#prevalent sexually transmitted infections
Text
The Three Most Prevalent STIs: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and HPV
Introduction:
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and human papillomavirus (HPV) are among the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). These infections can cause serious health problems if left untreated and can affect anyone who is sexually active. In this post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of these three prevalent STIs.
Chlamydia:
Causes and Risk Factors:
Chlamydia is…
View On WordPress
#Chlamydia causes#Chlamydia symptoms#Common STIs#Gonorrhea causes#Gonorrhea symptoms#HPV transmission#HPV types#HPV vaccination#prevalent sexually transmitted infections#regular STI testing#safe sex practices#STI treatment options
0 notes
Text
Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs). Part-1: Prevalence and types
in this Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs), part 1, I will discuss the prevalence and types of sexually transmitted Infections which are group of infections that spread through sexual contact. Also, they are called Sexually transmitted Diseases (STDs). These infections can have a variable range of symptoms, from mild to serious), and health effects, (from none to fatal). STIs are don’t affect…
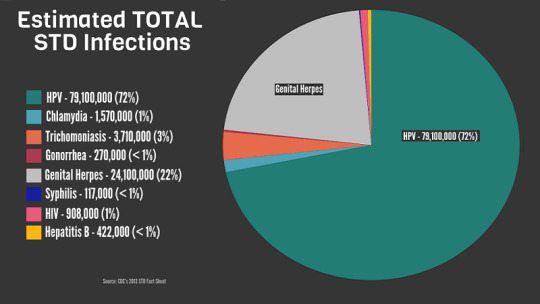
View On WordPress
0 notes
Note
I heard we are now at the cusp of chlamydia being untreatable via antibiotics, fun times
In United States, drug-resistant gonorrhea is a public health problem of national concern. But untreatable gonorrhea isn’t the only STD that has health officials worried.
Earlier this week, the World Health Organization released new treatment guidelines for three common sexually transmitted diseases — chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis— in response to increasing antibiotic resistance.
Gonorrhea has developed the strongest resistance to drugs, but the worries about untreatable syphilis and chlamydia come at a time when rates for the three STDs are rising rapidly in the U.S, especially among young people ages 20 to 24. According to data published by the CDC in 2014, the most recent year available: cases of chlamydia have increased 2.5 percent; gonorrhea 5.1 percent; and syphilis 15.1 percent. This is the first increase in the United States since 2006.
How worried should we be?
“STDs are hidden epidemics of enormous health and economic consequence in the United States,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In the US, STDs are most frequent among college-age women, the highest prevalence being among women, ages 20 to 24.
According to the CDC, there are about 820,000 new gonorrhea infections each year in the United States. In fact, gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease, after chlamydia.
In the past, gonorrhea was successful treated by several classes of antibiotics, including the ubiquitous penicillin. Over time, however, gonorrhea has developed resistance to many of them, and now, we are down to one recommended effective class of antibiotics to treat it.
The problem doesn’t end there. Gonorrhea is even starting to show decreased susceptibility to this “last line” treatment option. This makes this bacterium a multidrug-resistant organism, which are often called “superbugs”.
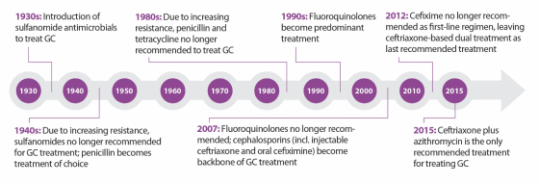
As for chlamydia and syphilis, drug resistant strains have not become common in the US yet, but the WHO report warns that this is a growing problem in many parts of the world.
How can untreatable STDs be prevented?
Anyone who is sexually active can get an STD.
That said, STDs are preventable and there are steps you can take to keep yourself and your partner healthy. Remember that protecting your health is your responsibility:
Condoms: Use them correctly every time you have sex.
Have fewer partners: Ideally, agree to only have sex with one person who agrees to only have sex with you.
Talk with your partner: Talk with your sex partner about STDs and staying safe before having sex.
Get tested: Make sure you both get tested to know for sure that neither of you has an STD.
Get vaccinated: Safe and highly effective vaccines are available for two STDs: hepatitis B and HPV. HPV is in fact the most common STD. There are specific recommendations for routine and catch up vaccinations for these two STDs.
____________________
This is from 2016 and I cut a bunch out of the middle.
2nd bullet point there probably gonna make some people grumpy, something about suggesting monogamy makes people mad.
102 notes
·
View notes
Photo

On this day, 18 August 1945, the Japanese Ministry of the Interior ordered police to be setting up "sexual comfort stations" (i.e., brothels) for US occupation troops, just before the start of surrender talks (content note: sexual violence). Local authorities and businessmen established a network of brothels under the Recreation and Amusement Association (RAA), which was state-funded, some in places like police dormitories. At its height, the RAA had 70,000 women working in its brothels, with around 80,000 at independent brothels for the 350,000 US troops in the country. The first brothel established by the RAA, Komachien ("The Babe Garden") had 38 women, who had 15-60 clients each day. The official justification for the network was "to create a breakwater to protect regular women and girls." US military officials were aware that some women in the brothels had been enslaved, and others coerced or tricked by responding to fake advertisements for other jobs. One 19 year old woman, Natsue Takita, responded to an ad for an office worker. She was then told the only available posts were for "comfort women" and persuaded to accept it. She died by suicide after jumping in front of a train a few days later. A memo from Lt Col Hugh MacDonald explained "The girl is impressed into contracting by the desperate financial straits of her parents and their urging, occasionally supplemented by her willingness to make such a sacrifice to help her family". He also admitted that "in urban districts the practice of enslaving girls, while much less prevalent than in the past, still exists." Eventually, facing rampant sexually transmitted infections amongst the troops, as well as complaints from army chaplains, Gen MacArthur declared the brothels off-limits to US personnel on 25 March 1946. https://www.facebook.com/workingclasshistory/photos/a.1819457841572691/2060642284120911/?type=3
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revealing Facts: A Helpful Guide on HIV/AIDS

You can have HIV without having any symptoms. This is why it’s extremely important to get tested regularly, even if you don’t feel sick.
According to WHO, the cases of HIV/AIDS have increased lately. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks a specific type of cell in your body’s immune system, which helps the system in fighting off infections and diseases. If HIV progresses, it can lead to AIDS, a more severe condition where the immune system is badly damaged. HIV is transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles, or from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth or breastfeeding. There are different symptoms at each stage of infection. Having these symptoms may suggest a person has HIV. If left untreated, HIV can lead tseo more serious health issues.
