cross#safe to cross#signs#signage#the 4 o'clock from new orleans#tracks#track#track of the day
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
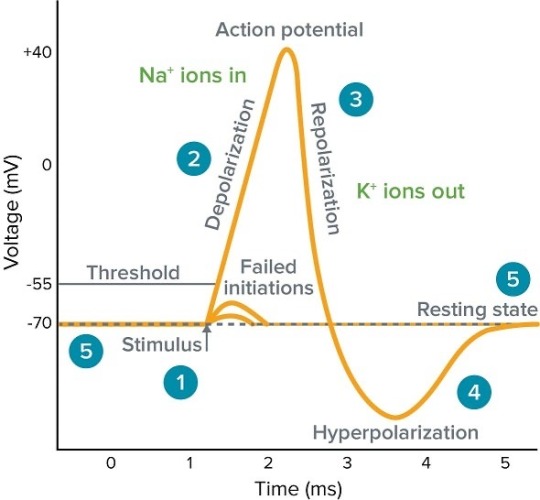
Neurophysiological Symphony: Decoding the Intricacies of Neuronal Action Potentials 🧠⚡️
Salutations, Tumblr scholars! 🎓 Prepare for a cerebral voyage as we delve into the profound intricacies of neuronal communication, spotlighting the ethereal ballet of action potentials! 🌌💫
Introduction:
Neurons, the virtuosos of our nervous system, engage in a sophisticated dialogue facilitated by the nuanced choreography of action potentials. Let us dissect this neurophysiological marvel with precision and finesse. 📚✨
1. The Prelude - Axon Hillock Overture:
Initiation unfolds at the axon hillock, a nexus of decision-making. Voltage-gated sodium channels undergo conformational changes, inducing an influx of sodium ions, thus instigating the critical decision to fire—an orchestration known as the initiation phase. ⚙️⚠️
2. Act I - Depolarization Crescendo:
The ensuing depolarization phase witnesses a surge in membrane voltage, orchestrated by the influx of positively charged sodium ions. This dynamic spectacle disrupts the membrane's resting potential, marking the commencement of the neuronal conversation with unparalleled fervor. 📈🎻
3. Act II - Repolarization Sonata:
Voltage-gated potassium channels, in a harmonious interlude, activate, allowing potassium efflux. Repolarization unfolds gracefully, reinstating the neuron's electrical equilibrium. The meticulous choreography readies the neuron for subsequent engagements. 🚪💨🔄
4. Act III - Hyperpolarization Cadence:
A brief hyperpolarization, an encore of sorts, ensues as potassium efflux persists, momentarily exaggerating the negative membrane potential. This nuanced cadence serves as a poetic pause before the neural narrative resumes. ⬇️🎭
5. Epilogue - Sodium-Potassium Pump Ballet:
In the epilogue, the sodium-potassium pumps elegantly perform their backstage ballet. Sodium is actively extruded, while potassium is ushered back onto the stage, meticulously restoring the resting membrane potential. A harmonious reset concludes this neurophysiological masterpiece. 🔄🔧
Embark on this odyssey through the synaptical intricacies! 🚀🔬
References:
1. Kandel, E. R., Schwartz, J. H., & Jessell, T. M. (2013). Principles of Neural Science.
2. Purves, D., Augustine, G. J., Fitzpatrick, D., et al. (2018). Neuroscience.
3. Bear, M. F., Connors, B. W., & Paradiso, M. A. (2016). Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain.
#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#neurobiology#neurology#neurophysiology
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Repolarization
Repolarization
by tricklesnitz
n. The restoration of a polarized state across a membrane, as in a muscle fiber following contraction. The act or process of polarizing again, a renewed polarization, the restoration of polarization.
-
Yaoyorozu goes beet red. “Well,” she starts, voice soft. “Um.” Aizawa puts his papers down and folds his hands together on top of the latest folder. “Is… there any way you can make changes to your gradebook?”
This was a surprise. Was Yaoyorozu going to ask him to cheat grades for her? “That depends. Grades? Absolutely not.”
Words: 3507, Chapters: 1/1, Language: English
Fandoms: 僕のヒーローアカデミア | Boku no Hero Academia | My Hero Academia
Rating: Teen And Up Audiences
Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply
Categories: Gen, M/M
Characters: Aizawa Shouta | Eraserhead, Yamada Hizashi | Present Mic, Yaoyorozu Momo, Shinsou Hitoshi, Yaoyorozu Momo's Parents
Relationships: Aizawa Shouta | Eraserhead/Yamada Hizashi | Present Mic
Additional Tags: Trans Male Character, Trans Aizawa Shouta | Eraserhead, Trans Yaoyorozu Momo, Trans Boy Yaoyorozu Momo, Minor Original Character(s), Married Aizawa Shouta | Eraserhead/Yamada Hizashi | Present Mic, Adopted Shinsou Hitoshi, Adopted Eri, Mild Transphobia, Autistic Aizawa Shouta | Eraserhead, Deaf Yamada Hizashi | Present Mic
Read Here: https://archiveofourown.org/works/28729494
#AO3 Feed#FanFiction#AO3 Dadzawa#♥#Erasermic#Momo Yaoyorozu#Hitoshi Shinsou#R:T#A:Tricklesnitz#Disability AU
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Neurophysiology
A. Electrical Properties of Neurons
1. How Does the Movement of Ions Create Electrical Charges in Neurons?
Cations: positively charged ions
- Examples: sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (CA2+)
Anions: negatively charged ions
- Examples: chloride (Cl-), protein molecules (A-)
Concentration gradient: differences in concentration of a substance among regions that allows the substance to diffuse from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- Diffusion: movement of ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through random motion
Electrical gradient: difference in charge between two regions that allows a flow of ions between the regions
- Opposite charges attract; similar charges repel
Electrochemical gradient: when they work together

