#French Revolutionary Army
Text
#OTD in 1798 – Irish Rebellion of 1798 | Irish rebels, with French assistance, establish the short-lived Republic of Connacht.
The Irish Republic more commonly referred to as the Republic of Connacht was a short-lived Irish breakaway puppet state established with French Directory military support for 13 days during the Irish Rebellion of 1798.
Below is an excerpt from the proclamation of General Humbert, the French General who led the French and Irish armed forces in the short-lived Republic. The proclamation was made on…

View On WordPress
#1798 United Irishmen Rebellion#Ballinamuck#British Army#Castlebar#England#France#French Revolutionary Army#General Jean Joseph Humbert#Irish Rebels#John Moore#Killala#Republic of Connacht#Republic of Ireland#The Year of the French
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
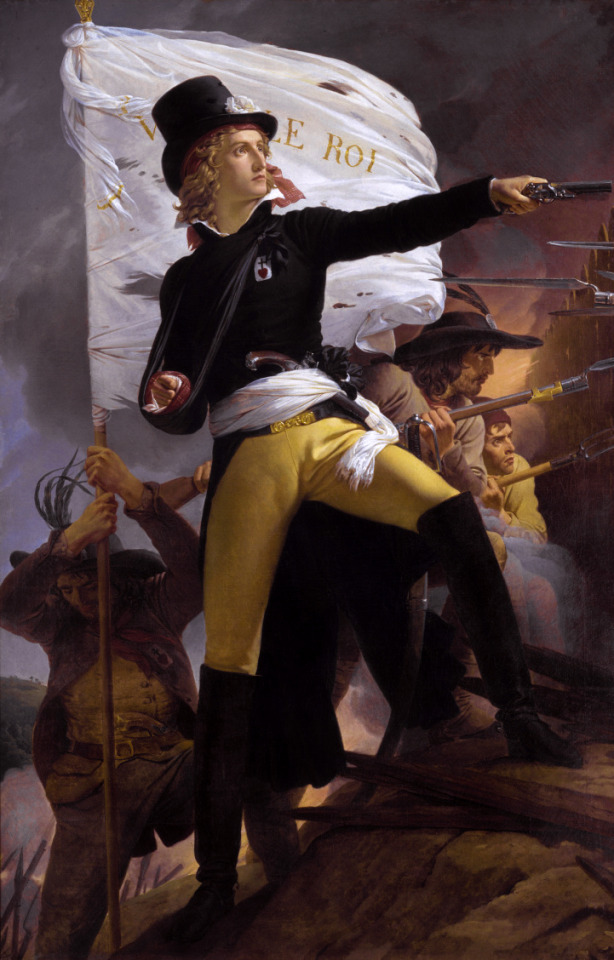

Henri de la Rochejaquelein by Pierre-Narcisse Guérin
#henri de la rochejaquelein#art#pierre narcisse guérin#portrait#war in the vendée#vendée#royalist#royalists#french revolutionary wars#french revolution#france#french#henri du vergier#vendéan#insurrection#rebellion#catholic#royal#history#europe#european#aristocratic#nobility#aristocrat#nobleman#kingdom of france#general#monarchy#army#vendéans
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
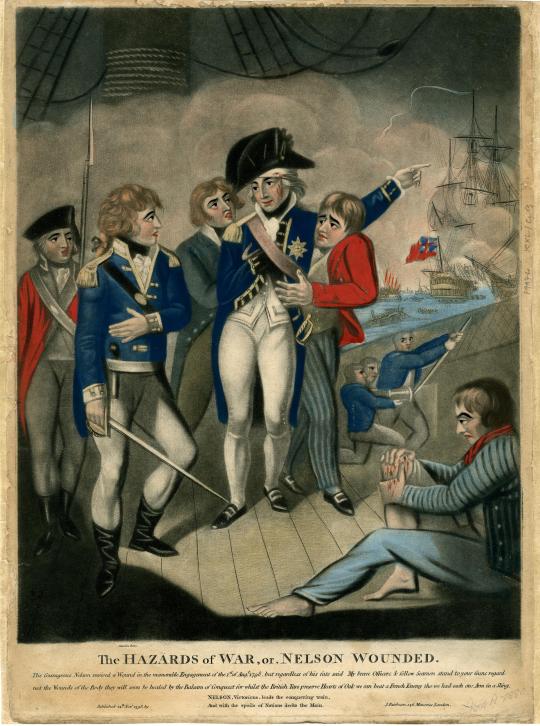

Familial connections were further evoked in the terms 'brother soldier' and 'brother officer', which can be found repeatedly across multiple memoirs. [...] Napier mourned a fellow officer with the admission that he had loved him 'with all a brother's affection', while Serjeant Butler was overcome by the kindness of a doctor who treated him without charge as a mark of his shared solidarity with 'an old fellow traveller and brother soldier'. Naval men shared the same concept. Nelson drew on Shakespearean fraternal imagery when commending his officers as 'Such as gallant set of fellows! Such a band of brothers! My heart swells at the thought of them!'
