#AutoGPT
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
🔍 What Exactly Is an AI Agent—and Why Are AI Agent Startups Different?
Not all AI startups are created equal. While traditional AI startups focus on static models like classifiers and prediction tools, AI agent startups are building something far more advanced.
AI agents can: ✔ Think ✔ Plan ✔ Act ✔ Learn …autonomously, with minimal human input.
They tackle multi-step, real-world problems end-to-end, without constant micromanagement.
What powers these AI agents?
Frameworks like Lucha, AutoGPT, and OpenAI Function Calling
Multimodal AI (text, image, voice integration)
Memory-augmented architectures
Tool-using APIs
These aren’t just smarter bots. They’re adaptive, decision-making systems that can navigate complexity and evolve in real time.
💡 As AI agents become more capable, the line between automation and intelligent assistance is fading fast.
👉 Are you ready for this shift? Contact Us - https://cizotech.com/
#ai#cizotechnology#techinnovation#app developers#appdevelopment#ios#mobileappdevelopment#iosapp#innovation#mobileapps#aiagents#aistartups#machinelearning#multimodalai#AutoGPT
0 notes
Text
LLMs as Operating Systems
Last month the Microsoft Research team shared some insights in a generative application framework called AutoGen that casts a spotlight on so many intriguing possibilities in AI. Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 can step up beyond simple tasks
[vc_row el_id=”blog__prefix-audience”][vc_column width=”1/4″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_column_text animation=”animation bottom-to-top”] People familiar with ChatGPT, GPT-3, and advancements in machine learning, Generative AI like Midjourney, or those who’ve used AI features on Snapchat, Khan Academy, or Duolingo’s personalized tutors [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row] Last month…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
AutoGPT
AutoGPT – krok w stronę walki z cyberprzestępcami za pomocą sztucznej inteligencji https://linuxiarze.pl/autogpt-krok-w-strone-walki-z-cyberprzestepcami-za-pomoca-sztucznej-inteligencji/
1 note
·
View note
Text

What is Auto-GPT? Why is it important?
In the end, Auto-GPT uses the versatility of OpenAI’s most recent AI models to communicate with services and software online which allows Auto-GPT to “autonomously” perform tasks like X and Y.
0 notes
Note
Have you seen the AutoGPT framework? That adds a scaffolding to LLMs so that they can run indefinitely with a memory store, would that be Turing complete?
so there's three caveats here:
it's been 20 years since I actually studied this topic, and have forgotten like 95% of what I've learned
a wrapper program that runs an FSM in a loop with extra input from an oracle (the internet) is a lot harder to reason about than an FSM on its own
I'm found the GitHub for this but I'm not gonna read that many lines of code for free
all that said, my initial skim of the AutoGPT codebase is that the way it's implemented is making some pretty extraordinary assumptions about GPT's ability to generate sensible results for the kind of prompts it uses.
it's essentially trying to break down work into bite sized pieces by telling the text generator to:
deepdream a bureaucracy of specialized task runners
handle a user request by writing delegated tasks for members of the bureaucracy
execute those tasks as though you're the recipient member of the bureaucracy
repeat until "done"
there's a couple different ways that this can go wrong
first off, it's not clear to me whether the above hierarchical breakdown of work is being done in a way that's allowed to loop "until done". if not, we're back at FSMs.
second off, it's not clear to me whether the text generator can generate subtasks competently, the way AutoGPT is requesting them, without already being turing complete. I see a lot of hay being made in the prompts about "explain your reasoning", as context to be passed along to future invocations in order to produce more meaningful results, but answering that prompt requires an amount of introspection where I'd be surprised if an FSM was capable of generating a real answer, instead of some "sounds normal" mimic handwave. and if these output fields are garbage, then the proof by induction falls apart that the preserved context is making outputs better and not worse; you'd get something that maybe has all the physical organs to emulate a turing machine, but miswired such that it'll never actually succeed at computing anything beyond the sum of its parts.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
MetaGPT is a framework that enables you to use natural language to create and execute meta programs for multi-agent collaboration and coordination. Meta programs are programs that can generate or modify other programs based on some input or context. In this article, you will find out how MetaGPT works, what are its key features and capabilities, and how it compares to other frameworks.
#MetaGPT#MultiAgent#MetaProgramming#AI#Opensource#datascience#MachineLearning#open source#artificial intelligence#machine learning#programming#data science
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
As much as I despise AI generated slop, and as much as I am comforted by Applesbannas747's story, I was still skeptical about AI art actually going away so easy. So I did some research in hopes of proving myself wrong.
https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2024/08/14/ai-copyright-lawsuit-artists-stability-midjourney/
It starts 😎
There's even an article on AUTOGPT called "AI Image Generators Face Major Legal Battle as Artists Gain Ground" that shows how worried the AI users are about this lol. As an artist, this makes me quite happy.

Reblog to kill it faster
297K notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Agents: The Next Leap in Intelligent Automation
As businesses continue to navigate the digital transformation wave, a new class of automation is emerging—AI agents. Unlike traditional AI tools that focus on single-task execution, AI agents are autonomous systems capable of planning, learning, and acting across multi-step workflows with minimal human intervention.

🚀 What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a system that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Think of it as a digital employee with reasoning capabilities. Powered by Generative AI, machine learning, and agentic frameworks like AutoGPT or LangChain, these agents can:
Understand complex instructions
Break down goals into subtasks
Access tools and APIs
Interact with apps or systems
Adapt to changes over time
Unlike static chatbots, AI agents operate more like autonomous assistants that can initiate action, not just respond to prompts.