Channels and Pumps
Ungated channels: allow the passage of ions
Gated channels: allow substances to pass only when gates are open.
- Voltage-gated channels: open or close only at specific membrane voltages (Na+ channel on the figure)
- Ligand-gated channels = transmitter-gated
Pump: actively transports a substance across the membrane


Neuronal Concentration Gradients

Concentration gradient pushes K+ ions out of the neuron through ungated K+ channels:

The neuron membrane is permeable to K+ ions, but not the anions (A-) inside the neuron. Anions following K+ ions are accumulated near the membrane from the inside, while K+ ions are accumulated near the membrane from the outside. Thus, charge separation across the neuron membrane is produced.

Charge Separation Across Neuronal Membrane

Resting Membrane Potential

Volt: a measure of a difference in electrical potential between two points
Voltmeter: a device that measures the difference in electrical potential between two points
Resting membrane potential: a difference in electrical potential between the inside and outside of the cell in the absence of stimulation.
- approximately -70 mV

By convention, the extracellular side of the membrane is given a charge of 0 mV; therefore the intracellular side of the membrane is -70 mV relative to the extracellular side. This measurement is the membrane’s resting potential.
2. Changes in Membrane Potential
A. Direction
Depolarization: decrease in difference in electrical potential across a membrane (more positive)
Hyperpolarization: increase in difference in electrical potential across a membrane (more negative)
B. Strength
Suprathreshold: action potential; only depolarizing response.
Subthreshold: graded potential; can be depolarizing and hyperpolarizing.