— Louise Carter, "Brothers in arms? Martial masculinities and family feeling in old soldiers' memoirs, 1793-1815", in Martial Masculinities: Experiencing and Imagining the Military in the Long Nineteenth Century, edited by Joanne Begiato, Michael Brown, and Anna Maria Barry.
The Hazards of War, or, Nelson Wounded, 1798 mezzotint (British Museum).
#horatio nelson#military history#masculinity#martial masculinities#royal navy#age of sail#british army#napoleonic wars#french revolutionary wars#quotes#brothers in arms
44 notes
·
View notes
Photo
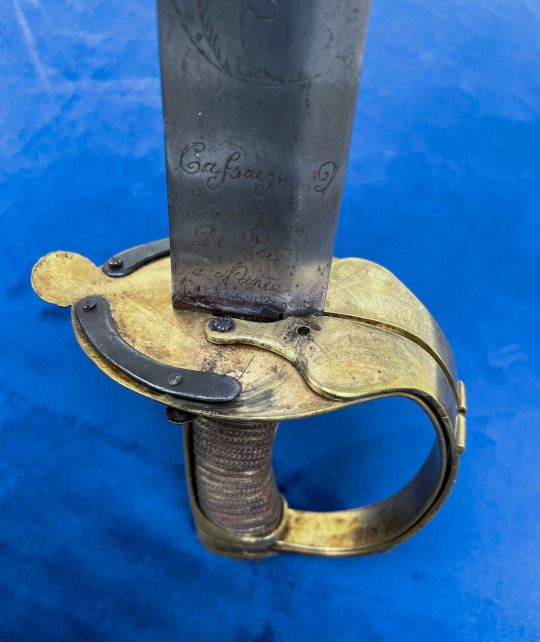
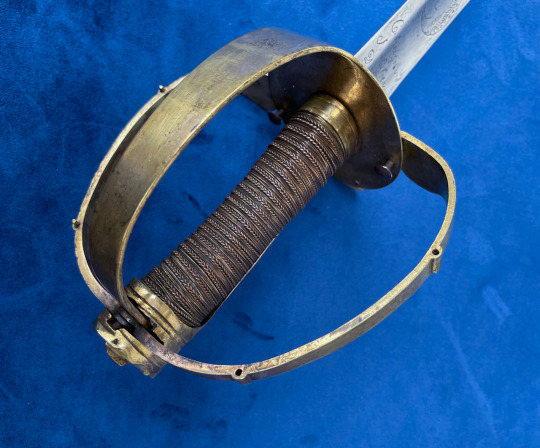
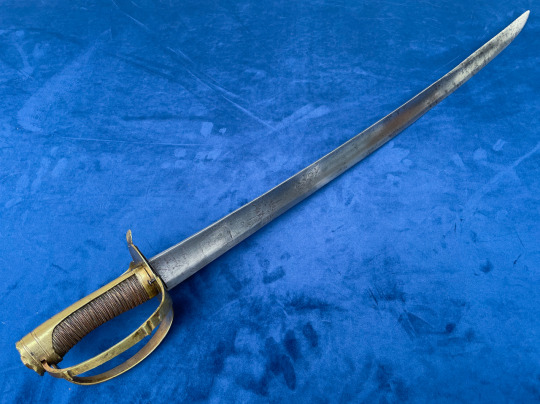
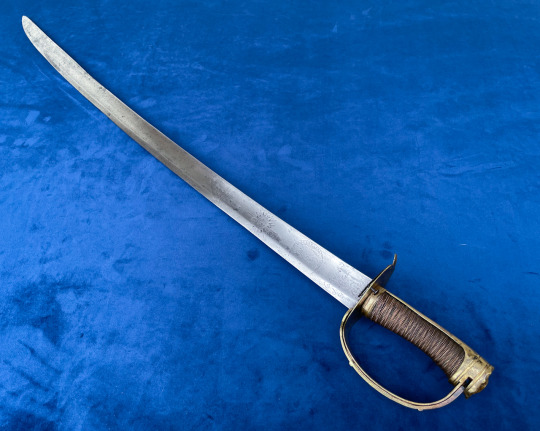







Mounted Infantry Officers Sabre with ‘Branches Tournantes’ - Rotating branches.