🔄 How AI Agents Work (Simplified Workflow)
Input Goal or Command (e.g., "Generate weekly sales report from CRM")
Task Decomposition – The agent identifies subtasks (log in, fetch data, clean, analyze, visualize)
Tool Use & Action Execution – It uses APIs or internal tools to perform tasks
Feedback Loop – It checks results and adjusts behavior if needed
Output Delivery – Final report is generated and emailed or uploaded
This makes them especially powerful for end-to-end workflows across sales, operations, support, and marketing.
🎯 Key Benefits of AI Agents
✅ Task Autonomy: Reduce human micromanagement
✅ Multistep Workflows: Execute complex logic with branching decisions
✅ Tool Orchestration: Integrate with APIs, CRMs, ERPs, and cloud tools
✅ 24/7 Availability: Great for support, scheduling, monitoring
✅ Scalability: Replicate agents across teams and tasks
Compared to traditional AI chatbots, AI agents go further by handling sequences of decisions and adapting dynamically to context—not just replying.
🏗️ AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries
Retail & E-commerce: Automated inventory sync, campaign setup, price monitoring
Manufacturing: Procurement tracking, quality checks, maintenance scheduling
Healthcare: Pre-visit patient screening, report generation, claim filing
Construction: Compliance document prep, project status summaries, shift coordination
EdTech: Content recommendation, progress follow-up, tutor scheduling
🧠 Kaopiz’s AI Agent Capabilities
At Kaopiz, we help clients move from experimentation to execution with custom-built AI agent solutions tailored to your tools, workflows, and goals. Our offerings include:
🎯 Use case consultation
🛠️ Agent design & prompt engineering
🔗 API/CRM/ERP integration
🔒 Secure deployment on cloud or on-prem
📊 Monitoring & performance tuning
Want to learn more about how AI agents can transform your business? Explore our AI integration services or speak to our team.
0 notes
Text
Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University: Master AI Automation and Build the Future of Digital Business
In an era where artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping the digital world, those who understand and utilize AI agents are the ones staying ahead. The Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University is a next-generation online course designed to equip digital entrepreneurs, freelancers, and professionals with the skills to create, manage, and monetize AI automation systems.
Whether you're a complete beginner or someone with tech experience, this course provides a clear roadmap to building AI agents that can handle tasks, serve clients, and scale your business — all without writing a single line of complex code.
What Is Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University?
The Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Program is an in-depth, step-by-step online course focused on helping you master AI automation by building AI agents using tools like ChatGPT, AutoGPT, Make, Zapier, and other modern platforms. These AI agents can perform tasks that traditionally require human effort — such as sending emails, handling customer support, managing workflows, scheduling meetings, and even creating content.
This course gives you everything from foundational knowledge to advanced implementation strategies. Unlike general AI courses that talk theory, the Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Online Program is built around action — helping you launch fully functional agents that work for you or your clients from day one.
Meet Your Instructor: Ethan Nelson
Ethan Nelson is a highly respected AI entrepreneur and automation strategist. He’s built AI systems that help businesses automate their entire backend—from lead generation and onboarding to communication and reporting. Known for simplifying technical concepts and turning them into practical solutions, Ethan’s approach makes even advanced AI workflows accessible for anyone.
The AI Agents University Online Course By Ethan Nelson reflects years of experimentation, real-world implementation, and client-tested strategies—all condensed into one cohesive learning experience.
What You’ll Learn Inside the Course
The Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Online Course is built around practical learning. It doesn’t just teach you about AI — it teaches you how to build working AI agents that create real-world results.
Here’s a breakdown of the major modules you’ll go through:
🔹 Module 1: AI Foundations & Agent Strategy
What are AI agents and why they’re the future of automation
Understanding workflows, intent, context, and logic trees
Differences between basic automations vs. intelligent agents
🔹 Module 2: Tools of the Trade
Overview of tools like OpenAI, Make.com, Zapier, Notion, and APIs
How to connect tools to create seamless automations
Using natural language to control your automations
🔹 Module 3: Building Your First AI Agent
Step-by-step process to build a simple but powerful AI assistant
Automating lead capture, CRM updates, and email follow-ups
Using agents to handle repetitive client and business tasks
🔹 Module 4: Advanced Use Cases
Building sales agents, content creation bots, and customer support agents
Automating proposal generation and onboarding workflows
Multi-step decision-making agents and memory chains
🔹 Module 5: Monetizing AI Agents
How to sell AI automation services to clients
Productizing your AI agents into monthly retainers
Pricing strategies and case studies from Ethan’s clients
🔹 Bonus: Pre-Built Templates and Agent Blueprints
Plug-and-play agent templates you can use immediately
Agent scripts for various industries (marketing, coaching, SaaS, agencies)
Ethan’s private SOPs and system-building frameworks
Who Should Take This Course?
The AI Agents University Online Program By Ethan Nelson is for anyone who wants to stay ahead in the AI revolution and learn how to use technology to save time and grow their business.
This course is ideal for:
✅ Freelancers and consultants looking to offer automation services
✅ Digital entrepreneurs who want to automate operations
✅ SaaS owners and startups building AI-powered tools
✅ Marketers and agencies seeking efficiency at scale
✅ Beginners curious about AI and automation, with no coding skills
Even if you’ve never built a workflow before, the course guides you from basics to advanced agent systems in a beginner-friendly manner.
Why AI Agents Are the Future
AI agents are intelligent systems that can autonomously complete tasks based on user input, context, and history. Instead of creating rigid automations that break easily, AI agents are adaptive, responsive, and increasingly human-like in their logic.
By learning how to build and use AI agents, you unlock a world of opportunities:
Automate 80% of your repetitive workload
Offer high-ticket AI automation services to clients
Create digital products and tools powered by agents
Stay relevant in a rapidly evolving digital market
The Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Online Program ensures that you’re not just keeping up with the trend — you're leading it.
