#oracle apps DBS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Java Consulting Company
Looking for a reliable Java consulting company? Associative in Pune, India, offers expert Java development, Spring Boot solutions, and enterprise-grade consulting services tailored to your business needs.
Expert Java Consulting Company in Pune – Powering Scalable Software Solutions
In the dynamic world of enterprise technology, finding a reliable Java consulting company that delivers scalable, secure, and high-performing solutions is essential. Associative, a leading software company based in Pune, India, is your trusted partner in unlocking the full potential of Java for business transformation.

Why Choose Associative for Java Consulting?
At Associative, we combine deep technical knowledge with strategic business insights to provide end-to-end Java consulting services. Whether you're building enterprise-grade software, optimizing legacy systems, or integrating Java with modern tech stacks, our team ensures future-ready solutions.
Our Java Consulting Services Include:
Custom Java Application Development: Tailored solutions built on robust Java frameworks like Spring Boot, Hibernate, and Struts.
Enterprise Java Architecture Consulting: Design scalable and modular architectures for enterprise-grade systems.
Java Performance Tuning & Optimization: Improve the speed and efficiency of your existing Java applications.
Java Migration & Modernization: Seamless migration from legacy systems to modern Java platforms.
Cloud Integration with Java: Deploy Java applications on AWS, GCP, or hybrid cloud environments.
Java API Development & Integration: Create secure, high-performance RESTful APIs for modern software ecosystems.
Industries We Serve
As a seasoned Java consulting company, Associative supports startups, SMBs, and large enterprises across various domains including:
E-commerce and Retail
Banking and Finance
Education and E-learning
Healthcare and Wellness
Gaming and Entertainment
Blockchain and Web3
End-to-End Expertise in Java & Beyond
Our capabilities don’t stop at Java. Associative’s diverse technology stack includes:
Mobile App Development for Android & iOS
Web & E-commerce Development on platforms like Magento, Shopify, and WordPress
Frontend & Backend Development using Node.js, React.js, Express.js
Full-stack Java Development with Spring Boot and Oracle DB
Cloud & DevOps with AWS and GCP
Web3 and Blockchain Integration
Game Development & Software Solutions
Digital Marketing & SEO Services
Partner with Associative – Your Trusted Java Consulting Company
With years of hands-on experience and a strong focus on client satisfaction, Associative stands out as a dependable Java consulting company in India. We ensure transparent communication, agile development processes, and 24/7 technical support to keep your projects running smoothly.
youtube
0 notes
Text
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market in the United States entering an era of unstoppable scalability
Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 17.51 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 77.65 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.07% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is experiencing robust expansion as enterprises prioritize scalability, real-time access, and cost-efficiency in data management. Organizations across industries are shifting from traditional databases to cloud-native environments to streamline operations and enhance agility, creating substantial growth opportunities for vendors in the USA and beyond.
U.S. Market Sees High Demand for Scalable, Secure Cloud Database Solutions
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market continues to evolve with increasing demand for managed services, driven by the proliferation of data-intensive applications, remote work trends, and the need for zero-downtime infrastructures. As digital transformation accelerates, businesses are choosing DBaaS platforms for seamless deployment, integrated security, and faster time to market.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6586
Market Keyplayers:
Google LLC (Cloud SQL, BigQuery)
Nutanix (Era, Nutanix Database Service)
Oracle Corporation (Autonomous Database, Exadata Cloud Service)
IBM Corporation (Db2 on Cloud, Cloudant)
SAP SE (HANA Cloud, Data Intelligence)
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (RDS, Aurora)
Alibaba Cloud (ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB)
MongoDB, Inc. (Atlas, Enterprise Advanced)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB)
Teradata (VantageCloud, ClearScape Analytics)
Ninox (Cloud Database, App Builder)
DataStax (Astra DB, Enterprise)
EnterpriseDB Corporation (Postgres Cloud Database, BigAnimal)
Rackspace Technology, Inc. (Managed Database Services, Cloud Databases for MySQL)
DigitalOcean, Inc. (Managed Databases, App Platform)
IDEMIA (IDway Cloud Services, Digital Identity Platform)
NEC Corporation (Cloud IaaS, the WISE Data Platform)
Thales Group (CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager, Data Protection on Demand)
Market Analysis
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is being shaped by rising enterprise adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, growing volumes of unstructured data, and the rising need for flexible storage models. The shift toward as-a-service platforms enables organizations to offload infrastructure management while maintaining high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Key players in the U.S. are focusing on vertical-specific offerings and tighter integrations with AI/ML tools to remain competitive. In parallel, European markets are adopting DBaaS solutions with a strong emphasis on data residency, GDPR compliance, and open-source compatibility.
Market Trends
Growing adoption of NoSQL and multi-model databases for unstructured data
Integration with AI and analytics platforms for enhanced decision-making
Surge in demand for Kubernetes-native databases and serverless DBaaS
Heightened focus on security, encryption, and data governance
Open-source DBaaS gaining traction for cost control and flexibility
Vendor competition intensifying with new pricing and performance models
Rise in usage across fintech, healthcare, and e-commerce verticals
Market Scope
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market offers broad utility across organizations seeking flexibility, resilience, and performance in data infrastructure. From real-time applications to large-scale analytics, the scope of adoption is wide and growing.
Simplified provisioning and automated scaling
Cross-region replication and backup
High-availability architecture with minimal downtime
Customizable storage and compute configurations
Built-in compliance with regional data laws
Suitable for startups to large enterprises
Forecast Outlook
The market is poised for strong and sustained growth as enterprises increasingly value agility, automation, and intelligent data management. Continued investment in cloud-native applications and data-intensive use cases like AI, IoT, and real-time analytics will drive broader DBaaS adoption. Both U.S. and European markets are expected to lead in innovation, with enhanced support for multicloud deployments and industry-specific use cases pushing the market forward.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/cloud-database-and-dbaas-market-6586
Conclusion
The future of enterprise data lies in the cloud, and the Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is at the heart of this transformation. As organizations demand faster, smarter, and more secure ways to manage data, DBaaS is becoming a strategic enabler of digital success. With the convergence of scalability, automation, and compliance, the market promises exciting opportunities for providers and unmatched value for businesses navigating a data-driven world.
Related reports:
U.S.A leads the surge in advanced IoT Integration Market innovations across industries
U.S.A drives secure online authentication across the Certificate Authority Market
U.S.A drives innovation with rapid adoption of graph database technologies
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Mail us: [email protected]
#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market Growth#Cloud Database and DBaaS Market Scope
0 notes
Text
Database Management System (DBMS) Development

Databases are at the heart of almost every software system. Whether it's a social media app, e-commerce platform, or business software, data must be stored, retrieved, and managed efficiently. A Database Management System (DBMS) is software designed to handle these tasks. In this post, we’ll explore how DBMSs are developed and what you need to know as a developer.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System is software that provides an interface for users and applications to interact with data. It supports operations like CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete), query processing, concurrency control, and data integrity.
Types of DBMS
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): Organizes data into tables. Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle.
NoSQL DBMS: Used for non-relational or schema-less data. Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, CouchDB.
In-Memory DBMS: Optimized for speed, storing data in RAM. Examples: Redis, Memcached.
Distributed DBMS: Handles data across multiple nodes or locations. Examples: Apache Cassandra, Google Spanner.
Core Components of a DBMS
Query Processor: Interprets SQL queries and converts them to low-level instructions.
Storage Engine: Manages how data is stored and retrieved on disk or memory.
Transaction Manager: Ensures consistency and handles ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
Concurrency Control: Manages simultaneous transactions safely.
Buffer Manager: Manages data caching between memory and disk.
Indexing System: Enhances data retrieval speed.
Languages Used in DBMS Development
C/C++: For low-level operations and high-performance components.
Rust: Increasingly popular due to safety and concurrency features.
Python: Used for prototyping or scripting.
Go: Ideal for building scalable and concurrent systems.
Example: Building a Simple Key-Value Store in Python
class KeyValueDB: def __init__(self): self.store = {} def insert(self, key, value): self.store[key] = value def get(self, key): return self.store.get(key) def delete(self, key): if key in self.store: del self.store[key] db = KeyValueDB() db.insert('name', 'Alice') print(db.get('name')) # Output: Alice
Challenges in DBMS Development
Efficient query parsing and execution
Data consistency and concurrency issues
Crash recovery and durability
Scalability for large data volumes
Security and user access control
Popular Open Source DBMS Projects to Study
SQLite: Lightweight and embedded relational DBMS.
PostgreSQL: Full-featured, open-source RDBMS with advanced functionality.
LevelDB: High-performance key-value store from Google.
RethinkDB: Real-time NoSQL database.
Conclusion
Understanding how DBMSs work internally is not only intellectually rewarding but also extremely useful for optimizing application performance and managing data. Whether you're designing your own lightweight DBMS or just exploring how your favorite database works, these fundamentals will guide you in the right direction.
0 notes
Text
Become an Oracle Fusion Technical & OIC Expert – Step-by-Step Training
Oracle Fusion Applications have revolutionized enterprise solutions, offering seamless cloud-based services that streamline business processes. As organizations increasingly adopt Oracle Fusion for financials, supply chain management, human capital management, and more, there is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can configure, customize, and integrate these applications effectively.
