#red hat linux 8
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Now, both versions of RHEL8 are EOL.
Red Hat Linux 8 (2002)
172 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Własny serwer Red Hat cz.8 - Statystyki serwera
W tym tutaorialu zainstalujemy Webalizer w dystrybucji Rocky Linux, bazującej na Red Hat i kompatybilnej z jego klonami, takimi jak CloudLinux, AlmaLinux, EuroLinux, CentOS Stream, MIRACLE Linux, etc. https://linuxiarze.pl/wlasny-serwer-red-hat-cz-8-statystyki-serwera/

0 notes
Text
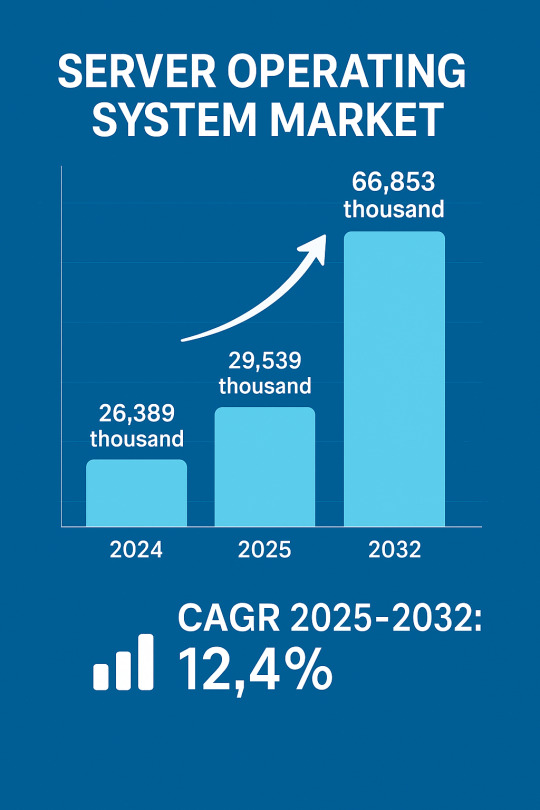
🖥️ Server Operating System Market to Reach 66.8 Million Units by 2032. Here’s What’s Driving the Growth.
Fresh market insights show the Server Operating System Market is quietly but steadily expanding — and it’s set for more than 2.5x growth over the next 8 years. Let’s unpack the numbers:
📊 Server OS Market Forecast (2025–2032)
💾 2024 Market Size: 26,389 thousand units 🔮 2025 Projection: 29,539 thousand units 🚀 2032 Forecast: 66,853 thousand units 📈 CAGR (2025–2032): 12.4%
That’s consistent, healthy growth — powered by demand for enterprise scalability, cloud-native environments, and edge computing.
🌎 North America & Asia-Pacific Are in the Lead
North America continues to dominate in terms of deployment scale, but markets in Asia-Pacific are surging as enterprises adopt hybrid cloud infrastructure and government digitalization programs ramp up.
🔑 Key Drivers Behind the Growth:
☁️ 1. Cloud Computing & Hybrid Infrastructure As businesses shift workloads to cloud-native platforms, the need for robust, scalable server OS platforms is soaring, especially those optimized for containers and virtualization.
🔐 2. Cybersecurity & Compliance Pressures Security is no longer optional. Enterprise-grade server OS systems are evolving to offer built-in security, auditing, and compliance features, driving upgrades.
🏢 3. Data Center Expansion From hyperscalers to on-prem setups, the demand for reliable, high-performance server operating systems continues to rise alongside global data center investments.
🔄 4. Open Source is Gaining Ground Linux-based systems are seeing increased enterprise adoption, with Red Hat, Ubuntu Server, and other open-source platforms reshaping the ecosystem.
📶 5. Edge Computing & 5G Rollouts As edge deployments multiply — from retail to manufacturing — lightweight and adaptable server OS platforms are becoming essential for decentralized computing environments.
🧠 What Does This Mean for Builders and Investors?
We're in the era of infrastructure standardization. Think beyond just the OS — it's about integration, modularity, and security.
If you're building: Prioritize support for hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Automation, orchestration, and AI-powered system monitoring are huge value adds. If you're investing: Server OS may not be flashy, but it’s mission-critical. Look into plays around enterprise Linux, cloud-native stacks, and edge OS platforms with strong enterprise uptake.
0 notes
Text
Modern Tools Enhance Data Governance and PII Management Compliance

Modern data governance focuses on effectively managing Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Tools like IBM Cloud Pak for Data (CP4D), Red Hat OpenShift, and Kubernetes provide organizations with comprehensive solutions to navigate complex regulatory requirements, including GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act). These platforms offer secure data handling, lineage tracking, and governance automation, helping businesses stay compliant while deriving value from their data.
PII management involves identifying, protecting, and ensuring the lawful use of sensitive data. Key requirements such as transparency, consent, and safeguards are essential to mitigate risks like breaches or misuse. IBM Cloud Pak for Data integrates governance, lineage tracking, and AI-driven insights into a unified framework, simplifying metadata management and ensuring compliance. It also enables self-service access to data catalogs, making it easier for authorized users to access and manage sensitive data securely.
Advanced IBM Cloud Pak for Data features include automated policy reinforcement and role-based access that ensure that PII remains protected while supporting analytics and machine learning applications. This approach simplifies compliance, minimizing the manual workload typically associated with regulatory adherence.
The growing adoption of multi-cloud environments has necessitated the development of platforms such as Informatica and Collibra to offer complementary governance tools that enhance PII protection. These solutions use AI-supported insights, automated data lineage, and centralized policy management to help organizations seeking to improve their data governance frameworks.
