#the Battle of Marengo
Text
So I'm a few days late, work and life and stuff got the best of me, but I made some belated Chicken Marengo

14 notes
·
View notes
Text

#napoleon bonaparte#napoléon bonaparte#marengo#horse#art#napoleon#bonaparte#napoléon#history#battlefield#battle#napoleonic#napoleonic wars#europe#european#france#french#general#moon
259 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon’s letter the day after the death of Desaix

“The news of the army is very good. I shall soon be in Paris. I cannot tell you more; I am in the deepest sorrow at the death of the man I loved and esteemed the most.”
— Napoleon
Source: Letters and Documents of Napoleon by J. E. Howard
#Louis Desaix#J. E. Howard#Howard#desaix#Letters and Documents of Napoleon by J. E. Howard#napoleon#napoleonic era#napoleonic#napoleon bonaparte#first french empire#19th century#french empire#Marengo#battle of Marengo#history#france#french revolution#frev#la révolution française#révolution française#2nd coalition#consulate#consul#first consul#quotes by Napoleon#Napoleon quotes#french history
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

From a letter Eugène de Beauharnais wrote to his sister on 3 Messidor an VIII (22 June 1800), a couple of days after the battle of Marengo. He's on his way home, like the rest of the French troops, and tells his sister that Murat feels depressed.
[Transcription and translation to the best of my abilities.]
Murat est bien triste, il n'a pas reçu une lettre de sa femme depuis qu'elle l'a quitté. C'est affreux à Caroline si elle est dans son tort. Je le console du mieux que je peux mais c'est une entreprise un peu difficile.
Murat is very sad, he hasn't received a single letter from his wife since she left him. It's terrible for Caroline if she's in the wrong. I'm consoling him as best as I can, but it's a rather difficult business.
Considering that Hortense and Caroline were close friends and Hortense surely would tell her, I assume Eugène probably wrote this in order to get the message to Caroline and to warn her about Murat's state of mind. I also assume that this was merely a case of delayed mail during wartimes, and of Murat being overly emotional as was often the case.
#napoleon's marshals#joachim murat#napoleon's family#eugene de beauharnais#hortense de beauharnais#caroline murat#milan 1800#battle of marengo
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
No one:
Absolutely no one:
Not even the soldiers randomly eating onions at Marengo:
Napoleon: "THERE'S NOTHING BETTER TO EAT WHEN YOU ARE PLANNING TO STEP ON THE PATH OF GLORY"
Well I plan to illustrate this scene. At least someday.
#Napoleon#dear#you are really too much intense for you army's sake#they created a whole iconic song about how much fried onions are good#they really loved him#from Marengo I personally prefer the chicken#I sincerely don't know if it's known outside of Italy#but here there's a chicken-based dish called because that's what Napoleon ate during the battle#pollo alla marengo#chanson de l'oignon#one would say that Marengo was all just a stormy Masterchef episode#j'aime l'oignon frit à l'huile#j'aime l'oignon car il est bon#au pas camarades
18 notes
·
View notes
Text




Account of the Battle of Marengo presented to the Emperor on the field of battle by Marshal of the Empire Alexandre Berthier. I don’t know whether this is the battle of Marengo or whether they are interrupting him at some other battle to present him with this lovely map. The guy is holding a marshal’s baton and there were no marshals at Marengo.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon the Great :: Andrew Roberts

View On WordPress
#978-1-8461-4027-3#austerlitz#battle borodino#battle marengo#books by andrew roberts#brumaire#campaign#confederation rhine#elba#emperors france#first french empire#french emperor#french emperors#french history#french kings#french rulers#french statesmen#history france#marengo#napoleon i#napoleonic france#napoleonic wars#polish campaigns#st helena#syrian campaigns#waterloo
1 note
·
View note
Text
Happy Julius Caesar gets stabbed day! Here’s a Les Mis take on the subject, courtesy of Grantaire’s Drunken Rambles:
Whom do you admire, the slain or the slayer, Cæsar or Brutus? Generally men are in favor of the slayer. Long live Brutus, he has slain! There lies the virtue. Virtue, granted, but madness also. There are queer spots on those great men. The Brutus who killed Cæsar was in love with the statue of a little boy. This statue was from the hand of the Greek sculptor Strongylion, who also carved that figure of an Amazon known as the Beautiful Leg, Eucnemos, which Nero carried with him in his travels. This Strongylion left but two statues which placed Nero and Brutus in accord. Brutus was in love with the one, Nero with the other. All history is nothing but wearisome repetition. One century is the plagiarist of the other. The battle of Marengo copies the battle of Pydna; the Tolbiac of Clovis and the Austerlitz of Napoleon are as like each other as two drops of water. I don’t attach much importance to victory. Nothing is so stupid as to conquer; true glory lies in convincing. But try to prove something! If you are content with success, what mediocrity, and with conquering, what wretchedness! Alas, vanity and cowardice everywhere. Everything obeys success, even grammar. Si volet usus, says Horace. Therefore I disdain the human race.
