#CFO Financial Services
Text
Maximizing Financial Performance: The Role of CFO Financial Services
In the realm of modern business, navigating the intricacies of finance is essential for sustained growth and prosperity. For companies seeking to elevate their financial strategies and operations to new heights, CFO Financial Services emerge as indispensable allies. These services, provided by seasoned financial experts, offer tailored solutions designed to optimize financial performance, mitigate risks, and drive strategic decision-making. Let's explore the multifaceted role of CFO Financial Services and how they empower businesses to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
Strategic Financial Planning
At the core of CFO Financial Services lies strategic financial planning. Seasoned CFO consultants collaborate closely with business leaders to develop comprehensive financial strategies aligned with organizational goals and market dynamics. Whether it's crafting annual budgets, forecasting financial performance, or evaluating investment opportunities, CFO Financial Services provide the strategic insights needed to chart a course for sustainable growth.
Efficiency Optimization
Efficiency is the cornerstone of financial success. CFO Financial Services specialize in identifying inefficiencies within financial processes and implementing targeted solutions to streamline operations. From optimizing cash flow management to improving accounts receivable and payable processes, CFO consultants leverage their expertise to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maximize profitability.
Risk Management and Compliance
In today's complex regulatory environment, navigating compliance requirements and mitigating financial risks are paramount. CFO Financial Services offer comprehensive risk management solutions tailored to the unique needs of each client. Whether it's ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, implementing robust internal controls, or conducting risk assessments, CFO consultants provide the expertise needed to safeguard assets and protect against potential liabilities.
Mergers and Acquisitions Support
Mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures present unique financial challenges and opportunities. CFO Financial Services play a crucial role in guiding companies through the complexities of these transactions. From conducting financial due diligence to structuring deals and negotiating terms, CFO consultants provide invaluable support at every stage of the M&A process, ensuring that clients maximize value and achieve seamless integration or divestiture outcomes.
Financial Modeling and Analysis
Informed decision-making relies on accurate financial modeling and analysis. CFO Financial Services excel in developing sophisticated financial models and conducting in-depth analysis to assess the financial viability of various scenarios and initiatives. Whether it's evaluating new business ventures, assessing capital investment opportunities, or conducting sensitivity analysis, CFO consultants provide the quantitative insights needed to make informed strategic decisions.
Strategic Cost Management
Cost management is a key driver of profitability and sustainability. CFO Financial Services assist companies in identifying cost-saving opportunities and implementing strategic cost management initiatives. Whether it's renegotiating vendor contracts, optimizing supply chain operations, or rationalizing overhead expenses, CFO consultants help businesses achieve cost efficiencies without compromising quality or performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CFO Financial Services play a pivotal role in optimizing financial performance, mitigating risks, and driving strategic decision-making for businesses across industries. By leveraging the expertise of seasoned CFO consultants, companies can navigate financial complexities with confidence, unlock new growth opportunities, and achieve sustainable success in today's ever-evolving marketplace. Whether it's strategic financial planning, efficiency optimization, risk management, or M&A support, CFO Financial Services provide the specialized expertise needed to thrive in an increasingly competitive business landscape.
0 notes
Text
What are The Benefits of Having Financial Director?

A competent CFO’s impact on your cash flow and profitability is substantial. If you also want to maintain a healthy cash flow in your organization, you need to get the best virtual chief financial officer near your location.
Visit Now: https://accountoutsourcing.wordpress.com/2024/03/12/what-are-the-benefits-of-having-financial-director/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
When it comes to developing your financial strategy and safeguarding your small business’s financial future, you may find yourself facing this common dilemma: You need expert financial guidance and support, but you don’t yet have the budget or resources to hire a full-time, in-house, fully qualified financial team.
If that problem sounds familiar, you’re not alone. As many as 80% of early-stage small businesses operate without a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) or controller in place. And unfortunately, what they don’t have can seriously cost them. That’s why an outsourced CFO or financial controller can be one of the most valuable — and cost-effective — financial strategy investments you can make in your small business.
Content Source: - https://escalon.services/blog/outsourced-cfo-vs-controller-which-is-right-for-your-financial-strategy/
#Outsourced CFO#Financial Strategy#Financial Management#Controller Services#Outsourcing Financial Functions#Strategic Financial Planning#Cash Flow Management
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
As an outsourced CFO, ViTWO provides a unique approach that ensures complete data security, 24x7 accessibility, and intelligent finance optimizations. ViTWO is the leading virtual CFO service provider based in India for over 6 years.
With our end-to-end automated financial management solution, a shared CFO experience enhances traditional accounting, compliance, fund management, and strategy-building services.
ViTWO envisions reshaping the vision of how businesses see financial management.
So, if you want to integrate the growth in finances of your business, book a FREE DIAGNOSTIC STUDY NOW!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating Financial KPIs with Fractional CFO Services
In today's fast-paced business environment, understanding and effectively managing your financial Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for success. However, for many small to medium-sized businesses, the complexity of financial data can feel overwhelming. This is where Navigating Financial KPIs with Fractional CFO Services. These part-time financial experts bring a wealth of knowledge and strategic insight, helping you decipher the intricate details of your financial health without the hefty price tag of a full-time CFO. By leveraging their expertise, you can navigate your financial KPIs with confidence, ensuring your business stays on the right track towards growth and profitability. Let's explore how fractional CFOs can transform your financial management and drive your business forward.
What Are Financial KPIs?
The Lifeblood of Your Business
Financial KPIs are more than just numbers on a spreadsheet. They are the heartbeat of your business, telling you whether you're healthy and thriving or in need of some serious TLC. Think of KPIs as the vital signs your business needs to keep an eye on to stay afloat and grow.