It is generally believed that this non-regulation style of sabre, with the rotating guard appeared around 1784, possibly corresponding to the Chasseur a Pied or Hunters on Foot, a Light Company style infantry unit that engaged in scouting and skirmishing actions.
To distinguish themselves from the regular line infantry, many officers adopted this model with an iron guard to match the silver on their uniforms.
Swords with brass guards followed around 1786 as officers of the line began to adopt the sabre for themselves as well. And on 14th May 1788 a Royal decision was announced, authorizing them to carry a sabre rather than a sword.
While predominantly taken up by infantry or naval officers, some were carried by mounted officers as well, and can be identified by their length and having three instead of two scabbard fittings so that it could be suspended from the officers’ belt.
Their use continued through the revolution, and they remained in service until around 1798 when they fell out of fashion.
This type of sword is a unique attempt to solve the issue of providing maximum hand protection when in use while being less of an encumbrance when worn at the side. They came with varying degrees of decoration from plain oval guards with one or two folding branches to pierced guards or even a full collapsing basket.
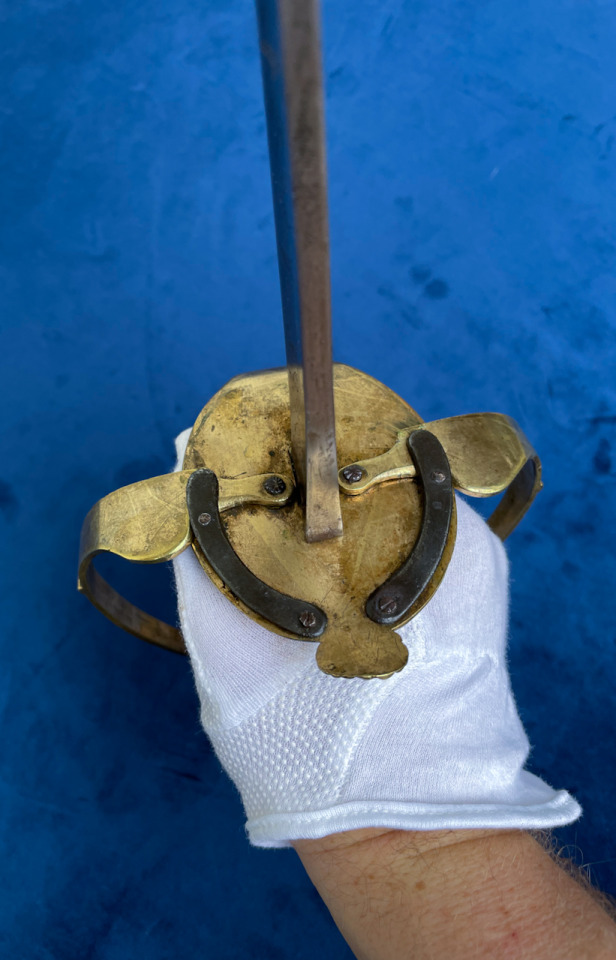
The mechanism is simple with the branches pivoting on their anchor points on the guard plate and a pin where they join the pommel. A piece of spring steel with a pin, holds the branch in place when extended and there is a button attached to the end to release it to fold back for when not in use.
On this sword, the two side branches fold out to offer plenty of space for the hand, but because of where the branches meet with the pommel, the sword is not suited to point work (like many basket hilts).

