#1790s Britain
Text
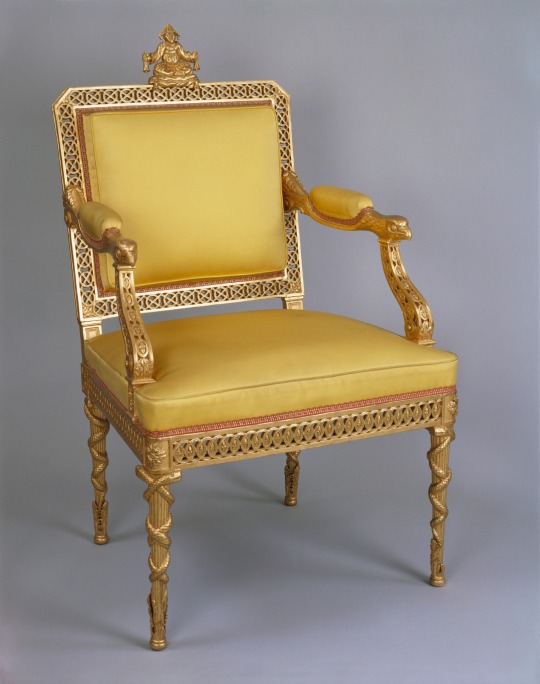

Yellow Silk and Giltwood Armchair, 1790, British.
Designed by François Hervé.
Owned by George IV.
Royal Collection Trust.
#yellow#silk#chair#armchair#giltwood#royal collection trust#royal#George iv#François Hervé#1790#1790s furniture#1790s Britain
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
SO fucking funny that apush will find every possible way to make britain look stupid
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I like how many films set in 1790s britain are too cowardly to give the love interests of any of the characters/the sexy male hero wigs and so they instead opt to make the entire male cast look like a london corresponding society cell wrt the hairstyles
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
After African missionaries circulated initial reports about the slave labor behind sugar in the 1790s, some consumers desisted from sugar entirely -- "anti-saccharites", mostly fervent Christians such as Quakers. As the East India importers created a market in Britain, anti-slavery societies became their free marketing teams, widely distributing pamphlets such as "What Does Your Sugar Cost?" A Cottage Conversation on the Subject of British Negro Slavery. Meanwhile, in America, the free-produce movement was led by black women, who encouraged their segregated groceries to buy only slavery-free goods.
The bind that free Black Americans faced in sourcing their food and raw materials was especially harsh. They were forced to buy "ethical" expensive cotton from white farmers instead of black slaves, which frustrated those trying to support black businesses. They sought coffee from Liberia and Haiti, hoping that the majority black demographics of these countries would support black uplift and prevent slave labor, and these created natural (and, indeed, slavery-free) coffee industries in those countries which indeed persisted for some decades.
The most surprising part of this story comes in the 1840s. After abolishing slavery in 1836, Britain had placed tariffs on slave-produced sugar in order to ensure fairness for British sugar producers who paid their laborers. This inflated sugar prices generally. Without tariffs, "free-labour sugar" would cost three times as much as its competition, defeating the East Indian importers' argument that slavery was a corrupt process which artificially inflated prices. It soon became clear that the writing was on the wall. In 1845, the primary importer of "free-labour sugar" exited the sugar market, and the following year, Britain decided to remove all the tariffs, for the benefit of consumers. Free-labour sugar completely vanished as a category thereafter.
Meanwhile in the United States, abolitionists criticized the free-produce movement as ineffective; similar to "free-labour sugar", it only placed an extra economic burden on those struggling to live ethically. It was recognized on both sides of the Atlantic that making individual consumer choices was not enough, and that systemic change was necessary to permanently eliminate slavery. As a status symbol, though, "free cotton made by escaped slaves" continued to be worn in Britain and attracted comment in aristocratic salons into the 1860s. In this final stage of the movement, free labor was considered to be part of a civilizing project, a way to train ex-slaves in useful arts.