Breaking Down the Jargon
Let's decode this jargon a bit. KPIs are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. These could be anything from profit margins to customer acquisition costs. Each KPI is a puzzle piece, contributing to the overall picture of your business’s financial health.
Why You Need a Fractional CFO
The Superhero Your Business Deserves
Imagine having a financial superhero at your disposal, but only when you need them. That's a fractional CFO for you. These part-time financial officers swoop in, analyze your KPIs, provide strategic insights, and help steer your business toward success without the hefty price tag of a full-time CFO.
Cost-Effective Expertise
Hiring a full-time CFO can be a costly affair, especially for small to medium-sized businesses. Fractional CFOs, however, offer the same expertise on a part-time basis, making it a cost-effective solution. You get top-tier financial advice without breaking the bank.
Key Financial KPIs to Track
Revenue Growth Rate
Measuring Your Success
Revenue growth rate is the pace at which your company’s revenue is increasing or decreasing. It’s like tracking your speed on the highway to success. A higher growth rate indicates you're on the fast track, while a sluggish rate might mean it’s time to refuel and reassess.
Gross Profit Margin
The Profitability Indicator
Gross profit margin measures the money left after subtracting the cost of goods sold from your revenue. It’s the golden nugget that shows how efficiently your business is producing its goods or services. A healthy margin is a good sign, but if it's too low, it’s a red flag waving at you to cut costs or hike prices.
Net Profit Margin
The Bottom Line
Net profit margin is your final profit after all expenses have been deducted from total revenue. It’s the ultimate indicator of your business’s profitability. Think of it as the money you get to keep after everyone else has taken their share. Keeping an eye on this KPI is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Operating Cash Flow
The Cash Lifeline
Operating cash flow is the cash generated from your business’s core operations. It’s the lifeline that keeps your business breathing. Positive cash flow means you’re doing well, while negative cash flow could indicate trouble ahead. It's like checking your bank account to ensure you have enough to cover your bills.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
The Spending Gauge
CAC is the cost of acquiring a new customer. It includes all marketing and sales expenses. Lowering this cost while maintaining or increasing the number of customers is key to growing your business. Imagine fishing – the goal is to catch the most fish with the least bait.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
The Long-Term Profit Predictor
CLV estimates the total revenue you can expect from a customer over the duration of their relationship with your company. It’s like predicting how much fruit a tree will bear over its lifetime. A higher CLV means a more fruitful relationship, making it worth investing in customer retention strategies.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The Risk Assessor
This ratio measures your company’s financial leverage by comparing its total liabilities to its shareholder equity. A lower ratio generally indicates a healthier business with less risk, while a higher ratio could be a warning sign of potential financial distress. Think of it as balancing on a financial tightrope.
How Fractional CFOs Help with KPIs
Strategic Planning and Forecasting
Fractional CFOs are your strategic planning gurus. They help set realistic financial goals and create forecasts that guide your business decisions. It's like having a GPS for your financial journey, ensuring you stay on the right path.
Performance Monitoring and Analysis
These experts constantly monitor your KPIs, providing detailed analysis and insights. They don’t just tell you what the numbers are but explain what they mean and how they impact your business. It’s like having a financial translator who speaks the language of numbers fluently.
Financial Reporting
Fractional CFOs ensure your financial reporting is accurate and timely. They prepare comprehensive reports that give you a clear picture of your financial health. Think of them as your financial narrators, telling the story of your business in numbers.
Risk Management
Managing financial risk is crucial for any business. Fractional CFOs identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. It’s like having a safety net to catch you before you fall.
The Fractional CFO Advantage
Flexibility and Scalability
One of the biggest advantages of fractional CFOs is their flexibility. You can scale their involvement up or down based on your business needs. It's like having a dial to adjust the level of expertise you require.
Access to a Wealth of Experience
Fractional CFOs often have a wealth of experience across different industries. This broad perspective can provide valuable insights and innovative solutions tailored to your business. It’s like having a seasoned sailor who has navigated many seas, guiding your ship.
Enhanced Decision-Making
With expert analysis and insights from fractional CFOs, your decision-making process becomes more informed and strategic. It’s like having a crystal ball that helps you foresee the impact of your decisions on your business’s future.
Implementing Fractional CFO Services
Assessing Your Needs
Before bringing a fractional CFO on board, assess your business needs. Identify which KPIs you need help with and what specific expertise you require. It’s like preparing a shopping list before going to the store.
Finding the Right Fit
Not all fractional CFOs are created equal. Look for someone with experience in your industry and a track record of success. Think of it as finding the right puzzle piece that fits perfectly into your business.
Onboarding and Integration
Once you’ve found your fractional CFO, ensure a smooth onboarding process. Integrate them into your team and provide access to all necessary financial data. It’s like setting up the sails before a voyage.
youtube
Real-World Success Stories
Case Study: Startup Growth
Consider a tech startup struggling with cash flow management. They brought in a fractional CFO who identified inefficiencies in their spending and helped streamline operations. Within six months, their cash flow improved dramatically, allowing them to scale and attract new investors.
Case Study: Turnaround Success
A mid-sized manufacturing company was facing declining profit margins. A fractional CFO analyzed their financials, identified cost-saving opportunities, and renegotiated supplier contracts. The result? A significant boost in their gross profit margin and overall profitability.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex world of financial KPIs can be challenging, but with the right guidance, it becomes manageable and even exciting. Fractional CFO services offer the expertise, flexibility, and strategic insights your business needs to thrive. Whether you’re a startup or a growing company, these financial wizards can help you decode the treasure map of your business’s financial health and steer you toward success.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Streamline Your Financial Processes: Virtual CFO Services

Managing finances effectively is crucial for business success, but not every company can afford a full-time CFO. That's where SAI CPA Services comes in with our virtual CFO services.
Our experienced professionals act as your virtual chief financial officer, providing strategic financial guidance tailored to your business needs. From financial planning and analysis to budgeting and forecasting, we offer the expertise you need to make informed decisions.
With SAI CPA Services as your virtual CFO, you can access high-level financial expertise without the hefty price tag. Contact us today to learn more about our virtual CFO services and take your financial management to the next level.
Stay tuned for more insights into our comprehensive range of accounting and financial services, designed to support your business's success.
Connect Us: https://www.saicpaservices.com/contact-us/
908-380-6876
1 Auer Ct, 2nd Floor
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
#saicpaservices#financial#virtual cfo services#businesssuccess#accounting firm#financialplanning#cpa services#accounting services#financialmanagement
1 note
·
View note
Text
Samichinam Solutions Can Help You Streamline Pharma Operations with QMS, eBPR, & More
Use Samichinam Solutions to increase operational efficiency in the pharmaceutical industry. QMS, eBPR, and premium software for cleaning validation, equipment validation, and clinical trials are all part of our all-inclusive suite. Discover our specialized offerings for the pharmaceutical sector right now."
#strategy consultant#business strategy consultant#financial planning & analysis#virtual cfo services
0 notes
Text

