#south africa in the british empire
Text

"Near Victory Turned to Defeat for British Forces," Kingston Whig-Standard. June 26, 1942. Page 10.
----
When these pictures were made in Libya a few short weeks ago things were going well for the British German tanks like the captured one above were being tested. German prisoners like these at left below were being taken. South African gunners like those at right below were blistering the desert with bullets. But Rommel came back with bigger, better armored tanks to take many more thousands of British prisoners, a large part of them South Africans.
#tobruk#battle of tobruk#second battle of tobruk#south african army#south africa in the british empire#afrika korps#panzerarmee afrika#armored warfare#desert air force#prisoners of war#british empire#western desert campaign#north africa campaign#italian libya#world war ii
1 note
·
View note
Text

Three generations of Boer fighters, during the South African War, 1899 - 1902. Boer composed of P.J. Lemmer (66 years old), D.L. Botha (15 years old), C.I. Pretorius (43 years old) armed with Mauser rifles.
#boer war#south africa#1900s#1890s#twentieth century#britain#circa 1900#circa 1901#great britain#1902#africa#africa history#british empire#mauser#soldiers#19th century#boer#the Boer war#photography#photoshoot#war history#history
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Journey back in time on the luxury rail route across southern Africa
#Rovos Rail#luxury train#Pretoria#South Africa#Victoria Falls#Zimbabwe#retro#romantic travel#dining car#British Empire
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
On May 28, 1914, the Institut für Schiffs-und Tropenkrankheiten (Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases, ISTK) in Hamburg began operations in a complex of new brick buildings on the bank of the Elb. The buildings were designed by Fritz Schumacher, who had become the Head of Hamburg’s building department (Leiter des Hochbauamtes) in 1909 after a “flood of architectural projects” accumulated following the industrialization of the harbor in the 1880s and the “new housing and working conditions” that followed. The ISTK was one of these projects, connected to the port by its [...] mission: to research and heal tropical illnesses; [...] to support the Hamburg Port [...]; and to support endeavors of the German Empire overseas.
First established in 1900 by Bernhard Nocht, chief of the Port Medical Service, the ISTK originally operated out of an existing building, but by 1909, when the Hamburg Colonial Institute became its parent organization (and Schumacher was hired by the Hamburg Senate), the operations of the ISTK had outgrown [...]. [I]ts commission by the city was an opportunity for Schumacher to show how he could contribute to guiding the city’s economic and architectural growth in tandem, and for Nocht, an opportunity to establish an unprecedented spatial paradigm for the field of Tropical Medicine that anchored the new frontier of science in the German Empire. [...]
[There was a] shared drive to contribute to the [...] wealth of Hamburg within the context of its expanding global network [...]. [E]ach discipline [...] architecture and medicine were participating in a shared [...] discursive operation. [...]
---
The brick used on the ISTK façades was key to Schumacher’s larger Städtebau plan for Hamburg, which envisioned the city as a vehicle for a “harmonious” synthesis between aesthetics and economy. [...] For Schumacher, brick [was significantly preferable] [...]. Used by [...] Hamburg architects [over the past few decades], who acquired their penchant for neo-gothic brickwork at the Hanover school, brick had both a historical presence and aesthetic pedigree in Hamburg [...]. [T]his material had already been used in Die Speicherstadt, a warehouse district in Hamburg where unequal social conditions had only grown more exacerbated [...]. Die Speicherstadt was constructed in three phases [beginning] in 1883 [...]. By serving the port, the warehouses facilitated the expansion and security of Hamburg’s wealth. [...] Yet the collective profits accrued to the city by these buildings [...] did not increase economic prosperity and social equity for all. [...] [A] residential area for harbor workers was demolished to make way for the warehouses. After the contract for the port expansion was negotiated in 1881, over 20,000 people were pushed out of their homes and into adjacent areas of the city, which soon became overcrowded [...]. In turn, these [...] areas of the city [...] were the worst hit by the Hamburg cholera epidemic of 1892, the most devastating in Europe that year. The 1892 cholera epidemic [...] articulated the growing inability of the Hamburg Senate, comprising the city’s elite, to manage class relationships [...] [in such] a city that was explicitly run by and for the merchant class [...].
In Hamburg, the response to such an ugly disease of the masses was the enforcement of quarantine methods that pushed the working class into the suburbs, isolated immigrants on an island, and separated the sick according to racial identity.
In partnership with the German Empire, Hamburg established new hygiene institutions in the city, including the Port Medical Service (a progenitor of the ISTK). [...] [T]he discourse of [creating the school for tropical medicine] centered around city building and nation building, brick by brick, mark by mark.
---
Just as the exterior condition of the building was, for Schumacher, part of a much larger plan for the city, the program of the building and its interior were part of the German Empire and Tropical Medicine’s much larger interest in controlling the health and wealth of its nation and colonies. [...]
Yet the establishment of the ISTK marked a critical shift in medical thinking [...]. And while the ISTK was not the only institution in Europe to form around the conception and perceived threat of tropical diseases, it was the first to build a facility specifically to support their “exploration and combat” in lockstep, as Nocht described it.
The field of Tropical Medicine had been established in Germany by the very same journal Nocht published his overview of the ISTK. The Archiv für Schiffs- und Tropen-Hygiene unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Pathologie und Therapie was first published in 1897, the same year that the German Empire claimed Kiaochow (northeast China) and about two years after it claimed Southwest Africa (Namibia), Cameroon, Togo, East Africa (Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda), New Guinea (today the northern part of Papua New Guinea), and the Marshall Islands; two years later, it would also claim the Caroline Islands, Palau, Mariana Islands (today Micronesia), and Samoa (today Western Samoa).
---
The inaugural journal [...] marked a paradigm shift [...]. In his opening letter, the editor stated that the aim of Tropical Medicine is to “provide the white race with a home in the tropics.” [...]
As part of the institute’s agenda to support the expansion of the Empire through teaching and development [...], members of the ISTK contributed to the Deutsches Kolonial Lexikon, a three-volume series completed in 1914 (in the same year as the new ISTK buildings) and published in 1920. The three volumes contained maps of the colonies coded to show the areas that were considered “healthy” for Europeans, along with recommended building guidelines for hospitals in the tropics. [...] "Natives" were given separate facilities [...]. The hospital at the ISTK was similarly divided according to identity. An essentializing belief in “intrinsic factors” determined by skin color, constitutive to Tropical Medicine, materialized in the building’s circulation. Potential patients were assessed in the main building to determine their next destination in the hospital. A room labeled “Farbige” (colored) - visible in both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications - shows that the hospital segregated people of color from whites. [...]
---
Despite belonging to two different disciplines [medicine and architecture], both Nocht and Schumacher’s publications articulate an understanding of health [...] that is linked to concepts of identity separating white upper-class German Europeans from others. [In] Hamburg [...] recent growth of the shipping industry and overt engagement of the German Empire in colonialism brought even more distant global connections to its port. For Schumacher, Hamburg’s presence in a global network meant it needed to strengthen its local identity and economy [by purposefully seeking to showcase "traditional" northern German neo-gothic brickwork while elevating local brick industry] lest it grow too far from its roots. In the case of Tropical Medicine at the ISTK, the “tropics” seemed to act as a foil for the European identity - a constructed category through which the European identity could redescribe itself by exclusion [...].
What it meant to be sick or healthy was taken up by both medicine and architecture - [...] neither in a vacuum.
---
All text above by: Carrie Bly. "Mediums of Medicine: The Institute for Maritime and Tropical Diseases in Hamburg". Sick Architecture series published by e-flux Architecture. November 2020. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Text within brackets added by me for clarity. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticism purposes.]
#abolition#ecology#sorry i know its long ive been looking at this in my drafts for a long long time trying to condense#but its such a rich comparison that i didnt wanna lessen the impact of blys work here#bly in 2022 did dissertation defense in architecture history and theory on political economy of steel in US in 20s and 30#add this to our conversations about brazilian eugenics in 1930s explicitly conflating hygiene modernist architecture and white supremacy#and british tropical medicine establishment in colonial india#and US sanitation and antimosquito campaigns in 1910s panama using jim crow laws and segregation and forcibly testing local women#see chakrabartis work on tropical medicine and empire in south asia and fahim amirs cloudy swords#and greg mitmans work on connections between#US tropical medicine schools and fruit plantations in central america and US military occupation of philippines and rubber in west africa#multispecies#imperial#indigenous#colonial#landscape#temporal#see also us mosquito campaigns in panama and british urban planning in west africa and rohan deb roy work on india bengal entomology#ecologies#bugs#tidalectics#archipelagic thinking#plantations#intimacies of four continents#carceral geography
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo

13 notes
·
View notes
Text
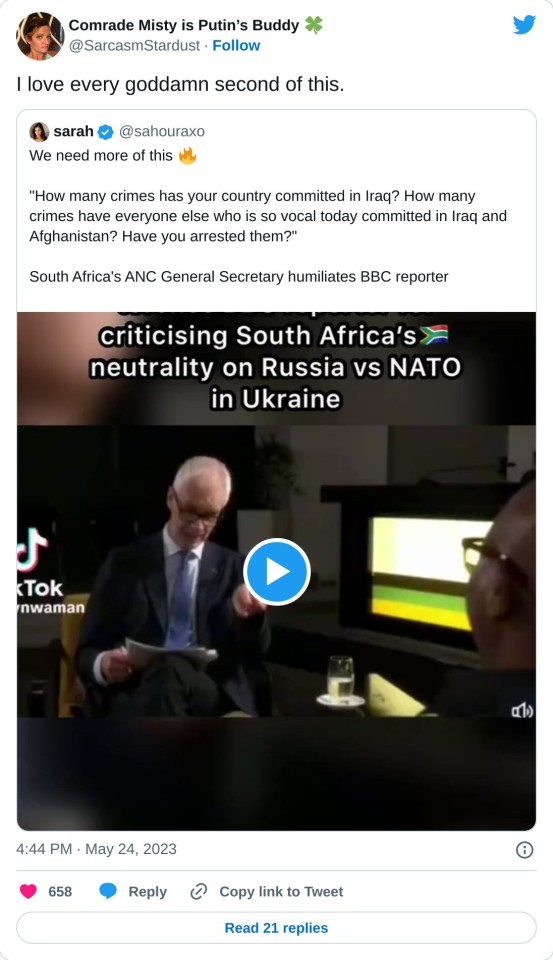
This shit is funny as fuck. 😂😂
"We don't have much time left. " Nah son, he owned your network and nation.
#stop imperialism#british empire#british history#south africa#empire in decline#russia ukraine conflict#iraq war#double standards#bbc news world
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Visit the Empire - London Underground poster, 1933 // Design by Ernest Michael Dinkel
Source
#ernest michael dinkel#london underground#london underground poster#vintage travel poster#colonialism#imperialism#british empire#australia#burma#india#south africa#british east indies#malaya#nigeria
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
People do not realize that when we say Israel is a settler-colonial state, we mean it was literally devised in junction with European imperialism around the turn of the century.
Political Zionism was founded by Theodore Herzl. Originally, Zionists were not specifically interested in the land of Palestine as a colonial project. In fact, Herzl was debating making Argentina the focus of mass Zionist migration, which is quite ironic considering Argentina's colonial and Aryanist past. British-controlled Uganda was also offered as a possibility by Joseph Chamberlain, a Conservative imperialist.
To encourage mass Jewish migration to Palestine, he worked with the British, who had recently drove the Ottoman Empire out of the Levant, and now boasted political dominance in the region, thanks to the Sykes–Picot Agreement between the UK, France, Italy, and Russia which covertly authorized British influence in Palestine, which had become a target of colonial expansion. He specifically wished to collaborate with Cecil Rhodes, a British imperialist who played a lead role in colonizing Zimbabwe and Zambia, and later took inspiration from his time spent extracting wealth from Africa as the founder of mining conglomerate the British South Africa Company.
Herzl’s personal goals for Zionism were colonial. He said in a letter to Rhodes:
“You are being invited to help make history. It doesn’t involve Africa, but a piece of Asia Minor; not Englishmen but Jews […] How, then, do I happen to turn to you since this is an out-of-the-way matter for you? How indeed? Because it is something colonial […] I […] have examined this plan and found it correct and practicable. It is a plan full of culture, excellent for the group of people for whom it is directly designed, and quite good for England, for Greater Britain [...]”
At that time, Palestine was predominately populated with Arab Muslims and Christians, as well as Arab Jews (Old Yishuv) and Druze. Jews made up around 6% of the population. The Ottoman government specifically released a manifesto at the start of Zionist migration condemning the colonization, stating:
“[Jews] among us […] who have been living in our province since before the war; they are as we are, and their loyalties are our own.”
The Balfour Declaration of 1917 on behalf of parliament, officially established the British Mandate of Palestine, sowing the seeds for the modern state of Israel, by means of the UK's ongoing occupation of the region.
Zionism was never about promoting Jewish culture or safety; it has always been tied up in Western (settler-)colonial expansion. !من النهر إلى البحر
#palestine#since you guys are being obtuse😔#1) the ottoman empire was bad#2) herzl is obviously not the only representative of zionism#3) both zionism and anti zionism have complex discourses within them#4) jewish people are not a monolith
13K notes
·
View notes
Photo