https://www.reddit.com/r/AskHistorians/comments/138i5at/comment/jj04qsx/?context=3
886 notes
·
View notes
Text
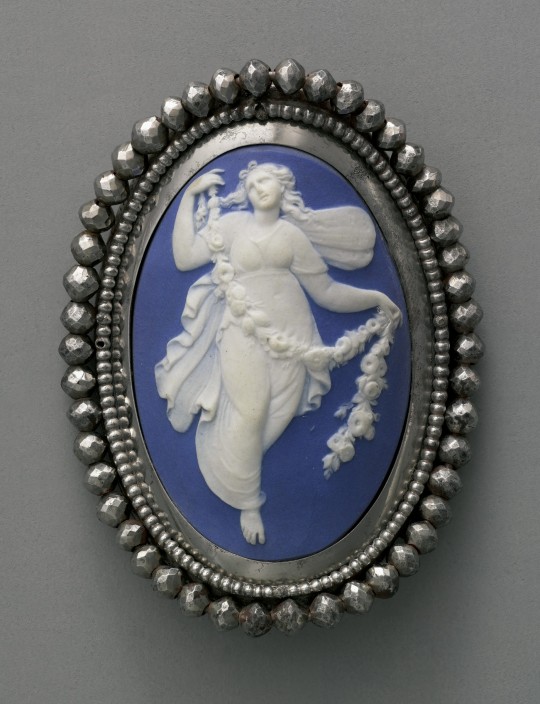

Cameo brooch with an image of Flora, 1790, Britain.
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Josh Marshall
I want to return to this revelatory interview with coconspirator John Eastman, the last portion of which was published Thursday by Tom Klingenstein, the Chairman of the Trumpite Claremont Institute and then highlighted by our Josh Kovensky. There’s a lot of atmospherics in this interview, a lot of bookshelf-lined tweedy gentility mixed with complaints about OSHA regulations and Drag Queen story hours. But the central bit comes just over half way through the interview when Eastman gets into the core justification and purpose for trying to overturn the results of the 2020 election and overthrow the constitutional order itself. He invokes the Declaration of Independence and says quite clearly that yes, we were trying to overthrow the government and argues that they were justified because of the sheer existential threat America was under because of the election of Joe Biden.
Jan 6th conspirators have spent more than two years claiming either that nothing really happened at all in the weeks leading up to January 6th or that it was just a peaceful protest that got a bit out of hand or that they were just making a good faith effort to follow the legal process. Eastman cuts through all of this and makes clear they were trying to overthrow (“abolish”) the government; they were justified in doing so; and the warrant for their actions is none other than the Declaration of Independence itself.
“Our Founders lay this case out,” says Eastman. “There’s actually a provision in the Declaration of Independence that a people will suffer abuses while they remain sufferable, tolerable while they remain tolerable. At some point abuses become so intolerable that it becomes not only their right but their duty to alter or abolish the existing government.”
“So that’s the question,” he tells Klingenstein. “Have the abuses or the threat of abuses become so intolerable that we have to be willing to push back?”
The answer for Eastman is clearly yes and that’s his justification for his and his associates extraordinary actions.
Let’s dig in for a moment to what this means because it’s a framework of thought or discourse that was central to many controversies in the first decades of the American Republic. The Declaration of Independence has no legal force under American law. It’s not a legal document. It’s a public explanation of a political decision: to break the colonies’ allegiance to Great Britain and form a new country. But it contains a number of claims and principles that became and remain central to American political life.
The one Eastman invokes here is the right to overthrow governments. The claim is that governments have no legitimacy or authority beyond their ability to serve the governed. Governments shouldn’t be overthrown over minor or transitory concerns. But when they become truly oppressive people have a right to get rid of them and start over. This may seem commonsensical to us. But that’s because we live a couple centuries downstream of these events and ideas. Governments at least in theory are justified by how they serve their populations rather than countries being essentially owned by the kings or nobilities which rule them.
But this is a highly protean idea. Who gets to decide? Indeed this question came up again and again over the next century each time the young republic faced a major political crisis, whether it was in the late 1790s, toward the end of the War of 1812, in 1832-33 or finally during the American Civil War. If one side didn’t get its way and wanted out what better authority to cite than the Declaration of Independence? There is an obvious difference but American political leaders needed a language to describe it. What they came up with is straightforward. It’s the difference between a constitutional or legal right and a revolutionary one. Abraham Lincoln was doing no more than stating a commonplace when he said this on the eve of the Civil War in his first inaugural address (emphasis added): “This country, with its institutions, belongs to the people who inhabit it. Whenever they shall grow weary of the existing Government, they can exercise their constitutional right of amending it or their revolutionary right to dismember or overthrow it.”
In other words, yes, you have a revolutionary right to overthrow the government if you really think its abuses have gotten that intractable and grave. But the government has an equal right to stop you, to defend itself or, as we see today, put you on trial if you fail. The American revolutionaries of 1776 knew full well that they were committing treason against the British monarchy. If they lost they would all hang. They accepted that. They didn’t claim that George III had no choice but to let them go.
From the beginning the Trump/Eastman coup plotters have tried to wrap their efforts in legal processes and procedures. It was their dissimulating shield to hide the reality of their coup plot and if needed give them legal immunity from the consequences. The leaders of the secession movement tried the same thing in 1861.