261 notes
·
View notes
Text


Napoleonic era French light cavalry officers' sabre with the à la Marengo style hilt
This style of sabre hilt, with the rounded langets and semi-S shaped guard. Is one of two types that are associated with the la Marengo type. The other has a similar cross guard but a pommel cap that bends towards the knuckle bow, decorated with a lions' face.


These styles are said to have gained popularity following Consular Napoleon's victory over the Austrians in Jun 1800 at the Battle of Marengo. French sword cutlers purportedly drew their inspiration from the sabre carried by Napoleon during the campaign.
It has been claimed that only officers who had participated in the battle were permitted to carry this style of hilt, however this is unlikely to have been true, given the number of surviving examples.
This sword carries a Solingen made 'export' blade with generic engraving that would originally have been highlighted in gold on a background of blue.


Stats:
Overall Length - 935 mm
Blade Length - 795 mm
Curve - 54 mm
Point of Balance - 140 mm
Grip Length - 125 mm
Inside Grip Length - 105 mm
Weight - 700 grams
#swords#sabre#Napoleonic era#military antiques#antiques#sabres#cavalry swords#military#19th Century#Light cavalry#French military
71 notes
·
View notes
Photo

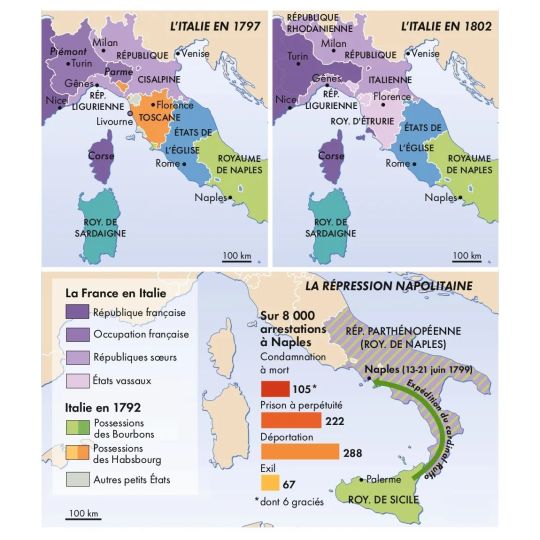

Italy from 1796 to 1805
Cartes 1-4 & 6 : « Atlas de la révolution française », Beaurepaire & Marzagalli, Autrement, 2016
Carte 5 : « Atlas de l’empire napoléonien », Chappey & Gainot, Autrement, 2e éd., 2015
by cartesdhistoire
The incursion of Bonaparte's army into Italy in the spring of 1796 was primarily a diversion to relieve pressure on the Rhine front. However, its success quickly opened up new possibilities: French support and the activism of local patriots led to the establishment of sister republics. Over three years (1796-1799), known as the Triennio, the political landscape and institutions of the peninsula underwent significant changes. This period, marked by reforms and democratic achievements, as well as the involvement of individuals previously excluded from public affairs, is crucial for understanding how the Triennio influenced the attitudes of both elites and the general populace during and after the Napoleonic era.
However, the sister republics collapsed in the spring of 1799 in the face of the successes of the Austro-Russian armies of the Second Coalition and the armed uprisings of peasants incited by the clergy and angered by French abuses. Naples surrendered in June 1799, and the repression there was severe.