0 notes
Text
Understanding Company Liquidation in the UAE: A Comprehensive Guide

Liquidation is a legal procedure applicable to companies or partnerships, involving the appointment of a liquidator to oversee the cessation of a company’s operations. This process effectively brings an end to the company’s existence, with the primary aim being to ensure that all the company’s affairs are appropriately handled and its assets are realized. JYWA SETTLERS assumes a crucial role in supporting businesses in Dubai in navigating the intricate landscape of corporate tax compliance. Through their tailored services and specialized expertise, they assist companies in adhering to the laws and regulations set forth by the Federal Tax Authority. This proactive approach not only safeguards the financial well-being of businesses but also protects their reputation in Dubai’s fiercely competitive business environment.
At its core, liquidation involves the orderly winding up of a company’s affairs, which encompasses various tasks such as settling outstanding debts, liquidating assets, and distributing proceeds to creditors. This process is essential for bringing closure to the company in a systematic and legally compliant manner. JYWA SETTLERS recognizes the significance of this process and offers invaluable assistance to businesses embarking on the liquidation journey.
One of the key aspects of liquidation is the appointment of a liquidator, who assumes the responsibility of overseeing the entire process. The liquidator plays a pivotal role in managing the company’s assets, identifying and prioritizing creditor claims, and ensuring that all legal obligations are met. JYWA SETTLERS collaborates closely with appointed liquidators, providing them with the necessary support and expertise to navigate the complexities of corporate tax compliance throughout the liquidation process.
In addition to managing the liquidation process, JYWA SETTLERS also offers tailored services aimed at ensuring companies remain fully compliant with Federal Tax Authority laws and regulations. This involves conducting thorough assessments of each company’s tax obligations, identifying areas of potential risk or non-compliance, and implementing effective strategies to mitigate these risks.
By proactively addressing tax compliance issues, JYWA SETTLERS helps companies avoid costly penalties and safeguard their financial health.
Moreover, JYWA SETTLERS recognizes that each business is unique and may have specific tax compliance requirements based on its industry, size, and operating model. As such, they offer customized solutions designed to meet the individual needs of each client. Whether it involves navigating complex tax laws, preparing and filing tax returns, or representing clients in tax audits, JYWA SETTLERS provides comprehensive support every step of the way.
In Dubai’s competitive business landscape, maintaining compliance with tax laws and regulations is paramount to the long-term success and sustainability of businesses. By partnering with JYWA SETTLERS, companies can benefit from their extensive experience and expertise in corporate tax compliance.
Through proactive planning, strategic guidance, and meticulous attention to detail, JYWA SETTLERS empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of tax compliance with confidence, ensuring their continued growth and prosperity in the dynamic business environment of Dubai.
Accounting services in Dubai
Auditors in Dubai
Best audit firms in Dubai
Auditing companies in Dubai
Accounting & bookkeeping services in Dubai
#accounting services#accounting software#audit firms#audit firms in dubai#audit firms in uae#auditors in uae#cfo services in uae#corporate tax services in uae#financial advisor in uae#vat accountant
0 notes
Text
Dive into our comprehensive guide on outsourced CFO services. Discover how leveraging external financial expertise can benefit your business's financial management. Learn about the latest trends, innovative solutions, and emerging technologies transforming the role of outsourced CFOs in today's dynamic business landscape. Gain insights for smarter decision-making and enhanced financial performance.
#cfo services for small businesses#cfo solution#outsourced cfo companies#Outsourced CFO Services#outsourced chief financial officer#what is cfo services
0 notes
Text
Understanding Financial Success: The Role of a Family Office CFO in Charlottesville, VA
In the serene and historic setting of Charlottesville, VA, families often turn to the expertise of a dedicated Chief Financial Officer (CFO) within their family office to navigate the complexities of wealth management. As stewards of financial well-being, these professionals play a crucial role in safeguarding and growing the assets of affluent families while ensuring the legacy they've built endures for generations.

At the heart of the CFO's responsibilities lies a deep understanding of the family's unique financial goals, values, and aspirations. By crafting tailored strategies, the CFO aligns investment decisions with the family's vision, balancing risk and return to optimize long-term financial performance.
In addition to investment management, the CFO oversees tax planning, estate planning, and philanthropic endeavors, collaborating with a network of legal, tax, and investment professionals to ensure comprehensive wealth management solutions. Through meticulous analysis and strategic foresight, they anticipate challenges and seize opportunities to preserve and enhance the family's wealth.
Moreover, the CFO serves as a trusted advisor, offering guidance on matters beyond finance, such as family governance, succession planning, and intergenerational wealth transfer. By fostering open communication and facilitating family meetings, they promote harmony and unity, empowering family members to make informed decisions aligned with their shared values and objectives.
In Charlottesville, Manchester Capital Management stands out as a beacon of excellence in providing comprehensive financial services to affluent families. With a team of seasoned professionals and a client-centric approach, Manchester Capital Management is committed to safeguarding and growing the wealth of its clients, empowering them to achieve their financial goals with confidence and peace of mind.
In conclusion, the role of a Family Office CFO in Charlottesville, VA, extends far beyond number crunching; it encompasses stewardship, collaboration, and vision. By leveraging expertise, insight, and innovation, these professionals uphold the financial legacy of families, ensuring prosperity for generations to come.
#top family office firms#family office cfo charlottesville va#family office service virginia#financial advisor Charlottesville VA
0 notes
Text
Utilizing Technology for Financial Management with CFO Services

Small businesses can enhance financial management by leveraging technology alongside CFO services. Integrating accounting software, data analytics tools, and cloud-based platforms streamlines processes, improves accuracy, and provides real-time insights. Experts offering CFO services for small businesses harness the power of technology to optimize financial operations, drive informed decision-making, and foster growth in today's digital landscape.
0 notes
Text

Within the ever-changing Indian startup scene, virtual CFO services have emerged as a key player, redefining the parameters of financial management for emerging businesses. This creative method breaks through conventional wisdom and gives startups a tactical advantage when handling complex financial nuances.
#cfo services#virtual cfo services#cfosolutions#california#financial management#indian startups#data strategy#tailored solutions#financial experts#financial planning#analysis#strategic vision#financial strategies#sustainable growth#strategy#management system#Cfo Accounting Services#advanced analytics#investment banking#accounting services#usa#san jose california#blog#tumblr#cheezbot
1 note
·
View note
Text
GAAP vs IFRS

Decoding US Accounting Rules: GAAP vs IFRS | Expert Insights in 2024
Navigate the GAAP vs IFRS debate in US Accounting effortlessly. Gain expert insights, make sense of regulations. Your guide to financial clarity.
The evolving landscape of accounting standards unfolds a nuanced debate between the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and the International Financial Reporting Standards. These two frameworks, while sharing a common goal of transparent financial reporting, diverge in their approaches, giving rise to a multifaceted discourse with far-reaching implications for the financial world.