Mr. Valihora has extensive experience with IBM InfoSphere Information Server “MicroServices” products (which are built upon Red Hat Enterprise Linux Technology – in conjunction with Docker\Kubernetes.) Tim Valihora - President of TVMG Consulting Inc. - has extensive experience with respect to:
IBM InfoSphere Information Server “Traditional” (IIS v11.7.x)
IBM Cloud PAK for Data (CP4D)
IBM “DataStage Anywhere”
Mr. Valihora is a US based (Vero Beach, FL) Data Governance specialist within the IBM InfoSphere Information Server (IIS) software suite and is also Cloud Certified on Collibra Data Governance Center.
Career Highlights Include: Technical Architecture, IIS installations, post-install-configuration, SDLC mentoring, ETL programming, performance-tuning, client-side training (including administrators, developers or business analysis) on all of the over 15 out-of-the-box IBM IIS products Over 180 Successful IBM IIS installs - Including the GRID Tool-Kit for DataStage (GTK), MPP, SMP, Multiple-Engines, Clustered Xmeta, Clustered WAS, Active-Passive Mirroring and Oracle Real Application Clustered “IADB” or “Xmeta” configurations. Tim Valihora has been credited with performance tuning the words fastest DataStage job which clocked in at 1.27 Billion rows of inserts\updates every 12 minutes (using the Dynamic Grid ToolKit (GTK) for DataStage (DS) with a configuration file that utilized 8 compute-nodes - each with 12 CPU cores and 64 GB of RAM.)
0 notes
Text
Red Hat Summit 2025: Microsoft Drives into Cloud Innovation

Microsoft at Red Hat Summit 2025
Microsoft is thrilled to announce that it will be a platinum sponsor of Red Hat Summit 2025, an IT community favourite. IT professionals can learn, collaborate, and build new technologies from the datacenter, public cloud, edge, and beyond at Red Hat Summit 2025, a major enterprise open source event. Microsoft's partnership with Red Hat is likely to be a highlight this year, displaying collaboration's power and inventive solutions.
This partnership has changed how organisations operate and serve customers throughout time. Red Hat's open-source leadership and Microsoft's cloud knowledge synergise to advance technology and help companies.
Red Hat's seamless integration with Microsoft Azure is a major benefit of the alliance. These connections let customers build, launch, and manage apps on a stable and flexible platform. Azure and Red Hat offer several tools for system modernisation and cloud-native app development. Red Hat OpenShift on Azure's scalability and security lets companies deploy containerised apps. Azure Red Hat Enterprise Linux is trustworthy for mission-critical apps.
Attend Red Hat Summit 2025 to learn about these technologies. Red Hat and Azure will benefit from Microsoft and Red Hat's new capabilities and integrations. These improvements in security and performance aim to meet organisations' digital needs.
WSL RHEL
This lets Red Hat Enterprise Linux use Microsoft Subsystem for Linux. WSL lets creators run Linux on Windows. RHEL for WSL lets developers run RHEL on Windows without a VM. With a free Red Hat Developer membership, developers may install the latest RHEL WSL image on their Windows PC and run Windows and RHEL concurrently.
Red Hat OpenShift Azure
Red Hat and Microsoft are enhancing security with Confidential Containers on Azure Red Hat OpenShift, available in public preview. Memory encryption and secure execution environments provide hardware-level workload security for healthcare and financial compliance. Enterprises may move from static service principals to dynamic, token-based credentials with Azure Red Hat OpenShift's managed identity in public preview.
Reduced operational complexity and security concerns enable container platform implementation in regulated environments. Azure Red Hat OpenShift has reached Spain's Central region and plans to expand to Microsoft Azure Government (MAG) and UAE Central by Q2 2025. Ddsv5 instance performance optimisation, enterprise-grade cluster-wide proxy, and OpenShift 4.16 compatibility are added. Red Hat OpenShift Virtualisation on Azure is also entering public preview, allowing customers to unify container and virtual machine administration on a single platform and speed up VM migration to Azure without restructuring.
RHEL landing area
Deploying, scaling, and administering RHEL instances on Azure uses Azure-specific system images. A landing zone lesson. Red Hat Satellite and Satellite Capsule automate software lifecycle and provide timely updates. Azure's on-demand capacity reservations ensure reliable availability in Azure regions, improving BCDR. Optimised identity management infrastructure deployments decrease replication failures and reduce latencies.
Azure Migrate application awareness and wave planning
By delivering technical and commercial insights for the whole application and categorising dependent resources into waves, the new application-aware methodology lets you pick Azure targets and tooling. A collection of dependent applications should be transferred to Azure for optimum cost and performance.
JBossEAP on AppService
Red Hat and Microsoft developed and maintain JBoss EAP on App Service, a managed tool for running business Java applications efficiently. Microsoft Azure recently made substantial changes to make JBoss EAP on App Service more inexpensive. JBoss EAP 8 offers a free tier, memory-optimized SKUs, and 60%+ license price reductions for Make monthly payments subscriptions and the soon-to-be-released Bring-Your-Own-Subscription to App Service.
JBoss EAP on Azure VMs
JBoss EAP on Azure Virtual Machines is currently GA with dependable solutions. Microsoft and Red Hat develop and maintain solutions. Automation templates for most basic resource provisioning tasks are available through the Azure Portal. The solutions include Azure Marketplace JBoss EAP VM images.
Red Hat Summit 2025 expectations
Red Hat Summit 2025 should be enjoyable with seminars, workshops, and presentations. Microsoft will offer professional opinions on many subjects. Unique announcements and product debuts may shape technology.
This is a rare chance to network with executives and discuss future projects. Mission: digital business success through innovation. Azure delivers the greatest technology and service to its customers.
Read about Red Hat on Azure
Explore Red Hat and Microsoft's cutting-edge solutions. Register today to attend the conference and chat to their specialists about how their cooperation may aid your organisation.