One of the key components of Oracle Fusion is Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC), which enables businesses to integrate various applications and automate workflows. Mastering Oracle Fusion Technical and OIC will open doors to high-paying jobs and career growth opportunities in cloud technology.
Why Choose This Training?
This training is structured to provide a step-by-step learning experience, making it easy for participants to understand the concepts, implement them practically, and apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios. Whether you are an aspiring Oracle Fusion Technical Consultant, an OIC Developer, or an IT professional looking to upskill, this course will empower you with the proper knowledge and hands-on expertise.
Key Highlights of the Training
✔ Comprehensive Coverage – Learn Fusion Technical concepts (BIP Reports, OTBI, FBDI) and OIC integration techniques.
✔ Step-by-Step Learning – A well-structured training program for beginners and experienced professionals.
✔ Hands-on Practice – Access to real-time Oracle Cloud instances for practical learning.
✔ Expert Trainers – Learn from industry experts with extensive experience in Oracle Cloud technologies.
✔ Real-World Scenarios – Practical use cases to ensure job readiness.
✔ Interview Preparation – Guidance on interview questions, real-world project scenarios, and best practices.
Who Should Enroll?
This training is ideal for:
✅ Oracle Fusion Technical Consultants who want to master OIC for integrations.
✅ Developers & IT Professionals aiming to work on Oracle Cloud integrations.
✅ Business Analysts who want to understand the technical aspects of Oracle Fusion.
Course Modules
Module 1: Introduction to Oracle Fusion Technical
🔹 Overview of Oracle Fusion Applications
🔹 Understanding the Fusion Cloud Architecture
🔹 Security & User Roles in Oracle Fusion
🔹 Introduction to Fusion Technical Components
Module 2: BI Publisher (BIP) Reports
🔹 Introduction to BI Publisher
🔹 Creating and Designing Reports
🔹 Understanding Data Models and Templates
🔹 Scheduling and Managing BIP Reports
Module 3: Oracle Transactional Business Intelligence (OTBI)
🔹 Overview of OTBI Reporting
🔹 Creating and Customizing OTBI Reports
🔹 Understanding Dashboards and Data Visualization
Module 4: Data Migration – FBDI & ADF DI
🔹 Overview of FBDI (File-Based Data Import)
🔹 Hands-on FBDI Implementation
🔹 Using ADF DI (ADF Desktop Integration) for Data Management
Module 6: Introduction to Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC)
🔹 Overview of Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC)
🔹 Understanding OIC Components – Integrations, Lookups, Adapters
🔹 Security & Authentication in OIC
Module 7: Designing & Developing OIC Integrations
🔹 Creating App-Driven & Scheduled Integrations
🔹 Using Pre-Built Adapters (ERP, REST, SOAP, FTP, DB, etc.)
🔹 Hands-on Integration Flows & Mappings
Benefits of Taking This Course
✔ Master OIC integrations & automation workflows.
✔ Be prepared for real-world projects & job interviews.
✔ Get expert guidance, study materials, and recorded sessions.
✔ Become job-ready and boost your career opportunities in Oracle Cloud.
Job Roles You Can Target After This Training
🎯 Oracle Fusion Technical Consultant
🎯 Oracle OIC Developer
🎯 Oracle Cloud Integration Specialist
🎯 Fusion ERP Integration Consultant
🎯 Oracle Cloud Solution Architect
Final Thoughts
Oracle Fusion and OIC are among the most in-demand skills in today's cloud computing landscape. If you want to build a successful career in Oracle Cloud, mastering Fusion Technical & OIC is essential.
With this step-by-step training, you will gain the confidence, knowledge, and practical experience to work on real-world projects, crack job interviews, and become a skilled Oracle Fusion Technical & OIC expert.
Conclusion
Oracle Fusion Technical and Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) are among the most in-demand skills in today's cloud-driven enterprise world. Businesses are actively seeking professionals who can develop, customize, and integrate Oracle Fusion applications to enhance efficiency and streamline operations.

0 notes
Text
Full Stack developer with Web ops
JOB OVERVIEW looking for AWS, Vutr, DO, developementin HTML5, CSS3, Tailwind CSS, JAVASCRIPT, PHP, ASP.NET, Python, Django, Flask, Ruby, Node.js, Mongo DB, Maria DB, Oracle, MySQL. Also, I have developed a lot of Mobile Apps using Kotli… Apply Now
0 notes
Text
Cloud Providers Compared: AWS, Azure, and GCP
This comparison focuses on several key aspects like pricing, services offered, ease of use, and suitability for different business types. While AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, and GCP (Google Cloud Platform) are the “big three” in cloud computing, we will also briefly touch upon Digital Ocean and Oracle Cloud.
Launch Dates AWS: Launched in 2006 (Market Share: around 32%), AWS is the oldest and most established cloud provider. It commands the largest market share and offers a vast array of services ranging from compute, storage, and databases to machine learning and IoT.
Azure: Launched in 2010 (Market Share: around 23%), Azure is closely integrated with Microsoft products (e.g., Office 365, Dynamics 365) and offers strong hybrid cloud capabilities. It’s popular among enterprises due to seamless on-premise integration.
GCP: Launched in 2011 (Market Share: around 10%), GCP has a strong focus on big data and machine learning. It integrates well with other Google products like Google Analytics and Maps, making it attractive for developers and startups.
Pricing Structure AWS: Known for its complex pricing model with a vast range of options. It’s highly flexible but can be difficult to navigate without expertise. Azure: Often considered more straightforward with clear pricing and discounts for long-term commitments, making it a good fit for businesses with predictable workloads.
GCP: Renowned for being the most cost-effective of the three, especially when optimized properly. Best suited for startups and developers looking for flexibility.
Service Offerings AWS: Has the most comprehensive range of services, catering to almost every business need. Its suite of offerings is well-suited for enterprises requiring a broad selection of cloud services.
Azure: A solid selection, with a strong emphasis on enterprise use cases, particularly for businesses already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem. GCP: More focused, especially on big data and machine learning. GCP offers fewer services compared to AWS and Azure, but is popular among developers and data scientists.
Web Console & User Experience AWS: A powerful but complex interface. Its comprehensive dashboard is customizable but often overwhelming for beginners. Azure: Considered more intuitive and easier to use than AWS. Its interface is streamlined with clear navigation, especially for those familiar with Microsoft services.
GCP: Often touted as the most user-friendly of the three, with a clean and simple interface, making it easier for beginners to navigate. Internet of Things (IoT)
AWS: Offers a well-rounded suite of IoT services (AWS IoT Core, Greengrass, etc.), but these can be complex for beginners. Azure: Considered more beginner-friendly, Azure IoT Central simplifies IoT deployment and management, appealing to users without much cloud expertise.
GCP: While GCP provides IoT services focused on data analytics and edge computing, it’s not as comprehensive as AWS or Azure. SDKs & Development All three cloud providers offer comprehensive SDKs (Software Development Kits) supporting multiple programming languages like Python, Java, and Node.js. They also provide CLI (Command Line Interfaces) for interacting with their services, making it easy for developers to build and manage applications across the three platforms.
Databases AWS: Known for its vast selection of managed database services for every use case (relational, NoSQL, key-value, etc.). Azure: Azure offers services similar to AWS, such as Azure SQL for relational databases and Cosmos DB for NoSQL. GCP: Offers Cloud SQL for relational databases, BigTable for NoSQL, and Cloud Firestore, but it doesn’t match AWS in the sheer variety of database options.
No-Code/Low-Code Solutions AWS: Offers services like AWS AppRunner and Honeycode for building applications without much coding. Azure: Provides Azure Logic Apps and Power Automate, focusing on workflow automation and low-code integrations with other Microsoft products.
GCP: Less extensive in this area, with Cloud Dataflow for processing data pipelines without code, but not much beyond that. Upcoming Cloud Providers – Digital Ocean & Oracle Cloud Digital Ocean: Focuses on simplicity and cost-effectiveness for small to medium-sized developers and startups. It offers a clean, easy-to-use platform with an emphasis on web hosting, virtual machines, and developer-friendly tools. It’s not as comprehensive as the big three but is perfect for niche use cases.
Oracle Cloud: Strong in enterprise-level databases and ERP solutions, Oracle Cloud targets large enterprises looking to integrate cloud solutions with their on-premise Oracle systems. While not as popular, it’s growing in specialized sectors such as high-performance computing (HPC).