In a way I admire Eastman for coming clean. I don’t know whether he sees the writing on the wall and figures he might as well lay his argument out there or whether his grad school political theory pretensions and pride got the better of him and led him to state openly this indefensible truth. Either way he’s done it and not in any way that’s retrievable as a slip of the tongue. They knew it was a coup and they justified it to themselves in those terms. He just told us. They believed they were justified in trying to overthrow the government, whether because of OSHA chair size regulations or drag queens or, more broadly, because the common herd of us don’t understand the country’s “founding principles” the way Eastman and his weirdo clique do. But they did it. He just admitted it. And now they’re going to face the consequences.
#us politics#news#talking points memo#2023#op eds#Tom Klingenstein#Claremont Institute#john eastman#Josh Kovensky#Josh Marshall#jan 6 investigation#jan 6 insurrection#domestic terrorism#treason#traitors#donald trump#capitol riot investigation#Declaration of Independence
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
Planting trees does not necessarily mean a forest is being restored.
---
But efforts to increase global tree cover to limit climate change have skewed towards erecting plantations of fast-growing trees. The reasons are obvious: planting trees can demonstrate results a lot quicker than natural forest restoration. This is helpful if the objective is generating a lot of timber quickly or certifying carbon credits which people and firms buy to supposedly offset their emissions. [...] [I]ll-advised tree planting can unleash invasive species [...]. For more than 200 years India has experimented with tree plantations, offering important lessons about the consequences different approaches to restoring forests have on local communities and the wider environment. This rare long-term perspective should be heeded [...].
Britain extended its influence over India and controlled much of its affairs [...] from the mid-18th century onwards. Between 1857 and 1947, the Crown ruled the country directly and turned its attention to the country’s forests. Britain needed great quantities of timber to lay railway sleepers and build ships in order to transport the cotton, rubber and tea it took from India.
Through the Indian Forest Act of 1865, forests with high-yielding timber trees such as teak, sal and deodar became state property. To maximise how much timber these forests yielded, British colonial authorities restricted the rights of local people to harvest much beyond grass and bamboo. [...] Meanwhile plantations of teak (Tectona grandis), a species well adapted to India’s hot and humid climate and a source of durable and attractive timber, spread aggressively. [...]
---
[G]rasslands and open scrub forest gave way to teak monocultures.
Eucalyptus and other exotic trees which hadn’t evolved in India were introduced from around 1790. British foresters planted pines from Europe and North America in extensive plantations in the Himalayan region as a source of resin and introduced acacia trees from Australia for timber, fodder and fuel.
One of these species, wattle (Acacia mearnsii), first introduced in 1861 with a few hundred thousand saplings, was planted in the Nilgiris district of the Western Ghats. This area is what scientists all a biodiversity hotspot – a globally rare ecosystem replete with species. Wattle has since become invasive and taken over much of the region’s mountainous grasslands.
Similarly, pine has spread over much of the Himalayas and displaced native oak trees while teak has replaced sal, a native hardwood, in central India. Both oak and sal are valued for fuel, fodder, fertiliser, medicine and oil. Their loss [...] impoverished many.
---
India’s national forest policy [...] aims for trees on 33% of the country’s area. Schemes under this policy include plantations consisting of a single species such as eucalyptus or bamboo which grow fast and can increase tree cover quickly, demonstrating success according to this dubious measure. Sometimes these trees are planted in grasslands and other ecosystems where tree cover is naturally low. The result is that afforestation harms rural and indigenous people who depend on these ecosystems [...].
In the Kachchh grasslands of western India communities were able to restore grasslands by removing the invasive gando bawal (meaning “mad tree”) first introduced by British foresters in the late 19th century. [...]
The success of forest restoration efforts cannot be measured by tree cover alone. The Indian government’s definition of “forest” still encompasses plantations of a single tree species, orchards and even bamboo, which actually belongs to the grass family. This means that biennial forest surveys cannot quantify how much natural forest has been restored, or convey the consequences of displacing native trees with competitive plantation species or identify if these exotic trees have invaded natural grasslands which have then been falsely recorded as restored forests. [...]
Planting trees does not necessarily mean a forest is being restored. And reviving ecosystems in which trees are scarce is important too.
---
Text by: Dhanapal Govindarajulu. "India was a tree planting laboratory for 200 years - here are the results." The Conversation. 10 August 2023. [Bold emphasis, some paragraph breaks/contractions, and italicized first line in this post added by me.]
141 notes
·
View notes
Note
How do you feel about nation jobs or finances in your universe? Like are modern Matt or Alfred on government payroll even if they don’t do anything? I know you’re mentioned that Alfred is better at managing his money than Matt, is he rich??
Sorry I’m not phrasing this very well 😅
This is somewhat esoteric even for me, but I tied their abilities with money to their economic histories.
