#19th century Serbia
Text

🔸Serbian girl dressed in serbian traditional clothes from Central Serbia 🇷🇸
🔸Time : 1870s
#serbian#balkan#europe#serbian beauty#serbian traditional clothes#serbian folklor#slavic#serbian women#serbian tradition#Serbian culture#Culture#Tradition#Folklor#19th century#19th century Serbia#serbian aesthetic#central serbia#Centralna Srbija#Srbija#Srpkinja#Narodna nošnja
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
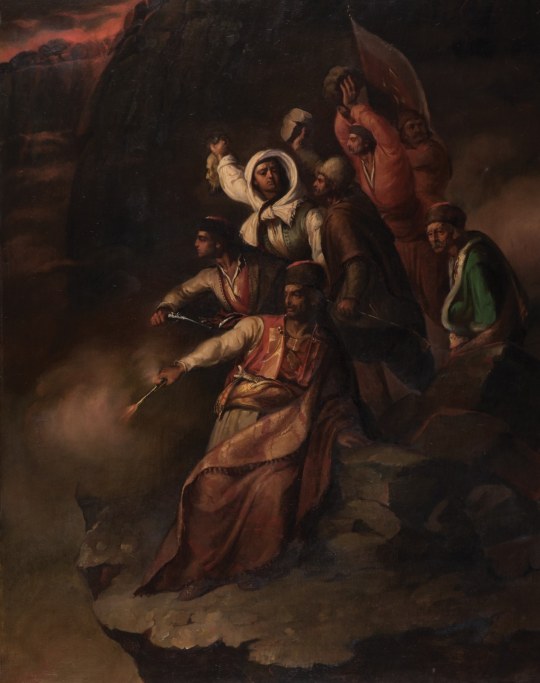




Ђура Јакшић - Јевропи
Đura Jakšić - To Europe
#đura jakšić#djura jaksic#serbian art#serbian poetry#serbian history#serbia#art#serbian painters#serbian culture#poem#poems#painting#19th century art#19th century
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
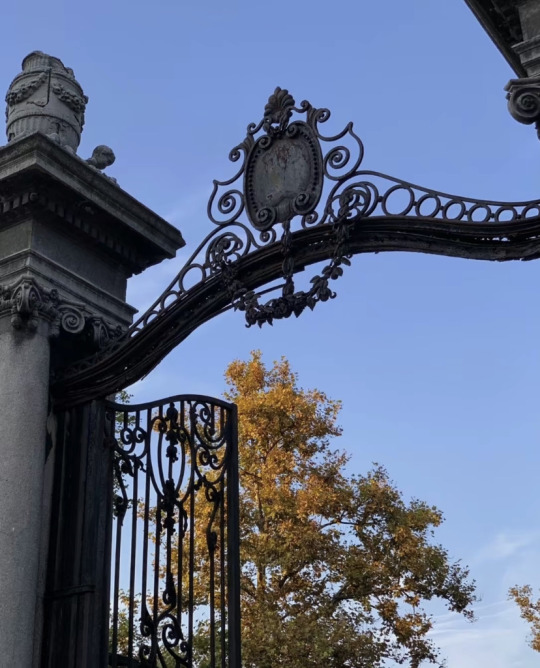

Academic Park, Belgrade, Serbia.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Academic_Park
🍂🍂🍂🍇🍂🍂🍂🇷🇸🍂🍂🍂🍇🍂🍂🍂
#balkanwonders#europe#balkans#balkan#travel#serbia#srbija#balkania#belgrade#european architecture#park#19th century#explore europe#european history
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Two paintings by Đorđe Krstić at the National Museum in Belgrade
#paintings#Đorđe Krstić#dorde krstic#19th century painting#art#mypost#belgrade#serbia#national museum in belgrade#serbian art
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
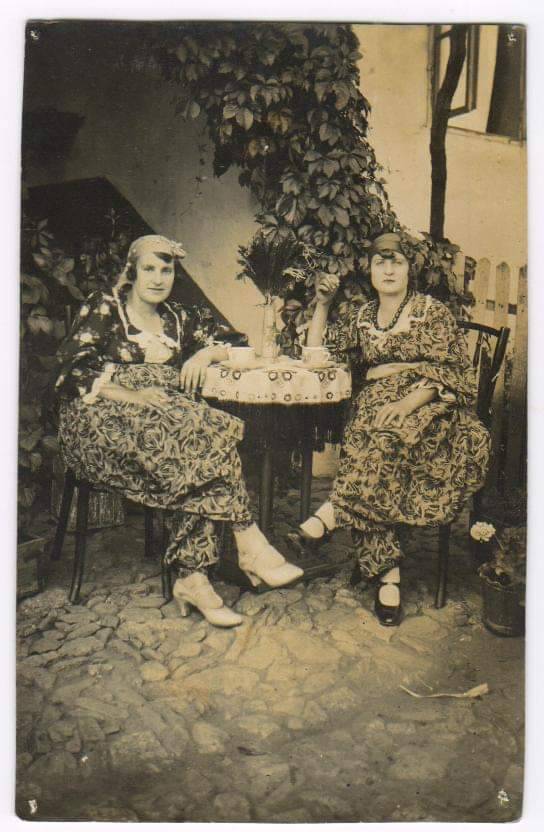

Ljubinka Hadži-Nikolić and Zora Jezinka, Vranje, Serbia. cred. Aleksandra Hadži-Nikolić
#hadži-nikolić#vranje#gradska nošnja#serbia#southern serbia#slavic#balkan#eastern europe#19th century
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
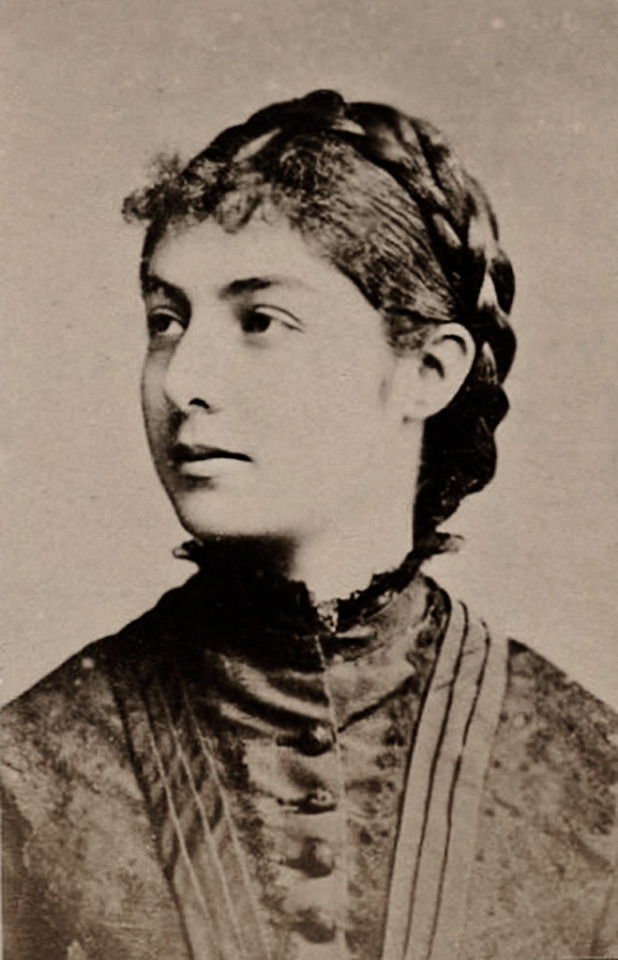



Natalija Obrenović, née Cheșcu/Keshko, Queen Consort of Serbia (1882–1889).