Summary AWS: Best for large enterprises with extensive needs. It offers the most services but can be difficult to navigate for beginners. Azure: Ideal for mid-sized enterprises using Microsoft products or looking for easier hybrid cloud solutions. GCP: Great for startups, developers, and data-heavy businesses, particularly those focusing on big data and AI. To learn more about cloud services and computing, Please get in touch with us
0 notes
Text
Create a RAC One Node database by converting the existing RAC database
Create a RAC one node database from existing two node RAC in Oracle Check the status for current running RAC instances: [oracle@host01 ~]$ . oraenv ORACLE_SID = [oracle] ? orcl The Oracle base has been set to /u01/app/oracle [oracle@host01 ~]$ [oracle@host01 ~]$ srvctl status database -db orcl Instance orcl1 is running on node host01 Instance orcl2 is running on node host02 Remove the 2nd…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
devlog
i’ve been working on a little web app in golang as a self service front end for the discord server’s reaction image bot (named sasuke bot bc its original purpose was to drop a giant pieced together sasuke in the chat). at the moment i have to manually add any new images + modify the json config file and then push to the github repo, which is honestly kind of gross? the whole thing is deployed on a free oracle cloud ampere instance rn and i’m fetching the static files from the local file system to serve, but i really should move the handler/image metadata into a real data store instead of a json file that i’m changing by hand LOL and the static assets into whatever object store oracle gives me for free
so anyway i’m in the middle of setting up the security/authentication portions of the app rn being like no one should ever be entering real passwords into this app because i do Not know if what i’m doing is actually secure. however i do want accounts because i’ll be slapping a real public internet facing domain name on this baby and i cannot have potential randos trying to upload things like that. i’ll also need new accounts to be approved by me before they can upload images. not sure how i want to do that yet. maybe just add a column to the user table that’s like active/inactive. i’ll have to look into making an admin account for myself or else i’ll have to be manually activating accounts in the db which is sus. idk what i’m doing but i’ve been having fun with making a web app in golang. haven’t built a proper CRUD app with a front end since college
future roadmap is to get this running on k8s i guess. shouldn’t be too bad since it’s mostly containerized already
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn Oracle Apps DBA Online with Professional Training

Oracle Applications Database Administrator (Oracle Apps DBA) is an important skill for anyone looking to work in the field of database management. Oracle Apps DBA professionals are responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining Oracle software applications and databases. This includes tasks such as creating databases, updating software patches, managing security, and troubleshooting problems. As this skill is in high demand, many are looking to learn Oracle Apps DBA online with professional training.
What is Oracle Apps DBA?
Oracle Applications Database Administrator (Oracle Apps DBA) is a complex and expert-level job that requires a high degree of knowledge in database architecture and administration. Oracle Apps DBA professionals are responsible for maintaining, configuring, and troubleshooting Oracle applications and databases. This includes tasks such as creating databases, setting up user accounts, granting privileges, updating software patches, managing security, and troubleshooting problems. In addition to these technical tasks, Oracle Apps DBA professionals may also be involved in the design, implementation, and customization of Oracle applications.
Oracle Apps DBA professionals must have a strong understanding of the Oracle database architecture and be able to work with multiple versions of the Oracle database. They must also be able to work with different operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and UNIX. Oracle Apps DBA professionals must also have a good understanding of the Oracle Application Server and be able to configure and troubleshoot it. Finally, Oracle Apps DBA professionals must have excellent communication and problem-solving skills in order to effectively work with customers and other stakeholders.
Benefits of Online Oracle Apps DBA Training
Online Oracle Apps DBA training provides a great opportunity for those looking to learn this complex skill set. By taking courses online, students can save time and money by studying at their own pace and in their own environment. Additionally, online training offers the flexibility to study at any time of day or night, as well as the ability to pause or rewind lessons when needed. Most importantly, online training provides access to experienced instructors who can answer questions and provide feedback when needed.
Online Oracle Apps DBA training also offers the convenience of being able to access course materials from any device with an internet connection. This makes it easy to review course materials and practice skills on the go. Furthermore, online training can be tailored to the individual student’s needs, allowing them to focus on the topics that are most relevant to their career goals. With the right online training program, students can become Oracle Apps DBAs in no time.
Finding the Right Professional Oracle Apps DBA Training
When selecting an online Oracle Apps DBA training course, it is important to choose one that is taught by experienced professionals. Look for courses that provide detailed instruction on the various aspects of Oracle database administration, including installation, configuration, maintenance, security, and troubleshooting. Additionally, look for courses that are designed with the latest version of Oracle in mind. Finally, consider the cost of the course and ensure that it is within your budget.
It is also important to make sure that the course is comprehensive and covers all the topics that you need to know. Additionally, look for courses that offer hands-on practice and real-world examples to help you gain a better understanding of the material. Finally, make sure that the course is accredited and that it meets the standards of the Oracle certification program.
What to Look for in an Oracle Apps DBA Trainer
When selecting an Oracle Apps DBA trainer, it is important to consider the experience and qualifications of the instructor. Look for someone who has years of experience working with Oracle applications and databases, as well as a deep understanding of database architecture and administration. Additionally, look for trainers who have certifications from Oracle or other industry-recognized organizations that demonstrate their expertise in the field.
It is also important to consider the type of training the instructor offers. Look for trainers who provide hands-on training, as this will give you the opportunity to practice the skills you are learning. Additionally, look for trainers who offer a variety of training options, such as online courses, in-person classes, and one-on-one tutoring. This will ensure that you can find the best training option for your needs.
The Advantages of Professional Oracle Apps DBA Training
Professional Oracle Apps DBA training courses offer a number of advantages over self-study options. A professional instructor can provide a more comprehensive approach to learning this complex skill set by offering in-depth instruction on topics such as installation, configuration, maintenance, security, and troubleshooting. Additionally, a professional instructor can answer questions and provide feedback when needed. Finally, a professional instructor can help prepare students for their Oracle Apps DBA certification exam.
In addition to the advantages of professional instruction, Oracle Apps DBA training courses also provide students with access to the latest tools and technologies. This allows students to gain hands-on experience with the latest Oracle products and services. Furthermore, the courses provide students with the opportunity to network with other Oracle professionals, which can be invaluable for career advancement. Finally, the courses provide students with the opportunity to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Oracle database architecture and its associated technologies.
Tips for Getting the Most Out of Your Online Oracle Apps DBA Training
When taking an online Oracle Apps DBA course, it is important to make sure you are getting the most out of your studies. To maximize the effectiveness of your training experience, be sure to set realistic learning goals and stay organized. Additionally, be sure to review each lesson thoroughly before moving on to the next one. Finally, don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek help if needed.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Oracle Apps DBA Training
When taking an online Oracle Apps DBA course, there may be times when you run into difficulties or have questions about specific topics. In these instances, it is important to reach out for help as soon as possible. Most online courses offer assistance via email or phone support. Additionally, you may find helpful information on online forums or by consulting with more experienced colleagues.
Preparing for Your Oracle Apps DBA Certification Exam
Once you have completed your online Oracle Apps DBA training course, you will need to prepare for your certification exam. The best way to do this is by attending review sessions offered by your course instructor or by taking practice exams that cover all topics included in the exam. Additionally, it may be helpful to create study guides or flashcards with key concepts and terms. Finally, be sure to set aside enough time to study and review material prior to taking the exam.
Continuing Education and Career Opportunities with Oracle Apps DBA
Once you have obtained your Oracle Apps DBA certification, there are many opportunities for continuing education and career advancement. For example, you may choose to pursue additional certifications in related fields such as SQL or database design. Additionally, there are many career paths available for Oracle Apps DBA professionals including software engineering, database design and analysis, technical support, and more. With a combination of experience and additional certifications, you can open up even more possibilities in the field.
Conclusion
Oracle Apps DBA online training provides you with the necessary skills and knowledge to become an Oracle Applications Database Administrator. The course covers a variety of topics such as installing, managing, and upgrading Oracle E-Business Suite, patching and cloning, performance tuning, troubleshooting, and backup and recovery. With the right training and guidance, you can become an Oracle Applications Database Administrator in no time.
Our knowledgeable educator offers Oracle Apps online training at a fair price.
Call us at +91 872 207 9509 for more information.
www.proexcellency.com
#online courses#online education#online training#online#trainer#live trainer#elearning#online course#online trainer#training#oracle apps DBS
0 notes
Text
russian hackers
DotNek is European based experienced mobile app development team with 20 years of development experience in custom software, mobile apps, and mobile games. DotNek's focus lies on iOS & Android app development, mobile games, web-standard analysis, and app monetizing analysis. DotNek is also capable of developing custom software in almost every programming language and for every platform, using any type of technology, and for all kinds of business categories. We are world class developers for world class business applications.
Our mobile apps and games are based on Xamarin Android, Xamarin iOS, & Xamarin UWP. We write one cross-platform code for all platforms, including Android, iOS, & Windows. This saves a lot of time and costs for clients. Our 2nd field is custom software development, mostly based on C#.Net, Asp.Net MVC, Php, Java, and Web API based on SQL Server, NoSQL, or Oracle DB. Additionally, we can develop your software in any other programming language based on your needs.
https://www.dotnek.com/Blog/Apps/enabling-xamarin-push-notifications-for-all-p
1 note
·
View note
Text
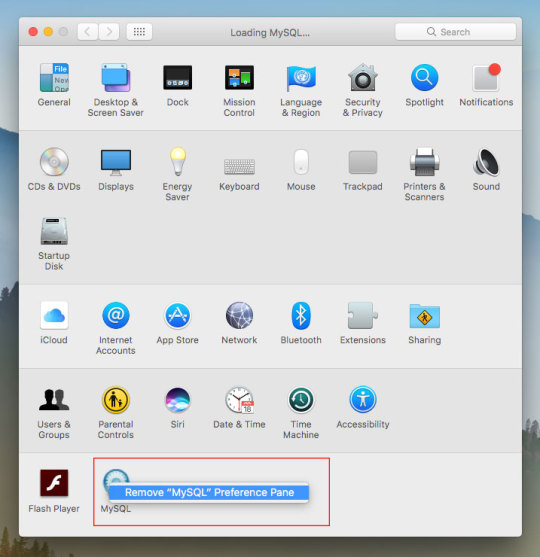
Mysql Download For Mac Mojave

Mysql Workbench Download For Mac
Mysql Install Mac Mojave
I am more of a command line user when accessing MySQL, but MySQLWorkBench is by far a great tool. However, I am not a fan of installing a database on my local machine and prefer to use an old computer on my network to handle that. If you have an old Mac or PC, wipe it and install Linux Server command line only software on it. Machines as old as 10/15 years and older can support Linux easily. You don't even need that much RAM either but I'd got with minimum of 4GB for MySQL.
