#DeepSource
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
DeepSource Open Sources Globstar Alternative to Semgrep to Analyze Code
http://securitytc.com/TJNrXs
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Hacktoberfest 2021 swag unboxing
Hacktoberfest 2021 swag unboxing
My Hacktoberfest 2021 swags have finally arrived. Check out this post and watch Hacktoberfest 2021 swag unboxing For the third consecutive year I have I have completed the Hacktoberfest challenge check post here.Check out the unboxing video below: Thank you, Intel, Digital Ocean, GitHub Education, Appwrite, DeepSource Follow me on Instagram That’s it for now. If you liked this article,…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
What is digital ocean?
Through the program, local area creators assist with developing DigitalOcean's library of DevOps, programming improvement, and creation frameworks instructional exercises generally founded on free and open-source programming. These creators then get an individual payout and select a tech-centered cause to get a gift. Our instructional exercises assist engineers at all levels with tackling issues, answer questions, and do things they couldn't do before with open-source programming. DigitalOcean, Inc. is an American cloud foundation supplier organization.[3] Digital sea settled are situated in New York City with server farms worldwide.[4] DigitalOcean gives engineers, new businesses, and SMBs with cloud framework as-a-administration platforms.[5] DigitalOcean additionally runs Hacktoberfest, a one drawn out festival of open source programming held in October. Every year, etcit's accomplices work together with various programming organizations. They incorporate Past accomplices like GitHub, Twilio, Dev.to, Intel, AppWrite, and DeepSource. digital ocean In 2003, Ben and Moisey Uretsky, who established the ServerStack, an oversaw facilitating business,[6] needed to make another item which would join web facilitating and virtual servers and target pioneering with programming developers.[7][6] In 2011, the Uretskys established DigitalOcean, an organization which would give server provisioning and cloud facilitating for programming developers.[8]
In 2012, the Uretskys met prime supporter Mitch Wainer they following Wainer's reaction to a Craigslist work listing.[9] Mitch Wainer organization sent off their beta item in January 2012.[10] In mid of 2012, the establishing group comprised of Ben Uretsky, Moisey Uretsky, Mitch Wainer, Jeff Carr, and Alec Hartman. After quite a while DigitalOcean acknowledged the proposal of TechStars 2012's startup gas pedal in Boulder, Colorado, the authors moved to Boulder to deal with the product.[11] In the finish of the gas pedal program in August 2012, the organization had joined 400 clients and sent off around 10,000 cloud server instances.[11][12] On January 16, 2018, new bead (virtual machines) plans were presented their blog.[13] In May 2018, the organization reported the send off of its Kubernetes-based compartment service.[14][15] On January 15, 2013, DigitalOcean became one of the main cloud-facilitating organizations to offer SSD-based virtual machines.[20] Following a TechCrunch[20] audit, which was partnered by Hacker News, DigitalOcean saw a quick expansion in customers.[11] In December 2013, DigitalOcean opened its first European server farm situated in Amsterdam.[21] During 2014, the organization proceeded with its development, opening new server farms in Singapore and London.[22] During 2015 DigitalOcean extended further with a server farm in Toronto, Canada.[23] and Frankfurt,[24] Germany. Later in 2016 they proceeded with extension to Bangalore, India.[25] DigitalOcean offers virtual private servers (VPS), or "drops" utilizing DigitalOcean phrasing, involving KVM as the hypervisor[38] and can be made in different sizes (isolated in 2 classes: standard, and streamlined), in 13 distinct server farm districts (as of December 2020[39]) and with different choices out of the container, including 6 Linux disseminations and many a single tick applications. In mid 2017, DigitalOcean extended their list of capabilities by adding load balancers to their offering.[40] Their foundation is an elective cloud offering and the organization targets more modest designers, permitting them to spend just 5 dollars on their foundation. DigitalOcean was generally censured for its job in making an unreasonable motivating force when it advanced Hacktoberfest 2020 with free shirts for commitments to open source projects, bringing about monstrous fake draw demands on open source GitHub stores, adding up to an accidental "corporate-supported disseminated forswearing of administration assault against the open source maintainer community".[48][49][50][51] DigitalOcean rushed to answer, and gave updates to Hacktoberfest to assist with forestalling this, by permitting open source maintainers to explicitly pick into Hacktoberfest, refreshing the Hacktoberfest interaction to permit maintainers to check malicious substance, and forestalling storehouses set up to game the framework from taking part.