#natalie of serbia#natalia of serbia#natalija obrenović#serbia#royalty#royal family#royals#victorian#victorian era#history#historic#19th century
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo










Fashion in Modern Serbia
Fashion in Serbia in the 19th and early 20th Centuries in the Collection of the Museum of Applied Art in Belgrade
Draginja Maskareli
Museum of Applied Art, Belgrade 2019, 144 pages, 25 cm, Text in Serbian and English, ISBN 978-86-7415-217-1
euro 40,00
email if you want to buy :[email protected]
The exhibition presents a selection of 81 fashion items from the 19th and early 20th centuries held by the Museum’s Textile and Costume Collection, accompanied with reproductions of bourgeois portraits and documentary materials from different public and private collections.
The 19th century witnessed major changes in the political, social, cultural and economic spheres in Serbia. The uprisings against centuries-long Ottoman rule, in 1804 and 1815, led to the enactment of two sultan’s hatt-i sharifs, in 1830 and 1831, the establishment of the autonomous Principality of Serbia, Serbia’s full independence, confirmed at the Congress of Berlin in 1878, and the proclamation of the Kingdom of Serbia in 1882. The transition from a feudal to a capitalist society was accompanied with the establishment of new cultural models with a local imprint and the adoption of cultural models common in bourgeois Europe.
In this period, fashion gained an important role in visual representation and identity construction among individuals, members of ruling families and the bourgeois class of modern Serbia. In the context of the process of building a modern state and society, fashion developed in an environment marked by 19th-century cultural pluralism, making a transition from the Ottoman-Balkan cultural model at the beginning of the century to the inclusion into the European system of modern fashion in its second half of the 19th century. During this period, fashion-related changes were not only visible in the forms of clothing but also in the way of its production and market placement.
30/12/22
orders to: [email protected]
ordini a: [email protected]
twitter: @fashionbooksmi
instagram: fashionbooksmilano, designbooksmilano tumblr: fashionbooksmilano, designbooksmilano
#Fashion Modern Serbia#fashion exhibition catalogue#Museum Applied Art Belgrade 2019#19th & early 20th Centuries#textiles & costume collection#Serbia#fashion books#fashionbooksmilano
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
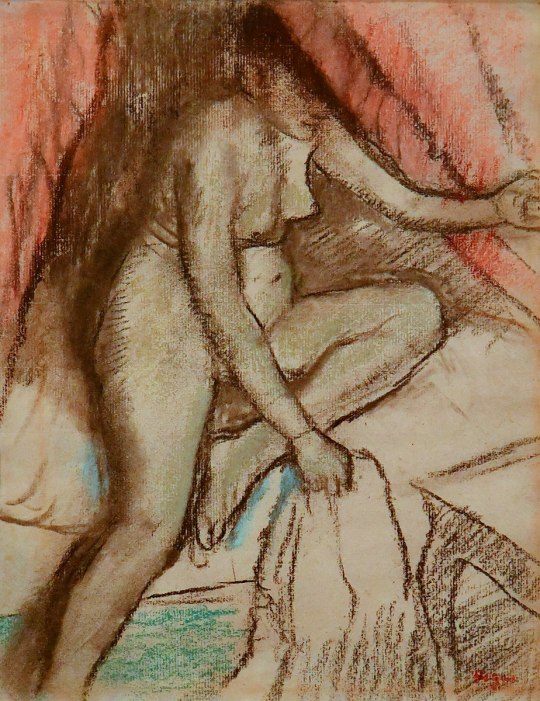
"Le Coucher" ("Bedtime") by Edgar Degas
French, 1883
rayeshistory.com
0 notes
Text
Arguments against giving personifications a universal language (or another method of communicating with each other immediately and without any problem)
(Ok, this was a little clickbaity. First of all, I absolutely don’t intend to say that whoever does it is wrong. Like everything in Hetalia worldbuilding, it’s a matter of personal preference and goals we set for our story. Additionally I absolutely think that heavy focus on this matter would be detrimental for the story and unapproachable by audience other than a couple of crazy linguists.
Unfortunately I happen to be a crazy linguist, so here’s what I actually mean by this post:)
Fun linguistic things to consider in the context of Hetalia :D
Now, personally, I feel like the universal language takes away from the naturality of their relationships, *especially* so-called “first contact”, but not only that. Language is an enormous part of international relationships through the ages and removing this part from the equation results in the personifications not experiencing this side of their people’s history.
Sometimes in a story you don’t want two nations to understand each other. It happens. I’d much rather have choice than create a rule that takes this possibility from me.
The question of “which languages these two characters share” is interesting; it silently reminds of their history and points to cultural circles they belong to, as a subtle storytelling tool. (Other than that, deciding that is insanely fun, but this might be a linguist thing?)
Languages can be symbolic for other details of relationships. Think Lithuania speaking outdated Polish, from 19th century at best, because he didn’t have many opportunities to catch-up with the living language after that, now they’re not together with Poland anymore. [/personal hc, but even if they were, I think he’d still lag behind].
Another case, think a weaker country speaking the language of the stronger country, never the other way around, indicating a power imbalance between them.
Think a weaker country [personally I’m thinking a friend’s Serbia] absolutely refusing to speak the language of the stronger country, forcing them to seek compromises or use an interpreter or more drastic measures.
The lingua franca, whatever it would be, automatically carries a huge cultural and social influence with it. I believe the personifications should be prone to it too.
Another linguist thing, but I find communication struggles fascinating and endearing. There’s so much cultural exchange to be drawn from a second language user: which parts of learning are difficult for them, which are easy; what mistakes they make and how are these influenced by their native speech; what words do they choose to use, what do they think a chair’s gender is, do they sound soft or harsh or have an accent? If two Slavs talk to each other in English, is it correct English or do they use Slavic pronunciation and grammar to make it easier for themselves, causing a distress for each anglophone that hears them?
Another linguist thing, but a lot of pairs of countries that technically don’t have a common language can probably communicate with ease anyway. I want to see them go wild. I want to see them make a mixtape out of their French and Latin to talk to an Italian, I want distant Asian countries to talk to each other in English that no actual English person would understand, I want to see Latin America NOT understanding each other despite theoretically all speaking Spanish. And I want to see two distant countries find out that their only common language is something completely unexpected they’ve studied out of boredom.
I want to see the poor couple of nations without decent linguistic skills SUFFER.