Having accurate information is crucial to avoid any false assumptions related to HIV/AIDS. HIV/AIDS is surrounded by many myths and misunderstandings such as; it is spread through sneezing, coughing or sharing drinks. This is not true, the way it is transmitted is through specific bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
In a world where misinformation about HIV/AIDS is prevalent, it's crucial to clear up these misunderstandings and ensure everyone knows the facts. Normalising getting tested is the first step in managing the virus and preventing the spread of false stigmas about HIV. Let's all do our part by sharing the correct information and supporting those dealing with HIV to create a world without judgement and false ideas about this virus.
To know more about HIV/AIDS its symptoms, unknown facts, and risk factors, read the blog on Riomed's site.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since the start of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, more than 62,000 Russians and 20,000 Ukrainians have relocated to Georgia. Meanwhile, Georgia itself has seen a rise in HIV infections, with almost 400 new cases reported in the first eight months of 2023, despite having been lauded among European countries for its effective HIV and AIDS policies in recent years. This has led some Georgian doctors and media outlets to attribute the worsening HIV situation to the wartime influx of Russian and Ukrainian migrants — the latest iteration of a theory that’s found resonance in a number of countries, particularly among conservative politicians. Meduza takes a look at the reasons behind the widespread popularity of this dubious hypothesis.
A lack of evidence
In late June, Professor Maya Butsashvili, an infectious disease specialist who works at Tbilisi’s NEOLAB clinic, expressed concern on Facebook regarding the large number of Russians entering the country. Arguing that Russia was grappling with an HIV epidemic and that unprotected sexual encounters between local residents and migrants could lead to an increase in HIV infections in Georgia, she urged officials to remind citizens about safe practices to avoid sexually transmitted infections.
Shortly after, Tengiz Tsertsvadze, the director of Georgia's main infectious disease hospital, said that Butsashvili's theory “had some truth to it” but suggested that the increase in cases might have “less to do with the influx of migrants and more to do with the end of the COVID-19 pandemic, the lifting of restrictions, and an increase in testing.” He noted that since the wartime migration of Russian and Ukrainian citizens had begun, Georgia’s HIV and AIDS Control Service had intensified its surveillance and implemented measures for prevention and treatment. Tsertsvadze also emphasized the importance of only using sterile medical instruments and avoiding unprotected sexual contact, encouraging those with suspected infections to seek medical assistance.
Nonetheless, Butsashvili remained firm in her stance, insisting that migrants were a “high-risk group.” In August, she recommended a policy of mandatory HIV testing for people entering the country and urged local residents to “abstain from unprotected sexual contact.”
Butsashvili, whose Facebook page has some 7,000 followers, has been widely quoted in the Georgian media for her statements, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Her opinions on the role of migrants in HIV transmission have sparked huge debates across social media platforms. According to her profile, she studied epidemiology at the State University of New York and is currently a faculty member at the University of Georgia.
Skewed by the pandemic
Georgia was seeing record spikes in HIV rates well before the recent influx of migrants from Russia began. In 2018, for instance, the country identified 672 new HIV cases, while it saw 719 in 2016, which remains the highest year on record. In 2022, 617 new cases were recorded, and in the first eight months of this year, 393 cases were confirmed.
In August 2023, the total number of HIV infections in Georgia reached 10,170, with the majority of cases in Tbilisi (3,830). According to the Georgian Center for Research of Infectious Diseases and AIDS, the virus is transmitted primarily through heterosexual contact (51.4%) and intravenous drug use (32.6%). HIV prevalence in Georgia, at 0.27% of the total population, is substantially lower than in Russia (0.8%) and Ukraine (approximately 0.55%).
Georgia's HIV and AIDS policy, according to WHO estimates, has been one of the most effective in Europe. The country introduced antiretroviral therapy (ARV therapy) in the 1990s and ensured universal access in the 2000s, significantly reducing AIDS-related mortality. In 2011, Georgia established a national AIDS information system, creating a comprehensive database of demographic, epidemiological, clinical and laboratory data on all AIDS patients. The government also actively promotes ARV therapy and health services for all, regardless of gender, ethnicity, or viral load.
Despite these efforts, Georgia fell short of its goal to provide ARV therapy to 90% of the infected population by 2020, with only 76% of virus carriers knowing their status and only 65% receiving ARV therapy. Even fewer individuals (65% of those on therapy) have managed to suppress the virus's activity.
A more plausible explanation
One epidemiologist, who asked to remain anonymous for security reasons, acknowledged that Russia and Ukraine have significant HIV epidemics and that migrants are a particularly vulnerable group. But at the same time, he said, Georgia’s rise in infections cannot be unequivocally attributed to the influx in migrants without a comprehensive analysis of the epidemiological data.
The Georgian Center for Infectious Diseases and AIDS Research reported more HIV cases in 2022 than in 2020 and 2021. However, this increase could be attributed at least in part to reduced testing during the COVID-19 pandemic, when resources were diverted to coronavirus prevention efforts.
The epidemiologist further explained that there’s little to no evidence that compulsory testing, entry restrictions, or deportation are effective public health measures. In fact, such measures may even hinder HIV prevention and treatment as they make individuals more likely to hide their status, avoid seeking help, and then propagate the virus as a result.
The U.N.’s note on HIV/AIDS and the Protection of Refugees states:
Detention or restrictions on the freedom of movement of persons living with HIV and AIDS would be in violation of the fundamental rights to liberty and security of the person, as well as the right to freedom of movement, if carried out solely on the basis of a person’s actual or suspected HIV status. There is no public health justification for restrictions of these rights due to a person’s HIV status alone. Moreover such restrictions would be discriminatory.
In Russia, however, it remains legally permissible to deport migrants based solely on their HIV status. In 2021, Fedot Tumusov, a deputy from the political party “A Just Russia — For Truth,” proposed a bill to abolish these measures due to their lack of effectiveness, but the State Duma ignored his proposal. According to the head of one public organization that works with individuals affected by HIV in Eastern Europe and Central Asia, who asked to remain anonymous, there’s no reasonable basis for a country to deport foreigners with HIV. Many developed countries have already repealed such laws.
An easy scapegoat
One human rights activist who specialises in HIV issues and wished to maintain anonymity told Meduza that the practice of blaming migrants, a vulnerable group, for various societal problems is not unique to Georgia; it’s a common rhetorical move employed by conservative political figures worldwide. In Georgia, she argued, negative sentiments regarding migrants may have been exacerbated by the strain on public health and the surge in migration caused by the war, leading to concerns and frustrations among local residents that politicians can exploit for political gain.
Georgian political scientist Gela Vasadze has also suggested that accusing migrants of spreading HIV may be an element of the political campaigns of right-wing opposition parties in the upcoming 2024 elections. He told the outlet Paper Kartuli that the Georgian authorities should address the migration crisis by reducing the stay period of visitors with uncertain legal status and making it easier for migrants to obtain residence permits.