What Makes This Course Unique?
There are many courses out there that talk about AI, but very few walk you through the practical creation and monetization of AI agents like this one does.
Here’s what makes this course stand out:
✅ No fluff, just real-world application
✅ Beginner-friendly but highly advanced in value
✅ Built-in templates to save time
✅ Focus on making money using AI, not just learning tech
✅ Continually updated content as tools evolve
Whether you're looking to replace tedious manual work, offer automation services to clients, or build a fully agent-powered business, this course gives you the roadmap.
Real Student Results & Testimonials
"Before this course, I didn’t even know what AI agents were. Now I have three client projects running fully automated backends." "Ethan’s training turned my freelancing side hustle into a productized AI service business." "I used the AI Agents University Online Course By Ethan Nelson to automate my client outreach and doubled my response rate in two weeks."
These results are a testament to the power and practicality of what’s inside the course.
How to Get Access to the Course?
To access the full version of the Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Program, we highly recommend purchasing it from a reliable and trusted source.
👉 Buy now from: ECOMKEVIN COURSE
This is the best platform to get the updated version of the course, including all bonus materials, secure payment options, and ongoing support.
Final Thoughts
The rise of AI is not a trend—it’s a transformation. And those who learn how to work with AI, rather than compete against it, will win. The Ethan Nelson – AI Agents University Online Course is your chance to master the skills that the future demands.
By the end of this course, you won’t just understand AI — you’ll be building intelligent systems that work for you 24/7.
This isn’t just another course. It’s a launchpad into the next generation of digital entrepreneurship.
If you’re serious about leveraging AI to grow your business, boost your income, or launch a new career path — don’t miss out.
0 notes
Text
They Promised Us Agents, but All We Got Were Static Chains
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/they-promised-us-agents-but-all-we-got-were-static-chains/
They Promised Us Agents, but All We Got Were Static Chains
In the spring of 2023, the world got excited about the emergence of LLM-based AI agents. Powerful demos like AutoGPT and BabyAGI demonstrated the potential of LLMs running in a loop, choosing the next action, observing its results, and choosing the next action, one step at a time (also known as the ReACT framework). This new method was expected to power agents that autonomously and generically perform multi-step tasks. Give it an objective and a set of tools and it will take care of the rest. By the end of 2024, the landscape will be full of AI agents and AI agent-building frameworks. But how do they measure against the promise?
It is safe to say that the agents powered by the naive ReACT framework suffer from severe limitations. Give them a task that requires more than a few steps, using more than a few tools and they will miserably fail. Beyond their obvious latency issues, they will lose track, fail to follow instructions, stop too early or stop too late, and produce wildly different results on each attempt. And it is no wonder. The ReACT framework takes the limitations of unpredictable LLMs and compounds them by the number of steps. However, agent builders looking to solve real-world use cases, especially in the enterprise, cannot do with that level of performance. They need reliable, predictable, and explainable results for complex multi-step workflows. And they need AI systems that mitigate, rather than exacerbate, the unpredictable nature of LLMs.
So how are agents built in the enterprise today? For use cases that require more than a few tools and a few steps (e.g. conversational RAG), today agent builders have largely abandoned the dynamic and autonomous promise of ReACT for methods that heavily rely on static chaining – the creation of predefined chains designed to solve a specific use case. This approach resembles traditional software engineering and is far from the agentic promise of ReACT. It achieves higher levels of control and reliability but lacks autonomy and flexibility. Solutions are therefore development intensive, narrow in application, and too rigid to address high levels of variation in the input space and the environment.
To be sure, static chaining practices can vary in how “static” they are. Some chains use LLMs only to perform atomic steps (for example, to extract information, summarize text, or draft a message) while others also use LLMs to make some decisions dynamically at runtime (for example, an LLM routing between alternative flows in the chain or an LLM validating the outcome of a step to determine whether it should be run again). In any event, as long as LLMs are responsible for any dynamic decision-making in the solution – we are inevitably caught in a tradeoff between reliability and autonomy. The more a solution is static, is more reliable and predictable but also less autonomous and therefore more narrow in application and more development-intensive. The more a solution is dynamic and autonomous, is more generic and simple to build but also less reliable and predictable.
This tradeoff can be represented in the following graphic:
This begs the question, why have we yet to see an agentic framework that can be placed in the upper right quadrant? Are we doomed to forever trade off reliability for autonomy? Can we not get a framework that provides the simple interface of a ReACT agent (take an objective and a set of tools and figure it out) without sacrificing reliability?
The answer is – we can and we will! But for that, we need to realize that we’ve been doing it all wrong. All current agent-building frameworks share a common flaw: they rely on LLMs as the dynamic, autonomous component. However, the crucial element we’re missing—what we need to create agents that are both autonomous and reliable—is planning technology. And LLMs are NOT great planners.
But first, what is “planning”? By “planning” we mean the ability to explicitly model alternative courses of action that lead to a desired result and to efficiently explore and exploit these alternatives under budget constraints. Planning should be done at both the macro and micro levels. A macro-plan breaks down a task into dependent and independent steps that must be executed to achieve the desired outcome. What is often overlooked is the need for micro-planning aimed to guarantee desired outcomes at the step level. There are many available strategies for increasing reliability and achieving guarantees at the single-step level by using more inference-time computing. For example, you could paraphrase semantic search queries multiple times, you can retrieve more context per a given query, can use a larger model, and you can get more inferences from an LLM – all resulting in more requirements-satisfying results from which to choose the best one. A good micro-planner can efficiently use inference-time computing to achieve the best results under a given compute and latency budget. To scale the resource investment as needed by the particular task at hand. That way, planful AI systems can mitigate the probabilistic nature of LLMs to achieve guaranteed outcomes at the step level. Without such guarantees, we’re back to the compounding error problem that will undermine even the best macro-level plan.