Action Potential (impulse, spike)
large amplitude (reverse in polarity)
brief (1-2 milliseconds)
all-or-none response
Threshold Potential: voltage on a neural membrane at which an action potential is triggered (-50 to -40 mV)
Action potential is generated at the axon hillock.
Information coding via frequency of action potentials


Phases of action potential:
Depolarization
Repolarization
Hyperpolarization

Depolarization phase: massive influx of Na+ ions through voltage-gated Na+ channels

Depolarization of membrane opens voltage-gated Na+ channels.
Repolarization phase: massive efflux of K+ ions through voltage-gated K+ channels

Voltage-gated Na+ channels are more sensitive to depolarization than voltage-gated K+ channels and therefore open sooner.
3. Clinical Examples:

Pufferfish aka fugu fish
- secretes tetrodotoxin (TTX), a powerful poison
- mechanism of TTX action: block of voltage-gated Na+ channels
- symptoms of TTX poisoning:
numbness of tongue and lips
dizziness and vomiting
rapid heart rate
decreased blood pressure
muscle paralysis
inability to breath

Epilepsy
- EEG (electroencephalography) shows generalized seizure patterns
normal record before the attack
onset of the attack
clonic phase, in which the person makes rhythmic movements in time with large abnormal discharges
period of coma after the seizure ends
- Some epileptic drugs reduce activity of the voltage-gated sodium channels, which reduces excitation in the brain (ex. phenytoin AKA Dilantin)

4. Propagation of Action Potential Along the Axon
- The action potential generated at the axon hillock propagates as a wave along the axon.
- The currents flowing inwards at a point on the axon during an action potential spread out along the axon, and depolarize the adjacent sections of its membrane.
- Size and shape of action potential remain constant along the axon (all-or-none)

- Propagation of AP is much faster in myelinated axons than in unmyelinated ones.

Propagation of Action Potential Along the Myelinated Axon
- myelin sheaths
- Nodes of Ranvier: parts of axon not covered by myelin; where the action potentials are generated
- saltatory conduction: propagation of an action potential from one node of Ranvier to another; from Latin saltare (”to dance”)
- speed of 100-150 m/s, compared to 0.5-10 m/s in unmyelinated axons
1 note
·
View note
Text
Namaste 🙏 In light of the disproportionate activities for distractions, which suppositionally, pulls the heart chakra, though periodically, with the vibration of “woe” and dismayed vibrational chemical reactions. Which have been shown to affect as well as effect our protective circumference egg. 360* polarity which extends 6x6 . Which invariably has a psycho-somatic/systematic energetic ability for becoming symbiotic. In the similar guise of Spider-Man’s symbiotically attached suit. Which invariably revealed itself as an alien regressive life form. Which like any symbiosis affectation, looshes off its host Avatar. Yet this example though for contrivances sake is positronic. To maintain loftier signatures of a vibrational plateau, repolarization of focused mudra’s { affirmation} of benevolent intentions. A labeled diagram of an action potential. Repolarization takes place just after the peak of the action potential, when K+ ions rush out of the cell. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/repolarizes Repolarizes Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster
The meaning of REPOLARIZATION is restoration of the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the cell membrane following depolarization.
https://soundcloud.com/ashnaiaofficial/sacred-silence-full-album-mp3-320kbit
0 notes
Text
The funny current is an inward flow of K+ and Na+ that leads to depolarization.
From Wikipedia:
The pacemaker current (or If, or IKf, also referred to as the funny current) is an electric current in the heart that flows through the HCN channel or pacemaker channel. Such channels are important parts of the electrical conduction system of the heart and form a component of the natural pacemaker.
First described in the late 1970s in Purkinje fibers and sinoatrial myocytes, the cardiac pacemaker "funny" (If) current has been extensively characterized and its role in cardiac pacemaking has been investigated.[1][2][3] Among the unusual features which justified the name "funny" are mixed Na+ and K+ permeability, activation on hyperpolarization, and very slow kinetics
The funny current is highly expressed in spontaneously active cardiac regions, such as the sinoatrial node (SAN, the natural pacemaker region), the atrioventricular node (AVN) and the Purkinje fibres of conduction tissue. The funny current is a mixed sodium–potassium current that activates upon hyperpolarization at voltages in the diastolic range (normally from −60/−70 mV to −40 mV). When, at the end of a sinoatrial action potential, the membrane repolarizes below the If threshold (about −40/−50 mV), the funny current is activated and supplies inward current, which is responsible for starting the diastolic depolarization phase (DD); by this mechanism, the funny current controls the rate of spontaneous activity of sinoatrial myocytes, and thus the cardiac rate.
Ivabradine is a drug that can affect the funny current. MOA: blocks hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel in SA node, selectively inhibiting cardiac pacemaker current to decrease heart rate.
Ivabradine can be used in pts with HFrEF and LVEF of less than or equal to 35% who are already on guideline directed medical therapy for treatment of CHF (i.e., beta blocker + ACEI + spironolactone) to treat their CHF. Ivabradine can be used to decrease HR when you can't give additional beta blocker, because more beta blockade would cause hypotension.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Solarcaine