The ricasso is engraved with the makers name which reads:
Cassaignard Fourbisseur Du Roi à Nantes
Or translated:
Cassaignard, Cutler of the King in Nantes.
Cassaignard operated out of Nante from 1774 to 1812 as a Fourbisseur, an old French term for someone that finishes edged weapons, i.e. mounting hilts, decorating and polishing the blades. Being a port city, his mark in various forms appears on a lot of swords associated with Naval officers or Privateers. Due to the use of ‘Du Roi’ in the makers mark, we can be reasonably confident that this blade pre-dates the denouncement of King Louis XIV in 1792 when it became common practice to remove or deface the symbols of his reign.
The other decorations include the talismanic man in the moon, face in the sun and sword arm protruding from a cloud. These are typical of Solingen made blades, where Cassaignard likely purchased his stock from, and this combination of three items feature often on blades with his mark.
Overall Length: 920 mm
Blade Length: 788 mm
Grip Length: 130 mm
Inside Grip Length: 108 mm
Sword Weight: 810 grams
Total Weight: 1,180 grams
Point of Balance: 135 mm
Curve: 16 mm

#Sabre#Swords#French Revolution#18th Century#Infantry#Mounted officers#French Army#Antiques#Georgian Era#Revolutionary Wars
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aziraphale: I saved 3 children and shall fall for it! Wringing my hands as I accept my fate!
Also Aziraphale: RIP in peace French revolutionary human, Army Human(?), Wee Morag, and Magic Shop human. hope you got into heaven. anyway I gotta go get crepes and/or proceed with this foreplay scene I got going on.
#am I forgetting anyone?#he did feel bad about Morag but I’m not letting things like plot get in the way of my shitpost#Aziraphale’s body count is quite high and not in the sexy way#aziraphaaaaaale#good omens
671 notes
·
View notes
Text
OKAY HEAR ME OUT:
All of these edgy science fiction / fantasy novels about overthrowing evil empires and then becoming the very thing that you sought to destroy and the main character ending up as bad as the regime they overthrew and all that, you know?
You could very easily make a dramatised version of the life of Napoleon Bonaparte, transplant it into generic fantasy evil empire world, change the names of the historical figures to fictional names, and all the tumblrinas would eat that up.
Picture this: Napoleon Our protagonist is born the second child in a large family on Corsica generic fantasy island, is sent to a military academy in France evil empire, and begins to rise through the ranks of the army. A revolution occurs, in which the French evil empire monarchy is overthrown, and our protagonist, a supporter of the revolution, fights for the revolutionary government against royalist uprisings and the first coalition other evil empires. Along the way, our protagonist becomes increasingly powerful, as well as being an absolute slut. After a series of military campaigns, our protagonist, seeing the corruption of the directory new evil government, stages a coup and becomes first consul generic fantasy leader. However, over the course of the book, our protagonist has acquired a huge ego and lost many morals, and ends up themself the emperor of France fantasy kingdom. "Morally grey" shenanigans ensue. (Of course, our protagonist would have many many love interests, such as Josephine de Beauharnais hot milf, Jean-Andoche Junot hot best friend, and Tsar Alexander I enemies-to-lovers-to-enemies-again.) (Main character would be characterised as being the most pathetic little person to ever exist who is frequently bullied for being quirky and not-like-other-girls)
#THIS POST IS 100% SILLY OKAY PLEASE DON'T TAKE ANYTHING I SAY SERIOUSLY#history#napoleon#napoleonic#napoleonic era#napoleon bonaparte#books#bookblr#fantasy#fantasy books#fantasy writing#writing#writeblr#literature#locked tomb#iron widow#baru cormorant#i'm sorry for this
717 notes
·
View notes
Text
MARIE-THÉRÈSE FIGUEUR // SOLDIER
“She was a French soldier who fought in the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Unlike some female soldiers before the twentieth century, she did not disguise her gender when she enlisted, serving for twenty-two years under her own name in the French Revolutionary Army and the Grande Armée.”