Alfred was born looking pretty pathetic next to the Spanish possessions in Mexico and South America or even British holdings in the Caribbean but, in short order, made up a significant percentage of the ships, people, and wealth of the British Empire. He became that on what was primarily the efforts of private enterprise. Alfred grows up understanding he is valuable; he represents value, and his choices create value. He's easy to love because he's a goddamn cash cow for Arthur until the Seven Years War when Britain spent a shit ton and wanted the Yanks to pay their share, and we threw a bitch fit and declared independence.
Matt, however, has the French bitching about what a money hole he is from about 20 minutes after he comes into being. The Basque, by far, made the most money initially with their fishing and whaling in the east, following what was reasonably similar to the Viking routes into Newfoundland. The fur trade that drove French settlement faced collapse about a half dozen times in his childhood, and besides a short binge economy for Ginseng and its brief boom in China, his entire existence was just fur. Dead beavers and the black market. That's it.
While the US was building ships, growing cash crops, running a fur trade economy, engaging in fishing, rope making, pitch collection, barrel making and everything and anything else, in the Caribbean, they had 90+ control over sugar production and trade routes. Canada had 10% of the population and thus 10% of the market power. We didn't do shit except freeze, fire at the British, commit war crimes against the New Englanders, ditch the farms and run off to the west to make families with indigenous women and run furs up the rivers to the point that France tried to make it illegal for people to leave the settlements of Quebec City and Montreal without permission.
So from a relatively early point, Alfred is very smart with his investments, and he's been making his investments since the early 19th century, so there's a significant but often catastrophically destroyed habit of investing. When he was younger and incredibly newly independent, he got fleeced a few times, but he's called smart and secure, especially since the 1929 crash. It's not remarkably large amounts of money because he'll never completely trust the government, and he doesn't want to attract attention or pay massive amounts of taxes, so he's very well diversified. But he's certainly not poor. All his more expensive hobbies come from a particular office in the state department that Alfred sometimes cooperates with and sometimes doesn't, depending on how anti-establishment he and the public feel.
As for Matt, having spent a lot longer as a colonial subject, it's not that he's entirely shit with money but what he knew how to do. The heart of the empire was the financial hub and was outside his control long after even the Confederation in the 1860s. The money situation has been a nightmare since the earliest days of the French Regime using playing cards to pay people. Colonial America had some similar issues. The whole concept of the US dollar originated in the 1690 invasion of Quebec when the Massachusetts Bay Colony printed its own money to fund the expedition, but Alexander Hamilton did some flash economic magic for the US in this department in the 1790s, so it got its shit together long before Canada. Matt knows what he needs to know. He was stationed in various Canadian ports, keeping an eye on his father's investments, not his own.
So, in the modern day, Alfred reads his bank statements every month, keeps track of his subscriptions and bills, and probably has an accountant. Matt is more aware of Alfred's money habits than his own. Because he's over here just kind of vaguely wondering if his debit card will work because my man cannot make heads or tails of his economy (no, seriously, Canadian economists have no idea how Canada's own shit works. Sometimes it's pretty fascinating, there's often no real consensus like the US academic economist have.) And international investors in Canada are always freaking out because the Canadian economy is always getting its shit rocked by the US economy. It's hilarious to think of people in Matt's life frustratedly trying to figure out where and what his money's doing. If their health is tied to their economies, Matt's in pretty good shape, thanks to close ties to the US, but he's randomly dying reasonably often because the US economy's tiny little ripples will randomly tear him apart. It's pretty funny (laughs so I don't sob in the Canadian job market.)
And that's pretty fitting, considering that most Canadian economic policy is boiled down to 'hope the Americans are feeling cooperative next time NAFTA comes up for debate.'
#the ask box || probis pateo#Alfred and Matt || lonely boys with the longest borders#Alfred || o beautiful for spacious skies#Matthew || my country is winter#meatsack mechanics || the sociology and biology of nations
58 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi!! big fan of your blog. you really changed my succession viewing experience and i can't wait to rewatch after reading the recs you've put up!
that being said, i read megan garber's piece in the atlantic about the animal imagery/darwinian implications in the show and really loved it (as a biologist with an interest in sociology lol). do you have any specific reading material relating to the topics in that piece? i'd just love to read more but not super sure what i'm even asking/looking for, so feel free to ignore!