1. Introduction
The evolution of accounting standards has witnessed the crystallization of two dominant frameworks – General Accounting Accepted Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards. In the labyrinth of financial reporting, companies grapple with choosing between these standards, each with its unique history, principles, and global relevance. The debate surrounding GAAP vs IFRS is not a mere academic exercise but a pivotal consideration with implications for investment decisions, legal compliance, and the global financial landscape.
1.1. Evolution of Accounting Standards
The journey of accounting standards traces back to the aftermath of the 1929 stock market crash when the need for standardized, transparent financial reporting became glaringly apparent. What emerged were the General Accounting Accepted Principles, designed to restore investor confidence by providing a reliable framework for financial statements. Over time, GAAP has become deeply embedded in the U.S. financial system, shaping the way companies communicate their financial health.
On the global stage, the International Financial Reporting Standards evolved as a response to the growing interconnectedness of economies. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) took the reins in developing IFRS, aiming for a standardized global language of financial reporting. This set the stage for a two-pronged approach to financial reporting standards – General Accounting Accepted Principles dominating in the U.S. and International Financial Reporting Standards gaining traction internationally.
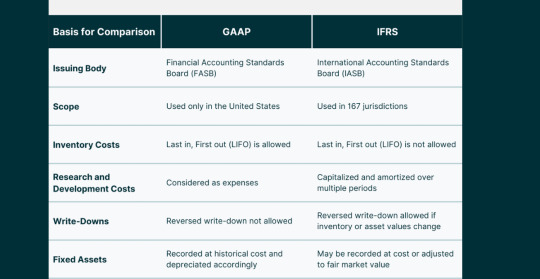
1.2. The Crucial Role of GAAP and IFRS
GAAP stands as the bedrock of accounting standards in the United States, overseen by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Its principles, rooted in historical cost, revenue recognition, and matching, provide stability and a familiar structure for U.S. businesses. On the other hand, IFRS, under the stewardship of the IASB, operates as a global player, emphasizing fair value, substance over form, and materiality.
The significance of General Accounting Accepted Principles lies in its historical context and its alignment with the unique needs of the U.S. business environment. Its principles have served as a guiding light for American companies, offering a consistent framework for financial reporting. International Financial Reporting Standards, with its global perspective, caters to the interconnectedness of today’s businesses, providing a common language for multinational corporations.
1.3. Navigating the GAAP vs IFRS Dilemma
The choice between General Accounting Accepted Principles and International Financial Reporting Standards is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Companies grapple with a complex decision-making process, considering factors such as their geographical reach, industry nuances, and investor preferences. This debate is not isolated to boardrooms; it resonates in financial markets, legal proceedings, and regulatory landscapes, shaping the very fabric of financial reporting practices.
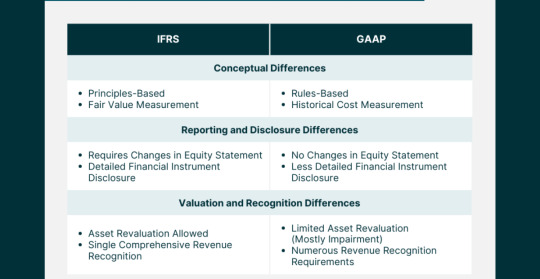
2. Understanding GAAP
2.1. The Foundation of GAAP
a. Historical Roots and Evolution
GAAP’s roots delve deep into the need for a standardized accounting framework post the 1929 stock market crash. FASB emerged as a response to the chaos that ensued, charged with the responsibility of establishing and improving financial accounting and reporting standards. The journey of GAAP has been one of continuous evolution, adapting to the changing business landscape and regulatory requirements.
b. FASB’s Ongoing Influence
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) stands as the guardian of GAAP, playing a pivotal role in setting and refining accounting standards. FASB’s mission goes beyond rule-making; it seeks to improve financial reporting, providing transparency and relevance in financial statements. The ongoing influence of FASB ensures that GAAP remains adaptive and responsive to the dynamic nature of business transactions.
2.2. Core Principles Anchoring GAAP
a. Embracing the Historical Cost Principle
One of the cornerstones of GAAP is the historical cost principle, dictating that assets should be recorded at their original cost. This principle provides stability and reliability in financial statements, allowing users to assess the financial health of a company based on the actual cost of its assets at the time of acquisition. While critics argue that this approach may not reflect current market values, proponents emphasize the prudence and consistency it offers.
b. Revenue Recognition as a Cornerstone
GAAP’s approach to revenue recognition centers on the realization and earned criteria. Revenue is recognized when it is realized or realizable and earned. This conservative approach ensures that revenue is not prematurely recognized, aligning with the matching principle. While this method may defer recognizing revenue until later stages in the sales cycle, it safeguards against potential overstatement and presents a cautious picture to investors.
c. The Significance of the Matching Principle
The matching principle is a guiding force in GAAP, emphasizing the alignment of expenses with the revenue they generate. This principle ensures that the costs associated with generating revenue are recognized in the same period as the revenue itself, presenting a more accurate portrayal of a company’s profitability. While adhering to the matching principle might result in lower reported profits during high-revenue periods, it provides a more realistic long-term view.
2.3. Scrutinizing Criticisms and Recognizing Limitations
a. Rigidity vs. Stability
One common criticism leveled against GAAP is its perceived rigidity, particularly regarding the historical cost principle. Critics argue that this approach may not capture the true economic value of assets, especially in industries with rapidly changing market conditions. However, proponents assert that this rigidity provides stability and consistency, allowing for easier comparison across periods and industries.
b. The Balancing Act of Revenue Recognition
The conservative approach to revenue recognition in GAAP has faced scrutiny for potentially understating a company’s immediate financial performance. Critics argue that this caution may not be reflective of a company’s true economic position, especially in industries where revenue realization is instantaneous. However, the balancing act lies in mitigating the risk of premature revenue recognition, ensuring financial statements maintain integrity and accuracy.
c. Challenges in Adhering to the Matching Principle
While the matching principle aligns expenses with revenue, critics contend that it introduces complexities in determining the direct association between costs and specific revenue streams. This challenge becomes more pronounced in industries with diverse revenue sources. Despite these challenges, adhering to the matching principle remains integral in presenting a holistic view of a company’s financial health, helping investors make informed decisions.
3. Embracing IFRS
3.1. IFRS: A Global Framework
a. The Rise of International Financial Reporting Standards
The emergence of IFRS marks a significant shift towards a globalized approach to financial reporting. As businesses expanded internationally, the need for a common accounting language became evident. IFRS, under the stewardship of the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), rose to prominence as a framework that transcends borders, providing a standardized set of principles for companies operating on the world stage.
b. IASB’s Pivotal Role in Shaping IFRS
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) shoulders the responsibility of developing and maintaining IFRS. Unlike GAAP, IFRS operates under a principles-based approach, focusing on broad principles rather than detailed rules. This flexibility allows for easier adaptation to diverse business environments, making IFRS an attractive choice for multinational corporations seeking a harmonized approach to financial reporting.
3.2. Unpacking Core Principles of IFRS
a. Fair Value Measurement: A Paradigm Shift
One of the fundamental differences between GAAP and IFRS lies in the approach to asset valuation. While GAAP predominantly adheres to the historical cost principle, IFRS leans towards fair value measurement. Fair value reflects the current market value of assets, providing a more dynamic and responsive perspective. Critics argue that fair value introduces volatility, but proponents emphasize its relevance in capturing real-time economic conditions.
b. Substance Over Form: Emphasizing Economic Reality
In IFRS, the substance of transactions takes precedence over their legal form. This principle ensures that financial statements reflect the economic reality of transactions, promoting transparency and accuracy. While this approach aligns with the overarching goal of providing relevant information to users, it requires careful judgment and interpretation, potentially introducing subjectivity in financial reporting.
c. Materiality’s Role in Flexibility
IFRS introduces greater flexibility in materiality judgments compared to GAAP. Materiality refers to the threshold at which information becomes relevant to users. The more flexible stance in IFRS allows entities to exercise judgment in determining what information is material, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors. This flexibility, while enhancing the adaptability of IFRS, also raises concerns about potential inconsistencies in financial reporting.
3.3. Weighing Advantages and Drawbacks
a. IFRS Flexibility: A Double-Edged Sword
The flexibility embedded in IFRS is both its strength and weakness. Proponents argue that this adaptability makes IFRS suitable for diverse business environments, allowing for easier integration with various industries and legal systems. However, critics contend that this very flexibility can lead to inconsistencies and a lack of comparability, challenging the reliability of financial statements for investors and stakeholders.
b. Global Appeal vs. Application Challenges
The global nature of IFRS makes it an attractive choice for multinational companies aiming for consistency in financial reporting across borders. The common language of IFRS facilitates international transactions and fosters a seamless global financial landscape. However, the application of IFRS can pose challenges in jurisdictions with varying legal and regulatory frameworks, potentially leading to complexities in implementation and interpretation.