The Mojave installer app will be in your Applications folder, so you can go there and launch it later to upgrade your Mac to the new operating system. Make a bootable installer drive: The quick way. Sep 27, 2018 So before you download and install macOS 10.14 Mojave, make sure your Mac is backed up. For information on how to do this, head over to our ultimate guide to backing up your Mac. How to download.
Apr 24, 2020 Download macOS Mojave For the strongest security and latest features, find out whether you can upgrade to macOS Catalina, the latest version of the Mac operating system. If you still need macOS Mojave, use this App Store link: Get macOS Mojave.
Oct 08, 2018 Steps to Install MySQL Workbench 8.0 on Mac OS X Mojave Step 1. Download the Installer. Follow this link to download the latest version of MySQL Workbench 8.0 for Mac. When I write this article, the Workbench version 8.0.12 is available. Save the file to your download directory.
Or...
Use Virtualbox by Oracle to create a virtual server on your local machine. I recommend Centos 7 or Ubuntu 18.04. The latter I used to use exclusively but it has too many updates every other week, whereas Centos 7 updates less often and is as secure regardless. But you will need to learn about firewalls, and securing SSH because SSH is how you will access the virtual machine for maintenance. You will have to learn how to add/delete users, how to use sudo so you can perform root based commands etc. There is a lot more to the picture than meets the eye when you want to use a database.
I strongly recommend not installing MySQL on your local machine but use a Virtual Machine or an old machine that you can connect to on your local area network. It will give you a better understanding of security when you have to deal with a firewall and it is always a good practice to never have a database on the same server/computer as your project. Databases are for the backend where access is secure and severely limited to just one machine via ssh-keys or machine id. If you don't have the key or ID you ain't getting access to the DB.
There are plenty of tutorials online that will show you how to do this. If you have the passion to learn it will come easy.
Posted on
Apple released every update for macOS, whether major or minor, via Mac App Store. Digital delivery to users makes it easy to download and update, however, it is not convenient in certain scenarios. Some users might need to keep a physical copy of macOS due to slow Internet connectivity. Others might need to create a physical copy to format their Mac and perform a clean install. Specially with the upcoming releasee of macOS Mojave, it is important to know how the full installer can be downloaded.
We have already covered different methods before which let you create a bootable USB installer for macOS. The first method was via a terminal, while the second method involved the usage of some third-party apps, that make the whole process simple. However, in that guide, we mentioned that the installer has to be downloaded from the Mac App Store. The installer files can be used after download, by cancelling the installation wizard for macOS. However, for some users, this might not be the complete download. Many users report that they receive installation files which are just a few MB in size.
Luckily, there is a tool called macOS Mojave Patcher. While this tool has been developed to help users run macOS Mojave/macOS 10.14 on unsupported Macs, it has a brilliant little feature that lets you download the full macOS Mojave dmg installer too. Because Mojave will only download on supported Macs, this tool lets users download it using a supported Mac, created a bootable USB installer and install it on an unsupported Mac. Here is how you can use this app.
Download macOS Mojave installer using macOS Mojave Patcher

Download the app from here. (Always use the latest version from this link.)
Opening it might show a warning dialogue. You’ll have to go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy to allow the app to run.Click Open Anyway in Security & Privacy.
Once you are able to open the app, you’ll get a message that your machine is natively supported. Click ok.
Go to Tools> Download macOS Mojave, to start the download. The app will ask you where you want to save the installer file. Note that the files are downloaded directly from Apple, so you wouldn’t have to worry about them being corrupted.The download will be around 6GB+ so make sure that you have enough space on your Mac.Once the download starts, the app will show you a progress bar. This might take a while, depending on your Internet connection speed.
Mysql Workbench Download For Mac
Once the download is complete, you can use this installer file to create a bootable USB.
Mysql Install Mac Mojave
P.S. if you just want to download a combo update for Mojave, they are available as small installers from Apple and can be downloaded here.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Top 5 Abilities Employers Search For
What Guard Can As Well As Can Not Do
#toc background: #f9f9f9;border: 1px solid #aaa;display: table;margin-bottom: 1em;padding: 1em;width: 350px; .toctitle font-weight: 700;text-align: center;
Content
Professional Driving Capacity
Whizrt: Simulated Intelligent Cybersecurity Red Team
Add Your Call Information Properly
Objectsecurity. The Security Plan Automation Company.
The Kind Of Security Guards
Every one of these courses supply a declarative-based strategy to reviewing ACL information at runtime, releasing you from requiring to compose any type of code. Please refer to the example applications to discover just how to make use of these courses. Spring Security does not offer any type of special integration to immediately create, update or delete ACLs as component of your DAO or repository operations. Rather, you will require to compose code like revealed above for your private domain name objects. It deserves taking into consideration using AOP on your solutions layer to instantly integrate the ACL details with your services layer procedures.
zie deze pagina
cmdlet that can be made use of to listing techniques and buildings on an object quickly. Figure 3 shows a PowerShell manuscript to mention this details. Where feasible in this research, typical customer benefits were used to supply insight into readily available COM things under the worst-case situation of having no administrative advantages.
Whizrt: Simulated Intelligent Cybersecurity Red Group
Users that are members of several teams within a duty map will constantly be approved their greatest consent. For instance, if John Smith is a member of both Team An and Group B, and Team A has Manager opportunities to an object while Team B just has Audience civil liberties, Appian will treat John Smith as an Administrator. OpenPMF's support for advanced access control versions consisting of proximity-based accessibility control, PBAC was likewise even more prolonged. To fix numerous challenges around applying safe and secure distributed systems, ObjectSecurity released OpenPMF variation 1, during that time among the first Attribute Based Gain access to Control (ABAC) items in the market.
The picked users and functions are now listed in the table on the General tab. Opportunities on dices allow customers to accessibility service actions and execute analysis.
Object-Oriented Security is the technique of making use of usual object-oriented style patterns as a system for accessibility control. Such mechanisms are commonly both simpler to utilize and also more effective than conventional security designs based upon globally-accessible resources safeguarded by accessibility control lists. Object-oriented security is closely pertaining to object-oriented testability as well as various other advantages of object-oriented style. When a state-based Accessibility Control Checklist (ACL) is as well as exists integrated with object-based security, state-based security-- is offered. You do not have consent to view this object's security homes, also as a management individual.
You might write your ownAccessDecisionVoter or AfterInvocationProviderthat respectively fires before or after an approach invocation. Such classes would certainly useAclService to obtain the relevant ACL and after that callAcl.isGranted( Permission [] permission, Sid [] sids, boolean administrativeMode) to determine whether permission is granted or denied. At the same time, you could utilize our AclEntryVoter, AclEntryAfterInvocationProvider orAclEntryAfterInvocationCollectionFilteringProvider courses.
What are the key skills of safety officer?
Whether you are a young single woman or nurturing a family, Lady Guard is designed specifically for women to cover against female-related illnesses. Lady Guard gives you the option to continue taking care of your family living even when you are ill.
Include Your Contact Information Properly

It permitted the central authoring of accessibility policies, as well as the automated enforcement throughout all middleware nodes making use of neighborhood decision/enforcement factors. Thanks to the assistance of several EU funded study jobs, ObjectSecurity discovered that a main ABAC strategy alone was not a convenient means to execute security plans. Visitors will get a comprehensive consider each element of computer system security and exactly how the CORBAsecurity requirements fulfills each of these security requires.
Understanding facilities It is a best practice to provide specific teams Visitor civil liberties to understanding centers as opposed to setting 'Default (All Other Customers)' to customers.
This suggests that no fundamental user will certainly have the ability to start this process design.
Appian recommends giving customer accessibility to specific teams instead.
Appian has detected that this process version might be utilized as an action or related action.
Doing so makes sure that record folders as well as records embedded within understanding facilities have actually specific visitors set.
You have to also provide benefits on each of the measurements of the dice. Nonetheless, you can establish fine-grained gain access to on a measurement to restrict the advantages, as defined in "Creating Data Security Plans on Cubes and dimensions". You can withdraw as well as set object privileges on dimensional objects using the SQL GIVE and REVOKE commands. You provide security on views and also emerged sights for dimensional objects similarly as for any kind of other views and also emerged sights in the database. You can provide both data security and object security in Analytic Work area Manager.
What is a security objective?
General career objective examples Secure a responsible career opportunity to fully utilize my training and skills, while making a significant contribution to the success of the company. Seeking an entry-level position to begin my career in a high-level professional environment.
