#writing JSX code
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Purecode | Adhering to these best practices for writing JSX code
Adhering to these best practices for writing JSX code can significantly improve the development experience and outcome of your React projects. By keeping components small, ensuring proper tag closure, using camelCase for properties, and applying other recommended strategies, you create a foundation for clean, efficient, and maintainable code.
#writing JSX code#clean#efficient#and maintainable code.#React Project#purecode#purecode ai company reviews#purecode ai reviews#purecode software reviews#purecode company#purecode reviews
0 notes
Text
i wanna fling someone off a roof cause all this escalation from michael's parents was "what will the extended family think"
and now that it's just a week and a half out from the wedding and they have relatives asking them "oh a western style wedding how unique" they're acting NORMAL again are you kidding me are you FUCKING KIDDING ME?????????
so we had to deal w/ 18 months of actually demented behavior for WHAT??????? what was this all for?????? we had to book this out 18 months in advance to not have to spend an extra 10k, but was 10k usd worth this stupidity
"oh if you work it looks bad", "actually wait... now that people know where u work they respect us" UH DUH??? DUH???????? DUH??????? are you fucking kidding me duhhhh???? duh? you could have avoided the whole ass "it looks poor for our dil to work" shitfit, and a few dozen schemes to get me to quit, if you had listened to that... i work at [redacted] corporate on the art/product development team and not at the [redacted] store.....and hadn't told family i was refusing to quit my job at the [redacted] /store/.... FOR FUCKS SAKE i had a ft art job that paid well......literally before i graduated? i had it lined up before i graduated, other than 6 months during lockdowns i've worked in art since 2 days before my graduation date
can i bite people??????????? i really want to start biting? we won't get an apology out of these freaks but umm WHAT THE FUCK?
"what will the relatives think" well acshually... the relatives are like "uhmmm my daughter wants to go to school for animation or graphic design can you tell her what you did to actually get work?"
#personal#i mean i rlly don't know how it's THAT hard to understand that i have like.... a LOT of people's dream job???????#and that i'm paid well..... and my job is incredibly flexible hybrid with good insurance#AND it's practically recession proof cause americans get weird about sports during economic downturns lol#AND shit i've worked on is in nearly every country... including a few tees that i did more creative work on (nooooot ttttt my fave#at first i was like... hmmm kinda grumpy im not in a creative role... now i'm like... creative role makes me anxious i'll write more code t#automate stuff for factories lol (jsx scripting for ai/indd/ps for the win))#still find it soooo weird the like first restaurant we went to in sweden there was boy wearing a shirt i did the print prodution work on#it's gonna happen in japan in march too lol cuz at work we do the production for one tokyo team
0 notes
Text
Mini React.js Tips #4 | Resources ✨

Continuing the #mini react tips series, one of the important things I wanted to learn QUICK was how to add new CSS files to my project correctly. I am an SCSS > CSS person, but the guide will focus on CSS for now! Next, I will make a guide for SCSS/SASS files~!
What you'll need:
know how to create a React project >> click
know the default React project's file structure >> click
know how to create a component >> click
know basic CSS
basic knowledge of using the Terminal

[ 1 ] Navigate to the src folder: The src folder is where you will find the 'assets' folder, .jsx files, and .css files.
[ 2 ] Create your .css file: In the src folder, create the .css file. You can create a subfolder to place the new .css or just leave it in the src folder. Example 'main.css'
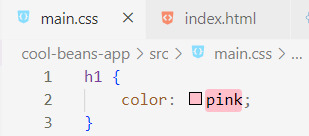
[ 3 ] Add the styling: In the new file, add the styling code inside for elements in your React app. Here we are going to target the h1 tag in the Header component.
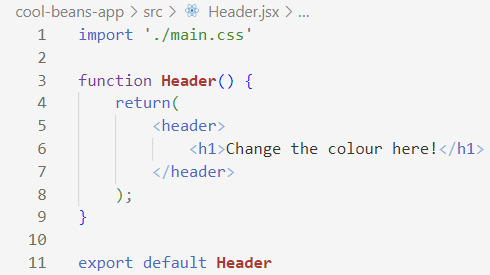
[ 4 ] Import the CSS file to the component file: Personally, if it's not a global CSS styling but specifically for a component, I will import the CSS straight into the component's .jsx file. If it's global, I would add it in the App.jsx file instead. At the top of the file, add:
import './[location of the CSS file]'
[ 5 ] Run the Development Server: Start your development server with the command in the Terminal (the 'Local' link) + make sure your component is in the App() in App.jsx:
npm run dev
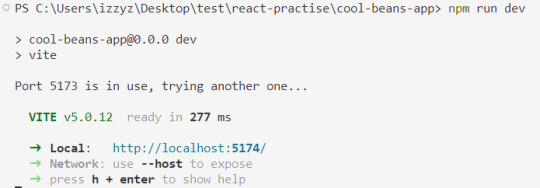
[ 6 ] View the changes: See if you can view your styling!


Congratulations! You've successfully added CSS files to your React project! Try adding more styling to the same component or globally across all your other components!
If you run into errors, do make sure your referencing to the CSS file's location is correct. Adding './' in front is important before adding the location of the CSS file. I ran into a lot of errors because of this for some reason?? :
'./styles.css' = correct
'styles.css' = incorrect
Resources:
BroCode's 'React Full Course for Free' 2024 >> click
Different Ways to Write CSS in React >> click
W3School's Styling React Using CSS >> click
React Official Website >> click
🐬Previous Tip: Tip #3 Creating A Component >> click
Stay tuned for the other posts I will make on this series #mini react tips~!
#mini react tips#my resources#resources#codeblr#coding#progblr#programming#studyblr#studying#javascript#react.js#reactjs#coding tips#coding resources
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good Code is Boring
Daily Blogs 358 - Oct 28th, 12.024
Something I started to notice and think about, is how much most good code is kinda boring.
Clever Code
Go (or "Golang" for SEO friendliness) is my third or fourth programming language that I learned, and it is somewhat a new paradigm for me.
My first language was Java, famous for its Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) paradigms and features. I learned it for game development, which is somewhat okay with Java, and to be honest, I hardly remember how it was. However, I learned from others how much OOP can get out of control and be a nightmare with inheritance inside inheritance inside inheritance.
And then I learned JavaScript after some years... fucking god. But being honest, in the start JS was a blast, and I still think it is a good language... for the browser. If you start to go outside from the standard vanilla JavaScript, things start to be clever. In an engineering view, the ecosystem is really powerful, things such as JSX and all the frameworks that use it, the compilers for Vue and Svelte, and the whole bundling, and splitting, and transpiling of Rollup, ESBuild, Vite and using TypeScript, to compile a language to another, that will have a build process, all of this, for an interpreted language... it is a marvel of engineering, but it is just too much.
Finally, I learned Rust... which I kinda like it. I didn't really make a big project with it, just a small CLI for manipulating markdown, which was nice and when I found a good solution for converting Markdown AST to NPF it was a big hit of dopamine because it was really elegant. However, nowadays, I do feel like it is having the same problems of JavaScript. Macros are a good feature, but end up being the go-to solution when you simply can't make the code "look pretty"; or having to use a library to anything a little more complex; or having to deal with lifetimes. And if you want to do anything a little more complex "the Rust way", you will easily do head to head with a wall of skill-issues. I still love it and its complexity, and for things like compiler and transpilers it feels like a good shot.