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/South_Africa_Medal_(1880)
0 notes
Text
OK, as an Indian person and ESPECIALLY as a Scottish person I have to say this.
The current Palestinian Genocide (let's call a spade a spade) and lack of response is an unambiguously, direct result of British Colonialism.
Palestine was given/promised/whatever word you want to use to describe it to Israel by the British Empire to whom it "belonged" as a colony.
Everything that happened thereafter, the Nakba, every invasion, every injustice is a result of that colonial attitude from which Israel was born.
Everywhere the British Empire has been it has sewn chaos and promoted the abuse of human rights as it left. It has happened in India, it happened in Nigeria, South Africa, Cameroon and Australia.
The reason for such a lax UK governmental response is because if they acknowledge what's going on is fucked they have to take responsibility for so much more. By leaving these countries originally the UK has "washed their hands of it."
I want to make this extremely clear.
Britain's hands will NEVER be clean
The British Empire has committed the greatest atrocities known to mankind and the British Government does not want to acknowledge that.
Israel has been built from these imperial attitudes, has repeatedly and continually committed war crimes and human rights abuses and governments just... don't care
It's actually insane and we need to recognise the root of these humanitarian calamities and hold our government accountable.
Write to your MPs, your MSPs, your MSs make your voice heard in whatever way that you can! Your voice may seem weak but it is so incredibly powerful if enough people speak up, if enough people make sure that the government never forgets about these things we can make REAL CHANGE. The link below will allow for you to find your government representative be that N.Ireland Assembly Scottish, Welsh or UK Parliament as well as their emails.
https://www.theyworkforyou.com/
Tell them how horrible things are in Gaza, tell them about Israel's repeated and continuous mistreatment of the Palestinian people, tell them how the UK cannot continue to plug our ears and ignore the fallout of our past. Just say something!
975 notes
·
View notes
Text
“This raises the question: if industrial production is necessary to meet decent-living standards today, then perhaps capitalism—notwithstanding its negative impact on social indicators over the past five hundred years—is necessary to develop the industrial capacity to meet these higher-order goals. This has been the dominant assumption in development economics for the past half century. But it does not withstand empirical scrutiny. For the majority of the world, capitalism has historically constrained, rather than enabled, technological development—and this dynamic remains a major problem today.
It has long been recognized by liberals and Marxists alike that the rise of capitalism in the core economies was associated with rapid industrial expansion, on a scale with no precedent under feudalism or other precapitalist class structures. What is less widely understood is that this very same system produced the opposite effect in the periphery and semi-periphery. Indeed, the forced integration of peripheral regions into the capitalist world-system during the period circa 1492 to 1914 was characterized by widespread deindustrialization and agrarianization, with countries compelled to specialize in agricultural and other primary commodities, often under “pre-modern” and ostensibly “feudal” conditions.
In Eastern Europe, for instance, the number of people living in cities declined by almost one-third during the seventeenth century, as the region became an agrarian serf-economy exporting cheap grain and timber to Western Europe. At the same time, Spanish and Portuguese colonizers were transforming the American continents into suppliers of precious metals and agricultural goods, with urban manufacturing suppressed by the state. When the capitalist world-system expanded into Africa in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, imports of British cloth and steel destroyed Indigenous textile production and iron smelting, while Africans were instead made to specialize in palm oil, peanuts, and other cheap cash crops produced with enslaved labor. India—once the great manufacturing hub of the world—suffered a similar fate after colonization by Britain in 1757. By 1840, British colonizers boasted that they had “succeeded in converting India from a manufacturing country into a country exporting raw produce.” Much the same story unfolded in China after it was forced to open its domestic economy to capitalist trade during the British invasion of 1839–42. According to historians, the influx of European textiles, soap, and other manufactured goods “destroyed rural handicraft industries in the villages, causing unemployment and hardship for the Chinese peasantry.”
The great deindustrialization of the periphery was achieved in part through policy interventions by the core states, such as through the imposition of colonial prohibitions on manufacturing and through “unequal treaties,” which were intended to destroy industrial competition from Southern producers, establish captive markets for Western industrial output, and position Southern economies as providers of cheap labor and resources. But these dynamics were also reinforced by structural features of profit-oriented markets. Capitalists only employ new technologies to the extent that it is profitable for them to do so. This can present an obstacle to economic development if there is little demand for domestic industrial production (due to low incomes, foreign competition, etc.), or if the costs of innovation are high.
Capitalists in the Global North overcame these problems because the state intervened extensively in the economy by setting high tariffs, providing public subsidies, assuming the costs of research and development, and ensuring adequate consumer demand through government spending. But in the Global South, where state support for industry was foreclosed by centuries of formal and informal colonialism, it has been more profitable for capitalists to export cheap agricultural goods than to invest in high-technology manufacturing. The profitability of new technologies also depends on the cost of labor. In the North, where wages are comparatively high, capitalists have historically found it profitable to employ labor-saving technologies. But in the peripheral economies, where wages have been heavily compressed, it has often been cheaper to use labor-intensive production techniques than to pay for expensive machinery.
Of course, the global division of labor has changed since the late nineteenth century. Many of the leading industries of that time, including textiles, steel, and assembly line processes, have now been outsourced to low-wage peripheral economies like India and China, while the core states have moved to innovation activities, high-technology aerospace and biotech engineering, information technology, and capital-intensive agriculture. Yet still the basic problem remains. Under neoliberal globalization (structural adjustment programs and WTO rules), governments in the periphery are generally precluded from using tariffs, subsidies, and other forms of industrial policy to achieve meaningful development and economic sovereignty, while labor market deregulation and global labor arbitrage have kept wages extremely low. In this context, the drive to maximize profit leads Southern capitalists and foreign investors to pour resources into relatively low-technology export sectors, at the expense of more modern lines of industry.
Moreover, for those parts of the periphery that occupy the lowest rungs in global commodity chains, production continues to be organized along so-called pre-modern lines, even under the new division of labor. In the Congo, for instance, workers are sent into dangerous mineshafts without any modern safety equipment, tunneling deep into the ground with nothing but shovels, often coerced at gunpoint by U.S.-backed militias, so that Microsoft and Apple can secure cheap coltan for their electronics devices. Pre-modern production processes predicated on the “technology” of labor coercion are also found in the cocoa plantations of Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire, where enslaved children labor in brutal conditions for corporations like Cadbury, or Colombia’s banana export sector, where a hyper-exploited peasantry is kept in line by a regime of rural terror and extrajudicial killings overseen by private death squads.
Uneven global development, including the endurance of ostensibly “feudal” relations of production, is not inevitable. It is an effect of capitalist dynamics. Capitalists in the periphery find it more profitable to employ cheap labor subject to conditions of slavery or other forms of coercion than they do to invest in modern industry.”
Capitalism, Global Poverty, and the Case for Democratic Socialism by Jason Hickle and Dylan Sullivan
595 notes
·
View notes
Text