4. Key Differences Between GAAP and IFRS
4.1. Delving into Variances
a. Revenue Recognition: The GAAP-IFRS Divergence
One of the pivotal differences between GAAP and IFRS lies in the recognition of revenue. While both frameworks aim to depict the economic reality of transactions, their approaches diverge in certain key aspects. GAAP tends to be more prescriptive, providing specific guidelines for various industries, whereas IFRS adopts a broader principles-based approach, allowing entities more room for interpretation.
b. Inventory Valuation: Differing Approaches
The treatment of inventory valuation varies significantly between GAAP and IFRS. GAAP typically follows a specific set of rules for valuing inventory, such as the Last In, First Out (LIFO) or First In, First Out (FIFO) methods. In contrast, IFRS permits the use of various methods, including FIFO and weighted average, offering companies more flexibility in choosing an approach that aligns with their specific business dynamics
c. Consolidation Methods: Navigating Complexity
Consolidation methods, particularly in the context of subsidiaries and investments, showcase differences between GAAP and IFRS. GAAP often employs a more rule-based approach, specifying conditions for consolidation. In contrast, IFRS focuses on a principles-based approach, considering the substance of relationships rather than relying on rigid criteria. This variance introduces nuances in financial reporting, influencing how companies present their financial position and performance.
4.2. The Impact on Financial Statements
a. Shaping Investor Perception
The differences in revenue recognition, inventory valuation, and consolidation methods contribute to variations in financial statements produced under GAAP and IFRS. Investors, as key stakeholders, must navigate these differences to gain an accurate understanding of a company’s financial health. The choice between GAAP and IFRS significantly shapes investor perception, influencing investment decisions and risk assessments.
b. Decision-Making Dynamics
Companies, in choosing between GAAP and IFRS, must consider the implications on decision-making dynamics. The framework adopted affects how financial information is presented, potentially influencing strategic decisions, mergers and acquisitions, and capital-raising activities. Understanding the impact of these frameworks on decision-making is crucial for entities operating in dynamic and competitive business environments.
4.3. Global Adoption Trends: A Comparative Analysis
The adoption trends of GAAP and IFRS provide insights into the global dynamics of financial reporting standards. While GAAP maintains dominance within the United States, IFRS has gained traction in numerous jurisdictions worldwide. Understanding the factors influencing these trends, such as regulatory requirements, investor preferences, and global market integration, sheds light on the evolving landscape of accounting standards.
“Accounting isn’t just about profits and losses; it’s about sculpting the financial soul of a company.” Michael Johnson

5. The Evolution of Accounting Standards
5.1. GAAP’s Historical Odyssey
a. Post-1929: A Catalyst for Change
The stock market crash of 1929 served as a catalyst for rethinking the approach to financial reporting. The chaos that ensued prompted the establishment of standardized accounting principles, laying the foundation for what would later become GAAP. The primary goal was to restore investor confidence by providing a reliable framework for financial statements, reducing uncertainty and fostering stability in financial markets.
b. Amendments and Updates: Shaping GAAP’s Trajectory
GAAP’s journey has not been static; it has evolved through amendments and updates to address emerging challenges and align with changing business dynamics. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) plays a pivotal role in shaping GAAP, ensuring that it remains relevant, transparent, and responsive to the needs of companies and investors. The ongoing commitment to refinement reflects a dedication to maintaining the integrity of financial reporting.
5.2. Internationalization Efforts
a. Pioneering Attempts at Global Standardization
As globalization gained momentum, so did the recognition of the need for global accounting standards. Efforts were made to align U.S. GAAP with international standards, but achieving a universal standard proved challenging. The push for global standardization gained traction with the rise of IFRS, offering a framework that transcends national boundaries and facilitates consistency in financial reporting for multinational corporations.
b. The Challenge of Aligning U.S. Standards Globally
While the concept of global accounting standards gained support, aligning U.S. GAAP with international standards presented formidable challenges. The unique legal, regulatory, and cultural landscape in the United States posed hurdles to seamless integration. Despite these challenges, the pursuit of convergence and harmonization continued, reflecting the recognition of the interconnectedness of global economies.
5.3. Convergence Initiatives
a. The Ongoing Pursuit of Harmonization
Convergence initiatives aimed at harmonizing GAAP and IFRS gained prominence in the early 21st century. The objective was to reduce disparities between the two frameworks, fostering a more standardized global approach to financial reporting. While full convergence remained elusive, progress was made in aligning specific standards, reflecting a commitment to minimizing inconsistencies and facilitating ease of comparison for investors and stakeholders.
b. Prospects and Hurdles in a Unified Global Standard
The prospects of a unified global accounting standard remain a tantalizing goal, promising enhanced comparability and consistency in financial reporting. However, hurdles such as divergent national interests, legal complexities, and varying levels of standard-setting infrastructure continue to challenge the realization of this vision. Navigating these obstacles requires ongoing collaboration and a commitment to the overarching goal of global financial transparency.