But why can’t LLMs serve as planners? After all, they are capable of translating high-level instructions into reasonable chains of thought or plans defined in natural language or code. The reason is that planning requires more than that. Planning requires the ability to model alternative courses of action that may reasonably lead to the desired outcome AND to reason about the expected utility and expected costs (in compute and/or latency) of each alternative. While LLMs can potentially generate representations of available courses of action, they cannot predict their corresponding expected utility and costs. For example, what are the expected utility and costs of using model X vs. model Y to generate an answer per a particular context? What is the expected utility of looking for a particular piece of information in the indexed documents corpus vs. an API call to the CRM? Your LLM doesn’t begin to have a clue. And for good reason – historical traces of these probabilistic traits are rarely found in the wild and are not included in LLM training data. They also tend to be specific to the particular tool and data environment in which the AI system will operate, unlike the general knowledge that LLMs can acquire. And even if LLMs could predict expected utility and costs, reasoning about them to choose the most effective course of action is a logical decision-theoretical deduction, that cannot be assumed to be reliably performed by LLMs’ next token predictions.
So what are the missing ingredients for AI planning technology? We need planner models that can learn from experience and simulation to explicitly model alternative courses of action and corresponding utility and cost probabilities per a particular task in a particular tool and data environment. We need a Plan Definition Language (PDL) that can be used to represent and reason about said courses of action and probabilities. We need an execution engine that can deterministically and efficiently execute a given plan defined in PDL.
Some people are already hard at work on delivering on this promise. Until then, keep building static chains. Just please don’t call them “agents”.
#2023#2024#agent#agents#ai#ai agent#AI AGENTS#AI systems#AI21#API#approach#atomic#AutoGPT#autonomous#BabyAGI#Building#code#computing#course#courses#crm#data#development#engine#engineering#enterprise#Environment#event#exploit#framework
0 notes
Text
I'm a GitHub Expert and I'm Shocked by These Trending AI Projects! #93

I'm a GitHub Expert and I'm Shocked by These Trending AI Projects! #093 #githubprojects #aiprojects #autogpttutorials 👉 Try FREE Aiarty Image Enhancer: Enhance & Upscale images up to 32K : https://www.aiarty.com/midjourney-prompts/?ttref=2410-ytb-aia-aigcmj-mgg-text-3l "🚀Explore the latest trending open-source GitHub projects focusing on AI frameworks, large language models (LLMs), and AI-powered investment research tools. Whether you're a developer looking for new AI frameworks, an investor seeking advanced research tools, or an AI enthusiast exploring LLM innovations, this video has you covered! Join us as we delve into groundbreaking projects like RouteLLM for efficient LLM routing, OpenBB for AI-driven investment research, and much more. 👍 Like, share, and subscribe for more updates on AI advancements. Drop your thoughts and questions in the comments below! #AITechnology #GitHubProjects #Innovation #AutoGPTTutorial #tensorart" 📌 Video Project Details. 🔗 Get FREE AI Project Updates : https://manuagi.beehiiv.com/subscribe 📌 Important AI Tools (affiliate) 🔗 Build Your AI Startup : https://shipfa.st/?via=autogpt 🔗 AI Voice - https://try.elevenlabs.io/0wgaz29csuo5 🔗 Try NordVPN : https://nordvpn.sjv.io/autogpt 🔗 NextJS Directory : https://nextjsdirectory.com?aff=j1Dej 📌 Timestamps : 00:00 - Intro Part 00:28 - o1-engineer : https://github.com/Doriandarko/o1-engineer 02:27 - BaseAI : https://github.com/LangbaseInc/BaseAI 04:39 - Crawl4AI : https://github.com/unclecode/crawl4ai 07:01 - ChatMLX : https://github.com/maiqingqiang/ChatMLX 09:23 - RouteLLM : https://github.com/lm-sys/RouteLLM 11:39 - OpenBB : https://github.com/OpenBB-finance/OpenBB 13:54 - EXO : https://github.com/exo-explore/exo 15:56 - Netdata : https://github.com/netdata/netdata 18:10 - Fragments by E2B : https://github.com/e2b-dev/fragments 20:25 - GenAI Agents: https://github.com/NirDiamant/GenAI_Agents 👍 Enjoyed the breakdown? Give us a thumbs up! 🔔 Stay updated with the latest in tech by subscribing. 💬 Share your thoughts or suggest projects for our next review in the comments!" Tags: I'm a GitHub Expert and I'm Shocked by These Trending AI Projects,GitHub Expert,Trending AI Projects,Github projects,github tutorial,github,ai projects,ai,ai tools,open source projects,open source,ai news,autogpt,manuagi,elon musk,chatgpt,RouteLLM,OpenBB,BaseAI,PodSnap AI,GenAI Agents 📈 Subscribe for more AI tutorials, tips, and industry insights. Don't forget to like, comment, and share with your tech-savvy friends! Hashtags: #OpenSourceProjects #GitHubTrends #CodingWonders #AIDevelopment #MachineLearning #ArtificialIntelligence #TechInnovation #MLflow #Playwright #OpenSource #AIProjects #DevTools #LeapAI #TechnologyTrends #AIInnovation #LLM #AIProjects #DeepLearning #MachineLearning #TechTrends #FutureOfAI #mentat #TechInnovation #FutureOfAI #AIProjects #DeveloperTools #AutoGPTTutorials #AITech #GitHubProjects #Innovations #TechTrends source Read the full article
#ai#ainews#aiprojects#AITools#autogpt#BaseAI#ChatGPT#elonmusk#GenAIAgents#github#GitHubExpert#GitHubProjects#githubtutorial#I'maGitHubExpertandI'mShockedbyTheseTrendingAIProjects#manuagi#opensource#opensourceprojects#OpenBB#opensourceai#PodSnapAI#RouteLLM#TrendingAIProjects
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Entrepreneurs Are Building Startups with GPTs and Autonomous Agents
In the not-so-distant past, launching a startup often meant finding the perfect co-founder—someone with complementary skills, shared vision, and an equal willingness to endure sleepless nights and uncertain paychecks. Today, however, a new trend is disrupting this dynamic: artificial intelligence is stepping into the role of co-founder. Entrepreneurs are increasingly turning to AI-powered tools like OpenAI’s GPT-4, AutoGPT, and other autonomous agents to ideate, build, and scale their startups, often without a human partner.