Since their security is acquired by all objects embedded within them by default, expertise facilities and also regulation folders are taken into consideration high-level objects. For example, security set on expertise facilities is inherited by all embedded record folders and papers by default. Also, security established on regulation folders is inherited by all embedded policy folders and also rule things including user interfaces, constants, expression rules, choices, and assimilations by default.
Objectsecurity. The Security Policy Automation Company.
In the instance above, we're obtaining the ACL connected with the "Foo" domain object with identifier number 44. We're after that including an ACE to make sure that a principal named "Samantha" can "administer" the object.
youtube
The Types Of Security Guards
Topics covered include verification, recognition, and advantage; accessibility control; message security; delegation as well as proxy issues; auditing; and, non-repudiation. The author additionally provides many real-world examples of how protected object systems can be utilized to impose useful security plans. after that pick both of the worth from drop down, right here both worth are, one you appointed to app1 and also various other you designated to app2 and also maintain adhering to the step 1 to 9 meticulously. Right here, you are defining which individual will see which app and by following this remark, you specified you problem user will see both application.
What is a good objective for a security resume?
Career Objective: Seeking the position of 'Safety Officer' in your organization, where I can deliver my attentive skills to ensure the safety and security of the organization and its workers.
Security Vs. Presence
For object security, you also have the option of using SQL GIVE and REVOKE. provides fine-grained control of the data on a cellular degree. When you want to limit accessibility to particular areas of a cube, you just require to specify information security plans. Data security is carried out using the XML DB security of Oracle Data source. The next step is to really make use of the ACL details as component of permission decision logic as soon as you have actually used the above strategies to store some ACL details in the data source.
#objectbeveiliging#wat is objectbeveiliging#object beveiliging#object beveiliger#werkzaamheden beveiliger
1 note
·
View note
Text
U.S. Cloud DBaaS Market Set for Explosive Growth Amid Digital Transformation Through 2032
Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 17.51 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 77.65 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18.07% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is witnessing accelerated growth as organizations prioritize scalability, flexibility, and real-time data access. With the surge in digital transformation, U.S.-based enterprises across industries—from fintech to healthcare—are shifting from traditional databases to cloud-native solutions that offer seamless performance and cost efficiency.
U.S. Cloud Database & DBaaS Market Sees Robust Growth Amid Surge in Enterprise Cloud Adoption
U.S. Cloud Database And DBaaS Market was valued at USD 4.80 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 21.00 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.82% from 2024-2032.
Cloud Database and DBaaS Market continues to evolve with strong momentum in the USA, driven by increasing demand for managed services, reduced infrastructure costs, and the rise of multi-cloud environments. As data volumes expand and applications require high availability, cloud database platforms are emerging as strategic assets for modern enterprises.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6586
Market Keyplayers:
Google LLC (Cloud SQL, BigQuery)
Nutanix (Era, Nutanix Database Service)
Oracle Corporation (Autonomous Database, Exadata Cloud Service)
IBM Corporation (Db2 on Cloud, Cloudant)
SAP SE (HANA Cloud, Data Intelligence)
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (RDS, Aurora)
Alibaba Cloud (ApsaraDB for RDS, ApsaraDB for MongoDB)
MongoDB, Inc. (Atlas, Enterprise Advanced)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB)
Teradata (VantageCloud, ClearScape Analytics)
Ninox (Cloud Database, App Builder)
DataStax (Astra DB, Enterprise)
EnterpriseDB Corporation (Postgres Cloud Database, BigAnimal)
Rackspace Technology, Inc. (Managed Database Services, Cloud Databases for MySQL)
DigitalOcean, Inc. (Managed Databases, App Platform)
IDEMIA (IDway Cloud Services, Digital Identity Platform)
NEC Corporation (Cloud IaaS, the WISE Data Platform)
Thales Group (CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager, Data Protection on Demand)
Market Analysis
The Cloud Database and DBaaS (Database-as-a-Service) Market is being fueled by a growing need for on-demand data processing and real-time analytics. Organizations are seeking solutions that provide minimal maintenance, automatic scaling, and built-in security. U.S. companies, in particular, are leading adoption due to strong cloud infrastructure, high data dependency, and an agile tech landscape.
Public cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market, while niche players continue to innovate in areas such as serverless databases and AI-optimized storage. The integration of DBaaS with data lakes, containerized environments, and AI/ML pipelines is redefining the future of enterprise database management.
Market Trends
Increased adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid database architectures
Growth in AI-integrated database services for predictive analytics
Surge in serverless DBaaS models for agile development
Expansion of NoSQL and NewSQL databases to support unstructured data
Data sovereignty and compliance shaping platform features
Automated backup, disaster recovery, and failover features gaining popularity
Growing reliance on DBaaS for mobile and IoT application support
Market Scope
The market scope extends beyond traditional data storage, positioning cloud databases and DBaaS as critical enablers of digital agility. Businesses are embracing these solutions not just for infrastructure efficiency, but for innovation acceleration.
Scalable and elastic infrastructure for dynamic workloads
Fully managed services reducing operational complexity
Integration-ready with modern DevOps and CI/CD pipelines
Real-time analytics and data visualization capabilities
Seamless migration support from legacy systems
Security-first design with end-to-end encryption
Forecast Outlook
The Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is expected to grow substantially as U.S. businesses increasingly seek cloud-native ecosystems that deliver both performance and adaptability. With a sharp focus on automation, real-time access, and AI-readiness, the market is transforming into a core element of enterprise IT strategy. Providers that offer interoperability, data resilience, and compliance alignment will stand out as leaders in this rapidly advancing space.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/cloud-database-and-dbaas-market-6586
Conclusion
The future of data is cloud-powered, and the Cloud Database and DBaaS Market is at the forefront of this transformation. As American enterprises accelerate their digital journeys, the demand for intelligent, secure, and scalable database services continues to rise.
Related Reports:
Analyze U.S. market demand for advanced cloud security solutions
Explore trends shaping the Cloud Data Security Market in the U.S
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
Slow database? It might not be your fault
<rant>
Okay, it usually is your fault. If you logged the SQL your ORM was generating, or saw how you are doing joins in code, or realised what that indexed UUID does to your insert rate etc you’d probably admit it was all your fault. And the fault of your tooling, of course.
In my experience, most databases are tiny. Tiny tiny. Tables with a few thousand rows. If your web app is slow, its going to all be your fault. Stop building something webscale with microservices and just get things done right there in your database instead. Etc.
But, quite often, each company has one or two databases that have at least one or two large tables. Tables with tens of millions of rows. I work on databases with billions of rows. They exist. And that’s the kind of database where your database server is underserving you. There could well be a metric ton of actual performance improvements that your database is leaving on the table. Areas where your database server hasn’t kept up with recent (as in the past 20 years) of regular improvements in how programs can work with the kernel, for example.
Over the years I’ve read some really promising papers that have speeded up databases. But as far as I can tell, nothing ever happens. What is going on?
For example, your database might be slow just because its making a lot of syscalls. Back in 2010, experiments with syscall batching improved MySQL performance by 40% (and lots of other regular software by similar or better amounts!). That was long before spectre patches made the costs of syscalls even higher.
So where are our batched syscalls? I can’t see a downside to them. Why isn’t linux offering them and glib using them, and everyone benefiting from them? It’ll probably speed up your IDE and browser too.
Of course, your database might be slow just because you are using default settings. The historic defaults for MySQL were horrid. Pretty much the first thing any innodb user had to do was go increase the size of buffers and pools and various incantations they find by googling. I haven’t investigated, but I’d guess that a lot of the performance claims I’ve heard about innodb on MySQL 8 is probably just sensible modern defaults.
I would hold tokudb up as being much better at the defaults. That took over half your RAM, and deliberately left the other half to the operating system buffer cache.
That mention of the buffer cache brings me to another area your database could improve. Historically, databases did ‘direct’ IO with the disks, bypassing the operating system. These days, that is a metric ton of complexity for very questionable benefit. Take tokudb again: that used normal buffered read writes to the file system and deliberately left the OS half the available RAM so the file system had somewhere to cache those pages. It didn’t try and reimplement and outsmart the kernel.
This paid off handsomely for tokudb because they combined it with absolutely great compression. It completely blows the two kinds of innodb compression right out of the water. Well, in my tests, tokudb completely blows innodb right out of the water, but then teams who adopted it had to live with its incomplete implementation e.g. minimal support for foreign keys. Things that have nothing to do with the storage, and only to do with how much integration boilerplate they wrote or didn’t write. (tokudb is being end-of-lifed by percona; don’t use it for a new project 😞)
However, even tokudb didn’t take the next step: they didn’t go to async IO. I’ve poked around with async IO, both for networking and the file system, and found it to be a major improvement. Think how quickly you could walk some tables by asking for pages breath-first and digging deeper as soon as the OS gets something back, rather than going through it depth-first and blocking, waiting for the next page to come back before you can proceed.
I’ve gone on enough about tokudb, which I admit I use extensively. Tokutek went the patent route (no, it didn’t pay off for them) and Google released leveldb and Facebook adapted leveldb to become the MySQL MyRocks engine. That’s all history now.