Namibia was glad to come under British rule after World War I
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
do you know any texts on the connection between fascism/the right and cleanliness/hygiene (purity) rhetoric? anything that goes a bit in depth on the topic?
Getting Under Our Skin: The Cultural and Social History of Vermin (2021). Sarasohn, Lisa Tunick. ISBN: 9781421441382
Dirt: New Geographies of Cleanliness and Contamination (2007). Campkin, Ben & Cox, Rosie (Eds.). ISBN: 9781845116729
The Sanitation of Brazil: Nation, State, and Public Health, 1889-1930 (2016). Hochman, Gilberto. ISBN: 9780252099052
Clean and White: A History of Environmental Racism in the United States (2015). Zimring, Carl A. ISBN: 9781479826940
Colonial Pathologies: American Tropical Medicine, Race, and Hygiene in the Phillipines (2006). Anderson, Warwick H. ISBN: 0822338041
Bacteriology in British India: Laboratory Medicine and the Tropics (2017). Chakrabarti, Pratik. ISBN: 9781580465908
The Great Hanoi Rat Hunt: Empire, Disease, and Modernity in French Colonial Vietnam (2018). Vann, Michael G. & Clarke, Liz. ISBN: 9780190602697
Soap and Water: Cleanliness, Dirt and the Working Classes in Victorian and Edwardian Britain (2010). Kelley, Victoria. ISBN: 9781848850521
Contagion: Disease, government, and the “social question” in 19th-century France (1999). Aisenberg, Andrew R.
Rome, Pollution, and Propriety: Dirt, Disease, and Hygiene in the Eternal City from Antiquity to Modernity (2012). Bradley, Mark & Stow, Kenneth R. ISBN: 9781107014435
Sanitizing South Africa: Race, Racism and Germs in the Making of the Apartheid State, 1880-1980 (2015). Fabio Terence Palmi Zoia. PhD. Dissertation, Indiana University. Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (1682266398)
there are also a few theoretical texts in social / cultural anthropology that will be frequent touchstones here, including norbert elias's 'the civilising process' (first published 1939) and mary douglas's 'purity and danger' (1966). i don't honestly think it's worth it or necessary to read these directly, both because they're dated in certain ways and because i think the historical studies are generally more useful. but you will probably notice these two texts & a handful of others repeatedly cropping up in introductory footnotes on this topic.
941 notes
·
View notes
Text