6. Regulatory Bodies Influencing GAAP
6.1. FASB’s Pivotal Role
a. GAAP’s Guardian: The FASB Mandate
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) stands as the guardian of GAAP, wielding influence over the development and refinement of accounting standards. FASB’s mandate goes beyond rule-making; it encompasses a commitment to improving financial reporting, ensuring that standards are not only relevant but also responsive to the evolving needs of businesses and investors.
b. FASB’s Mission in Financial Reporting Improvement
FASB’s mission revolves around the improvement of financial reporting through the development of high-quality accounting standards. The board operates under a due process system, seeking input from various stakeholders, including investors, auditors, and preparers of financial statements. This collaborative approach ensures that GAAP remains a robust and adaptive framework that reflects the intricacies of modern business transactions.
6.2. SEC’s Watchful Eye
a. SEC’s Authority in Recognizing GAAP Standards
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) plays a crucial role in the oversight of financial reporting in the United States. While the FASB sets accounting standards, the SEC has the authority to recognize and prescribe the principles used in the preparation of financial statements for publicly traded companies. This dual-layered system ensures a balance between industry expertise and regulatory oversight in shaping GAAP.
b. SEC’s Contributions to Financial Transparency
The SEC’s contributions to financial transparency extend beyond its recognition of GAAP standards. The commission actively engages in rule-making and enforcement to ensure that companies adhere to accounting principles and provide accurate and timely financial information to investors. The synergy between the SEC and FASB reinforces the integrity of financial reporting in the U.S. capital markets.
6.3. AICPA’s Industry Impact
a. AICPA: Nurturing Professional Standards
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) plays a vital role in shaping professional standards within the accounting industry. While not directly involved in setting GAAP, the AICPA contributes to the development of ethical and professional standards that guide the conduct of accountants. This commitment to excellence enhances the credibility of financial reporting, reinforcing the trust that stakeholders place in GAAP.
b. Industry-Wide Compliance through AICPA Guidance
The AICPA’s influence extends beyond standards development to encompass industry-wide compliance. The organization provides guidance on best practices, ethical considerations, and emerging issues within the accounting profession. This guidance ensures a cohesive and ethical approach to financial reporting, aligning with the principles embedded in GAAP and contributing to the overall reliability of financial statements.

7. International Bodies Shaping IFRS
7.1. IASB’s Global Mandate
a. IASB’s Significance in IFRS Development
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) holds a central role in the development and maintenance of IFRS. Unlike the FASB’s role in the U.S., the IASB operates on a global scale, aiming to set accounting standards that are applicable and relevant to entities worldwide. The IASB’s commitment to a principles-based approach reflects its recognition of the diverse needs of global businesses.
b. A Global Perspective in Standard Setting
The IASB’s global perspective is intrinsic to its standard-setting process. The board considers input from various regions, industries, and stakeholders, ensuring that IFRS reflects the nuances of international business. The principles-based approach allows for adaptability, catering to the diverse legal, economic, and cultural landscapes in which entities operate globally.
7.2. IFRIC’s Interpretative Role
a. Navigating Grey Areas: IFRIC’s Guidance
The International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC) plays a crucial role in navigating interpretative challenges within IFRS. Given the principles-based nature of IFRS, grey areas may arise, requiring clarification and guidance. IFRIC addresses these challenges by providing interpretations and guidance, ensuring consistent application of IFRS standards across diverse industries and jurisdictions.
b. Consistent Application of IFRS Standards
Consistency in the application of IFRS standards is paramount to ensuring comparability and reliability in financial reporting. IFRIC’s interpretative role contributes to this objective by offering guidance on ambiguous or complex issues. This commitment to clarity and consistency aligns with the overarching goal of IFRS – to provide a common language for financial reporting that transcends geographical and industry-specific boundaries.
7.3. Monitoring Board’s Oversight
a. Ensuring Independence in Standard Setting
The Monitoring Board plays a crucial oversight role in ensuring the independence and effectiveness of the IFRS Foundation, which houses the IASB. Independence is a cornerstone of credible standard-setting, and the Monitoring Board’s role is to safeguard the integrity of the standard-setting process. This commitment to independence reinforces the trust that global stakeholders place in IFRS as a reliable and unbiased framework.
b. The Role of the Monitoring Board in IFRS Integrity
The Monitoring Board’s vigilance extends beyond independence to the broader integrity of the IFRS framework. By overseeing the activities of the IFRS Foundation and IASB, the Monitoring Board contributes to the credibility of IFRS as a global accounting standard. This oversight ensures that IFRS continues to meet the evolving needs of global financial markets and remains a trusted framework for transparent financial reporting.

8. Impact on Financial Reporting
8.1. Side-by-Side Comparison
a. Financial Statement Variances: GAAP vs IFRS
A side-by-side comparison of financial statements prepared under GAAP and IFRS reveals variances arising from differences in principles, approaches, and interpretations. These variances extend to revenue recognition, asset valuation, and consolidation methods, influencing the reported financial position and performance of entities. Investors and analysts must navigate these differences to glean accurate insights into a company’s financial health.
b. Interpretation Challenges for Investors
Investors face interpretation challenges when analyzing financial statements prepared under different frameworks. Understanding the nuances of GAAP and IFRS differences is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The ability to discern how specific accounting choices impact financial metrics empowers investors to evaluate risks, assess potential returns, and navigate the complexities of the global investment landscape.
8.2. Revenue Recognition Dynamics
a. The Nuances of Revenue Recognition
The nuances of revenue recognition under GAAP and IFRS reflect the underlying philosophies of each framework. GAAP, with its prescriptive guidelines, provides specific criteria for recognizing revenue in various industries. In contrast, IFRS adopts a broader approach, emphasizing the substance of transactions over rigid rules. Navigating these nuances requires a deep understanding of industry dynamics and the specific requirements of each framework.
b. Implications for Investor Decision-Making
The implications of revenue recognition dynamics extend to investor decision-making. Differences in when and how revenue is recognized can influence perceptions of a company’s immediate financial performance. Investors must factor in these nuances to make informed decisions, considering the impact on key financial metrics such as earnings per share, profit margins, and return on investment.
8.3. Asset Valuation Approaches
a. Valuation Philosophies: Fair Value vs. Historical Cost
The variance in asset valuation philosophies between GAAP and IFRS introduces complexities in financial reporting. GAAP’s adherence to historical cost provides stability and consistency, albeit potentially understating the current market value of assets. In contrast, IFRS’s emphasis on fair value introduces a more dynamic and responsive approach to asset valuation. Companies must navigate the trade-offs between stability and accuracy in presenting their financial position.
b. Balancing Accuracy and Stability in Asset Reporting
Balancing accuracy and stability in asset reporting requires careful consideration of the trade-offs between fair value and historical cost. Companies must weigh the benefits of presenting current market values against the potential volatility introduced by fair value measurements. Striking the right balance ensures that financial statements accurately reflect the economic reality of a company’s assets while providing stakeholders with a stable and reliable foundation for decision-making.