In the actual storage engines themselves there have been lots of advances. Fractal Trees came along, then there was a SSTable+LSM renaissance, and just this week I heard about a fascinating paper on B+ + LSM beating SSTable+LSM. A user called Jules commented, wondered about B-epsilon trees instead of B+, and that got my brain going too. There are lots of things you can imagine an LSM tree using instead of SSTable at each level.
But how invested is MyRocks in SSTable? And will MyRocks ever close the performance gap between it and tokudb on the kind of workloads they are both good at?
Of course, what about Postgres? TimescaleDB is a really interesting fork based on Postgres that has a ‘hypertable’ approach under the hood, with a table made from a collection of smaller, individually compressed tables. In so many ways it sounds like tokudb, but with some extra finesse like storing the min/max values for columns in a segment uncompressed so the engine can check some constraints and often skip uncompressing a segment.
Timescaledb is interesting because its kind of merging the classic OLAP column-store with the classic OLTP row-store. I want to know if TimescaleDB’s hypertable compression works for things that aren’t time-series too? I’m thinking ‘if we claim our invoice line items are time-series data…’
Compression in Postgres is a sore subject, as is out-of-tree storage engines generally. Saying the file system should do compression means nobody has big data in Postgres because which stable file system supports decent compression? Postgres really needs to have built-in compression and really needs to go embrace the storage engines approach rather than keeping all the cool new stuff as second class citizens.
Of course, I fight the query planner all the time. If, for example, you have a table partitioned by day and your query is for a time span that spans two or more partitions, then you probably get much faster results if you split that into n queries, each for a corresponding partition, and glue the results together client-side! There was even a proxy called ShardQuery that did that. Its crazy. When people are making proxies in PHP to rewrite queries like that, it means the database itself is leaving a massive amount of performance on the table.
And of course, the client library you use to access the database can come in for a lot of blame too. For example, when I profile my queries where I have lots of parameters, I find that the mysql jdbc drivers are generating a metric ton of garbage in their safe-string-split approach to prepared-query interpolation. It shouldn’t be that my insert rate doubles when I do my hand-rolled string concatenation approach. Oracle, stop generating garbage!
This doesn’t begin to touch on the fancy cloud service you are using to host your DB. You’ll probably find that your laptop outperforms your average cloud DB server. Between all the spectre patches (I really don’t want you to forget about the syscall-batching possibilities!) and how you have to mess around buying disk space to get IOPs and all kinds of nonsense, its likely that you really would be better off perforamnce-wise by leaving your dev laptop in a cabinet somewhere.
Crikey, what a lot of complaining! But if you hear about some promising progress in speeding up databases, remember it's not realistic to hope the databases you use will ever see any kind of benefit from it. The sad truth is, your database is still stuck in the 90s. Async IO? Huh no. Compression? Yeah right. Syscalls? Okay, that’s a Linux failing, but still!
Right now my hopes are on TimescaleDB. I want to see how it copes with billions of rows of something that aren’t technically time-series. That hybrid row and column approach just sounds so enticing.
Oh, and hopefully MyRocks2 might find something even better than SSTable for each tier?
But in the meantime, hopefully someone working on the Linux kernel will rediscover the batched syscalls idea…? ;)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Databases: how they work, and a brief history
My twitter-friend Simon had a simple question that contained much complexity: how do databases work?
Ok, so databases really confuse me, like how do databases even work?
— Simon Legg (@simonleggsays) November 18, 2019
I don't have a job at the moment, and I really love databases and also teaching things to web developers, so this was a perfect storm for me:
To what level of detail would you like an answer? I love databases.
— Laurie Voss (@seldo) November 18, 2019
The result was an absurdly long thread of 70+ tweets, in which I expounded on the workings and history of databases as used by modern web developers, and Simon chimed in on each tweet with further questions and requests for clarification. The result of this collaboration was a super fun tiny explanation of databases which many people said they liked, so here it is, lightly edited for clarity.
What is a database?
Let's start at the very most basic thing, the words we're using: a "database" literally just means "a structured collection of data". Almost anything meets this definition – an object in memory, an XML file, a list in HTML. It's super broad, so we call some radically different things "databases".
The thing people use all the time is, formally, a Database Management System, abbreviated to DBMS. This is a piece of software that handles access to the pile of data. Technically one DBMS can manage multiple databases (MySQL and postgres both do this) but often a DBMS will have just one database in it.
Because it's so frequent that the DBMS has one DB in it we often call a DBMS a "database". So part of the confusion around databases for people new to them is because we call so many things the same word! But it doesn't really matter, you can call an DBMS a "database" and everyone will know what you mean. MySQL, Redis, Postgres, RedShift, Oracle etc. are all DBMS.
So now we have a mental model of a "database", really a DBMS: it is a piece of software that manages access to a pile of structured data for you. DBMSes are often written in C or C++, but it can be any programming language; there are databases written in Erlang and JavaScript. One of the key differences between DBMSes is how they structure the data.
Relational databases
Relational databases, also called RDBMS, model data as a table, like you'd see in a spreadsheet. On disk this can be as simple as comma-separated values: one row per line, commas between columns, e.g. a classic example is a table of fruits:
apple,10,5.00 orange,5,6.50
The DBMS knows the first column is the name, the second is the number of fruits, the third is the price. Sometimes it will store that information in a different database! Sometimes the metadata about what the columns are will be in the database file itself. Because it knows about the columns, it can handle niceties for you: for example, the first column is a string, the second is an integer, the third is dollar values. It can use that to make sure it returns those columns to you correctly formatted, and it can also store numbers more efficiently than just strings of digits.
In reality a modern database is doing a whole bunch of far more clever optimizations than just comma separated values but it's a mental model of what's going on that works fine. The data all lives on disk, often as one big file, and the DBMS caches parts of it in memory for speed. Sometimes it has different files for the data and the metadata, or for indexes that make it easier to find things quickly, but we can safely ignore those details.
RDBMS are older, so they date from a time when memory was really expensive, so they usually optimize for keeping most things on disk and only put some stuff in memory. But they don't have to: some RDBMS keep everything in memory and never write to disk. That makes them much faster!
Is it still a database if all the structured data stays in memory? Sure. It's a pile of structured data. Nothing in that definition says a disk needs to be involved.
So what does the "relational" part of RDBMS mean? RDBMS have multiple tables of data, and they can relate different tables to each other. For instance, imagine a new table called "Farmers":
IDName 1bob 2susan
and we modify the Fruits table:
Farmer IDFruitQuantityPrice 1apple105.00 1orange56.50 2apple206.00 2orange14.75
.dbTable { border: 1px solid black; } .dbTable thead td { background-color: #eee; } .dbTable td { padding: 0.3em; }
The Farmers table gives each farmer a name and an ID. The Fruits table now has a column that gives the Farmer ID, so you can see which farmer has which fruit at which price.
Why's that helpful? Two reasons: space and time. Space because it reduces data duplication. Remember, these were invented when disks were expensive and slow! Storing the data this way lets you only list "susan" once no matter how many fruits she has. If she had a hundred kinds of fruit you'd be saving quite a lot of storage by not repeating her name over and over. The time reason comes in if you want to change Susan's name. If you repeated her name hundreds of times you would have to do a write to disk for each one (and writes were very slow at the time this was all designed). That would take a long time, plus there's a chance you could miss one somewhere and suddenly Susan would have two names and things would be confusing.
Relational databases make it easy to do certain kinds of queries. For instance, it's very efficient to find out how many fruits there are in total: you just add up all the numbers in the Quantity column in Fruits, and you never need to look at Farmers at all. It's efficient and because the DBMS knows where the data is you can say "give me the sum of the quantity colum" pretty simply in SQL, something like SELECT SUM(Quantity) FROM Fruits. The DBMS will do all the work.
NoSQL databases
So now let's look at the NoSQL databases. These were a much more recent invention, and the economics of computer hardware had changed: memory was a lot cheaper, disk space was absurdly cheap, processors were a lot faster, and programmers were very expensive. The designers of newer databases could make different trade-offs than the designers of RDBMS.
The first difference of NoSQL databases is that they mostly don't store things on disk, or do so only once in a while as a backup. This can be dangerous – if you lose power you can lose all your data – but often a backup from a few minutes or seconds ago is fine and the speed of memory is worth it. A database like Redis writes everything to disk every 200ms or so, which is hardly any time at all, while doing all the real work in memory.
A lot of the perceived performance advantages of "noSQL" databases is just because they keep everything in memory and memory is very fast and disks, even modern solid-state drives, are agonizingly slow by comparison. It's nothing to do with whether the database is relational or not-relational, and nothing at all to do with SQL.
But the other thing NoSQL database designers did was they abandoned the "relational" part of databases. Instead of the model of tables, they tended to model data as objects with keys. A good mental model of this is just JSON:
[ {"name":"bob"} {"name":"susan","age":55} ]
Again, just as a modern RDBMS is not really writing CSV files to disk but is doing wildly optimized stuff, a NoSQL database is not storing everything as a single giant JSON array in memory or disk, but you can mentally model it that way and you won't go far wrong. If I want the record for Bob I ask for ID 0, Susan is ID 1, etc..