According to the anonymous human rights activist, migrants are a vulnerable group with limited political and civil rights, which makes them easy scapegoats for various social problems. This phenomenon is not unique to Georgia but is a broader issue tied to policies and levels of tension within countries.
Russia is no exception: it, too, has a long history of public figures making public health-related xenophobic statements. In 2009, for example, the country’s then-Chief Health Inspector, Gennady Onishchenko, alleged that migrants “contribute significantly to the HIV and AIDS epidemic.” Similar sentiments were echoed in 2012, when the chairman of the Moscow City Duma’s healthcare commission, Lyudmila Stebenkova, proposed putting out public service announcements to warn Muscovites about the risk of contracting HIV from migrants.
Over the past two decades, however, Georgia has been decidedly receptive to international recommendations, focusing on testing and treatment while avoiding discriminatory policies. Anyone who’s in the country legally has the right to receive assistance, including refugees, who can access ARV treatment while their asylum requests are being processed.
At the same time, the activist said, there’s no question that the Georgian healthcare system was unprepared for the influx of migrants. While Georgia has been proactive in HIV prevention, migrants have encountered difficulties in accessing HIV treatment.
According to the experts who spoke to Meduza, effectively addressing Georgia’s HIV problem will require ensuring equal access to healthcare, repealing discriminatory laws, and prioritizing prevention programs and HIV awareness campaigns. Providing free counselling, testing, and treatment to all individuals living with HIV, regardless of their legal status, is paramount.
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Some Important Information On Yeast Infection Symptoms In Men
Yeast infection in men is real; so are the yeast infection symptoms in men. This yeast infection called candidiasis occurring in both men and women has prompted companies to look for a cure to this medical condition. The fact remains that click here women have a higher tendency to develop the yeast infections, but the other fact is that even men can develop these genital yeast infection.
Areas which are warm, dark and moist are perfect for the breeding of the yeast called candida. Even in a healthy person, such exposed areas can result in candida overgrowth. Whenever we are off guard, or not taking care of our diet, we may be promoting the growth of the fungus. Antibiotics, diet and hygiene contribute towards genital yeast infections.
There are other causes of yeast infection aside from candida. People suffering from this condition are usually made fun of by others, hence making it a social torment for them. Various factors cause penile yeast infection in man. It is very unpleasant to see the symptoms of yeast infection in men.
The symptoms include a burning sensation and a discharge of white liquid. The other symptoms are blisters and sores on the head of the male reproductive organ. Besides, there may also be severe itching. But usually, there are no symptoms in the early stages of this yeast infection.
Yeast infections will be more prevalent in diabetic men as they have high sugar levels in their urine.
This yeast also resides in the mouth and skin, naturally.
This is a fungal infection which keeps on occurring again and again. Hence the best option is prevention of this disease. Taking care of the digestive tract is a good alternative. Infected people need to keep the area dry as well as clean. This will aid in effective healing of the infection.
A proper diagnosis needs to be done by a doctor in case the man observes any of these symptoms. A professional diagnosis is very important for the following reasons –
1. In case a man is not getting his yeast infection treated, he may end up passing it to his partner. Similarly, she too can pass it back to him. The yeast infection can be erased completely only if both sexual partners get them treated.
2. The man may be suffering from a medical condition called genital herpes, but he may be under the impression that he is having yeast infection. A disease transmitted sexually and having symptoms of itchy bumps is called genital herpes. The medicines used to treat yeast infection can not be used to treat genital herpes which is a chronic disease.
It is for these same reasons that a person suffering from these same reasons avoids self diagnosis and gets himself investigated by a health care provider.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some nineteenth-century doctors had suggested that girls might be susceptible to gonorrhea infection from unsanitary contacts, such as with a wet sponge that moved directly from the genitals of an infected woman to a girl. But they never suggested that such a narrow chain of events could explain how every girl, or even most girls, became infected. Only after they discovered that infection was widespread among girls from their own class did twentieth-century doctors expand the possible virulence of nonsexual contacts with the gonorrhea bacterium beyond the probable. They had no evidence to support such a connection but repeated it so often that by the 1940s medical textbooks removed gonorrhea vulvovaginitis, gonorrhea infection of girls’ genitals, from the category of sexually transmitted diseases.
Doctors were not naive to the fact that men sexually assaulted girls, including their own daughters. But doctors and reformers could not believe that incest occurred frequently enough among white middle- and upper class Americans to account for the incidence of infection. The speculations of anxious health care professionals and social reformers pitched a noisy silence over the implications of the new data on the prevalence and incidence of infection, signaling their resolve to find a source, any source, of infection other than the girls’ fathers. The silence is audible in the medical records of social welfare institutions and private doctors; in hundreds of articles in the medical, public health, nursing, and medical social work literature; in the reports of blue ribbon committees organized by charitable organizations; in scores of criminal court records and newspaper reports; and in the private and published writings of reformers of all stripes.
Lynn Sacco, Unspeakable: Father-Daughter Incest in American History
#incest tw#csa tw#rape tw#this is what gale swiontkowski was saying in the introduction to imagining incest#it's such a deeply upsetting thing to me - to think of all these women left by their own devices because men refused#to believe the status quo was not what they thought it was
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The consequences of intoxication can go well beyond individual brains. For example, impaired judgment can result in inappropriate sexual behavior, sexually transmitted infections, and unwanted pregnancies. It can also contribute to sexual assault, rape, and sexual trauma. Nearly 700,000 students a year in the United States between the ages of eighteen and twenty-four are assaulted by another student who has been drinking. In addition, about a third of all traffic-related fatalities in the United States are related to alcohol intoxication, and numerous studies have found a high correlation between substance use and intimate partner violence.
Excessive, chronic drinking leads to cardiovascular problems including stroke and high blood pressure; liver problems such as steatosis (fatty liver), alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis; pancreatitis; and increased risk of various cancers (including of the mouth, esophagus, larynx, pharynx, breast, liver, colon, and rectum). But even moderate drinking is harmful. A recent study evaluated the effects of drinking in over half a million people around the world and found that even one drink a day is associated with a number of diseases (including cancers and cardiovascular issues) that lead to premature death.
The more people drank, the worse the outcome: about two drinks a day shaves a year or two off the life span, and reduced intake increases life expectancy. In addition, alcohol use during pregnancy can lead to a wide range of disabilities in children, the most severe of which is fetal alcohol syndrome, characterized by intellectual disabilities, speech and language delays, poor social skills, and sometimes facial deformities.
Despite these grim outcomes, it seems that we can neither get enough of the drug nor get it fast enough. In the United States, more than a quarter of people over eighteen reported that they engaged in binge drinking during the previous month. This pattern is even more prevalent among college students, nearly 40 percent of whom reported binge drinking in the previous month. Whether cause or effect, about half of these students (20 percent) meet the criteria for an alcohol use disorder, and 25 percent report academic consequences from drinking.