Going Go
This year I started to learn Go (or "Golang" for SEO friendliness), and it has being kinda awesome.
Go is kinda like Python in its learning curve, and it is somewhat like C but without all the needing of handling memory and needing to create complex data structured from scratch. And I have never really loved it, but never really hated it, since it is mostly just boring and simple.
There are no macros or magic syntax. No pattern matching on types, since you can just use a switch statement. You don't have to worry a lot about packages, since the standard library will cover you up to 80% of features. If you need a package, you don't need to worry about a centralized registry to upload and the security vulnerability of a single failure point, all packages are just Git repositories that you import and that's it. And no file management, since it just uses the file system for packages and imports.
And it feels like Go pretty much made all the obvious decisions that make sense, and you mostly never question or care about them, because they don't annoy you. The syntax doesn't get into your way. And in the end you just end up comparing to other languages' features, saying to yourself "man... we could save some lines here" knowing damn well it's not worth it. It's boring.
You write code, make your feature be completed in some hours, and compile it with go build. And run the binary, and it's fast.
Going Simple
And writing Go kinda opened a new passion in programming for me.
Coming from JavaScript and Rust really made me be costumed with complexity, and going now to Go really is making me value simplicity and having the less moving parts are possible.
I am becoming more aware from installing dependencies, checking to see their dependencies, to be sure that I'm not putting 100 projects under my own. And when I need something more complex but specific, just copy-and-paste it and put the proper license and notice of it, no need to install a whole project. All other necessities I just write my own version, since most of the time it can be simpler, a learning opportunity, and a better solution for your specific problem. With Go I just need go build to build my project, and when I need JavaScript, I just fucking write it and that's it, no TypeScript (JSDoc covers 99% of the use cases for TS), just write JS for the browser, check if what you're using is supported by modern browsers, and serve them as-is.
Doing this is really opening some opportunities to learn how to implement solutions, instead of just using libraries or cumbersome language features to implement it, since I mostly read from source-code of said libraries and implement the concept myself. Not only this, but this is really making me appreciate more standards and tooling, both from languages and from ecosystem (such as web standards), since I can just follow them and have things work easily with the outside world.
The evolution
And I kinda already feel like this is making me a better developer overhaul. I knew that with an interesting experiment I made.
One of my first actual projects was, of course, a to-do app. I wrote it in Vue using Nuxt, and it was great not-gonna-lie, Nuxt and Vue are awesome frameworks and still one of my favorites, but damn well it was overkill for a to-do app. Looking back... more than 30k lines of code for this app is just too much.
And that's what I thought around the start of this year, which is why I made an experiment, creating a to-do app in just one HTML file, using AlpineJS and PicoCSS.
The file ended up having just 350 files.
Today's artists & creative things Music: Torna a casa - by Måneskin
© 2024 Gustavo "Guz" L. de Mello. Licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
What’s new in React?
React is a continuously evolving library in the ever-changing web development landscape. As you embark on your journey to learn and master React, it’s important to understand the evolution of the library and its updates over time.
One of the advantages of React is that its core API has remained relatively stable in recent years. This provides a sense of continuity and allows developers to leverage their knowledge from previous versions. The conceptual foundation of React has remained intact, meaning that the skills acquired three or five years ago can still be applied today. Let’s take a step back and trace the history of React from its early versions to the recent ones. From React 0.x to React 18, numerous pivotal changes and enhancements have been made as follows: 1. React 0.14: In this version, the introduction of functional components allowed developers to utilize functions as components, simplifying the creation of basic UI elements. At that time, no one knew that now we would write only functional components and almost completely abandon class-based components.
2. React 15: With a new versioning scheme, the next update of React 15 brought a complete overhaul of the internal architecture, resulting in improved performance and stability.
3. React 16: This version, however, stands as one of the most notable releases in React’s history. It introduced hooks,a revolutionary concept that enables developers to use state and other React features without the need for class components. Hooks make code simpler and more readable, transforming the way developers write components.Additionally, React 16 introduced Fiber, a new reconciliation mechanism that significantly improved performance, especially when dealing with animations and complex UI structures.
4. React 17: This version focused on updating and maintaining compatibility with previous versions. It introduced a new JSX transform system.
5. React 18: This is the latest stable release, which continues the trajectory of improvement and emphasizes performance enhancements and additional features, such as the automatic batching of renders, state transitions, server components, and streaming server-side rendering.
Setting up a new React project There are several ways to create a React project when you are getting started. In this section, let's explore three common approaches: • Using web bundlers • Using frameworks • Using an online code editor
Using web bundlers Using a web bundler is an efficient way to create React projects, especially if you are building a Single-Page Application (SPA). Vite is known for its remarkable speed and ease of setup and use.
Using frameworks For real-world and commercial projects, it is recommended to use frameworks built on top of React. These frameworks provide additional features out of the box, such as routing and asset management (images, SVG files, fonts, etc.). They also guide you in organizing your project structure effectively, as frameworks often enforce specific file organization rules. Some popular React frameworks include Next.js, Gatsby, and Remix.
Online code editors Online code editors combine the advantages of web bundlers and frameworks but allow you to set up your React development environment in the cloud or right inside of the browser. This eliminates the need to install anything on your machine and lets you write and explore React code directly in your browser. While there are various online code editors available, some of the most popular options include CodeSandbox, StackBlitz, and Replit. These platforms provide a user-friendly interface and allow you to create, share, and collaborate on React projects without any local setup.To get started with an online code editor, you don’t even need an account. Simply follow this link on your browser:(https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-new?utm_source=dotnew). In a few seconds, you will see that CodeSandbox is ready to work with a template project, and a live preview of the editor is available directly in the browser tab. If you want to save your changes, then you need to create an account.Using online code editors is a convenient way to learn and experiment with React, especially if you prefer a browser-based development environment.
Reference material: React and React Native

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
React JS
Component-Based Architecture:
React applications are built using components, which are reusable, self-contained pieces of the UI. Components can be nested, managed, and handled independently, leading to better maintainability and scalability.
JSX (JavaScript XML):
React uses JSX, a syntax extension that allows HTML to be written within JavaScript. This makes the code more readable and easier to write.
Virtual DOM:
React maintains a virtual DOM, an in-memory representation of the actual DOM. When the state of an object changes, React updates the virtual DOM and efficiently determines the minimal set of changes needed to update the real DOM, leading to performance improvements.
One-Way Data Binding:
Data flows in one direction, from parent to child components, which makes the data flow and logic easier to understand and debug.
State Management:
React components can maintain internal state, making it easy to build dynamic and interactive UIs. For more complex state management, libraries like Redux or Context API can be used.
Advantages of Using React
Performance:
Due to the virtual DOM, React minimizes direct manipulation of the DOM, resulting in better performance for dynamic applications.
Reusable Components:
Components can be reused across different parts of an application, reducing the amount of code and enhancing consistency.
Strong Community and Ecosystem:
A large community and a rich ecosystem of tools and libraries support React, making it easier to find solutions, get support, and integrate with other technologies.
SEO Friendly:
React can be rendered on the server using Node.js, making web pages more SEO-friendly compared to traditional client-side rendering.
Getting Started with React
To start building applications with React, you need to have Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) installed. Here’s a basic setup to create a new React application:
Install Node.js and npm:
Download and install from Node.js website.