One advantage here is that I don't need to plan in advance what I put in each record, I can just throw anything in there. It can be just a name, or a name and an age, or a gigantic object. With a relational DB you have to plan out columns in advance, and changing them later can be tricky and time-consuming.
Another advantage is that if I want to know everything about a farmer, it's all going to be there in one record: their name, their fruits, the prices, everything. In a relational DB that would be more complicated, because you'd have to query the farmers and fruits tables at the same time, a process called "joining" the tables. The SQL "JOIN" keyword is one way to do this.
One disadvantage of storing records as objects like this, formally called an "object store", is that if I want to know how many fruits there are in total, that's easy in an RDBMS but harder here. To sum the quantity of fruits, I have to retrieve each record, find the key for fruits, find all the fruits, find the key for quantity, and add these to a variable. The DBMS for the object store may have an API to do this for me if I've been consistent and made all the objects I stored look the same. But I don't have to do that, so there's a chance the quantities are stored in different places in different objects, making it quite annoying to get right. You often have to write code to do it.
But sometimes that's okay! Sometimes your app doesn't need to relate things across multiple records, it just wants all the data about a single key as fast as possible. Relational databases are best for the former, object stores the best for the latter, but both types can answer both types of questions.
Some of the optimizations I mentioned both types of DBMS use are to allow them to answer the kinds of questions they're otherwise bad at. RDBMS have "object" columns these days that let you store object-type things without adding and removing columns. Object stores frequently have "indexes" that you can set up to be able to find all the keys in a particular place so you can sum up things like Quantity or search for a specific Fruit name fast.
So what's the difference between an "object store" and a "noSQL" database? The first is a formal name for anything that stores structured data as objects (not tables). The second is... well, basically a marketing term. Let's digress into some tech history!
The self-defeating triumph of MySQL
Back in 1995, when the web boomed out of nowhere and suddenly everybody needed a database, databases were mostly commercial software, and expensive. To the rescue came MySQL, invented 1995, and Postgres, invented 1996. They were free! This was a radical idea and everybody adopted them, partly because nobody had any money back then – the whole idea of making money from websites was new and un-tested, there was no such thing as a multi-million dollar seed round. It was free or nothing.
The primary difference between PostgreSQL and MySQL was that Postgres was very good and had lots of features but was very hard to install on Windows (then, as now, the overwhelmingly most common development platform for web devs). MySQL did almost nothing but came with a super-easy installer for Windows. The result was MySQL completely ate Postgres' lunch for years in terms of market share.
Lots of database folks will dispute my assertion that the Windows installer is why MySQL won, or that MySQL won at all. But MySQL absolutely won, and it was because of the installer. MySQL became so popular it became synonymous with "database". You started any new web app by installing MySQL. Web hosting plans came with a MySQL database for free by default, and often no other databases were even available on cheaper hosts, which further accelerated MySQL's rise: defaults are powerful.
The result was people using mySQL for every fucking thing, even for things it was really bad at. For instance, because web devs move fast and change things they had to add new columns to tables all the time, and as I mentioned RDBMS are bad at that. People used MySQL to store uploaded image files, gigantic blobs of binary data that have no place in a DBMS of any kind.
People also ran into a lot of problems with RDBMS and MySQL in particular being optimized for saving memory and storing everything on disk. It made huge databases really slow, and meanwhile memory had got a lot cheaper. Putting tons of data in memory had become practical.
The rise of in-memory databases
The first software to really make use of how cheap memory had become was Memcache, released in 2003. You could run your ordinary RDBMS queries and just throw the results of frequent queries into Memcache, which stored them in memory so they were way, WAY faster to retrieve the second time. It was a revolution in performance, and it was an easy optimization to throw into your existing, RDBMS-based application.
By 2009 somebody realized that if you're just throwing everything in a cache anyway, why even bother having an RDBMS in the first place? Enter MongoDB and Redis, both released in 2009. To contrast themselves with the dominant "MySQL" they called themselves "NoSQL".
What's the difference between an in-memory cache like Memcache and an in-memory database like Redis or MongoDB? The answer is: basically nothing. Redis and Memcache are fundamentally almost identical, Redis just has much better mechanisms for retrieving and accessing the data in memory. A cache is a kind of DB, Memcache is a DBMS, it's just not as easy to do complex things with it as Redis.
Part of the reason Mongo and Redis called themselves NoSQL is because, well, they didn't support SQL. Relational databases let you use SQL to ask questions about relations across tables. Object stores just look up objects by their key most of the time, so the expressiveness of SQL is overkill. You can just make an API call like get(1) to get the record you want.
But this is where marketing became a problem. The NoSQL stores (being in memory) were a lot faster than the relational DBMS (which still mostly used disk). So people got the idea that SQL was the problem, that SQL was why RDBMS were slow. The name "NoSQL" didn't help! It sounded like getting rid of SQL was the point, rather than a side effect. But what most people liked about the NoSQL databases was the performance, and that was just because memory is faster than disk!
Of course, some people genuinely do hate SQL, and not having to use SQL was attractive to them. But if you've built applications of reasonable complexity on both an RDBMS and an object store you'll know that complicated queries are complicated whether you're using SQL or not. I have a lot of love for SQL.
If putting everything in memory makes your database faster, why can't you build an RDBMS that stores everything in memory? You can, and they exist! VoltDB is one example. They're nice! Also, MySQL and Postgres have kind of caught up to the idea that machines have lots more RAM now, so you can configure them to keep things mostly in memory too, so their default performance is a lot better and their performance after being tuned by an expert can be phenomenal.
So anything that's not a relational database is technically a "NoSQL" database. Most NoSQL databases are object stores but that's really just kind of a historical accident.
How does my app talk to a database?
Now we understand how a database works: it's software, running on a machine, managing data for you. How does your app talk to the database over a network and get answers to queries? Are all databases just a single machine?
The answer is: every DBMS, whether relational or object store, is a piece of software that runs on machine(s) that hold the data. There's massive variation: some run on 1 machine, some on clusters of 5-10, some run across thousands of separate machines all at once.
The DBMS software does the management of the data, in memory or on disk, and it presents an API that can be accessed locally, and also more importantly over the network. Sometimes this is a web API like you're used to, literally making GET and POST calls over HTTP to the database. For other databases, especially the older ones, it's a custom protocol.
Either way, you run a piece of software in your app, usually called a Client. That client knows the protocol for talking to the database, whether it's HTTP or WhateverDBProtocol. You tell it where the database server is on the network, it sends queries over and gets responses. Sometimes the queries are literally strings of text, like "SELECT * FROM Fruits", sometimes they are JSON payloads describing records, and any number of other variations.
As a starting point, you can think of the client running on your machine talking over the network to a database running on another machine. Sometimes your app is on dozens of machines, and the database is a single IP address with thousands of machines pretending to be one machine. But it works pretty much the same either way.
The way you tell your client "where" the DB is is your connection credentials, often expressed as a string like "http://username:[email protected]:1234" or "mongodb://...". But this is just a convenient shorthand. All your client really needs to talk to a database is the DNS name (like mydb.com) or an IP address (like 205.195.134.39), plus a port (1234). This tells the network which machine to send the query to, and what "door" to knock on when it gets there.
A little about ports: machines listen on specific ports for things, so if you send something to port 80, the machine knows the query is for your web server, but if you send it to port 1234, it knows the query is for your database. Who picks 1234 (In the case of Postgres, it's literally 5432)? There's no rhyme or reason to it. The developers pick a number that's easy to remember between 1 and 65,535 (the highest port number available) and hope that no other popular piece of software is already using it.
Usually you'll also have a username and password to connect to the database, because otherwise anybody who found your machine could connect to your database and get all the data in it. Forgetting that this is true is a really common source of security breaches!
There are bad people on the internet who literally just try every single IP in the world and send data to the default port for common databases and try to connect without a username or password to see if they can. If it works, they take all the data and then ransom it off. Yikes! Always make sure your database has a password.
Of course, sometimes you don't talk to your database over a network. Sometimes your app and your database live on the same machine. This is common in desktop software but very rare in web apps. If you've ever heard of a "database driver", the "driver" is the equivalent of the "client", but for talking to a local database instead of over a network.
Replication and scaling
Remember I said some databases run on just 1 machine, and some run on thousands of machines? That's known as replication. If you have more than one copy of a piece of data, you have a "replica" of that data, hence the name.
Back in the old days hardware was expensive so it was unusual to have replicas of your data running at the same time. It was expensive. Instead you'd back up your data to tape or something, and if the database went down because the hardware wore out or something, then you'd buy new hardware and (hopefully) reinstall your DBMS and restore the data in a few hours.
Web apps radically changed people's demands of databases. Before web apps, most databases weren't being continuously queried by the public, just a few experts inside normal working hours, and they would wait patiently if the database broke. With a web app you can't have minutes of downtime, far less hours, so replication went from being a rare feature of expensive databases to pretty much table stakes for every database. The initial form of replication was a "hot spare".
If you ran a hot spare, you'd have your main DBMS machine, which handled all queries, and a replica DBMS machine that would copy every single change that happened on the primary to itself. Primary was called m****r and the replica s***e because the latter did whatever the former told it to do, and at the time nobody considered how horrifying that analogy was. These days we call those things "primary/secondary" or "primary/replica" or for more complicated arrangements things like "root/branch/leaf".