Ingredient: Lidocaine and Aloe barbadensis leaf juice.
Dosage Form:
Cool Aloe Burn Relief Gel: Lidocaine HCl 0.5% with Aloe barbadensis leaf juice.
Cool Aloe Burn Relief Spray: Lidocaine HCl 0.5% with Aloe barbadensis leaf juice.
FDA Indication/Dosages:
For the temporary relief of pain and itching due to sunburn, minor cuts, scrapes, minor burns, insect bites, and minor skin irritations (Cool Aloe Burn Relief): Apply to affected area 3-4 times daily. Do not spray on the face, instead apply to the palm of the hand and gently apply to face.
Not indicated for use in children under the age of 2 years.
Pharmacology:
Lidocaine exhibits neuronal membrane-stabilizing properties by combining with fast sodium channels during their inactive state to inhibit repolarization. The amount of lidocaine that penetrates the skin from topical application is sufficient to produce an analgesic effect but less than the amount necessary to produce a complete sensory block.
Evaluation:
Pain is a normal defense mechanism the body uses to alert the body that tissue damage has occurred or is about to occur. Minor cuts, scrapes, and burns, including sunburn, damages the epidermal layer of the skin and causes sensory pain impulses to occur and increases the risk for infection at the damage site. The deeper the damage to the skin, the higher the risk for infection. Topical antiseptics and anesthetics can help to relieve the pain of and prevent infection in minor cuts, scrapes, and burns. Insect bites and stings usually produce localized irritation including erythema, pruritis, and pain. Formation of pus in any cut or burn indicates an infection and a physician should be consulted.
Contraindications/Precautions:
Do not use any of these products over a large area of the body. Do not use in or around the eyes. Do not use on puncture wounds, animal bites, or serious burns.
Adverse Effects:
The most common adverse effect is a temporary burning or stinging upon application.
Patient Consultation:
Ask how long the symptoms have been present and if previous therapy has been successful.
Do not use in or around the eyes, mouth, or nose.
Do not spray on the face, instead spray on the palms and gently apply to the face.
Do not use on a large area of the body.
If no improvement is seen after 7 days, consult a physician.
If area becomes swollen or bleeds after use, consult a physician.
If the condition gets worse, or cleans up then reoccurs, consult a physician.
#sigler nonprescription drug cards#10th edition#solarcaine#lidocaine#aloe barbadensis leaf juice#drug facts
0 notes
Text
fundamentals of neuroscience (I)
conclusion 3.
The main electrical signal used by neurons to convey info is the action potential. Action potentials are all-or-nothing signals characterized by large and rapid changes in membrane potential. The existence of voltages-gated channels that open and close with particular speeds in relation to each other is an importante property of neurons.
The action potential itself has many phases. The rising phase is defined as a time when the Vgated Na+ channels have opened while Vgated K+ channels remain closed, allowing the membrane to become depolarized (less negative) as Na+ ions rush in. The falling phase is a time when the voltage-gated sodium channels have become inactivated while the Vgated K+ channels are opening, leading to an efflux of K+ ions and repolarization. The actions of 1000 of these molecular machines leads to particular ions flowing into or out of the neuron at certain times and this gives us the characteristic action potential.
0 notes