0 notes
Text
Open-Source Alternatives Amid Semgrep Licensing Controversy
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/open-source-alternatives-amid-semgrep-licensing-controversy/
Open-Source Alternatives Amid Semgrep Licensing Controversy


The security community witnessed a seismic shift in January 2025, as rival companies united to launch Opengrep—a fork of static application security testing tool, Semgrep. Once celebrated for its community-driven open-source ethos, Semgrep ignited controversy when it altered its licensing model in December 2024. These licensing changes restricted the use of contributed rules in commercial products and shifted key features behind a paywall.
Semgrep became an essential tool for developers worldwide due to its ability to detect vulnerabilities across multiple programming languages. However, the company’s decision risks stifling innovation in an area vital to modern cybersecurity.
Amid the controversy, DevSecOps startup DeepSource launched Globstar, a new open-source toolkit for code security. Built from scratch and released under the MIT license, Globstar says it aims to provide unrestricted commercial and full public access to its code.
“Through Globstar, we are offering a fresh approach to custom static analysis, designed with the needs of security teams in mind. It emerged from an internal framework we had developed for threat detection,” Sanket Saurav, co-founder and CEO of DeepSource, told me. “Semgrep is already in capable hands, and our goal was to take a distinct path. We see ourselves not as a replacement, but an alternative who brings a new perspective to the space.”
The company has raised a total of $7.7M in funding and is currently being backed by Y-Combinator investors.
Developed utilizing the Go programming language and integrated with Tree-sitter, Globstar supports over 20 programming languages. The toolkit features an intuitive YAML interface for creating custom security checkers and an advanced Go interface for complex, cross-file analysis.
“When a project is forked, it often takes a different trajectory—but when constrained to building on top of an existing product, innovation can be limited,” said Sanket. “We created a system that simplifies the process of writing custom code checkers.”
Business Necessity Versus Open-Source Preservation
On Dec. 13, 2024, Semgrep revamped its licensing model to restrict third-party use of contributed rules in competing commercial products without authorization. Moreover, the company rebranded its open-source version to “Semgrep CE” (Community Edition). Semgrep claims that its licensing changes are essential to protect intellectual property and ensure sustainable revenue. The company contends that restricting commercial use helps curb unauthorized repackaging and supports long-term innovation.
“When engineers write code to solve a problem, static analysis examines the code without execution, identifying patterns and potential issues early in the development process. Semgrep is a respected player in this space, and I hold them in high regard,” said Sanket. “However, their shift in licensing for commercial users reflects a broader reality: VC-backed companies must balance open-source principles with sustainable business models.”
He notes that while the change didn’t directly impact end users, it raises an ongoing debate about whether open source should remain entirely unrestricted or evolve to ensure long-term viability.
On January 2025, 10 DevSec firms including Aikido Security, Arnica, Amplify Security, Endor Labs, Jit, Kodem, Legit Security, Mobb and Orca Security—formed a consortium to launch Opengrep. Traditionally fierce competitors, the new consortium directly plans to challenge Semgrep’s decision to limit functionality in favor of commercial gain. In a blog post, Endor Labs stated that static code analysis is “too important to restrict”.
However, it’s not yet clear if Opengrep merely repackages legacy code rather than offering a completely new solution.
The Rise of Open-Source Alternatives
DeepSource recognized a growing need among developers for a tool that does not inherit legacy constraints. “Enterprise customers don’t want to juggle multiple tools—it creates integration challenges and drives demand for an all-in-one solution,” explained Sanket. “Static analysis plays a crucial role in understanding code architecture, which is why we’ve positioned ourselves as a unified platform.”
However, DeepSource’s Globstar is not alone, several static code analysis alternatives have gained traction following the Semgrep licensing controversy. For instance, SonarQube is a code analysis platform that offers both a free Community Edition and paid versions, for static code analysis, integration support and metrics tracking. Likewise, ShellCheck is another alternative specifically used for analyzing shell scripts, and aids developers in catching scripting errors that could later lead to major bugs or inefficiencies. It flags commands or syntax that may not be portable across different shell environments. Due to its ease of use—ability to run from the command line and easily integrate into CI/CD pipelines, ShellCheck has become an increasingly popular choice.