twitter thread by Mouin Rabbani
March 14, 2024
Who was there first? The short answer is that the question is irrelevant. Claims of ancient title (“This land is ours because we were here several thousand years ago”) have no standing or validity under international law.
For good reason, because such claims also defy elementary common sense. Neither I nor anyone reading this post can convincingly substantiate the geographical location of their direct ancestors ten or five or even two thousand years ago.
If we could, the successful completion of the exercise would confer exactly zero property, territorial, or sovereign rights.
As a thought experiment, let’s go back only a few centuries rather than multiple millennia. Do South Africa’s Afrikaners have the right to claim The Netherlands as their homeland, or even qualify for Dutch citizenship, on the basis of their lineage?
Do the descendants of African-Americans who were forcibly removed from West Africa have the right to board a flight in Atlanta, Port-au-Prince, or São Paolo and reclaim their ancestral villages from the current inhabitants, who in all probability arrived only after – perhaps long after – the previous inhabitants were abducted and sold into slavery half a world away?
Do Australians who can trace their roots to convicts who were involuntarily transported Down Under by the British government have a right to return to Britain or Ireland and repossess homes from the present inhabitants even if, with the help of court records, they can identify the exact address inhabited by their forebears? Of course not.
In sharp contrast to, for example, Native Americans or the Maori of New Zealand, none of the above can demonstrate a living connection with the lands to which they would lay claim.
To put it crudely, neither nostalgic attachment nor ancestry, in and of themselves, confer rights of any sort, particularly where such rights have not been asserted over the course of hundreds or thousands of years.
If they did, American English would be the predominant language in large parts of Europe, and Spain would once again be speaking Arabic.
Nevertheless, the claim of ancient title has been and remains central to Zionist assertions of not only Jewish rights in Palestine, but of an exclusive Jewish right to Palestine.
For the sake of argument, let’s examine it. If we put aside religious mythology, the origin of the ancient Israelites is indeed local.
In ancient times it was not unusual for those in conflict with authority or marginalized by it to take to the more secure environment of surrounding hills or mountains, conquer existing settlements or establish new ones, and in the ultimate sign of independence adopt distinct religious practices and generate their own rulers. That the Israelites originated as indigenous Canaanite tribes rather than as fully-fledged monotheistic immigrants or conquerors is more or less the scholarly consensus, buttressed by archeological and other evidence. And buttressed by the absence of evidence for the origin stories more familiar to us.
It is also the scholarly consensus that the Israelites established two kingdoms, Judah and Israel, the former landlocked and covering Jerusalem and regions to the south, the latter (also known as the Northern Kingdom or Samaria) encompassing points north, the Galilee, and parts of contemporary Jordan. Whether these entities were preceded by a United Kingdom that subsequently fractured remains the subject of fierce debate.
What is certain is that the ancient Israelites were never a significant regional power, let alone the superpower of the modern imagination.
There is a reason the great empires of the Middle East emerged in Egypt, Mesopotamia, Persia, and Anatolia – or from outside the region altogether – but never in Palestine.
It simply lacked the population and resource base for power projection. Jerusalem may be the holiest of cities on earth, but for almost the entirety of its existence, including the period in question, it existed as a village, provincial town or small city rather than metropolis.
Judah and Israel, like the neighboring Canaanite and Philistine entities during this period, were for most of their existence vassal states, their fealty and tribute fought over by rival empires – Egyptians, Assyrians, Babylonians, etc. – rather than extracted from others.
Indeed, Israel was destroyed during the eighth century BCE by the Assyrians, who for good measured subordinated Judah to their authority, until it was in the sixth century BCE eliminated by the Babylonians, who had earlier overtaken the Assyrians in a regional power struggle.
The Babylonian Exile was not a wholesale deportation, but rather affected primarily Judah’s elites and their kin. Nor was there a collective return to the homeland when the opportunity arose several decades later after Cyrus the Great defeated Babylon and re-established a smaller Judah as a province of the Persian Achaemenid empire. Indeed, Mesopotamia would remain a key center of Jewish religion and culture for centuries afterwards.
Zionist claims of ancient title conveniently erase the reality that the ancient Israelites were hardly the only inhabitants of ancient Palestine, but rather shared it with Canaanites, Philistines, and others.
The second part of the claim, that the Jewish population was forcibly expelled by the Romans and has for 2,000 years been consumed with the desire to return, is equally problematic.
By the time the Romans conquered Jerusalem during the first century BCE, established Jewish communities were already to be found throughout the Mediterranean world and Middle East – to the extent that a number of scholars have concluded that a majority of Jews already lived in the diaspora by the time the first Roman soldier set foot in Jerusalem.
These communities held a deep attachment to Jerusalem, its Temple, and the lands recounted in the Bible. They identified as diasporic communities, and in many cases may additionally have been able to trace their origins to this or that town or village in the extinguished kingdoms of Israel and Judah. But there is no indication those born and bred in the diaspora across multiple generations considered themselves to be living in temporary exile or considered the territory of the former Israelite kingdoms rather than their lands of birth and residence their natural homeland, any more than Irish-Americans today feel they properly belong in Ireland rather than the United States.
Unlike those taken in captivity to Babylon centuries earlier, there was no impediment to their relocation to or from their ancestral lands, although economic factors appear to have played an important role in the growth of the diaspora.
By contrast, those traveling in the opposite direction appear to have done so, more often than not, for religious reasons, or to be buried in Jerusalem’s sacred soil.
Nations and nationalism did not exist 2,000 years ago.
Nor Zionist propagandists in New York, Paris, and London incessantly proclaiming that for two millennia Jews everywhere have wanted nothing more than to return their homeland, and invariably driving home rather than taking the next flight to Tel Aviv.
Nor insufferably loud Americans declaring, without a hint of irony or self-awareness, the right of the Jewish people to Palestine “because they were there first”.
Back to the Romans, about a century after their arrival a series of Jewish rebellions over the course of several decades, coupled with internecine warfare between various Jewish factions, produced devastating results.