#RedHatSummit2025#RedHatSummit#AzureRedHatOpenShift#RedHat#RedHatEnterprise#RedHatEnterpriseLinux#technology#technologynews#TechNews#news#govindhtech
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Install Ansible: A Complete Guide
Ansible is a powerful open-source automation tool that simplifies configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. It is widely used in Red Hat environments and is a key skill covered in Red Hat training programs. This guide will walk you through installing Ansible on a Red Hat-based system. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional at HawkStack Technologies, this tutorial will help you set up Ansible seamlessly.
Prerequisites
Before installing Ansible, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
A Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) system (version 8 or later recommended)
Root or sudo access
Internet connectivity to download packages
Step-by-Step Installation of Ansible on RHEL
Step 1: Update Your System
Before installing any new packages, it's best practice to update your system’s repositories and installed packages. Run the following command:sudo dnf update -y
Step 2: Enable the EPEL Repository
The Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repository provides additional software packages, including Ansible. Enable it using:sudo dnf install epel-release -y
Step 3: Install Ansible
Once the EPEL repository is enabled, you can install Ansible with:sudo dnf install ansible -y
Step 4: Verify the Installation
To ensure that Ansible has been installed correctly, check its version:ansible --version
You should see output similar to:
ansible [core 2.x.x]
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
python version = 3.x.x
...
Configuring Ansible
After installation, configure Ansible to manage remote servers. Edit the inventory file located at /etc/ansible/hosts and add your managed nodes:sudo nano /etc/ansible/hosts
Add your servers under a group name, such as:[webservers] 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.11
Save the file and test connectivity using:
ansible all -m ping
If everything is set up correctly, you will see successful ping responses from the managed nodes.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed and configured Ansible on Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Ansible is an essential tool for IT automation, making system management efficient and scalable. If you’re looking to deepen your knowledge of Ansible and automation, consider enrolling in Red Hat training programs. At HawkStack Technologies, we specialize in DevOps solutions and can assist with your Ansible deployments.#Ansible #DevOps #Automation #OpenSource #AnsiblePlaybooks
For more information www.hawkstack.com
For more insights on automation and infrastructure management, stay tuned to our blog!
0 notes
Text
Red Hat’s Vision for an Open Source AI Future
Red Hat’s Vision for an Open Source AI Future -The world of artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving at a lightning pace. As with any transformative technology, one question stands out: what’s the best way to shape its future? At Red Hat, we believe the answer is clear—the future of AI is open source
This isn’t just a philosophical stance; it’s a commitment to unlocking AI’s full potential by making it accessible, collaborative, and community-driven. Open source has consistently driven innovation in the technology world, from Linux and Kubernetes to OpenStack. These projects demonstrate how collaboration and transparency fuel discovery, experimentation, and democratized access to groundbreaking tools. AI, too, can benefit from this model.
Why Open Source Matters in AI
In a field where trust, security, and explainability are critical, AI must be open and inclusive. Red Hat is championing open source AI innovation to ensure its development remains a shared effort—accessible to everyone, not just organizations with deep pockets.
Through strategic investments, collaborations, and community-driven solutions, Red Hat is laying the groundwork for a future where AI workloads can run wherever they’re needed. Our recent agreement to acquire Neural Magic marks a significant step toward achieving this vision – Amrita Technologies.
Building the Future of AI on Three Pillars
1.Building the Future of AI on Three Pillars
AI isn’t just about massive, resource-hungry models. The focus is shifting toward smaller, specialized models that deliver high performance with greater efficiency.
For example, IBM Granite 3.0, an open-source family of models licensed under Apache 2.0, demonstrates how smaller models (1–8 billion parameters) can run efficiently on a variety of hardware, from laptops to GPUs. Such accessibility fosters innovation and adoption, much like Linux did for enterprise computing.
Optimization techniques like sparsification and quantization further enhance these models by reducing size and computational demands while maintaining accuracy. These approaches make it possible to run AI workloads on diverse hardware, reducing costs and enabling faster inference. Neural Magic’s expertise in optimizing AI for GPU and CPU hardware will further strengthen our ability to bring this efficiency to AI.
2. Training Unlocks Business Advantage
While pre-trained models are powerful, they often lack understanding of a business’s specific processes or proprietary data. Customizing models to integrate unique business knowledge is essential to unlocking their true value.
To make this easier, Red Hat and IBM launched Instruct Lab, an open source project designed to simplify fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs). Instruct Lab lowers barriers to entry, allowing businesses to train models without requiring deep data science expertise. This initiative enables organizations to adapt AI for their unique needs while controlling costs and complexity
3. Choice Unlocks Innovation
AI must work seamlessly across diverse environments, whether in corporate datacenters, the cloud, or at the edge. Flexible deployment options allow organizations to train models where their data resides and run them wherever makes sense for their use cases.
Just as Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) allowed software to run on any CPU without modification, our goal is to ensure AI models trained with RHEL AI can run on any GPU or infrastructure. By combining flexible hardware support, smaller models, and simplified training, Red Hat enables innovation across the AI lifecycle.
With Red Hat OpenShift AI, we bring together model customization, inference, monitoring, and lifecycle management. Neural Magic’s vision of efficient AI on hybrid platforms aligns perfectly with our mission to deliver consistent and scalable solutions – Amrita Technologies.
Welcoming Neural Magic to Red Hat
Neural Magic’s story is rooted in making AI more accessible. Co-founded by MIT researchers Nir Shavit and Alex Matveev, the company specializes in optimization techniques like pruning and quantization. Initially focused on enabling AI to run efficiently on CPUs, Neural Magic has since expanded its expertise to GPUs and generative AI, aligning with Red Hat’s goal of democratizing AI.
The cultural alignment between Neural Magic and Red Hat is striking. Just as Neural Magic strives to make AI more efficient and accessible, Red Hat’s Instruct Lab team works to simplify model training for enterprise adoption. Together, we’re poised to drive breakthroughs in AI innovation.