While Opengrep seeks to preserve a legacy tool’s open roots, other alternatives like SonarQube, Globstar and ShellCheck also offer a fresh, forward-thinking solution. As the open-source debate unfolds, developers and enterprises face pivotal choices that may redefine the landscape of code analysis.
#2024#2025#Analysis#Application Security#approach#architecture#Blog#bugs#Building#Business#CEO#challenge#change#CI/CD#code#command#command line#Community#Companies#cybersecurity#december#detection#developers#development#Devsecops#endor labs#engineers#enterprise#Enterprises#Explained
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Hot new product on Product Hunt: DeepSource Discover https://ift.tt/349zFb4
0 notes
Photo

DeepSource Reset Login Following Phishing Attack On Employee #hacking #hacker #cybersecurity #hack #ethicalhacking #hacknews
0 notes
Link
via Twitter https://twitter.com/PatrickCMiller
0 notes
Photo
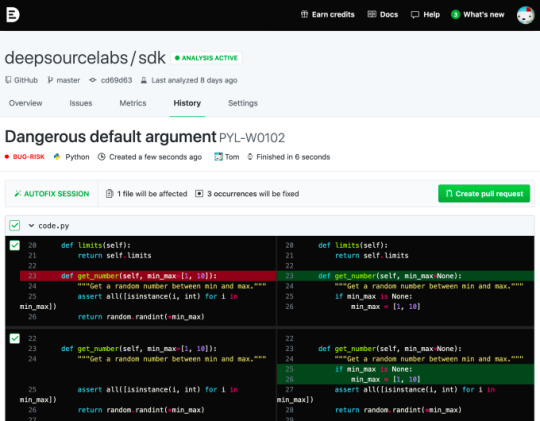
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis https://ift.tt/3e9bQCS
0 notes
Photo

DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis https://ift.tt/2YJhRQl
0 notes
Photo
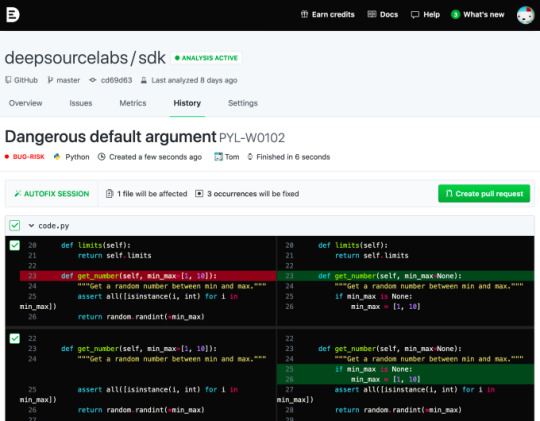
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis
0 notes
Text
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis
DeepSource, a member of the Winter 2020 Y Combinator cohort, announced a $2.6 million seed investment today. The company is building a solution to help developers automate static code analysis to find certain errors before going through human code review.
645 Ventures led the round with help from Y Combinator, FundersClub, Pioneer Fund, Liquid 2 Ventures and a slew of individual investors. The company had previously raised $140,000 in pre-seed capital.
DeepSource is taking advantage of a process called static analysis. Company co-founders Jai Pradeesh and Sanket Saurav are software engineers, and saw the static analysis tools that ship with language packages like Python and Go as overly complex and hard to use. Pradeesh said that as a result, most developers have not embraced them.
“What we’re trying to do is use static analysis to figure out if we can automate the objective parts of the code review. […] Whenever a software developer makes a commit or introduces any change in code, DeepSource automatically runs analysis on that code. It then flags issues like security issues, anti-patterns, progress performance issues and things like that,” Pradeesh explained.
By automating parts of the review process, it allows the human code reviewers to concentrate on the less objective parts of the review and find a myriad of issues before it even goes to human review. DeepSource gives the developer a report with the error and an explanation of how to fix it.