hi! so, there's quite a large body of literature in history of biology that deals with the politics of evolutionary theory, including darwinism. you can read these in any order, though i would recommend starting with bob young's 'malthus and the evolutionists: the common context of biological and social theory' if you haven't already encountered it. this was a signal essay in historically grounding the argument that darwinian evolutionary theory read victorian industrial capitalism and malthusian population anxiety into the natural world, which was why it appealed to victorian men of science in a way that previous theories of evolution (sometimes referred to as species transformation or transmutationism, or transformisme / transformismo in france / italy) hadn't. bob was a marxist historian at a time when history of biology had been largely written by working scientists and naive positivists, and his methodological influence continues to be felt in the field today. anyway, these are only starting points and are centred on france and britain, and also i excluded p*ter b*wler because i hate his ass:
the politics of evolution: morphology, medicine, and reform in radical london, by adrian desmond
utopia's garden: french natural history from old regime to revolution, by emma spary
the age of lamarck: evolutionary theories in france, 1790–1830, by pietro corsi
l'introduction du darwinisme en france au xixe siècle, by yvette conry (<- i can't remember whether this was translated into english, sorry)
faces of degeneration: a european disorder, 1848–1918, by daniel pick
darwin: the life of a tormented evolutionist, by adrian desmond and james moore
the cuvier-geoffroy debate: french biology in the decades before darwin, by toby appel
evolution before darwin: theories of the transmutation of species in edinburgh, 1804–1834, by bill jenkins
the spirit of system: lamarck and evolutionary biology, by richard burkhardt
the meaning of evolution: the morphological construction and ideological reconstruction of darwin's theory, by robert j richards
the great nation in decline: sex, modernity, and health crises in revolutionary france, c. 1750–1850, by sean quinlan
lamarck, the mythical precursor: a study of the relations between science and ideology, by madeleine barthélemy-madaule
victorian sensation: the extraordinary publication, reception, and secret authorship of vestiges of the natural history of creation, by james secord
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Oil painting, 1792, British.
Portraying Joanna de Silva in a white dress and cream shawl.
Painted by William Wood.
Met Museum.
#1792#1790s#1790s dress#1790s painting#1790s britain#Britain#shawl#Joanna de silva#William wood#met museum
28 notes
·
View notes
Text


The French Revolution from children's perspective - Some historical background
My current plotline is rather strictly dictated by economic considerations: I'm trying to show the French Revolution with the limited cast of a Sims-story. So it was only logic to take the children's perspective, who are kept away from the mass-riots. Now I don't actually know about direct sources about the French Revolution from children's perspective. It would be a great research-topic, but I don't speak enough French for that.
However, I had some great inspo in my PhD project. These are some more works of Christoph von Schmid, whose story The Mute Child I adapted as an autumn-special 2022. He was a catholic priest in rural Germany during the 1790s and when he started writing for children from 1810 onwards, he made the fate of French refugee children one of his main subjects.
I actually researched about that topic before: German priests played a central role in helping French refugees. Lots of them were clergy themselves, and then the village priest was often the only person who spoke any French at all. I do know sources from the clergy's perspective, and some of them sounded really traumatizing.
Schmid's stories are all centred around religion and morality. And he knows better than to confront his young audience with anything downright cruel. In the end, the lost child is always reunited with their family, thanks to their faith and good deeds. On one level, the Revolution provided a perfect background for this, because in Biedermeier times it was much rarer for upper- and middle-class children to get lost. On another level - although Schmid rubs this in comparatively little - there's also the subtle message that trying to abolish monarchy will have dire consequences.
(Title-images digitized by the Bavarian State Library: 1, 2)
In Der Kanarienvogel (The Canary Bird) a family gets separated on their flight. Mother and son end up in Switzerland, father and daughter in Germany, each supposing the other group to be dead. They find each other again because the son teaches the father's self-composed gospel song to a canary bird. The bird gets stolen and sold in Germany where the father and daughter recognize the song.
Ludwig der kleine Auswanderer (Louis the Little Emigrant) is set in a German village where a group of French aristocrats passes through in great haste. They accidentally leave little Louis behind, who gets adopted by a family and tutored by the village-priest. Some villagers are rather xenophobic, and there's a legal squabble over some gold-coins sewn into Louis' jacket. Later he makes himself useful, as war breaks out and there's an injured French soldier to be nursed. Louis, being French can translate for him. In the end Louis' mother finds him again, through hearing about the lawsuit. Everyone gets rewarded or punished for their behaviour.
I also drew some inspiration from Die Himbeeren (The Raspberries), but this doesn't have a good picture to show and may be the most spoilery of the three plots...
* * *
A completely different point is that in my B.A. years I worked for a Jewish museum and helped with research about Jewish children fleeing to Britain. From the British perspective, the Revolution- and Napoleonic wars are often compared to the Second World War, one of the points being the arrival of refugees. Although these were different historical situations, I wanted to show some of the trauma that came with public order turning against one, losing ones home and making a fresh start in a foreign country in wartime. I think that might have been similar to what the French children felt.