A large proportion of the Jewish population was killed in battle, massacred, sold into slavery, or exiled. Many towns and villages were ransacked, the Temple in Jerusalem destroyed, and Jews barred from entering the city for all but one day a year.
Although a significant Jewish presence remained, primarily in the Galilee, the killings, associated deaths from disease and destitution, and expulsions during the Roman-Jewish wars exacted a calamitous toll.
With the destruction of the Temple Jerusalem became an increasingly spiritual rather than physical center of Jewish life. Jews neither formed a demographic majority in Palestine, nor were the majority of Jews to be found there.
Many of those who remained would in subsequent centuries convert to Christianity or Islam, succumb to massacres during the Crusades, or join the diaspora. On the eve of Zionist colonization locally-born Jews constituted less than five per cent of the total population.
As for the burning desire to return to Zion, there is precious little evidence to substantiate it. There is, for example, no evidence that upon their expulsion from Spain during the late fifteenth century, the Sephardic Jewish community, many of whom were given refuge by the Ottoman Empire that ruled Palestine, made concerted efforts to head for Jerusalem. Rather, most opted for Istanbul and Greece.
Similarly, during the massive migration of Jews fleeing persecution and poverty in Eastern Europe during the nineteenth century, the destinations of choice were the United States and United Kingdom.
Even after the Zionist movement began a concerted campaign to encourage Jewish emigration to Palestine, less than five per cent took up the offer. And while the British are to this day condemned for limiting Jewish immigration to Palestine during the late 1930s, the more pertinent reality is that the vast majority of those fleeing the Nazi menace once again preferred to relocate to the US and UK, but were deprived of these havens because Washington and London firmly slammed their doors shut.
Tellingly, the Jewish Agency for Israel in 2023 reported that of the world’s 15.7 million Jews, 7.2 million – less than half – reside in Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories.
According to the Agency, “The Jewish population numbers refer to persons who define themselves as Jews by religion or otherwise and who do not practice another religion”.
It further notes that if instead of religion one were to apply Israel’s Law of Return, under which any individual with one or more Jewish grandparent is entitled to Israeli citizenship, only 7.2 of 25.5 million eligible individuals (28 per cent) have opted for Zion.
In other words, “Next Year in Jerusalem” was, and largely remains, an aspirational religious incantation rather than political program. For religious Jews, furthermore, it was to result from divine rather than human intervention.
For this reason, many equated Zionism with blasphemy, and until quite recently most Orthodox Jews were either non-Zionist or rejected the ideology altogether.
Returning to the irrelevant issue of ancestry, if there is one population group that can lay a viable claim of direct descent from the ancient Israelites it would be the Samaritans, who have inhabited the area around Mount Gerizim, near the West Bank city of Nablus, without interruption since ancient times.
Palestinian Jews would be next in line, although unlike the Samaritans they interacted more regularly with both other Jewish communities and their gentile neighbors.
Claims of Israelite descent made on behalf of Jewish diaspora communities are much more difficult to sustain. Conversions to and from Judaism, intermarriage with gentiles, absorption in multiple foreign societies, and related phenomena over the course of several thousand years make it a virtual certainty that the vast majority of Jews who arrived in Palestine during the late 19th and first half of the 20th century to reclaim their ancient homeland were in fact the first of their lineage to ever set foot in it.
By way of an admittedly imperfect analogy, most Levantines, Egyptians, Sudanese, and North Africans identify as Arabs, yet the percentage of those who can trace their roots to the tribes of the Arabian Peninsula that conquered their lands during the seventh and eighth centuries is at best rather small.
Ironically, a contemporary Palestinian, particularly in the West Bank and Galilee, is likely to have more Israelite ancestry than a contemporary diaspora Jew.
The Palestinians take their name from the Philistines, one of the so-called Sea Peoples who arrived on the southern coast of Canaan from the Aegean islands, probably Crete, during the late second millennium BCE.
They formed a number of city states, including Gaza, Ashdod, and Ashkelon. Like Judah and Israel they existed primarily as vassals of regional powers, and like them were eventually destroyed by more powerful states as well.
With no record of their extermination or expulsion, the Philistines are presumed to have been absorbed by the Canaanites and thereafter disappear from the historical record.
Sitting at the crossroads between Asia, Africa, and Europe, Palestine was over the centuries repeatedly conquered by empires near and far, absorbing a constant flow of human and cultural influences throughout.
Given its religious significance, pilgrims from around the globe also contributed to making the Palestinian people what they are today.
A common myth is that the Palestinian origin story dates from the Arab-Muslim conquests of the seventh century. In point of fact, the Arabs neither exterminated nor expelled the existing population, and the new rulers never formed a majority of the population.
Rather, and over the course of several centuries, the local population was gradually Arabized, and to a large extent Islamized as well.
So the question as to who was there first can be answered in several ways: “both” and “irrelevant” are equally correct.
Indisputably, the Zionist movement had no right to establish a sovereign state in Palestine on the basis of claims of ancient title, which was and remains its primary justification for doing so.
That it established an exclusivist state that not only rejected any rights for the existing Palestinian population but was from the very outset determined to displace and replace this population was and remains a historical travesty.
That it as a matter of legislation confers automatic citizenship on millions who have no existing connection with the land but denies it to those who were born there and expelled from it, solely on the basis of their identity, would appear to be the very definition of apartheid.
The above notwithstanding, and while the Zionist claim of exclusive Israeli sovereignty in Palestine remains illegitimate, there are today several million Israelis who cannot be simply wished away.
A path to co-existence will need to be found, even as the genocidal nature of the Israeli state, and increasingly of Israeli society as well, makes the endeavor increasingly complicated.
The question, thrown into sharp relief by Israel’s genocidal onslaught on the Palestinian population of the Gaza Strip, is whether co-existence with Israeli society can be achieved without first dismantling the Israeli state and its ruling institutions.
258 notes
·
View notes
Photo