Create a New React Application:
You can use Create React App, an officially supported way to create single-page React applications with no configuration required:
npx create-react-app my-app cd my-app npm start
import React from 'react';
function Welcome(props) { return
Hello, {props.name}
; }
export default Welcome;
#React JS#Front end Developer#Advanced JavaScript#coding#html css#htmlcoding#html#css#php#website#html5 css3#software#React Training
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
React training in hyderabad

Introduction to React JS
React is like the carpenter’s toolbox for building web interfaces. Created by the folks at Facebook, it’s a set of tools that makes crafting interactive and dynamic websites a whole lot easier. Imagine it as a set of magic building blocks that help developers create sleek, responsive, and engaging front-end applications. Since its debut in 2013, React has become a favorite among web developers, kind of like the go-to tool when you want to make your website not just look good but also feel lively and interactive. It’s a bit like the secret sauce behind many of the awesome websites you use every day.
Features of React JS
Declarative Syntax: React uses a declarative syntax, allowing developers to describe the desired outcome, and React takes care of the underlying logic to achieve that outcome. This makes the code more predictable and easier to understand.
2. Component-Based Architecture: React follows a component-based architecture where the UI is broken down into reusable components. Each component manages its own state and can be composed to build complex user interfaces.
3. Virtual DOM: React uses a virtual DOM to improve performance. Instead of directly manipulating the actual DOM, React creates a virtual representation of it in memory and updates only the parts of the actual DOM that have changed. This minimizes the number of DOM manipulations, resulting in faster updates.
4. JSX (JavaScript XML): React uses JSX, a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows you to write HTML elements and components in a syntax similar to XML or HTML. JSX makes the code more readable and helps with the integration of UI components.
Components in React
In React, think of components as building blocks for your user interface — they’re like Lego pieces that you can assemble to create your application. These components are self-contained and can be reused, making it easier to manage and organize your user interface. It’s as if you’re constructing your application with Lego bricks, where each brick represents a specific part of your user interface.
This modular approach simplifies the development process and encourages a more flexible and maintainable code structure.
Dumb components: Think of these components as the friendly faces you see in a store’s display window. They’re there to catch your eye and make everything look inviting. These components are all about the visual appeal, like the welcoming decor of a shop, without getting into the technical details or behind-the-scenes work.
2. Smart components:Think of these components as the wise decision-makers. They not only handle the important business details but also decide when and how things should appear on the screen. It’s like having an event planner for your app — they manage the behind-the-scenes work and ensure everything shows up at just the right time and in the best way possible.
NOTE 🤓:These components can come to life either as classes or functions. They’re adaptable, like a versatile tool that can be crafted in different ways based on your needs.
State of a component
In the world of React, think of the state as a component’s personal notebook — it’s where the component keeps track of information that can change over time. This information might shift based on how users interact with the component or how the outside world reacts to it. Whether the component is a classic novel (a class) or a snappy note (a function), it handles its state in its own unique way. What’s really neat is that when this internal state undergoes a change, it’s like the component automatically freshens up, updating its look without any fuss — kind of like a quick, seamless makeover happening in the background.
Properties of a component
In React, components communicate with each other through a feature called “Props.” It’s like sharing notes or gifts between them, but here’s the catch: the communication is a one-way street, flowing strictly from a parent component to its child. Imagine it as a parent passing a sealed letter to their child. What’s interesting is that these messages, or props, are unchangeable once delivered. It’s akin to sending a secure package — the information remains intact, ensuring a clear and organized flow of data between React components.
Life cycle of a component
Components in React have a lifecycle, and it’s like understanding the natural flow of a component’s journey. This lifecycle serves as our guide, allowing us to make smart decisions at different points in the component’s existence. It’s a bit like knowing when to take specific actions, such as making an HTTP request or tidying up the user interface.
componentDidMount: Think of this as the behind-the-scenes moment when the component takes its place on the UI stage for the first time.
componentDidUpdate:Picture this as the component’s way of adapting and evolving — a sort of behind-the-scenes dance that happens when the component experiences a change in its mood or receives something new to work with.
componentWillUnmount: Function executed when the component is unmounted from the UI.
React Hooks are a set of functions that were introduced in React 16.8 to enable the use of state and other React features in functional components. Before the introduction of hooks, state and lifecycle methods were primarily associated with class components. Hooks allow functional components to have state, lifecycle features, and more, making them a powerful and concise alternative to class components.
The most commonly used React Hooks include:
use State: Enables functional components to manage state.
2. use Effect: Provides a way to perform side effects in functional components, similar to component DidMount and component DidUpdate in class components.
3. use Context: Allows functional components to subscribe to React context without introducing a nested component.
4. use Reducer: An alternative to use State for managing more complex state logic in functional components.
5. use Callback and use Memo: Optimize performance by memoizing functions and values to prevent unnecessary re-renders.
Hello world with create react app
Create React App is a ready-to-go setup designed for building React applications. It works seamlessly with Node version 14.0.0 or higher and npm version 5.6 or higher. To kickstart a new project, simply run the following commands in your terminal:
“npx create-react-app your-project-name”
Most used add-on libraries in React JS
1. Redux: A predictable state container for managing the state of your application in a more organized and scalable way.
2. React Router: Provides navigation and routing functionalities for React applications, allowing you to create dynamic and SPA (Single Page Application) experiences.
3. Axios: A promise-based HTTP client that simplifies making HTTP requests in React applications.
4. Styled-components: Enables writing CSS directly in your JavaScript files using tagged template literals, promoting component-based styling.
5. Material-UI: A popular React component library that implements Google’s Material Design, offering a set of pre-designed and customizable components.
6. Formik: A form management library that simplifies form building, validation, and handling form submissions.
7. React Query: A library for managing, caching, and syncing asynchronous data in React applications, making it easier to work with API calls and data fetching.
8. Chakra UI: A component library for React that provides a set of accessible and customizable UI components.
9. React Helmet: Allows manipulation of the document head, useful for managing meta tags, titles, and other document head elements.
10. React-Bootstrap: Integrates the Bootstrap CSS framework with React components, providing a set of responsive and customizable UI elements.
Recursos React JS
React Official Website: Explore the heart of React at React official websites. Immerse yourself in comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and fundamental concepts that form the backbone of React development.
React Blog: Stay updated on the latest in React by checking out the React Blog. Dive into news, official articles, and insightful posts that illuminate the evolving world of React development.
Thinking in React: Embark on your React journey by embracing the philosophy of “Thinking in React.” Learn how to kickstart your understanding by focusing on the core concept of thinking in components. The journey begins with a guide to getting started thinking in components. This course is designed to provide students with a solid understanding of the architecture and functionality of MuleSoft’s integration platform.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Master React: A Complete React Tutorial for Beginners
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, React has emerged as one of the most powerful and popular JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces. Developed and maintained by Facebook, React allows developers to create dynamic, high-performance web applications with ease. If you’re a beginner looking to dive into the world of React, this comprehensive tutorial, "Master React: A Complete React Tutorial for Beginners," will guide you through the essential concepts, tools, and techniques needed to become proficient in React development.
What is React?
React is a declarative, component-based library that enables developers to build reusable UI components. Its primary goal is to make the process of creating interactive user interfaces more efficient and manageable. Unlike traditional web development approaches that manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM) directly, React uses a virtual DOM to optimize rendering performance. This means that React only updates the parts of the UI that have changed, resulting in faster and more responsive applications.