The political landscape of the peninsula was once again reshaped by France following the Second Italian Campaign, which began in 1800. The Cisalpine Republic, reinstated after the Battle of Marengo and expanded during the Peace of Lunéville, gave way to the Italian Republic in 1802, then became a kingdom in 1805. The kingdom's territory expanded to include Veneto and Istria (1805), the Marche region (1808), and South Tyrol (1810). Thanks to the Vice-President of the Italian Republic, Francesco Melzi d'Eril, the political efforts during these years resulted in the establishment of a modern state and significant reforms in administration, justice, and the military.
The Napoleonic experience helped to politically educate the Italian elites, providing them with a shared institutional and legal framework, as well as standardized administrative practices, which made the idea of unity feasible.
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
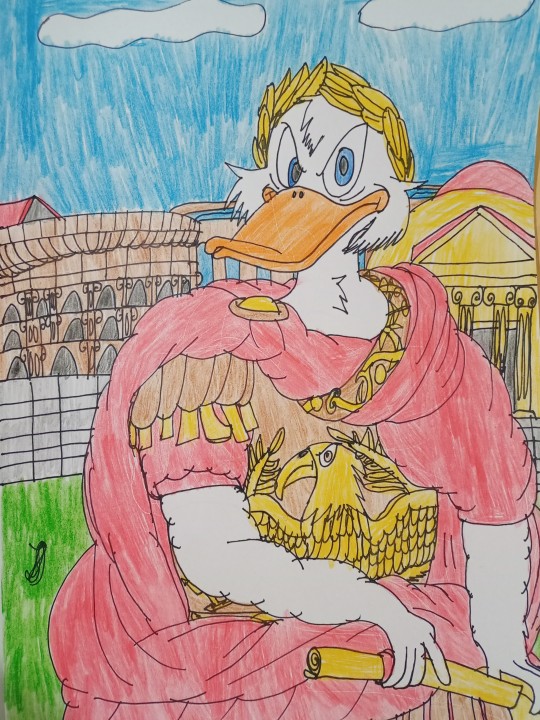
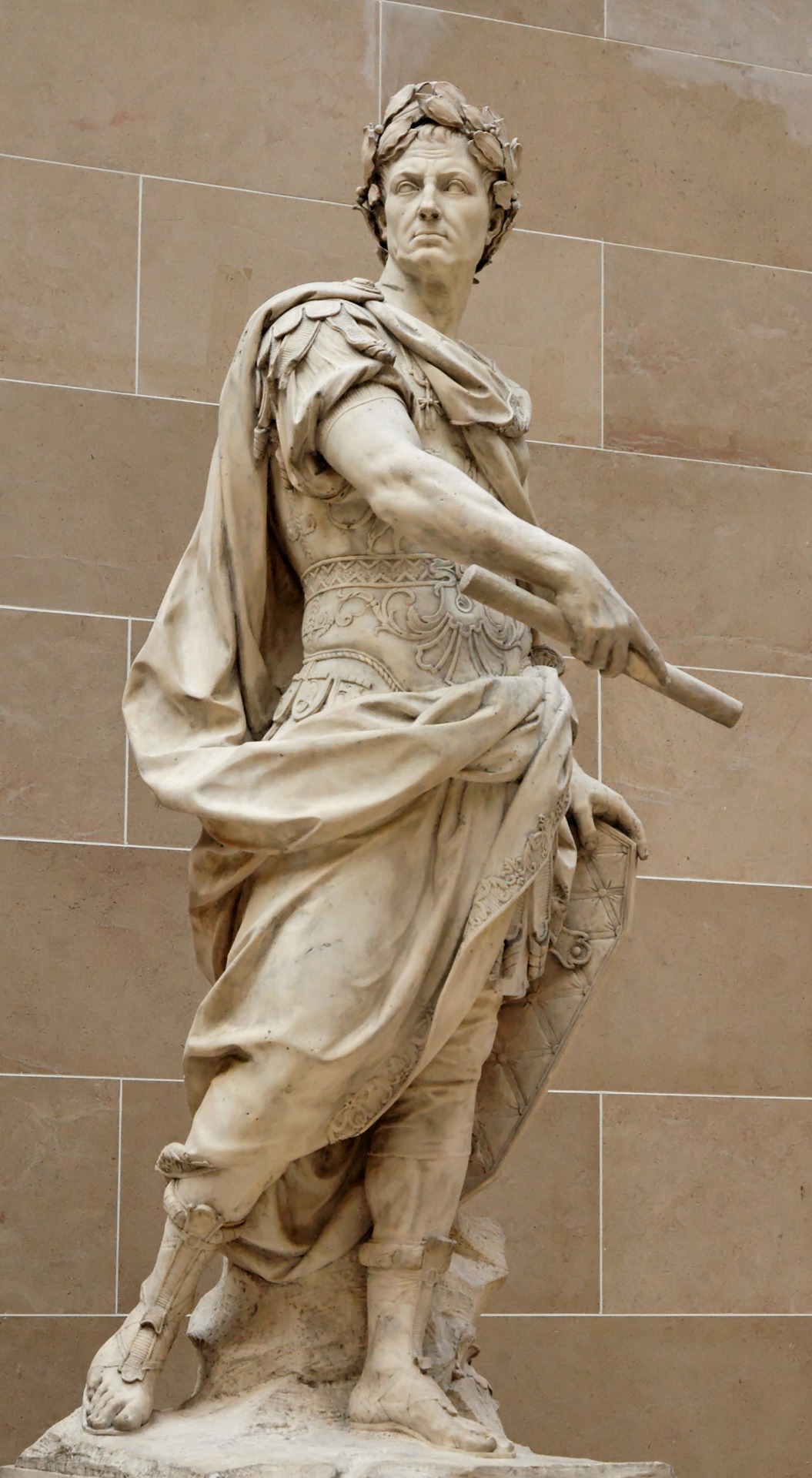
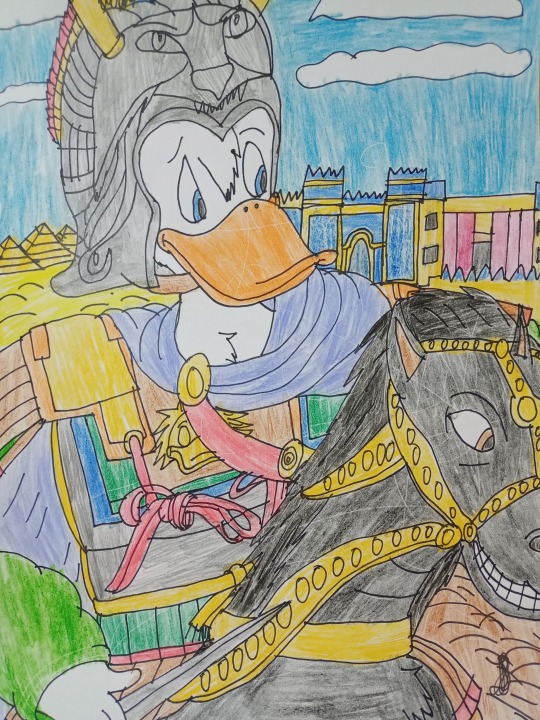









Donald Duck as Napoleon Bonaparte, Scrooge McDuck as Gaius Julius Caesar and Louie Duck (Quack Pack) as Alexander the Great - Conquerors - Real Ducks in History - History in Duckverse
I've always wanted to do a special project called Duckverse in History and my plan is to draw my favorite characters as redraws from famous works of art as well as famous historical figures. And since history is my favorite science, and my favorite field, I definitely wanted to do something related to it and related to one of my favorite historical characters. Since I don't want to complicate the situation, I will gradually publish a drawing related to that historical figure from time to time. I started this last year for Duckvember only to finish at the end of last month.