Open Source: Unlocking AI’s Potential
At Ruddy Cap, we accept that openness opens the world’s potential. By building AI on a establishment of open source standards, we can democratize get to, quicken advancement, and guarantee AI benefits everyone. With Neural Enchantment joining Ruddy Cap, we’re energized to increase our mission of conveying open source AI arrangements that enable businesses and communities to flourish in the AI period. Together, we’re forming a future where AI is open, comprehensive, and transformative – Amrita Technologies.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Simply about Linux Security
Linux is often praised as one of the best operating systems in terms of security due to several key factors that make it inherently secure and resilient against many types of attacks. Here's why:
1. Open-Source Nature
Transparency: Linux is open-source, meaning its source code is publicly available for review. This transparency allows anyone (including security experts) to examine the code for vulnerabilities, report bugs, and contribute fixes. This collaborative approach leads to faster identification and patching of security issues compared to proprietary systems.
Community and Auditing: Since many users and organizations contribute to Linux's development, any vulnerabilities discovered are often addressed quickly.
2. User Privileges and Access Control
Least Privilege Principle: In Linux, by default, users do not have administrative (root) access to the system. Administrative rights are required to make significant system changes, reducing the risk of malware or attackers exploiting a compromised user account to take control of the system.
Sudo Command: Administrative tasks are typically carried out using sudo (superuser do), which provides controlled, time-limited access to root privileges. This limits potential damage by preventing unnecessary exposure of administrative rights.
3. Strong File Permissions and Ownership
Linux enforces strict file permissions for users and groups, ensuring that only authorized users can access, modify, or execute files. This is a fundamental aspect of Linux's security model, making it difficult for unauthorized users or malware to alter important system files.
Each file has an owner, a group, and a set of permissions (read, write, execute), allowing for detailed control over who can do what with each file.
4. Security Modules and Features
SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux): This is a set of kernel-level security enhancements that implement mandatory access control (MAC). It adds an additional layer of security by enforcing strict access policies that restrict how processes interact with the system and each other.
AppArmor: Similar to SELinux, AppArmor is a security module that restricts programs to a set of predefined security profiles, preventing them from performing unauthorized actions.
Chroot and Namespaces: These tools allow isolation of processes, limiting the damage they can do even if compromised.
5. Frequent Security Patches
The Linux community is very active in identifying and fixing vulnerabilities. Most Linux distributions offer regular updates, including security patches, making it quick and easy to keep the system secure.
Security advisories and patches for distributions (like Debian, Ubuntu, or Red Hat) are generally well-documented and quickly available.
6. Minimal Attack Surface
Linux distributions can be customized to include only the necessary components, reducing the attack surface. Users can install a minimal version of Linux with only the essential software, which reduces the number of potential vulnerabilities.
Many server-focused Linux distributions, such as CentOS or Ubuntu Server, come with fewer default applications, reducing the chances of exploitable vulnerabilities.
7. Robust Package Management
Package managers like apt, yum, and dnf ensure that software installed on Linux is vetted and comes from trusted repositories. This reduces the risk of installing malicious or untrusted software.
Additionally, Linux distributions often come with tools to verify the integrity of installed packages and update software automatically.
8. Lower Target for Malware
Popularity in Specific Use Cases: While Linux is widely used for servers, many personal users still prefer other operating systems (like Windows). This makes Linux less of a target for mass-market malware.
Open-Source Security Tools: Many Linux distributions have strong built-in security tools, and the OS itself is often the platform for security professionals and penetration testers, further boosting its reputation as a secure platform.
9. Security by Design
Linux has security mechanisms built into its design, such as:
Stack Protection: Linux uses techniques like stack canaries and non-executable memory to prevent stack-based buffer overflow attacks.
Data Execution Prevention (DEP): This feature prevents code from executing in areas of memory that should contain only data.
Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR): Randomizing memory addresses for processes makes it harder for attackers to predict the location of critical system functions.
10. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Since many security professionals and ethical hackers use Linux, the system is often subjected to rigorous security testing. This helps find vulnerabilities before they are exploited in real-world attacks.
Conclusion
Linux's security is driven by its open-source nature, strong access controls, and a thriving community that quickly identifies and fixes vulnerabilities. Combined with its robust security tools, regular updates, and user-centric design, it offers a highly secure environment, making it a popular choice for critical applications like web servers, networking, and cloud computing. However, like any system, its security ultimately depends on how it's configured and maintained.
for more details please visit
www.qcsdclabs.com,
www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learning Linux
Linux is an open-source operating system that powers everything from smartphones to supercomputers. Unlike proprietary operating systems like Windows and macOS, Linux is freely available to everyone. It’s known for its stability, security, and flexibility, making it an ideal choice for developers, system administrators, and tech enthusiasts.
Why Learn Linux?
1. High Demand for Linux Professionals Learning Linux opens up numerous job opportunities in fields like system administration, software development, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Linux is the backbone of many cloud services, data centers, and tech companies.
2. Open-Source Nature Linux is open-source, meaning it is free to use, and its source code is available to modify. This is a key reason why it’s favored by tech communities worldwide.
3. Flexibility and Control Linux gives users full control over their system. It is highly customizable, allowing you to build an operating system tailored to your needs.
4. Learn Command-Line Skills The command line is a powerful tool in Linux, and mastering it will help you become more proficient in navigating and managing your system efficiently.
What You Will Learn in This Linux Course
Here’s a breakdown of the essential skills and concepts that would be covered in a comprehensive Linux course.
1. Basic Linux Commands You’ll start with basic commands like ls, cd, pwd, and mkdir. These are the building blocks that help you navigate the file system and manage files.
2. File Permissions and Ownership Learn how to manage file permissions and ownership to secure your system and ensure that users and groups have the correct access rights to files.
3. File System Structure Understand the Linux directory structure, including root directories (/, /home, /etc, etc.), and how to efficiently navigate through the filesystem.
4. User Management You’ll learn how to create, delete, and modify user accounts, as well as manage groups and user permissions.
5. Process Management Linux gives you full control over running processes. You’ll learn how to manage processes with commands like ps, top, kill, and how to use nice and renice to control process priorities.