9. Challenges in Adoption
9.1. Corporate Resistance Factors
a. Unpacking Corporate Hesitations
The decision to adopt new accounting standards, whether transitioning from GAAP to IFRS or vice versa, is met with corporate hesitations. Companies fear the potential disruptions, costs, and uncertainties associated with the transition. Understanding these resistance factors is essential for regulatory bodies, standard-setters, and industry stakeholders to develop strategies that facilitate smoother adoptions and ensure widespread compliance.
b. Overcoming Corporate Resistance Challenges
Overcoming corporate resistance challenges requires a multi-faceted approach. Clear communication on the benefits of the new standards, comprehensive training programs, and support mechanisms can alleviate concerns. Regulators and standard-setters must collaborate with industry representatives to address specific challenges faced by different sectors, fostering a cooperative environment conducive to successful adoptions.
9.2. Implementation Costs
a. Financial and Operational Impacts
The implementation of new accounting standards incurs financial and operational impacts for companies. Costs associated with staff training, system upgrades, and adjustments to internal processes contribute to the overall financial burden. Companies must carefully assess these costs and develop comprehensive implementation plans to mitigate disruptions and ensure a seamless transition to the new standards.
b. Strategies for Mitigating Implementation Costs
Strategies for mitigating implementation costs involve proactive planning, phased adoption approaches, and leveraging technology. Companies can benefit from engaging with industry peers that have successfully navigated similar transitions, learning from best practices and challenges. Collaboration between standard-setters, regulatory bodies, and industry associations plays a crucial role in developing strategies that balance the need for improved standards with the practicalities of implementation.
9.3. Training and Skill Gaps
a. The Need for Specialized Training
The adoption of new accounting standards introduces the need for specialized training to ensure that professionals possess the skills required for compliance. Training programs must address the nuances of the new standards, focusing on changes in accounting principles, reporting requirements, and the application of new methodologies. Bridging skill gaps is crucial for maintaining the integrity and accuracy of financial reporting.
b. Collaborative Approaches to Skill Development
Collaborative approaches to skill development involve partnerships between educational institutions, professional organizations, and industry players. The goal is to create comprehensive training programs that equip professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary for successful compliance. Standard-setters and regulators can play a pivotal role in promoting and endorsing such collaborative initiatives, fostering a culture of continuous learning within the accounting profession.

10. Legal Implications for Corporations
10.1. Legal Challenges in GAAP Compliance
a. Litigation Risks in GAAP Adherence
The legal challenges associated with GAAP compliance include litigation risks arising from alleged non-compliance. Companies adhering to GAAP must navigate the complexities of the legal landscape, ensuring that their financial statements withstand scrutiny. Implementing robust internal controls, engaging in transparent communication, and staying abreast of legal developments are essential strategies for mitigating litigation risks.
b. Strategies for Legal Compliance in GAAP
Strategies for legal compliance in GAAP involve proactive measures to minimize litigation risks. This includes fostering a culture of compliance within the organization, conducting regular internal audits, and seeking legal counsel to ensure alignment with evolving regulations. Companies that prioritize legal compliance contribute to the overall stability and trustworthiness of the financial reporting ecosystem.
10.2. Legal Battles in IFRS Adoption
a. Navigating Legal Challenges in IFRS Transition
The transition to IFRS introduces legal battles that companies must navigate effectively. Disputes may arise over interpretations of IFRS standards, potentially leading to litigation. Companies must engage in comprehensive risk assessments, understanding the legal implications of IFRS adoption, and implementing measures to mitigate potential legal challenges.
b. Legal Safeguards for Companies Adopting IFRS
Legal safeguards for companies adopting IFRS involve proactive steps to minimize legal risks. This includes engaging legal experts in the transition process, conducting impact assessments, and implementing robust governance structures. Companies that prioritize legal safeguards position themselves to navigate the complexities of IFRS adoption with resilience and integrity.
10.3. Risk Mitigation Strategies
a. Legal Safeguards: Mitigating Risks in Regulatory Compliance
Legal safeguards play a pivotal role in mitigating risks associated with regulatory compliance. Companies must implement effective risk management strategies, including regular legal audits, compliance training, and a responsive approach to legal developments. A proactive stance towards legal safeguards enhances a company’s ability to navigate the intricate landscape of financial reporting standards.
b. Strategies for Minimizing Legal Challenges in Reporting Standards
Strategies for minimizing legal challenges in reporting standards involve a holistic approach to risk management. This includes collaboration with legal professionals, staying informed about evolving regulations, and fostering a culture of compliance within the organization. Companies that prioritize these strategies not only mitigate legal challenges but also contribute to the overall reliability and credibility of financial reporting standards.

11. Investor Perspectives
11.1. Investor Preferences
a. Surveying Investor Preferences: GAAP or IFRS?
Understanding investor preferences is crucial in the GAAP vs. IFRS discourse. Surveys play a valuable role in gauging investor sentiment and preferences regarding financial reporting standards. The insights gleaned from such surveys inform standard-setters, regulators, and companies in aligning financial reporting practices with investor expectations.
b. Implications of Investor Preferences on Reporting Standards
The implications of investor preferences on reporting standards are far-reaching. Companies that align with investor preferences enhance transparency and communication, fostering trust and confidence. Standard-setters and regulators, informed by investor feedback, can shape standards that not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to the information needs of investors in a dynamic and competitive market.
11.2. Impact on Investment Decision-Making
a. Investor Decision Dynamics: GAAP vs IFRS
Investor decision dynamics are influenced by the choice between GAAP and IFRS. Differences in financial reporting standards can impact the comparability of financial statements, influencing investment decisions. Investors must consider the implications of these standards on key metrics, risk assessments, and overall financial analysis to make informed and strategic investment decisions.
b. Strategic Impacts on Investment Choices
The strategic impacts of financial reporting standards on investment choices go beyond compliance. Companies that recognize the link between transparent financial reporting and investor confidence gain a strategic advantage. Similarly, investors who factor in the nuances of GAAP and IFRS differences in their decision-making processes navigate the complexities of the investment landscape more effectively.
11.3. Investor Education Initiatives
a. The Imperative of Investor Education
The imperative of investor education underscores the need for initiatives that enhance investor understanding of financial reporting standards. Educational programs, informational resources, and collaborative efforts between financial institutions and regulatory bodies contribute to a more informed investor community. An educated investor base not only demands higher standards of transparency but also actively participates in shaping the future trajectory of financial reporting.
b. Educating Investors on GAAP vs IFRS Implications
Educating investors on GAAP vs. IFRS implications involves demystifying the complexities of these frameworks. Providing accessible information, conducting investor workshops, and leveraging digital platforms for educational outreach are essential components. Investors empowered with a deeper understanding of financial reporting standards contribute to market efficiency and hold companies accountable for transparent and reliable reporting.