Binge drinking is risky for anyone, but particularly for those whose brains are still developing. The impact of high alcohol concentrations during this “plastic” period leads to lasting alterations in brain structure and function and is more likely to result in an alcohol use disorder. The converse is also true: one of the most effective ways to curtail the risk of addiction is to avoid intoxication during periods of rapid brain development. People who begin drinking in their early teens, as I did, are at least four times more likely to eventually meet the criteria for an alcohol use disorder. In fact, the lifetime risk for substance abuse and dependence decreases about 5 percent with each additional year between ages thirteen and twenty-one.
Yet young people are especially prone to binge drinking in part because they are neurobiologically primed to seek and appreciate novel and high-risk experiences. Though their parents may not appreciate it, for adolescents these tendencies are well timed to promote the development of adult goals and identity formation.
While the consequences have generally gotten stricter, the per capita consumption both here and worldwide has been rising fairly steeply since my heyday. Excessive use of alcohol now results in about 3.3 million deaths around the world each year. In Russia and its former satellite states, one in five male deaths is caused by drinking. And in the United States during the period between 2006 and 2010, excessive alcohol use was responsible for close to 90,000 deaths a year, including one in ten deaths among adults aged twenty to sixty-four, translating to 2.5 million years of potential life lost. More than half of these deaths and three-quarters of the years of potential life lost were due to binge drinking.
Alcohol use also substantially contributes to automobile accidents, domestic abuse, and other forms of violence. Roughly a third of all visits to emergency rooms for injuries in 2016 were alcohol related. Given all this, it is perhaps surprising that alcohol is only the second most lethal drug—trailing not opiates as one might suspect after reading almost any newspaper or magazine but the other legal substance: tobacco. In fact, alcohol killed about twice as many people in 2016 as prescription opioids and heroin overdoses combined, and even this number would be almost three times higher if it included drunk-driving-related deaths.
-- Judith Grisel, Never Enough
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Types of Risk Associated with HPV Viruses: A Detailed Guide
HPV is a very prevalent sexually transmitted infection in the world. 8 out of 10 sexually active people will get HPV at some point in their lives. Some people will get it for a long time, but the majority of people clear it from their system. Although a mild infection in most cases, there is a high risk of certain types of genital cancers if you contract any of the high-risk strains of the virus.
That’s why you need to be aware of the different types of risk associated with HPV viruses and how they affect each person differently. In this article, we’ll discuss what you need to know about the different types of risk associated with HPV, as well as ways to reduce that risk.
What is HPV?
HPV stands for human papillomavirus, a common virus that causes genital warts and certain cancers. It’s the most common sexually transmitted infection in the world and the most frequently reported cause of cervical cancer. It can also cause genital warts and cancers of the anus and throat.
About 80% of people who are sexually active will get HPV at some point in their lives, but most people clear it from their bodies within a short span of time. There are more than 100 types of HPV, and many of them don’t cause any serious harm or any harm at all. Some types of HPV are highly contagious and can lead to infection in your mouth, on your head, and outside your body. The most common type of genital HPV infection is 6 and 11; Genital HPV infections are most common in sexually active young people between the ages of 15 and 25.
High-Risk HPV and Its Effect on Your Body
Out of the 100 strains of HPV, some 14 strains are known to be carcinogenic; they can also cause cancers of your cervix, vagina, vulva, and anus. These strains are called high-risk HPVs.
The type of HPV that causes cervical cancer can also cause cancers of the vagina, vulva, anus, and penis. Most people with cervical cancer have either HPV 16 or 18. The type of HPV that causes anal and anal-rectal cancers can also cause cancers of the penis, vulva, and anus. Most people with anal-rectal cancers also have HPV to blame.
The virus causes these cancers by triggering abnormal cell growth in the infected area. This is a long process that goes largely undetected, and by the time symptoms show up, it might be too late. Therefore it is advised to get screened for these types of cancers periodically. Early detection can save lives.
Low-Risk HPV and Its Effect on Your Body
The majority of people with HPV infections never develop any symptoms or problems. If you have a low-risk infection, it can cause genital warts. Other than genital warts, there can be warts on the infected area anywhere on the body. The risk of having an HPV infection that causes genital warts is very low. Even if there are genital warts, they clear up on their own, and no treatment is required.
In cases of lower levels of immunity, some treatment may be required. There are many OTC creams that can be used, but they are generally discouraged by doctors. Instead, the doctors have certain prescription creams and compounds that can help treat genital warts. In some cases of warts not responding to the treatment or simply being too big, surgical procedures might be required.
How can you protect yourself against HPV?
There are multiple ways to lower your risk of contracting HPV. The first and foremost is to follow safe sex practices. Using a condom lowers the risk of HPV infection by almost 70 per cent. However, it is still possible to catch the virus since it spreads through skin-to-skin contact of any kind.
Therefore, the HPV vaccine is the most potent defence against HPV. It can offer protection against the most dangerous and common strains of HPV. It is advised to get the vaccine as early in life as possible.
Finally, regular testing for cancers, especially cervical cancer, is a must. HPV-related cancers are more common in women, with cervical cancer being caused exclusively by HPV infections. Pap smear tests can help mitigate the effects of these health complications by letting the doctors detect any signs of cancer early.
Final Words
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that can infect your body in different ways. It can affect your mouth, throat, genital and anal area. Since HPV is so common, the only way to protect yourself is by regular screening, taking care of your general health and getting the HPV vaccine. Stay vigilant and enjoy a healthy life!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
CONTRACEPTIVE UTILIZATION AMONG UNDERGRADUATES STUDENTS
Young people's sexual habits are on the rise all over the world, with a trend toward early onset. Many young adults began their first sexual activity while still in adolescence. Up to 6% of all sexually active teenage girls in Nigeria could have become pregnant and had an induced abortion. Sexual behavior has been characterized as any activity that causes sexual arousal, with biology and the degree of sociocultural control exerted on an individual's ability to express sexuality being two major determinants. Individuals' or couples' desire to live a satisfying and healthy sexual life is critical to sexual health. If the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) for sexual inclusion, maternal health, and HIV/AIDS are to be met, inclusive environments in which healthy sexual activity can occur are critical. Traditionally, public health has concentrated on the negative consequences of sexual behavior. Sexual behaviors contribute significantly to the burden of disease as essential determinants of reproductive patterns and transmission of sexually transmitted infections. Sexual rights have received increased attention in the foreign policy arena over the last decade, and new norms for the development and preservation of a sexually safe community, based on values of integrity, respect, and choice, are being developed. The design and evaluation of strategies to improve sexual health include information about sexual conduct and activity. Importantly, too, empirical evidence is needed to correct myths in public perception of behaviors. Yet despite being scrutinized everywhere, sexual behavior poses challenges for scientific enquiry. In terms of intervention, the same paradox exists: sexual behavior is tightly controlled in almost every country, but changing it to improve sexual wellbeing has proven difficult. In the last two decades, the need to predict and avoid HIV transmission has given a valuable impetus to both sexual activity and intervention studies. Some regions have more data than others, especially those with low HIV prevalence or strict sex prohibitions, or both. African countries, for example, have received much less attention from researchers than Asian countries, resulting in a limited evidence base. Even so, the vast number of developing countries with comparable data (those for which a Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) has been conducted) and other countries with comparable national surveys will provide a fair global impression. Data is also accumulating from evaluations of the effectiveness of programs aimed at improving sexual health.