6. Package Management Linux distributions use package managers to install, remove, and update software. Learn how to use package managers like apt (for Debian-based systems) or yum (for Red Hat-based systems).
7. Networking Basics Linux provides a variety of networking tools. You’ll learn how to configure network interfaces, troubleshoot connections, and use tools like ping, netstat, and ifconfig.
8. Shell Scripting One of the most valuable skills in Linux is shell scripting. You'll learn how to write scripts to automate tasks, save time, and enhance productivity.
9. System Logs and Monitoring Linux systems generate logs that are crucial for troubleshooting. Learn how to read and interpret system logs, and use tools like dmesg and journalctl to monitor system performance.
10. Security Practices Linux is known for its security features, and in this course, you’ll learn how to harden your system with firewalls, SELinux, and user authentication mechanisms.
How to Get Started
Step 1: Choose a Linux Distribution There are many flavors of Linux to choose from. For beginners, distributions like Ubuntu, Fedora, or Linux Mint are excellent choices. You can download and install them on a virtual machine (VM) or set up a dual boot alongside your main OS.
Step 2: Install VirtualBox or VMware If you prefer to learn without changing your current system, installing a Linux distribution on a virtual machine is a great option. VirtualBox and VMware are free tools that allow you to run Linux on top of your current OS.
Step 3: Use Linux Regularly The best way to learn Linux is by using it regularly. Install it on your computer or run it from a USB stick to get hands-on experience. The more you use it, the more comfortable you will become.
Step 4: Join Linux Communities There are active Linux communities where you can ask questions, share knowledge, and collaborate. Websites like Stack Overflow, Reddit's rlinux, and Linux forums are great resources.
0 notes
Text

Red Hat Linux 8 (2002)
226 notes
·
View notes
Note
Linux ask game: 1,2,3,7,8,9
-Ahrah
Red Hat! We had no idea what this ting was, ADHD and dissociation whoo. We managed to get it to boot with no clue what it was other than "there's a non-Windows option?" but had no working networking. So we concluded "well this is pretty cool, but without Internet I can't do anything with it" xD
blkdiscard -vf /dev/mmcblk1
Yup, we rm'd our Chromebooks root too xD That's actually recoverable, albeit painfully.. (we may actually still have an untapped disk image that we've just put off dealing with)
7. Hmmmm most likely the Dell Dimension C521
8. uh, Hmmm... :w, :wq, :i, iirc. We stick to nano as much as pawsible x3
9. Favorite non-OS software... damn I can't count my headmate $_ it technically does operate the body hardware at times and this would be an OS x3 suppose I'll go with Syncthing.
(the ask q's:)
https://www.tumblr.com/dragongirlcock/763629772890865664
0 notes
Text
Red Hat Training Categories: Empowering IT Professionals for the Future
Red Hat, a leading provider of enterprise open-source solutions, offers a comprehensive range of training programs designed to equip IT professionals with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the rapidly evolving world of technology. Whether you're an aspiring system administrator, a seasoned DevOps engineer, or a cloud architect, Red Hat's training programs cover key technologies and tools that drive modern IT infrastructures. Let’s explore some of the key Red Hat training categories.
1. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
RHEL is the foundation of many enterprises, and Red Hat offers extensive training to help IT professionals master Linux system administration, automation, and security. Key courses in this category include:
Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA): An essential certification for beginners in Linux administration.
Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE): Advanced training in system administration, emphasizing automation using Ansible.
Security and Identity Management: Focuses on securing Linux environments and managing user identities.
2. Ansible Automation
Automation is at the heart of efficient IT operations, and Ansible is a powerful tool for automating tasks across diverse environments. Red Hat offers training on:
Ansible Basics: Ideal for beginners looking to understand how to automate workflows and deploy applications.
Advanced Ansible Automation: Focuses on optimizing playbooks, integrating Ansible Tower, and managing large-scale deployments.
3. OpenShift Container Platform
OpenShift is Red Hat’s Kubernetes-based platform for managing containerized applications. Red Hat training covers topics like:
OpenShift Administration: Learn how to install, configure, and manage OpenShift clusters.
OpenShift Developer: Build, deploy, and scale containerized applications on OpenShift.
4. Red Hat Cloud Technologies
With businesses rapidly adopting cloud technologies, Red Hat’s cloud training programs ensure that professionals are prepared for cloud-native development and infrastructure management. Key topics include:
Red Hat OpenStack: Learn how to deploy and manage private cloud environments.
Red Hat Virtualization: Master the deployment of virtual machines and manage large virtualized environments.
5. DevOps Training
Red Hat is committed to promoting DevOps practices, helping teams collaborate more efficiently. DevOps training includes:
Red Hat DevOps Pipelines and CI/CD: Learn how to streamline software development, testing, and deployment processes.
Container Development and Kubernetes Integration: Get hands-on experience with containerized applications and orchestrating them using Kubernetes.
6. Cloud-Native Development
As enterprises move towards microservices and cloud-native applications, Red Hat provides training on developing scalable and resilient applications:
Microservices Architecture: Learn to build and deploy microservices using Red Hat’s enterprise open-source tools.
Serverless Application Development: Focus on building lightweight applications that scale on demand.
7. Red Hat Satellite
Red Hat Satellite simplifies Linux system management at scale, and its training focuses on:
Satellite Server Administration: Learn how to automate system maintenance and streamline software updates across your RHEL environment.
8. Security and Compliance
In today's IT landscape, security is paramount. Red Hat offers specialized training on securing infrastructure and ensuring compliance:
Linux Security Essentials: Learn to safeguard Linux environments from vulnerabilities.
Advanced Security Features: Cover best practices for maintaining security across hybrid cloud environments.
Why Red Hat Training?