Some of you speak like not having a common language was an unconquerable obstacle that would destroy all the fun and be a giant problem in the storyline. But I don’t really see how? Our ancestors did it. They travelled, they met other nations and they had to learn how to communicate with them. Some of them saw the opposite thing happen: they used to understand their neighbours without problem, but as the nations found themselves under different influences, the languages drifted away from each other until the similarities became unrecognizable. People across the ages have been learning languages, travelling and communicating. There are teachers, translators (my friend Laurynas says he’d like to see translators acknowledged), interpreters, etymology, lingua franca and body language all for them to use. I am not 25 yet and I speak 4, with a certain pain I can communicate in 6, and I could probably visit 100 countries of the world without worrying about the language issue at all. My nations are 100 years old. I just don’t think they need additional help. They'll slay :D
There were a couple ideas I’ve seen pro-universal language that I liked, so thought I’d share:
One, as beetroot said, being able to communicate with one personification doesn’t mean the countries wouldn’t have to learn languages, as the rest of the society wouldn’t be able to understand it. Therefore, most of these “fun linguist things” would appear anyway, just not between personifications. For me it’s a bummer, although acceptable. For someone else it can be more than enough.
Two, a quote from my friend Huku:
“Universal language is also a thing that helps them identify each other, which is a cool trick. It explains why, upon finding a personification in a swamp, the nation knows that this child is a personification and not some random mortal. Besides, nations from distant cultures also find it hard to communicate initially, because maybe the language is universal, but the context is foreign, the metaphors unreadable, the wording strange.”
Three, at first I didn't like morgenlich’s version that the language “can’t be written down because of magic”, but after seeing a suggestion that it wouldn’t be an actual language, just a mysterious way of understanding each other, the idea sounds more approachable to me. Cheers!
#hetalia#hetalia headcanons#historical hetalia#hetalia worldbuilding#nation lore#ness cinematic universe#nessay#if i've ever seen one
166 notes
·
View notes
Text

◾Full-length shot of a Serbian man dressed in Serbian traditional clothes. 🇷🇸
◾Place: Belgrade, Serbia.
◾Time: 1860.
◾Photographer: Stoyanovitsh/Karastoyanov
#serbian#balkan#europe#serbian beauty#serbian traditional clothes#serbian folklor#Serbian man#Serbian men#Retro Serbia#Vintage#19th century#Serb#Serbs#Dinaric#Srbin#Srbi#Срби
176 notes
·
View notes
Text




Павле Симић - Српска народна скупштина 1. маја 1848.
Pavle Simić - Serbian national assembly 1st of May 1848.
#pavle simic#pavle simić#serbian art#serbian history#serbian painters#19th century art#19th century#painting#art#history#serbia#vojvodina
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
• 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐅𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭 𝐖𝐨𝐫𝐥𝐝 𝐖𝐚𝐫 •
The First World War accelerated the path to modernity. It was the "Primal catastrophe" of the 20th century, an era of war, violence and displacement. It cost the lives of around 17 million soldiers and civilians, destroyed large parts of Europe and left behind unresolved problems that led to further violent conflicts.
[Without the First World War, the rise of fascism and communism and the transition to systemic competition between West and East, the 20th century cannot be understood.]
The assassination of the Austro-Hungarian heir Franz Ferdinand and his wife in Sarajevo on June 28, 1914 is regarded as the trigger for the First World War. In Vienna, the military pressed for a swift retaliatory strike against Serbia. The German Reich assured Austria-Hungary of its unrestricted loyalty to the Danube monarchy.
On July 28: Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia - Russia starts mobilization.
On August 1: The German Empire declares war on the Russian Empire.
August 2: Invasion of German troops in Luxembourg.
August 3: Invasion of German Troops in Belgium - the First World War begins.
The age of weapons of mass destruction and industrial warfare began in early 1915 with the German chlorine gas attack on the Ypernbogen. Almost two million German, French and British soldiers died on the barren battlefields and in the trenches of the "Hell of Verdun" in 1916. However, the course of the front changed only slightly as a result of these material battles.
In total, the war claimed 17 million lives. It ended on November 11, 1918 with an armistice and the defeat of the German Reich. In Germany, the monarchy collapsed and the Weimar Republic was founded.
In 1917/1918, numerous monarchies collapsed in quick succession and were replaced by democratic republics, as was the case in Germany in November 1918.
After 1918, no new stable framework of order was recognizable - neither socially, politically nor internationally.
The new models of the Russian Bolsheviks, the fascists in Italy and the National Socialists in Germany were unmistakably opposed to the liberal legacy of the 19th century, not least in their pronounced willingness to use violence. This had to do with the diverse experiences of world war, the transitions from state war to revolution and civil war, as well as the disappointed expectations in many societies in view of the peace treaties of 1919.
#german history#history#teaching#studyblr#studying#booklr#books#literature#I will teach you history on a creative way not the boring teacher way#aestetictumblr#germany#italy#russia#history is important#world war#world war ii#world war 1#20th century#19th century#political#politics#study blog#study motivation#I Love studying lmao unpopular opinion#I’m new on Tumblr#spread knowledge#knowledge#I want to know everything like Faust#important history#historical facts
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know I'm a nerd because the amount of time I've spent obsessing over the Vojvodina dress is. Way too much.
This dress doesn't actually have a name (probably), but it's from late 19th century Vojvodina, and I kind of obsessed over it when I was at the Serbian Ethnographic Museum in Belgrade (main site is available only in Serbian).
(Unfortunately, I'm trying to work within the tumblr image limit, but here's a google drive!)
BTW, if you enjoy this post, please consider leaving a tip! I spent more time than is reasonable putting this together.
Also, due to tumblr being Odd, you may want to open this in a new tab to avoid having the posts expand to full; the dashboard view only lets there be one image per line, for some reason. If you open in a new tab, they are much more neatly organized into sets, and quicker to scroll past.
Due to the fact that I can't really describe these photos in a way that means anything to readers unless they have a large technical vocabulary or background in Balkan fashion history, and there being so many pictures, I will not be including image descriptions. However, my commentary on those photos throughout the latter half of the post should hopefully give you a solid summary on what the photos contain, even if it's not going into details for most.