The research that has resulted offers a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to assess sexual behavior and attempts to protect sexual health at the dawn of the twenty-first century. Both secular and non-secular social movements have an effect on sexual behavior. Poverty, schooling, and housing have all changed dramatically in recent decades. Seasonal labor, rural-to-urban migration, and social instability due to war and political instabilities have all resulted in demographic shifts in the age structure of populations, the timing of marriage, and the rate of mobility and migration between and within countries. Many countries have changed their attitudes about sexual behavior. Worldwide communications, including the internet, have influenced social norms by transporting sexual images from more liberal to more conservative societies, especially in societies where information technology advancements have been rapid. With advancements in contraceptives, sexual identity is becoming largely free of its reproductive effects. Health-care policy and regulations, as well as public-health policies, have changed; access to family planning services has improved, and attempts to prevent HIV transmission have impacted few areas. We discuss emerging trends and patterns in key sexual behavior variables, as well as their consequences for sexual health and the design of sexual health interventions.
Given the widespread AIDS epidemic that has gripped many countries, as well as a persistently high rate of childbearing at a young age, adolescent sexual and reproductive health is a crucial policy and programmatic problem in Sub-Saharan Africa. At the end of 2005, an estimated 4.3 percent of young women and 1.5 percent of young men in Sub-Saharan Africa were living with HIV, and 9-13 percent of young women had given birth by the age of 16. To minimize their risk of contracting HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as well as unwanted pregnancies and very early childbearing, young people clearly need access to preventive knowledge and skills before they become sexually active. The most difficult task is determining what unique information to provide young undergraduates, from what sources, at what ages, and in what ways.
Browse free undergraduate research topics and guides for students
Understanding the emerging sexual and reproductive health habits and needs of very young teenagers is one of the first steps in answering these concerns. In Nigeria, contraceptives are given free of charge at government health facilities. Referral hospitals, primary hospitals, main clinics, university clinics, mobile clinics, health posts and the Botswana Family Welfare Association, as well as sexual and reproductive centers, are among the facilities available. The residents' homes are within a 15-kilometer radius of these health centers (UNFPA Case Study 2013). Because of strong cultural and religious values, the use of contraception is not freely debated by young single women or undergraduates in higher education, exposing young women to an increased risk of unwanted/unintended pregnancies. Pregnancy before marriage is also considered an abomination in many African traditional cultures. As a result, many single females who become pregnant unintentionally seek abortion care for fear of social stigma. Since abortion is illegal in Nigeria, it is generally dangerous and is often performed by traditional herbalists, which raises the risk of maternal deaths. Despite engaging in high-risk sexual behaviors, students in Nigeria did not have access to sexual and reproductive health services or HIV/AIDS-related programs, according to two major surveys conducted among university students. The findings also revealed that a quarter of university students (25%) had unmet contraceptive needs, despite having a high degree of contraceptive knowledge. Knowledge, attitudes, and expectations about sexual and reproductive health could influence contraceptive use, implying that interventions may result in fewer unintended pregnancies. The university community is a miniature world in which various demographic groups interact with an emphasis on information development and dissemination: males, females, teenagers and young adults, adults, elders, teachers, lecturers, administrative staff, and many others. The social structure of most university environments not only brings both sexes together at the point of study, but it also significantly increases interaction between them beyond what is allowed in the pre-university setting. Unrestricted social interaction, such as that found in many public universities, continues to encourage young people to engage in heterosexual behaviors beyond the platonic stage. Pre-marital heterosexual connections among a large proportion of unmarried youth in Nigerian higher institutions, according to studies that examine sexual values among teenagers and the rate of use of contraceptives in preventing pregnancy(Ortese, 2019; Aziken, Okonta and Ande, 2013), Ethiopia (Kibret, 2013) in Nigeria (Chappell, Rule, Dlamini and Nkala, 2014; Hogue and Ghuman, 2011) are high and rising
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Six Symptoms You Shouldn't Be Embarrassed Of When You Visit a Doctor

How to deal with being embarrassed at the doctor
A lot of people delay seeking medical attention because of supposedly uncomfortable symptoms. A timely diagnosis can save lives and delay the need for future invasive or complicated procedures.
Even if your symptom doesn't seem significant, you should still have it examined, especially if it's affecting your quality of life. You have a right to happiness and health.
It can be challenging to communicate effectively when you're embarrassed. Note down your problems and any queries you have prior to your appointment. You may find it easier to recall everything with this. If you find it difficult to speak what you've written, you can even show your doctor many business listings.
Keep in mind that your doctor is not a mind reading. Tell them if you're feeling awkward. They will find it simpler to offer you the encouragement and tolerance you require as a result. It's a good idea to be prepared with statements like "This is uncomfortable for me to say" and "I've never told anyone this before."
Your doctor may be able to support you more effectively the more details you can provide.
Problems you shouldn't be ashamed to consult your doctor about
Understand the warning signs and symptoms that indicate when to consult a doctor:
1. You have a bleeding bottom
Don't freak out if you find blood on your stool or on the toilet paper after wiping your bottom. It might be a sign of piles, a tear (after constipation), or a less serious adverse effect of medication in such instances. You should have it checked if bleeding continues for longer than three weeks business listings.
Investigate any blood in your stool that is black or redder than usual. There could be stomach or intestinal bleeding. Another sign of colon cancer may be rectal bleeding. Your doctor should always be consulted rather than being left in the dark, and they are skilled in checking bottoms.
2. You have an ectopic discharge
Although vaginal discharge is a typical sign, if it isn't clear or smell-free, you may be infected. Bleeding after or between periods may indicate a tear or an infection. However, polyps, fibroids, cancer, and cervical abnormalities might also be to blame. Postmenopausal bleeding is typically not dangerous, but it should be treated properly because it may be a sign of malignancy. Schedule a consultation with your doctor; they'll be in the best position to advise you and allay your concerns free business listings.
Men may experience discharge from the penis because of itchiness or inadequate hygiene. Inflammation of the urethra or a sexually transmitted infection are further possibilities. You can feel sore and uncomfortable when the discharge is happening, or you might need to urinate a lot. For guidance and treatment, consult your doctor.
