#military architecture
Text


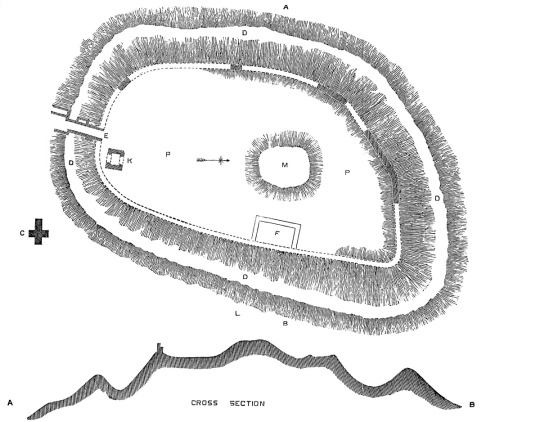
Mediæval Military Architecture in England, by George Thomas Clark
#architecture#urbanism#military#military architecture#England#medieval#medieval architecture#George Thomas Clark
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

Golubac fortress (XIV century) Serbia, Danube Right Bank
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

https://archive.org/details/VietCongAndNVATunnelsAndFortificationsOfTheVietnamWar/mode/2up
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Castillo de San Servando (Toledo): vista general
Castillo de San Servando (Toledo): vista general.
La última vez que estuve en Toledo, dándome un paseo por las orillas del río Tajo, vi este Castillo en el que nunca había reparado y del que desconocía su existencia. Así que tengo una asignatura pendiente: ir y verlo por dentro:
El Castillo de San Servando, ubicado en Toledo junto al río Tajo, es un monumento histórico de gran…

View On WordPress
#Alfonso VI de Castilla#Alta Edad Media#Arquitectura#Castillo de San Servando#Edad Media#El Cid Campeador#En Español#España#Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar (El Cid Campeador)#Siglo XI#Toledo#Urbanismo#middle ages#Castles#Spanish Castles#architecture#military architecture#Spain#11th century
0 notes
Photo
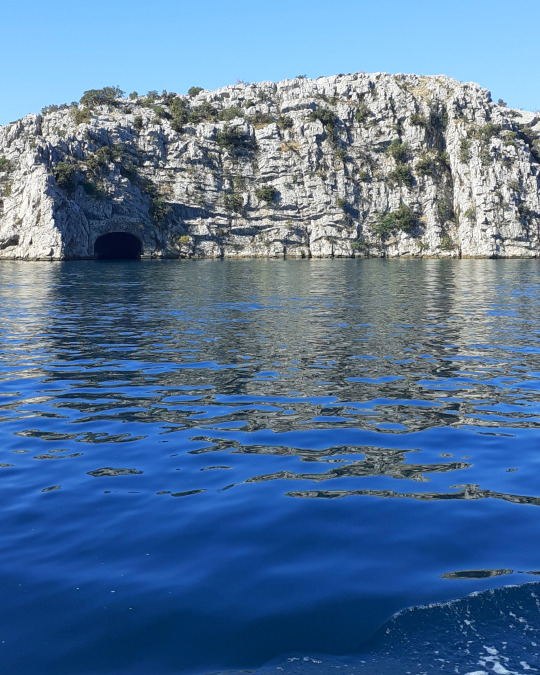

WWII tunnel, channel of St Anthony, near Šibenik. Built by the Germans, later used by Yugoslavian army
#tunel sv ante#šibenik#wwii history#photo#military architecture#underwater tunnel#secret tunnel#military history
1 note
·
View note
Text
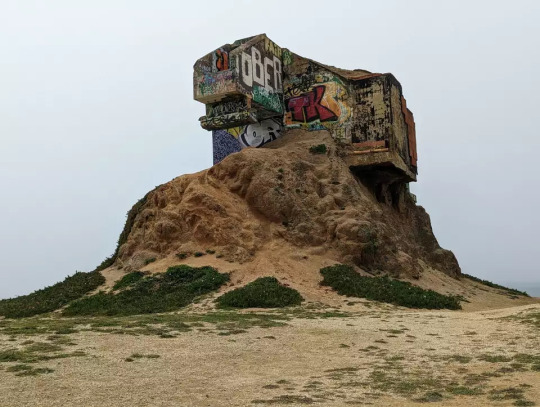