17 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! So this is gonna sound weird, but I’ve kinda been learning about Irish history backwards? Like, I started with the Troubles (bc of family involvement), then back to the 1916 rising which got me more interested in the people involved which took me further back and etc etc. I know I’ve been doing it “wrong” but I’m just starting to come up to the 1798. Do you happen to have any recommended readings or particular persons of interest to read? Any collections of primary sources would be more than welcome!
Secondary sources I would recommend:
The Year of Liberty by Thomas Pakenham - about the rebellion in general
The People's Rising by Daniel Gahan - about the rebellion in Wexford
The Summer Soldiers by ATQ Stewart - about the rebellion in Ulster
Wolfe Tone: Prophet of Irish Independence by Marianne Elliott - about Wolfe Tone
The Life and Times of Mary Ann McCracken by Mary McNeill - technically this is just about Mary Ann but I think it's pretty good for Henry Joy McCracken too because there aren't many biographies of him
Orangeism in Ireland and Britain 1795 - 1836 by Hereward Senior - obviously exercise caution on whether or not you think you can mentally handle this subject but book about loyalism during 1798
Castlereagh: War, Enlightenment, and Tyranny by John Bew - about Lord Castlereagh
2 things that I would also recommend reading about for context are the French Revolution and the British radical movement of the late 18th century. for the French Revolution 1 book I would say is good is Liberty or Death by Peter McPhee and for the British radical movement... the book The English Jacobins by Carl B Cone does a good enough job
Primary sources:
The Memoirs of Theobald Wolfe Tone by Theobald Wolfe Tone - title is pretty self explanatory. It's Tone's account of his own life + his diary
The United Irishmen, Their Lives and Times by RR Madden - this is considered to be the 1st history of the rising & was written with the help of many people who lived through it, so it includes a lot of first hand accounts. HOWEVER. beware that Madden was your archetypical mid 19th century Catholic Irish nationalist and the bias created due to that shows through in every single part of these books
Memoirs of the different Rebellions in Ireland by Sir Richard Musgrave - this is another very early history of the rising, also written with the help of people who lived through, also including a lot of first hand accounts. HOWEVER. Musgrave is like Madden's Orange counterpart in that this book is also wildly biased and should also be read with a degree of caution
Personal Narrative of the "Irish Rebellion" of 1798, Sequel to Personal Narrative of the "Irish Rebellion" of 1798, and History and Consequences of the Battle of the Diamond by Charles Hamilton Teeling - 3 accounts of politics in Ireland in the 1790s written by someone who as a young man led the Catholic paramilitary the Defenders
The Drennan letters (a collection of letters that Belfast doctor William Drennan and his sister, Martha McTier, wrote to each other between the 1770s and 1820s), if you can find them, are another great primary source on both the United Irishmen & on what life was like back then in general, as are the McCracken letters, which I know are available free online somewhere I just can't remember where exactly I got the pdf from
There are a lot of them but if you're interested in primary sources you might also read some of the political pamphlets/books that were going around back then -- the most famous that come to mind in this context are Wolfe Tone's Argument on Behalf of the Catholics in Ireland, Thomas Paine's The Rights of Man, and Edmund Burke's Reflections on the Revolution in France but there are wayyy more than that and at least some of them are on the internet archive
195 notes
·
View notes
Text

Christmas Punch
Some point to the ancient Hindustani word "paanstch", which means five: a great drink prepared from five key elements - sweet, sour, alcohol (arrak), water and spices. Some, however, attribute it to English merchant sailors who, though they did not invent the punch, very much drank it. Men working on British East India Company ships used it as a beer alternative in the 17th century. The sailors were known to consume large quantities of beer on their voyages, but when the ships reached the warmer waters of the Indian Ocean, the beer in the cargo bays became rancid and stale. Once the ships reached the coast, the sailors created new drinks from ingredients native to their destination: Arrack, citrus fruits and spices. Back at sea or at home, rum or brandy or other wines were more likely to be used.

Naval Officers and a Bowl of Punch by Thomas Rowlandson c.1790 (x)
The sailors brought punch back with them to Britain. With its exotic flavours and expensive ingredients, it became a fixture in the elite homes of 17th-century England and then a staple. Some parties, however, tended to get out of hand. Like the celebration of Edward Russel, captain-general and commander in chief in the Mediterranean. On 25 October 1694 he had a garden party for 6000 guests in his villa, and had his marble fountain filled with punch. For this, 4 hogsheads (c. 960l) of brandy, 8 hogsheads of water, 25000 lemons 75l of lime juice. 560kg of sugar, 3kg of nutmeg, 300 toasted biscuits and a pipe of dry mountain Malaga. The punch was served by a ship's boy who rowed through the fountain in a small boat.