3. Your testicles feel lumpy
Everyone's testicles are varied in size and shape, so the trick is to watch for deviations from the standard. The majority of alterations are minor; nonetheless, testicular swelling may be malignant. Testicular carcinoma is the most prevalent type of cancer among men under 50. The good news is that 95% of men with testicular cancer are cured after early detection and treatment. The important thing is not to put off going to the doctor since the sooner you go, the faster it can be resolved.
4. You become aware of your memory loss
An adverse drug reaction, dehydration, stress, melancholy, menopause, or a sleep disorder are just a few of the conditions that might affect memory. Additionally, memory loss or brain fog may result from prolonged caffeine consumption.
As we get older, it's normal to lose track of names and other details. However, you shouldn't disregard memory problems or confusion. Make an appointment with your GP if you are concerned about your (or a loved one's) memory. They could suggest that you do some additional testing because a diagnosis could lead to a remedy that will lessen your symptoms. Learn more about dementia if you're worried.
5. You have enigmatic bruises
Occasionally, finding an unexpected bruise can be a sign that you fell over unintentionally. Additionally, as we age and our skin thins, we bruise more easily. If a bruise doesn't go away or if you experience unexplained bruises regularly, it is advisable to see a doctor. These could also be a sign of an underlying illness. Schedule a consultation, particularly if you notice any additional changes in your health.
6. You feel tense or depressed
You are not alone in your struggles and having mental health issues is nothing to be embarrassed of. Any year will have an impact on one in four of us. You should get help if anxiety or depression are interfering with your daily life or making routine tasks challenging. It's crucial to address the problem because persistent anxiety might result in additional health issues. Your doctor of general practice can provide you advice on local resources for support and medical care.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Urethral Stricture Treatment Devices Market: An Overview
Theurethral stricture treatment devices market is a crucial segment within the broader urological devices industry. Urethral stricture, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the urethra due to inflammation, infection, or injury, can lead to significant morbidity. This condition affects both men and women, although it is more prevalent in men. The treatment for urethral stricture often involves the use of specialized medical devices designed to dilate, incise, or reconstruct the urethral passage.

Market Dynamics
1. Increasing Prevalence of Urethral Strictures: The rising incidence of urethral strictures, driven by factors such as aging populations, increasing cases of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and trauma, is a significant driver of market growth.
2. Advancements in Medical Technology: Innovations in urological devices, including minimally invasive techniques and the development of biocompatible materials, have improved treatment outcomes, thereby boosting market demand.
3. Awareness and Diagnosis: Enhanced awareness and improved diagnostic techniques for urethral stricture are leading to earlier detection and treatment, which in turn fuels the market for treatment devices.
For a comprehensive analysis of the market drivers, visit https://univdatos.com/report/urethral-stricture-treatment-devices-market/
Challenges
1. High Cost of Treatment: The cost of advanced urethral stricture treatment devices can be prohibitive, limiting their accessibility, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
2. Complications and Recurrence: Post-treatment complications and the high recurrence rate of urethral strictures pose significant challenges to the market.
Opportunities
1. Emerging Markets: There is substantial growth potential in emerging economies where the prevalence of urological conditions is rising, and healthcare infrastructure is improving.
2. Telemedicine and Remote Diagnosis: The integration of telemedicine in urological care can enhance patient management and follow-up, potentially reducing recurrence rates and improving outcomes.
Key Segments
1. Urethral Dilators: These devices are commonly used to widen the narrowed segment of the urethra. They are often the first line of treatment.
2. Endoscopic Devices: These include cystoscopes and resectoscopes used for visualizing and treating the stricture through minimally invasive procedures.
3. Stents and Implants: Used in more severe cases, these devices help maintain urethral patency over the long term.
End Users
1. Hospitals: Major healthcare facilities where complex urethral stricture treatments are performed.
2. Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs): These centers provide a setting for less complex procedures, contributing to market growth due to their convenience and lower cost structure.
3. Specialty Clinics: Urology clinics specializing in the treatment of urethral strictures play a significant role in the market.
Regional Analysis
1. North America: Dominates the market due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness, and the presence of major market players.
2. Europe: Follows closely with significant investments in healthcare and a high prevalence of urological conditions.
3. Asia-Pacific: Expected to witness the fastest growth owing to increasing healthcare expenditure, improving healthcare infrastructure, and rising awareness about urological health.
4. Latin America and Middle East & Africa: These regions are gradually emerging as potential markets due to improving healthcare facilities and increasing focus on urological health.
For a sample report, visit https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=22347
Competitive Landscape
The urethral stricture treatment devices market is highly competitive with numerous players striving to enhance their market share. Key players are focusing on product innovation, strategic collaborations, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their position. Notable companies include:
Conclusion
The urethral stricture treatment devices market is poised for significant growth in the coming years. The increasing prevalence of urethral strictures, coupled with advancements in medical technology and improved healthcare infrastructure, is driving the market. However, addressing challenges such as high treatment costs and post-treatment complications will be crucial for sustained growth. As the market evolves, emerging regions and technological advancements will present new opportunities for stakeholders in this dynamic field.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos Market Insights
Email - [email protected]
Contact Number - +1 9782263411x
Website -www.univdatos.com
#Urethral Stricture Treatment Devices Market#Urethral Stricture Treatment Devices Market Report#Urethral Stricture Treatment Devices Market Forecast#Urethral Stricture Treatment Devices Market Trends
0 notes
Text
Best Circumsicion Surgery in Basavanagudi Bangalore — Himas Hospital
Circumcision surgery is a common procedure with significant health, cultural, and religious implications. In Basavanagudi, Bangalore, Himas Hospital is renowned for offering top-notch circumcision services. This article explores why Himas Hospital stands out as the best choice for circumcision surgery in this vibrant area.
Understanding Circumcision Surgery
What is Circumcision?
Circumcision is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the foreskin from the male genitalia. It is often performed for various medical, cultural, and religious reasons.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Circumcision has been practiced for thousands of years and holds deep cultural and religious significance in many communities worldwide. It is a rite of passage in some cultures and a religious mandate in others.
Medical Reasons for Circumcision
Medically, circumcision can be performed to address conditions such as phimosis (tight foreskin), recurrent infections, or to reduce the risk of certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Why Choose Himas Hospital for Circumcision?
Advanced Surgical Techniques
Himas Hospital employs the latest surgical techniques to ensure the procedure is as safe and effective as possible. This includes the use of minimally invasive methods and advanced pain management protocols.
Experienced and Qualified Surgeons
The hospital boasts a team of highly skilled and experienced surgeons who specialize in circumcision procedures. Their expertise ensures high success rates and patient satisfaction.
Comprehensive Pre- and Post-Operative Care
Himas Hospital provides comprehensive care before and after the surgery, ensuring patients and their families are well-informed and comfortable throughout the process.