138 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Revolts and revolutions in Italy under the Restoration
“Atlante storico”, Garzanti, 1966
by cartesdhistoire
The Congress of Vienna divided Italy into ten largely reactionary states, against which the secret society of Charbonnage, originating in the Kingdom of Naples in 1807, opposed itself. The "Carbonari," mainly from the middle classes, whose growth had been favored by French domination, claimed inspiration from the constitution of Cádiz promulgated by the Spanish parliament with Napoleon's agreement in 1812.
Revolutionary movements erupted first in Naples in the summer of 1820, followed by Palermo, which became the scene of a genuine civil war. The insurrection spread to Piedmont from March 1821; the insurgents were defeated in Novara on April 8, with Austrian assistance, leading to ruthless repression until October. Order on the peninsula was only fully restored in early 1822 by the Austrian army. Severe anti-liberal repression was felt in Modena, the Papal State, and Milan. At least 3,000 patriots went into exile between 1821 and 1823.
Echoing the Parisian revolution of 1830, which had a profound impact in Italy, an uprising erupted in early 1831 in Modena, Parma, and Bologna. On March 4, the Austrian army entered the Duchy of Modena, and on the 29th, the last remnants of the insurgent army capitulated. Fierce repression followed.
Patriots were divided into two models: revolutionary and democratic or liberal and moderate. The latter, itself subdivided into two currents, one advocating unification under the pope's auspices and the other under the leadership of the House of Savoy. The revolutionary model, predominant until 1848, found its embodiment in Giuseppe Mazzini, who envisioned a popular insurrection to overcome resistance from princes and local particularisms, leading to a republic. Mazzini's activism played a significant role in shaping the Italian people's national consciousness, but the utopian nature of the insurrectional path ultimately led to a deadlock.
70 notes
·
View notes
Note
petition for that long rant on revolutions here, i really enjoyed the way you laid out your facts and explained the first rant and am not too good at reading theory myself (i am still trying tho) thanks!!
Okay okay so the problem with revolutions is they get messy. Real messy. You get counter-revolutionaries, moderates, extremists, loyalists, and everything in between. One revolution turns into 5, and even if your side wins, its almost guaranteed to have been tainted some way or another along the way.
Take the first french revolution. It started as civil unrest, the estates general initially called for reform of the french state into a constitutional monarchy similar to Britain. Even king louis XVI was in support of this. But extremists wanting a republic and counter-revolutionaries wanting absolute monarchy clashed and things became more and more chaotic and violent. Eventually the extremists won, the jacobin reign of terror ensued, and 10s of thousands of people were executed. Now don't get me wrong, i am all for executing monarchs and feudal lords, but look what happened a few years later; Napoleon used the political instability to declare himself emperor, a few more years later his empire had crumbled, and the monarchy was back with Louis XVIII.
Or take the 1979 iranian revolution. It started as protests against pahlavi, who was an authoritarian head of state and an American pawn. As the protests turned into civil resistance and guerilla warfare it took on many different forms. There were secularists vs islamic extremists. There were democrats vs theocrats vs monarchists. Etc. Through all the chaos, Khomeini seized power, held a fake referendum, and declared himself supreme leader and enforced many strict laws, particularly on women who previously had close to equal rights. Many of the millions of women involved in the revolution later said they felt bettayed by the end result.
Or the Russian Revolution. It started as protests, military strikes, and civil unrest during WW1 directed at the tsar. He stepped down in 1917 and handed power over to the Duma, the russian parliament. This new provisionary government initially had the support of soviet councils, including socialist groups like the menshiviks. But they made the major mistake of deciding to continue the war. Lenins bolsheviks were originally a very tiny group on the fringes of russian politics, but they were the loudest supporters of peace, so they gained support and organised militias into an army and thus began the russian civil war. Lenin won and followed through on his promise to end the war against germany, but its a bit ironic that they fought a civil war, that killed about 10 million people, just to end another war.
Im not saying any of these results were either bad or good. They all have nuance and its all subjective. But the point i am trying to make is that they get messy. The initial goals will always be twisted.
France wanted a constitutional monarchy, they got an autocratic emporer.
Iran wanted democracy and an end to American influence, and well they ended american influence alright but also got a totalitarian theocrat.
Russia wanted an end to world war 1 and got one of the bloodiest civil wars in history.
I cant think of a single revolution in history that achieved the goals it set out to achieve.