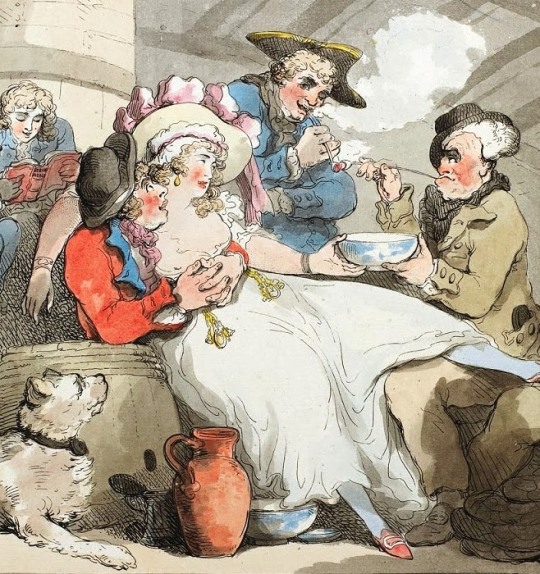
Sailors sharing both punch and wenches. Taken from “Grog on Board” by Thomas Rowlandson, 1789 (x)
Punch entered the middle class as ingredients became more affordable during the 18th century. Punch was ubiquitous in the British Atlantic world and spread to the American colonies. So why is it considered more of a Christmas drink. It was because many of the merchants stayed at home during the winter months and made punch for the family on Christmas Day with the spices they had bought for themselves locally. This made it something special and is therefore often associated with the Christmas season, even though it was served all year round, especially when the spices became affordable for many.
And if you want to make now your own punch here is a nice recipe.
Bombay Presidency Punch in Bombay Government, August 13, 1694
Servings: 2
Prep Time: 5 minutes
2 Tbsp sugar
2 Tbsp lime or lemon juice
1/2 cup rum
3/4 cups water
nutmeg
In a non-reactive bowl or pitcher, mix together the sugar and the juice and stir until dissolved. (Please use a glass, pottery, or stainless steel bowl or pitcher. Copper, cast iron, and aluminum will react with the acid in the lemon juice.)
Remove any seeds that may have made their way into the bowl. Blend in the rum, and then the water.
Add ice. Then grate nutmeg over the top.
Enjoy your tipple!
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
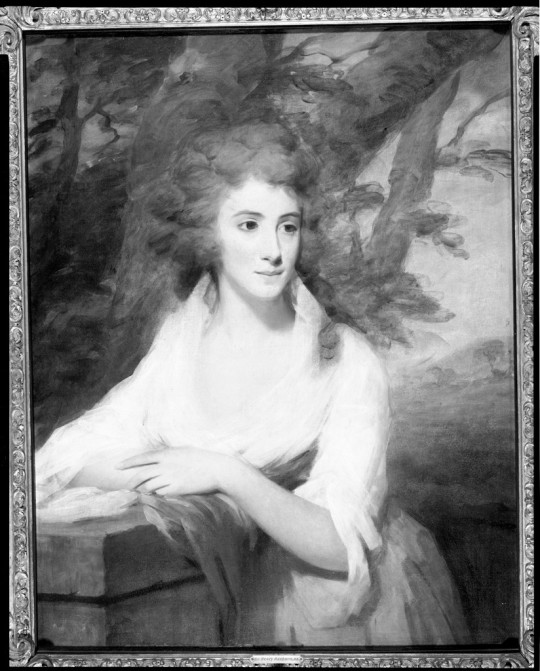

Mary Ann Leslie Rutherford, 1790, Britain.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Jory, he/him. disabled trans bisexual. my main blog is @werewolfetone
I love history and classic literature and politics. most (all) of what I write is fuelled by the history I study. most of it is set in the 18th or very early 19th centuries in Britain and/or Ireland
In terms of content I like historical fiction, gothic horror, cosmic horror, regular horror, and occasionally dark fantasy. I like fucked up character dynamics, political fiction, religious themes, disabled characters, and I love it when writing has Themes And Motifs. not terribly keen on ya or sci fi but I'm willing to tolerate it.
Also I do art! mainly my ocs but also I draw historical figures sometimes. possibly commissions might be set up at a later date.
WIPS INCLUDE:
Living Ghosts (active)
The lives and times of an extended friend group that essentially explores the idea, "what if your found family was far worse than your actual family." very character-driven. set in the late 18th century.