Here is the general shape of what you see in 19th century Serbia (incl. Kosovo), Montenegro, Bosnia&Herzegovina, and Croatia:
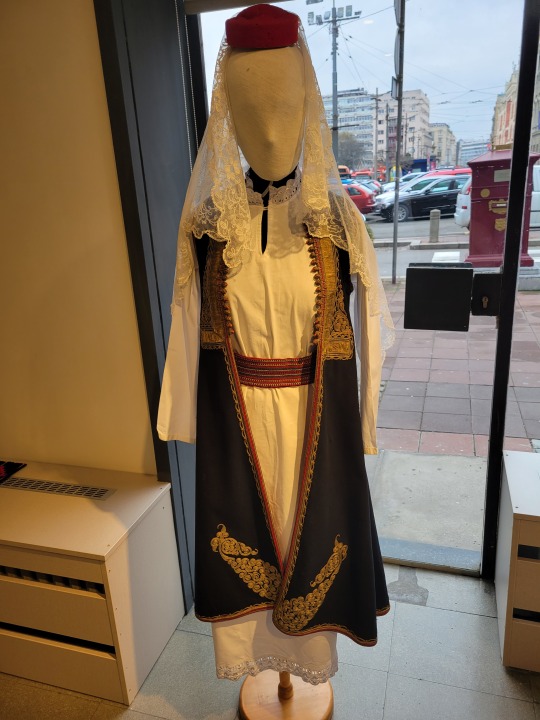
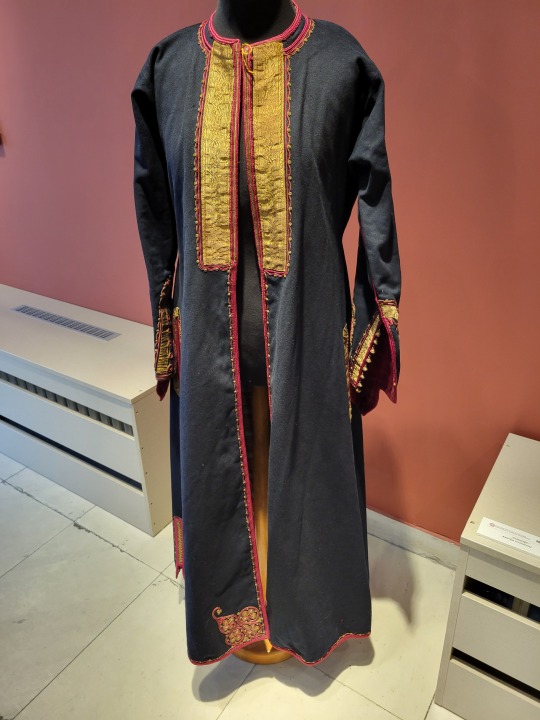
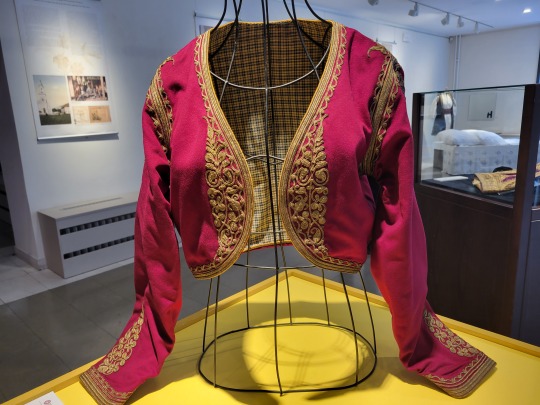
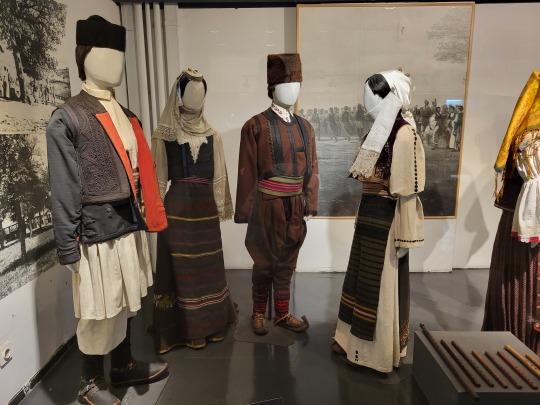
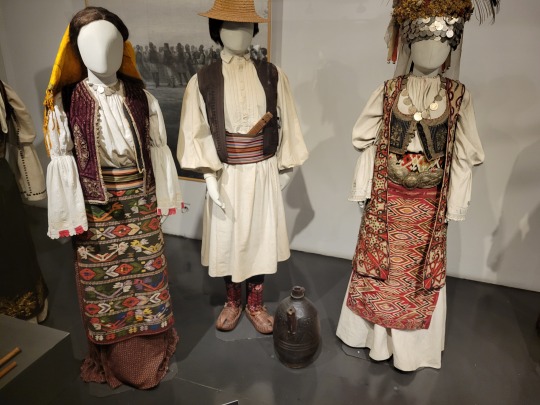
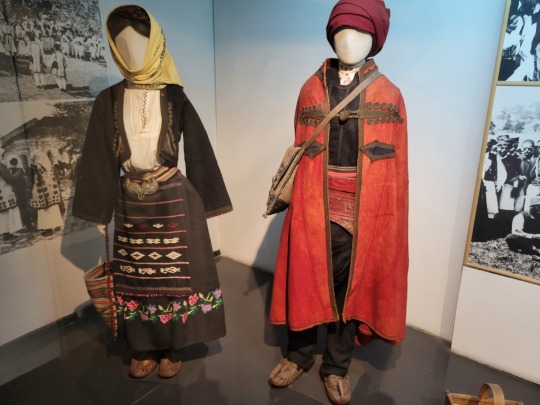
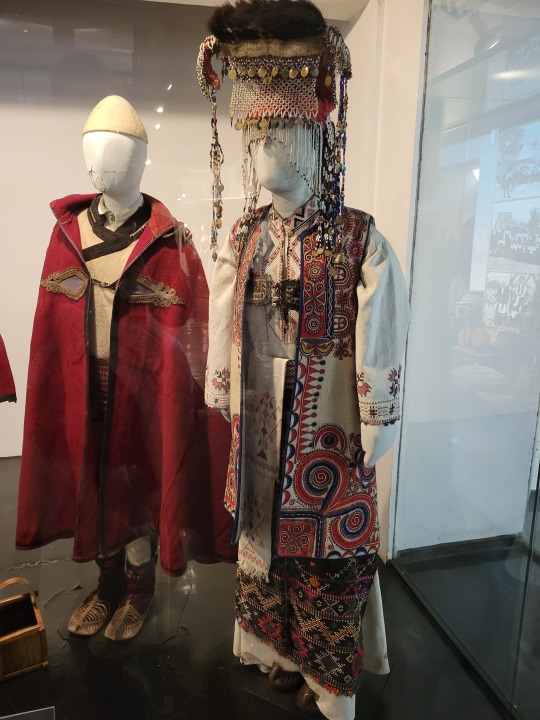
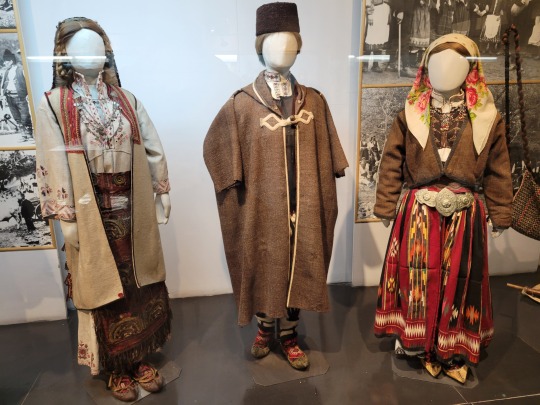
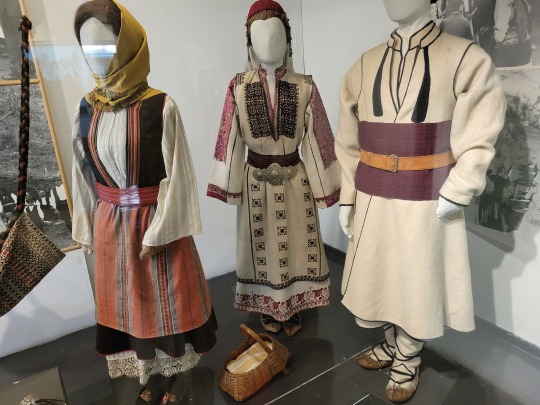
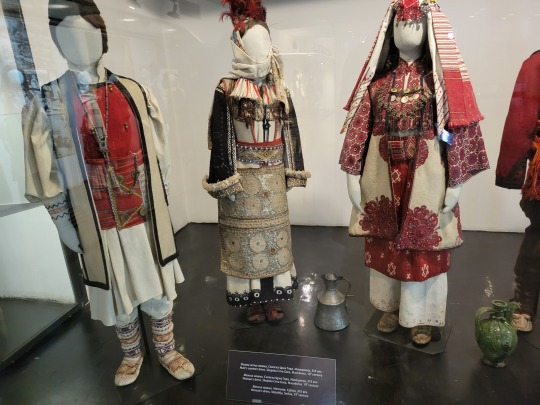
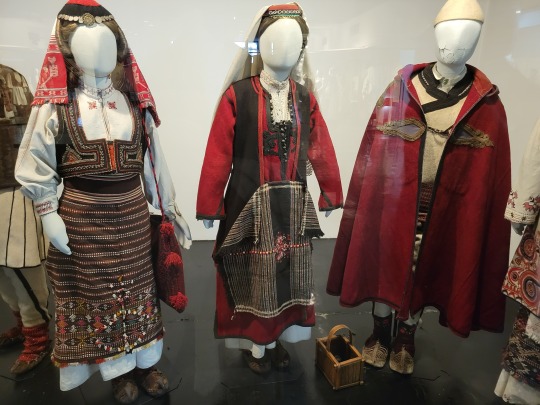
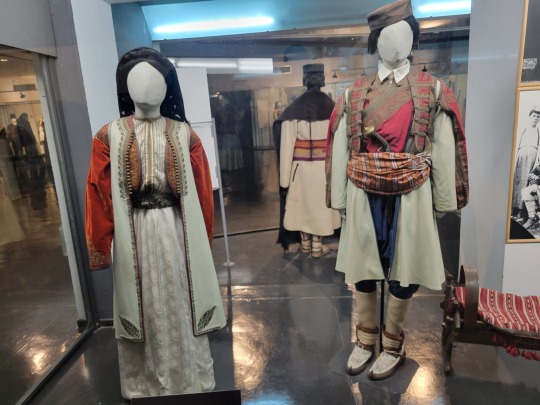
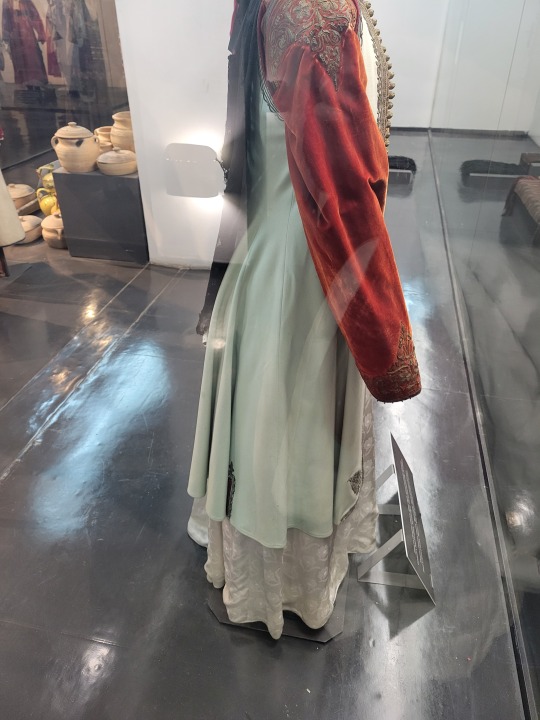
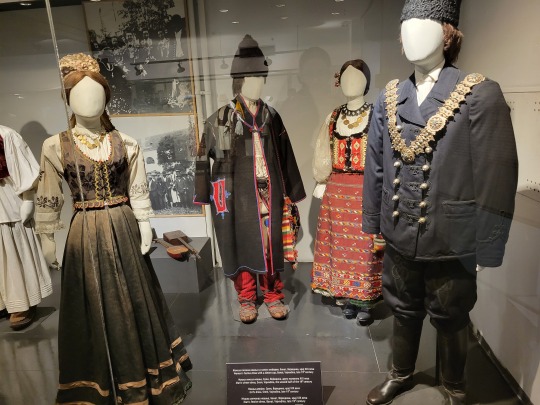
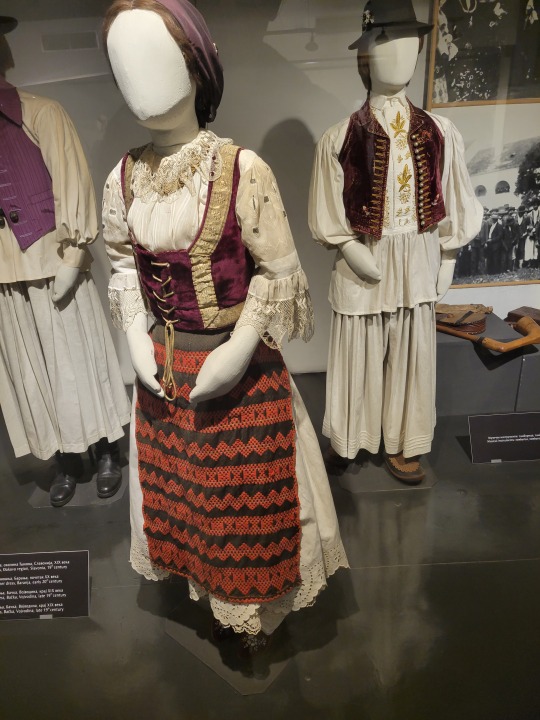
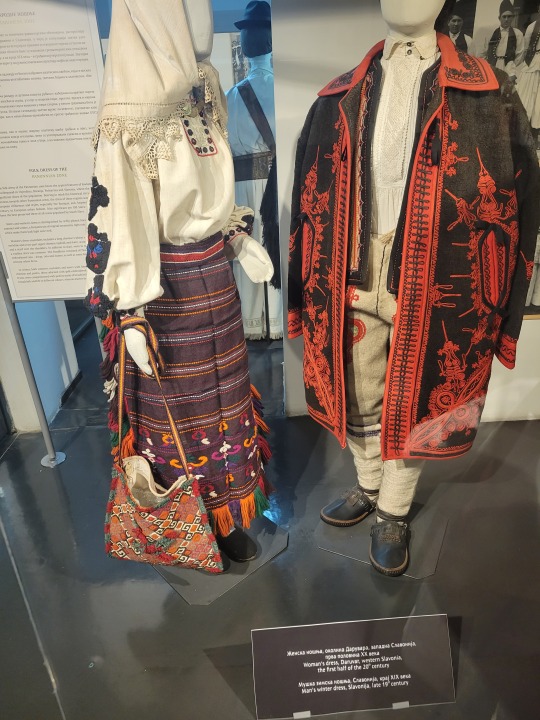
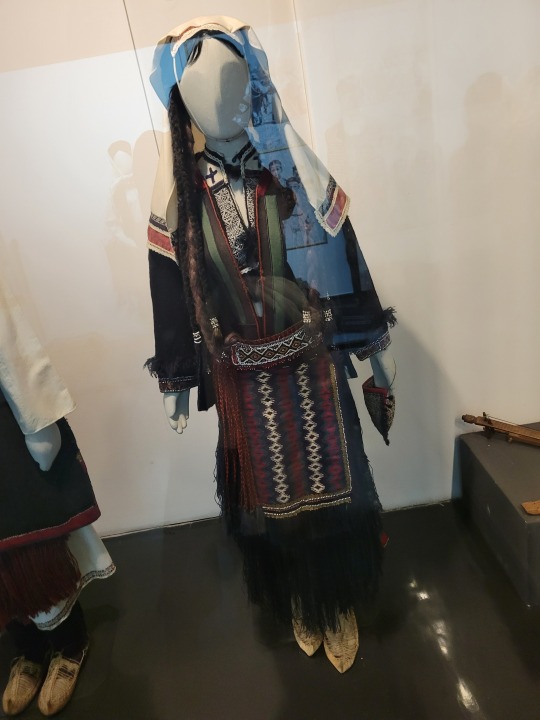
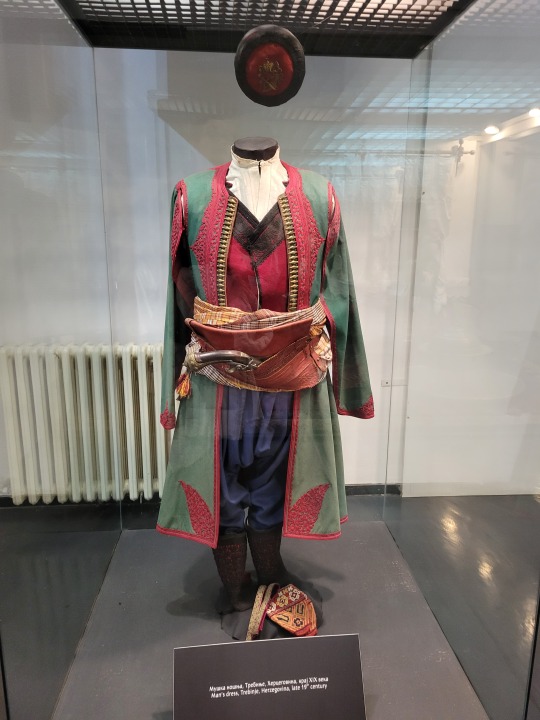
























You can see a few throughlines, even with the variety from one region to the next. Certain types of fabric are more common, especially that heavy plain-weave white fiber (I think usually cotton, nowadays, but probably historically flax) with the small knots; my grandmother's apartment is still stocked with that as the default bed linen! You see it all through the exhibit, most frequently in the skirts, but often for blouses or chemises, too.
There are a lot of hand-woven fabrics, which you can see on display best with the aprons, and a very specific style of applique trimmings on the cropped vest. The arm's eyes and necklines have similar proportions. The lengths are similar. Most things are cut on the rectangular, or not cut at all. Hems are often tassled, for complex weaves, or simply folded under for the white base fabrics; plain, non-white fabrics tend to get a textured applique at the hems. Lace is usually eyelet.