Types of Circumcision Procedures at Himas Hospital
Infant Circumcision
Infant circumcision is commonly performed within the first few days to weeks of life. It is a quick procedure with minimal recovery time for the baby.
Adult Circumcision
Adult circumcision is more complex and typically involves a longer recovery period. It is performed for medical reasons or personal preference.
Laser Circumcision
Laser circumcision is a modern technique that uses laser technology to remove the foreskin. It offers benefits such as reduced bleeding, less pain, and quicker recovery times.
Benefits of Circumcision
Health and Hygiene Advantages
Circumcision can lead to improved genital hygiene and a reduced risk of infections. It can also lower the chances of developing certain diseases later in life.
Reduced Risk of Infections
Studies have shown that circumcision can reduce the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs), penile infections, and certain STIs.
Potential Long-Term Health Benefits
Long-term health benefits of circumcision may include a reduced risk of penile cancer and a lower prevalence of cervical cancer in female partners.
Innovations in Circumcision Surgery at Himas Hospital
Latest Technological Advancements
Himas Hospital continuously invests in the latest surgical technologies, ensuring that patients benefit from the most advanced procedures available.
Research and Development
The hospital is actively involved in research and development, contributing to advancements in circumcision techniques and improving patient care.
Future Directions in Circumcision Procedures
Ongoing research and innovation at Himas Hospital are paving the way for even more effective and less invasive circumcision procedures in the future.
Conclusion
Circumcision is a significant procedure with numerous health benefits. Himas Hospital in Basavanagudi, Bangalore, offers exceptional circumcision services, combining advanced surgical techniques with compassionate care. Whether you are considering circumcision for your child or yourself, Himas Hospital ensures a safe, comfortable, and positive experience.
0 notes
Text
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market Trends, Challenges, Key Suppliers Analysis and Growth By 2024 - 2031

The "Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market" is a dynamic and rapidly evolving sector, with significant advancements and growth anticipated by 2031. Comprehensive market research reveals a detailed analysis of market size, share, and trends, providing valuable insights into its expansion. This report delves into segmentation and definition, offering a clear understanding of market components and drivers. Employing SWOT and PESTEL analyses, the study evaluates the market's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, alongside political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors. Expert opinions and recent developments highlight the geographical distribution and forecast the market's trajectory, ensuring a robust foundation for strategic planning and investment.
What is the projected market size & growth rate of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market?
Market Analysis and Insights:
Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market
The sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market is expected to gain growth at a potential rate of 7.10% in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028. The rise in awareness among people regarding the disease is the factors for the market growth.
The infection which is transmitted through sexual contact, caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites are known as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).Chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and syphilis are the four most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
The rapid technological advancements have improved the diagnosis facilities and treatments which are expected to accelerate the market growth in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028. Likewise, the rise in the prevalence of unprotected sex and rise in prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases are also predictable to enhance the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market growth. Furthermore, the rapid change in the lifestyle and having several casual sex partners is resulting to increase prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases is also projected to drive the market growth rate. Also, the rise in the incidence of numerous sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, chancroid, herpes simplex virus, human papilloma virus, vaginitis and trichomonas vaginalis are also expected to influence the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market growth globally.
In addition, the rise in government initiatives, improvements in healthcare facilities and increase in awareness regarding infectious diseases are likely to create various new opportunities that will impact this sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market growth in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028.
However, the lack of awareness and low rate of detection for diseases are also expected to act as major restraints towards the growth of the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market, and will further challenge the growth of the target market in the above mentioned forecast period.
This sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market report provides details of market share, new developments, and product pipeline analysis, impact of domestic and localized market players, analyses opportunities in terms of emerging revenue pockets, changes in market regulations, product approvals, strategic decisions, product launches, geographic expansions, and technological innovations in the market. To understand the analysis on the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market scenario contact Data Bridge Market Research for an Analyst Brief, our team will help you create a revenue impact solution to achieve your desired goal.
Browse Detailed TOC, Tables and Figures with Charts which is spread across 350 Pages that provides exclusive data, information, vital statistics, trends, and competitive landscape details in this niche sector.
This research report is the result of an extensive primary and secondary research effort into the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market. It provides a thorough overview of the market's current and future objectives, along with a competitive analysis of the industry, broken down by application, type and regional trends. It also provides a dashboard overview of the past and present performance of leading companies. A variety of methodologies and analyses are used in the research to ensure accurate and comprehensive information about the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market.
Get a Sample PDF of Report - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-sexually-transmitted-diseases-stds-antimicrobial-medication-market
Which are the driving factors of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
The driving factors of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market include technological advancements that enhance product efficiency and user experience, increasing consumer demand driven by changing lifestyle preferences, and favorable government regulations and policies that support market growth. Additionally, rising investment in research and development and the expanding application scope of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication across various industries further propel market expansion.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market - Competitive and Segmentation Analysis:
Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market, By Drug Type (Antiviral / Antiretrovirals, Antibiotics, Vaccines), Disease Type (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Genital herpes, HPV, HIV / AIDS), End User (Hospital, Clinics, Others), Country (U.S., Canada, Mexico, Peru, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Hungary, Lithuania, Austria, Ireland, Norway, Poland, Rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Rest of Asia Pacific, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, Kuwait, Israel, Egypt, Rest of Middle East and Africa) Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
How do you determine the list of the key players included in the report?
With the aim of clearly revealing the competitive situation of the industry, we concretely analyze not only the leading enterprises that have a voice on a global scale, but also the regional small and medium-sized companies that play key roles and have plenty of potential growth.
Which are the top companies operating in the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
The major players covered in the sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication market report are GlaxoSmithKline plc, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Sanofi, Cipla Inc., Pfizer, Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Novartis AG, Mylan N.V., AbbVie Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Services Inc., Bayer AG, Eli Lilly and Company, Lupin, AstraZeneca, and Gilead Sciences, Inc., among other domestic and global players. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) antimicrobial medication
Short Description About Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market:
The Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market is anticipated to rise at a considerable rate during the forecast period, between 2024 and 2031. In 2023, the market is growing at a steady rate and with the rising adoption of strategies by key players, the market is expected to rise over the projected horizon.
North America, especially The United States, will still play an important role which can not be ignored. Any changes from United States might affect the development trend of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication. The market in North America is expected to grow considerably during the forecast period. The high adoption of advanced technology and the presence of large players in this region are likely to create ample growth opportunities for the market.
Europe also play important roles in global market, with a magnificent growth in CAGR During the Forecast period 2024-2031.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market size is projected to reach Multimillion USD by 2031, In comparison to 2024, at unexpected CAGR during 2024-2031.
Despite the presence of intense competition, due to the global recovery trend is clear, investors are still optimistic about this area, and it will still be more new investments entering the field in the future.