The Devil's Slide bunker near San Francisco.
(SF Gate)
628 notes
·
View notes
Text
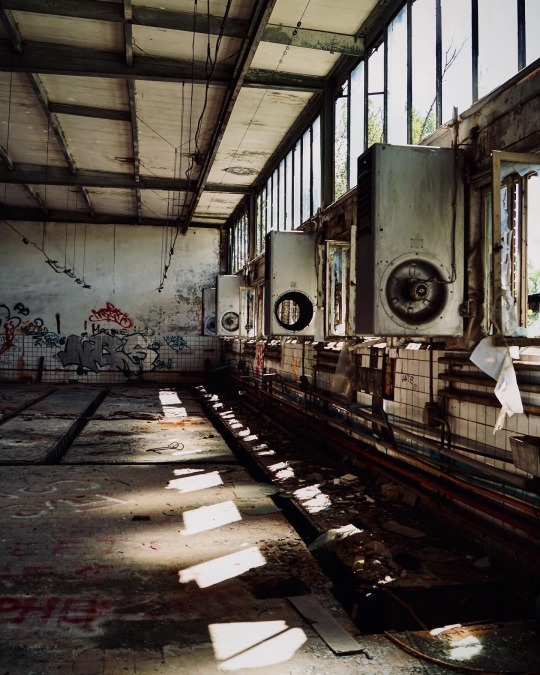

Flugplatz Rangsdorf, Brandenburg, Germany
#photography#architecture#urban exploration#urbex#airfield#military#architecture photography#aircraft hangar#red army#ddr#forgotten places#lost places#decay#derelict#abandoned places#abandoned#brandenburg#urbex germany#germany#east germany#urban explorers#urban photography#urban#urban decay#industrial#industrial photography#urbexdecay#urbexphotography#urbexplaces#urbexworld
185 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ukrainian soldiers sheltering from the rain near frescoes in St Michael's Cathedral in Kyiv. Photo by Sergei Supinsky.
#my post#eastern orthodoxy#ukraine#russian war on ukraine#russian invasion#ukrainian#russian ukrainian war#ukrainian military#orthodox christian#eastern orthodox#orthodox christianity#kyiv#church#cathedral#religious architecture#religion
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vardzia, a Medieval Cave City in Georgia (South Caucasus), built in 1150-1200 CE: Vardzia was designed to be used as a fortress/monastery; it was accessible only through hidden passageways, and it contained more than 6,000 caves, 15 chapels, 25 wine cellars, an apothecary, a forge, a bakery, farming terraces, and an irrigation system
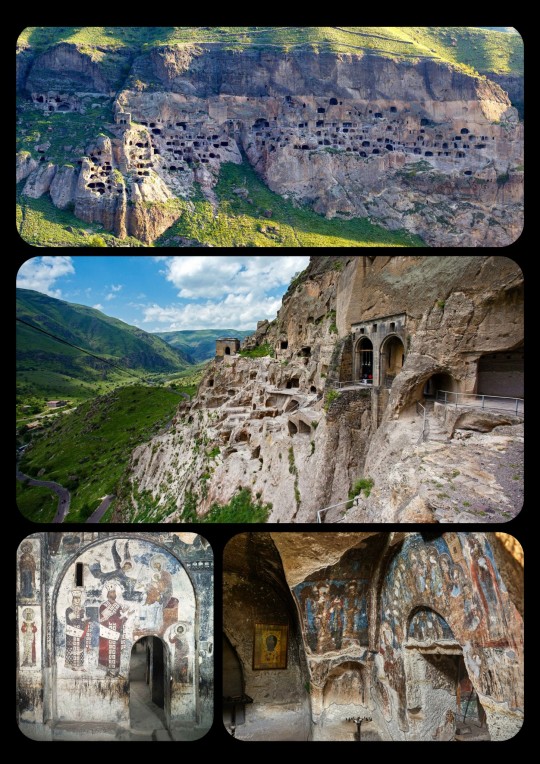

The monastic caves at Vardzia cover an area of about 500 meters. They are carved into the cliffs along the Erusheti mountains, which are located in Javakheti (a southern province near the borders between Georgia, Turkey, and Armenia).
Vardzia was originally meant to serve as a fortress, particularly in the event of a Mongol Invasion. It was protected by defensive walls, and the cave system itself was largely concealed within the mountain (though much of it is now exposed); it also contained a secret escape tunnel and several dead-end tunnels that were designed to delay/confuse enemy forces. The cave city could only be accessed through a series of hidden passageways that began near the banks of the Mtkvari River (which runs through the valley below the cave complex). Water was supplied through an irrigation system that was connected to the river, providing the inhabitants with both drinking water and agricultural irrigation, as the site contained its own terraced farmland.
The cave complex also functioned as a monastery, with a large collection of manuscripts and relics ultimately being housed at the site.

In its prime, the complex at Vardzia was inhabited by tens of thousands of residents.