This transformation isn't science fiction. It’s happening now—and it's reshaping the entrepreneurial landscape in profound ways.
From Solopreneur to AI-Enhanced Startup Founder
For many solo entrepreneurs, one of the biggest challenges is wearing multiple hats: marketing, coding, customer support, business strategy, and more. Tools powered by large language models (LLMs) are now able to shoulder many of these burdens. GPT-4, for example, can brainstorm product names, write investor pitch decks, generate social media campaigns, draft legal contracts, and even debug code.
Autonomous agents like AutoGPT or AgentGPT take it a step further by autonomously chaining tasks together to complete objectives with minimal human input. Imagine telling an AI agent, “Build me a landing page and create a 30-day email campaign for my productivity app,” and watching it do just that—sourcing content, writing emails, scheduling campaigns, and even analyzing A/B testing data.
Gaurav Mohindra, a legal and technology expert with deep ties to the startup world, puts it this way: “AI co-founders are the ultimate multitaskers. They never sleep, don’t argue, and can switch from branding to backend development in milliseconds. That’s a powerful partner for any entrepreneur.”
Automating Ideation and Execution
One of the most valuable aspects of AI as a co-founder is its ability to accelerate ideation. Where a human might take hours to research market opportunities or brainstorm ideas, GPT-4 can do it in minutes—and do it well. Solopreneurs can now validate business ideas by simulating customer feedback, running competitive analyses, and even modeling business strategies—all within a single AI prompt.
Autonomous agents can execute entire business models end-to-end. For instance, an entrepreneur looking to build a dropshipping business can use AI to identify trending products, build a Shopify store, write product descriptions, and craft Google ad copy—all without writing a line of code themselves.
This ability to compress the startup cycle has led to a wave of “micro-startups”—small, AI-assisted ventures that can be rapidly built, tested, and either scaled or shut down with minimal cost. In essence, AI is allowing founders to run experiments at startup speed without startup risk.
“Founders are no longer bottlenecked by bandwidth or expertise,” says Gaurav Mohindra. “With the right AI tools, a single person can launch what used to take an entire team. It’s democratizing innovation like never before.”
Real-World Applications
The rise of AI co-founders isn’t just theoretical. Real startups are already using this model to go to market faster and smarter.
A Los Angeles-based entrepreneur recently built and launched an AI-powered resume review service using nothing but GPT-4 and a no-code platform. The AI handled everything from branding to writing code snippets, to generating customer FAQs and setting up email automation. The founder reached 1,000 paying users in less than two months—without hiring a single employee.
In another example, a fintech startup used autonomous agents to simulate hundreds of market scenarios and generate investment strategies that were later used to train its core algorithm. The AI not only provided creative insights but reduced what would have been months of research into days of simulation.
These examples highlight a key shift: AI isn’t just a tool. It’s becoming a thinking partner—capable of generating value at every stage of the startup journey.
Ethical and Strategic Implications
Of course, this trend isn’t without its challenges. The idea of AI acting as a co-founder raises important ethical and legal questions. Can AI hold equity in a company? Who is liable if an AI makes a bad decision? What about intellectual property created by AI agents?
Currently, the law doesn’t allow AI to hold ownership or sign contracts, but that hasn’t stopped founders from granting “honorary” co-founder status to GPT-based agents, sometimes even naming them as contributors on pitch decks or websites. While these moves are mostly symbolic, they reflect a larger cultural shift toward viewing AI as a partner rather than a mere tool.
There’s also the question of dependence. Relying too heavily on AI could stifle human creativity, especially when founders lean on it for decision-making instead of critical thinking. Ethical entrepreneurs will need to strike a balance between delegation and oversight.
“AI is a phenomenal co-founder,” says Gaurav Mohindra, “but it’s not a moral compass. Founders still need to lead with ethics, empathy, and vision. AI can execute, but only humans can inspire.”
What’s Next: The Future of AI-Driven Startups
As AI continues to evolve, the concept of the AI co-founder is likely to grow in sophistication. We can expect smarter agents capable of reasoning, negotiating, and collaborating in increasingly human-like ways. Some startups are even building “personal boardrooms” composed entirely of AI agents—each representing a function like finance, marketing, or product strategy.
There’s also the potential for industry-specific AI co-founders. Imagine a healthcare startup launching with a medical AI partner trained on decades of research, or a legal-tech startup built alongside an AI trained on every major case law precedent.
The key trend is clear: AI is moving from assistant to collaborator.
“Ten years ago, startups were built on code,” says Gaurav Mohindra. “Today, they’re built on prompts. The next generation of entrepreneurs won’t ask, ‘Who’s your co-founder?’ but ‘Which model are you building with?’ That’s the new startup DNA.”
Conclusion
The rise of AI co-founders is more than a novel concept—it’s a seismic shift in how businesses are built. For solo entrepreneurs and small teams, the ability to tap into superintelligent partners who can execute across domains is a game-changer. It lowers the barrier to entry, speeds up innovation, and redefines what it means to be a founder in the modern age.