Red Hat certifications are globally recognized, validating your expertise in open-source technologies. They offer hands-on, practical training that helps professionals apply their knowledge directly to real-world challenges. By investing in Red Hat training, you are preparing yourself for future innovations and ensuring that your skills remain relevant in an ever-changing industry.
Conclusion
Red Hat training empowers IT professionals to build, manage, and secure the enterprise-grade systems that are shaping the future of technology. Whether you're looking to enhance your Linux skills, dive into automation with Ansible, or embrace cloud-native development, there’s a Red Hat training category tailored to your needs.
For more details click www.hawkstack.com
#redhatcourses#docker#information technology#kubernetes#containerorchestration#container#linux#dockerswarm#hawkstack#hawkstack technologies
0 notes
Text

Overview Of RHCE | RH294 | RHEL-9 There is Linux Automation training available for Linux system administrators and developers who need to automate provisioning, configuration, application deployment, and orchestration. This section covers configuring managed hosts for automation, building Ansible Playbooks to automate tasks, setting up Ansible on a management workstation, and running Playbooks to ensure servers are deployed and configured correctly.
Why Learn RHCE? Acquire Advanced Knowledge: Expand your knowledge of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Industry Recognition: Within the IT industry, the RHCE certification is highly regarded. Employment Growth: With RHCE proficiency, you can open up new employment prospects. Operational Mastery: Be an expert in network management and Linux systems.
Prerequisites: Get Red Hat Enterprise Linux knowledge and expertise equivalent to that of a Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA). Hold a Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE) or Red Hat Certified Specialist in Ansible Automation certification for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, or exhibit a comparable level of Ansible expertise. For further information visit our Website: krnetworkcloud.org
0 notes
Text
Stay Safe Online with Nessus: A Top Web Security Scanner

Nessus is a complete vulnerability assessment tool that uses thorough scans and customizable reports to help businesses find and deal with security risks. You can safely deal with various online threats using one of the best vulnerability scanners, Nessus. One thing that makes Nessus stand out is that it's free to use. It also offers a full vulnerability scanner. Nessus makes it an excellent choice for people and small companies that want to improve their security without spending much money. The Origin Of Nessus Initiated by Tenable co-founder Renaud Deraison, a cybersecurity specialist, Nessus started its path in 1998 as part of the Nessus Project. The effort sought a free, remote security scanner for the online community. This program became well-known among cybersecurity experts quite fast. However, in 2005, Nessus moved from free, open-source software to a proprietary, closed-source solution. Despite this change, Tenable has kept providing Nessus with free and premium options to maintain its competitive edge in the market. Nessus and Tenable: Key Facts You Need to Know Tenable is a notable cybersecurity firm headquartered in Columbia, Maryland, USA. Tenable has become a leader in the market since more than 40,000 companies all over depend on its security solutions. Though not wildly original, their official website has a clear design and simple navigation, facilitating user experience. It also has an active blog, routinely changed with fresh material to keep people updated. Those wishing to remain in touch with Tenable can follow on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube. Prices and Plans for Nessus To meet various user needs, the Nessus vulnerability scanner provides three editions: Previously called "Nessus Home," this issue is free. It is a perfect starting point for cybersecurity since it offers the necessary tools for novices and students. Professional Nessus: Designed for professional customers that need sophisticated capabilities, this edition, priced at €3,875.71 ($3,795) annually, Users pick between annual, biannual, or triennial billing cycles; longer memberships save more. Costing: €8,563.14 ($8,391), the most complete edition is Nessus Expert. Though these add-ons are more expensive, they comprise enterprise-level security solutions with extra capabilities, including sophisticated support and on-demand training. Tenable lets users try the features of their paid plans for a free trial lasting seven days, enabling financial commitment free from influence. Among the payment options are main credit and debit cards, PayPal, Google Pay, Amazon Pay, Apple Pay, and Shop Pay. Comprehensive Features and Limitless Potential in Web Security Operating systems ranging from Windows (versions 7, 8, and 10) to SOSE Linux, Ubuntu, Debian/Kali Linux, Fedora, FreeBSD, macOS X, Red Hat/Centos/Oracle Linux, and Windows Server (2008 and 2012) fit Nessus. On both 32-bit and 64-bit computers, the program operates perfectly to guarantee extensive usability. The basic functionality of the free "Nessus Essentials" edition includes asset discovery scanning limited to 16 IPs for vulnerability assessment. This edition is designed for personal use only and lacks sophisticated features like scan scheduling capabilities and compliance/audit check tools. However, it offers a great beginning point for students and newbies to networking technology since it opens a portal into the Tenable ecosystem. Paid plans provide help from the Nessus community, unlimited IT assessments, configuration assessments, and customizable real-time reports. Features such as external attack surface scanning, domain addition capability, scan cloud infrastructure, and 500 pre-built scanning policies also abound in the "Nessus Expert" edition. User-Friendly Security Scanning for Everyone Starting with the Nessus vulnerability scanner is not tricky. Select a plan, provide your details, and get an email with a one-time activation code. Download and install Nessus on your selected operating system using the detailed instructions offered. Nessus's user interface is remarkably straightforward and inviting. Navigate to the "Scans" part of the main menu, select "New Scan," pick a scan template with pre-configured settings, and click "Launch." Customizable viewing choices and colour-coded markers help to interpret scan data. Scanning targets, found vulnerabilities arranged by severity, remedial details, extra scan data, and a list of scans arranged by start time, end time, and status are viewable to users. Thanks to the thorough manuals and simple-to-use design, the free edition has a generally good user experience, even if it might have certain speed restrictions. Client Support Tenable provides phone, live chat, email, and community forum-based customer service around the clock. Users of the free edition may thus have slower response times of up to 24 hours and lack phone or email assistance. Tenable offers thorough self-help alternatives, including a detailed FAQ section, how-to manuals, a resource library, and documentation pages for individuals wanting to handle problems alone. Additionally, a great source of advice and troubleshooting is the Nessus community. How