There are exceptions, of course. I'd love to know more about that mint green cardigan(?) from Montenegro, with the gored pieces. I think it's made of doeskin (the tight wool weave, not the leather), and I wish I could get more information on the history. Most of the larger green dyes, not counting floral motifs or minor elements of a multicolored weave, are from the Bosnian section of the display (wide stripes along the collar, for instance), presumably due to Ottoman influence leaving a large Muslim population. And then there's this mint green cardigan from Montenegro made of a fabric I'm not seeing on any other garments? Tell me more, please.
(Also, in the close-ups, you can see that the hook and eye closure has released rust stains onto the blouse!)
There are so many more pictures, but unfortunately, I have a thirty-image max and really want to talk about this one specific dress:
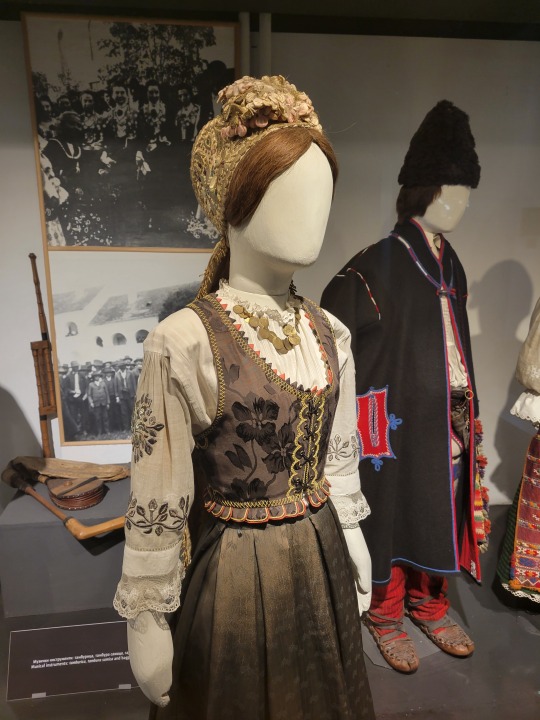


The image description on the floor below describes this as:
Woman's festive dress with a zlatara cap, Banat, Vojvodina, late 19th century
(I have minimal commentary on the hat. It's a traditionally Serbian vestment, but there's nothing too unusual about it.)
So, here are a few things to note at first glance:
The arm's eye on the vest is wide. It dips further in towards the neck than most vests, and swoops further down towards the ribs. Most of the traditional vests have a much tighter arm's eye.