But like all powerful tools, AI must be wielded wisely. The future will belong to those who can merge the speed and precision of machines with the creativity and ethics of humans.
In this hybrid world, success won’t just be about working harder or faster. It’ll be about working smarter—with AI as you’re most reliable co-founder.
Originally Posted: https://gauravmohindrachicago.com/rise-of-ai-co-founders/
0 notes
Text
Meet the Machines That Think for Themselves: AI Agent Development Explained
Here is your full 1500-word blog post titled:
Meet the Machines That Think for Themselves: AI Agent Development Explained

For decades, artificial intelligence (AI) has largely been about recognition—recognizing images, processing language, classifying patterns. But today, AI is stepping into something more profound: autonomy. Machines are no longer limited to reacting to input. They’re learning how to act on goals, make independent decisions, and interact with complex environments. These are not just AI systems—they are AI agents. And they may be the most transformative development in the field since the invention of the neural network.
In this post, we explore the world of AI agent development: what it means, how it works, and why it’s reshaping everything from software engineering to how businesses run.
1. What Is an AI Agent?
At its core, an AI agent is a software system that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve specific goals—autonomously. Unlike traditional AI tools, which require step-by-step commands or input prompts, agents:
Operate over time
Maintain a memory or state
Plan and re-plan as needed
Interact with APIs, tools, and even other agents
Think of the difference between a calculator (traditional AI) and a personal assistant who schedules your meetings, reminds you of deadlines, and reschedules events when conflicts arise (AI agent). The latter acts with purpose—on your behalf.
2. The Evolution: From Models to Agents
Most of today’s AI tools, like ChatGPT or image generators, are stateless. They process an input and return an output, without understanding context or goals. But humans don’t work like that—and increasingly, we need AI that collaborates, not just computes.
AI agents represent the next logical step in this evolution: PhaseCharacteristicsRule-based SystemsHardcoded logic; no learningMachine LearningLearns from data; predicts outcomesLanguage ModelsUnderstands and generates natural languageAI AgentsThinks, remembers, acts, adapts
The shift from passive prediction to active decision-making changes how AI can be used across virtually every industry.
3. Key Components of AI Agents
An AI agent is a system made up of many intelligent parts. Let’s break it down:
Core Brain (Language Model)
Most agents are powered by an LLM (like GPT-4 or Claude) that enables reasoning, language understanding, and decision-making.
Tool Use
Agents often use tools (e.g., web search, code interpreters, APIs) to complete tasks beyond what language alone can do. This is called tool augmentation.
Memory
Agents track past actions, conversations, and environmental changes—allowing for long-term planning and learning.
Looped Execution
Agents operate in loops: observe → plan → act → evaluate → repeat. This dynamic cycle gives them persistence and adaptability.
Goal Orientation
Agents aren’t just reactive. They’re goal-driven, meaning they pursue defined outcomes and can adjust their behavior based on progress or obstacles.
4. Popular Agent Architectures and Frameworks
AI agent development has gained momentum thanks to several open-source and commercial frameworks:
LangChain
LangChain allows developers to build agents that interact with external tools, maintain memory, and chain reasoning steps.
AutoGPT
One of the first agents to go viral, AutoGPT creates task plans and executes them autonomously using GPT models and various plugins.
CrewAI
CrewAI introduces a multi-agent framework where different agents collaborate—each with specific roles like researcher, writer, or strategist.
Open Interpreter
This agent runs local code and connects to your machine, allowing more grounded interaction and automation tasks like file edits and data manipulation.
These platforms are making it easier than ever to prototype and deploy agentic behavior across domains.
5. Real-World Use Cases of AI Agents
The rise of AI agents is not confined to research labs. They are already being used in practical, impactful ways:
Personal Productivity Agents
Imagine an AI that manages your schedule, drafts emails, books travel, and coordinates with teammates—all while adjusting to changes in real time.
Examples: HyperWrite’s Personal Assistant, Rewind’s AI agent
Enterprise Workflows
Companies are deploying agents to automate cross-platform tasks: extract insights from databases, generate reports, trigger workflows in CRMs, and more.
Examples: Bardeen, Zapier AI, Lamini
Research and Knowledge Work
Agents can autonomously scour the internet, summarize findings, cite sources, and synthesize information for decision-makers or content creators.
Examples: Perplexity Copilot, Elicit.org
Coding and Engineering
AI dev agents can write, test, debug, and deploy code—either independently or in collaboration with human engineers.
Examples: Devika, Smol Developer, OpenDevin
6. Challenges in Building Reliable AI Agents
While powerful, AI agents also come with serious technical and ethical considerations:
Planning Failures
Long chains of reasoning can fail or loop endlessly without effective goal-checking mechanisms.
Hallucinations
Language models may invent tools, misinterpret instructions, or generate false information that leads agents off course.
Tool Integration Complexity
Agents often need to interact with dozens of APIs and services. Building secure, resilient integrations is non-trivial.
Security Risks
Autonomous access to files, databases, or systems introduces the risk of unintended consequences or malicious misuse.
Human-Agent Trust
Transparency is key. Users must understand what agents are doing, why, and when intervention is needed.
7. The Rise of Multi-Agent Collaboration
One of the most exciting developments in AI agent design is the emergence of multi-agent systems—where teams of agents work together on complex tasks.
In a multi-agent environment:
Agents take on specialized roles (e.g., researcher, planner, executor)
They communicate via structured dialogue
They make decisions collaboratively
They can adapt roles dynamically based on performance
Think of it like a digital startup where every team member is an AI.