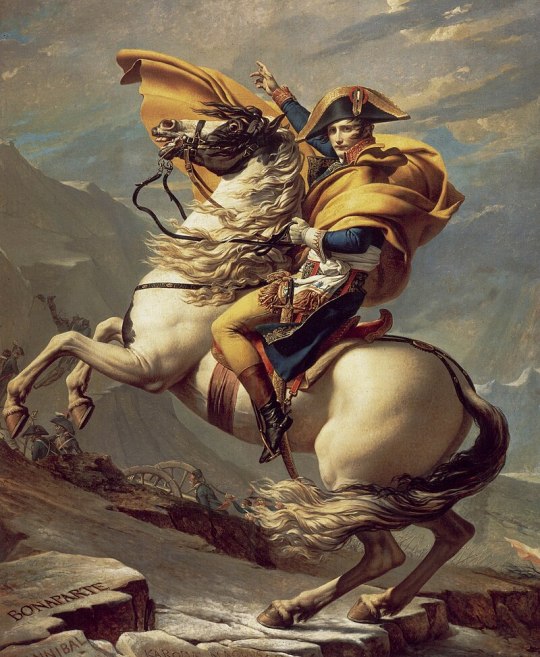
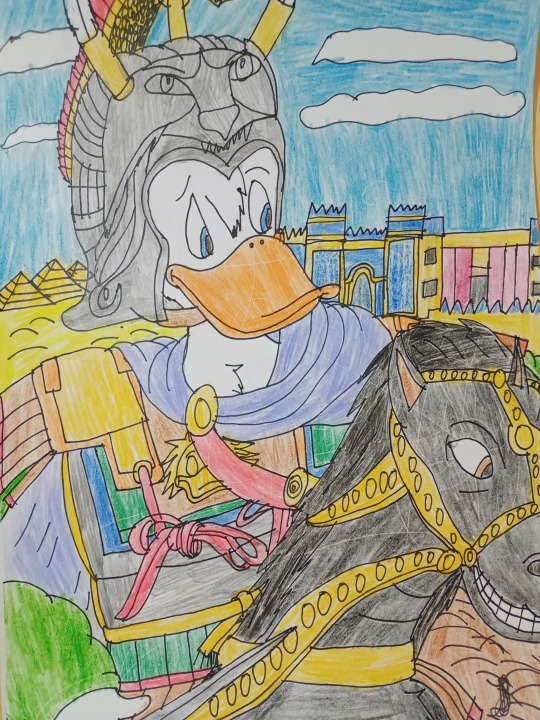
The first drawing is a redraw from Jacques Louis David's famous early 19th century artwork depicting Napoleon Bonaparte crossing the Alps in 1800 before the Battle of Marengo. Napoleon Bonaparte was the most famous French military leader, general, consul and emperor who waged war with all of Europe at the time and managed to subjugate it in its entirety except for the Ottoman Empire, Russia and Great Britain. He is from Corsica, but he left a lot for France and proved that France is not worth messing with easily. He also gave many reforms and his Civil Code which spread throughout Europe and brought order in France after the French Revolution. Napoleon's nature is very similar to Donald Duck and I drew Donald as Napoleon since he was created for that role and I drew him riding his horse Marengo in my own style, but in a realistic way and that Donald has five fingers.
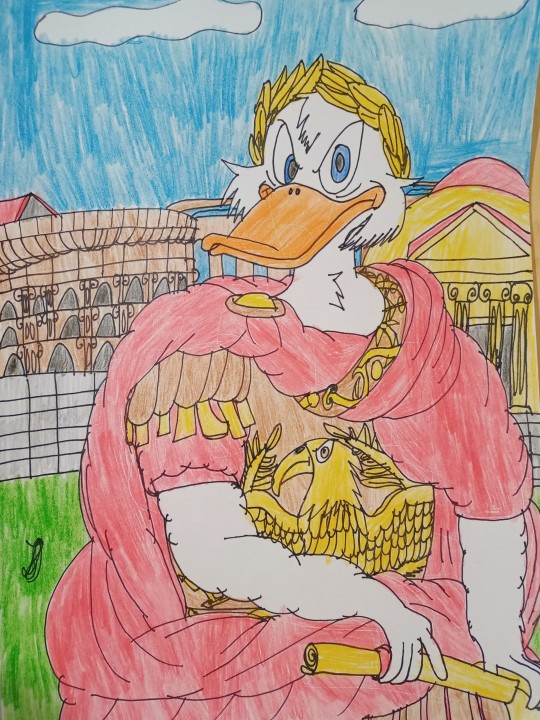
The second drawing is a redraw of a statue made by Nicolas Coustou at the end of the 17th century for the decoration of Versailles, which depicts the greatest Roman, Gaius Julius Caesar. Although he was not an emperor, certainly many presented him, but he was a dictator, consul, general, writer, historian, engineer, constructor, and a great military leader who changed the Roman Republic into an almost Roman Empire. His fights against the Gauls, as well as the conflict with Pompey and his love with Cleopatra, are known, but he also changed a lot in Rome and was extremely rich. And he lived during the first century BC. That's why I drew Scrooge McDuck as Gaius Julius Caesar since Scrooge is a great leader and he also strived for fame and fortune and to be remembered in the future and he plays the role of the best Roman. Behind it are the Colosseum (built a century after him), the aqueduct (then irrigation) and the Pantheon (built two centuries after him), as well as a Roman temple that symbolizes Rome at that time, as well as the roads themselves. In addition, Topolino (Italian comics) are showed Scrooge as Caesar two or three times so that's where my inspiration came from.