Relatedly, the straps are much thinner than most of the vests, maybe half as wide. This is partly the arm's eye, and partly the width of the neckline to start!
The vest comes down in a slightly pointed oval ending at the swell of the bust, rather than curving back up or being a rounded shape a few inches higher. It's also finished with these little satin triangles?
The vest is laced at front, rather than hook and eye closure.
The bottom edge has tabs!
The hems on those tabs are chain stitched in yellow, and then the hem is wrapped in a thin orange ribbon that I would hesitantly say is satin? Plus all the other yellow embroidery, which to my eye looks really different from the embroidery you see on various aprons, and also different from the metallic appliques you see on most vests!
That bottom edge also appears to be straight across (most of the vests curve up slightly at front), and is very tight to the body. While some of the vests are tight, those are generally the shorter ones. Longer vests are much looser than this one, which cuts off and cinches at the waist, right where it meets the skirt.
The fabric itself! I'll get back to this but it seems to be a satin jacquard??? A jacquard that matches (in thread, not in pattern) to the skirt? Insane.
[Disclaimer: Some of these deviations, such as the arm's eye size or the dropped shoulder hem, could be a matter of the mannequin being the wrong size for the clothing. Unfortunately, I don't have enough background information to be sure. It could be just the right size. It could be far too small. I only have these photos and the most basic of background information to go off of.]