8. AI Agents vs Traditional Automation
It’s worth comparing agents to traditional automation tools like RPA (robotic process automation): FeatureRPAAI AgentsRule-basedYesNo (uses reasoning)AdaptableNoYesGoal-drivenNo (task-driven)YesHandles ambiguityPoorlyWell (via LLM reasoning)Learns/improvesNot inherentlyPossible (with memory or RL)Use of external toolsFixed integrationsDynamic tool use via API calls
Agents are smarter, more flexible, and better suited to environments with changing conditions and complex decision trees.
9. The Future of AI Agents: What’s Next?
We’re just at the beginning of what AI agents can do. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
Agent Networks
Future systems may consist of thousands or millions of agents interacting across the internet—solving problems, offering services, or forming digital marketplaces.
Autonomous Organizations
Agents may be used to power decentralized organizations where decisions, operations, and strategies are managed algorithmically.
Human-Agent Collaboration
The most promising future isn’t one where agents replace humans—but where they amplify them. Picture digital teammates who never sleep, always learn, and constantly adapt.
Self-Improving Agents
Combining LLMs with reinforcement learning and feedback loops will allow agents to learn from their successes and mistakes autonomously.
10. Getting Started: Building Your First AI Agent
Want to experiment with AI agents? Here's how to begin:
Choose a Framework: LangChain, AutoGPT, or CrewAI are good places to start.
Define a Goal: Simple goals like “send weekly reports” or “summarize news articles” are ideal.
Enable Tool Use: Set up access to external tools (e.g., web APIs, search engines).
Implement Memory: Use vector databases like Pinecone or Chroma for contextual recall.
Test in Loops: Observe how your agent plans, acts, and adjusts—then refine.
Monitor and Gate: Use human-in-the-loop systems or rule-based checks to prevent runaway behavior.
Conclusion: Thinking Machines Are Already Here
We no longer need to imagine a world where machines think for themselves—it’s already happening. From simple assistants to advanced autonomous researchers, AI agents are beginning to shape a world where intelligence is not just available but actionable.
The implications are massive. We’ll see a rise in automation not just of tasks, but of strategies. Human creativity and judgment will pair with machine persistence and optimization. Entire business units will be run by collaborative AI teams. And we’ll all have agents working behind the scenes to make our lives smoother, smarter, and more scalable.
In this future, understanding how to build and interact with AI agents will be as fundamental as knowing how to use the internet was in the 1990s.
Welcome to the age of the machines that think for themselves.
0 notes
Text
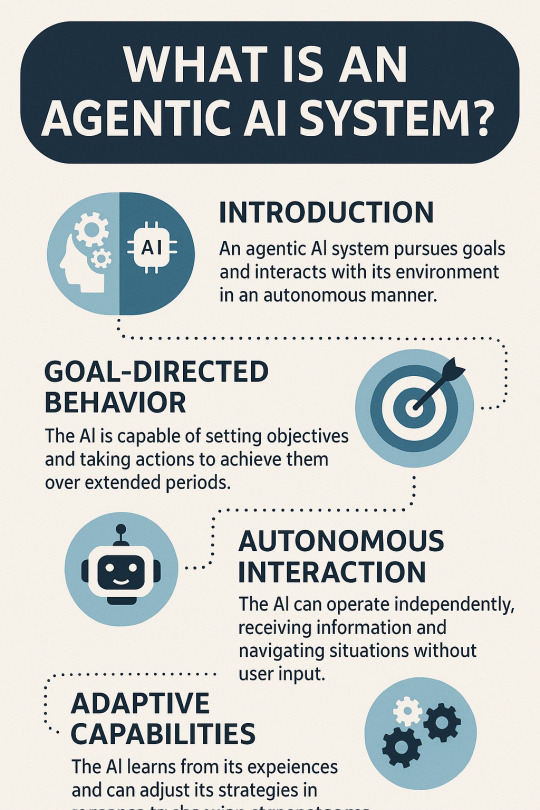
What is an Agentic AI system?

Artificial intelligence (AI) has undergone transformative evolution in recent decades — from simple rule-based systems to complex, self-learning neural networks. A relatively new and increasingly important concept in this continuum is the development of agentic AI systems. Unlike traditional AI, which often operates passively within predefined tasks, agentic AI refers to systems capable of pursuing goals, interacting autonomously with their environment, and adapting their strategies over time. These qualities bring both powerful potential and significant responsibility for developers, users, and regulators.
Let’s understand what Agentic AI systems are, how they function, and the implications of their use.
Defining Agentic AI
The term agentic is derived from the word agency, which refers to the capacity of an entity to act independently and make its own choices. In the context of AI, an agentic system is one that is capable of taking initiative, setting or interpreting goals, and acting in a way that’s not merely reactive but purpose-driven.
An agentic AI system:
Acts autonomously without requiring step-by-step instruction.
Is goal-oriented and often capable of setting sub-goals.
Adapts its behavior based on changing environments or feedback.
Can operate across extended time horizons and in complex, dynamic scenarios.
Examples include AI personal assistants that schedule tasks with minimal oversight, robotic systems that explore unknown environments, or AI agents that negotiate contracts or coordinate teams.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Goal-Directed Behavior
The defining feature of agentic AI is its ability to pursue goals. These goals may be set externally by a human or internally inferred by the system. Unlike simple automation, agentic AI systems plan and execute sequences of actions to achieve objectives — often optimizing for long-term outcomes.
For instance, a logistics AI might not only deliver a parcel, but also decide when and how to reroute in case of traffic or mechanical issues to minimize delays.
Autonomous Operation
Agentic systems operate with a high degree of autonomy. Once initialized, they do not rely on constant human input. They perceive their environment, make decisions, and act — often in real-time — based on sensory data, predictive models, and learned experiences.