12. Ethical Considerations
12.1. Ethical Dimensions in Financial Reporting
a. Ethics in Financial Reporting Standards
Ethical considerations are integral to the formulation and adherence to financial reporting standards. The principles of integrity, objectivity, and transparency underpin ethical financial reporting. Standard-setters, regulators, and companies must navigate ethical dimensions to ensure that financial reporting serves the interests of investors and the broader public.
b. Upholding Integrity and Objectivity in Reporting
Upholding integrity and objectivity in reporting requires a commitment to ethical conduct. Companies must prioritize accurate representation over short-term gains, fostering a culture that values transparency. Regulators play a crucial role in setting the ethical tone, emphasizing the importance of unbiased and principled financial reporting in maintaining the integrity of capital markets.
12.2. Ethical Challenges for Accountants
a. Common Ethical Dilemmas in GAAP and IFRS
Accountants face common ethical dilemmas in navigating the intricacies of GAAP and IFRS. Issues such as revenue recognition, asset valuation, and disclosure requirements present challenges where ethical considerations intersect with professional responsibilities. Accountants must navigate these dilemmas with a commitment to ethical conduct, considering the broader impact on stakeholders and financial markets.
b. Navigating Ethical Challenges in Reporting Standards
Navigating ethical challenges in reporting standards involves equipping accountants with the tools and guidance needed for principled decision-making. Ongoing professional development, ethical training programs, and mentorship initiatives contribute to a culture of ethical awareness within the accounting profession. Companies, in turn, benefit from the assurance that financial reporting is not only compliant but also aligns with the highest ethical standards.
12.3. Regulatory Measures for Integrity
a. Regulatory Safeguards: Ensuring Ethical Conduct
Regulatory safeguards play a crucial role in ensuring ethical conduct in financial reporting. Regulatory bodies must establish and enforce ethical standards, conduct regular audits, and impose sanctions for non-compliance. A robust regulatory framework promotes integrity in financial reporting, reinforcing public trust in the accuracy and reliability of financial statements.
b. Maintaining the Integrity of Financial Reporting Standards
Maintaining the integrity of financial reporting standards requires a collaborative effort between regulators, standard-setters, and industry stakeholders. Periodic reviews, stakeholder consultations, and responsiveness to emerging ethical challenges contribute to the ongoing refinement of standards. The commitment to upholding ethical principles ensures that financial reporting continues to serve as a cornerstone of trust in the global business landscape.

13. Future Trajectories
13.1. The Evolution of Reporting Standards
a. Anticipating Future Changes
Anticipating future changes in reporting standards involves considering the dynamic nature of global business, technological advancements, and shifts in investor expectations. Standard-setters must adopt a forward-looking approach, engaging in scenario planning and staying attuned to emerging trends. The ability to anticipate future changes ensures that reporting standards remain relevant and adaptive to the evolving needs of the business environment.
b. Technological Innovations and Reporting
Technological innovations are poised to shape the future trajectory of reporting standards. The integration of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics introduces opportunities for enhanced accuracy, efficiency, and transparency in financial reporting. Standard-setters and companies must embrace these innovations responsibly, balancing the benefits of technology with the imperative of maintaining ethical and transparent financial practices.
13.2. Convergence vs. Divergence
a. Assessing Convergence Prospects
The prospects of convergence between GAAP and IFRS continue to be a topic of consideration. While convergence offers the promise of a more standardized global approach, challenges such as differing legal frameworks and regulatory philosophies persist. Assessing convergence prospects involves a nuanced examination of global trends, regulatory developments, and ongoing efforts by standard-setters to bridge divergences.
b. Navigating Divergences in Global Standards
Navigating divergences in global standards requires a pragmatic approach that acknowledges the unique needs of individual jurisdictions. The coexistence of multiple standards necessitates effective communication, education, and cross-border collaboration. Standard-setters can play a pivotal role in facilitating harmonization efforts, fostering a global financial reporting landscape that balances convergence with the flexibility needed to accommodate diverse economic and regulatory environments.
13.3. Sustainable Reporting Paradigms
a. The Rise of Sustainable Reporting
The rise of sustainable reporting reflects a paradigm shift in the broader understanding of corporate performance. Investors, regulators, and the public increasingly recognize the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Future reporting standards are likely to integrate sustainable reporting paradigms, providing a more comprehensive view of a company’s long-term value creation and societal impact.
b. Integrating ESG Metrics into Reporting Standards
Integrating ESG metrics into reporting standards requires a collaborative effort between standard-setters, regulators, and industry stakeholders. The development of clear guidelines, standardized metrics, and transparent disclosure requirements enhances the credibility of sustainable reporting. Companies embracing ESG considerations in their financial reporting contribute to a more informed and responsible investment landscape.

14. Conclusion
Financial reporting standards, whether grounded in GAAP or IFRS, serve as the bedrock of transparency, trust, and accountability in the global business landscape. The evolution of these standards reflects a journey of adaptation to changing business dynamics, regulatory landscapes, and investor expectations. While GAAP and IFRS diverge in certain philosophies and approaches, they share a common goal – to provide reliable and relevant information for decision-making.
As we navigate the complexities of GAAP vs. IFRS, it is imperative to recognize the strengths and limitations of each framework. GAAP, with its historical cost emphasis and rule-based approach, offers stability and comparability. In contrast, IFRS, operating under a principles-based approach, provides flexibility and a global perspective. Understanding the variances in revenue recognition, asset valuation, and consolidation methods is essential for investors, analysts, and companies alike.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of reporting standards involves a delicate balance – between convergence and divergence, between technological innovation and ethical considerations, and between traditional financial metrics and sustainable reporting paradigms. The future holds the promise of more standardized, adaptive, and responsible reporting standards that cater to the diverse needs of a dynamic global economy.
In conclusion, as the landscape of financial reporting continues to evolve, stakeholders must remain vigilant, adaptive, and collaborative. Whether one adheres to GAAP or IFRS, the shared commitment to integrity, transparency, and accountability ensures that financial reporting remains a cornerstone of trust in the interconnected world of business and finance.

#cfo#banking#accounting#finance#investment#personal finance#international finance assignment help service#financial management#financial markets#financial modeling#financial planning#financial dominance#financial services#financial literacy#financial drain#management#business#entrepreneur
0 notes
Text
Hiree Financial Solutions: Elevate Your Business with Expert Accounting Consultancy Services

Unlock the full potential of your business with Hiree, your trusted partner in accounting consultancy services. At Hiree Financial Solutions, we understand the complexities of managing finances, and our team of seasoned experts is dedicated to providing tailored solutions for your unique needs. From streamlining financial processes to ensuring compliance, Hiree empowers your business with strategic insights and efficient accounting practices. Experience the difference of precision and professionalism with Hiree - Your pathway to financial success.
#accounting consultancy services#outsourcing finance and accounting services#outsourced cfo services#virtual chief financial officer#australia
0 notes
Text
What Should Small Businesses Know About 1099s?
In Sonnenburg Consulting's latest blog, "What Should Small Businesses Know About 1099s?" discover essential insights and expert advice on handling 1099 forms. From understanding the intricacies of contractor classification to ensuring compliance with tax regulations, this comprehensive guide empowers small businesses to navigate the complexities of 1099 reporting with confidence. For more information contact us at 801-984-3805.
#CFO services utah#Nationwide Financial Services in Utah#National Outsourced Accounting Services in Utah#National Outsourced Accounting Services#outsourced accounting services#Nationwide Bookkeeping Services in Utah#Nationwide Outsourced CFO Services in Utah#outsourced CFO services#Nationwide Business Consulting Services in Utah#business consulting services#CFO outsource services#CFO consultant service#difference between payroll tax and income tax#CFO outsourcing services
0 notes