(via Krum 🇳🇿🇻🇦 on Twitter: "We do not need to larp as Rome for the British Empire surpassed Rome https://t.co/zyjxBORChL" / Twitter)
1 note
·
View note
Text

How Hadrian’s Wall is Revealing a Hidden Side of Roman History
A party invitation. A broken flipflop. A wig. Letters of complaint about road conditions, and an urgent request for more beer.
It sounds like the aftermath of a successful spring break, but these items are nearly 2,000 years old.
They’re just some of the finds from Hadrian’s Wall – the 73-mile stone wall built as the northwestern boundary of the Roman Empire, sealing off Britannia (modern-day England and Wales) from Caledonia (essentially today’s Scotland).
While most of us think of Pompeii and Herculaneum if we’re thinking of everyday objects preserved from ancient Rome, this outpost in the wild north of the empire is home to some of the most extraordinary finds.
“It’s a very dramatic stamp on the countryside – there’s nothing more redolent of saying you’re entering the Roman empire than seeing that structure,” says Richard Abdy, lead curator of the British Museum’s current exhibition, Legion, which spotlights the everyday life of Roman soldiers, showcasing many finds from Hadrian’s Wall in the process. A tenth of the Roman army was based in Britain, and that makes the wall a great source of military material, he says.
But it’s not all about the soldiers, as excavations are showing.
A multicultural melting pot

Hadrian, who ordered the wall to be built in 122CE after a visit to Britannia, had a different vision of empire than his predecessors, says Frances McIntosh, curator for English Heritage’s 34 sites along Hadrian’s Wall.
“All the emperors before him were about expanding the empire, but Hadrian was known as the consolidator,” she says. He relinquished some of the territory acquired by his predecessor Trajan, and “decided to set the borders” – literally, in some cases, with wooden poles at sites in Germany, or with stone in Britannia. Where those poles rotted thousands of years ago, the wall is still standing: “A great visual reminder” of the Roman empire, says McIntosh.
It’s not just a wall. There’s a castle every mile along, and turrets at every third-of-a-mile point, with ditches and banks both north and south. “You can imagine the kind of impact that would have had, not just on the landscape but on the people living in the area,” says McIntosh.
And thanks to the finds from the wall, we know a surprising amount about those people.
Although historians have long thought of army outposts as remote, male-dominant places, the excavations along the wall show that’s not the case. Not only were soldiers accompanied by their families, but civilians would settle around the settlements to do business. “ You can almost see Housesteads as a garrison town,” says McIntosh. “There were places you could go for a drink and so on.”
The Roman rule of thumb was not to post soldiers in the place they came from, because of the risk of rebellion. That meant Hadrian’s Wall was a cultural melting point, with cohorts from modern-day Netherlands, Spain, Romania, Algeria, Iraq, Syria – and more. “It was possibly more multicultural because it was a focus point,” says McIntosh, who says that the surrounding community might have included traders from across the empire.
Soldiers were split into two groups. Legionaries were Roman citizens from Italy, who had more rights than other soldiers and imported olive oil, wine and garum (a sauce made from decomposing fish).
They worked alongside auxiliaries – soldiers from conquered provinces, who had fewer rights, but could usually acquire citizenship after 25 years of service.