Think of a self-driving car navigating through a city: it must continuously observe its surroundings, make split-second decisions, and adapt to traffic laws and unpredictable obstacles.
Adaptability and Learning
Adaptation is crucial for agentic behavior. Through reinforcement learning, fine-tuning, or continuous learning techniques, agentic AI systems can adjust their strategies based on past outcomes and new information. This learning loop enables them to become more efficient, accurate, or aligned with changing contexts.
A customer support chatbot that learns how to better handle rare queries over time is a simple example of this adaptive capacity.
Environmental Interaction
Agentic AI systems must engage with the environment — whether that environment is physical (as with robots), digital (as with software agents), or social (as with conversational agents). They receive feedback, assess the impact of their actions, and adjust accordingly.
For example, a trading AI agent evaluates financial market data and modifies investment strategies to maximize returns.
Examples of Agentic AI in Practice
Autonomous Drones: These navigate complex terrain, identify objects or people, and make decisions without human pilots.
AI Negotiators: Used in supply chains or corporate deals, they can evaluate options, make offers, and accept compromises based on predefined constraints and objectives.
AI Research Agents: Tools like AutoGPT or open-agent frameworks can self-prompt, run tasks, evaluate results, and iterate on their process without direct user supervision.
Virtual Companions: AI characters in games or virtual worlds that interact with players as if they have personality, memory, and long-term motivations.
Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI
FeatureTraditional AIAgentic AIOperationReactiveProactiveGoal SettingHuman-defined, staticMay interpret or set sub-goalsAutonomyLimitedHighLearningOften fixed or offlineContinuous and adaptiveTime HorizonShort-term tasksLong-term strategies
The Agentic AI builds upon traditional models but introduces an additional layer of complexity and independence. While traditional AI may classify images or detect fraud in transactions, agentic AI could design experiments, investigate fraud, and even recommend policy actions in response.
Risks and Challenges
Agentic AI systems introduce new types of risks:
Misalignment: If an AI interprets its goals in an unintended way, it may pursue actions that conflict with human values or objectives. This is a major concern in AI safety research.
Unpredictability: High autonomy and adaptive behavior can lead to unpredictable outcomes, especially in open or poorly defined environments.
Accountability: If an AI agent acts independently, who is responsible for its actions — the developer, the user, or the AI itself?
Security and Control: Malicious actors could exploit agentic AI to create systems that act independently in harmful ways (e.g., autonomous cyberattacks).
Governance and Ethics
As agentic AI becomes more widespread, ensuring it operates within ethical and legal boundaries is essential. This includes:
Transparency: Making it clear when users are interacting with an agentic system.
Explainability: Ensuring AI decisions can be understood and questioned.
Oversight: Developing mechanisms for monitoring and controlling agentic behavior.
Alignment: Researching ways to ensure agentic AI systems pursue human-aligned goals.
Regulators, researchers, and industry leaders must collaborate to establish frameworks that balance innovation with caution.
The Future of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is not science fiction — it is already here in early forms and will become increasingly common across industries. Whether it’s co-piloting software development, managing autonomous systems, or acting as virtual project managers, agentic AI promises to dramatically expand what machines can do independently.
However, this future must be approached with vigilance. Agentic AI systems are powerful tools, and like any tool, they can be misused or misdirected. The goal must be to build systems that are not just autonomous and intelligent — but also safe, transparent, and aligned with human values.
Agentic AI represents a critical shift in the landscape of artificial intelligence — from passive tools to active agents. By pursuing goals, interacting autonomously with environments, and adapting through learning, these systems open new possibilities across science, industry, and society. But with this power comes new responsibilities for how we build, manage, and govern AI in the years to come.
As we stand at the threshold of this new era, understanding what agentic AI is — and what it can become — is essential for anyone shaping the future of technology.
0 notes
Text
AI in 2025: What Just Changed Last Month (That You Should Know)

Intro: Every month, AI evolves, but May 2025 brought some major game-changers. If you're working in tech, marketing, business, or content, these updates will affect you sooner than you think.
Here’s a roundup of the most important changes you should know about.
1. ChatGPT’s Major Upgrade (Multi-Modal Mastery)
OpenAI rolled out GPT-4.5o, and it’s significantly better at handling images, tone, and speed. From understanding sarcasm in memes to interpreting complex visuals, this update makes ChatGPT feel even more like a human co-worker.
Faster responses
Improved memory
Enhanced image interpretation
2. Sora Is Live — AI Video Is Real Now
OpenAI’s video model, Sora, went live for selected creators. You can now describe a scene like “a futuristic cityscape with flying cars,” and it will generate an actual video.
This isn't the future — it’s already happening.
3. Apple and Google Integrate AI into Their Operating Systems
Apple is preparing iOS 19 with deep AI-powered features. Google is not far behind with Gemini AI enhancements in Android. It’s not just about apps anymore — AI is now embedded into every tap and swipe.
4. AI Agents Are Becoming Autonomous
AI tools like Devin and AutoGPT are no longer just reactive — they are planning and executing entire workflows:
Scheduling meetings
Conducting data analysis
Writing and debugging code
Posting content across platforms
Think of them as tireless interns who work 24/7.
5. Global AI Regulation is Accelerating
Governments across the US, EU, and India are actively drafting AI regulations. May witnessed a surge in discussions around ethics, deepfakes, misinformation, and the impact on employment.
Final Thoughts
AI is no longer just a trend; it has become a fundamental part of work, communication, creativity, and governance. Staying updated is no longer optional.
#AI2025#ArtificialIntelligence#AIEvolution#OpenAI#ChatGPT#TechNews#FutureOfWork#AIInBusiness#DigitalTransformation#MachineLearning
1 note
·
View note