Memoirs of an Infantryman (active)
The fictitious memoirs of Michael Sherman, covering his time as a British soldier and then a deserter in the American Revolution, the Volunteering period in Ireland, and his friendship with the daughter of a deposed Jacobite noble. set in the late 18th century.
The Blue Cockade (active)
Whiteboy leader Martin d'Hermite and evil landlord Robert Nelson are both in love with a local woman named Shreya Kumar. Consequently over ten people die. set in the late 18th century.
The Friends of the Working Man (backburner)
After several very bad days working class lad Jeremy Thorne and his sister Margaret start a reform society in 1790s Scotland. several minor politicians work very hard to make them regret it.
The Well (backburner)
A young woman looks for love in a small town but it keeps ending badly. meanwhile her friend has an evil boyfriend and there are ghosts Lurking. set in the early 19th century.
This Happy Constitution (backburner)
Doctor Ernst Leitner and his whaler friends learn how to raise the dead and therefore make a deal with an aristocratic patron for further funding. it goes downhill from there. set in the early 19th century.
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
There is a direct connection between the expansion of [...] new [coffee] consumer culture in Europe [...] and the expansion of plantation slavery in the Caribbean. [...] [S]lave-based coffee was more important to the Dutch [Netherlands] economy than previously [acknowledged] [...]. [T]he phenomenal growth of [plantation slavery in] Saint Domingue [the French colony of Haiti] was partly made possible by the export market along the Rhine that was opened up by the Dutch Republic. [...] [E]arly in the eighteenth century, the Dutch and French began production in their respective West Indian colonies [the Caribbean] [...]. [C]offee was still a very exclusive product in Europe. [...] From the late 1720s, [...] in the Netherlands [...] coffee was especially widespread [...]. From the late 1750s the volume of Atlantic coffee production [...] increased significantly. It was at that time that the habit of drinking coffee spread further inland [...] [especially] in Rhineland Germany [...] [and] inland Germany [due to Dutch shipments via the river].
Although its consumption may not have been as widespread as the tea-sugar complex in Britain, there certainly was a similar ‘coffee-sugar complex’ in continental Europe [...] spread during the eighteenth century [...]. The total amount of coffee imported to Europe (excluding the Italian [...] trade) was less than 4 million pounds per year during 1723–7 and rose to almost 100 million pounds per year around 1788 [...]. In 1790 [...] almost half of the value of [Dutch] exports over the Rhine [to Germany] was coffee. [...]
---
The rising prices in the 1760s encouraged more investment in coffee in Dutch Guiana and the start of new plantations in Saint Domingue [Haiti]. Production in Saint Domingue skyrocketed and surpassed all the others, so that this colony provided 60% of all the coffee in the world by 1789. [Necessitating more slave labor. The Haitian revolution would manifest about a decade later.] [...]
In French historiography, the ‘Dutch problems’ are considered to be the slave revolts (the Boni-maroon wars) [at Dutch plantations]. [...] France made use of the Dutch ‘troubles’ to expand its market share and coffee production in Saint Domingue [Haiti], which accelerated at an exponential rate. [...]
---
[T]he Dutch Guianas [were] producing over a third of the coffee consumed in Europe [...] [by] 1767. The Dutch were the first Europeans to bring coffee cultivation under [substantial] European control [...]. Additionally, the Dutch regularly shipped and traded about one fifth of French coffee [most of which was produced by slaves in Haiti]. The Dutch flooded the Rhine region with coffee and sugar, creating a lasting demand for both commodities, as the two are typically consumed together. [...]
[T]he history of the slave-based coffee production in Surinam and Saint Domingue [Haiti] was pivotal in starting the mass consumption of coffee in Europe. [...] Coffee was a relatively ‘new’ product to Europeans: in one century coffee changed from being a [...] novelty [...] in [...] [urban] capitals to [...] [a product consumed regularly by many people]. The Dutch merchant-bankers organised coffee investment, enslavement, and planting and selling; [all] while not leaving the town of Amsterdam [...].
[This market] expansion ends in crisis [...] - a crisis caused by uprisings and revolutions, most notably, the Haitian one. Yet Germans still liked coffee. And the Dutch colonial merchant-banker[s] [...] learned something about [...] production, and perhaps also something about the role of the state in labour control: as soon as they could, they sent Johannes van der Bosch [governor-general of the East Indies] to Surinam and Java in order to solve the labour issues [by imposing the notoriously brutal cultuurstelsel "enforced planting" labour regime] and expand the colonial production of coffee.
---
Text above by: Tamira Combrink. "Slave-based coffee in the eighteenth-century and the role of the Dutch in global commodity chains". Slavery & Abolition Volume 42, Issue 1, pages 15-42. Published online 28 February 2021. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Italicized text within brackets added by me.]
63 notes
·
View notes