But again, im not saying this is necessarily a bad thing, just a warning against revolutionary rhetoric and criticisms of reformism. Sometimes revolution is the only option, when you're faced with an authoritarian government diametrically opposed to change, then a revolution may be worth the risk. But it is a risk.
But if you live in a democracy, claiming revolution is the only way is actively choosing both bloodshed and the risk of things going horribly wrong over the choice of peaceful reform.
So when i go online in some leftist spaces and see people claiming revolution in America or UK or wherever is the only way out of capitalism I cant help but feel angry.
I know our democracy is flawed, and reform is slow and can even go backwards, but we owe it to all the people who would die in a revolution to try reform first.
I know socialist reform is especially hard in our flawed democracy where capitalists own the media, but if we can't convince enough people to vote for socialist reform what hope do we have of convincing enough people to join a socialist revolution. Socialism is supposed to be for the people, but how can you claim your revolution is for the people if you can't even get the support of the people?
So what I'm trying to say is; if youre one of those leftists that are sitting around waiting for the glorious revolution, doing nothing but posting rhetoric online - at least try doing something else while you wait. Join your labour union, recruit your coworkers, get involved in your local socialist parties, call your local representatives (city council, senator, governor, member of parliament, whatever) and make your opinions known, push them further left, and keep pushing.
#thank you anon this waa fun#also when i say i cant think of any revolution in history that achieved its goals#im not counting wars of independence#i know americans call the american war of independence the revolutionary war but its not a revolution l#(for reference - the first rant that anon mentions is a reblog a couple days ago about the communist manifesto)
68 notes
·
View notes
Photo

On this day, 20 July 1925, Frantz Omar Fanon, psychiatrist, revolutionary and pioneering anti-colonialist theorist was born in the French colony of Martinique. Fanon served in the Free French Army during World War II in North Africa, and like many Black colonial troops, experienced racism. Living in Algeria he supported the independence movement until he was forced to leave the country, at which point he became an ambassador for the Algerian National Liberation Front. His seminal works include 'Black Skin, White Masks' 'The Wretched of the Earth', and focused not just on the politics and economics of colonialism but also its internal and psychological effects. More information, sources and map: https://stories.workingclasshistory.com/article/9275/frantz-fanon-born https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=664955625677656&set=a.602588028581083&type=3
218 notes
·
View notes
Text
#OTD in 1798 – Irish Rebellion of 1798 | Irish rebels, with French assistance, establish the short-lived Republic of Connacht.
#OTD in 1798 – Irish Rebellion of 1798 | Irish rebels, with French assistance, establish the short-lived Republic of Connacht.
The Irish Republic more commonly referred to as the Republic of Connacht was a short-lived Irish breakaway puppet state established with French Directory military support for 13 days during the Irish Rebellion of 1798.
Below is an excerpt from the proclamation of General Humbert, the French General who led the French and Irish armed forces in the short-lived Republic. The proclamation was made on…

View On WordPress
#1798 United Irishmen Rebellion#Ballinamuck#British Army#Castlebar#England#France#French Revolutionary Army#General Jean Joseph Humbert#Irish Rebels#John Moore#Killala#Republic of Connacht#Republic of Ireland#The Year of the French
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Napoleon Bonaparte reviewing the Army of Italy in Nice on 27 March 1796 by Jacques Onfroy de Bréville
#napoleon bonaparte#napoléon bonaparte#armée d'italie#italian campaign#jacques onfroy de bréville#job#art#french revolutionary wars#france#french#nice#italy#history#europe#european#napoleon#napoléon#napoleonic#army#italian campaigns#soldiers#troops#inspection#general#command#bonaparte
58 notes
·
View notes
Text


Mariquita Tennant (born Maria Francesca Eroles i Eroles) was a Catalan woman who protected abused and poor women in Windsor (England).
How did she end up in England?
Mariquita was born in the village Pla de Sant Tirs, in the High Pyrenees of Catalonia. During the war between those who wanted an absolutist monarchy and the liberals, Mariquita's father was involved in the liberal side and between 1821 and 1823 he was the leader the local miquelets (militia). When the King of France sent the army known as the Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis to help restore the absolute monarchy, many liberals went on exile to England. Mariquita followed her father, mother and three siblings on exile to London.
They settled in Somers Town, a neighbourhood that had become home to many exiles from Catalonia and the Valencian Country and that had previously also become home to exiled French revolutionaries and American independentists. In February 1833, Mariquita married David Reid, son of a Scottish beer maker who had become wealthy running a pub chain in England. But in November of the same year, David threw himself down a window during an epileptic attack, resulting in his death. Soon after, Mariquita's first and last daughter Mary was born, but she also died soon. Some years later, Mariquita married again. Her new husband was Robert Tennant, but he died a sudden death in 1842.
In 1846, at 38 years old, her first husband's family allowed her to live in one of their properties. She turned this house into a shelter for girls who had been abused by society. There were many girls and women in this situation, so the house was full very soon. Quickly, Mariquita looked for funds and allied with the Anglican church to create a local branch of the House of Mercy. In 50 years, this institution attended and housed 2,500 girls in Windsor, many of which were girls who had been forced into prostitution by poverty and until then had had no way to escape.

The house that Mariquita's first husband's family let her live in, and which she turned into a shelter.
Mariquita suffered bad health for most of her years of service, and in the end died in 1860. She's buried in Saint Andrew's cemetery, overlooking the house she turned into a shelter.
In 2005, the Windsor and Maidenhead city council uncovered a blue plaque to remember her (in England, blue plaques mark the place where a historical event happened or recognise a historical person), though there's a small mistake because it says she was born in 1811 but she was actually born on November 9th 1807.
She's the only Catalan person to have an English blue plaque.
#història#mariquita tennant#windsor#london#england#pla de sant tirs#ribera d'urgellet#catalunya#history#1800s#19th century history#women in history#english history#uk history#women's history#women's rights#europe
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
imagine you're in the french army, and you're just blasting away at some revolutionary teenagers, and you look past the barricade and see the former mayor that disappeared nine years ago
941 notes
·
View notes
Text
Citizen Cooks in the Age of Napoleon
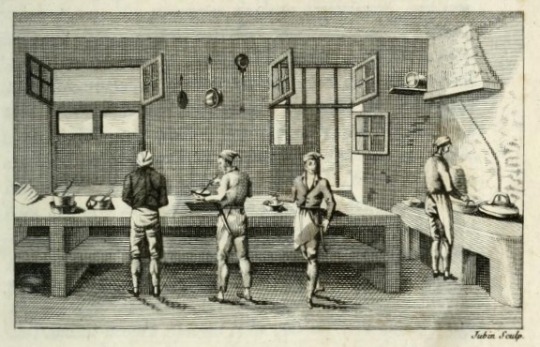
Excerpt about the role of cooks in France after the abolition of culinary guilds, and how they navigated a world which demanded for them to find new ways to stay relevant and prosperous. From Defining Culinary Authority: The Transformation of Cooking in France, 1650-1830 by Jennifer J. Davis:
French cooks sought new sites upon which to rebuild the authority of culinary labor. Throughout the early nineteenth century cooks increasingly adopted scientific terms to demonstrate their reliability and profound knowledge of the culinary arts. Such language communicated the author's education and distinction, just as an appeal to an elite patron had done in the 1660s and referral to a cook's professional expertise had done in the 1760s. The rhetoric and institutions of scientific knowledge also provided a means of distinguishing men's work from women's in the post-revolutionary era. During the early nineteenth century, cooks' claims to scientifically valuable savoir-faire rested on three crucial points of culinary innovation: food preservation, the improved production of bouillon, and gelatin extraction.
As these processes left the realm of traditional knowledge and became sites of scientific inquiry by tradespeople and amateurs alike, cooks sought to maintain authority in this arena by including scientific terms and theories in cookbooks, advertisements, and government petitions.
Two factors encouraged cooks' claims to scientific knowledge during this era. First, when Napoleon Bonaparte took the reins of government as first consul in 1799 and established himself as emperor in 1804, he raised medical doctors and academic scientists, Idéologues, to positions of political prominence. From these posts, the Idéologues subsidized experiments and inventions deemed useful to the nation and encouraged the popularization of science in the public sphere through state sponsorship of exhibitions and print forums. The Idéologues particularly supported research related to food preparation and preservation that might benefit France's armies and navies, with obvious benefits for professional cooks. Many cooks presented their particular techniques to the government during this time, seeking both financial recompense and public acclaim. Second, a voluntary association closely allied with the Idéologues' vision, the Société d'encouragement pour l'industrie nationale (Society for the Encouragement of National Industry), provided a forum in which formally trained scientists, politicians, merchants, artisans, and curious educated men might unite to address questions that inhibited French science and industry.
Together, these men sought to develop a more coherent program for industrial advancement than any one group could achieve independently. The society explicitly sought to join scientific knowledge to artisanal practical expertise, recognizing that each group had strengths that would benefit industrial development. This association invested heavily in three diffuse projects that eventually infused the most basic culinary processes with scientific awareness: new methods of food preservation to benefit the nation's armies and navies, new methods of stock preparation to sustain the nation's poor, and new methods of extracting gelatin from bones to improve hospital and military diets at little added expense.
#Illustration from L'art du Cuisinier by Antoine Beauvilliers (1814)#Defining Culinary Authority: The Transformation of Cooking in France 1650-1830#Jennifer J. Davis#David#citizen cooks#napoleon#napoleon bonaparte#napoleonic#napoleonic era#first french empire#french empire#19th century#french revolution#cooks#food#culinary history#france#1800s#history#french history#Antoine Beauvilliers#Beauvilliers#Society for the Encouragement of National Industry#Société d'encouragement pour l'industrie nationale
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

Oil on canvas, Charles Louis Mozin
The Capture of the Dutch Fleet at Den Helder, 23rd of January 1795
In which the French armed forces demonstrates that not having the best navy can in fact be okay.
Context
The French Revolution in 1789, followed by the imprisonment and then execution of Louis the XVIth in 1793, led to most major autocratic powers in Europe declaring war on France to restore the status quo. France was thus engaged on multiple fronts by many of its neighbors which, surprisingly, at the time included Austria through their ownership of the Southern Netherlands. Both Netherlandses had witnessed failed republican uprisings in the previous decades, and as such the new France Republic pushed through the Austrian Netherlands to declare war on the -nominally only- Republic of United Netherlands in the North.
The “Battle”
After two years of campaign the combined efforts of the French revolutionary army and Dutch patriots had all but closed this front of the war, and the French commander of the Army of the North was garrisoned in Amsterdam when he caught wind of the Dutch fleet being anchored at the mouth of the Zuiderzee bay, just north of there. Due to temperatures averaging -10°C in the past weeks, the entire bay had frozen over, which he decided to use to his advantage.
He immediately sent Dutch patriot Gnl. Jan Willem de Winter at the head of about two hundred men from the French 8th Hussar and the 3rd Battalion of Belgian Skirmishers, also raised from sympathizers to the republican cause. Muffling the sound of their horses’ hooves with cloth and arriving during the night each with a Belgian infantryman riding with them, the hussars sneaked on the entire Dutch fleet frozen at anchor and captured it without a fight.

In a single cavalry charge the French Republic had captured five ships-of-the-line, three frigates, six corvettes and several merchantmen with crew, for a total of about 850 guns. This is one of only two recorded instances of a cavalry force charging and capturing ships in a battle and one of few instances where having light infantry ride as voltigeurs proved to be even remotely useful.
There is debate whether the Dutch sailors and marines would have actually resisted capture however, as the Netherlands had essentially already been knocked out of the war by then and might have been ordered to surrender, which the French may have known as well. It is hard to discern the truth of the matter when what was two hundred men sent to secure a fleet that may have already been surrendered to them gets painted as a full army corps marching in tight formation on the ice.
In any case, a squadron of hussars captured a fleet of ships and that’s awesome.
Following the capture of the fleet, the evacuation of the remaining Allied troops to other fronts or England and finally the surrender of the Austrian duchy of Luxembourg, the Dutch Patriot party were given the reins of the Netherlands renamed as the Batavian Republic - more or less a puppet state and the future Netherlands - while the Austrian Netherlands - future Belgium - and Luxembourg were incorporated in the French Republic as new departments.
The captured fleet was ransomed back to the Batavian Republic in exchange of a small loan of a hundred million guilders.
235 notes
·
View notes