Sometimes, people would think having a hot spare meant they didn't need a backup. This is a huge mistake! Remember, the replica copies every change in the main database. So if you accidentally run a command that deletes all the data in your primary database, it will automatically delete all the data in the replica too. Replicas are not backups, as the bookmarking site Magnolia famously learned.
People soon realized having a whole replica machine sitting around doing nothing was a waste, so to be more efficient they changed where traffic went: all the writes would go to the primary, which would copy everything to the replicas, and all the reads would go to the replicas. This was great for scale!
Instead of having 1 machine worth of performance (and you could swap to the hot spare if it failed, and still have 1 machine of performance with no downtime) suddenly you had X machines of performance, where X could be dozens or even hundreds. Very helpful!
But primary/secondary replication of this kind has two drawbacks. First, if a write has arrived at the primary database but not yet replicated to all the secondary machines (which can take half a second if the machines are far apart or overloaded) then somebody reading from the replica can get an answer that's out of date. This is known as a "consistency" failure, and we'll talk about it more later.
The second flaw with primary/second replication is if the primary fails, suddenly you can no longer write to your database. To restore the ability to do writes, you have to take one of the replicas and "promote" it to primary, and change all the other replicas to point at this new primary box. It's time-consuming and notoriously error-prone.
So newer databases invented different ways of arranging the machines, formally called "network topology". If you think of the way machines connect to each other as a diagram, the topology is the shape of that diagram. Primary/secondary looks like a star. Root/branch/leaf looks like a tree. But you can have a ring structure, or a mesh structure, or lots of others. A mesh structure is a lot of fun and very popular, so let's talk about more about them.
Mesh replication databases
In a mesh structure, every machine is talking to every other machine and they all have some portion of the data. You can send a write to any machine and it will either store it, or figure out what machine should store it and send it to that machine. Likewise, you can query any machine in the mesh, and it will give you the answer if it has the data, or forward your request to a machine that does. There's no "primary" machine to fail. Neat!
Because each machine can get away with storing only some of the data and not all of it, a mesh database can store much, much more data than a single machine could store. If 1 machine could store X data, then N machines could theoretically store N*X data. You can almost scale infinitely that way! It's very cool.
Of course, if each record only existed on one machine, then if that machine failed you'd lose those records. So usually in a mesh network more than one machine will have a copy of any individual record. That means you can lose machines without losing data or experiencing downtime; there are other copies lying around. In some mesh databases can also add a new machine to the mesh and the others will notice it and "rebalance" data, increasing the capacity of the database without any downtime. Super cool.
So a mesh topology is a lot more complicated but more resilient, and you can scale it without having to take the database down (usually). This is very nice, but can go horribly wrong if, for instance, there's a network error and suddenly half the machines can't see the other half of the machines in the mesh. This is called a "network partition" and it's a super common failure in large networks. Usually a partition will last only a couple of seconds but that's more than enough to fuck up a database. We'll talk about network partitions shortly.
One important question about a mesh DB is: how do you connect to it? Your client needs to know an IP address to connect to a database. Does it need to know the IP addresses of every machine in the mesh? And what happens when you add and remove machines from the mesh? Sounds messy.
Different Mesh DBs do it differently, but usually you get a load balancer, another machine that accepts all the incoming connections and works out which machine in the mesh should get the question and hands it off. Of course, this means the load balancer can fail, hosing your DB. So usually you'll do some kind of DNS/IP trickery where there are a handful of load balancers all responding on the same domain name or IP address.
The end result is your client magically just needs to know only one name or IP, and that IP always responds because the load balancer always sends you to a working machine.
CAP theory
This brings us neatly to a computer science term often used to talk about databases which is Consistency, Availability, and Partition tolerance, aka CAP or "CAP theory". The basic rule of CAP theory is: you can't have all 3 of Consistency, Availability and Partition Tolerance at the same time. Not because we're not smart enough to build a database that good, but because doing so violates physics.
Consistency means, formally: every query gets the correct, most up-to-date answer (or an error response saying you can't have it).
Availability means: every query gets an answer (but it's not guaranteed to be the correct one).
Partition Tolerance means: if the network craps out, the database will continue to work.
You can already see how these conflict! If you're 100% Available it means by definition you'll never give an error response, so sometimes the data will be out of date, i.e. not Consistent. If your database is Partition Tolerant, on the other hand, it keeps working even if machine A can't talk to machine B, and machine A might have a more recent write than B, so machine B will give stale (i.e. not Consistent) responses to keep working.
So let's think about how CAP theorem applies across the topologies we already talked about.
A single DB on a single machine is definitely Consistent (there's only one copy of the data) and Partition Tolerant (there's no network inside of it to crap out) but not Available because the machine itself can fail, e.g. the hardware could literally break or power could go out.
A primary DB with several replicas is Available (if one replica fails you can ask another) and Partition Tolerant (the replicas will respond even if they're not receiving writes from the primary) but not Consistent (because as mentioned earlier, the replicas might not have every primary write yet).
A mesh DB is extremely Available (all the nodes always answer) and Partition Tolerant (just try to knock it over! It's delightfully robust!) but can be extremely inconsistent because two different machines on the mesh could get a write to the same record at the same time and fight about which one is "correct".
This is the big disadvantage to mesh DBs, which otherwise are wonderful. Sometimes it's impossible to know which of two simultaneous writes is the "winner". There's no single authority, and Very Very Complicated Algorithms are deployed trying to prevent fights breaking out between machines in the mesh about this, with highly variable levels of success and gigantic levels of pain when they inevitably fail. You can't get all three of CAP and Consistency is what mesh networks lose.
In all databases, CAP isn't a set of switches where you are or aren't Consistent, Available, or Partition Tolerant. It's more like a set of sliders. Sliding up the Partition Tolerance generally slides down Consistency, sliding down Availability will give you more Consistency, etc etc.. Every DBMS picks some combination of CAP and picking the right database is often a matter of choosing what CAP combination is appropriate for your application.
Other topologies
Some other terms you frequently hear in the world of databases are "partitions" (which are different from the network partitions of CAP theorem) and "shards". These are both additional topologies available to somebody designing a database. Let's talk about shards first.
Imagine a primary with multiple replicas, but instead of each replica having all the data, each replica has a slice (or shard) of the data. You can slice the data lots of ways. If the database was people, you could have 26 shards, one with all names starting with A, one with all the names starting with B, etc..
Sharding can be helpful if the data is too big to all fit on one disk at a time. This is less of a problem than it used to be because virtual machines these days can effectively have infinity-sized hard drives.
The disadvantage of sharding is it's less Available: if you lose a shard, you lose everybody who starts with that letter! (Of course, your shards can also have replicas...) Plus your software needs to know where all the shards are and which one to ask a question. It's fiddly. Many of the problems of sharded databases are solved by using mesh topologies instead.
Partitions are another way of splitting up a database, but instead of splitting it across many machines, it splits the database across many files in a single machine. This is an old pattern that was useful when you had really powerful hardware and really slow disks, because you could install multiple disks into a single machine and put different partitions on each one, speeding up your achingly slow, disk-based database. These days there's not a lot of reason to use partitions of this kind.
Fin
That concludes this impromptu Databases 101 seminar! I hope you enjoyed learning a little bit more about this fantastically fun and critically important genre of software. from Seldo.Com Feed https://ift.tt/32XwZth
1 note
·
View note
Text
Advantages Of AWS Online Training
Advantages of AWS Course
1. First things first, Cost:-
There might be a slight increase in the cost depending on the products you use. For example, AWS’s RDS is slightly higher in cost compared to GCP. Same with EC2 and GCE instances. EC2 is higher in price compared to Google GCE. Here are some comparisons, that helped me with my research.
2. Second, Instances and its availability:-
If you really care about the instance quality and availability (and I think everyone should), you should accept the fact that its gonna cost a little extra. AWS Training has more availability zones than any other cloud computing products. Your software will perform the same all around the world. And they have more instance types. Mostly used were Ubuntu, Debian, and Windows server. But who knows you may use Oracle Linux, which Google doesn’t have.
3. Third, Variety of Products or Technologies:-
Google and AWS both have a wide range of products/technologies available. But AWS Online Training has much more than GCP like AWS SQS, Kinesis, Fire hose, Redshift, Aurora DB, etc. Also, AWS has a great monitoring tool that works for every product. If you are using AWS, you gotta use Cloud monitoring.
4. Finally, Ease of development and integration:-
Both are really good at documentation. But AWS Training needs a little more effort when developing and learning a new product. Even though it gives you more control over what you do, it’s easy to screw things in AWS if you don’t know what you are doing. I guess it’s the same for any cloud platform. It’s from my experience. But, AWS Training supports many languages that GCP doesn’t. Like Node.js, Ruby, etc. If you like out of the box deployment platform like Elastic Bean Stalk or Google App Engine, GAE only supports some languages (Go, Python, Perl, Java) but EBS support a few of other languages as well (not Go :) ).There might be other differences like Customer/Developer support both companies offer, etc.
<a href="https://www.visualpath.in/amazon-web-services-aws-training.html">AWS Online Training institute</a>
1 note
·
View note