Why Learn React?
Learning React is a valuable investment for any aspiring web developer. Here are a few reasons why you should consider mastering React:
Popularity and Demand: React is widely used by companies of all sizes, from startups to tech giants like Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb. Proficiency in React can significantly enhance your job prospects and career opportunities. Component-Based Architecture: React’s component-based structure promotes reusability and modularity, making it easier to manage and scale applications. This approach allows developers to break down complex UIs into smaller, manageable pieces. Rich Ecosystem: React has a vast ecosystem of libraries and tools that complement its functionality. From state management solutions like Redux to routing libraries like React Router, the React ecosystem provides everything you need to build robust applications. Strong Community Support: With a large and active community, finding resources, tutorials, and support for React development is easier than ever. Whether you’re facing a coding challenge or looking for best practices, the community is there to help.
Setting Up Your React Environment
Before diving into coding, you need to set up your development environment. The easiest way to get started with React is by using the Create React App (CRA) tool, which sets up a new React project with a single command. To create a new React application, follow these steps:
Install Node.js: Ensure you have Node.js installed on your machine. You can download it from the official website.
Create a New React App: Open your terminal and run the following command:
npx create-react-app my-first-react-app cd my-first-react-app npm start
This command creates a new directory called my-first-react-app and starts a development server that you can access at http://localhost:3000.
Understanding React Components
At the heart of React are components. A component is a self-contained piece of UI that can be reused throughout your application. There are two main types of components in React:
Functional Components: These are JavaScript functions that return JSX (JavaScript XML), which looks similar to HTML. Functional components are simpler and easier to read, making them the preferred choice for most developers. Example of a functional component:
function Welcome(props) { return <h1>Hello, {props.name}!</h1>; }
Class Components: These are ES6 classes that extend the React.Component class. Class components can hold state and lifecycle methods, but with the introduction of hooks, functional components are now more commonly used. Example of a class component:
class Welcome extends React.Component { render() { return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}!</h1>; } }
JSX: The Syntax of React
JSX is a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows you to write HTML-like code within your JavaScript files. It makes it easier to visualize the structure of your UI. JSX expressions can include JavaScript expressions wrapped in curly braces {}.
Example of JSX:const element = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>;
State and Props: Managing Data in React
In React, data flows in one direction, from parent components to child components. This is achieved through props (short for properties) and state.
Props: Props are read-only attributes passed from a parent component to a child component. They allow you to customize components and make them reusable. Example of using props:
function Greeting(props) { return <h1>Welcome, {props.name}!</h1>; }
State: State is a built-in object that allows components to manage their own data. Unlike props, state is mutable and can be updated using the setState method in class components or the useState hook in functional components. Example of using state with hooks:
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function Counter() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); return ( <div> <p>You clicked {count} times</p> <button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button> </div> ); }
Lifecycle Methods and Hooks
In class components, React provides lifecycle methods that allow you to run code at specific points in a component's life, such as when it mounts or unmounts. Common lifecycle methods include componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, and componentWillUnmount.
With the introduction of hooks in React 16.8, functional components can now manage side effects and lifecycle events using the useEffect hook. This allows for cleaner and more concise code.
Example of using useEffect:import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react'; function DataFetcher() { const [data, setData] = useState(null); useEffect(() => { fetch('https://api.example.com/data') .then(response => response.json()) .then(data => setData(data)); }, []); // Empty array means this runs once on mount return <div>{data ? JSON.stringify(data) : 'Loading...'}</div>; }
Routing with React Router
For building single-page applications (SPAs), React Router is an essential library that enables navigation between different components without refreshing the page. It allows you to define routes and render components based on the current URL.
Example of setting up React Router:import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Switch } from 'react-router-dom'; function App() { return ( <Router> <Switch> <Route path="/about" component={About} /> <Route path="/" component={Home} /> </Switch> </Router> ); }
State Management with Context and Redux
As your application grows, managing state across multiple components can become challenging. React Context provides a way to share data globally without prop drilling, while Redux is a popular state management library that offers a centralized store and predictable state updates.
Best Practices for React Development
To ensure your React applications are maintainable and efficient, consider the following best practices:
Keep Components Small and Focused: Each component should have a single responsibility, making it easier to understand and test.
Use Functional Components and Hooks: Prefer functional components and hooks over class components for cleaner and more concise code.
Leverage PropTypes or TypeScript: Use PropTypes for type checking or consider using TypeScript for static type checking to catch errors early.
Optimize Performance: Use React. Memo to prevent unnecessary re-renders and implement lazy loading for components to improve performance. Maintain a Modular Folder Structure: Organize your project files in a way that promotes modularity and ease of navigation.
Building Real-World Projects
The best way to solidify your React skills is by building real-world projects. Start with simple applications like a to-do list or a weather app, and gradually move on to more complex projects like an e-commerce site or a social media platform. This hands-on experience will help you apply what you’ve learned and prepare you for real-world development challenges.
Conclusion
Mastering React is a rewarding journey that opens up numerous opportunities in web development. This tutorial, "Master React: A Complete React Tutorial for Beginners," has provided you with a solid foundation in React concepts, tools, and best practices. By dedicating time to practice and build projects, you will gain the confidence and skills needed to create dynamic, high-performance web applications. Embrace the challenge, stay curious, and let your journey into the world of React begin! Whether you’re looking to enhance your career or simply explore the exciting realm of web development, mastering React will empower you to create innovative solutions that make a difference.
0 notes
Text
What is Tailwind CSS React
Tailwind CSS React
Tailwind CSS is a modern way to style your website or app using utility classes. It helps developers design faster by writing classes directly in the HTML or JSX (in React).
In this guide, we will learn what Tailwind CSS is and how you can use it step-by-step in a React project.
🌟 What is Tailwind CSS?
Tailwind CSS is a utility-first CSS framework. This means it gives you ready-made CSS classes that you can use directly in your code.
For example:
htmlCopy
Edit
<button class="bg-blue-500 text-white px-4 py-2 rounded">Click Me</button>
In React, you can write these classes inside your className attribute.
⚛️ Why Use Tailwind CSS with React?
Speeds up the development process
Easy to make responsive designs
No need to write custom CSS for every component
Clean and consistent layout
✅ Step-by-Step: How to Add Tailwind CSS to a React Project
Step 1: Create a React App
If you don’t have a React app yet, create one using the command below:
bashCopy
Edit
npx create-react-app my-app cd my-app
Step 2: Install Tailwind CSS
Run the following command to install Tailwind CSS and its dependencies:
bashCopy
Edit
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer npx tailwindcss init -p
This will create two files:
tailwind.config.js
postcss.config.js
Step 3: Configure Tailwind
Open tailwind.config.js and add this under content:
jsCopy
Edit
module.exports = { content: ["./src/**/*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}"], theme: { extend: {}, }, plugins: [], }
This tells Tailwind to look for classes in your React files.
Step 4: Add Tailwind to Your CSS
Open src/index.css and replace everything with the following:
cssCopy
Edit
@tailwind base; @tailwind components; @tailwind utilities;
This will load Tailwind’s default styles into your project.
Step 5: Start Using Tailwind Classes
Now, you can use Tailwind classes directly inside your React components.
Example (App.js):
jsxCopy
Edit
function App() { return ( <div className="text-center p-10"> <h1 className="text-4xl font-bold text-blue-600">Hello Tailwind!</h1> <p className="mt-4 text-gray-700">This is a React app using Tailwind CSS.</p> </div> ); }
Step 6: Run Your App
Now start the app:
bashCopy
Edit
npm start
Open your browser and go to http://localhost:3000. You should see the styles applied.
🎯 Summary
Tailwind CSS is a utility-first CSS framework.
It works well with React.
You don’t need to write separate CSS files.
You just write utility classes in your JSX.
It makes your design process faster and easier.
Using Tailwind CSS in React is a great way to build modern web apps with clean and responsive designs quickly.
0 notes
Text
Why CodingBrushup is the Ultimate Tool for Your Programming Skills Revamp
In today's fast-paced tech landscape, staying current with programming languages and frameworks is more important than ever. Whether you're a beginner looking to break into the world of development or a seasoned coder aiming to sharpen your skills, Coding Brushup is the perfect tool to help you revamp your programming knowledge. With its user-friendly features and comprehensive courses, Coding Brushup offers specialized resources to enhance your proficiency in languages like Java, Python, and frameworks such as React JS. In this blog, we’ll explore why Coding Brushup for Programming is the ultimate platform for improving your coding skills and boosting your career.

1. A Fresh Start with Java: Master the Fundamentals and Advanced Concepts
Java remains one of the most widely used programming languages in the world, especially for building large-scale applications, enterprise systems, and Android apps. However, it can be challenging to master Java’s syntax and complex libraries. This is where Coding Brushup shines.
For newcomers to Java or developers who have been away from the language for a while, CodingBrushup offers structured, in-depth tutorials that cover everything from basic syntax to advanced concepts like multithreading, file I/O, and networking. These interactive lessons help you brush up on core Java principles, making it easier to get back into coding without feeling overwhelmed.
The platform’s practice exercises and coding challenges further help reinforce the concepts you learn. You can start with simple exercises, such as writing a “Hello World” program, and gradually work your way up to more complicated tasks like creating a multi-threaded application. This step-by-step progression ensures that you gain confidence in your abilities as you go along.
Additionally, for those looking to prepare for Java certifications or technical interviews, CodingBrushup’s Java section is designed to simulate real-world interview questions and coding tests, giving you the tools you need to succeed in any professional setting.
2. Python: The Versatile Language for Every Developer
Python is another powerhouse in the programming world, known for its simplicity and versatility. From web development with Django and Flask to data science and machine learning with libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and TensorFlow, Python is a go-to language for a wide range of applications.
CodingBrushup offers an extensive Python course that is perfect for both beginners and experienced developers. Whether you're just starting with Python or need to brush up on more advanced topics, CodingBrushup’s interactive approach makes learning both efficient and fun.
One of the unique features of CodingBrushup is its ability to focus on real-world projects. You'll not only learn Python syntax but also build projects that involve web scraping, data visualization, and API integration. These hands-on projects allow you to apply your skills in real-world scenarios, preparing you for actual job roles such as a Python developer or data scientist.
For those looking to improve their problem-solving skills, CodingBrushup offers daily coding challenges that encourage you to think critically and efficiently, which is especially useful for coding interviews or competitive programming.
3. Level Up Your Front-End Development with React JS
In the world of front-end development, React JS has emerged as one of the most popular JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces. React is widely used by top companies like Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb, making it an essential skill for modern web developers.
Learning React can sometimes be overwhelming due to its unique concepts such as JSX, state management, and component lifecycles. That’s where Coding Brushup excels, offering a structured React JS course designed to help you understand each concept in a digestible way.
Through CodingBrushup’s React JS tutorials, you'll learn how to:
Set up React applications using Create React App
Work with functional and class components
Manage state and props to pass data between components
Use React hooks like useState, useEffect, and useContext for cleaner code and better state management
Incorporate routing with React Router for multi-page applications
Optimize performance with React memoization techniques
The platform’s interactive coding environment lets you experiment with code directly, making learning React more hands-on. By building real-world projects like to-do apps, weather apps, or e-commerce platforms, you’ll learn not just the syntax but also how to structure complex web applications. This is especially useful for front-end developers looking to add React to their skillset.
4. Coding Brushup: The All-in-One Learning Platform
One of the best things about Coding Brushup is its all-in-one approach to learning. Instead of jumping between multiple platforms or textbooks, you can find everything you need in one place. CodingBrushup offers:
Interactive coding environments: Code directly in your browser with real-time feedback.
Comprehensive lessons: Detailed lessons that guide you from basic to advanced concepts in Java, Python, React JS, and other programming languages.
Project-based learning: Build projects that add to your portfolio, proving that you can apply your knowledge in practical settings.
Customizable difficulty levels: Choose courses and challenges that match your skill level, from beginner to advanced.
Code reviews: Get feedback on your code to improve quality and efficiency.
This structured learning approach allows developers to stay motivated, track progress, and continue to challenge themselves at their own pace. Whether you’re just getting started with programming or need to refresh your skills, Coding Brushup tailors its content to suit your needs.
5. Boost Your Career with Certifications
CodingBrushup isn’t just about learning code—it’s also about helping you land your dream job. After completing courses in Java, Python, or React JS, you can earn certifications that demonstrate your proficiency to potential employers.
Employers are constantly looking for developers who can quickly adapt to new languages and frameworks. By adding Coding Brushup certifications to your resume, you stand out in the competitive job market. Plus, the projects you build and the coding challenges you complete serve as tangible evidence of your skills.
6. Stay Current with Industry Trends
Technology is always evolving, and keeping up with the latest trends can be a challenge. Coding Brushup stays on top of these trends by regularly updating its content to include new libraries, frameworks, and best practices. For example, with the growing popularity of React Native for mobile app development or TensorFlow for machine learning, Coding Brushup ensures that developers have access to the latest resources and tools.
Additionally, Coding Brushup provides tutorials on new programming techniques and best practices, helping you stay at the forefront of the tech industry. Whether you’re learning about microservices, cloud computing, or containerization, CodingBrushup has you covered.
Conclusion
In the world of coding, continuous improvement is key to staying relevant and competitive. Coding Brushup offers the perfect solution for anyone looking to revamp their programming skills. With comprehensive courses on Java, Python, and React JS, interactive lessons, real-world projects, and career-boosting certifications, CodingBrushup is your one-stop shop for mastering the skills needed to succeed in today’s tech-driven world.
Whether you're preparing for a new job, transitioning to a different role, or just looking to challenge yourself, Coding Brushup has the tools you need to succeed.
0 notes
Text
this is my old account and me and I am the CEO of NPC Jax theory and ceo needs to stay loyal. To company. Anyway so JSX is a way of coding yeah. It allows coders to write code in a more simple way (HTML like) and is more like human??? I guess?? You know?? Also Jax is the only one to otherwise have a meaningless name. Ragatha is rag. Kinger is chess piece. Pomni means remember in Russian. Like “WHY CANT I REMEMBER MY NAME??” Your name is remember. Goofy. Gangle is gangly and gangle of ribbons. Zooble is based off Zooble toy. Caine is malicious god related and shares a name with Cain from Bible who is also that. Bubble is bubble. Gummigoo is gummi. Orbsman? Orbs. Spudsy was originally gonna be a potato. 🥔 for that promo pic. Gloinks look exactly like how you’d expect a Gloink to. And they make Gloink sound when they jump I think. But Jax is… a rabbit. His name does not mean anything or describe what he is at all. Unless Jax is …. JSX code?????? Also A and S are RIGHT next to each other on the qwerty keyboard!!!!!haha
“Jax is an NPC” theory post with a bunch of evidence.
‼️most of this came from other posts, I’m just compiling it‼️
@fungi-rat made this post
Here are the pins so you can see what these posts are talking about





@cccccccoooooo made the below post

Also, as many people have been pointing out, Jax was really upset when there wasn’t any violence. This could either be the fact that he just.. likes violence.. or (the one that proves my theory), since this is about him being an NPC, that would make him from an adventure, and maybe the reason he craves violence so much and does something that led everyone to believe him to be getting angst in this episode, along with getting the most villain-arc looking shot towards the end, this might be because he was a villain in that adventure that he was from. Or he was supposed to be violent or it happened after he became self aware. Or I’m reading way too far into this.
Also in the pilot he just kinda.. teleported? I don’t know but it doesn’t seem like any of the other cast can do that, other than Caine, who isn’t a human. So yeah. @skekilla made the points below



Another point is that Jax breaks the fourth wall by looking at the ‘camera’, and referring to pomni as “a new character”. I also might be reading too far into this but it’s something that just... due to goose confirming that there’s a lot of symbolism, I don’t think they’d do that for no reason. Plus how he said “another one of your NPC’s” which is strange, because NPC’s aren’t allowed in the circus, and so there aren’t any. Maybe, if he is one, he thought that they were allowed in the circus .

Plus this point 👆🏼 I didn’t make it but I don’t remember who did
and the one below made by @zooblenation touching on the same topic.

Point below made by @strawtebby
Below points by @akumax666

Will hopefully add on to this eventually.
as I said in a post saying I would make this, I said I like this theory because of the angst potential. also because I had an au about it in November that I never posted about and I just got excited when I saw people theorizing about that.
201 notes
·
View notes
Text
GPT-3: All you need to know about the AI language model

Cast your mind back to June 2020. The world was grappling with unprecedented changes, and in the midst of it all, the field of artificial intelligence experienced a seismic shift with the arrival of OpenAI's GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3). Even now, as we stand in May 2025 surrounded by even more advanced AI, understanding GPT-3 is crucial to appreciating the incredible journey of language models and how we've arrived at today's sophisticated AI landscape.
This blog post revisits GPT-3: what it was, the capabilities that captivated the world, its profound impact, its inherent limitations, and its enduring legacy in an era now dominated by its more powerful successors.
What Was GPT-3? The Technical Snapshot
When OpenAI unveiled GPT-3, its sheer scale was breathtaking. It was a language model built upon the Transformer architecture, like its predecessor GPT-2, but boasted an astounding 175 billion parameters. This was an order of magnitude larger than any publicly known language model at the time.
Trained on a massive and diverse dataset culled from the internet (including sources like Common Crawl, WebText2, books, and Wikipedia), GPT-3 learned to predict the next word in a sequence with remarkable proficiency. This seemingly simple objective, when scaled up, unlocked a surprising array of language capabilities.
The "Magic" of GPT-3: Key Capabilities That Amazed
GPT-3 wasn't just bigger; it was qualitatively different in what it could achieve without task-specific fine-tuning:
Remarkably Coherent Text Generation: GPT-3 could write essays, articles, summaries, and even poetry that was often difficult to distinguish from human-written text, especially in shorter forms.
Few-Shot Learning: This was a game-changer. Unlike previous models that often required extensive fine-tuning for new tasks, GPT-3 could perform a new task with just a few examples (or "shots") provided in the prompt. Sometimes, it could even perform tasks in a "zero-shot" fashion, based purely on a description.
Versatile Language Tasks: It demonstrated competence in translation, question-answering, and summarization across a wide range of topics.
Early Coding Abilities: GPT-3 could generate code snippets in languages like Python, CSS, and JSX, hinting at the future potential of AI in software development.
Why GPT-3 Caused Such a Stir: Its Monumental Impact
The release of GPT-3, particularly access to it via an API, had a ripple effect across the tech world and beyond:
Demonstrated the Power of Scale: It provided compelling evidence that scaling up model size and training data could lead to significant improvements in capability and generalization.
Democratized Access to Powerful AI: The API allowed developers and researchers worldwide to experiment with and build applications on top of a state-of-the-art language model, sparking a wave of innovation and new startups.
Expanded Imagination for AI Applications: From content creation and chatbots to coding assistance and idea generation, GPT-3 showcased a vast array of potential use cases.
Brought AI Ethics to the Forefront: Its capabilities also highlighted potential risks, including the generation of misinformation, spam, biased content, and the potential for malicious use, leading to more mainstream discussions about responsible AI development.
The Not-So-Perfect Picture: GPT-3's Limitations
For all its prowess, GPT-3 was far from perfect. Understanding its limitations is key to appreciating the advancements that followed:
Factual Inaccuracies ("Hallucinations"): GPT-3 could confidently generate text that sounded plausible but was factually incorrect or nonsensical.
Lack of True Understanding or Reasoning: While it excelled at pattern matching and text generation, it didn't possess genuine understanding, common sense, or the ability to reason deeply about complex topics.
Bias from Training Data: It could reproduce and sometimes amplify biases present in its vast internet training data.
Verbosity and Coherence Issues: Over longer text generations, its coherence could sometimes degrade, and it often tended to be overly verbose.
Knowledge Cutoff: Its knowledge was limited to the data it was trained on, meaning it wasn't aware of events or information that emerged after its training period (around early 2020).
No Real-time Internet Access: It couldn't browse the live internet for up-to-date information.
GPT-3's Enduring Legacy in 2025: Paving the Way for Giants
In May 2025, while GPT-3 itself might be considered a legacy model (with OpenAI even retiring older GPT-3.5 Turbo models from its API), its impact is undeniable. It was a crucial stepping stone that laid the foundational principles for the more advanced and capable models that are now prevalent, such as the GPT-4 series (including GPT-4o and its variants like GPT-4.1) and even the anticipated next-generation models like GPT-5.
These successors have built upon GPT-3's foundation by:
Increasing Model Size and Efficiency: While exact parameter counts are often not disclosed, newer models are significantly more capable.
Improving Reasoning and Accuracy: Current models demonstrate vastly improved logical reasoning, reduced hallucinations, and better factual grounding.
Embracing True Multimodality: Models in 2025 seamlessly process and generate not just text, but also images, audio, and even video.
Expanding Context Windows: The ability to process and remember much longer conversations and documents has dramatically increased their utility.
More Up-to-Date Knowledge: Newer models generally have more recent knowledge cutoffs and, in some cases, can access and process real-time information.
Enhanced Safety and Alignment: Significant efforts have been made (and continue to be made) to make models safer, less biased, and better aligned with human values.
The core concepts of large-scale pre-training on diverse text data and the power of the Transformer architecture, which GPT-3 so effectively showcased, remain central to AI language model development today.
Conclusion: A Landmark in the AI Timeline
GPT-3's arrival was a landmark event in the history of artificial intelligence. It shifted our understanding of what AI language models could do and set the stage for an incredibly rapid period of innovation. While the cutting edge of AI in 2025 has moved far beyond GPT-3's specific capabilities, its launch was a pivotal moment that ignited the AI revolution we are experiencing today. It reminds us how quickly this field moves and how foundational breakthroughs can pave the way for even more astonishing advancements in a very short time.
0 notes
Text

Full-Stack Face-Off: Breaking Down MERN and MEAN Stacks
Introduction
In today’s ever-changing tech world, choosing the right full‑stack approach can feel overwhelming. Two popular choices stand out: the MERN and MEAN stacks. Both bring together powerful JavaScript frameworks and tools to help developers build dynamic, end‑to‑end web applications. Whether you represent a MERN Stack development company or a MEAN Stack development firm, understanding the strengths and trade‑offs of each is essential. In this guide, we’ll walk through the basics, explore individual components, and help you decide which path aligns best with your project goals.
Understanding the MERN and MEAN Stacks
At a high level, both stacks rely on JavaScript across the entire application. This common language makes it easier for teams to collaborate and share code between client and server. The core difference lies in the front-end framework:
MERN: MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js
MEAN: MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js
MongoDB handles data storage in both cases as a flexible, document‑oriented database. Express and Node serve as the backbone for server‑side logic and routing. React and Angular provide the user interface layer, each with its own philosophy on component management and data flow. For a MERN Stack development company, React’s component‑driven model allows for fine‑grained control and reuse. On the other hand, a MEAN Stack development company may favor Angular’s built‑in features like dependency injection and two‑way data binding for rapid prototyping.
Exploring MEAN Stack Components
MongoDB: This NoSQL database stores data in JSON‑like documents, making it simple to scale and adapt as your app grows.
Express.js: A minimalist web framework for Node.js that simplifies building robust RESTful APIs.
Angular: A full‑featured front‑end framework maintained by Google. It offers out‑of‑the‑box support for forms, HTTP services, and routing.
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine, enabling server‑side scripting and non‑blocking I/O.
When a MEAN Stack development company takes on a project, they often appreciate Angular’s opinionated structure. Angular enforces a clear project layout, with modules, components, and services neatly separated. This structure promotes consistency, especially for larger teams. The built‑in CLI tools streamline tasks like scaffolding components or running tests. However, the learning curve for Angular can be steeper compared to React, since it has its own templating syntax and TypeScript at its core.
Exploring MERN Stack Components
MongoDB: Just like in MEAN, your data is stored in flexible, JSON‑style documents.
Express.js: Manages your server’s routes, middleware, and API endpoints.
React: A library for building interactive UIs with a virtual DOM and component‑based architecture.
Node.js: Powers the backend with efficient, event‑driven operations.
For MERN Stack development, React’s learning curve is often gentler. Developers pick up JSX quickly, writing HTML‑like syntax combined with JavaScript logic. A MERN Stack development company will benefit from React’s thriving ecosystem: hooks, context API, and a wealth of third‑party libraries. React’s unopinionated nature gives teams freedom to choose their own state management, styling approaches, and routing solutions. While this flexibility is appealing, it requires a bit more decision‑making during project setup.
Choosing Between MERN and MEAN Stacks: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to selecting the ideal stack, consider the following factors:
Team Expertise: If your developers are comfortable with TypeScript and enjoy a more prescriptive framework, MEAN might be a better fit. Conversely, if your team prefers flexible libraries and a quick start, a MERN Stack development approach could be more efficient.
Project Size and Scope: Large enterprise applications can benefit from Angular’s mature feature set, making MEAN development smoother at scale. Smaller to mid‑sized projects, or those requiring rapid iteration, often find MERN development to be more nimble.
Performance Needs: Both stacks are performant, but React’s lightweight core can deliver snappier interactions for complex user interfaces. Angular’s built‑in change detection and optimizations shine when building heavy, data‑driven apps.
Ecosystem and Libraries: MERN’s ecosystem is rich in community‑driven packages, while Angular offers more official, first‑party solutions. Choose the stack whose library landscape aligns with your project requirements.
Community Support and Cost Considerations
Whether you lean toward a MEAN Stack development company or a MERN Stack development company, community support plays a vital role. Both stacks enjoy active user bases, extensive tutorials, and frequent updates. However, there are subtle differences:
MERN Community: Enormous number of React resources, tutorials, and third‑party tools. React’s popularity means you’ll find plenty of open-source components and UI libraries, often at no cost. For a MERN Stack development company, this translates into faster development cycles and reduced licensing expenses.
MEAN Community: While smaller than React’s, Angular’s community is backed by Google and offers official tooling, detailed documentation, and enterprise‑grade support. Some parts of Angular’s ecosystem, like certain enterprise integrations, may carry licensing fees, but most core features are freely available.
When budgeting, factor in training time and tooling costs. A MEAN Stack development company may need to invest more initially in Angular workshops, whereas a MERN Stack development company might spend time vetting and maintaining community‑built libraries.
Conclusion
In the battle of MERN vs. MEAN, there’s no one‑size‑fits‑all winner. Both stacks harness JavaScript to build full‑fledged web apps, but they cater to different development styles and project demands. If you value a structured, feature‑rich framework and seamless TypeScript integration, MEAN Stack development could be your go‑to choice. If you prefer flexibility, rapid prototyping, and a massive ecosystem of community tools, MERN Stack development might be the way forward. Ultimately, the best stack aligns with your team’s strengths, your project’s needs, and your long‑term vision.
#MERN Stack development company#MERN Stack development#MEAN Stack development#MEAN Stack development company
1 note
·
View note
Text
React JS Development: The Ultimate Guide to Building Modern Web Applications
In the rapidly evolving world of web development, building fast, interactive, and scalable applications is no longer optional—it's essential. Among the many technologies available today, React JS development has emerged as a top choice for developers and businesses alike. Created by Facebook, React.js simplifies front-end development while delivering a superior user experience.
Whether you're a business owner exploring tech options or a developer seeking efficient tools, this guide covers everything you need to know about React JS development, its advantages, real-world applications, and why it continues to dominate the front-end ecosystem.
What is React.js?
React.js is an open-source JavaScript library used for building user interfaces—particularly single-page applications (SPAs). It allows developers to create reusable UI components that update in real time as data changes.
Unlike traditional web frameworks that manipulate the DOM (Document Object Model) directly, React uses a virtual DOM to optimize updates, making apps faster and more responsive.
Key Features of React JS Development
1. Component-Based Architecture
React promotes modular development. Instead of building large monolithic pages, developers create reusable components that make development faster and more organized.
2. Virtual DOM for High Performance
React’s virtual DOM efficiently updates only the changed parts of the UI, improving performance and reducing unnecessary re-renders.
3. Unidirectional Data Flow
Data flows in one direction, making application behavior more predictable and easier to debug.
4. JSX Syntax
JSX (JavaScript XML) allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript, making UI code easier to read and maintain.
5. Strong Ecosystem and Community
With millions of developers worldwide and a vast number of open-source tools and libraries, React JS development benefits from a rich ecosystem.
Why Choose React JS Development?
Fast Development
React’s reusable components, efficient rendering, and active community support make development faster and easier.
Scalability
React can scale from a simple web widget to a full-fledged enterprise application with complex UI logic.
Cross-Platform Possibilities
React Native, a framework based on React.js, allows developers to build mobile apps for iOS and Android using the same codebase.
SEO-Friendly SPAs
Using server-side rendering (SSR) with tools like Next.js, React JS development can be optimized for search engines, solving one of SPA’s biggest issues.
Use Cases of React JS Development
React is used by some of the world’s largest companies, including Facebook, Netflix, Airbnb, and Uber. Common use cases include:
Single Page Applications (SPAs)
Dashboards and Admin Panels
E-commerce Frontends
Social Media Platforms
Real-time Chat and Messaging Apps
Interactive Data Visualizations
Tech Stack for React JS Development
React.js often works best when paired with other modern tools:
Frontend: React, Redux, Tailwind CSS, React Router
Backend: Node.js, Express.js
Database: MongoDB, PostgreSQL
Build Tools: Vite, Webpack, Babel
Deployment: Vercel, Netlify, Heroku
Getting Started with React JS Development
To begin your journey with React.js:
Install Node.js (if not already installed)
Create a new React project
Start building components, connecting APIs, and customizing your UI.
There are also advanced setups like Next.js for server-side rendering and static site generation.
Best Practices for React JS Development
Use functional components and Hooks instead of class components.
Keep components small and focused.
Use PropTypes or TypeScript for type checking.
Implement code splitting and lazy loading to improve performance.
Maintain a consistent folder structure and follow naming conventions.
React JS Development Trends in 2025
As of 2025, React.js continues to lead the front-end world due to:
Ongoing performance improvements
The rise of frameworks like Next.js and Remix
Enhanced support for concurrent rendering
Growing adoption in enterprise-level applications
React is not just a library—it's a central part of the modern development stack, and its role is only growing.
Conclusion
React JS development offers an unmatched combination of speed, efficiency, and flexibility for building user interfaces. Whether you're developing a simple dashboard or a complex web app, React gives you the tools to create clean, maintainable, and dynamic interfaces that users love.
If you're considering front-end development for your next project, investing in React JS development could be one of the smartest choices you make.
0 notes
Text
Power Up Your Web Development Career with MERN Stack Training in Kochi – Techmindz
Web development has evolved dramatically, and companies today are seeking developers who can manage both frontend and backend with ease. That’s where MERN Stack comes in—a powerful JavaScript-based technology stack that's become a go-to for full stack development. If you're looking to master this in-demand skill set, Techmindz offers the most practical and job-oriented MERN Stack training in Kochi.
Whether you’re a student, fresher, or professional looking to switch to web development, Techmindz can help you become a full stack developer with real-world skills.
What is MERN Stack?
MERN stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js—a full stack combination used to build high-performance web applications.
MongoDB – A flexible NoSQL database that stores data in JSON-like documents.
Express.js – A fast, minimalistic backend web application framework for Node.js.
React.js – A leading frontend library by Meta (Facebook) for building user interfaces.
Node.js – A runtime environment that executes JavaScript on the server side.
Together, this stack allows developers to write the entire application—from client to server—using JavaScript, making it efficient, fast, and scalable.
Why Choose MERN Stack?
In-Demand Skillset: Companies are actively hiring MERN developers due to the scalability and performance of this stack.
Single Language Across the Stack: JavaScript handles both frontend and backend—easy to learn, easy to manage.
Rapid Development: Great tools and a huge community make the development process smoother and faster.
Versatile Career Paths: Once you master MERN, you can work as a frontend developer, backend developer, or full stack developer.
Why Techmindz Offers the Best MERN Stack Training in Kochi
At Techmindz, we go beyond traditional classroom learning. We provide industry-relevant training with hands-on experience, so our students don’t just learn—they build.
1. Comprehensive, Hands-On Curriculum
Our MERN Stack course is structured to take you from the basics to building fully functional, live web applications. You’ll learn:
Frontend Development with React
JSX, components, props, state, hooks
Routing, form handling, API integration
Responsive design with Bootstrap/Tailwind
Backend with Node.js & Express
REST APIs, middleware, routing
User authentication and authorization
Error handling, security practices
Database with MongoDB
CRUD operations, schema design, Mongoose
Integrating with Express and Node
Real-time data handling
Deployment & Version Control
Git & GitHub
Hosting apps on cloud platforms (Vercel, Render, Heroku)
By the end of the course, you will have built multiple real-world projects, which you can add to your portfolio.
2. Trainers with Industry Expertise
Our instructors are experienced MERN stack developers who bring real-world insights into every session. They provide live coding, debug with you, and mentor you on project development.
3. Project-Based Learning
Learning code isn’t enough. At Techmindz, we focus on building complete, functional applications. From e-commerce websites and dashboards to real-time chat apps and blog platforms, you’ll get hands-on experience that mimics what you’ll be doing in a job.
4. Placement-Focused Approach
Techmindz isn’t just a training institute—we’re your career partner. Our MERN Stack training in Kochi includes:
Resume & GitHub profile building
Mock interviews with coding rounds
Communication & soft skills training
Direct placement assistance with our hiring partners in Infopark and beyond
5. Flexible Learning Options
We offer both offline training at our Kochi center and online live sessions, making it easy for college students, job seekers, or working professionals to join at their convenience. Weekend batches are also available.
Who Can Join the MERN Stack Course?
This course is perfect for:
Students pursuing B.Tech, BCA, MCA, or any IT-related course
Fresh graduates looking to enter web development
Backend/frontend developers who want to become full stack developers
Freelancers and aspiring entrepreneurs building their own platforms
No prior experience in JavaScript? No problem! We start from the fundamentals and guide you all the way to advanced application development.
Career Paths After MERN Stack Training
After completing the course, you'll be ready to take up roles such as:
Full Stack Developer
Web Application Developer
JavaScript Developer
Frontend/Backend Developer
Freelance Web Developer
With tech companies in Kochi and across India shifting to modern web stacks, MERN developers are in high demand.
Final Thoughts
Techmindz is proud to offer one of the most practical and career-driven MERN Stack training programs in Kochi. We focus on outcomes—ensuring our students not only learn but launch their careers in web development with confidence.
Whether you dream of joining a top IT company, working on your own startup, or freelancing with international clients, learning the MERN Stack with Techmindz is the first step.
👉 Enroll today. Build real apps. Get hired. That’s the Techmindz way.
https://www.techmindz.com/mean-stack-training/
0 notes
Text
Unlock your front-end development potential with Fusion Software Institute’s React JS course
Our React JS course is designed to provide a balanced mix of theoretical knowledge and practical experience, ensuring that students are well-prepared for real-world challenges. Why Choose Fusion Software Institute for React JS? Fusion Software Institute stands out for its commitment to delivering quality education through: Expert Instructors: Learn from industry professionals with real-world experience in React development. Comprehensive Curriculum: The course covers essential topics, including JSX, components, state management, hooks, routing, and integration with backend services. Hands-On Projects: Apply your learning through practical projects that simulate real-world scenarios. Flexible Learning Options: Choose from various learning modes to fit your schedule and learning style. Course Highlights Fundamentals of React: Understand the core concepts that make React a powerful tool for front-end development. Component-Based Architecture: Learn how to build reusable components to create scalable applications. State and Props Management: Master the techniques for managing data within your applications. React Hooks: Dive into hooks to write cleaner and more efficient code. Routing with React Router: Implement navigation within your single-page applications. Integration with APIs: Learn how to connect your React applications to backend services. Deployment: Gain the skills to deploy your applications to various platforms. To join the React JS course at Fusion Software Institute, visit their official website at fusion-institute.com or contact us at +91 7498992609 / +91 9890647273.
0 notes