Nessus Works? Nessus thoroughly scans an entire IT system to find holes and weak spots. Here's a quick rundown of what it can do: Types of Scans: Nessus has different types of scans, such as vulnerability scans, compliance checks, and configuration evaluations. TechRadar says users can choose from scan files already set up or make their own that fit their needs. Deployment: Nessus can be used with many different operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and several different versions of Linux. To set up the software, you have to choose the correct version, install it, and then use a registration code Tenable gives you to make it work. Scanning Process: To do a scan, users go to the "Scans" area, click "New Scan," and pick a template. The scan can be started immediately or set to happen later once it has been set up. The results are shown in an easy-to-understand colour-coded style that indicates the seriousness of the vulnerabilities and details how to fix them. Real-Time Reviews Of Nessus Héctor Joel (Information Technology and Services, 11-50 employees) Rating: 5/5 Pros: Nessus is praised for its thorough vulnerability scans and easy-to-use graphics interface. It has been easier to find and fix weaknesses with this tool. Cons: None were mentioned; overall, it was a good experience. Review: "Nessus has a great tool for finding and fixing vulnerabilities." From the discovery stages on, the information given is very complete. We are very happy with how the tool was set up and the results it gives us. Carol (Chemicals, 10,000+ employees) Rating: 4/ 5 Pros: It works well to check for vulnerabilities, is easy to set up, sends alerts quickly, and updates often. Cons: It gives some false results and costs a lot for extra features. Review: "Nessus has done a great job giving our company a vulnerability assessment." Simple steps were needed to set up Nessus, and it quickly did thorough checks. It's great to make your tests and use various tools. Pros and Cons Of Nessus Pros Cons Comprehensive Expensive User-friendly False Positives Detailed Customizable Reliable - Rivals of Nessus When seeking alternatives to Nessus, a popular vulnerability assessment tool, several options cater to various needs and budgets. Here’s a detailed look at three notable rivals: OpenVAS, Probely, and Vega. 1. OpenVAS Overview: OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System) is an accessible and cost-effective alternative to Nessus. As an open-source vulnerability scanner, OpenVAS is part of the Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM) solution. Key Features: - Free and Open-Source: Completely free, making it ideal for organizations with budget constraints. - Comprehensive Scanning: Provides detailed vulnerability assessments for network devices and servers, including checks for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and outdated software. - Community Support: Backed by a strong community, offering regular updates and support through forums and mailing lists. - Extensive Plugin Library: Includes thousands of regularly updated vulnerability tests (VTs). Limitations: - UsabiPluginThe setup and configuration can be more complex than those of commercial alternatives. - Documentation: The polished and extensive documentation in paid solutions may be lacking. Best Suited For: - Organizations and individuals need a robust, cost-free tool for vulnerability scanning. - Users are willing to invest time in learning and configuring the tool. 2. Probely Overview: Probely is a cloud-based vulnerability scanner focusing on ease of use and business needs. It’s particularly appealing to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking for an efficient yet cost-effective solution. Key Features: - Business-Oriented Packages: Offers a range of pricing plans, including a "Pro" package that balances cost and features, making it an affordable option compared to Nessus. - Integration-Friendly: Easily integrates with CI/CD pipelines, making it suitable for DevSecOps environments. - User-Friendly Interface: Simplifies vulnerability management with a clean and intuitive user interface. - Automated Scanning: Provides automated web application scanning and clear guidance on remediation steps. Limitations: - Scope: Primarily focuses on web application scanning, which might not cover all network vulnerabilities. - Feature Set: It may lack advanced features and depth offered by more established tools like Nessus. Best Suited For: - Businesses are seeking a straightforward, cloud-based vulnerability scanner focusing on web applications. - Users are looking for a tool that integrates seamlessly into their development workflows. 3. Vega Overview: Vega is a free and open-source web application scanner known for its extensibility and flexibility. It caters to technically proficient users who need a customizable tool for web security assessments. Key Features: - Free and Open-Source: No cost involved, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious users. - Extensibility: Allows users to write custom scripts and extend functionality using JavaScript, providing flexibility for unique scanning requirements. - Comprehensive Web Scanning: Can detect various web vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and more. - Graphical User Interface: Offers a user-friendly GUI for easy navigation and use. Limitations: - Complexity: Requires technical expertise to leverage its scripting and customization capabilities fully. - Limited Network Scanning: Primarily focused on web applications, not designed for comprehensive network vulnerability assessments. Best Suited For: - Tech-savvy users and developers who need a versatile tool for web security testing. - Individuals or small teams are looking for a free scanner that can be customized to meet specific needs. Verdict Though not the most often used security scanner, Nessus is a strong competitor in the cybersecurity field. Its developer community has produced several plug-ins, risk-based vulnerability prioritizing, adjustable real-time reporting, an easy-to-use interface, and an extensive range of scans. Nessus offers a strategy to fit your demands and keep you secure online regardless of your experience level—beginner, professional, or corporate user. FAQs For what purposes is Nessus used? Vulnerability assessment makes use of nessus to enable companies to find and fix security flaws in their IT systems. Does a free edition of Nessus? The free edition, A: Nessus Essentials, provides restricted basic vulnerability assessment capabilities spanning just 16 IP addresses. For small-scale use and students in particular, it's perfect. What is the Frequency of Nessus updates? Nessus routinely changes its vulnerability database to guarantee users are shielded against the most recent security risks. What distinguishes Professional, Expert, and Essentials from one another primarily? While Nessus Professional and Expert provide more thorough scanning capabilities including compliance checks, scan scheduling, and support for bigger networks, A: Nessus Essentials is free and restricted in features. Among other things, Nessus Expert offers cloud infrastructure evaluations and external attack surface detection. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
AlloyDB Omni Version 15.7.0 Improves PostgreSQL Workflows

AlloyDB Omni boosts performance with vector search, analytics, and faster transactions.