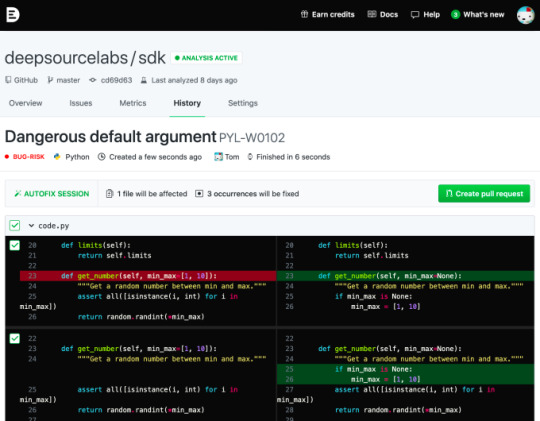
But the founders recognized the drudgery of constantly repairing the same sorts of errors over and over. So they created an automated repair tool called Autofix that goes through and fix a set of common errors automatically for the developer.
Autofix in action. Image Credit: DeepSource
While Pradeesh says the automation tool only covers around 12% of errors so far, part of the investment will go towards helping build out additional coverage. For now the company supports Python and Go programming languages, but plans to add additional languages over time. It already released a Ruby on Rails version a couple of months ago in Beta, and support for JavaScript is on the way, he said.
The company currently has 12 people, including the two co-founders, based in Bangalore in India, but has plans to eventually move to the U.S. when the pandemic allows. It also plans to hire another 10-15 people over the next 12 to 18 months, primarily in engineering. The startup is working with YC advisors on building a diversity plan now, understanding that it is at a pivotal point in its evolution.
He says that the YC experience taught him and his co-founder about building more refined user personas for design and marketing purposes. Instead of broadly looking at the market as all developers, they could begin to focus on different aspects of that pool like a large team versus an engineering manager. He said they also learned to explore usage data to understand things like what kinds of errors were most common, which helped inform the creation of the Autofix feature.
Being part of YC also helped them when they had to leave the office and go remote earlier this year due to the pandemic. Pradeesh admitted he had no experience running a remote team and his YC advisors helped him get comfortable with the process to the point they have good systems in place now.
“We put in these separate processes so that we do these bi-weekly sprints, and have learned ways to make sure everybody in the team communicates. Now that we have started putting these processes in place, the team is getting more and more used to it,” he said.
0 notes
Photo
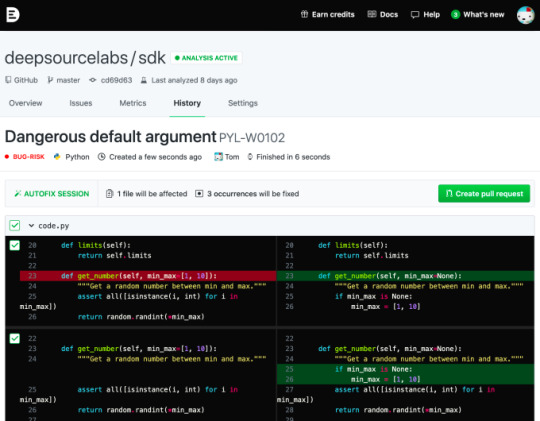
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis
0 notes
Text
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis
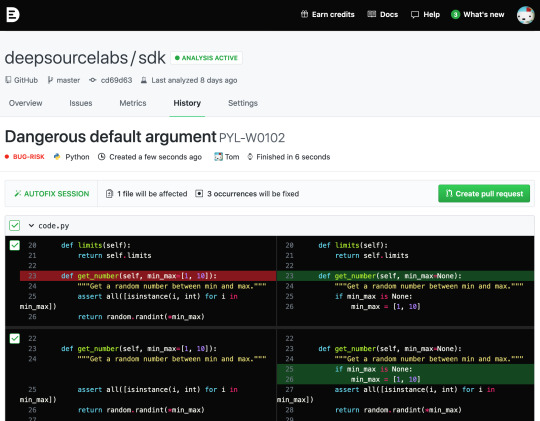
DeepSource, a member of the Winter 2020 Y Combinator cohort, announced a $2.6 million seed investment today. The company is building a solution to help developers automate static code analysis to find certain errors before going through human code review.
645 Ventures led the round with help from Y Combinator, FundersClub, Pioneer Fund, Liquid 2 Ventures and a slew of individual investors. The…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo
DeepSource announce $2.6M seed round to automate static code analysis https://ift.tt/2YJhRQl
0 notes