Okay moving on to the blouse:
It's not completely unique to be sheer, but it's definitely uncommon!
The chest is not pintucked or a flat weave, but rather the sheer fabric has thin stripes of more opaque weave? I don't actually remember what that's called but it's definitely cool to see.
We also see a net lace at the cuffs, which is similarly uncommon; most of the fashions I saw had eyelet lace instead (which we can see at the collar of the blouse).
The dropped shoulder! The shoulder seam sits much higher on most of the pieces I saw (there are a few exceptions, but mostly from regions nearby). In fact, most of the examples had the shoulder seam hidden, between the higher seam and the width of the vest; it's both the dropped seam and the thin straps of the vest that let us see this here!
That metallic embroidery. Again, most of the embroidery we see on the other pieces is cross stitch or done with a much thicker thread; sometimes, you get lineart, but not filled in in this manner. This kind of thin-thread embroidery that fills the space between the lines isn't common in the other pieces!
I don't think I can actually say much about the sleeve length? I feel like most of the pieces have sleeves that are full or bracelet length, while this one is a three-quarter, but I'm not 100% on that actually being true. It's a bit hard to tell in some cases. Might just be summer clothes?
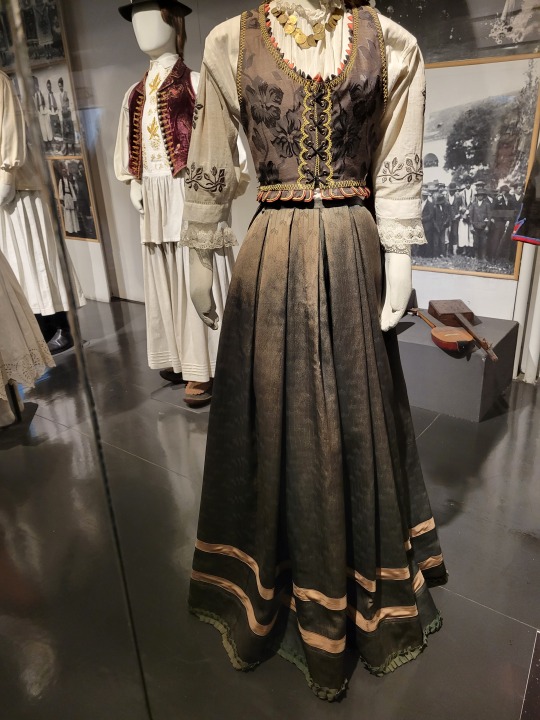
The skirt:
SATIN JACQUARD
BOX PLEATS
SLIGHT OVAL HEM
SATIN RIBBON TRIM
I'm gonna be honest this was a huge part of why I began to obsess over this dress let me just. Whoo!
This fabric is, as far as I can tell, a satin jacquard, very probably machine-woven. It is very different from basically every other fabric we see in this exhibit. This is not a plain weave, and it is not a hand-woven design. This is a meticulously, mechanically repetitive pattern done using satin-weave manipulation to adjust which sections have shine and which don't. Given the time period, it's probably silk. (Take a look at this portion of a video on silk by Nicole Rudolph to understand what I mean by jacquard. If you want to know more about satin weave, you can watch the full video.)
I'd guess that the vest is made of the same type of fabric, even the same threads, just in a different pattern.
The pleating! If you take a look at the other photos, the general pattern is 'put together some rectangles, gather at top, and you have a dress. Cover with a hand-woven apron in front and possibly in back.' There are, again, some exceptions, but this dress has both the box pleating and the satin jacquard. The structure of this skirt is completely different from 90% of this exhibit.
In conjunction with the pleating, the skirt had a very slight oval shape around the bottom. I didn't get a good photo of that part, but it's typical of 1890s dresses in Western Europe to have a sort of egg-shaped hem if you look at them from above, through use of pleating, strategic panel shapes, and bum pads or petticoats. In short, the dress is just slightly longer at back without being a full-on train. Most of the other pieces, due to the rectangles and gathers, are a much simpler circle shape around bottom.
Length! Part of why the egg-shaped hem is happening is because this dress actually brushes the floor. Ankle-length is the default across the exhibit, even for formal wear.
Simple satin ribbons for decorative trim, rather than something textured, shaped, or multicolor!
Then, the actual hem of the skirt: a center-pleated green ribbon. This is, again, really different from most of the hems. Most of the skirts don't reach the ground, and aren't made of a fancy fabric. Those white dresses/skirts that form the base of most looks are easily washed and have hems that don't drag on the ground. If they aren't left to just the selvage, they're very simply hemmed; I think what I saw most frequently was a double-folded hem. The pieces that have more decorative hems, like blouses and vests and aprons, aren't pieces that get the same form of wear.
However, since this dress does reach the ground, it needs a centimeter or so of additional fabric to take some of that wear to protect the fancier skirt fabric, like hem braid, which the easily-replaced ribbon could conceal for this skirt since it's a festival item.
I think that might also be part of why there's a seam about twenty centimeters up from the bottom edge; it's a replaceable section in case it needs replacement, or the seam is for a protective layer inside. However, it could also be a seam used for a stiff inner lining meant to help the skirt flare out just a touch, like this.
Now, finally, why is all this even a thing, and why do I care?
Vojvodina, the region this outfit is from, was under Austro-Hungarian control during the latter half of the 19th century; whether it was officially Hungarian, Austrian, or both changed from one decade to the next, but it was definitely under that sphere of influence for a very long time. Despite this, it was and is culturally Serbian, and is majority Serbian in terms of population; it was even back then! However, the 19th century saw a large number of ethnic Hungarians and ethnic Germans in the region as well, and the cultural impact from Vienna was not to be underestimated.
This dress is a great example of how a culturally Serbian individual would have clothing that integrated those foreign influences. For most of the Balkans, the greatest influence was the Ottomans, due to five centuries of imperial rule, but this dress is a great contrast due to Hungarian occupation, and then Austrian. It contains elements of the culture that birthed it, yes, but the influence of the West is so very, very clear.
(I wish I could talk more about the Pannonian elements in general, but I'm still learning.)
I hope you enjoyed this rambling deep dive into a single outfit from the Serbian Ethnographic Museum. Visit it if you get a chance!
And if you've read this whole thing and feel like dropping a tip, you can do so on this blog, post, or over on ko-fi. You could even join my Patreon!