This report focuses on the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication in global market, especially in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa. This report categorizes the market based on manufacturers, regions, type and application.
Get a Sample Copy of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Report 2024
What are your main data sources?
Both Primary and Secondary data sources are being used while compiling the report. Primary sources include extensive interviews of key opinion leaders and industry experts (such as experienced front-line staff, directors, CEOs, and marketing executives), downstream distributors, as well as end-users. Secondary sources include the research of the annual and financial reports of the top companies, public files, new journals, etc. We also cooperate with some third-party databases.
Geographically, the detailed analysis of consumption, revenue, market share and growth rate, historical data and forecast (2024-2031) of the following regions are covered in Chapters
What are the key regions in the global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
North America (United States, Canada and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia and Turkey etc.)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Vietnam)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, Columbia etc.)
Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria and South Africa)
This Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market Research/Analysis Report Contains Answers to your following Questions
What are the global trends in the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
Would the market witness an increase or decline in the demand in the coming years?
What is the estimated demand for different types of products in Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication?
What are the upcoming industry applications and trends for Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
What Are Projections of Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Industry Considering Capacity, Production and Production Value? What Will Be the Estimation of Cost and Profit? What Will Be Market Share, Supply and Consumption? What about Import and Export?
Where will the strategic developments take the industry in the mid to long-term?
What are the factors contributing to the final price of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication?
What are the raw materials used for Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication manufacturing?
How big is the opportunity for the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market?
How will the increasing adoption of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication for mining impact the growth rate of the overall market?
How much is the global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market worth? What was the value of the market In 2020?
Who are the major players operating in the Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication market? Which companies are the front runners?
Which are the recent industry trends that can be implemented to generate additional revenue streams?
What Should Be Entry Strategies, Countermeasures to Economic Impact, and Marketing Channels for Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Industry?
Customization of the Report
Can I modify the scope of the report and customize it to suit my requirements? Yes. Customized requirements of multi-dimensional, deep-level and high-quality can help our customers precisely grasp market opportunities, effortlessly confront market challenges, properly formulate market strategies and act promptly, thus to win them sufficient time and space for market competition.
Inquire more and share questions if any before the purchase on this report at - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/inquire-before-buying/?dbmr=global-sexually-transmitted-diseases-stds-antimicrobial-medication-market
Detailed TOC of Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market Insights and Forecast to 2031
Introduction
Market Segmentation
Executive Summary
Premium Insights
Market Overview
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market By Type
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market By Function
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market By Material
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market By End User
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market By Region
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market: Company Landscape
SWOT Analysis
Company Profiles
Continued...
Purchase this report – https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/checkout/buy/singleuser/global-sexually-transmitted-diseases-stds-antimicrobial-medication-market
Data Bridge Market Research:
Today's trends are a great way to predict future events!
Data Bridge Market Research is a market research and consulting company that stands out for its innovative and distinctive approach, as well as its unmatched resilience and integrated methods. We are dedicated to identifying the best market opportunities, and providing insightful information that will help your business thrive in the marketplace. Data Bridge offers tailored solutions to complex business challenges. This facilitates a smooth decision-making process. Data Bridge was founded in Pune in 2015. It is the product of deep wisdom and experience.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC: +653 1251 975
Email:- [email protected]
Browse More Reports:
Global Emollient Esters Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2030
Global Fusion Protein Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
Global Bluetooth in Automotive Market - Industry Trends and Forecast to 2029
Global Veterinary Calcium Supplement Market - Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
Global Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) Antimicrobial Medication Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2028
0 notes
Text
Unveiling Common Gynaecological Conditions: Causes and Remedies
Understanding gynaecological conditions is crucial for maintaining women’s health and wellness. These conditions, though common, can significantly impact reproductive health and quality of life. This blog explores prevalent gynaecological issues, their causes, and effective remedies, while also highlighting the comprehensive women health care services provided by the BR Healthcare department gynaecology.
Common Gynaecological Conditions
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Causes: PCOS is a hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. It is marked by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, and weight gain. The exact cause is unknown, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to be involved.
Remedies: Managing PCOS often includes lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise. Medications like hormonal contraceptives can regulate menstrual cycles, and anti-androgens can help reduce hair growth.
Endometriosis
Causes: Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterine cavity, causing pain and potentially leading to fertility issues. The exact cause is not fully understood, but it may involve hormonal and immune system factors.
Remedies: Treatment options for endometriosis include pain relief medications, hormone therapy to suppress menstrual cycles, and surgical procedures to remove endometrial tissue.
Uterine Fibroids
Causes: Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in the uterus that can cause heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and reproductive issues. The exact cause is unclear, but factors such as genetics and hormones are believed to play a role.
Remedies: Treatments range from medications to manage symptoms to surgical options like myomectomy or hysterectomy, depending on the size and location of the fibroids and the patient’s fertility goals.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Causes: PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted bacteria. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as infertility.
Remedies: The primary treatment for PID is antibiotics to eliminate the infection. In more severe cases, hospitalization or surgery may be necessary.
Importance of Regular Gynaecological Care
Regular gynaecological care is essential for early detection and treatment of these conditions. The BR Healthcare department gynaecology offers extensive women health care services, focusing on preventive care, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment of various gynaecological issues. By maintaining regular check-ups, women can ensure their reproductive health and overall women wellness.
Promoting Reproductive Health and Women Wellness
Maintaining reproductive health is vital for overall women wellness. Regular screenings such as Pap smears and mammograms are crucial for early detection of potential issues. The BR Healthcare department gynaecology provides a wide range of women health care services, ensuring personalized and compassionate care for each patient.
Why Choose BR Healthcare?
BR Healthcare is committed to providing exceptional gynaecological care. Our experienced team of healthcare professionals utilizes the latest technology and techniques to diagnose and treat a wide range of gynaecological conditions. Conveniently located at Plot №13, Bawana Rd, Shabad Extension, Sector 17, Rohini, Delhi — 110089, BR Healthcare is easily accessible for all your gynaecological needs. For appointments or more information, please call us at +91–9205666381 or visit our website at BR Healthcare.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing common gynaecological conditions can significantly improve women’s health and quality of life. Regular visits to the BR Healthcare department gynaecology for check-ups and screenings are crucial for maintaining optimal reproductive health and overall women wellness. Our comprehensive women health care services are designed to address a wide range of gynaecological issues with personalized and empathetic care.
Taking proactive steps in managing your reproductive health can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life. Trust BR Healthcare to be your partner in achieving and maintaining excellent gynaecological health.
For parents seeking expert guidance and unwavering support in navigating pediatric orthopedic concerns, BR HEALTHCARE emerges as a trusted ally. Reach out to us today at +91–9205666381 or visit our website at BR Healthcare.
0 notes