Soldiers carved their names and regiments on stones to show which part of the wall they built – around 50 of them are on display at Chesters fort.
But the wall shows that women and children were equally present.
McIntosh says that pottery brought to the camps – from the Low Countries and North Africa – shows that the soldiers “brought their families, who cooked in traditional style.��� Archaeologists have found what seems to be an ancient tagine for North African-style cooking.
A tombstone from Arbeia fort for a woman named Regina shows she was a freed slave from southern Britain who was bought by – and married to – a Syrian soldier.
Another woman buried at Birdoswald fort was laid to rest with chainmail that appears to be from modern-day Poland. “Perhaps she married someone in the army,” says McIntosh, who calls the wall a “melting pot of people from all over the world under the banner of the army.”
“They brought their own religions, as well as worshipping Roman gods and adopting local deities,” she adds. At Carrawburgh, a temple to Mithras – an originally Persian deity – sat near a spring with a shrine to a local water spirit.
‘Wretched little Brits’

Some of the most extraordinary finds from the Roman empire are coming from one site on Hadrian’s Wall: Vindolanda. Here, archaeologists have found a wealth of organic remains because of what curator Barbara Birley calls the “unusual conditions onsite.”
At Vindolanda there are the remains of at least nine forts over 14 levels. “When the Romans would leave, they would knock down timber forts, and cover the area with turf and clay, sealing the layers underneath,” she says.
“Because it happened so many times, the bottom five or six layers are sealed in anaerobic conditions, so things don’t decay. When we get down there, we get wooden objects, textiles, anything organic.”
Vindolanda has the largest collection of Roman textiles from a single site in western Europe, as well as the largest leather collection of any site in the Roman empire – including 5,000 shoes, and even a broken leather flip-flop. “We probably had a population of 3,000 to 6,000 depending on the period, so 5,000 is a lot,” says Birley. For Abdy, the shoes evoke the conditions of the wet borderlands. “Women’s and children’s shoes are hobnailed – you needed it in the mucky frontier dirt tracks. They’re very evocative.”
There’s even a wig made from a local plant, hair moss, which is said to repel midges – the scourge of Scotland during the summer. A centurion’s helmet is also crested with hairmoss – the ancient equivalent of spraying yourself with insect repellent.
The first woman to write in Latin

One of the most famous finds is the trove of wooden writing tablets – the largest found anywhere.
“They give a snapshot of what life was actually like,” says Birley. “We understand so much more from written correspondence than from ‘stuff,’ and, archaeologically, it’s the stuff that usually survives – things like metals and ceramics.
“These were written in ink, not on a wax stylus tablet, and we believe they were used for what we’d put in emails: ‘The roads are awful,’ ‘The soldiers need more beer.’ Everyday business.”
The tablets – or “personal letters” as Birley describes them – were found on the site of a bonfire when the ninth cohort of Batavians (in the modern-day Netherlands) were told to move on.
“They had a huge bonfire and lots of letters were chucked in the fire. Some have been singed – we think it may have rained,” she says. One of them calls the locals “Britunculi” – “wretched little Brits.” Another talks about an outbreak of pinkeye. One claims that the roads are too bad to send wagons; another laments that the soldiers have run out of beer.

Among the 1,700 letters are 20 that mention a woman called Sulpicia Lepidina. She was the wife of the commander of the garrison, and seems to have played a crucial role. There’s a letter to her from another woman, Paterna, agreeing to send her two medicines, one a fever cure.
Birley says it’s similar to today. “If you’re a group of moms, still today we say, ‘Do you have the Calpol?’ It’s very human.” For Abdy, it’s a sign that women were traders. “She’s clearly flogging her medicines,” he says. “It’s really great stuff.”
Another tablet is an invite from Claudia Severa, the wife of another commander at a nearby camp. It’s an invitation to a birthday party. Under the formal invitation, presumably written by a scribe, is a scrawl in another hand: “I shall expect you, sister. Farewell, sister, my dearest soul.”

Presumably written by Claudia herself, it is thought to be the earliest example of a woman’s handwriting in Latin.
Without the organic finds – the shoes and the letters that indisputably belonged to women, unlike jewellery or weaving equipment – it’s difficult to prove conclusively that women lived in significant numbers. Vindolanda “illustrate the missing gaps,” says Abdy.
For Birley, they prove that women were as crucial a part of army communities as men. “Before the Lepidina tablets were found we didn’t really understand the interactions between the soldiers and their wives,” she says. Another tablet is written by what is thought to be a Spanish standard-bearer’s common-law wife, ordering military equipment for her partner.
“The Vindolanda collection is showing that there weren’t just camp followers and prostitutes; women were part of everyday life, and contributing to the military community in many ways,” says Birley.


Abdy says that Hadrian’s Wall is interesting because the resident women span “all classes of society,” from Regina – the dead freedwoman, who would have been “bottom of the heap” – to the trader Paterna and the noblewoman Lepidina.
And of course, there’s the wall itself.
“In the Netherlands and Germany the finds are often stunning and better preserved – you go to museums and are bowled over. But in terms of structural remains, Hadrian’s Wall must be among the best,” says McIntosh, modestly, of her site.
Abdy agrees: “I can’t think of many symbols so redolent of imperial will than that wall.”
By Julia Buckley.
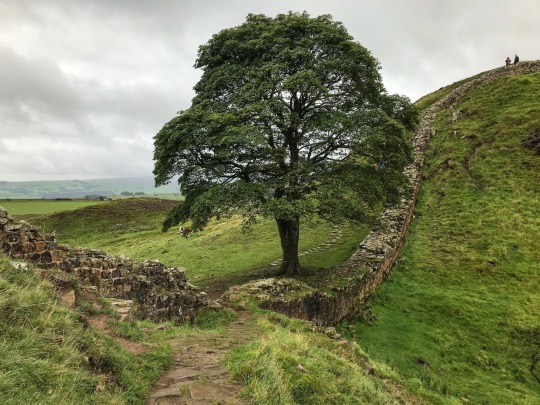

#How Hadrian’s Wall is Revealing a Hidden Side of Roman History#Hadrian’s Wall#emperor hadrian#northwestern boundary of the Roman Empire#Britannia#Caledonia#roman legions#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire#long post#long reads
110 notes
·
View notes