#serbia#vojvodina#fashion#fashion history#the vojvodina dress#serbian stuff#balkan stuff#balkans#Banat#Hungary#Austria Hungary#austro hungarian empire#phoenix posts
171 notes
·
View notes
Note
How old is the Croat/Serb ethnic feud? Is it purely a product of 20th century conditions or does it predate Yugoslavia?
any investigation into the 'true age' of the serb/croat ethnic feud is going to be complicated by skirmishes between the two predating any notion of them constituting two distinct ethnicities
croatian and serbian nationalism are the degenerate daughters of two separate pan-slavic movements that emerged more-or-less independently from one another, both of them considering the other nation to be part of their own. i mean this quite literally—consider the 18th century ethnographic work croatia rediviva, which grouped serbs with bulgarians, macedonians and thracians under the sobriquet 'red croats'. the serbian equivalent of this kind of pan-nationalism is pejoratively referred to as 'greater serbian chauvinism' nowadays, and it formed the basis for serbian foreign policy toward croatia since the establishment of a sovereign serbia in the first decade of the 19th century until, like, 1995
so, a substantial amount of early conflict between 'croats' and 'serbs' was really ideological conflict between two differing schools of pan-yugoslavism: part of it was a general unwillingness of the two traditions to use names foreign to them (serbs didn't want to call themselves croats; croats didn't want to call themselves serbs), but a lot of it revealed true differences in preference—the degree of loyalty to the habsburg monarchy, for instance, and how exactly should the serbo-croatian literary language look like (eventually resolved through the adoption of standard serbian as the basis for what is today standard croatian)
there's really no date for when did all these incongruities make the friction between the two schools disintegrate into ethnic conflict in the proper sense; one could make the argument they never did (see below). as late as the early 20th century you had things like the 'movement of catholic serbs in dubrovnik' that claimed themselves to be serbs because they were, by all standards, croats, and who worked in tandem with croatian nationalists in the region (until they didn't). much of it boils down to conflict between the orthodox inhabitants of what is today central croatia and the dalmatian hinterland (basically all of whom self-identified as serbs by the 20th century—given that we have records of albanians, aromanians and bulgarians settling in the so-called 'croatian military frontier' alongside serbs proper, it is likely their sympathy for serbian ethnic identity was partially downstream from them being catered to by the serbian orthodox church) and the territorial aspirations of the kingdom of croatia, which lobbied for the annexation of the croatian military frontier and dalmatia into croatia proper
the aforementioned distaste of the serb orthodox for incorporation into croatia boiled down to the preservation of an independent military frontier securing the religious liberty of the region's orthodox, and it giving them the ability to directly arbitrage with vienna. but it should be emphasised there were serbs that supported the territorial aspirations of croatia out of a basic sense of yugoslav solidarity; it took a while for the political loyalties of 'croats' and 'serbs' to truly solidify
anyway. some of the watershed moments in the pre-ww2 history of croat-serb relations were: the slow shift of dalmatian serbs toward political collaboration with italians (who favoured an independent kingdom of dalmatia) over croats (who favoured the kingdom's annexation into croatia); the establishment of the croatian party of rights in 1861, the first party to explicitly argue against the unification of croatia with serbia (though many of its early members never quite claimed croats to be ethnically distinct from serbs); the austrian occupation of bosnia in 1878, lauded by croatia and denounced by serbia (further exacerbated by austria-hungary's annexation of bosnia in 1908); the 1914 anti-serb riots in sarajevo, sparked by the assassination of franz ferdinand; the extremely unclear terms by which croatia was annexed into the kingdom of serbia after the first world war (1918) and dissatisfaction of croat republican parties with the 1921 yugoslav constitution; the partition of yugoslavia into banates in 1929, and the establishment of a semi-autonomous 'banate of croatia' in 1939, by which point serbs and croats behaved functionally if not formally as separate ethnicities
i think one could make the argument the split between croats and serbs was only finalised within the last, like, thirty years, if that. serbian popular consciousness and historiography is still quite on board w the notion croats constitute a branch of the serbian nation, even if serbia as a state no longer formally seeks the annexation of croatia; conversely, denial of a separate serb ethnicity (specifically the idea of serbs as ethnically mixed (derogatory), and us supposedly lacking our own language and tradition of statehood) is still central to croatian national identity. much of it comes down to croatian nationalists being kind of shit at articulating what makes them ethnically distinct from serbs, and serbian nationalists not even trying to imply any ethnic difference between the two (those maps of a 'greater serbia' that excludes the croatian heartland were a last resort proposal, made when the reintegration of all croatia into yugoslavia became a clear impossibility). grim situation all around
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

Village votive cross, standing next to a holy oak tree, at the edge of the village land, somewhere near Vlasotince, South Eastern Serbia, 19th century. Village masses were, and still are, held next these holy trees in Serbia. Holy trees and votive crosses were in the past located on village land boundaries. Cutting the holy tree and knocking down or moving a votive cross was a tabu, a huge sin. So they effectively preserved the borders and ensured peace between neighbours.
177 notes
·
View notes
Text
Being Serbian and not religious is complicated enough, but being queer on top of that is even more complicated and that's concerning.
You see, Serbs have a very unique history and bond with religion. Serbia was under Ottoman rule from the middle of the 15th century up until the begging of the 19th century which is a long long time. Being a part of Ottoman empire meant that they wanted to assimilate you and there were many awful things they did due but i won't go into that rn. What was weird about Ottoman empire compared to other oppressors was that they never banned different religions. Obviously your life would have been easier if you became muslim but it wasn't like they killed you for not doing that as Romans did. So Serbian people became very close to the church and it bound all of the folk customs and holidays to itself and saved them which is a great thing and I'm so thankful for that but nowadays it's impossible to separate them. Every aspect of culture is somehow made christian and Serbian people have accepted orthodox christianity as a part of their national identity. You can't imagine how many people I've met who were confused about how can someone be Serbian if they're not christian. And most of them don't even believe in God or what christianity preaches, it's a national identity for them. They can't imagine what Serbs actually are beyond the religion and it's sad.
Other important thing is that all of the holidays and customs are pagan. They have been pagan and then Serbs got christianised in a quick way which means that they just masked the paganism in chriatianity and called it a day. There's practiced whichcraft in Serbian orthodox christianity and people refuse to call it that because it's a normal christian thing for them. There's prayers, healing watter and oils, plants, various rituals for various days (not just Easter and Christmas but even those are completely different than how other christians celebrate them), there's days where you don't work or do certain things so that you don't get God angry, there's future predictions by looking in a cup or reading in the coal or hot iron and various other customs and beliefs. And no one accepts them as anything but chriatian.
So yeah separation of religion and nationality is crucial for Serbian people to move forward but it's also very hard to do and it's beneficial to the government so no one is doing anything about it. Nationalism is unfortunately on the rise among Serbian people and obviously christianity is also. There's people who are ready to fight for "holy places" and Serbian (read christian) values. There's diaspora that's trying to reconnect with their nationality and they just fall into christianty and nationalistic propaganda and it's awful. Most of these people are cowards so I have hope they won't do anything stupid as starting another war but it's still concerning. When your national identity is so strongly bound to christianty a threat to christian beliefs is a threat to your nationality and you already know who falls into that "threat" category.
Also, pagan slavic spaces got infected by fascists and white slavic supremacist? It's like what happened in nordic pagan spaces. I know I know it makes no sense for south slavs to be fascists when ww2 fascists targeted them but you have to understand that these people aren't smart enough to understand that and are egoistic enough to twist things to better suit their beliefs.
That's why queer Slavs and queer folk art and queer history of slavs is so important and even revolutionary in times and places like these. And of course this post is not against christians. One of my favorite things are loving non bigoted christians, especially if they are queer themselves.
41 notes
·
View notes