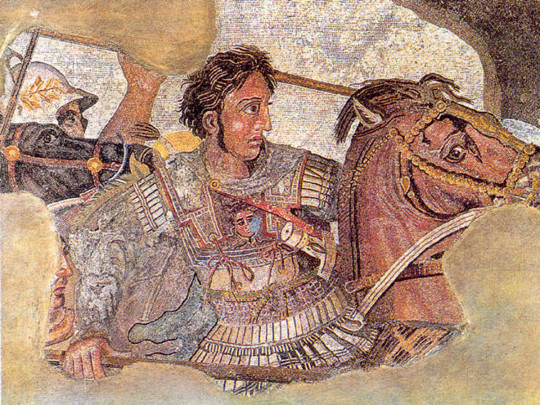
The third drawing shows Louie Duck (the Quack Pack version, not the Ducktales reboot) shows Alexander the Great, another brilliant conqueror from the fourth century BC and I drew it as a redraw from the mosaic of Alexander the Great from the battle of Issus in which he confronts the Persian king Darius III from Pompeii, probably from the first century BC. Alexander the Great was the son of Philip II and the king of Macedonia who united Greece and fought against Persia and managed to conquer an entire empire in his twenties. He traveled through the Persian Empire and reached India and wanted to continue, but his soldiers did not want to continue, so he returned to Babylon, his new capital. He certainly changed the world at that time and introduced a new culture, called Hellenism, as a combination of ancient Greek culture and the culture of the Ancient East and ancient India. I drew Louie as Alexander because as a young man he is a great adventurer and rides his black horse Bucephalus and is eager for extremes, yet unlike Alexander, Louie shows a bit of his shyness, but is still brave enough to take on new challenges. I also added a helmet as worn by Alexander III in his time. Behind Louie are the pyramids from Egypt, the Ishtar Gate from Babylon and the imperial palace from Persepolis where the Persian rulers lived and it actually shows the lands that Alexander the Great conquered.
I certainly hope you like these drawings and these ideas and that these characters have such historical roles. Of course, Duckverse in history I combine mostly everything related to Duckverse (Donald Duck comics, OG Ducktales, Three Caballeros, Darkwing Duck and Quack Pack) and it's mostly my version and my idea. By all means if you like this and support these ideas, feel free to like and reblog this, but please don't use these same ideas without mentioning me and without my permission. Thank you!
#my fanarts#traditional art#artists on tumblr#donald duck#history#duckverse#ducktales#napoleon bonaparte#gaius julius caesar#alexander the great#scrooge mcduck#louie duck#quack pack#disney ducks#duckverse in history#disney duck comics#rome#france#topolino#greece#disney duckverse#quack pack au#art#my redraws#the conquerors#my fanart#comics#cartoons#my style#julius ceaser
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy Chicken Marengo Day!
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
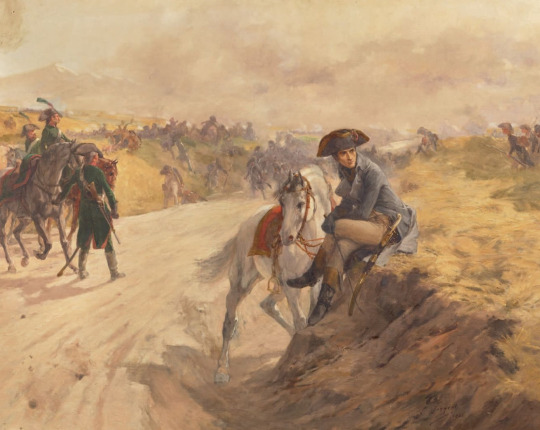

Battle scene around a road, with General Bonaparte seated on an embankment near his white horse in the foreground.
by Lucien-Pierre Sergent
#napoleon bonaparte#napoléon bonaparte#battle#scene#horse#marengo#art#lucien pierre sergent#france#europe#european#history#napoleonic#general#napoleon#napoléon#bonaparte#napoleonic wars#french revolutionary wars#landscape#italy
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon when Desaix showed up at Marengo with reinforcements:
#Napoleon#Desaix#Louis Desaix#napoleon bonaparte#napoleonic memes#Napoleon memes#napoleonic era#napoleonic#first french empire#history memes#vid#video#french empire#france#history#lol#Marengo#war of the 2nd coalition#battle of Marengo
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Battle of Marengo
… as described by one Eugène de Beauharnais in his memoirs. For context: Eugène, aide-de-camp to general Bonaparte, had left Egypt with his stepfather, in Paris had helped to reconcile his mother with general Bonaparte and assisted (according to his memoirs, without completely understanding what was going on) at the coup d’état of 19th Brumaire. However, once Bonaparte had become First Consul, Eugène gave up his post as ADC, as soon as it dawned on him that this job from now on would mostly consist of hanging out in an antechamber and politely introducing guests to the head-of-state of France. Having decided that this was totally uncool, he had gone back to the military. At the time of the second Italian campaign, he was an 18-year-old capitaine de la Garde des Consuls, commanding a compagnie of chasseurs à cheval.
We’re starting the relation a bit before Marengo, with the entry into Milan, as Eugène claims to have met Desaix there one last time.
I assisted at the combat of Buffalore, commanded by general Murat, who showed great vigour in this crossing of the Tésin [Ticino]; the enemy was pushed briskly up into Milan, where we entered in a jumble with his light troops. I made with my company a rather fine charge to force the enemy, who still held the field, to return to the citadel of Milan.
We remained three days in Milan, where the First Consul was occupied in reorganising the republican government; after which we proceeded to Pavia. General Lannes had made the crossing of the Po, about a league below this city. General Desaix had just arrived from Egypt and joined the army at Pavia, at the very moment when the First Consul left; as the troops of the guard were not to cross the Po until the night, I had time to go and see him. As a companion in arms from Egypt, we were delighted to meet again, and general Desaix treated me very well. He spoke to me much about the campaign which was opening and the command which he hoped to obtain; it seemed, moreover, that he foresaw his imminent end, for he uttered this singular statement : "Formerly, the Austrian bullets knew me, I am afraid that they may not recognize me any more."
We crossed the Po during the night, and the next day I was sent with my company, by Stradella, in the direction of Piacenza, to establish communication with general Murat, who had crossed the Po at this point and had effectively seized this city. The next day the affair of Montebello took place, which did so much honour to General Lannes; but I arrived too late to take part in it. The following evening, we pushed in the direction of Alexandria as far as Marengo, where there was a small combat to force the enemy to pass again the Bormida and to abandon this line. The day was very stormy and we had much difficulty in passing the Scrivia whose waters had become very rough. I witnessed the reports which several officers came to make, in the evening, to the first consul, at his bivouac. All agreed in saying that the enemy was withdrawing in haste and that he had broken all his bridges on the Bormida. The first consul had it repeated several times to be more sure, and it was in consequence of these false reports that he directed on Genoa the corps of troops of which he had just given the command to general Desaix in order to lift the siege of this important place, if there was still time.
But, the next morning, when a heavy cannonade was heard on the side of Alexandria, we were quickly drawn out of our error. Soon the first consul learned that the enemy was emerging in force on the plain of Alexandria, and that a great battle was inevitable. One can estimate the anxiety of the general in chief and the anger which he felt at the false reports which had been made to him the day before. Orders were dispatched in all haste to recall general Desaix, who was found near Novi, and who, in spite of this distance, still arrived in time to take part in the action and to decide the winning of the battle. I mentioned this circumstance because it exonerates the first consul from the reproach of improvidence which was made to him in several reports of the battle of Marengo. Those who have had great military commands know what the fate of battles depends on, and how an unforeseeable accident can disturb the best and most skilful combinations.
Our movement of retreat began towards midday and continued until four o'clock; it is during this time that the guard began to take a more active part in the affair. The troops of the line were tired and discouraged; the first consul sent us to support them; we carried ourselves sometimes on the left, sometimes on the right, according to the need; general Lannes, pressed a little sharply by the enemy, wanted to have us make a charge which did not succeed; he had in front of him two battalions and two pieces of artillery behind which was a mass of cavalry in close columns; his troops withdrew in disorder, so that, to give them time to breathe and to rally them, he ordered colonel Bessières, who commanded us, to charge on the enemy column. The terrain was not very favourable, because it was necessary to cross vineyards; nevertheless we passed and arrived within rifle range of these two battalions, which awaited us arms in hand and in the best of spirits. Colonel Bessières, having drawn us up, was preparing to command the charge, when he realised that the enemy cavalry was deploying on our left and was going to turn us. Consequently, he made us turn back to the left, and we crossed the vineyard under the fire of grapeshot and musketry; but, having arrived on the other side, we held our ground well enough to impose on the enemy cavalry. General Lannes was very dissatisfied with this operation and complained bitterly about it. However it is probable that, if we had carried out his orders, few of us would have returned. During the retreat, my chasseurs were charged with destroying the ammunition which we were forced to abandon, and performed this mission with great intrepidity, often waiting until they were joined by the enemy to set fire to the caissons and then jump on horseback.
Finally, towards five o'clock, General Desaix joined us, and the First Consul was able to resume the offensive. The troops of General Lannes, encouraged by this reinforcement, reformed, and soon the offensive began as well as the retrograde march of the enemy. The cavalry of General Kellermann made a very beautiful charge on our left, and, towards the evening, the cavalry of the guard made one not less brilliant. Although the ground did not favour us, since we had two ditches to cross, we rushed with vigour on a column of cavalry much more numerous than us, at the moment when it was deploying; we pushed it up to the first bridges over the waters of the Bormida, always sabering. The melee lasted ten minutes: I was happy enough to get away with two sabre blows on my chabraque. The following day, the first consul, on the account which was given to him of this affair, appointed me squadron leader. My company had suffered quite a bit, because, of one hundred and fifteen horses which I had in the morning, I had only forty-five left in the evening; it is true that a piquet of fifteen chasseurs had remained near the first consul, and that many chasseurs, dismounted or slightly wounded, returned successively.
The day after this battle (June 15, 1800), an armistice was concluded as well as an agreement for the evacuation of Italy; the first consul returned on the 16th to Milan, from where we were at a distance of forty Italian miles; I was charged to escort him from the battlefield to Milan, by following the post. This race, of more than twelve leagues always at the trot and without unbridling, was so tiring, that I arrived at Milan with only seven men.
I hope this is helpful to anyone who’s interested.
#napoleon's family#eugene de beauharnais#Jean-Baptiste Bessières#jean lannes#louis desaix#Battle of Marengo#italy 1800
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Pope Saint Pius V
1504-1572
Feast Day: April 30 (New), May 5 (Trad)
Patronage: Bosco Marengo, Italy
Pope from 1566-1572
Saint Pope Pius V, a Dominican, was a leader of the Catholic Reformation, especially by implementing the Council of Trent reforms. He established a Catechism, a missal, a seminary system, used a Tridentine approach to learning and preaching, had a residency requirement for Bishops and reformed women’s religious life. This formed the foundation of the Catholic Church for the next 500 years. In 1571, St. Pius V was instrumental in gathering a coalition of nations and petitioning prayers of Our Blessed Mother to save Europe from the Islamic Ottoman Turks at the Battle of Lepanto. He declared Mary as Our Lady of Victory because of this decisive battle. He died of natural causes.
Prints, plaques & holy cards available for purchase here: (website)
18 notes
·
View notes