Unfortunately, most of the original structures at Vardzia were destroyed by an earthquake that struck the region in 1283 CE, just a century after its construction; the earthquake sheared away the outer layer of the cliffside, exposed many of the caves, and demolished almost two-thirds of the site. The surviving structures represent only a fraction of the cave complex that once existed at Vardzia, with only about 500 caves still intact.
When the earthquake tore through the site in 1283, much of the fortress and many of its defenses were also destroyed, and Vardzia lost most of its military/defensive purposes. Still, it continued to operate as a Georgian Orthodox monastery for several hundred years after that. It narrowly escaped the Mongol Invasions of the 1290s, but it was raided by the Persians during the 16th century; the invading forces burned many of the manuscripts, relics, and other items that were stored within the cave system, leaving permanent scorch marks along the walls of the inner chambers. The site was abandoned shortly thereafter.

Medieval portrait of Queen/King Tamar: this portrait is one of the Medieval frescoes that still decorate the inner chambers of Vardzia; Tamar was the first queen regnant to rule over Georgia, meaning that she possessed the same power/authority as a king and, as a result, some Medieval sources even refer to her as "King Tamar"
Vardzia is often associated with the reign of Queen Tamar the Great, who ruled over the Kingdom of Georgia from 1184 to 1213 CE, during a particularly successful period that is often known as the "Golden Age" of Georgian history. Queen Tamar was also recognized as the Georgian King, with Medieval sources often referring to her as King Tamar. She possessed the powers of a sovereign leader/queen regnant, and was the first female monarch to be given that title in Georgia.
The initial phases of construction at Vardzia began under the command of King George III, but most of the complex was later built at the behest of his daughter, Queen Tamar, who owned several dedicated rooms at Vardzia and frequently visited the cave city. Due to her relationship with the cave complex at Vardzia, Queen Tamar is sometimes also referred to as the "Mountain Queen."
Despite the damage that the site has sustained throughout its history, many of the caves, tunnels, frescoes, and other structures have survived. The site currently functions as a monastery once more, with Georgian monks living in various chambers throughout the cave system.

I visited Vardzia back in 2011, during my first trip to Georgia. It's an incredible site, though some of the tunnels are very narrow, very dark, and very steep, which can get a bit claustrophobic.
Sources & More Info:
Atlas Obscura: Vardzia Cave Monastery
CNN: Exploring Vardzia, Georgia's Mysterious Rock-Hewed Cave City
Lonely Planet: Vardzia
Globonaut: 5 Facts about Vardzia, Georgia's Hidden Cave City
Wander Lush: Vardzia Cave Monastery (complete visitor's guide)
#archaeology#anthropology#history#vardzia#georgia#caucasus#cave city#cave complex#monastic caves#artifact#architecture#military history#Tamar#religon#comparative religion#medieval fortress#middle ages#medieval church#medieval europe#travel#I think I'd need#all 25 wine cellars#just to get through a Mongol invasion
393 notes
·
View notes
Text




空軍三重一村 // Sanchong Air Force Military Kindred Village No.1
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mediæval Military Architecture in England, by George Thomas Clark
#architecture#urbanism#military#military architecture#England#medieval#medieval architecture#George Thomas Clark
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
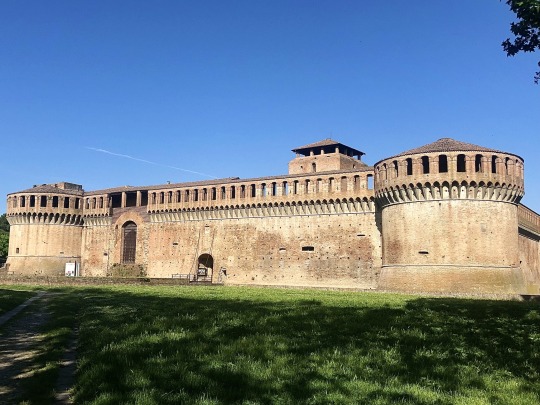


Rocca Sforzesca, Imola (BO), Italy Early Renaissance architecture
#italy#hdr#photography#imola#romagna#emilia romagna#castle#military architecture#architecture#renaissance architecture#europe#renaissance
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

https://archive.org/details/mediaevalmilitar02clar/page/n7/mode/2up
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Bunker - Kanton Uri - Schweiz 🇨🇭
#architecture#landscape#jason guilbeau#concrete#new topography#photography#artists on tumblr#new topographics#bunker#swiss alps#switzerland#swiss#war#festung#military#alps#kanton uri#uri#schweiz#spring#art#archiporn#architettura#architektur
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Submarine bunker on the island of Vis off the coast of Croatia. Fun fact: Mamma Mia! Here We Go Again was filmed near here.
252 notes
·
View notes