With its latest release AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0, AlloyDB Omni is back and is significantly improving your PostgreSQL workflows. These improvements include:
Quicker performance
A brand-new, lightning-fast disk cache
A better columnar engine
The widespread use of ScANN vector indexing
The AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator has been updated.
In your data center, on the edge, on your laptop, in any cloud, and with 100% PostgreSQL compatibility, this update offers on all fronts, from transactional and analytical workloads to state-of-the-art vector search.
AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0 is now broadly accessible (GA). The following updates and features are included in version AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0:
AlloyDB Version 15.7 of PostgreSQL is supported by Omni.
Previously known as postgres_scann, the alloydb_scann extension is now generally available (GA).
There is generally available (GA) support for Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.
You can preview the AlloyDB Omni columnar engine on ARM.
Because disk cache and columnar storage cache speed up data access for AlloyDB Omni in a container and on a Kubernetes cluster, they can enhance AlloyDB Omni performance.
It has applied security updates for CVE-2023-50387 and CVE-2024-7348.
The documentation for the AlloyDB Omni Reference is accessible. This comprises AlloyDB Omni 15.7.0 metrics, database flags, model endpoint management reference, and extension documentation.
AlloyDB The pg_ivm extension, which offers incremental view maintenance for materialized views, is compatible with Omni.
Numerous efficiency enhancements and bug fixes.
Let’s get started.
Improved performance
When compared to regular PostgreSQL, many workloads already experience an improvement. For transactional workloads, AlloyDB Omni outperforms regular PostgreSQL by more than two times in performance testing. The majority of the tuning is done automatically for you without the need for additional setups. The memory agent that maximizes shared buffers while preventing out-of-memory issues is one of the main benefits. AlloyDB Omni generally runs better with more memory configured because it can serve more queries from the shared buffers and eliminate the need for disk calls, which can be significantly slower than memory, especially when utilizing durable network storage.
An extremely fast disk cache
The introduction of an ultra-fast disk cache also made the trade-off between memory and disk storage more flexible. As an extension of Postgres’ buffer cache, it enables you to set up a quick, local, and perhaps brittle storage device. AlloyDB Omni can store a copy of not-quite-hot data in the disk cache, where it can be accessed more quickly than from the permanent disk, rather than aging out of memory to create room for new data.
Improved columnar engine
The analytics accelerator from AlloyDB Omni is revolutionizing mixed workloads. Because it eliminates the need to manage additional data pipelines or databases, developers are finding it helpful for extracting real-time analytical insights from their transactional data. To speed up queries, you can instead activate the columnar engine, allocate a piece of your memory to it, and let AlloyDB Omni to choose which tables or columns to load in the columnar engine. The columnar engine outperforms regular PostgreSQL by up to 100x in our benchmarks for analytical queries.
The amount of RAM you can allocate to the columnar engine dictates the analytics accelerator’s practical size limit. The ability to set up a quick local storage device for the columnar engine to spill to is a new feature. This expands the amount of data on which you may do analytical queries.
SCaNN becomes GA
Finally, AlloyDB Omni already provides excellent performance with pgvector utilizing either the ivf or hnsw indexes for vector database use cases. Vector indexes, however, can be slow to build and reload even though they are a terrific method to speed up queries. It added the ScaNN index as an additional index type at Google Cloud Next 2024. The ScaNN index from AlloyDB AI provides up to 4 times faster vector queries than the HNSW index used in ordinary PostgreSQL. ScaNN offers substantial benefits for practical applications beyond only speed:
Rapid indexing: With noticeably quicker index build times, you may expedite development and remove bottlenecks in large-scale deployments.
Optimized memory usage: Cut memory usage by three to four times as compared to PostgreSQL’s HNSW index. This improves performance for a variety of hybrid applications and enables larger workloads to operate on smaller hardware.
In general, AlloyDB AI ScANN indexing is accessible as of AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0.
A fresh Kubernetes administrator
Google Cloud has published version 1.2.0 of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator in addition to the latest version of AlloyDB Omni. With this release, you can now configure high availability to be enabled when a disaster recovery secondary cluster is promoted to primary, add more configuration options for health checks when high availability is enabled, and use log rotation to help manage the storage space used by PostgreSQL log files.
Version 1.2.0 of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator is now broadly accessible (GA). The following new features are included in version 1.2.0:
The interval between health checks can be set in seconds using the healthcheckPeriodSeconds option.
You can keep an eye on your database container’s performance with the following metrics. These measurements are all type gauge.
A database container’s memory limit is displayed by alloydb_omni_memory_limit_byte.
All replicas connected to the AlloyDB Omni primary node are shown in alloydb_omni_instance_postgresql_replication_state.
The database container’s memory usage is displayed in bytes via alloydb_omni_memory_used_byte.
When the following is true, a problem that briefly disrupted all database clusters has been resolved:
The AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator version 1.1.1 is being upgraded to a more recent version.
Version 15.5.5 or higher of the AlloyDB Omni database is what you’re using.
AI for AlloyDB is not activated.
Once promoted, high availability is supported on a secondary database cluster.
Model endpoint management can be enabled or disabled using Kubernetes manifests.
By setting thresholds depending on the size of the log files, the amount of time since the log file last rotated, or both, you may control when logs rotate.
To examine and troubleshoot the memory performance of the AlloyDB Omni Kubernetes operator, you can take a snapshot of its memory heap.
Note: Parameterized view features were accessible via the alloydb_ai_nl extension of AlloyDB Omni versions 15.5.5 and earlier. The parameterized_views extension, which you must develop before using parameterized views, contains the parameterized view features starting in AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0. The associated function, google_exec_param_query, has also been renamed to execute_parameterized_query and is accessible through the parameterized_views extension as of AlloyDB Omni version 15.7.0.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AlloyDBOmni#AlloyDB#PostgreSQL#Omni#AlloyDBOmniversion15.7.0#Cloudcomputing#ScaNNindex#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes