#漢朝
Photo
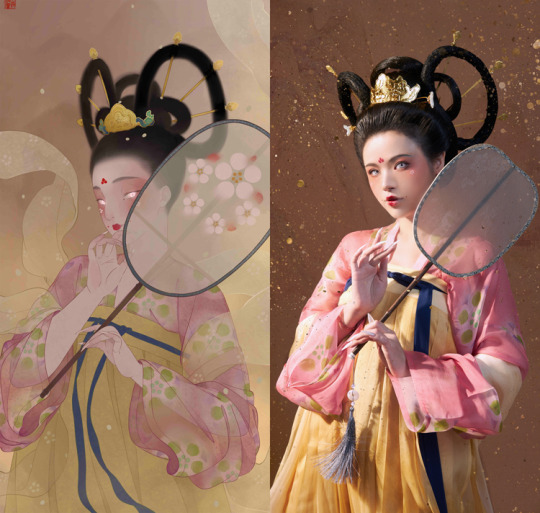
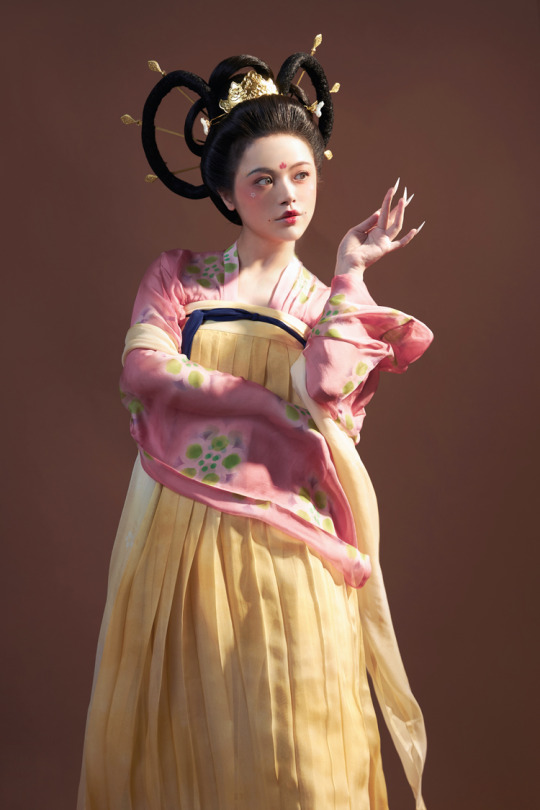
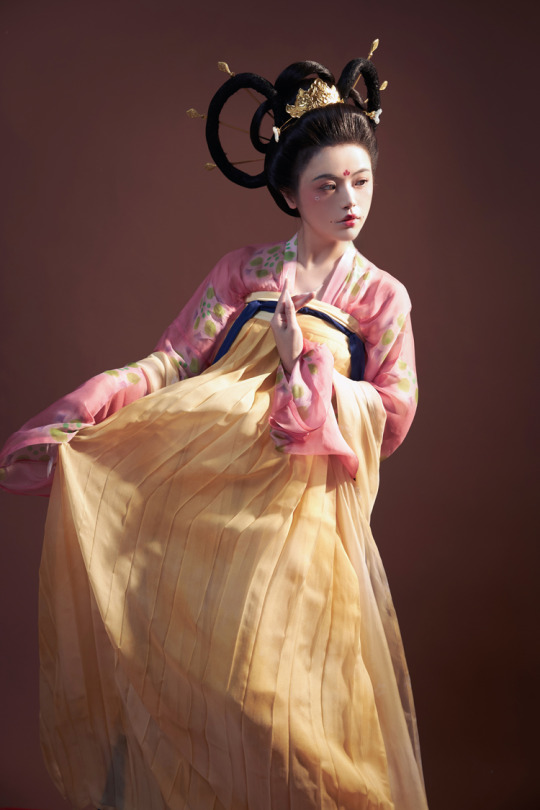
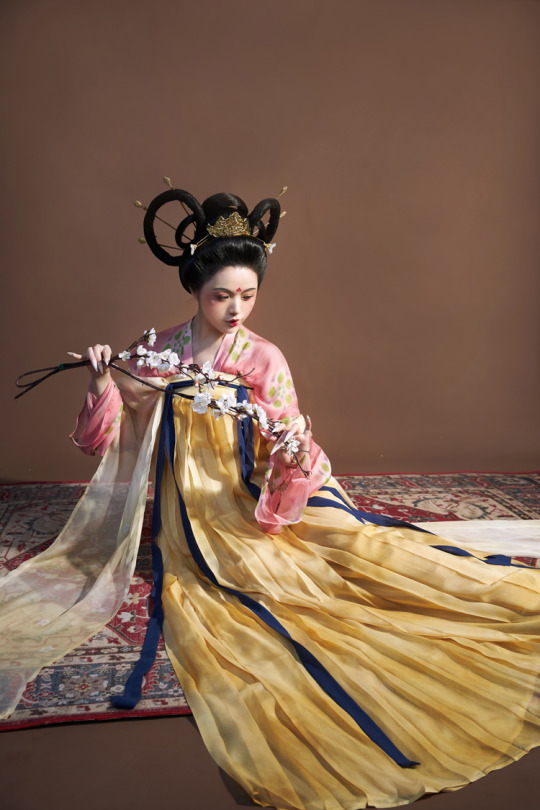
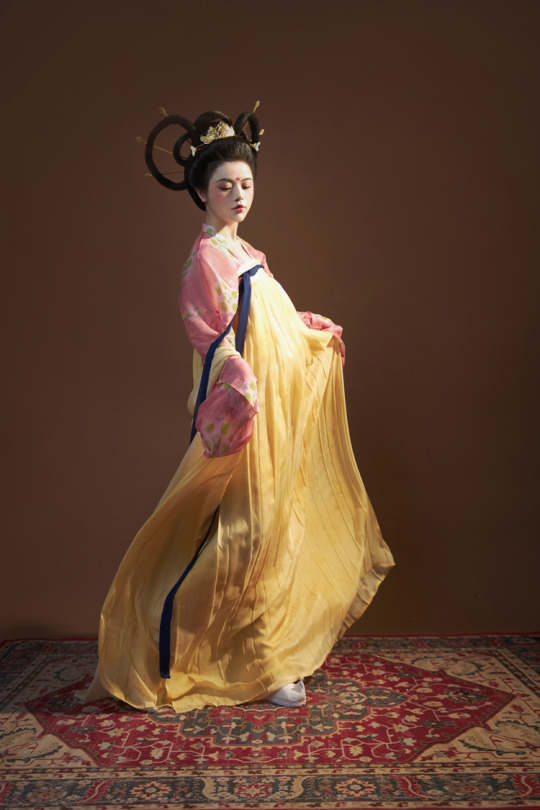
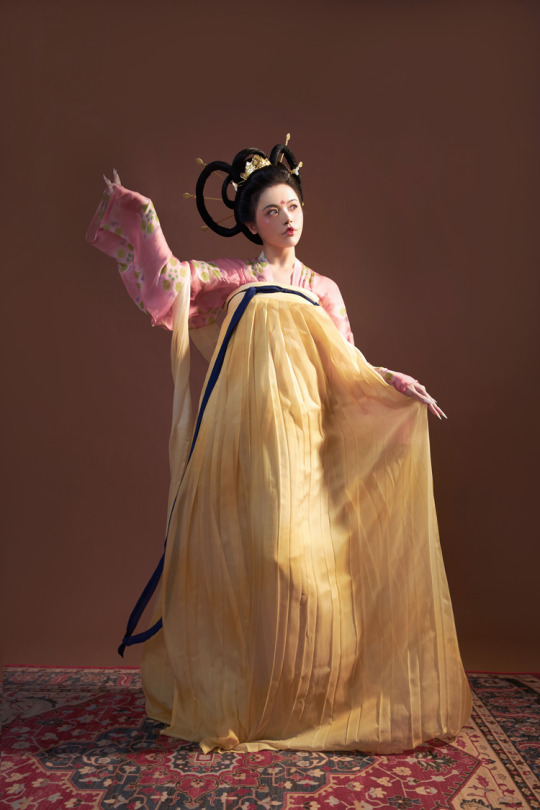
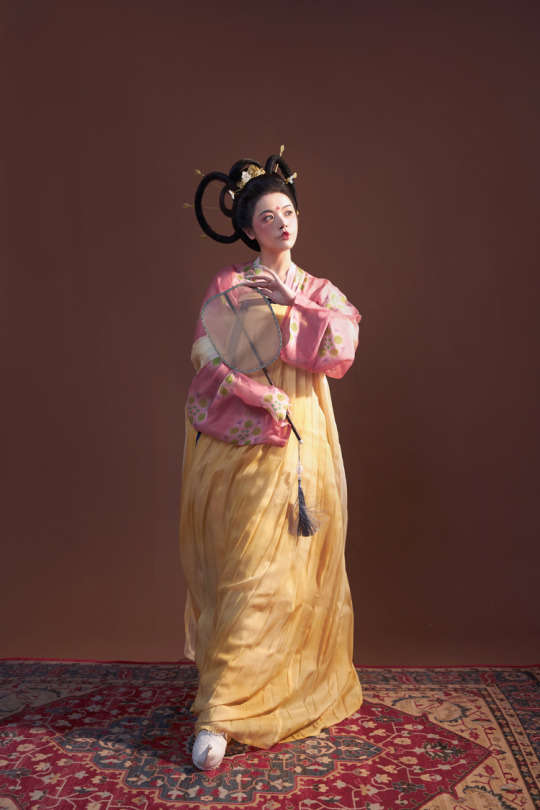
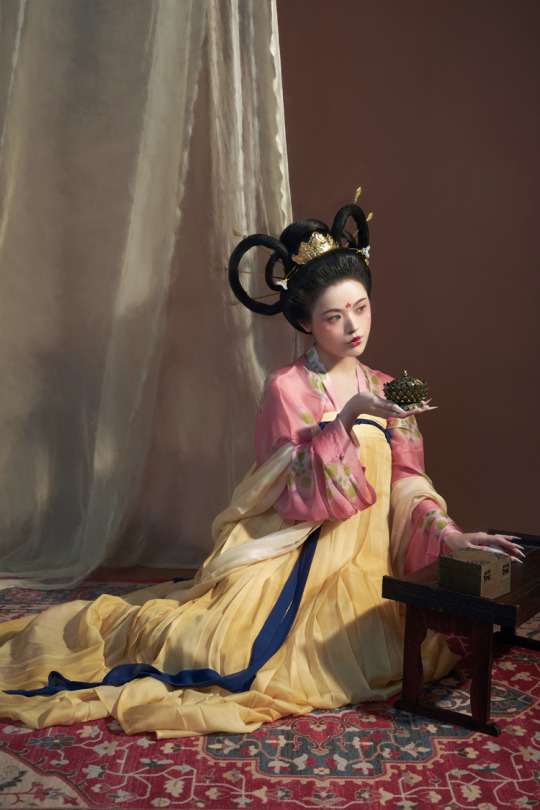
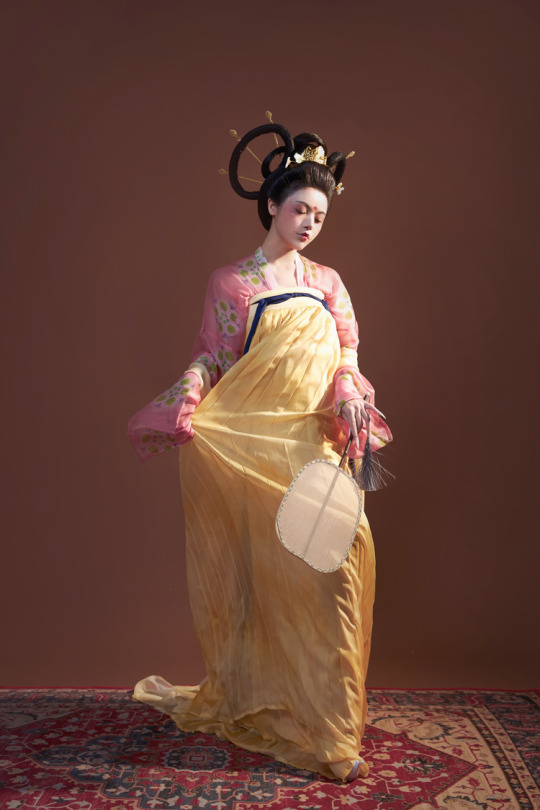












[Hanfu · 漢服]China Tang Dynasty Chinese Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoots Inspired by Artist @山野画皮匠 Hanfu Art【杏仙/Apricot Flowers Fairy】
—————————————-
Photo & Hanfu:@朝露之城
Weibo:https://weibo.com/2233116810/MbbsDo2wA
Taobao:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a230r.1.14.26.3731756dCSugZn&id=687445817234&ns=1&abbucket=15#detail
Artist @山野画皮匠 Twitter:https://twitter.com/ObNon2o/status/1505879743408791556
—————————————-
#Chinese Hanfu#Tang Dynasty#Hanfu#hanfu photoshoot#hanfu art#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese#chinese fashion#Chinese Costume#Chinese Style#Chinese Culture#Hanfu From China#chinese traditional clothing#朝露之城#山野画皮匠#杏仙#漢服#汉服
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

Japanese Kanji: morning - 朝
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#晨 #dawn #シン . #黎明 #朝 #morning #ペン習字 #筆ペン #漢字 #書道 #書法 #書遊 #毛筆 #墨 #習字 #日本文化 #筆文字 #文字 #和文化 #創作書道 #インスタ書道部 #書道好きな人と繋がりたい https://www.instagram.com/p/CiHweP2LUXD/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
🔥中共已難突破分化美日韓保台陣線?透視護身軍刀.漢光演習 台灣戰力大提升?千萬小心中共超限戰嫁禍台灣!國王人馬秦剛惹今上生氣?習換臉拉攏民企?|...
#youtube#新聞大破解#黃清龍#余宗基#秦剛#護身軍刀#漢光演習#中國經濟#毒包裹#朝鮮#新闻大破解#黄清龙#秦刚#护身军刀#汉光演习#中国经济#朝鲜#美日韓英澳#13國軍演#美日韩英澳#13国军演
1 note
·
View note
Text



草壁皋月 唐朝服裝 漢服 角色扮演 cosplay girls
head swap 同人 二次創作
0 notes
Photo

おはようございます。 12月12日月曜日、 いいじいいじ…と言うことで、本日は漢字の日だとか、そう言えば今年の漢字一文字は何でしょう?今日の午後2時、京都清水寺から発表されるようです。 ちなみに昨年は「金」でしたね。 うーむ、ブラボーを漢字にしたら何だろう?(と呟く) 高瀬美紀の 「おはよう鎌倉月曜日」 7時スタートです。 #漢字の日 #ブラボー #今朝は冷えます #おはよう鎌倉月曜日 #朝5時の月 (北鎌倉 Kita Kamakura) https://www.instagram.com/p/CmCqSdHSXDC/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Photo
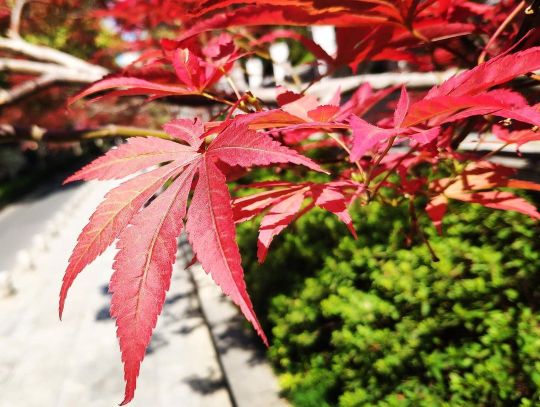

山行 唐 杜牧 遠上寒山石徑斜,白雲深處有人家。 停車坐愛楓林晚,霜葉紅於二月花。 #南京 #nanking #nanjing #史跡 #名勝 #冶山 #朝天宮 #autumn #秋 #秋天 #賞秋 #楓 #🍁 #楓葉 #kaede #漢詩 #唐詩 #七言絕句 #杜牧 (在 Nanjing, China) https://www.instagram.com/p/Cjj6tEehFMe/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Photo
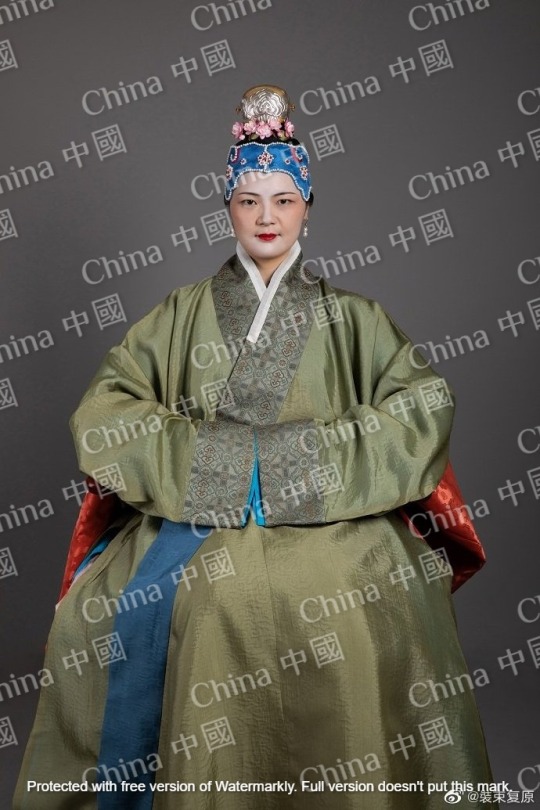


明朝服飾
Chinese Ming Dynasty clothing
#China#Ming Dynasty#Clothes#Chinese style#Hanfu#Chinese culture#Chinese history#Chinese clothing#Chinese fashion#history#culture#明朝#中國#中華文化#中國風#中華風#漢服#漢文化#Chinese#裝束復原#中華圈#華服#中華#華夏#華圈#華風#中式#چین#هانفو#Китай
0 notes
Video
youtube

0 notes
Text
2022【東澳秘境粉鳥林】宜蘭免費玩水親子景點
宜蘭在地人的玩水秘境,更是業者的浮潛天堂,日出SUP獨木舟的出發地,黃昏的藍綠寶石海,夜晚更是拍銀河的聖地,你怎能錯過!
(more…)

View On WordPress
#windguru 粉鳥林#一支小雨傘 粉鳥林#南澳漂漂河#國光客運 粉鳥林#宜蘭 東澳景點#宜蘭 粉鳥林#尤浪漢Yulanhan#愛情鎖海灘#朝陽步道 粉鳥林#東岳樟樹公園(原住民家屋)#東澳 粉鳥林#東澳 粉鳥林 交通#東澳 粉鳥林 餐廳#東澳景點#東澳景點 2天1夜#東澳景點 2天一夜#東澳景點 3d#東澳景點 3d光雕彩繪隧道#東澳景點 3天2夜#東澳景點 4天3夜#東澳景點2021#東澳景點2022#東澳火車站 粉鳥林#機車 粉鳥林#碧候溫泉#粉鳥林#粉鳥林 sup 漁船#粉鳥林 一日遊#粉鳥林 交通#粉鳥林 入口
0 notes
Photo

📍貳樓餐廳:台北市中山區中山北路二段16巷22號 早上上班前去了好幾年沒有去的#貳樓餐廳 🍰 當作#朝活 (あさかつ)哈哈! 最近在日本在流行「☀️朝活(あさかつ)」! #跟風 一下哈哈!😊(最近學到的中文哈哈) 如果有推薦的可以在早上做(朝活)的話,請你跟我分享✨ #朝活 (あさかつ) →早點起床上班前做跟平常稍微不一樣的事 #跟風(中文) →流行に乗る(日文) ✏️這次點的餐 ✔️經典貳樓早午餐:330元 ✔️酒香蒜味蛤蜊墨魚麵:350元 ✔️松露薯條:230元 *套餐可以選飲料/其中一杯可以無限續杯 #貳樓 #貳樓餐廳 #中山美食 #台北美食 #台北早午餐 #台北早餐 #日文老師 #永漢日語 #永漢 #日本語 #台灣美食 #台湾グルメ #台湾旅行 #台湾生活 #朝ご飯 #カフェ #台湾カフェ #片岡 (貳樓中山南西) https://www.instagram.com/p/CeobX-FPt1U/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
“这个位子 我有何坐不得?”
“我欲问鼎天下,试问谁与争锋”
"Why can't I sit in this seat?"
"I want to conquer the world, who can compete with me?"
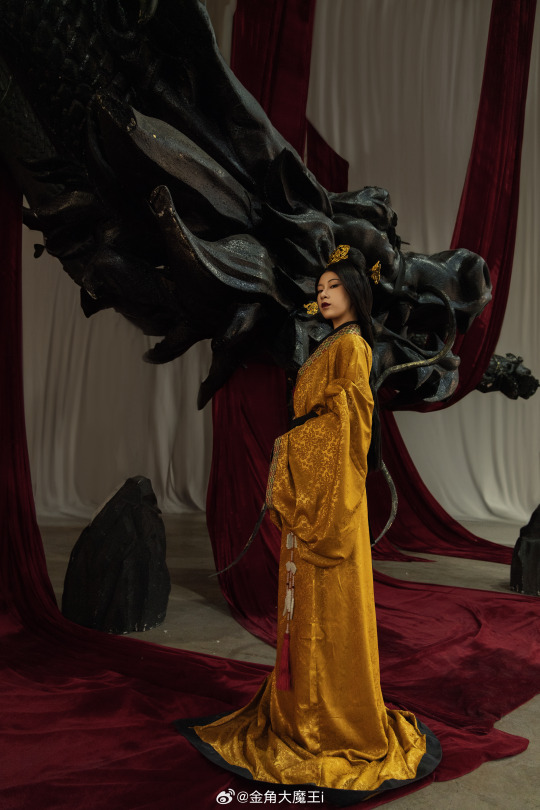
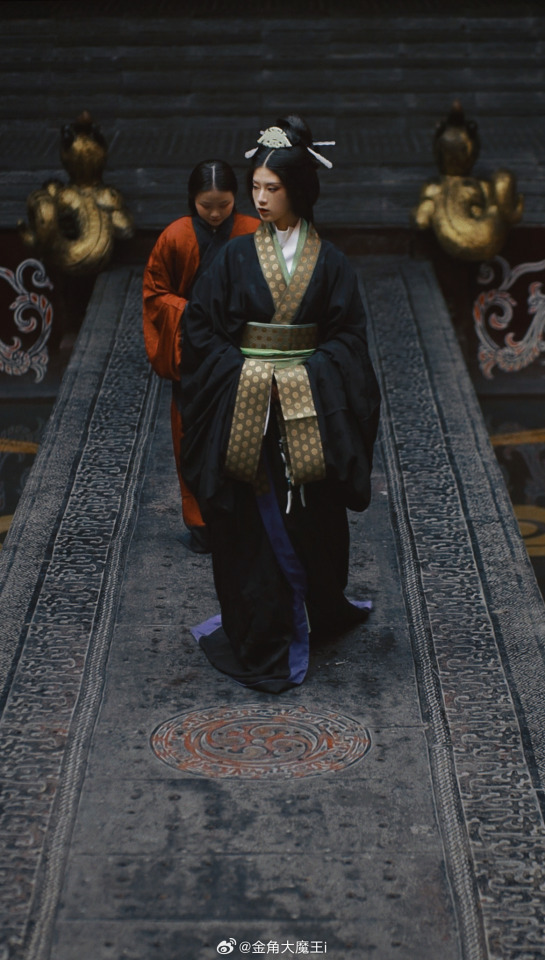
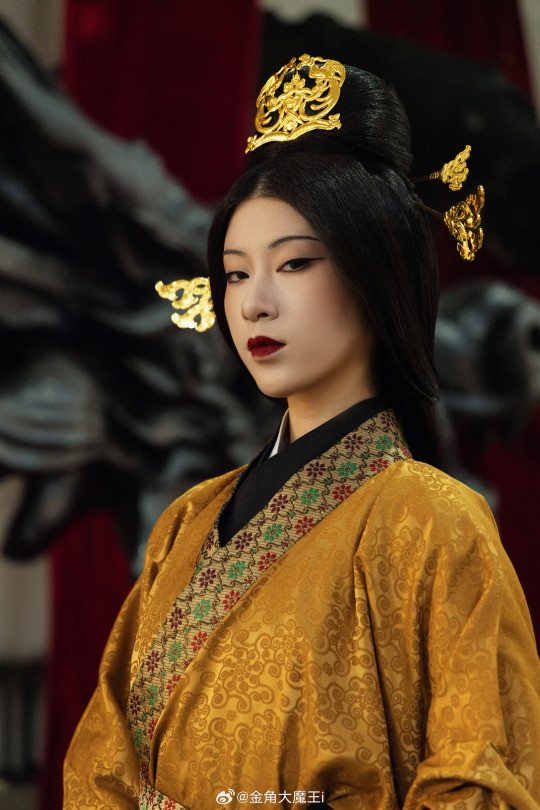
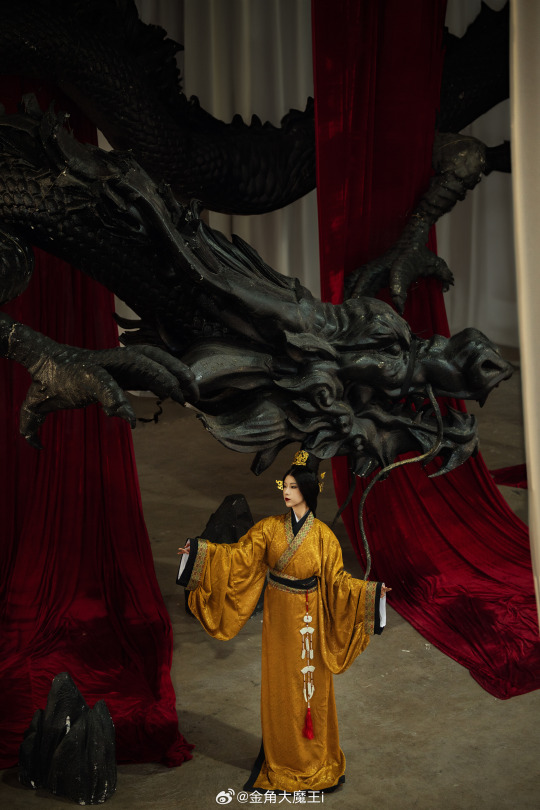
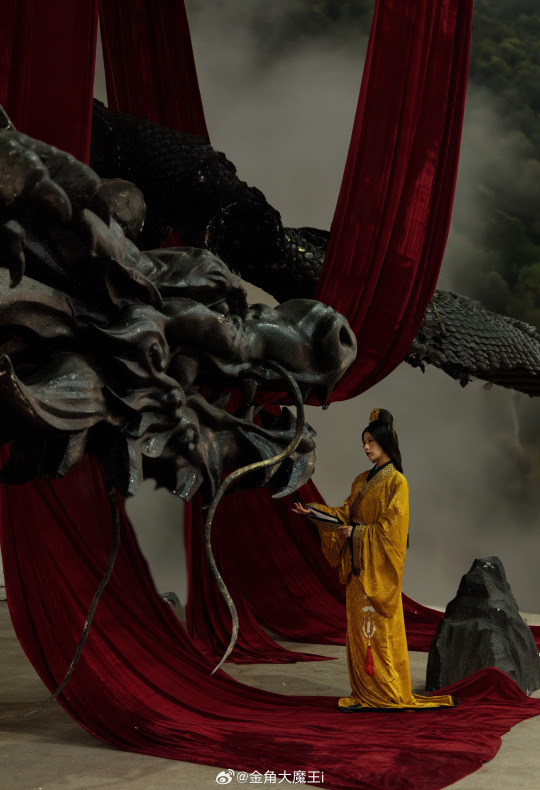








【About The First Empress of the Han Dynasty Empress Lü:Lǚ zhì(吕雉)】
Lü Zhi (241–18 August 180 BC), courtesy name E'xu (娥姁) and commonly known as Empress Lü (traditional Chinese: 呂后; simplified Chinese: 吕后; pinyin: Lǚ Hòu) and formally Empress Gao of Han (漢高后; 汉高后; Hàn Gāo Hòu), was the empress consort of Gaozu, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. They had two known children, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han) and Princess Yuan of Lu. Lü was the first woman to assume the title Empress of China and paramount power. After Gaozu's death, she was honoured as empress dowager and regent during the short reigns of Emperor Hui and his successors Emperor Qianshao of Han and Liu Hong (Emperor Houshao).
She played a role in the rise and foundation of her husband, Emperor Gaozu, and his dynasty, and in some of the laws and customs laid down by him. Empress Lü, even in the absence of her husband from the capital, killed two prominent generals who played an important role in Gaozu's rise to power, namely Han Xin and Peng Yue, as a lesson for the aristocracy and other generals. In June 195 BC, with the death of Gaozu, Empress Lü became, as the widow of the late emperor and mother of the new emperor, Empress Dowager (皇太后, Huángtàihòu), and assumed a leadership role in her son's administration. Less than a year after Emperor Hui's accession to the throne, in 194 BC, Lü had one of the late Emperor Gaozu's consorts whom she deeply hated, Concubine Qi, put to death in a cruel manner. She also had Concubine Qi's son Liu Ruyi poisoned to death. Emperor Hui was shocked by his mother's cruelty and fell sick for a year, and thereafter no longer became involved in state affairs, and gave more power to his mother. As a result, Empress dowager Lü held the court, listened to the government, spoke on behalf of the emperor, and did everything (臨朝聽政制, "linchao ting zhengzhi"). With the untimely death of her 22-year-old son, Emperor Hui, Empress dowager Lü subsequently proclaimed his two young sons emperor (known historically as Emperor Qianshao and Emperor Houshao respectively). She gained more power than ever before, and these two young emperors had no legitimacy as emperors in history; the history of this 8-year period is considered and recognized as the reign of Empress Dowager Lü. She dominated the political scene for 15 years until her death in August 180 BC, and is often depicted as the first woman to have ruled China. While four women are noted as having been politically active before her—Fu Hao, Yi Jiang, Lady Nanzi, and Queen Dowager Xuan—Lü was the perhaps first woman to have ruled over united China.
Lü Zhi was born in Shanfu County (單父; present-day Shan County, Shandong) during the late Qin Dynasty. Her courtesy name was Exu (Chinese: 娥姁; pinyin: Éxǔ). To flee from enemies, her father Lü Wen (呂文) brought their family to Pei County, settled there, and became a close friend of the county magistrate. Many influential men in town came to visit Lü Wen. Xiao He, then an assistant of the magistrate, was in charge of the seating arrangement and collection of gifts from guests at a banquet in Lü Wen's house, and he announced, "Those who do not offer more than 1,000 coins in gifts shall be seated outside the hall." Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han), then a minor patrol officer (亭長), went there bringing a single cent and said, "I offer 10,000 coins." Lü Wen saw Liu Bang and was so impressed with him on first sight, that he immediately stood up and welcomed Liu into the hall to sit beside him. Xiao He told Lü Wen that Liu Bang was not serious, but Liu ignored him and chatted with Lü. Lü Wen said, "I used to predict fortunes for many people but I've never seen someone so exceptional like you before." Lü Wen then offered his daughter Lü Zhi's hand in marriage to Liu Bang and they were wed. Lü Zhi bore Liu Bang a daughter (later Princess Yuan of Lu) and a son, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han).
Liu Bang later participated in the rebellion against the Qin Dynasty under the insurgent Chu kingdom, nominally-ruled by King Huai II. Lü Zhi and her two children remained with her father and family for most of the time during this period.
Even after Emperor Gaozu (Liu Bang)'s victory over Xiang Yu, there were still unstable areas in the empire, requiring the new government to launch military campaigns to pacify these regions thereafter. Gaozu placed Empress Lü Zhi and the crown prince Liu Ying (Lü Zhi's son) in charge of the capital Chang'an and making key decisions in court, assisted by the chancellor Xiao He and other ministers. During this time, Lü Zhi proved herself to be a competent administrator in domestic affairs, and she quickly established strong working relationships with many of Gaozu's officials, who admired her for her capability and feared her for her ruthlessness. After the war ended and Emperor Gaozu returned, she remained in power and she was always influential in many of the country's affairs.
In his late years, Emperor Gaozu started favouring one of his younger consorts, Concubine Qi(戚夫人), who bore him a son, Liu Ruyi, who was instated as Prince of Zhao in 198 BC, displacing Lü Zhi's son-in-law Zhang Ao (Princess Yuan of Lu's husband). Gaozu had the intention of replacing Liu Ying with Liu Ruyi as crown prince, reasoning that the former was too "soft-hearted and weak" and that the latter resembled him more. Since Lü Zhi had strong rapport with many ministers, they generally opposed Gaozu's decision but the emperor seemed bent on deposing Liu Ying. Lü Zhi became worried and she approached Zhang Liang for help, and the latter analysed that Gaozu was changing the succession on grounds of favouritism. Zhang Liang invited the "Four Whiteheads of Mount Shang", a group of four reclusive wise men, to persuade Gaozu to change his decision. The four men promised to assist Liu Ying in future if he became emperor, and Gaozu was pleased to see that Liu Ying had their support. Gaozu told Concubine Qi, "I wanted to replace (the crown prince). Now I see that he has the support of those four men; he is fully fledged and difficult to unseat. Empress Lü is really in charge!" This marked the end of the dispute over the succession and affirmed Liu Ying's role as crown prince.
In June 195 BC, Emperor Gaozu died and was succeeded by Liu Ying, who became historically known as Emperor Hui of Han. Lü Zhi was honoured by Emperor Hui as empress dowager. She exerted more influence during the reign of her son than she had when she was empress, and she became the powerful and effective lead figure in his administration.
Lü Zhi did not harm most of Gaozu's other consorts and treated them according to the rules and customs of the imperial family. For example, consorts who bore male children that were instated as princes were granted the title of "Princess Dowager" (王太妃) in their respective sons' principalities. One exception was Concubine Qi, whom Lü Zhi greatly resented because of the dispute over the succession between Liu Ruyi (Qi's son) and Liu Ying. Liu Ruyi, the Prince of Zhao, was away in his principality, so Lü Zhi targeted Concubine Qi. She had Qi stripped of her position, treated like a convict (head shaved, in stocks, dressed in prison garb), and forced to do hard labour in the form of milling rice.
Roles in the deaths of Concubine Qi and Liu Ruyi
Lü Zhi then summoned Liu Ruyi, who was around the age of 12 then, to Chang'an, intending to kill him together with his mother. However Zhou Chang (周昌), the chancellor in Liu Ruyi's principality, whom Lü Zhi respected because of his stern opposition to Emperor Gaozu's proposal to make Liu Ruyi crown prince, temporarily protected Liu Ruyi from harm by responding to Lü Zhi's order that, "The Prince of Zhao is ill and unfit for travelling over long distances." Lü Zhi then ordered Zhou Chang to come to the capital, had him detained, and then summoned Liu Ruyi again. Emperor Hui tried to save Liu Ruyi by intercepting his half-brother before the latter entered Chang'an, and kept Liu Ruyi by his side most of the time. Lü Zhi refrained from carrying out her plans for several months because she feared that she might harm Emperor Hui as well.
One morning in the winter of 195-194 BC, Emperor Hui went for a hunting trip and did not bring Liu Ruyi with him because the latter refused to get out of bed. Lü Zhi's chance arrived, so she sent an assassin to force poisoned wine down Liu Ruyi's throat. The young prince was dead by the time Emperor Hui returned. Lü Zhi then had Concubine Qi killed in an inhumane manner: she had Qi's limbs chopped off, eyes gouged out, ears sliced off, nose sliced off, tongue cut out, forced her to drink a potion that made her mute, and had her thrown into a latrine. She called Qi a "human swine" (人彘). Several days later, Emperor Hui was taken to view the "human swine" and was shocked to learn that it was Concubine Qi. He cried loudly and became ill for a long time. He requested to see his mother and said, "This is something done not by a human. As the empress dowager's son, I'll never be able to rule the empire" From then on, Emperor Hui indulged himself in carnal pleasures and ignored state affairs, leaving all of them to his mother, and this caused power to fall completely into her hands.
When Lu first came to the court, she planned to establish the Lu family members as "kings (nobles)". This was not only to commemorate her deceased relatives, but also to strengthen her power in the court. However, Wang Ling, the prime minister at the time, immediately pointed out that the great ancestor Liu Bang(Husband of Lu, founding emperor of Han Dynasty)once killed the white horse and agreed that "if someone who are not Liu family be come the king, the whole world should attack them." Therefore, the move of establishing a foreign surname as the king violated the ancestral system established by Liu Bang and was really inappropriate.
Faced with the obstruction of Wang Ling, Empress Lu responded by deposing him and insisting on honoring her deceased father and two brothers as King Lu Xuan, King Wu Wu, and King Zhao Zhao. After setting this precedent, Lu was out of control. She not only named her three nephews Lu Tai, Lu Chan, and Lu Lu as King Lu, King Liang, and King Zhao respectively, but also named her grandnephew Lu Tong. He was the King of Yan, and his grandson Zhang Yan was granted the title of King of Lu.
In addition, there are also quite a few people with the surname Lu who have been granted the title of marquis. As a result, it can be said that many princes surnamed Lu appeared in the court in the blink of an eye. They controlled the government and became the cornerstone and support for Empress Lu to control the right to speak in the court.
Empress Lu's life was emblematic of the intricate power dynamics of the Han Dynasty in ancient China. Born into a modest family, Lu rose to prominence through her marriage to Emperor Gaozu. Her astute political acumen and strategic alliances allowed her to wield significant influence behind the throne. As the mother of several emperors, she orchestrated their ascensions and manipulated court politics to consolidate power for her family. However, her ruthless pursuit of control and elimination of rivals earned her both admirers and enemies. In the end, her ambitions led to her downfall, as her unchecked power and manipulation of succession angered the nobility.As a result, after her death, the Lu family was retaliated and killed by the nobles and courtiers who supported the Han Dynasty, and the family was almost exterminated.Empress Lu's life illustrates the delicate balance of power, ambition, and intrigue in ancient Chinese imperial courts.
Literati in every dynasty in China often likened women who attempted to participate in government affairs and influence national policies to Empress Lü, saying they were vicious. One of them was Wu Zetian, the first official female emperor of China. However, compared with Empress Lü, Wu Zetian was more talented. Unlike Empress Lü, who was simply vicious, she ignored the system and stability of the empire and put personal and family interests first.
________________
📸Photo & Model :@金角大魔王i
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/NFVOXthxX
________________
#chinese hanfu#Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD)#hanfu#Empress Lü#Lǚ zhì(吕雉)#china history#chinese history#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#woman in history#漢服#汉服#中華風#金角大魔王i#historical fashion
174 notes
·
View notes
Text

❖ 昭和20年8月14日 ❖
白旗を上げた非武装の日本人数千名に、ソ連兵たちが銃弾をあびせ、戦車で引き殺した事件、『葛根廟大虐殺事件』があった日です。
一方的に条約を破り満州に侵攻してきたソ連兵は、日本人を戦車で引き殺したあと、銃剣でとどめをさし、2時間余りで千人以上を殺害。
9割が女子子供でした。
婦女子は暴行をされた後、乳房を切り落とされむごい方法で殺されました。
小屋に隠れていた婦女子には、朝まで強姦し続けた後、小屋に枯れ草を投げ入れ火を付け焼き殺しました。
自害するものもいる中、やっとの思いでかろうじて逃れた者は日本本土をめざし南下の途中、次に待っていたのは満洲人や支那人や朝鮮人の無慈悲な想像に耐え難い強姦暴行殺戮でした。
日本の地を踏むこと叶わず無惨に命を落としたのです。
その内の僅か数十人が残留孤児となりました。
本当に語り継がなければならないのは、
ウソで作られたK国がいう慰安婦問題でも、
C国がいう南京虐殺でもなく、
真実の『葛根廟大虐殺事件』の方なのです。
日本人が被害にあった事件は、全く教科書では教えないことが、最大の問題だと思います。
毎年8/14、東京目黒の五百羅漢寺で今日も供養が行われているそうです。

376 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#朝 #morning #dawning . #Sibu #シブ #マレーシア #Malaysia #ペン習字 #筆ペン #漢字 #書道 #書法 #書遊 #毛筆 #墨 #習字 #日本文化 #筆文字 #文字 #和文化 #創作書道 #インスタ書道部 #書道好きな人と繋がりたい (at Outright Coffee) https://www.instagram.com/p/Cnve9YuPivg/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#朝#morning#dawning#sibu#シブ#マレーシア#malaysia#ペン習字#筆ペン#漢字#書道#書法#書遊#毛筆#墨#習字#日本文化#筆文字#文字#和文化#創作書道#インスタ書道部#書道好きな人と繋がりたい
1 note
·
View note
Text
何故、中共は「中国4000年の歴史」とか「中華民族」とか見えすいた嘘を吐くのか?侵略の準備なんだよ!
本当は夏朝、殷、隋、唐、金、遼、元、清など全て騎馬民族など異民族支配で元々の漢民族は殆ど後漢で滅んでる
その王朝でも支配してたのは北京周辺であり今のチベット、内モンゴル、ウイグルなどの地域も異民族に支配されており、北京周辺王朝は貢いでたり、王族などから女を贈って、勘弁して貰ってた
女を贈って置いて「あの地方王朝の王は俺たちの婿様だから、あそこも中華王朝の一部」とか無理な事を言ってる
しかし中共はその論理でチベットを盗り、内モンゴルを裏切り、東トルキスタン(ウイグル)を強奪して、中共から人を沢山送り現地人をレイプ強姦して妊娠させ混血児を増やし、現地人には強制堕胎、強制不妊手術を行い純粋な現地人人口を減らし、言葉を奪い、文化や宗教を禁止して文字通り民族浄化して、根絶やしにしようとしている
「元々は中華の一部」「太古より中華民族(なんだソレ?)が住んでた」と言い張り、侵略している
同じ論理をプーチンがウクライナに言って「元々はロシアの一部」「昔からウクライナにもロシア人が住んでた」と言い張り、ロシア系住民保護と主張して、ウクライナに侵攻した
おんなじパターン
中共は「尖閣は中共の土地」「沖縄は中国(どの支那だよ?)に朝貢してた中国の一部」と主張している
北海道には沢山、移民させてる
次はどうなるかって?
そりゃ中共による尖閣、沖縄、北海道の侵略が始まるんだよ!
だから「中国4000年の歴史」とか「ずっと中国はあった」とか「偉大な中華民族(何ソレ?)」という嘘に加担しては駄目だ!
それは彼らの宣伝
それは彼らのプロパガンダ
なんだよ?
欧米なんか知ってか知らずか
鵜呑みにしてる
日本国民は洗脳されて
鵜呑みにしてる
まずそこを否定して
防衛強化して
教育を強化して行こう!
【関連】
828 :本当にあった怖い名無し :sage :2010/09/27(月) 12:12:24 ID:fsTA3r1B0(4)
支那人にも孔子、老子、孟子を生んだ立派な文明があると誤解している日本人が多いのだと思います。
漢文を通じて中国人を理解することぐらい、絶望的な行為はありません。何故なら漢文はこの二千年間というもの中国語とは全く関係がない。日本人のほとんどは漢文を中国語の古語と思ってきたのです。
つまり日本人が尊敬し 知っている漢民族は紀元二世紀でこの地球上から姿を消し、中国住民はそっくり北方の騎馬民族の子孫に何回も何回も入れ替わってしまったのです。
そして秦や漢時代の中国人は,そのほとんどが大陸から居なくなったということです。
ところが日本は遣隋使や遣唐使たちの使節が派遣され膨大な漢籍を大陸から持ち帰り,それを今日まで途切れることなく勉強してきたのです。
つまり日本人は騎馬民族の子孫である中国でなく2000年以上前のいなく なった漢民族の文化を勉強してきたのです。
日本人なら誰でも知っている儒教の開祖である孔子は,紀元前6~5世紀 中国各地の有力諸侯が覇権を争っていた春秋時代のことです
830 :本当にあった怖い名無し :sage :2010/09/27(月) 12:13:38 ID:fsTA3r1B0(4)
使節団が中国から持ち帰った無数の漢籍を日本人は今日まで約1300年間も読み込んできたのです。
早い話が遣隋使や遣唐使が持ち帰った「論語」や「漢詩」などによって 皮肉なことに中国人でなく日本人の人格が磨かれてきたのです。
中国語と漢文は全く関係がない、つまり漢文の読めない中国人にとって孔子や孟子の教えなど身につくはずもありません。
いわゆるこの二千年間というもの,漢文は中国語とは全く関係がないと いうことを多くの日本人は知らなかったのです。
私はこれらのことを中国史研究の第一人者である岡田英弘先生から教えてもらいました。
私も20年前 漢文を通じて身につけた中国イメージのまま中国に進出してそのギャップの大きさに仰天した記憶があります。
中国進出する前は、信義に厚く,礼を尊ぶ文化人の国であると信じていました。しかし現実にいるのは,油断も隙もならない、詐欺師の野蛮人ばかりでした。
中国人に取って漢文とは外国語同然なのです.中国で話されている言葉とは全く無縁の言語体系なのです。
831 :本当にあった怖い名無し :sage :2010/09/27(月) 12:14:22 ID:fsTA3r1B0(4)
現在の中国人は,彼らが使っている中国語が,実は文体もボキャブラリーも日本語からの借用であるということを隠そうとしています.現代日本文の真似をして前置詞や助動詞を明確に記すことによって、やっと文章が書けるようになったのです。
日清戦争後,日本に大量の清国留学生がやってきて,日本語を学び中国語を誰でもが読める中国語の表記法を改良していったのです.その中にかの有名な魯迅もいたのです。
日本語をマスターした魯迅の頭の中は日本語の文章があり,それを漢字に置き換えて表現することによって原文一致体の「白話文」が生まれました。
そして試行錯誤の結果 現在における中国語は北京語を元にした「普通話」がやっと確立されたのです。
つねに色んな異民族に取って変わられた中国の歴史を眺めたとき,中国政府が宣伝している四千年の歴史は中国人の歴史ではなく中国大陸の歴史だということがわかります。
中国には単一民族としての中国人は一度も存在しなかった.中国語には
北京語,上海語,福建語などの言葉があることを知られていますが、実際はもっと言語は細分化されています。これらは単なる方言というのでなく,ほとんど共通点がありません。
そこで中国政府は各国が持っている「国民国家」というシステムを作るために国民を北京語に統一して教育してきたのです。それもまだ100年足らずのことです。
833 :本当にあった怖い名無し :sage :2010/09/27(月) 12:16:10 ID:fsTA3r1B0(4)
そして言語だけでなく異文化、異言語の人々の寄せ集め集団である中国を統一するために歴史も歪曲せざるをえなかった。
毛沢東は少数民族を含めて全ての中国人を漢族にしてしまうために少数民族の文化を奪い、抵抗するものは容赦なく抹殺してきたのです。
もし少数民族の自治や、言論の自由といったものを実現させれば、中国政府が意図する最強の「国民国家」システムの改造計画が頓挫してしまいます。
この中国共産党の意図が理解できたとき、日本人やアメリカ人が思っている「中国は資本主義開放経済への道を進めば自然に民主国家になっていく」という考えが いかに愚かな事であるかということがわかっていただけたとおもいます。
http://2nnlove.blog114.fc2.com/blog-entry-2836.html
402 notes
·
View notes
Photo

日暮途遠,人間何世?(庾信《哀江南賦》) 山阿寂寥,千載誰賞!(孔稚珪《北山移文》) #南京 #nanjing #nanking #summer #☁ #🌄 #sunset #江南 #登高 #登高望遠 #丘陵 #⛰️ #summer #夏 #夏日 #夏天 #漢文 #駢文 #駢句 #摘句 #南朝 #庾信 #孔稚珪 #哀江南賦 #北山移文 (at Nanjing, China) https://www.instagram.com/p/CfdyZdTlF7k/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes